Placental ACE2 Expression: A Possible Pathogenetic Mechanism for Infantile Hemangiomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verano-Braga, T.; Martins, A.L.V.; Motta-Santos, D.; Campagnole-Santos, M.J.; Santos, R.A.S. ACE2 in the renin-angiotensin system. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 3063–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamanna, S.; Lumbers, E.R.; Morosin, S.K.; Delforce, S.J.; Pringle, K.G. ACE2: A key modulator of the renin-angiotensin system and pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2021, 321, R833–R843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, A.; Yagil, Y.; Bursztyn, M.; Barkalifa, R.; Scharf, S.; Yagil, C. ACE2 expression and activity are enhanced during pregnancy. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1953–R1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnihan, K.B.; Neves, L.A.; Anton, L.; Joyner, J.; Valdes, G.; Merrill, D.C. Enhanced expression of Ang-(1-7) during pregnancy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2004, 37, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaleyeva, L.M.; Pulgar, V.M.; Lindsey, S.H.; Yamane, L.; Varagic, J.; McGee, C.; Da Silva, M.; Lopes Bonfa, P.; Gurley, S.B.; Brosnihan, K.B. Uterine artery dysfunction in pregnant ACE2 knockout mice is associated with placental hypoxia and reduced umbilical blood flow velocity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E84–E94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaleyeva, L.M.; Sun, Y.; Bledsoe, T.; Hoke, A.; Gurley, S.B.; Brosnihan, K.B. Photoacoustic imaging for in vivo quantification of placental oxygenation in mice. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 5520–5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.J.F.; Friedlander, S.F.; Guma, M.; Kavanaugh, A.; Chambers, C.D. Infantile Hemangiomas: An Updated Review on Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Bandera, A.I.; Sebaratnam, D.F.; Wargon, O.; Wong, L.F. Infantile hemangioma. Part 1: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1379–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebaratnam, D.F.; Rodríguez Bandera, A.L.; Wong, L.F.; Wargon, O. Infantile hemangioma. Part 2: Management. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasbani, D.J.; Hamie, L. Infantile Hemangiomas. Dermatol. Clin. 2022, 40, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munden, A.; Butschek, R.; Tom, W.L.; Marshall, J.S.; Poeltler, D.M.; Krohne, S.E.; Alió, A.B.; Ritter, M.; Friedlander, D.F.; Catanzarite, V.; et al. Prospective study of infantile haemangiomas: Incidence, clinical characteristics and association with placental anomalies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 170, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resta, L.; Vimercati, A.; Cazzato, G.; Mazzia, G.; Cicinelli, E.; Colagrande, A.; Fanelli, M.; Scarcella, S.V.; Ceci, O.; Rossi, R. SARS-CoV-2 and Placenta: New Insights and Perspectives. Viruses 2021, 13, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drolet, B.A.; Esterly, N.B.; Frieden, I.J. Hemangiomas in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggstrom, A.N.; Drolet, B.A.; Baselga, E.; Chamlin, S.L.; Garzon, M.C.; Horii, K.A.; Lucky, A.W.; Mancini, A.J.; Metry, D.W.; Newell, B.; et al. Prospective study of infantile hemangiomas: Demographic, prenatal, and perinatal characteristics. J. Pediatr. 2007, 150, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.D.; Ma, G.; Chen, H.; Ye, X.X.; Jin, Y.B.; Lin, X.X. Maternal and perinatal risk factors for infantile hemangioma: A case-control study. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2013, 30, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, S.; Itinteang, T.; Withers, A.H.; Davis, P.F.; Tan, S.T. Does hypoxia play a role in infantile hemangioma? Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2016, 308, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, P.E.; Waner, M.; Mizeracki, A.; Mihm, M.C., Jr. GLUT1: A newly discovered immunohistochemical marker for juvenile hemangiomas. Hum. Pathol. 2000, 31, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janmohamed, S.R.; Brinkhuizen, T.; den Hollander, J.C.; Madern, G.C.; de Laat, P.C.; van Steensel, M.A.; Oranje, A.P. Support for the hypoxia theory in the pathogenesis of infantile haemangioma. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 40, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, S.; Li, T.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Qian, X.; Bi, J.; Lin, Y. ACE2 inhibits breast cancer angiogenesis via suppressing the VEGFa/VEGFR2/ERK pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wan, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Ma, Q.; Han, B.; Xiang, Y.; Che, J.; Cao, H.; Fei, X.; et al. The angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in tumor growth and tumor-associated angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Du, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, B.; Xian, H. β-elemene affects angiogenesis of infantile hemangioma by regulating angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López Gutiérrez, J.C.; Avila, L.F.; Sosa, G.; Patron, M. Placental anomalies in children with infantile hemangioma. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2007, 24, 353–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, V.; Resta, L.; Napoli, A.; Bonifazi, E. Placental hypoxia and neonatal haemangioma: Clinical and histological observations. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snegovskikh, V.V.; Schatz, F.; Arcuri, F.; Toti, P.; Kayisli, U.A.; Murk, W.; Guoyang, L.; Lockwood, C.J.; Norwitz, E.R. Intra-amniotic infection upregulates decidual cell vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and neuropilin-1 and -2 expression: Implications for infection-related preterm birth. Reprod. Sci. 2009, 16, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatley, C.; Sole-Navais, P.; Vaudel, M.; Helgeland, Ø.; Modzelewska, D.; Johansson, S.; Jacobsson, B.; Njølstad, P. Placental weight centiles adjusted for age, parity and fetal sex. Placenta 2022, 117, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Study Group | Control Group | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
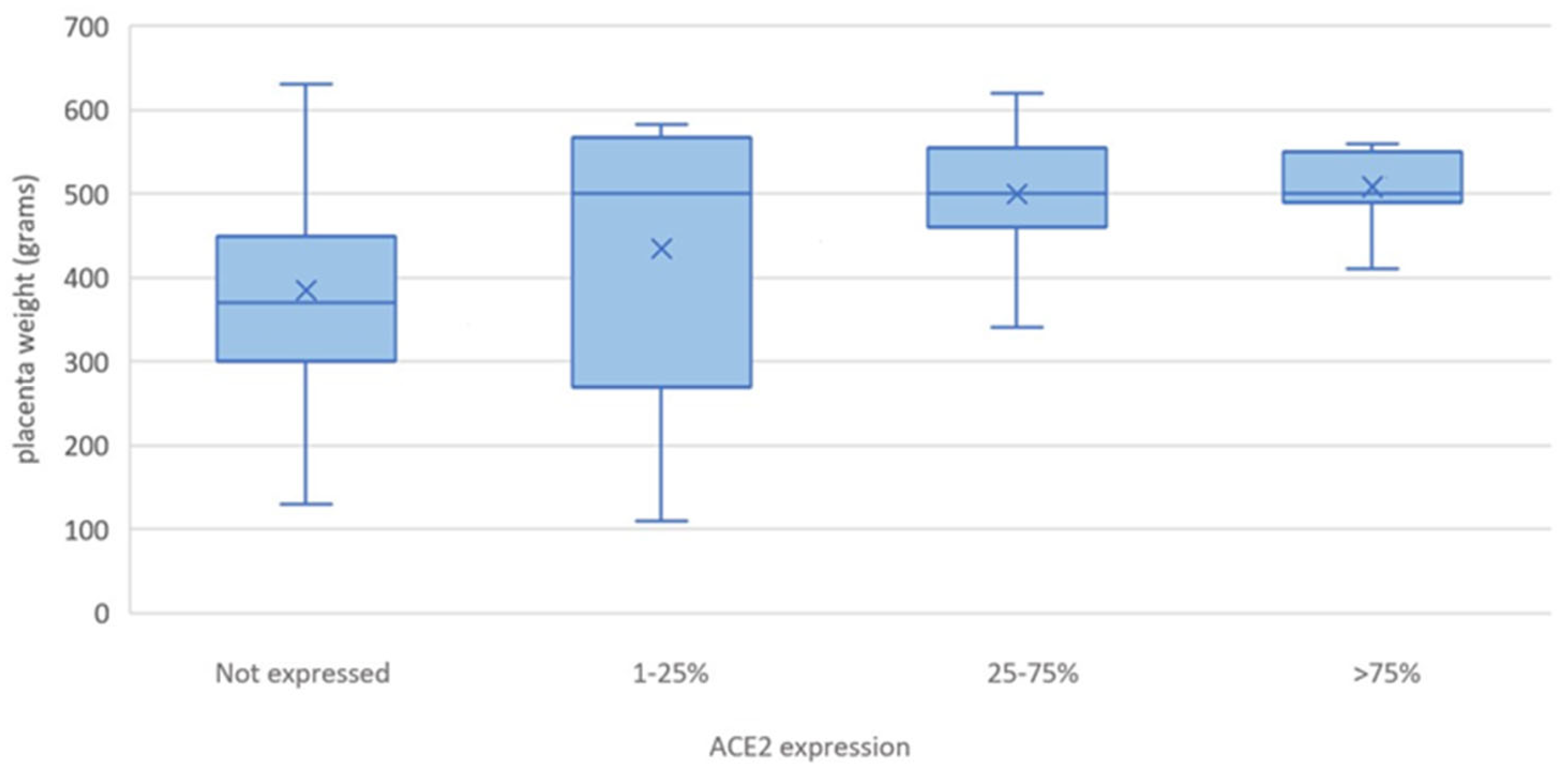
| Placental weight, mean (s.d.) | 380.6 (167.3) | 502.3 (64) | 0.005 |
| Gestational age, mean (s.d.) | 34.7 (2.7) | 35.6 (1.1) | 0.21 |
| Prematurity N (%) | 16 (80%) | 21 (78%) | 0.85 |
| Twins N (%) | 2 (10%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.57 |
| Maternal malperfusion N (%) | 13 (65%) | 11 (40.7%) | 0.1 |
| Decidual arteriopathy N (%) | 4 (20%) | 2 (7.4%) | 0.2 |
| Fetal malperfusion N (%) | 5 (25%) | 5 (18.5%) | 0.6 |
| Deciduitis N (%) | 2 (10%) | 0 | 0.17 |
| Intervillous fibrin deposition N (%) | 2 (10%) | 4 (14.8%) | 0.49 |
| Villous hypervascularity N (%) | 4 (20%) | 5 (18.5%) | 0.59 |
| Fetal thrombotic vasculopathy N (%) | 2 (10%) | 0 | 0.17 |
| Syncytial knots N (%) | 7 (35%) | 13 (48.2%) | 0.37 |
| Chorioamnionitis N (%) | 4 (20%) | 0 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marco, A.D.; Cazzato, G.; Maggialetti, R.; Ingravallo, G.; Fanelli, M.; Vimercati, A.; Cicinelli, E.; Laforgia, N.; Neri, I.; Bonifazi, E.; et al. Placental ACE2 Expression: A Possible Pathogenetic Mechanism for Infantile Hemangiomas. Dermatopathology 2024, 11, 192-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030020
Marco AD, Cazzato G, Maggialetti R, Ingravallo G, Fanelli M, Vimercati A, Cicinelli E, Laforgia N, Neri I, Bonifazi E, et al. Placental ACE2 Expression: A Possible Pathogenetic Mechanism for Infantile Hemangiomas. Dermatopathology. 2024; 11(3):192-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarco, Aurora De, Gerardo Cazzato, Rosalba Maggialetti, Giuseppe Ingravallo, Margherita Fanelli, Antonella Vimercati, Ettore Cicinelli, Nicola Laforgia, Iria Neri, Ernesto Bonifazi, and et al. 2024. "Placental ACE2 Expression: A Possible Pathogenetic Mechanism for Infantile Hemangiomas" Dermatopathology 11, no. 3: 192-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030020
APA StyleMarco, A. D., Cazzato, G., Maggialetti, R., Ingravallo, G., Fanelli, M., Vimercati, A., Cicinelli, E., Laforgia, N., Neri, I., Bonifazi, E., & Bonamonte, D. (2024). Placental ACE2 Expression: A Possible Pathogenetic Mechanism for Infantile Hemangiomas. Dermatopathology, 11(3), 192-199. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology11030020