Factors Affecting Aggressiveness among Young Teenage Girls: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Measures
2.2.1. Demographics
2.2.2. Aggressiveness
2.2.3. General Health
2.2.4. Happiness
2.2.5. Social Acceptance
2.2.6. Loneliness
2.3. Statistical Analysis
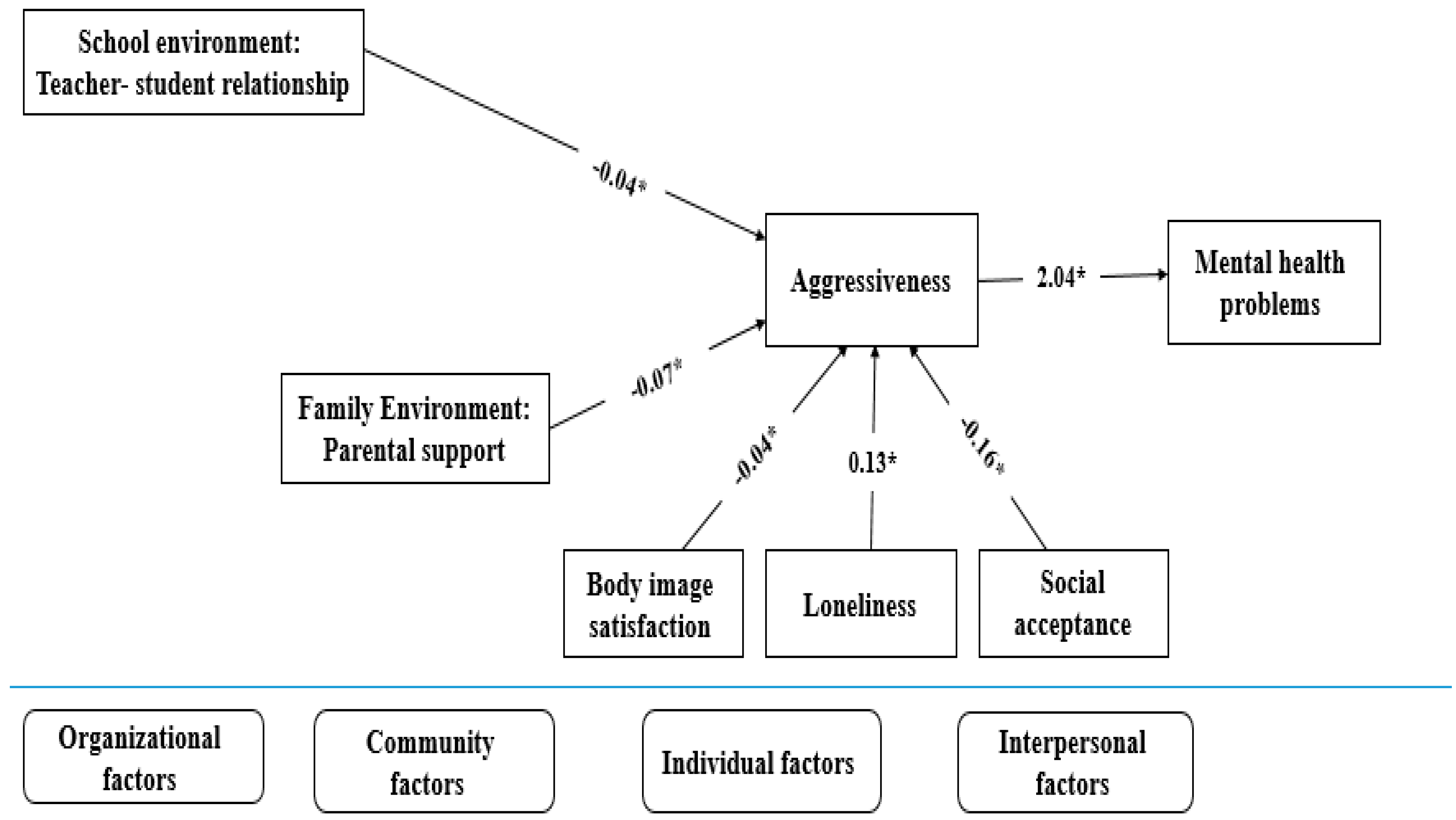
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlomer, G.L.; Cleveland, H.H.; Vandenbergh, D.J.; Mark, E.; Feinberg, M.E.; Neiderhiser, J.M.; Greenberg, M.T.; Spoth, R.; Redmond, C. Developmental Differences in Early Adolescent Aggression: A Gene × Environment × Intervention Analysis. J. Youth Adolesc. 2015, 44, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ye, P.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Tang, Q. Music-based intervention to reduce aggressive behavior in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e23894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, P.L.; Bootzin, R.R.; Smith, L.; Cousins, M.; Stevens, S. Sleep and aggression in substance- abusing adolescents: Results from an integrative behavioral sleep-treatment pilot program. Sleep 2006, 29, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Ramos, S.; Romero-Abrio, A.; Martínez-Ferrer, B.; Musitu, G. Psychosocial variables and overt school violence among adolescents. Psychosoc. Interv. 2017, 26, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.J. Relationships among children’s aggression, temperament, home environment, and school adjustment. J. Child. Edu. 2007, 16, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Heizomi, H.; Nadrian, H. What determines psychological well-being among Iranian female adolescents? Perceived stress may overshadow all determinants. Health Promot. Perspect 2018, 8, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mundy, L.K.; Simmons, J.G.; Allen, N.B.; Viner, R.M.; Bayer, J.K.; Olds, T.; Williams, J.; Olsson, C.; Romaniuk, H.; Mensah, F.; et al. Study protocol: The Childhood to Adolescence Transition Study (CATS). BMC Pediatr. 2012, 13, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabbani, A.; Mahmoudi-Gharaei, J.; Mohammadi, M.; Motlagh, M.; Mohammad, K.; Ardalan, G.; Maftoon, F. Mental health problems of Iranian female adolescents and its association with pubertal development: A nationwide study. Acta Med. Iran. 2012, 50, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Straus, M.A. Future research on gender symmetry in physical assaults on partners. Violence Against Women 2006, 12, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collishaw, S.; Gardner, F.; Maughan, B.; Scot, J.; Pickles, A. Do historical changes in parent-child relationships explain increases in youth conduct problems? J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2012, 40, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, A.; Redzuan, M. Women Physical Aggression (A Review). Am. J. Sci. 2010, 6, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild, G.; Hagan, C.C.; Walsh, N.D.; Passamonti, L.; Calder, A.J. Brain structure abnormalities in adolescent girls with conduct disorder. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2013, 54, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, M.; Hawkins, S.; Chiancone, J.; Whitworth, A. Girls Study Group: Charting the Way to Delinquency Prevention for Girls; Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Obradovic-Tomasevic, B.; Santric-Milicevic, M.; Vasic, V.; Vukovic, D.; Sipetic-Grujicic, S.; Bjegovic-Mikanovic, V.; Terzic-Supic, Z.; Tomasevic, R.; Todorovic, J.; Babic, U. Prevalence and Predictors of Violence Victimization and Violent Behavior among Youths: A Population-Based Study in Serbia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Chiu, W.; Won, D. Effects of physical education, extracurricular sports activities, and leisure satisfaction on adolescent aggressive behavior: A latent growth modeling approach. PLoS ONE 2017, e0174674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denson, T.F.; O’Dean, S.M.; Blake, K.R.; Beames, J.R. Aggression in Women: Behavior, Brain and Hormones. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rinnewitz, L.; Parzer, P.; Koenig, J.; Bertsch, K.; Brunner, R.; Resch, F.; Kaess, M. A Biobehavioral Validation of the Taylor Aggression Paradigm in Female Adolescents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonell, C.; Allen, E.; Warren, E.; Gowan, J.; Bevilacqua, L.; Jamal, F.; Legood, R.; Viner, R.M. Effects of the Learning Together intervention on bullying and aggression in English secondary schools (INCLUSIVE): A cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 2452–2464. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buchmann, A.; Hohmann, S.; Brandeis, D.; Banaschewski, T.; Poustka, L. Aggression in children and adolescents. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rub, M.A. An Assessment of Bullying/Victimization Behaviors among Third-Graders in Jordanian Public Schools. Int. J. Res. Educ. 2018, 42, 337–367. [Google Scholar]
- Kann, L.; Kinchen, S.; Shanklin, S.; Flint, K.H.; Hawkins, J.; Harris, W.A.; Lowry, R.; Olsen, E.O. Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance—United States, 2013. Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2014, 63, 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Halpern, C.T.; Oslak, S.G.; Mary, L.; Young, M.L.; Martin, S.L.; Kupper, L.L. Partner Violence Among Adolescents in Opposite-Sex Romantic Relationships: Findings from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent Health. Am. J. Public Health 2001, 91, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. School Violence and Bullying: Global Status and Trends, Drivers and Consequences; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, D.K.; Kann, L.; Kinchen, S.; Shanklin, S.; Ross, J.; Hawkins, J.; Harris, W.A.; Lowry, R.; McManus, T.; Chyen, D.; et al. Youth risk behavior surveillance-United States, 2007. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2008, 57, 1–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eaton, D.K.; Kann, L.; Kinchen, S.; Shanklin, S.; Flint, K.H.; Hawkins, J.; Harris, W.A.; Lowry, R.; McManus, T.; Chyen, D.; et al. Youth risk behavior surveillance-United States, 2012. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2012, 61, 1–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ansari, H.; Kelishadi, R.; Qorbani, M.; Mansourian, M.; Ahadi, Z.; Motlagh, M.E.; Ardalan, G.; Safiri, S.; Asayesh, H.; Mohammadi, R.; et al. Is Meal Frequency Associated with Mental Distress and Violent Behaviors in Children and Adolescents? the CASPIAN IV Study. Int. J. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 2247–2255. [Google Scholar]
- Estévez, E.; Jiménez, T.I.; Moreno, D. Aggressive behavior in adolescence as a predictor of personal, family, and school adjustment problems. Psicothema 2018, 30, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, N.; Karimi-Shahanjarini, A.; Rezapur-Shahkolai, F.; Hamzeh, B.; Roshanaei, G.; Babamiri, M. Aggression and its predictors among elementary students. J. Inj. Violence Res. 2019, 11, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, L.N.; Demaray, M.K.; Tennant, J. Social, emotional, and cognitive factors associated with bullying. School Psych. Rev. 2017, 46, 42–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odgers, C.L.; Moffitt, T.E.; Broadbent, J.M.; Dickson, N.; Hancox, R.J. Female and male antisocial trajectories: From childhood origins to adult outcomes. Dev. Psychopathol. 2008, 20, 673–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, D.; Lepore, G. Sexual Risk and Protective Factors Affecting Teen Sexual Behavior, Pregnancy, Childbearing and Sexually Transmitted Disease: Which Are Important? Which Can You Change? Associates and the National Campaign to Prevent Teen and Unplanned Pregnancy: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Putallaz, M.; Bierman, K.L. Girls who bully: A developmental and relational perspective. In Aggression, Antisocial Behavior, and Violence Among Girls: A Developmental Perspective; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 90–109. [Google Scholar]
- Buka, S.L.; Stichick, T.L.; Birdthistle, I.; Earls, F.J. Youth exposure to violence: Prevalence, risks, and consequences. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 2001, 71, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Card, N.A.; Stucky, B.D.; Sawalani, G.M.; Little, T.D. Direct and indirect aggression during childhood and adolescence: A meta-analytic review of gender differences, intercorrelations, and relations to maladjustment. Child Dev. 2008, 79, 1185–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrenkohl, T.I.; Catalano, R.F.; Hemphill, S.A.; Toumbourou, J.W. Longitudinal Examination of Physical and Relational Aggression as Precursors to Later Problem Behaviors in Adolescents. Violence Vict. 2009, 24, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sette, S.; Spinrad, T.; Baumgartner, E. Links Among Italian Preschoolers’ Socio-Emotional Competence, Teacher-Child Relationship Quality and Peer Acceptance. Early Educ. Dev. 2013, 24, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Henneberger, A.K.; Varga, S.M.; Moudy, A.; Tolan, P.H. Family Functioning and High Risk Adolescents’ Aggressive Behavior: Examining Effects by Ethnicity. J. Youth Adolesc. 2016, 45, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xiong, R.; Xia, Y.; Li, S.D. Perceived Discrimination and Aggression Among Chinese Migrant Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Model. Front Psychol. 2021, 12, 651270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Bhilwar, M.; Kapoor, R.; Sharma, P.; Parija, P. Prevalence of Aggression among School-Going Adolescents in India: A Review Study. Ind. J. Youth Adol. Health 2016, 3, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, T. Applying the socio-ecological model to improving fruit and vegetable intake among low-income African Americans. J. Community Health 2008, 33, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F.; Owen, N.; Fisher, E. Ecological models of health behavior. Health Behav. 2015, 5, 43–64. [Google Scholar]
- Glanz, K.; Rimer, B.K.; Viswanath, K. Health Behavior and Health Education: Theory, Research, and Practice; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Krug, E.; Mercy, J.A.; Dahlberg, L.L.; Zwi, A.B. The world report on violence and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtari, F.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Allahverdipour, H.; Nikookheslat, S.D.; Nourizadeh, R. Explaining the role of personal, social and physical environment factors on employed women’s physical activity: A structural equation analysis. Glob. J. Health Sci. 2013, 5, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bakhtari, F.; Nadrian, H.; Matlabi, H.; Sarbakhsh, P.; Bidar, M. Personal, interpersonal, and organizational predictors of the mode of delivery among urban women: A prospective study with socio-ecological approach. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2017, 28, 280–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Plan of Action to Strengthen the Role of the Health System within a National Multisectoral Response to Address Interpersonal Violence, in Particular against Women and Girls, and Against Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg, L.L.; Krug, E.G. Violence: A global public health problem. In World Report on Violence and Health; Krug, E., Dahlberg, L.L., Mercy, J.A., Zw, A.B., Lozano, R., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Buss, A.; Perry, M. The aggression questionnaire. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1992, 63, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivari-Rahman, M.; Lesani, M.; Shokouhi-Moqaddam, S. Comparison of Mental Health, Aggression and Hopefulness between Student Drug-Users and Healthy Students (A Study in Iran). Addict Health 2012, 4, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moeini, B.; Shafii, F.; Hidarnia, A.; Babaii, G.R.; Birashk, B.; Allahverdipour, H. Perceived stress, self-efficacy and its relations to psychological well-being status in Iranian male high school students. Soc. Behav. Pers. 2008, 36, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, A.; Noorbala, A.A. A Preliminary Evaluation of the Validity and Reliability of the Oxford Happiness Questionnaire in Students in the Universities of Tehran. Iran J. Psychiatry Clin. Psychol. 1999, 5, 55–66. Available online: http://ijpcp.iums.ac.ir/article-1-1777-en.html. (accessed on 8 September 2020).
- Bidaki, R.; Mousavi, S.; Bashardoust, N.; Sabouri Ghannad, M.; Dashti, N. Individual Factors of Social Acceptance in Patients Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) at the Yazd Behavioral Consultation Center in Iran. Int. J. High Risk Behav. Addict. 2016, 5, e22243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamdarlo, G.; Dehshiri, G.; Shojaee, S.; Hakimirad, E. Health and Loneliness Status of the Elderly Living in Nursing Homes Versus Those Living with Their Families. Iran J. Ageing 2008, 3, 557–564. Available online: http://salmandj.uswr.ac.ir/article-1-90-en.html (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Russell, D.; Peplau, L.A.; Ferguson, M.L. Developing a measure of loneliness. J. Pers. Assess 1978, 42, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodani, M.; Shogaeyan, M.; Neysi, A. The effect of group logo-therapy on loneliness in retired men. Res. Cogn. Behav. Sci. 2012, 2, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, J.P. The Concepts and Understanding of the Structural Equation Model; Han Narae Academy Public: Seoul, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jessor, R. Successful adolescent development among youth in high-risk settings. Am. Psychol. 1993, 48, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colder, C.R.; Mott, J.A.; Flay, B.R.; Levy, S. The Relation of Perceived Neighborhood Danger to Childhood Aggression: A Test of Mediating Mechanisms. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2000, 28, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howley, C.; Strange, M.; Bickel, R. Research about School Size and School Performance in Impoverished Communities: Clearinghouse on Rural Education and Small Schools, Appalachia Educational Laboratory; ERIC Resource Center, 2000; Available online: http://www.ael.org/eric/digests/edorc0010.htm (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Chang, L.; Liu, H.; Fung, K.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Li, H.; Farver, J.M. The mediating and moderating effects of teacher preference on the relations between students’ social behaviors and peer acceptance. Merril Palmer Q. 2007, 53, 603–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.; Murray, K.M.; Waas, G.A. Child and teacher reports of teacher-student relationships: Concordance of perspectives and associations with school adjustment in urban kindergarten classrooms. J. Appl. Dev. Psychol. 2008, 29, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labella, M.H.; Masten, A.S. Family influences on the development of aggression and violence. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2018, 19, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerestes, G.; Rezo, I.; Ajdukovic, M. Links between attachment to parents and internalizing problems in adolescence: The mediating role of adolescents’ personality. Curr. Psychol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal Yagız, A.; Kugu, N.; Semiz, M.; Kavakci, O. The Relationship Between Anger Expression, Body Image and Eating Attitudes in Social Anxiety Disorder. Turk Psikiyatri. Derg. 2016, 27, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sethi, D.; Hughes, K.; Bellis, M.; Mitis, F.; Racioppi, F. (Eds.) European Report on Preventing Violence and Knife Crime among Young People; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Twenge, J.M.; Baumeister, R.F.; Tice, D.M.; Stucke, T.S. If you can’t join them, beat them: Effects of social exclusion on aggressive behavior. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2002, 81, 1058–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, E.; Leaper, C. A longitudinal investigation of sport participation, peer acceptance, and self-esteem among adolescent girls and boys. Sex Roles 2006, 55, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelishadi, R.; Qorbani, M.; Djalalinia, S.; Sheidaei, A.; Rezaei, F.; Arefirad, T.; Safiri, S.; Asayesh, H.; Motlagh, M.E. Physical inactivity and associated factors in Iranian children and adolescents: The Weight Disorders Survey of the CASPIAN-IV study. J. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Res. 2017, 9, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohebi, F.; Mohajer, B.; Yoosefi, M.; Sheidaei, A.; Zokaei, H.; Damerchilu, B.; Mehregan, A.; Shahbal, N.; Rezaee, K.; Khezrian, M.; et al. Physical activity profile of the Iranian population: STEPS survey, 2016. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuzer, Y.; Albayrak, G.; Kilicarslan, S. Relationships Amongst Aggression, Self-Theory, Loneliness, and Depression in Emerging Adults. Psychol. Rep. 2018, 122, 1235–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagchandani, R.K. Effect of Loneliness on the Psychological Well-Being of College Students. Int. J. Social. Scienc Humanit. 2017, 7, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezan, A.F. Psychological well-being predicting loneliness among university students. J. Soc. Sci. 2007, 16, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Fiori, K.L.; Denckla, C. Social support and mental health in middle-aged men and women: A multidimensional approach. J. Aging Health 2012, 24, 407–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, A.; Gerstein, L.; Chan, Y.; Engebretson, J. Relationship of Aggression to Anxiety, Depression, Anger, and Empathy in Hong Kong. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2015, 24, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyrueix, L.; Durham, G.; Miller, J.; Smalley, K.B.; Warren, J.C. Association between Depression and Aggression in Rural Women. J. Health Dispar. Res. Pract. 2015, 8, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Towsend, M.C. Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing: Concepts of Care in Evidence-Based Practice, 6th ed.; F.A. Davis Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Aggressiveness n (%) | Non-Aggressiveness n (%) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||
| 13 | 20 (8.5) | 214 (91.5) | |
| 14 | 30 (12.9) | 202 (87.1) | 0.23 |
| 15 | 31 (12.9) | 210 (87.1) | |
| Birth Order | |||
| 1 | 47 (13.1) | 313 (86.9) | |
| 2 | 24 (10.5) | 205 (89.5) | 0.53 |
| 3 | 7 (9.0) | 71 (91.0) | |
| ≥4 | 3 (7.5) | 37 (92.5) | |
| Number of Family Members | |||
| 2 | 1 (14.3) | 6 (85.7) | 0.47 |
| 3 | 6 (7.5) | 74 (92.5) | |
| 4 | 51 (12.9) | 343 (87.1) | |
| ≥5 | 23 (10.2) | 203 (89.8) | |
| Teacher–student Relationship | |||
| Very low | 8 (9.9) | 27 (4.3) | |
| Low | 9 (11.1) | 33 (5.3) | <0.05 |
| Moderate | 12 (14.8) | 116 (18.5) | |
| High | 23 (28.4) | 224 (35.8) | |
| Very high | 29 (35.8) | 226 (36.1) | |
| Friend Relationships | |||
| Very low | 2 (2.5) | 3 (0.5) | |
| Low | 0 (0.0) | 11 (1.8) | 0.10 |
| Moderate | 2 (2.5) | 28 (4.5) | |
| High | 22 (27.2) | 130 (20.8) | |
| Very high | 55 (67.9) | 454 (72.5) |
| Variables | Mean (SD) | X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1. Teacher–student relationship | 2.91 (1.10) | 1 | ||||||
| X2. Parental support | 0.88 (031) | 0.305 ** | ||||||
| X3. Body image | 0.85 (0.35) | 0.196 ** | 0.286 ** | |||||
| X4. Loneliness | 39.79 (10.11) | −0.275 ** | −0.339 ** | −0.240 ** | ||||
| X5. Social acceptance | 20.35 (4.59) | 0.358 ** | 0.235 ** | 0.218 ** | −0.356 ** | |||
| X6. Mental problems | 24.71 (16.32) | −0.365 ** | −0.402 ** | −0.298 ** | 0.494 ** | −0.501 ** | ||
| X7. Aggressiveness | 0.11 (0.31) | −0.072 | −0.140 ** | −0.091 * | 0.160 ** | −0.340 ** | 0.377 ** | 1 |
| Variables | Aggressiveness n (%) | Non-Aggressiveness n (%) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking status | |||
| Yes | 22 (27.2) | 59 (9.4) | <0.05 |
| No | 59 (72.8) | 567 (90.6) | |
| Being physically active | |||
| Yes | 39 (48.1) | 325 (51.9) | 0.30 |
| No | 42 (51.9) | 301 (48.1) | |
| Adequate sleep | |||
| Yes | 62 (76.5) | 538 (85.9) | <0.05 |
| No | 19 (23.5) | 88 (14.1) | |
| Body image satisfaction | |||
| Yes | 62 (76.5) | 542 (86.6) | <0.05 |
| No | 19 (23.5) | 84 (13.4) | |
| Conflict between Parents | |||
| Yes | 54 (66.7) | 254 (40.6) | <0.05 |
| No | 27 (33.3) | 372 (59.4) | |
| Having parental support | |||
| Yes | 62 (76.5) | 566 (90.4) | <0.05 |
| No | 19 (23.5) | 60 (9.6) | |
| Parents good relationship | |||
| Yes | 62 (76.5) | 561 (89.6) | <0.05 |
| No | 19 (23.5) | 65 (10.4) | |
| Satisfaction with parent–adolescent relationship | |||
| Yes | 52 (64.2) | 531 (84.8) | <0.05 |
| No | 29 (35.8) | 95 (15.2) | |
| Talking to your parents about your problems | |||
| Yes | 40 (49.4) | 433 (69.2) | <0.05 |
| No | 41 (50.6) | 193 (30.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heizomi, H.; Jafarabadi, M.A.; Kouzekanani, K.; Matlabi, H.; Bayrami, M.; Chattu, V.K.; Allahverdipour, H. Factors Affecting Aggressiveness among Young Teenage Girls: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2021, 11, 1350-1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11040098
Heizomi H, Jafarabadi MA, Kouzekanani K, Matlabi H, Bayrami M, Chattu VK, Allahverdipour H. Factors Affecting Aggressiveness among Young Teenage Girls: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education. 2021; 11(4):1350-1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11040098
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeizomi, Haleh, Mohammad Asghari Jafarabadi, Kamiar Kouzekanani, Hossein Matlabi, Mansour Bayrami, Vijay Kumar Chattu, and Hamid Allahverdipour. 2021. "Factors Affecting Aggressiveness among Young Teenage Girls: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach" European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education 11, no. 4: 1350-1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11040098
APA StyleHeizomi, H., Jafarabadi, M. A., Kouzekanani, K., Matlabi, H., Bayrami, M., Chattu, V. K., & Allahverdipour, H. (2021). Factors Affecting Aggressiveness among Young Teenage Girls: A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 11(4), 1350-1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe11040098







