Abstract
The heteroresistance phenotype refers to the presence of bacterial subpopulations with reduced antibiotic susceptibility compared with the main population. Mathematical modelling and computer simulations suggest that heteroresistance can lead to negative treatment outcomes and finally, treatment failure. Due to the low frequency and resistance level of resistant subpopulations, detection of heteroresistance phenotype in the diagnostic laboratory is problematic. Routine laboratory tests do not have the ability to accurately detect heteroresistance, but on the other hand, specific methods are time consuming and expensive. The emergence of colistin heteroresistance is a public health concern that threatens human health. Colistin heteroresistance to date has been reported in eight pathogens including Acinetobacter spp., Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp., Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (referred to as Salmonella Typhimurium), Neisseria meningitidis and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. The growing emergence of colistin heteroresistance worldwide underscores the crucial need for coordinated global action to combat it. Understanding the mechanisms of colistin heteroresistance can help to provide better guidelines for reducing antibiotic resistance and to achieve new therapeutic approaches. Our review showed that the prevalence of colistin heteroresistance strains varies in different countries. It seems that the use of different treatment strategies, especially combination therapy, can be effective in reducing the incidence of resistant subpopulations. Also, the use of new generation diagnostic methods can have a significant impact on treatment. Our findings in this review are needed to raise the awareness of microbiologists and specialists to the colistin heteroresistance mechanisms and to achieve effective treatment.
Introduction
Antibiotic resistance is a global health challenge that threatens the achievements of modern medicine. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), infections caused by antibiotic-resistant pathogens result in 23,000 deaths in the United States each year.[1] It is estimated that antibiotic resistance will cause 10 million deaths worldwide annually by 2050 and is therefore a serious threat to human health.[2] Because the development and application of new antimicrobial agents and treatment strategies may take a long time, it is worthwhile for health institutions to focus on the effective use of available antibiotics and prevent the spread of unrestrained antibiotic resistance.
In the last few decades, many studies on antibiotic resistance in various pathogens have been conducted, which has led to our better understanding of the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Acquired resistance is a resistance mechanism, which refers to mutation or horizontal transfer of a resistance gene, resulting in a predictable increase in phenotypic resistance. In fact, this indicates a correlation between bacterial genotype and bacterial phenotype.[3] However, phenotypic heterogeneity in terms of antibiotic susceptibility may be exhibited in subpopulations of a seemingly isogenic bacterial isolate. Heteroresistance denotes coexistence of susceptible and resistant strains in the same clinical sample, which makes it difficult to classify bacteria as susceptible or resistant.[4]
Therefore, since colistin heteroresistance is a challenging problem and no comprehensive study has been conducted on it, we focus in this review on colistin heteroresistance as an example of population heterogeneity. We discuss the impact of heteroresistance on the efficacy of treatment and the diagnostic methods and difficulties in detection of heteroresistance in pathogens. Next, we examine the prevalence and different mechanisms of colistin heteroresistance as well as treatment recommendations in gram negative pathogens based on all available studies.
Review criteria
This review provides an overview of the colistin heteroresistance research. Published works before 2025 on colistin heteroresistance studies were identified using the following search terms "heteroresistance”, "heteroresistant”, "colistin heteroresistance”, "population analysis profiles” and "population analysis profiling” in Medline, PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar. All original studies evaluating the prevalence, mechanism, diagnostic methods and therapeutic options of colistin heteroresistance in pathogens were eligible for review. Studies written in languages other than English were excluded.
Definition of heteroresistance
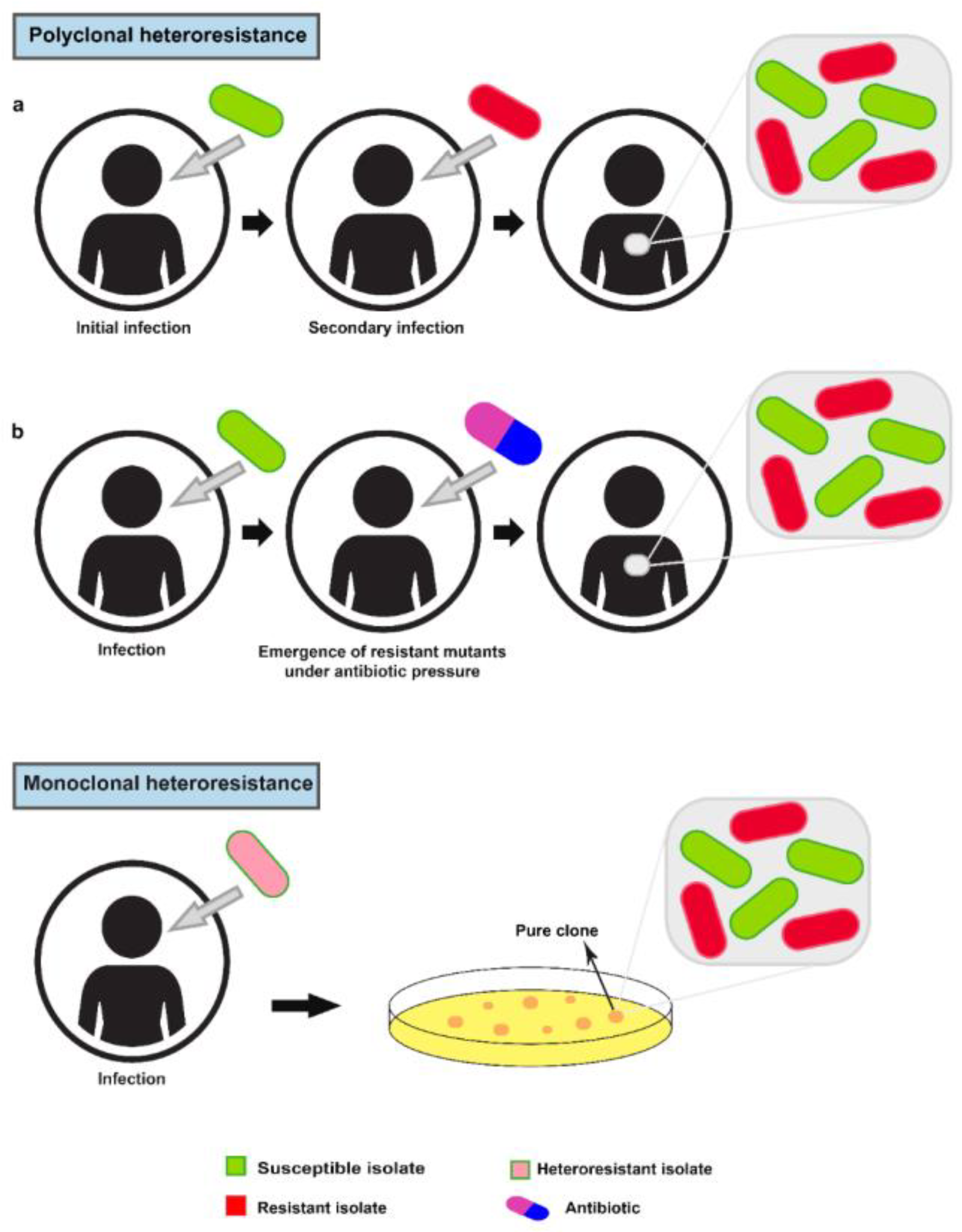
Heteroresistance was first described in the 1940s for Haemophilus influenzae.[5] Heteroresistance broadly refers to the presence of subpopulations that exhibit reduced antibiotic susceptibility compared with the main population.[4] It should be noted that, heterogeneity in resistance could be generated from different origins (polyclonal heteroresistance) or a single clone (monoclonal heteroresistance). In summary, polyclonal heteroresistance could be the result of mixed infections with different bacterial genera/species (susceptible and resistant bacteria) or the emergence and increase of rare spontaneous resistant mutants, in a population of susceptible bacteria, under antibiotic pressure (during antibiotic treatment). Alternatively, monoclonal heteroresistance is considered as the differentiation of a single clone into two susceptible and resistant populations (Figure 1).[6]
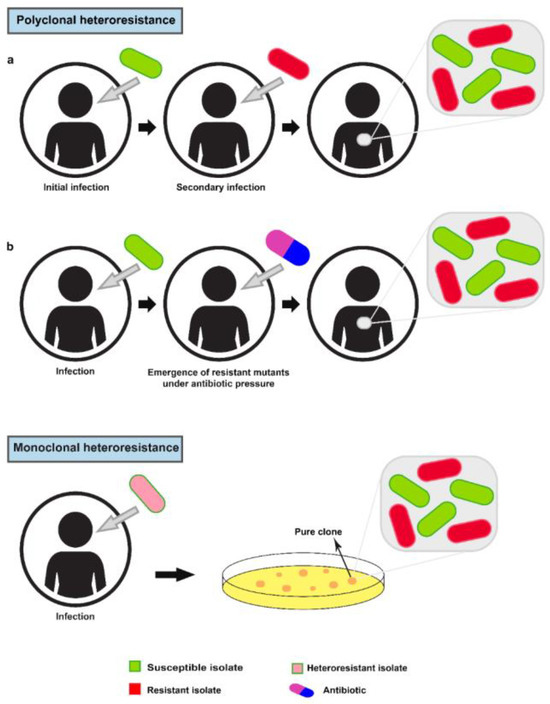
Figure 1.
Clonality of heteroresistance. Polyclonal heteroresistance: a) Polyclonal heteroresistance can result from mixed infections caused by the entry of susceptible and resistant bacteria during initial and secondary infection. b) The emergence and increase of rare resistant mutants in a population of susceptible bacteria during antibiotic treatment can lead to polyclonal heteroresistance. Monoclonal heteroresistance: Monoclonal heteroresistance is caused by differentiation of a single clone into susceptible and resistant populations (in the absence of antibiotic pressure). Unlike polyclonal heteroresistance, culturing a purified clone can identify the monoclonal heteroresistance phenotype.
The specific mechanisms of monoclonal heteroresistance formation are two: phenotypic or genetic basis. An example of phenotypic monoclonal heteroresistance has been reported in Enterobacter cloacae. It was shown that, in a murine model of infection, heteroresistant E. cloacae subpopulations survive colistin treatment and lead to treatment failure. This occurrence was dependent on the histidine kinase phoQ, part of the phoP-phoQ two-component system which activates by limiting Mg2+ concentrations and results in modifying the lipopolysaccharide component of the outer membrane and eventually resistance to colistin.[7]
By contrast, in genetic basis of monoclonal heteroresistance, often gene amplifications lead to increased resistance genes copy number, which results in higher expression levels and eventually decreased susceptibility. It is worthwhile to note that, because of instability of gene amplifications, resistant subpopulations can revert to susceptibility in the absence of antibiotic pressure. However, in polyclonal heteroresistance cases, resistance-causing mutations are maintained even in the absence of antibiotic pressure and give rise to genetically distinct cell lines.[8]
Of note, analysis of cultures from purified clones can detect monoclonal heteroresistance phenotype while not being able to detect polyclonal heteroresistance. In fact, in cases of polyclonal heteroresistance, depending on which populations (susceptible or resistant) the purified clone originated from, the result of antimicrobial susceptibility tests can be considered as fully susceptible or fully resistant.[6]
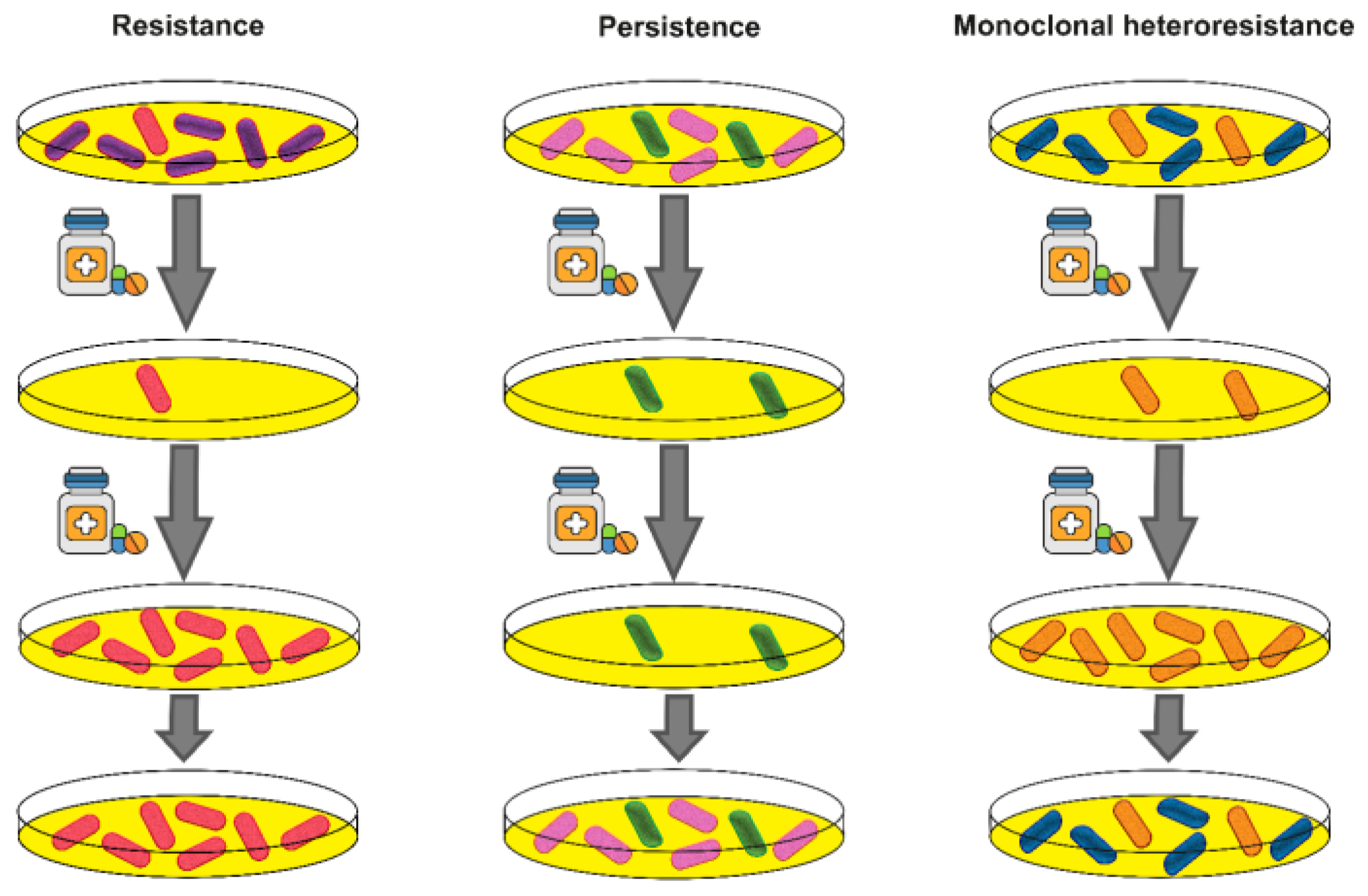
Another example of population heterogeneity has been described as persistence. This phenomenon similar to heteroresistance enable bacteria to survive antibiotic treatment, although persistent subpopulations do not have the ability to grow in the presence of antibiotics.[8] The difference between resistance, persistence and heteroresistance is shown in Figure 2.
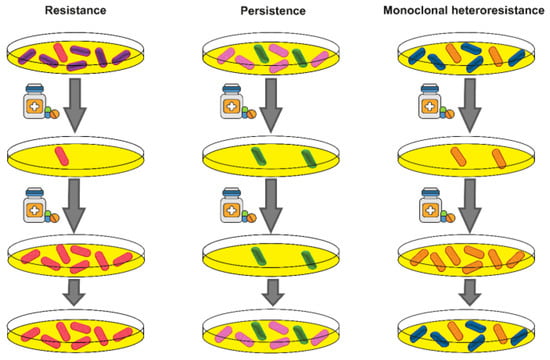
Figure 2.
Difference between resistance, persistence and heteroresistance. Resistance: Stable genetic changes lead to the development of resistant cells that can survive and grow in the presence of antibiotics. These resistant cells then expand and eventually form a new population. Persistence: persister cells, similar to heteroresistant cells, can survive antibiotic treatment but lack the ability to grow in the presence of antibiotic. After stopping antibiotic treatment, persister cells can return to the susceptible phenotype. Heteroresistance: heteroresistant cells, similar to resistant cells, have the ability to survive and grow in the presence of antibiotics. However, because resistance in monoclonal heteroresistant cells is unstable, they return to susceptible phenotype after cessation of antibiotic treatment.
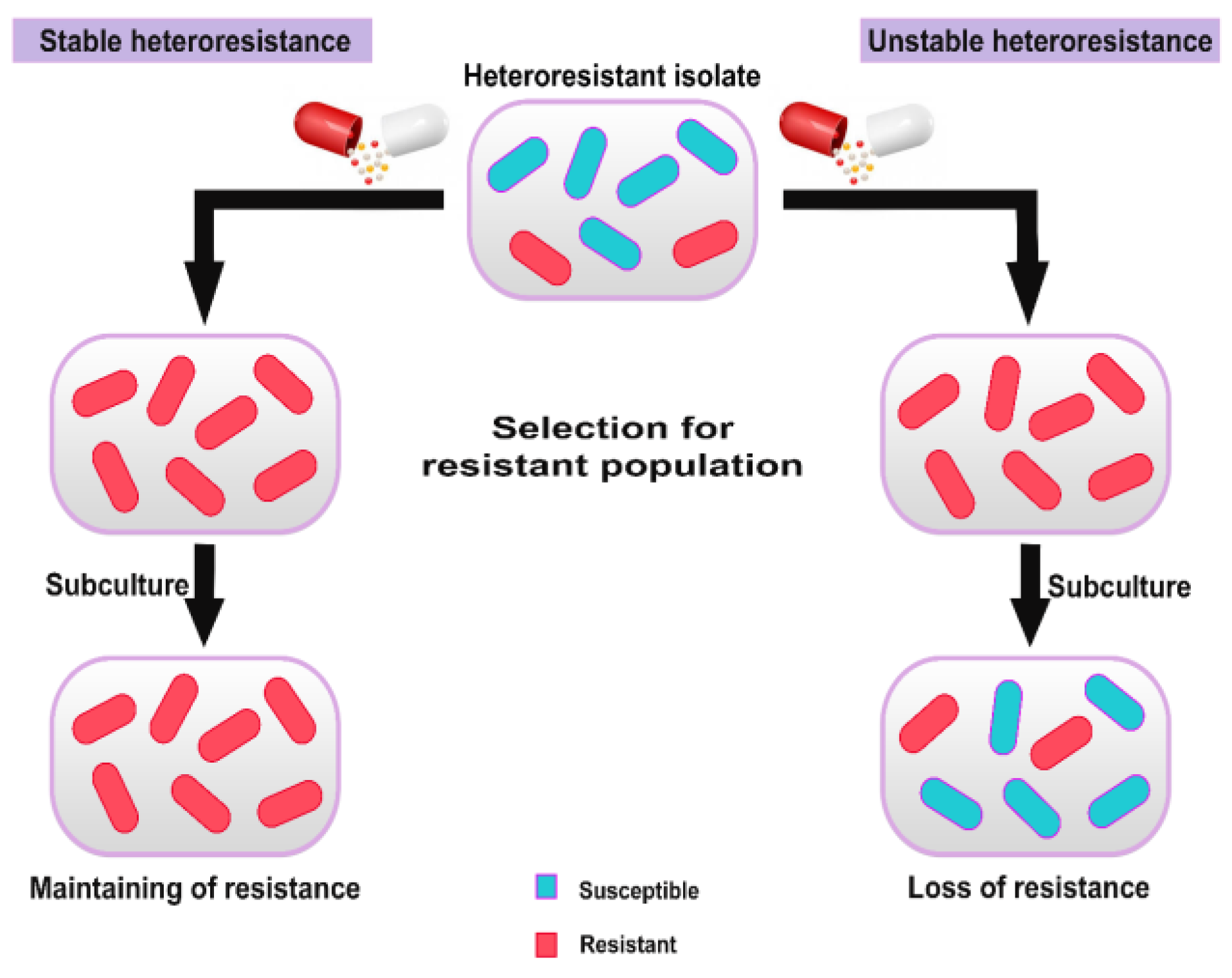
Another noteworthy point about heteroresistance is its stability. The results of various studies show that heteroresistance is stable or unstable (Figure 3). The unstable heteroresistance refers to whenever resistant subpopulations return to susceptible phenotype in the absence of antibiotic pressure during subculturing. Stable heteroresistance includes cases in which resistant subpopulations maintain the resistance phenotype even in the absence of antibiotic pressure.[9,10] Stable heteroresistance is caused by frequent mutations (for example, insertions, deletions and single nucleotide polymorphisms). If these resistance mutations confer low fitness cost, they are more likely to be stable in the absence of antibiotic selective pressure.[9] Various studies have demonstrated that efflux and influx of antibiotics play important role in resistance in subpopulations with stable heteroresistance. For example, in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates, stable imipenem heteroresistance was linked to overexpression of the efflux pump mexAB,[11] while it was observed that in E. coli fosfomycin-heteroresistant isolates, lack of the uhpT gene (encoding hexose-6-phosphate transporter involved in fosfomycin influx) was associated with stable and homogenous nonsusceptibility to fosfomycin.[12]
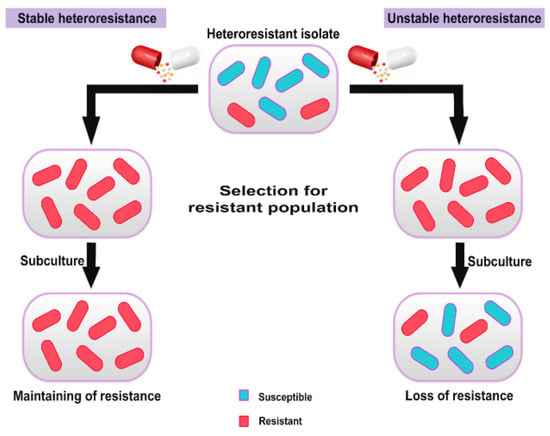
Figure 3.
Stability of heteroresistance.
The mechanisms involved in unstable heteroresistance (more common type of heteroresistance) can be divided into two main categories. The first mechanism is through stable resistance mutations with high fitness costs. The high fitness costs of these mutations may be the main factor in their reversibility during growth in the absence of antibiotic selective pressure. In fact, during several generations of pathogen growth in the absence of antibiotic, selection of compensatory mutations leads to a reduction in fitness cost and thus a reduction in resistance.[9,13,14] The selection of increased fitness and susceptibility through compensatory mutations has been shown in different bacteria such as K. pneumoniae, E. coli and S. Typhimurium.[9] Of note, it has been found that in imipenem-heteroresistant multidrug-resistant (MDR) A. baumannii isolates, insertion of ISAba1 into promoters of a β-lactamase-encoding gene (blaADC-29) is associated with unstable heteroresistance phenotype.[13]
The second mechanism consists of tandem gene amplifications that are mechanistically unstable and costly. The stability of amplifications is affected by frequent unequal crossing overs.[15,16,17] On the other hand, the fitness costs of tandem gene amplifications are associated with their reduction in copy number (reduction of resistance) in the absence of selective pressure.[18] In colistin-heteroresistant S. Typhimurium isolates, resistance was linked to amplification of chromosomal regions including the pmrD gene, which is involved in increasing colistin resistance by up-regulation of proteins involved in modification of lipid A. Indeed, increasing the copy number of resistance genes seems to be associated with the heteroresistance phenotype.[19] It should be noted that mathematical modeling has showed that unstable amplifications may evolve into stable resistance mutations in response to growth under antibiotic pressure.[20] Similarly, evaluation of A. baumannii isolates recovered from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples of a patient with meningitis has shown that colistin heteroresistance has evolved to complete resistance phenotype during a five-day treatment period.[21]
Heteroresistance and treatment failure
Whether the presence of resistant subpopulations is associated with treatment failure is still unclear. Numerous studies have linked treatment failure to heteroresistance in different pathogens. Several studies have shown an association between heteroresistant vancomycin Staphylococcus aureus (hVISA) and instances such as persistent bacteremia, prolonged hospital stays and increased mortality.[22,23] Another study on the epidemiological and clinical features of carbapenem heteroresistant A. baumannii showed similar results.[24] A retrospective study on a patient who experienced recurrent episodes of peritonitis indicated that treatment failure was associated with heterogeneous vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis.[25] Similarly, treatment failure has been linked to carbapenem heteroresistance in A. baumannii.[26]
Although the mentioned studies suggest that heteroresistance can lead to treatment failure, others show the opposite of this hypothesis. Several cohort studies on hVISA have observed no correlation between heteroresistant phenotypes and treatment failure.[23,27,28] Similar results have been found for colistin heteroresistant A. baumannii isolates.[29] These discrepancies between studies may be due to variations in sample sizes and the identification methods, which makes it difficult to compare independent studies. However, it should be noted that pharmacodynamic and mathematical modelling confirms the impact of heteroresistance on the efficacy of antibiotic treatment.[9,30]
Another issue discussed about heteroresistance is the possibility of an association between previous colistin exposure and the frequency of resistant subpopulations. Although the results of some studies indicate a link between prior exposure to colistin and a higher proportion of resistant subpopulations,[31] in some studies the existence of this association has been questioned.[32] Therefore, on the basis of these observations, further research is required to fully understand the parameters associated with heteroresistance.
Heteroresistance detection methods
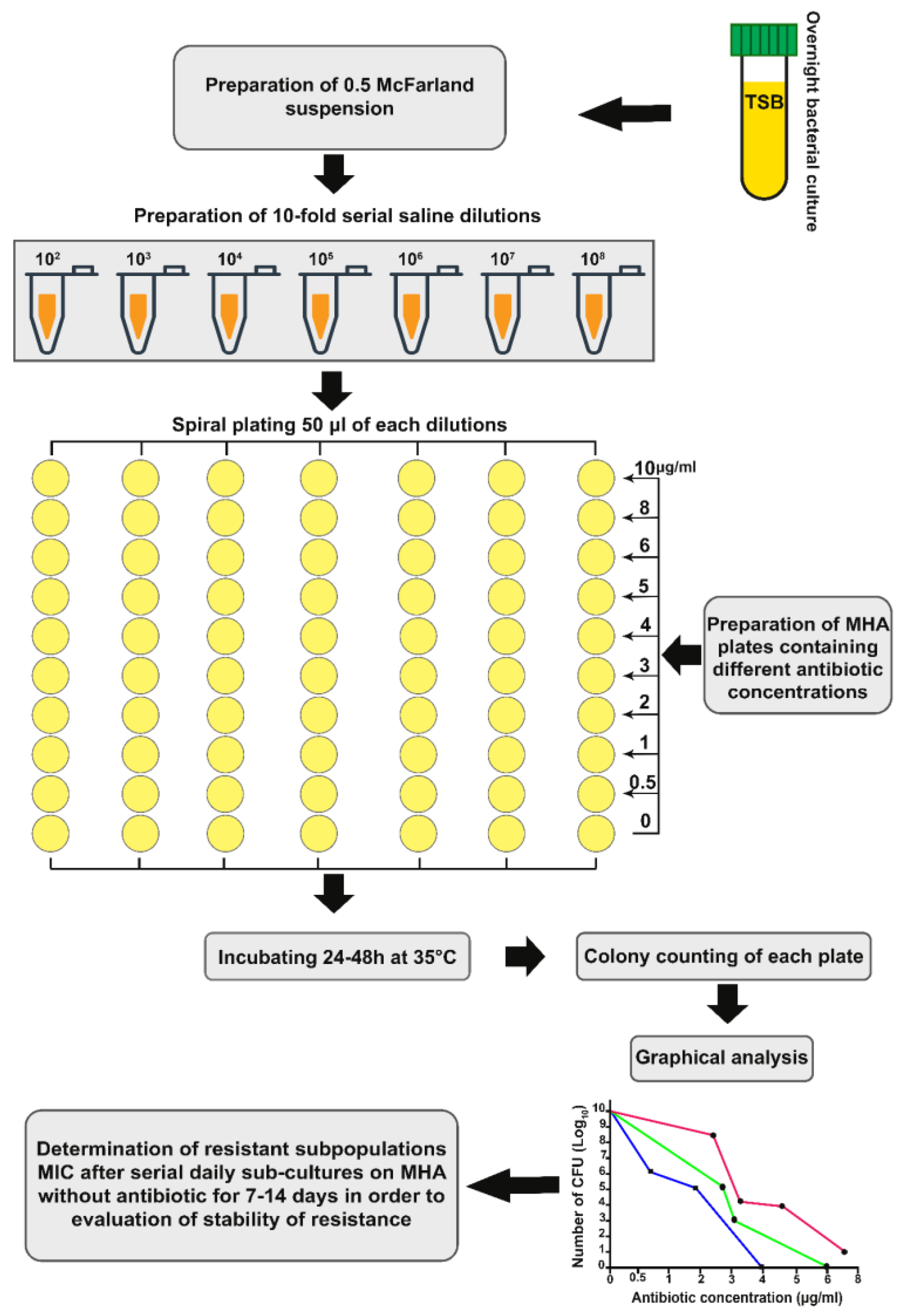
Although bacterial resistance to antibiotics can be assessed by various methods, heteroresistance becomes a health crisis because routine laboratory tests are unable to detect the presence of resistant subpopulations. Population analysis profile (PAP) test is considered as gold standard for identifying heteroresistance but it is time-consuming, costly and therefore not routinely performed in the microbiology laboratory.[4] In PAP method, after inoculation of bacteria at a variety of antibiotic concentrations in Mueller-Hinton (MH) medium, the frequency of the resistant subpopulation of cells is determined (Figure 4).[33] Although the PAP test is the most reliable method, other methods are currently used to identify heteroresistance such as disc diffusion, broth microdilution, E-test, agar screen, agar dilution, VITEK 2, BACTEC 960 liquid media system and molecular detection methods such as line probe assays.[6]
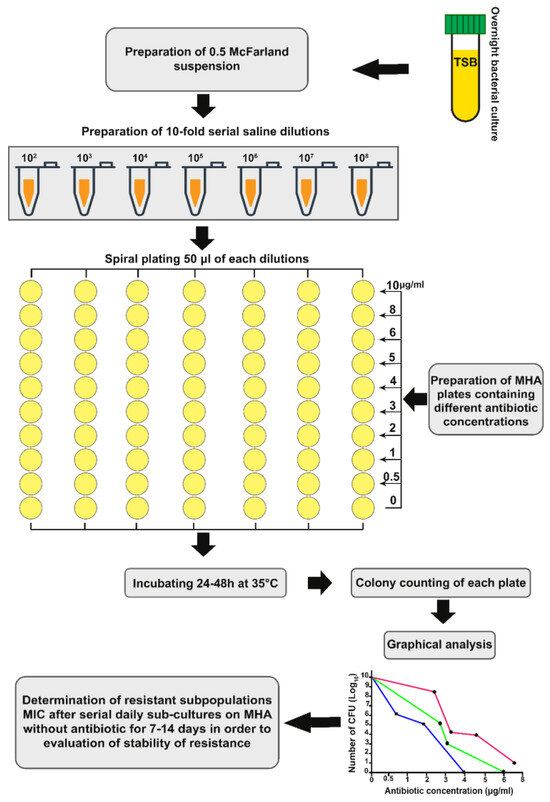
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of population analysis profile (PAP) test protocol to identify heteroresistance. After preparing MHA plates containing different antibiotic concentrations, serial dilutions of bacterial suspension are spread on the plates. The colonies of each plate are then counted after one day of incubation at 35°C. Finally, a graphical analysis of the results is performed. To evaluate the stability of the heteroresistance phenotype, a colony from the highest antibiotic concentration is selected and cultured on MHA without antibiotic for 7 to 14 days, and then the MIC is determined using the agar dilution method.
Comparison of these different methods for detecting colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii showed that VITEK 2 is not a proper method.[34]
However different methods mentioned above seem to have poor sensitivity and poor specificity compared to the PAP method for identification of resistant subpopulations. In addition, there are some new generation methods such as droplet digital PCR, whole genome sequencing and line probe assays that allow detection of genes and mutations involved in resistance. However, the use of these new methods is limited to some pathogens including Helicobacter pylori and Mycobacterium tuberculosis and cannot be applied to all antibiotics.[6,35,36]
Since the identification of heteroresistance phenotype is a prerequisite for choosing an appropriate treatment, it seems that the development of diagnostic tools can help achieve a successful treatment.
Heteroresistance in clinical isolates
Heteroresistance has been observed in a variety of pathogens, and against diverse antibiotics worldwide. Heteroresistance has been detected in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria such as staphylococci, enterococci, Clostridioides difficile, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii, Klebsiella spp., and others.[9] One of the most extensively studied cases is heteroresistance to vancomycin. Vancomycin heteroresistance in S. aureus was first observed in Japan and was then reported from numerous studies on staphylococci.[37] Additionally, the results of a meta-analysis covering 91 studies, showed an increase of the hVISA prevalence from 4.68% in studies before 2006 to 7.01% in 2014. In this study, most of the reports of hVISA prevalence belonged to Asia.[38] Heteroresistance phenotype has also been observed against carbapenems. In a cohort study of A. baumannii in Spain, 24% were heteroresistant to meropenem and 20% to imipenem.[14] Another study displayed imipenem heteroresistance (25%), ertapenem heteroresistance (17.2%) and meropenem heteroresistance (3.9%) among E. coli isolates in China.[39]
Furthermore, the emergence of heteroresistance to last-resort antibiotics such as polymyxins (polymyxin B and colistin) has caused concern. Numerous studies have been performed to identify polymyxins heteroresistance in pathogens, including Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp., Acinetobacter spp., E. coli, S. Typhimurium.[9,40] It should be noted that the variations between the results of studies investigating heteroresistance prevalence may be due to different definitions of heteroresistance and different detection methods.
Colistin resistance and heteroresistance
After the isolation of colistin (polymyxin E) from Paenibacillus polymyxa subsp. colistinus in 1947 by Koyama, this antibiotic was first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 1959.[41] Colistin was an appropriate choice for treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections due to its bactericidal activity through bacterial cell membrane destruction. Indeed, colistin has the ability to bind to anionic groups on the lipid A of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in Gram-negative bacteria through its cationic residues. However, the use of polymyxins was questioned in the 1970s due to reports of nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity and was limited to treatment of diseases such as cystic fibrosis.[42]
The increase in infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria presents a serious problem worldwide. Gram-negative bacteria have the ability to exhibit different resistance phenotypes such as MDR, extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and pan-drug-resistant (PDR) through multiple resistance mechanisms. The emergence and rapid spread of these superbugs (strains of bacteria that are resistant to most of available antibiotics commonly used for treatment) and the lack of new treatment strategies is considered a formidable menace. According to the above mentioned, despite their toxicity, older antibiotics such as colistin were recommended as "last resort” since the mid-1990s.[43]
Unfortunately, the emergence of colistin resistance in Gram-negative pathogens such as P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii and K. pneumoniae has become a global concern in recent years. Colistin resistance in Gram-negative bacteria occurs through various mechanisms.[44] A study showed 57% and 22% colistin resistance rate in K. pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa isolates.[45]
Heteroresistance to colistin was first detected in A. baumannii isolates in 2006.[46] The emergence of the colistin heteroresistance phenomenon has caused confusion in the diagnostic and treatment levels. In fact, the presence of clinically undetected colistin heteroresistance subpopulations leads to treatment failure, prolonged length of hospital stays and even the death of a patient.[47,48,49] According to the studies to date, colistin heteroresistance has been observed in different species including Acinetobacter spp., Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp., E. coli, S. Typhimurium, N. meningitidis and S. maltophilia. In the following section, studies on colistin heteroresistance in these pathogens are discussed.
Colistin heteroresistance in Gram-negative pathogens
1. Acinetobacter spp.
Among the various species of the genus Acinetobacter, A. baumannii is clinically the most important species. A. baumannii is one of the most successful Gram-negative bacteria responsible for a spectrum of nosocomial infections.[50] The ability of this pathogen to acquire resistance to commonly used antibiotics has led to the widespread prevalence of resistant isolates since the 1970s and it has caused global concern.[51] According to the Infectious Diseases Society of America A. baumannii is one of the 6 antibiotic resistant pathogens responsible for a high mortality rate among patients.[52] Although carbapenems have been known as a viable treatment option for multiple resistant A. baumannii, in recent decades studies have shown an upward trend in resistance to carbapenems.[51,53] According to the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Network (EARS-Net) in 2018, the rates of carbapenem resistance among A. baumannii isolates was more than 30%.[54] Increased resistance to carbapenems in MDR A. baumannii strains led to colistin being considered as a last resort treatment option.[51] However, after the first report of colistin resistant A. baumannii in Czech Republic in 1999,[55] the results of studies in different countries indicate the emergence of colistin resistance, mainly associated with monotherapy.[31] A study of 514 A. baumannii isolates collected from various sites across the USA and Puerto Rico showed 5.3% resistance to colistin among the isolates.[56] Based on the World Health Organization Regional Offices reports from 2000 to 2017, colistin resistance in clinical isolates of A. baumannii in Europe and South-East Asia was 1.8% and 6.7% respectively.[57]
1.1. Colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii
Colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii was fist described by Li et al.[46] in 2006 and raised an alarm over dangerous rates of colistin resistance. Colistin heteroresistance is defined as the presence of colistin resistant subpopulations within a susceptible main population. In fact, these subpopulations have the ability to grow in the presence of colistin due to their higher minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC ≥ 2- to 8-fold) than the main population (MIC ≤ 2 mg/L).[4,6] In recent years, there have been several reports of colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii from different parts of the world (Table 1). A number of studies have demonstrated that the emergence of colistin resistant subpopulations is associated with prior exposure to colistin. A report has shown that increased consumption of colistin in a university hospital of Argentina has led to high prevalence of colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii strains.[58] It is suggested that there are two types of colistin-heteroresistance in A. baumannii isolates. Type I has a typical heteroresistance phenotype that can be identified by gold standard method, PAP. Since colistin resistant subpopulations of this type became resistant after exposure to high colistin concentrations, it was suggested that treatment with high colistin concentrations may lead to the emergence of colistin resistance. In contrast, type II colistin-heteroresistant A. baumannii isolates could not survive in high colistin concentrations in PAP. Additionally, these findings indicate the instability of resistance in resistant subpopulations in both types of colistin heteroresistance. Based on these observations, it seems important to differentiate between the two types of heteroresistance because different treatment strategies must be considered for each type.[59]

Table 1.
Heteroresistance to colistin in Acinetobacter spp. isolates.
1.2. Mechanisms of heteroresistance
Although extensive studies have not been performed to investigate the mechanisms of colistin heteroresistance, the results of studies indicate the importance of the three main mechanisms. Mutations of lpxA, lpxC, and lpxD in A. baumannii might be the cause of colistin heteroresistance. lpxA/C/D are involved in the synthesis of the lipid A component of LPS, therefore any mutation within these genes can lead to loss or decrease in production of LPS.[76] It should be noted that such mutations may lead to increased bacterial susceptibility to several antibiotics such as carbapenems, rifampicin and ampicillin/sulbactam, by increasing the permeability of the outer membrane and thus better access to target sites for these antibiotics.[77,78] Furthermore, genetic changes in the pmrA or pmrB gene may lead to colistin heteroresistance. Such mutations can lead to upregulation of pmrCAB operon and the addition of phosphoethanolamine (PEtN) to lipid A through activation of pmrAB two-component system. Following these interactions, the negative charge of the outer membrane of A. baumannii and thus the binding of colistin reduces.[79] C.H. Rodriguez et al.[67] observed that A. baumannii isolates carrying mutations in the lpxC and pmrB genes presented slow growth. They believe that the slow growth of colistin resistant subpopulations can lead to misdetection in microbiology laboratories.
Also, it has been suggested that efflux system overexpression is associated with colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii. Therefore, it can be concluded that the use of efflux pump inhibitors as adjuvants along with colistin treatment can resensitize A. baumannii to colistin.[80]
1.3. Heteroresistance detection
The detection of resistant subpopulations by the traditional susceptibility testing methods is difficult. That is why colistin heteroresistant isolates are usually misdiagnosed as colistin sensitive. Several reasons have been suggested for the failure to identify colistin heteroresistant isolates, including low proportion of colistin-resistant subpopulations, slow growth of colistin-resistant subpopulations and MIC values close to breakpoint values.[67] This misdiagnosis, especially in the case of colistin as a last-line treatment option for MDR A. baumannii, can lead to ineffective treatment initiation, loss of golden treatment time and even increased patient mortality.
Although the gold standard method for identifying colistin heteroresistance is PAP,[4] there are several methods for detection of colistin heteroresistance, each with advantages and disadvantages over the other. However, there are not many studies available comparing different diagnostic methods to identify colistin heteroresistant isolates of A. baumannii. In 2007, Lo-Ten-Foe et al.[34] examined and compared several techniques (VITEK 2, E-test, agar dilution and disk diffusion) with broth microdilution, introduced as a reference method by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), for identifying colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii. The results of their study showed that although VITEK 2 is a reliable and an easy-to-use tool, it is better to be cautious in interpreting the results obtained from genera that typically have colistin heteroresistant subpopulations. In such genera, alternative and appropriate methods should be used to identify resistant subpopulations. The study suggests that if Iso-Sensitest agar is used in the disk diffusion and E-test methods instead of the Mueller-Hinton agar, the identification of resistant colonies within the colistin inhibition zone (known as colistin heteroresistant) is more accurate. The results of the agar dilution test showed high levels of agreement with the broth microdilution method. Of note, agar dilution test can detect colistin heteroresistant subpopulations of A. baumannii regardless of the use of Mueller-Hinton agar or Iso-Sensitest agar.[34]
In 2019, Sherman et al.[33] reviewed and compared three efficient methods for detection of colistin heteroresistance in A. baumannii including disc diffusion, E-test and PAP. As stated in the study by Lo-Ten-Foe et al.,[34] in the E-test technique, observation of colonies within the inhibition zone ellipse indicates a heteroresistant isolate. However, if the frequency of resistant subpopulations in heteroresistant isolates is low, no colony will be seen within the zone of clearing and therefore this technique will be ineffective in these cases. In addition, because E-test strips are expensive, this method may not be ideal as a routine laboratory diagnosis of heteroresistance. In contrast to E-test strips, colistin discs are cost effective and can be used to detect heteroresistance. It should be noted that E-test and disc diffusion are a non-quantitative methods.[33] Additionally, compared to PAP, the sensitivity of the disk diffusion and E-test is 22.9% and 54.2%, respectively; while the specificity of these methods is 100%.[81]
PAP is a reliable, quantitative and reproducible method for detecting heteroresistance. However, one of the disadvantages of this method is that it is time consuming and requires more materials than other techniques.[33]
In addition, there are two methods, including time-kill assay and resistant colony restreak, for differentiating between heteroresistance and other forms of resistance such as stable mutation or persister cells. Persisters, mutant subpopulations of a bacterial strain, does not have the ability to grow in the presence of antibiotics, unlike heteroresistant subpopulations. Therefore, time-kill assay method examines the ability of bacteria to grow in the presence or absence of colistin and thus confirms the heteroresistance of the isolate. On the other hand, in resistant colony restreak method, a single colony obtained from a PAP plate or from within the inhibition zone on a disk diffusion or E-test assay palate is transferred to a broth media in the absence of colistin. The decrease in the frequency of the resistant subpopulation after culture in the broth media confirms the colistin heteroresistance of the isolate.[33]
1.4. Therapeutic options
In addition to what was revealed about type I colistin-heteroresistant A. baumannii isolates, several studies have confirmed the conversion of colistin heteroresistant A. baumannii to colistin resistant during treatment.[31] High nephrotoxicity risk of colistin consumption has complicated the situation. However, there are several recommendations to confront with these problems. Combination therapy can be one of the solutions of interest. A study on two mouse infection models showed that amplification of colistin-resistant A. baumannii subpopulations was linked to monotherapy with colistin.[62] Rodriguez et al.[63] have shown that using rifampicin or imipenem with colistin has a synergistic effect on heteroresistant A. baumannii isolates and can help prevent the development of resistance. They also reported a 22-year-old case which developed fever and rise of CSF after surgery for meningioma and received various treatments and became resistant to colistin 48 hours after colistin administration. However, after 5 days of starting combination therapy with colistin and rifampicin, CSF cultures were sterilized and the patient was successfully treated.[48] Nonetheless, in the study by Gedik et al., conducted on 51 patients infected with colistin-only sensitive A. baumannii (heteroresistance was not checked), it was found that there was no significant difference between outcomes of colistin monotherapy and colistin combined therapy among patients with bloodstream infections and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). However, they noted that colistin monotherapy may result in the emergence of heteroresistant strains.[82]
Another way is to use polymyxin B instead of colistin. Aggarwal et al.[83] has recommended that polymyxin B could be used instead of colistin because of the high toxicity of colistin at their research recommended dose. Indeed, colistin nephrotoxicity is completely dose-dependent.
The third potential solution to the problem is to use antioxidants. The results obtained from Arslan et al. research have suggested that luteolin (a common flavonoid in different types of plants) can be used as an inhibitor of high nephrotoxicity, together with colistin. However, confirmation of this finding requires certain clinical studies.[84] It seems that confronting the emergence of colistin resistance requires the development of new therapeutic strategies.
2. Klebsiella spp.
A member of ESKAPE pathogens, rod-shaped Gram-negative K. pneumoniae is the most important species of the genus Klebsiella and the leading cause of community- and hospital-acquired infections. The ability of this pathogen to produce extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) has led to resistance to β-lactam antibiotics since 1983.[85] However, carbapenems seemed to be a good choice for treatment of infections caused by ESBL-producing pathogens until carbapenem-resistant strains were first reported in 1993.[86] The global prevalence of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae is associated with treatment failure and high mortality rate and thus has revived the use of colistin for critically ill patients.[87] With the start of colistin administration for the treatment of MDR K. pneumoniae, there were reports of colistin resistance from around the world and posed a serious threat to public health. Mutations in two-component regulatory systems and insertional inactivation of the mgrB regulator seem to be the most common colistin resistance mechanism in K. pneumoniae isolates.[88]
2.1. Colistin heteroresistance in K. pneumoniae
Since colistin is often the last resort for K. pneumoniae infections, reports of colistin heteroresistant K. pneumoniae in the last two decades are worrisome (Table 2).[89,90,91,92] The inability of routine susceptibility tests to identify colistin heteroresistant isolates is challenging for clinical laboratories and leads to treatment failure.[47] In the study by Poudyal et al.,[89] it was found that out of 16 colistin-susceptible isolates based on MICs, 15 isolates displayed colistin heteroresistance based on the PAP method. In addition, Band et al.[47] have reported instance of treatment failure result from undetected colistin heteroresistant K. pneumoniae which indicates that the usual colistin susceptibility tests are unreliable. The association between colistin exposure and the emergence of resistant subpopulations in K. pneumoniae has not been extensively investigated. However, Kim et al.[93] demonstrated that exposure to colistin increases MIC and causes diverse amino acid substitutions in pmrB, phoPQ and mgrB genes. Although Barragán-Prada et al.[32] found that direct colistin selective pressure was not the only cause of the emergence of colistin resistance in K. pneumoniae, similar to Seo et al.[94] they suggest that evaluation of colistin susceptibility should be done carefully, even in patients not exposed to colistin.

Table 2.
Heteroresistance to colistin in Klebsiella spp. isolates
Interestingly, some colistin resistant subpopulations from the same parental strain have shown different amino acid substitutions.[91,93] On the other hand, it has been reported that some colistin resistant subpopulations have no mutations in the genes responsible for resistance.[93] These observations suggest that the mechanisms of colistin resistance in K. pneumoniae are not yet fully understood and further studies are needed.
2.2. Mechanisms of heteroresistance
The deciphering of colistin heteroresistance mechanisms in K. pneumoniae was first performed in 2015 by Jayol et al.[106] They observed that amino acid substitutions in protein PhoP (a part of the PhoPQ two-component system) were involved in the development of colistin resistance. In following years, other instances of mutations in the phoPQ gene were reported from different countries.[91,92,95] phoPQ mutations lead to the overexpression of pmrE gene and pmrHFIJKLM operon (involved in 4-deoxyaminoarabinose (LAra4N) synthesis) and pmrC gene (involved in phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) synthesis). The addition of LAra4N and pEtN to lipid A increases the positive charges of the LPS and finally reduces the affinity of LPS to colistin.[107] Of note, the PhoP/PhoQ system is negatively regulated by mgrB. mgrB is a regulatory transmembrane protein and is produced upon activation of the phoPQ signaling system. Since the phoQ activates phoP by phosphorylation, mgrB can repress phoP phosphorylation by interaction with the sensor kinase phoQ. Therefore, alterations in mgrB can lead to up-regulation of the phoPQ system and then to colistin resistance by up-regulation of the pmrHFIJKLM operon.[108] Mutations in two-component regulatory systems, pmrAB, is another mechanism involved in colistin resistance in K. pneumoniae. PmrAB has the same mechanism of action as the PhoPQ.[91]
Additionally, a study of colistin-resistant subpopulations among ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae isolates showed that in addition to mutations in phoPQ and mgrB, mutations in the yciM and lpxM genes may also play a role in colistin resistance. Because mutation in yciM, a gene involved in LPS biosynthesis, leads to decreased susceptibility to colistin in Escherichia coli, probably also causes colistin resistance in K. pneumoniae. Moreover, lpxM is responsible for the acylation of lipid A in Enterobacteriaceae and thereby mutation in this gene is involved in colistin resistance.[95] Silva et al.[109] demonstrated for the first time that biofilm formation may be associated with the emergence of colistin heteroresistance in K. pneumoniae. Sato et al.[110] have reported that acquisition of colistin heteroresistance may be associated with disrupting mutation in the DNA repair enzyme MutS in K. pneumoniae. Albeit plasmid-mediated colistin resistance in the form of mcr-1 has received a lot of attention,[111] no mcr-1 plasmid-mediated gene have been found in studies on colistin heteroresistant K. pneumoniae isolates.[32,92,112]
2.3. Heteroresistance detection
Usually, methods other than PAP are not able to reliably identify resistant subpopulations because the proportion of heteroresistant cells is normally low. In the study by Meletis et al.[90] among the 20 K. pneumoniae clinical isolates that were classified as colistin-susceptible by routine susceptibility testing, 12 isolates contained resistant subpopulations. A study by Seo et al.[94] also showed that disc diffusion and E-test methods were not able to detect colistin heteroresistance compared to the PAP method. Additionally, Poudyal et al.[89] observed that detection of colistin heteroresistance by broth microdilution is not reliable.
2.4. Therapeutic options
Unfortunately, there is not much information on the treatment of heteroresistant K. pneumoniae isolates. However, it is suggested that colistin monotherapy and long dosage intervals may be problematic for the treatment of colistin-heteroresistant K. pneumoniae strains.[89] Cheong et al.[91] demonstrated that meropenem combined with colistin allowed rapid eradication of colistin-heteroresistant K. pneumoniae isolates. In addition, it has been shown that combination regimens in colistin-heteroresistant and fosfomycin-susceptible K. pneumoniae isolate had a more favorable effect than colistin monotherapy, while in colistin-heteroresistant and fosfomycin-resistant K. pneumoniae isolate no significant difference was seen.[113] In fact, it is necessary to examine the resistance patterns of the isolates before initiating combination therapy. Further investigations on therapeutic options for colistin-heteroresistant K. pneumoniae infections is warranted.
3. Enterobacter spp.
The opportunistic Enterobacter spp., a member of the ESKAPE group of significant bacterial pathogens in humans, have the ability to cause infections in the respiratory, urinary, blood and gastrointestinal tracts.[52,114] The emergence of multidrug resistance and carbapenem resistance in Enterobacter spp. due to several mechanisms caused colistin to be reconsidered as last line treatment option.[115] However, resistance to colistin has emerged recently as a consequence of chromosomal mutations and plasmid-mediated mcr-1 gene in Enterobacter spp. and has sounded the alarm.[116,117]
3.1. Colistin heteroresistance in Enterobacter cloacae
Colistin-heteroresistant E. cloacae first reported in 2007 and it was suggested that exposure to colistin induced resistance.[34] Subsequently, the second report of heteroresistance to colistin in E. cloacae was reported from the United States in 2014 and demonstrated that treatment with colistin has led to an increase in the frequency of the resistant subpopulations.[118] Additionally, the isolation of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacter strains with heteroresistance to colistin is worrisome because colistin is considered as the last resort for treatment of MDR infections.[119,120] The characteristics of studies on colistin heteroresistance in Enterobacter spp. are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Heteroresistance to colistin in Enterobacter spp. isolates
3.2. Mechanisms of heteroresistance
The major mechanism of colistin heteroresistance in E. cloacae is associated with the arnBCADTEF operon. Lipid A modification enzymes are regulated by PmrAB and PhoPQ two-component systems which directly activate arn expression in Enterobacteriaceae.[125] However, the results of studies show that unlike E. coli, Salmonella enterica or K. pneumoniae, colistin heteroresistance in E. cloacae involves a model of PmrAB-independent arn regulation. Indeed, PhoP can induce L-Ara4N biosynthesis through binding directly to the arnB promoter and PmrAB is unessential for colistin resistance in E. cloacae.[126] Additionally, Huang et al.[127] found that the presence of a new small transmembrane protein, encoded by the ecr gene, increases the expression of PhoP and the arnBCADTEF operon and thus contributes to colistin heteroresistance in E. cloacae complex. They also found that three genes phoP, dedA (encoding an inner membrane protein of the dedA family) and tolC (encoding part of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump) are involved in colistin heteroresistance. This is the first report of a correlation between the dedA gene and heteroresistance.[127] It was also previously found in a study that the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump proteins induction is triggered by a soxRS regulator. It has been suggested that cell stress produced by colistin leads to the overexpression of soxRS and thus overexpression of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump in colistin heteroresistant Enterobacter strains.[122] Outer membrane proteins (OMPs) analysis in colistin-susceptible and its colistin-heteroresistant Enterobacter asburiae counterpart confirms the role of the altered cell wall in resistance.[128] Association between the cluster membership and the heteroresistance phenotype to colistin in E. cloacae is debatable. A study reported that colistin heteroresistance in E. cloacae appeared cluster-dependent based on partial sequences of the hsp60 gene, while another study suggested that reduced colistin susceptibility occurs sporadically in this pathogen.[114,121]
3.3. Heteroresistance detection
Similar to the microorganisms mentioned above, in Enterobacter spp. PAP is described as gold standard method for detection of colistin heteroresistance. However, studies show that other methods have the ability to detect resistant subpopulations. Lo-Ten-Foe et al.[34] demonstrated that agar dilution, E-test, disk diffusion (all on Iso-Sensitest agar instead of MH agar) and broth microdilution methods have the ability to identify resistant subpopulations in E. cloacae while the VITEK 2 displayed low sensitivity and seemed to be unreliable in the identification of heteroresistance. However, another study showed that the broth microdilution method was not a reliable method for detecting heteroresistance.[121] In a study by Band et al.,[97] 93.2% of colistin heteroresistant isolates were classified as colistin susceptible by routine laboratory diagnostic methods. It has also been shown in E. cloacae that misclassification of a heteroresistant isolate as susceptible has led to colistin treatment failure.[7]
3.4. Therapeutic options
Although no specific study has been performed on the treatment of Enterobacter spp. colistin heteroresistant isolates, a study by Napier et al.[118] suggests that treatment of heteroresistant isolates with colistin leads to an increase in resistant subpopulations and induction of cross-resistance to the host antimicrobial lysozyme. These findings highlight the importance of identification of heteroresistance in microbiology laboratory before initiating treatment and the importance of combination therapy in colistin heteroresistant isolates.
4. Pseudomonas spp.
P. aeruginosa, well-defined species of the genus Pseudomonas, is a Gram-negative nonfermenting bacillus which has the ability to cause severe infections such as bloodstream infections, urinary tract infections, pneumonia and surgical site infections.[129] Unfortunately, improper use of antibiotics in recent years has led to spreading antimicrobial resistance in P. aeruginosa.[130] so for this reason carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa is on the "critical” group by the World Health Organization and is in urgent need of new antibiotics.[131] Because multidrug resistant P. aeruginosa has shown high susceptibility to colistin, colistin has been described as the last-line antibiotic for the treatment of MDR/XDR infections.[130] Over past years, reports of colistin-resistant P. aeruginosa outbreaks and plasmid-borne colistin resistance were published and caused public health concern worldwide.[132,133]
4.1. Colistin heteroresistance in P. aeruginosa
Co-existence of MDR and susceptible strains has been reported from a single P. aeruginosa isolate obtained from a cystic fibrosis patient in 2010. [134] Then in 2011 the first colistin heteroresistance in P. aeruginosa was reported by Bergen et al.[135] In a study by Juhasz et al.,[40] the prevalence of colistin heteroresistance among 152 Pseudomonas spp. clinical isolates from blood cultures was 27%. In addition, in a recent study of 143 colistin-susceptible carbapenem-resistant P. aeruginosa isolates, colistin heteroresistance was observed in up to 26% of the samples.[136] In the most recent study in 2024, Banerjee et al.[137] reported 1% colistin heteroresistance in P. aeruginosa.
4.2. Mechanisms of heteroresistance
The mechanisms involved in colistin heteroresistance in P. aeruginosa are examined only in one study. Of note, no significant difference was observed between the colistin resistance and colistin heteroresistance mechanism. Alterations of the PmrAB regulatory system was the main mechanism of heteroresistance in this study.[138]
4.3. Heteroresistance detection
Unfortunately, no specific studies have been performed on diagnostic methods of heteroresistance in Pseudomonas spp. Considering that routine susceptibility tests are not able to accurately identify the heteroresistance phenotype, the PAP test is still known as the gold standard. Lack of information in reviewing and comparing different diagnostic tests of heteroresistance highlights the need for further studies to introduce available and cost-effective identification methods.
4.4. Therapeutic options
Studies reveal that monotherapy leads to the emergence of colistin resistance, so combination therapy has been suggested to prevent this problem.[139,140] Colistin combined with meropenem and doripenem has shown a beneficial effect in patient care especially at the commencement of therapy. It has been suggested that colistin may improve bactericidal activity of meropenem and doripenem by affecting on membrane permeability which increases their access to the periplasmic space and penicillin-binding proteins. Thus, this finally reduces the amount of bacteria in the face of the immune system.[135,141]
5. Other Gram-negative pathogens
Limited studies have been performed on colistin heteroresistance in other Gram-negative bacteria. The prevalence of colistin heteroresistance among E. coli clinical isolates was reported in 2015 and 2017.[40,97] The first report for colistin-resistance and heteroresistance mechanisms in E. coli demonstrated that substitutions in pmrB and upregulation of the pmrCAB operon are mainly involved in colistin heteroresistance, while the presence of the mcr-1 gene contributed to resistance to colistin. Results of that study suggest that carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) action has a significant effect on colistin-heteroresistant isolates.[142] Then another study confirmed the role of mutations in pmrB and also showed that mutations in phoQ were associated with colistin heteroresistance in E. coli isolates in swine.[143] Additionally, it has been found that the plasmid-mediated Kluyvera-Like arnBCADTEF operon is a new colistin heteroresistance mechanism in E. coli.[144]
Results of a study revealed that over-expression of the pmrD gene conferred colistin resistance in S. Typhimurium and proposed that the variable copy number of the pmrD gene in subpopulations can explain the heteroresistance phenomenon.[19] Also, the first identifications of colistin heteroresistance in N. meningitidis and Citrobacter freundii were reported in 2019 and 2024, respectively.[145,146] The heteroresistance phenomenon has been described in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia too. Results of that study suggest that combination therapy should be used against S. maltophilia due to its ability to rapidly adapt to colistin.[147]
Conclusions
Labiaplasty, particularly through laser-assisted techniques, has proven effective for many women seeking relief from physical discomfort or dissatisfaction with labial appearance. While postoperative complications such as infection remain relatively uncommon, they can occur and should be proactively addressed through thorough preoperative screening, careful surgical technique, and structured aftercare. Despite increasing demand and high patient satisfaction, the field still lacks standardized definitions, classification systems, and large-scale outcome studies. To ensure safe, ethical, and patient-centered care, future research must focus on establishing evidence-based guidelines that balance functional outcomes, aesthetic goals, and psychological well-being.
Author Contributions
FD conceptualized and led the development of the manuscript based on her clinical experience, contributed substantially to the literature review, and drafted the initial version of the article. SA assisted in the development of the manuscript, supported the literature review, and contributed to drafting and editing the text. MMC contributed to the literature review and to revising the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. ASC provided academic supervision, contributed to the conceptual framing of the article, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of interest
All authors – none to declare.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States. 2013. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/media/pdfs/ar-threats-2013-508.pdf (accessed on day month year).
- O’Neill, J. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations; Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Environmental and genetic modulation of the phenotypic expression of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017, 41, 374–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Halfawy, O.M.; Valvano, M.A. Antimicrobial heteroresistance: an emerging field in need of clarity. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015, 28, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, H.E.; Leidy, G. Mode of action of streptomycin on type b H. influenzae: I. Origin of resistant organisms. J Exp Med. 1947, 85, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.I.; Nicoloff, H.; Hjort, K. Mechanisms and clinical relevance of bacterial heteroresistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2019, 17, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Band, V.I.; Crispell, E.K.; Napier, B.A.; et al. Antibiotic failure mediated by a resistant subpopulation in Enterobacter cloacae. Nat Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewachter, L.; Fauvart, M.; Michiels, J. Bacterial heterogeneity and antibiotic survival: understanding and combatting persistence and heteroresistance. Mol Cell. 2019, 76, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoloff, H.; Hjort, K.; Levin, B.R.; Andersson, D.I. The high prevalence of antibiotic heteroresistance in pathogenic bacteria is mainly caused by gene amplification. Nat Microbiol. 2019, 4, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plipat, N.; Livni, G.; Bertram, H.; Thomson, R.B., Jr. Unstable vancomycin heteroresistance is common among clinical isolates of methiciliin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2494–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Dong, C.; Chen, Y. Research of the heteroresistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to imipenem. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015, 8, 6129–6132. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, A.E.; Ito, R.; Mustapha, M.M.; et al. Frequency and mechanisms of spontaneous fosfomycin nonsusceptibility observed upon disk diffusion testing of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 2017, 56, e01368-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Chen, C.-L.; Wang, S.-B.; et al. Imipenem heteroresistance induced by imipenem in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanism and clinical implications. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011, 37, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenca, F.F.; Sánchez, M.d.C.G.; Caballero-Moyano, F.J.; et al. Prevalence and analysis of microbiological factors associated with phenotypic heterogeneous resistance to carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012, 39, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reams, A.B.; Roth, J.R. Mechanisms of gene duplication and amplification. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015, 7, a016592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Roth, J. Spontaneous tandem genetic duplications in Salmonella typhimurium arise by unequal recombination between rRNA (rrn) cistrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981, 78, 3113–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandegren, L.; Andersson, D.I. Bacterial gene amplification: implications for the evolution of antibiotic resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009, 7, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Anjum, M.; Berg, O.G.; Andersson, D.I.; Sandegren, L. High fitness costs and instability of gene duplications reduce rates of evolution of new genes by duplication-divergence mechanisms. Mol Biol Evol. 2014, 31, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjort, K.; Nicoloff, H.; Andersson, D.I. Unstable tandem gene amplification generates heteroresistance (variation in resistance within a population) to colistin in Salmonella enterica. Mol Microbiol. 2016, 102, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Berg, O.G.; Roth, J.R.; Andersson, D.I. Contribution of gene amplification to evolution of increased antibiotic resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 2009, 182, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavian, M.; Shoja, S.; Nashibi, R.; et al. Post neurosurgical meningitis due to colistin heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2014, 7, e12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Kim, Y.; Jung, S.-I.; et al. agr functionality affects clinical outcomes in patients with persistent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017, 36, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maor, Y.; Hagin, M.; Belausov, N.; Keller, N.; Ben-David, D.; Rahav, G. Clinical features of heteroresistant vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia versus those of methicillin-resistant S. aureus bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 2009, 199, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cuenca, F.; Gómez-Sánchez, M.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical features associated with colonisation/infection by Acinetobacter baumannii with phenotypic heterogeneous resistance to carbapenems. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012, 40, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieradzki, K.; Roberts, R.B.; Serur, D.; Hargrave, J.; Tomasz, A. Heterogeneously vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain causing recurrent peritonitis in a dialysis patient during vancomycin therapy. J Clin Microbiol. 1999, 37, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, P.G.; Schneiders, T.; Hamprecht, A.; Seifert, H. In vivo selection of a missense mutation in adeR and conversion of the novel blaOXA-164 gene into blaOXA-58 in carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a hospitalized patient. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 5021–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.-H.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Comparison of the clinical features, bacterial genotypes and outcomes of patients with bacteraemia due to heteroresistant vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-susceptible S. aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012, 67, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hal, S.J.; Jones, M.; Gosbell, I.B.; Paterson, D.L. Vancomycin heteroresistance is associated with reduced mortality in ST239 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus blood stream infections. PloS One. 2011, 6, e21217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, P.; Hunt, L.N.; Pouch, S.M.; et al. Detection of colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter baumannii from blood and respiratory isolates. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018, 91, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-H.; Li, J.; Nation, R.L. Activity of colistin against heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii and emergence of resistance in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3413–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakonstantis, S.; Saridakis, I. Colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter spp.: systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence and discussion of the mechanisms and potential therapeutic implications. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020, 56, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Prada, H.; Ruiz-Hueso, P.; Tedim, A.P.; et al. Emergence and dissemination of colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates expressing OXA-48 plus CTX-M-15 in patients not previously treated with colistin in a Spanish university hospital. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019, 93, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, E.X.; Wozniak, J.E.; Weiss, D.S. Methods to evaluate colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter baumannii. Methods Mol Biol. 2019, 1946, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo-Ten-Foe, J.R.; de Smet, A.M.G.; Diederen, B.M.; Kluytmans, J.A.; van Keulen, P.H. Comparative evaluation of the VITEK 2, disk diffusion, Etest, broth microdilution, and agar dilution susceptibility testing methods for colistin in clinical isolates, including heteroresistant Enterobacter cloacae and Acinetobacter baumannii strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 3726–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Talarico, S.; Yao, L.; et al. Droplet digital PCR detection of Helicobacter pylori clarithromycin resistance reveals frequent heteroresistance. J Clin Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00019-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operario, D.J.; Koeppel, A.F.; Turner, S.D.; et al. Prevalence and extent of heteroresistance by next generation sequencing of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. PLoS One. 2017, 12, e0176522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, K.; Aritaka, N.; Hanaki, H.; et al. Dissemination in Japanese hospitals of strains of Staphylococcus aureus heterogeneously resistant to vancomycin. Lancet. 1997, 350, 1670–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Chang, W.; Dai, Y.; Ma, X. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of vancomycin-intermediate and heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus isolates. PloS One. 2015, 10, e0136082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Huang, S.; Yang, S.; Pu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. Impact of carbapenem heteroresistance among clinical isolates of invasive Escherichia coli in Chongqing, southwestern China. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015, 21, 469.e1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhász, E.; Iván, M.; Pintér, E.; Pongrácz, J.; Kristóf, K. Colistin resistance among blood culture isolates at a tertiary care centre in Hungary. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2017, 11, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y. A new antibiotic ‘colistin’ produced by spore-forming soil bacteria. J Antibiot. 1950, 3, 457–458. [Google Scholar]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K. Colistin: the revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2005, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, K.S.; Pogue, J.M.; Tran, T.B.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Agents of last resort: polymyxin resistance. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2016, 30, 391–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialvaei, A.Z.; Samadi Kafil, H. Colistin, mechanisms and prevalence of resistance. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015, 31, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nawawy, A.; Ramadan, M.A.-F.; Antonios, M.A.-M.; Arafa, S.A.-F.; Hamza, E. Bacteriologic profile and susceptibility pattern of mechanically ventilated paediatric patients with pneumonia. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2019, 18, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Rayner, C.R.; Nation, R.L.; et al. Heteroresistance to colistin in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, V.I.; Satola, S.W.; Burd, E.M.; Farley, M.M.; Jacob, J.T.; Weiss, D.S. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae exhibiting clinically undetected colistin heteroresistance leads to treatment failure in a murine model of infection. mBio. 2018, 9, e02448-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernan, R.C.; Karina, B.; Gabriela, G.; Marcela, N.; Carlos, V.; Angela, F. Selection of colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in postneurosurgical meningitis in an intensive care unit with high presence of heteroresistance to colistin. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009, 65, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Kil, M.C.; Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.J.; Park, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; et al. Characterisation of successive Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from a deceased haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis patient. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017, 49, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbanipour, R.; Ghalavand, Z. Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, virulence factors, novel therapeutic options and mechanisms of resistance to antimicrobial agents with emphasis on tigecycline. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022, 47, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkshoorn, L.; Nemec, A.; Seifert, H. An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007, 5, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; et al. Bad bugs, no drugs: no ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi Nojookambari, N.; Sadredinamin, M.; Dehbanipour, R.; et al. Prevalence of β-lactamase-encoding genes and molecular typing of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates carrying carbapenemase OXA-24 in children. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in Europe 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hejnar, P.; Kolár, M.; Hájek, V. Characteristics of Acinetobacter strains (phenotype classification, antibiotic susceptibility and production of beta-lactamases) isolated from haemocultures from patients at the Teaching Hospital in Olomouc. Acta Univ Palacki Olomuc Fac Med. 1999, 142, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Queenan, A.M.; Pillar, C.M.; Deane, J.; et al. Multidrug resistance among Acinetobacter spp. in the USA and activity profile of key agents: results from CAPITAL Surveillance 2010. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012, 73, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pormohammad, A.; Mehdinejadiani, K.; Gholizadeh, P.; et al. Global prevalence of colistin resistance in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb Pathog. 2020, 139, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, C.H.; Nastro, M.; Fiorilli, G.; et al. Trends in the resistance profiles of Acinetobacter baumannii endemic clones in a university hospital of Argentina. J Chemother. 2016, 28, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.-K.; Kim, H.; Ko, K.S. Two types of colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2114–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.S.; Murray, C.K.; Jorgensen, J.H. Colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter and its association with previous colistin therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, W.; Owen, R.J.; Poudyal, A.; et al. Colistin hetero-resistance in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from the Western Pacific region in the SENTRY antimicrobial surveillance programme. J Infect. 2009, 58, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhani, R.V.; Turnidge, J.D.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. fAUC/MIC is the most predictive pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic index of colistin against Acinetobacter baumannii in murine thigh and lung infection models. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010, 65, 1984–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.H.; De Ambrosio, A.; Bajuk, M.; et al. In vitro antimicrobials activity against endemic Acinetobacter baumannii multiresistant clones. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2010, 4, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.E.; Mobilia, L.N.; Posse, G.R. Comparative evaluation of the sensitivity of Acinetobacter to colistin, using the prediffusion and minimum inhibitory concentration methods: detection of heteroresistant isolates. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2011, 43, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vidaillac, C.; Benichou, L.; Duval, R.E. In vitro synergy of colistin combinations against colistin-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4856–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; et al. The evaluation of four in vitro susceptibility testing methods for colistin on carbapenenm-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Jundishapur J Microbiol. 2017, 10, e55956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.H.; Traglia, G.; Bastias, N.; et al. Discrepancies in susceptibility testing to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii: The influence of slow growth and heteroresistance. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2019, 54, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezadi, F.; Jamali, A.; Heidari, A.; Javid, N.; Ardebili, A. Heteroresistance to colistin in oxacillinase-producing carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Gorgan, Northern Iran. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020, 21, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çağlan, E.; Nigiz, Ş.; Sancak, B.; Gür, D. Resistance and heteroresistance to colistin among clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2020, 67, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, J.; Lu, H.; et al. Deciphering colistin heteroresistance in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates from Wenzhou, China. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2020, 73, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, F.; Visca, P.; Runci, F.; Antonelli, G.; Raponi, G. Susceptibility testing of colistin for Acinetobacter baumannii: How far are we from the truth? Antibiotics (Basel). 2021, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.; Kwon, K.T.; Ko, K.S. Multiple heteroresistance to tigecycline and colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates and its implications for combined antibiotic treatment. J Biomed Sci. 2023, 30, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, H.; Hameir, A.; Nutman, A.; et al. Prevalence and clinical consequences of colistin heteroresistance and evolution into full resistance in carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol Spectr. 2023, 11, e0509322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, A.; Hanif, F.; Irfan, R.; Qasim, A.; Usman, J. Incidence of colistin heteroresistance among carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates in a tertiary care hospital in Pakistan. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2025, 44, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakzad, I.; Yarkarami, F.; Kalani, B.S.; Shafieian, M.; Hematian, A. Inhibitory effects of carvacrol on biofilm formation in colistin heteroresistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2024, 21, e280923221542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, J.H.; Harper, M.; Harrison, P.; et al. Colistin resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii is mediated by complete loss of lipopolysaccharide production. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4971–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Owen, R.J.; Wong, S.; Spelman, D.; Franklin, C. Antibiograms of multidrug-resistant clinical Acinetobacter baumannii: promising therapeutic options for treatment of infection with colistin-resistant strains. Clin Infect Dis. 2007, 45, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordqvist, H.; Nilsson, L.E.; Claesson, C. Mutant prevention concentration of colistin alone and in combination with rifampicin for multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016, 35, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D.; Nickel, G.C.; Bajaksouzian, S.; et al. Resistance to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii associated with mutations in the PmrAB two-component system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3628–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.; Antunes, J.; Simões, A.; et al. Contribution of efflux to colistin heteroresistance in a multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolate. J Med Microbiol. 2018, 67, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezadi, F.; Ardebili, A.; Mirnejad, R. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing for polymyxins: challenges, issues, and recommendations. J Clin Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01390-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşek, F.; Gedik, H.; Yıldırmak, M.; et al. Colistin against colistin-only-susceptible Acinetobacter baumannii-related infections: monotherapy or combination therapy? Indian J Med Microbiol. 2012, 30, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Dewan, A. Comparison of nephrotoxicity of colistin with polymyxin B administered in currently recommended doses: a prospective study. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2018, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, B.Y.; Arslan, F.; Erkalp, K.; et al. Luteolin ameliorates colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in the rat models. Ren Fail. 2016, 38, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, H.; Shah, P.; Krcmery, V.; Antal, M.; Mitsuhashi, S. Transferable resistance to cefotaxime, cefoxitin, cefamandole and cefuroxime in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens. Infection. 1983, 11, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Analysis of a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class A beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae and of its LysR-type regulatory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994, 91, 7693–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Duin, D.; Kaye, K.S.; Neuner, E.A.; Bonomo, R.A. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: a review of treatment and outcomes. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013, 75, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aris, P.; Robatjazi, S.; Nikkhahi, F.; Marashi, S.M.A. Molecular mechanisms and prevalence of colistin resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae in the Middle East region: a review over the last 5 years. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2020, 22, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudyal, A.; Howden, B.P.; Bell, J.M.; et al. In vitro pharmacodynamics of colistin against multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008, 62, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meletis, G.; Tzampaz, E.; Sianou, E.; Tzavaras, I.; Sofianou, D. Colistin heteroresistance in carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011, 66, 946–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Wi, Y.M.; Peck, K.R.; Ko, K.S. Colistin heteroresistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates and diverse mutations of PmrAB and PhoPQ in resistant subpopulations. J Clin Med. 2019, 8, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-León, F.; Lima, C.A.; González-Rocha, G.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Bello-Toledo, H. Colistin heteroresistance among extended spectrum β-lactamases-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microorganisms. 2020, 8, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Ko, K.S. Diverse genetic alterations responsible for post-exposure colistin resistance in populations of the same strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018, 52, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Wi, Y.M.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Ko, K.S. Detection of colistin-resistant populations prior to antibiotic exposure in KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. J Microbiol. 2021, 59, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaby, T.; Kucukkose, E.; Janssen, A.B.; et al. Genomic characterization of colistin heteroresistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae during a nosocomial outbreak. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6837–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, J.E.; Band, V.I.; Conley, A.B.; et al. A nationwide screen of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae reveals an isolate with enhanced virulence and clinically undetected colistin heteroresistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00107-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Band, V.I.; Satola, S.W.; Smith, R.D.; et al. Colistin heteroresistance is largely undetected among carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales in the United States. mBio. 2021, 12, e02881-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 98 Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, L.; et al. Heteroresistance is associated with in vitro regrowth during colistin treatment in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front Microbiol. 2022, 13, 868991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-León, I.; Pérez-Nadales, E.; Marín-Sanz, J.A.; García-Martínez, T.; Martínez-Martínez, L. Heteroresistance to colistin in wild-type Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from clinical origin. Microbiol Spectr. 2023, 11, e0223823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-León, I.; García-Martínez, T.; Diene, S.M.; Pérez-Nadales, E.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Rolain, J.-M. Heteroresistance to colistin in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae producing OXA-48. Antibiotics. 2023, 12, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, B.; Yu, H.; Jia, W.; Shan, B.; et al. Multicenter study of colistin heteroresistance in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains in China. Microbiol Spectr. 2023, 11, e0221822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakani, S.G.; Xavier, B.B.; Sey, A.; Mariem, E.B.; Lammens, C.; Goossens, H.; et al. Insight into antibiotic synergy combinations for eliminating Colistin Heteroresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Genes (Basel). 2023, 14, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Emergence of colistin-heteroresistant and carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2023, 35, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afyoncu, E.; Eryıldız, C. Investigation of colistin heteroresistance and the colistin resistance genes mcr-1 to mcr-5 in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates in a tertiary hospital in Turkey. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2024, 18, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braspenning, A.J.; Rajakani, S.G.; Sey, A.; et al. Assessment of colistin heteroresistance among multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from Intensive care patients in Europe. Antibiotics. 2024, 13, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P.; Brink, A.; Poirel, L. Heteroresistance to colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with alterations in the PhoPQ regulatory system. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.E.; Rafailidis, P.I.; Matthaiou, D.K. Resistance to polymyxins: mechanisms, frequency and treatment options. Drug Resist Updat. 2010, 13, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Jayol, A.; Bontron, S.; et al. The mgrB gene as a key target for acquired resistance to colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015, 70, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Sousa, A.M.; Alves, D.; Lourenço, A.; Pereira, M.O. Heteroresistance to colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae is triggered by small colony variants sub-populations within biofilms. Pathog Dis. 2016, 74, ftw036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Wada, T.; Nishijima, S.; et al. Emergence of the novel aminoglycoside acetyltransferase variant aac (6′)-Ib-D179Y and acquisition of colistin heteroresistance in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae due to a disrupting mutation in the DNA repair enzyme MutS. mBio. 2020, 11, e01954-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: a microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardet, L.; Baron, S.; Leangapichart, T.; Okdah, L.; Diene, S.M.; Rolain, J.-M. Deciphering heteroresistance to colistin in a Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate from Marseille, France. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00356-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, J.T.; Bai, Y.; Wang, R.; Cai, Y. Synergistic activity of colistin/fosfomycin combination against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic model. Biomed Res Int. 2018, 2018, 5720417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-K.; Lee, J.-Y.; Ko, K.S. Colistin resistance in Enterobacter spp. isolates in Korea. J Microbiol. 2018, 56, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Colistin in the 21st century. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2009, 22, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-K.; Ko, K.S. PmrAB and phoPQ variants in colistin-resistant Enterobacter spp. isolates in Korea. Curr Microbiol. 2019, 76, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.J.; Doi, Y.; Patil, S.; Huang, X.; Tian, G.B. Emergence of the plasmid-mediated mcr-1 gene in colistin-resistant Enterobacter aerogenes and Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3862–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, B.A.; Band, V.; Burd, E.M.; Weiss, D.S. Colistin heteroresistance in Enterobacter cloacae is associated with cross-resistance to the host antimicrobial lysozyme. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5594–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarumoto, N.; Kodana, M.; Watanabe, N.; et al. First report of the isolation of blaIMI-1-producing colistin-heteroresistant Enterobacter cloacae in Japan, September 2016. J Infect Chemother. 2018, 24, 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashaly, G.E.-S.; Mashaly, M.E.-S. Colistin-heteroresistance in carbapenemase-producing Enterobacter species causing hospital-acquired infections among Egyptian patients. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2021, 24, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérin, F.; Isnard, C.; Sinel, C.; et al. Cluster-dependent colistin hetero-resistance in Enterobacter cloacae complex. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016, 71, 3058–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telke, A.A.; Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.-M. soxRS induces colistin hetero-resistance in Enterobacter asburiae and Enterobacter cloacae by regulating the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017, 72, 2715–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Harada, K.; Usui, M.; Yokota S-i Horiuchi, M. Colistin susceptibility in companion animal-derived Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., and Enterobacter spp. in Japan: frequent isolation of colistin-resistant Enterobacter cloacae complex. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022, 12, 946841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzawa, S.; Sato, T.; Aoki, K.; et al. High prevalence of colistin heteroresistance in specific species and lineages of Enterobacter cloacae complex derived from human clinical specimens. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.-M. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front Microbiol. 2014, 5, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.N.; Klein, D.R.; Kazi, M.I.; et al. Colistin heteroresistance in Enterobacter cloacae is regulated by PhoPQ-dependent 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose addition to lipid A. Mol Microbiol. 2019, 111, 1604–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Feng, Y.; Zong, Z. Heterogeneous resistance to colistin in Enterobacter cloacae complex due to a new small transmembrane protein. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019, 74, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kádár, B.; Kocsis, B.; Tóth, Á.; et al. Colistin resistance associated with outer membrane protein change in Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter asburiae. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 2017, 64, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lister, P.D.; Wolter, D.J.; Hanson, N.D. Antibacterial-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: clinical impact and complex regulation of chromosomally encoded resistance mechanisms. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009, 22, 582–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, J.P.; Montero, M.; Oliver, A.; et al. Epidemiology and treatment of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019, 32, e00031–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; et al. Discovery, research, and development of new antibiotics: the WHO priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and tuberculosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, M.; Kerr, K.; Mooney, L.; et al. Transmission of colistin-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa between patients attending a pediatric cystic fibrosis center. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2002, 34, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, F.; Khan, M.A.; Muhammad, H.; Sarwar, T.; Bilal, H.; Rehman, T.U. Plasmid-mediated mcr-1 gene in Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: first report from Pakistan. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2019, 52, e20190237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahida, K.; Kwon, D.H. Co-existence of multidrug-resistant and-susceptible strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a single clinical isolate. Curr Microbiol. 2010, 61, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergen, P.J.; Forrest, A.; Bulitta, J.B.; et al. Clinically relevant plasma concentrations of colistin in combination with imipenem enhance pharmacodynamic activity against multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa at multiple inocula. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5134–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard-Anderson, J.; Davis, M.; Page, A.M.; et al. Prevalence of colistin heteroresistance in carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and association with clinical outcomes in patients: an observational study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022, 77, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, T.; Adwityama, A.; Sharma, S.; Mishra, K.; Prusti, P.; Maitra, U. Comparative evaluation of colistin broth disc elution (CBDE) and broth microdilution (BMD) in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with special reference to heteroresistance. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2024, 47, 100494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Xu, C.; Fang, R.; et al. Resistance and heteroresistance to colistin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Wenzhou, China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00556–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergen, P.J.; Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Coulthard, K.; Milne, R.W. Comparison of once-, twice-and thrice-daily dosing of colistin on antibacterial effect and emergence of resistance: studies with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008, 61, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kethireddy, S.; Lee, D.; Murakami, Y.; Stamstad, T.; Andes, D.; Craig, W. In vivo pharmacodynamics of colistin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in thighs of neutropenic mice [abstract A-1]. In Proceedings of the 47th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ly, N.S.; Bulitta, J.B.; Rao, G.G.; et al. Colistin and doripenem combinations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: profiling the time course of synergistic killing and prevention of resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015, 70, 1434–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Lin, J.; Jia, H.; et al. Resistance and heteroresistance to colistin in Escherichia coli isolates from Wenzhou, China. Infect Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3551–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Q.; He, D.; Sun, H.; et al. R93P substitution in the PmrB HAMP domain contributes to colistin heteroresistance in Escherichia coli isolates from swine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e01509-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, A.; Iglesias, M.-R.; Ugarte-Ruiz, M.; et al. The plasmid-mediated Kluyvera-Like arnBCADTEF operon confers colistin (hetero) resistance to Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e00091-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, Y.L.; Berman, Z.; Toh, E.; et al. Heteroresistance to the model antimicrobial peptide polymyxin B in the emerging Neisseria meningitidis lineage 11.2 urethritis clade: mutations in the pilMNOPQ operon. Mol Microbiol. 2019, 111, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Shin, D.; Kwon, K.T.; Ko, K.S. Colistin heteroresistance in Citrobacter freundii clinical isolates from Republic of Korea. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2024, 108, 116187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Servat, S.; Yero, D.; Huedo, P.; et al. Heterogeneous colistin-resistance phenotypes coexisting in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia isolates influence colistin susceptibility testing. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© GERMS 2025.