Abstract
Introduction: Salivary gland lithiasis is one of the most frequent causes of sialadenitis. We report the case of a patient who presented multiple episodes of subangulomandibular tumefaction, until salivary lithiasis was finally identified as the underlying condition and resolved through a minimally invasive approach. Case report: A 43-year-old male patient presented with a history of 12 episodes of recurring one-sided subangulomandibular tumefaction over the course of the past 3 years. A computed tomography of the head and neck revealed a large calculus on Wharton's duct and right lithiasic submaxillitis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory treatment and antibiotic treatment was administered, and after the complete resolution of the acute process, we performed a sialendoscopically-assisted sialolithotomy with complete removal of the calculus. Following the procedure, the patient was discharged on the same day, clinically well, and displayed no further recurrences over a follow-up duration of 12 months. Conclusions: The case we have reported highlights the importance of performing a correct differential diagnosis and of determining the underlying cause of recurrent sialadenitis, in order to ensure the most adequate therapeutic and, when warranted, minimally-invasive surgical management for definitive treatment.
Introduction
Sialadenitis is the inflammation of a salivary gland that can occur as an acute or chronic process, and can present as inflammation alone, or in conjunction with bacterial infection. The parotid gland is the most frequent reported location of sialadenitis, followed by the submandibular salivary gland. Decreased secretion of saliva is one of the main driving factors of sialadenitis, and it can be either constitutive, or pathological when induced by medication, obstruction, or a state of systemic disease. The second ranking causative factor is salivary duct obstruction, most frequently due to sialolithiasis.[1]
We report the case of a patient who presented multiple episodes of submandibular sialadenitis, for which interventional sialendoscopy was performed as definite treatment to prevent recurrences.
Case report
A 43-year-old male patient presented to our clinic with a history of 12 episodes of recurring one-sided subangulomandibular tumefaction having occurred over the course of the past 3 years, for which he had never received a definitive diagnosis. These had been managed in multiple different emergency services, and each time the symptoms disappeared after a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, but reappeared after a variable time interval.
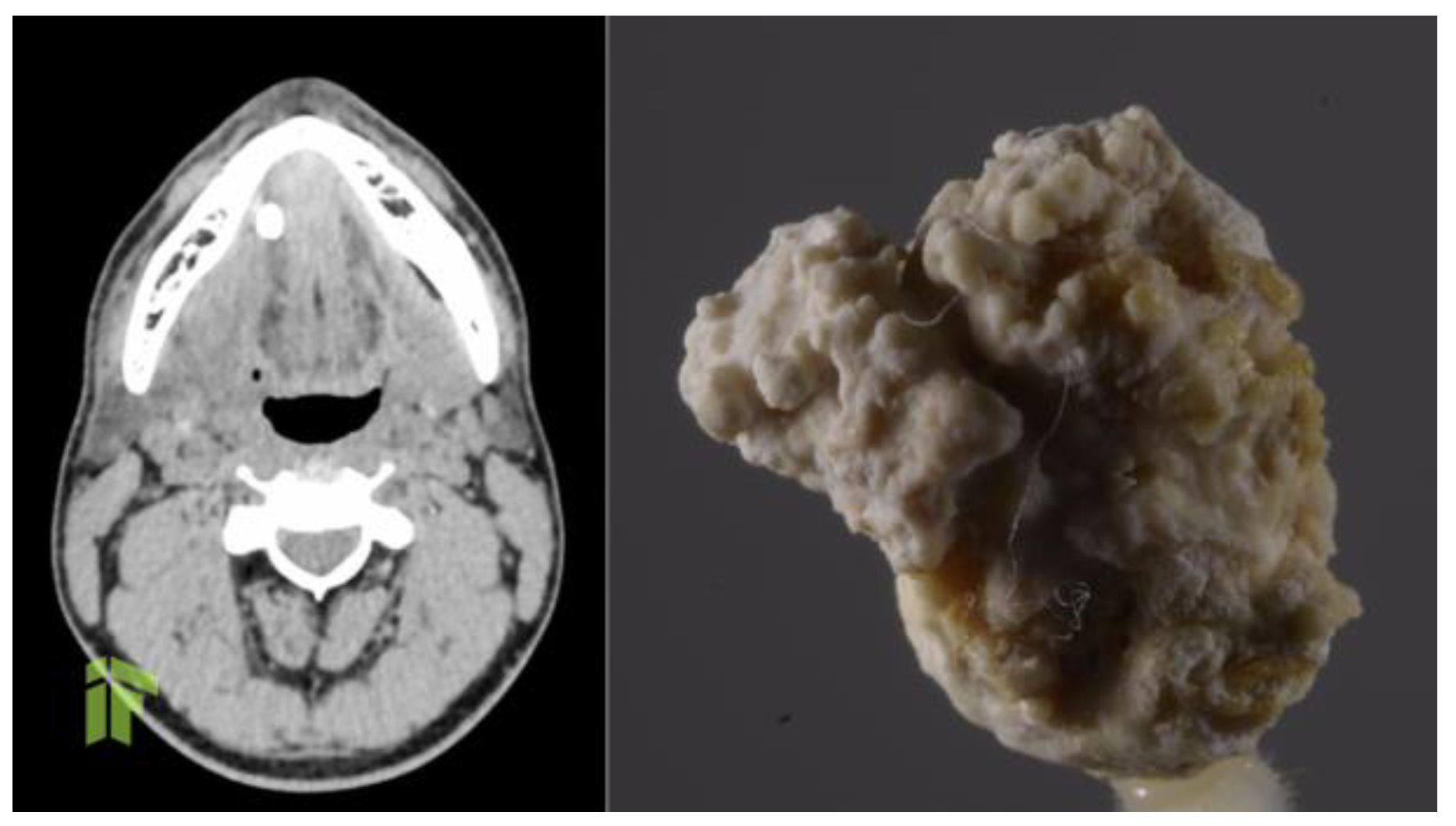
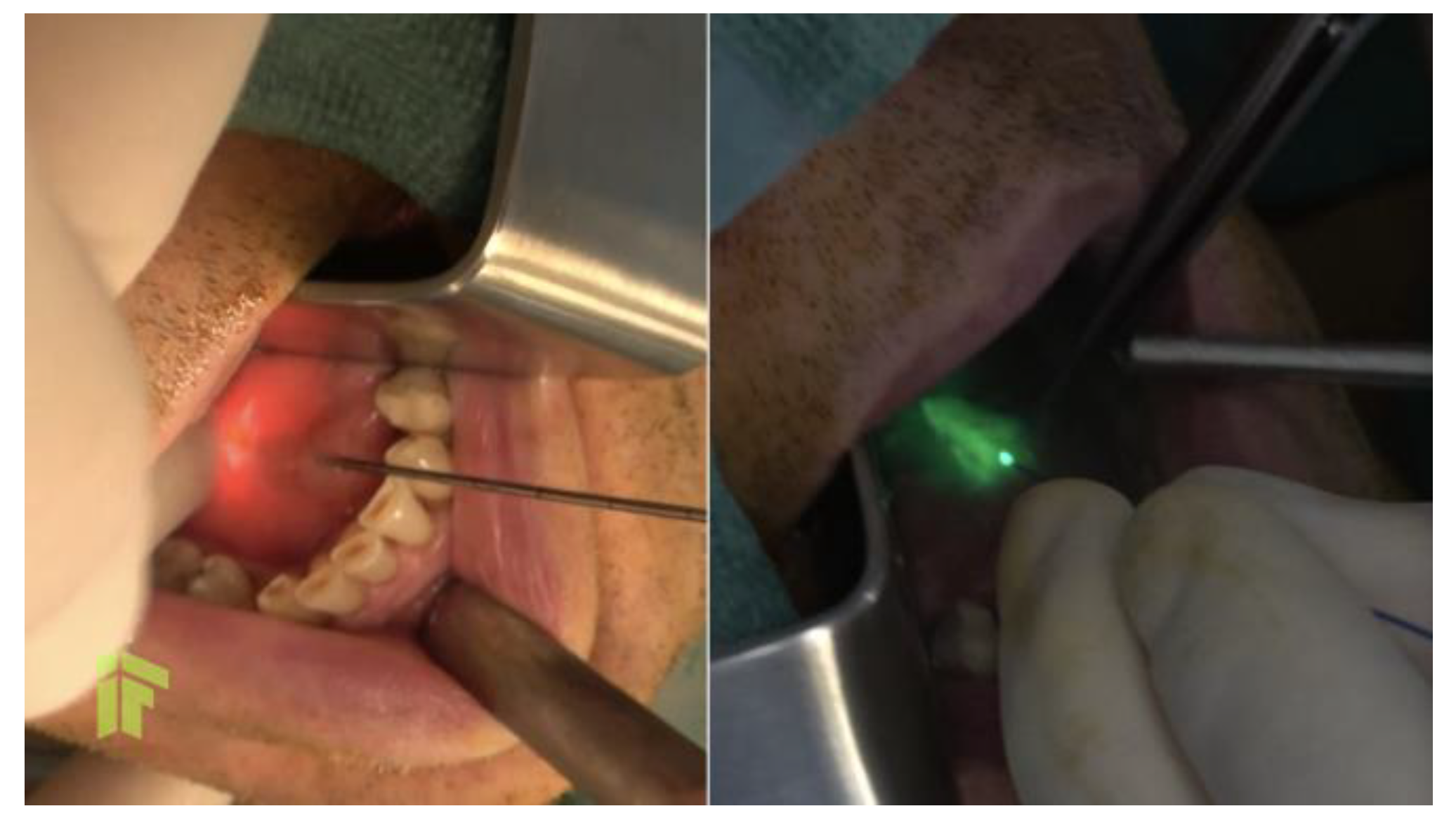
At the moment of presentation to our clinic, the patient was stable, with normal body temperature and normal vital signs, but he displayed right subangulomandibular tumefaction tender to palpation. In order to identify the cause of these multiple recurrences, and to establish a clinical diagnosis, computed tomography of the head and neck was performed, and revealed a very large calculus, of approximately 12/8 mm, on Wharton's duct and right lithiasic submaxillitis (Figure 1). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory treatment and antibiotic treatment with amoxicillin/clavulanate 1 g orally every 12 hours was administered for 7 days, and after the complete resolution of the acute process, we performed a sialendoscopical and laser-assisted sialolithotomy with endoscopic exploration and marsupialization of Wharton's duct (Figure 2). Following the sialendoscopic procedure, the patient was discharged the same day, clinically well, with permeable Wharton's duct. During 12 months of follow-up, the patient experienced no further episodes of sialadenitis.
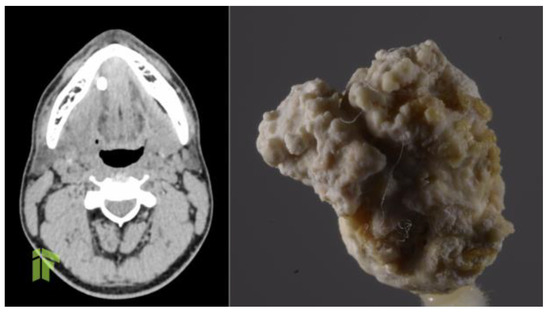
Figure 1.
Preoperative CT (left) showing a large calculus. Actual image of the calculus, after removal (right).
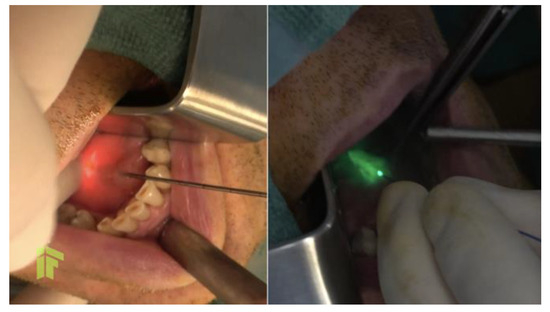
Figure 2.
Laser-assisted sialolithotomy and marsupialization of Wharton’s duct.
Discussion
When evaluating a patient, the first priority is establishing the clinical diagnosis. This will then allow further investigations to facilitate etiological diagnosis and to determine the most appropriate treatment. This requires in depth evaluation for the differential diagnosis of the clinical syndromes that may present with the same set of signs and symptoms. In the case we have presented, many of the 12 prior episodes of submandibular swelling had not been recognized as being due to sialadenitis, and had been treated in different emergency health services. Submandibular tumefaction can be unilateral or bilateral, and it can be due to different causes of inflammation and/or infection of the submandibular salivary glands, lymph nodes, or of the submandibular space itself. Infection should be suspected in cases where tumefaction is associated with important pain, erythema and warmth of the overlying skin, as well as fever and/or other associated general symptoms such as chills, or altered clinical state.
Severity can range from mild, for an isolated episode of salivary gland inflammation, to lifethreatening, if the tumefaction was actually a sign of infection of the submandibular space. For this reason, the identification of the root cause should be prioritized. In the case we have presented, the first essential step was to determine that the one-sided subangulomandibular tumefaction was due to sialadenitis, and the second step was to identify the cause of the repeated episodes of sialadenitis, which was the large calculus.
Sialadenitis can be either due to inflammation alone or also due to bacterial infection. The salivary gland most prone to infection is the parotid gland, with acute suppurative parotitis historically reported to occur in 0.01-0.02% of hospitalized adults.[2] The second most frequent location of sialadenitis is the submandibular gland, as was seen in the case we have reported.
Differential diagnosis should discern between infectious and non-infectious causes. Non-infectious etiologies include a long list of causes, such as sialolithiasis, foreign body, alcoholism, systemic disorders such as diabetes mellitus, cystic fibrosis, collagen vascular diseases, particularly Sjögren syndrome, sarcoidosis, uremia or gout, tumors or iatrogenic causes such as post-radiation, medication-induced hyposalivation due to antihistamines or anticholinergics. Infectious causes should also be differentiated into viral or bacterial. Viral causes generally lead to a nonsuppurative inflammatory clinical picture, and are more frequent when sialadenitis is located in the parotid gland.[3] Acute infections causative of parotitis include mumps, influenza and parainfluenza, infectious mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, herpes simplex virus, [3] adenovirus, enterovirus, parvovirus, [4] while chronic infections that can associate parotitis include HIV infection, and chronic hepatitis C.[3,5]
Bacterial agents lead to suppurative parotitis, which is a particular subset of salivary infection, and represents a medical emergency that should promptly be treated with antibiotics, since infection can easily spread to the deep fascial spaces of the head and neck. Its main etiologic agents in community settings include Staphylococcus aureus and agents routinely seen in the oral flora, such as Streptococcus spp. (including the viridans group), Haemophilus influenzae, as well as oral anaerobes such as Peptostreptococcus, Fusobacterium[3] or Bacteroides.[6] When presenting as healthcare-associated, suppurative parotitis has slightly different causative agents, with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacterales added to the etiological list above, and with a higher frequency of methicillin resistance among S. aureus strains.[3] Rare etiologies dependent on the local epidemiology also include actinomycosis[7] and mycobacteriosis.[8] Fungal agents are extremely rarely involved, and have only been reported from parotid abscesses from immunocompromised patients, particularly in the setting of diabetes mellitus.[9]
While the etiological spectrum of suppurative parotitis has been described through case reports and case series, as mentioned above, the etiology of infectious parotitis in other salivary glands, submandibular or sublingual, is underexplored. Suppurative sialadenitis is generally considered to be polymicrobial. Cultures from pus retrieved from suppurative sialadenitis have identified anaerobic germs alone in 41% of cases of suppurative parotitis and 33% of cases of suppurative submandibular sialadenitis, aerobic germs only in 34% and 44%, respectively, and mixed aerobic and anaerobic bacteria in 25% and 22% of parotid vs. submandibular cases of suppurative sialadenitis.[7] As many as four different pathogenic agents were reported from a case of suppurative parotitis occurring in an infant, specifically Klebsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter ursingii, and Acinetobacter junii.[10]
Management of sialadenitis includes antiinflammatory treatment, together with improved oral hygiene, warm external compresses, local salivary gland massage, rehydration, and stimulation of saliva production with lemon juice or other sour products. On top of this symptomatic and pathogenic treatment, antibiotics represent the mainstay therapeutic approach for bacterial sialadenitis.
Furthermore, it is essential to ensure that apart from treating the acute episode, the underlying cause is ascertained. As can be seen from the case we have reported, unless the underlying cause is completely addressed and treated, recurrence with ensue.
In recent years, surgical techniques have been gradually replaced by minimally-invasive procedures for treating sialolithiasis, among which interventional sialendoscopy is perhaps the most well studied.[11,12] A study from Poland has evaluated the outcomes of sialendoscopy and sialendoscopy-assisted surgery for salivary calculus removal in 397 patients, of which 175 had submandibular lithiasis. The immediate postoperative success rate of the procedure was 85%, with 11% of patients presenting residual calculi, and with only 4% consequent requirement for sialoadenectomy.[12]
The selection of the operating procedure depends on patient characteristics and, very importantly, on the location of the calculus. Nonimpacted calculi situated in the gland’s duct are the most likely to benefit from minimally-invasive techniques, but combined approaches can also be envisaged for calculi located in the gland’s hilum or the parenchyma, depending on calculus size, mobility, and operative accessibility.[13]
When performed successfully, definitive treatment removes the offending factor, as was the large obstructive calculus in the case that we have presented, and allows the resumption of the gland’s physiological function, preventing further future occurrences of sialadenitis.
Conclusions
The case we have reported highlights the importance of performing a correct differential diagnosis and of determining the underlying cause of recurrent sialadenitis, in order to ensure the most adequate therapeutic and, when warranted, minimally-invasive surgical management for definitive treatment.
Author Contributions
IF and MS contributed to conceptualization. IF contributed to investigation and visualization. IF and MS contributed to writing – original draft. IF, CMC and MS contributed to writing – review & editing. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors – none to declare.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report.
References
- Adhikari, R.; Soni, A. Submandibular sialadenitis and sialadenosis. StatPearls Publishing: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL), 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chandak, R.; Degwekar, S.; Chandak, M.; Rawlani, S. Acute submandibular sialadenitis-a case report. Case Rep Dent. 2012, 2012, 615375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, A. Suppurative parotitis in adults. Post, TE, Ed.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA:, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, H. Salivary gland swelling: Evaluation and diagnostic approach. Post, TE, Ed.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dajani, N.; Wootton, S.H. Cervical lymphadenitis, suppurative parotitis, thyroiditis, and infected cysts. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2007, 21, 523–541, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, I.; Frazier, E.H.; Thompson, D.H. Aerobic and anaerobic microbiology of acute suppurative parotitis. Laryngoscope. 1991, 101, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, I. Aerobic and anaerobic microbiology of suppurative sialadenitis. J Med Microbiol. 2002, 51, 526-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangore-Khasbage, S.; Bhowate, R.R.; Degwekar, S.S.; Bhake, A.S.; Lohe, V.K. Tuberculosis of parotid gland: a rare clinical entity. Pediatr Dent. 2015, 37, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poisbleau, D.; Ducroz, C.; Siest, R.; Giot, J.P.; Fabre, C. Bilateral candidal abscess of the parotid gland: a case report and literature review. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023, 124, 101355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paouris, D.; Dallos, T.; Pitiriga, V. Polymicrobial acute suppurative parotitis in a 33-day-old infant: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2022, 61, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carta, F.; Farneti, P.; Cantore, S.; et al. Sialendoscopy for salivary stones: principles, technical skills and therapeutic experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2017, 37, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopec, T.; Wierzbicka, M.; Kaluzny, J.; Mlodkowska, A.; Szyfter, W. Sialendoscopy and sialendoscopically-assisted operations in the treatment of lithiasis of the submandibular and parotid glands: our experience of 239 cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016, 54, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Mantsopoulos, K.; Muller, S.; Sievert, M.; Iro, H. Treatment of sialolithiasis: What has changed? An update of the treatment algorithms and a review of the literature. J Clin Med 2021, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2023.