Introduction
Infectious ventriculitis is a severe life-threatening infection [
1]. Common causes of community-acquired ventriculitis include extension of meningitis and rupture of a cerebral abscess into ventricles. However, nosocomial ventriculitis is typically associated with neurosurgical catheters such as external ventricular drains (EVD) [
2]. EVDs are commonly used to decrease increased intracranial pressure while patients are recovering from a wide range of ailments [
1,
2,
3]. The common ways EVDs become infected are at the time of insertion with poor sterile technique, retrograde translocation of skin microbiota and with repeat manipulations [
3,
4,
5]. The incidence of EVD-associated ventriculitis is correlated with longevity of the EVD, with some studies reporting rates as high as 22% [
3,
4,
5]. Traditional symptoms include fever, headache and altered mental status, which are nonspecific, given these symptoms are also associated with underlying neurological conditions, thus confounding diagnosis [
3]. Furthermore, diagnosis of nosocomial ventriculitis can be difficult because classic cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) parameters lack specificity and sensitivity compared to community-acquired meningitis [
2,
6,
7]. This is secondary to the indolent bacteria and biofilms on EVDs being implicated in EVD-associated ventriculitis. Herein, we report a rare case of
Sphingomonas paucimobilis ventriculitis in an immunocompetent host.
Case report
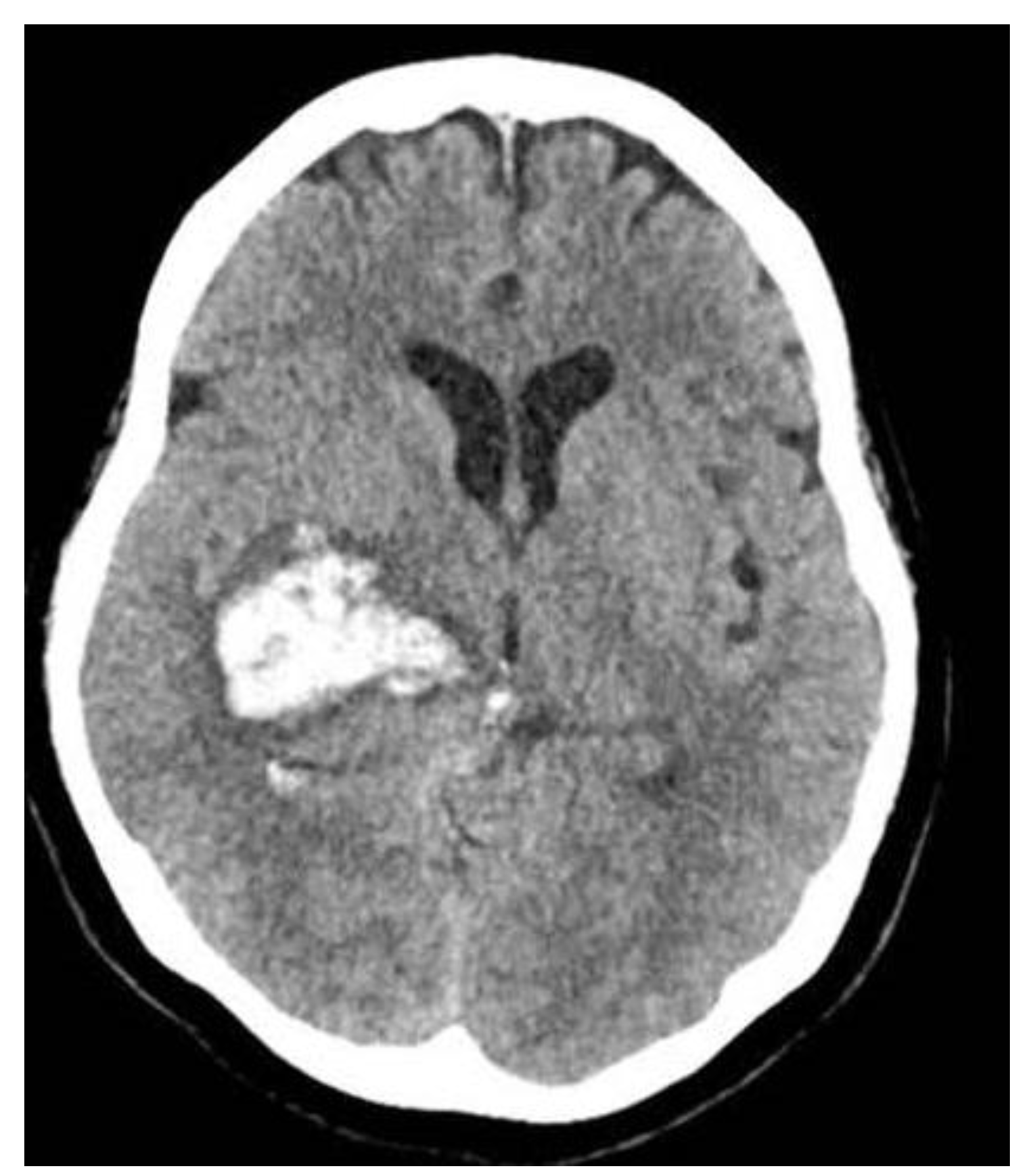
A 48-year-old woman with no significant past medical history presented to the local emergency room after experiencing acute onset severe headache and then left-sided paralysis. Computed tomography (CT) showed large right basal ganglia hemorrhage (
Figure 1). The patient experienced rapid decline in mentation and was urgently intubated and transferred to the University of Maryland Medical Center. Given the midline shift, an emergent left frontal EVD was placed. Four days later, her course was complicated by ventilator-associated pneumonia with methicillin-susceptible
Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) that was treated with intravenous cefazolin 2 grams every 8 hours for 7 days.
After she completed her cefazolin therapy, she was subsequently extubated but remained in the neurosurgical intensive care unit due to persistently elevated intracranial pressure requiring continued use of her initial EVD. She then developed fevers and worsening altered mental status and was started on intravenous vancomycin and cefepime due to concern for nosocomial ventriculitis. Associated with these symptoms was a white blood cell count of 15.7 K/mcL with 88.7% being neutrophils. Analysis of her CSF showed a relatively benign profile (lactate 1.7 mmol/L, white blood cells 4 cells/μL, glucose 86 mg/dL and protein 23 mg/dL). No organisms were observed on CSF Gram stain and blood cultures did not have bacterial growth. Consequently, antibiotics were changed to only intravenous cefepime to treat possible pneumonia despite the lack of tachypnea or increased sputum production. The patient’s fever improved on cefepime and the white blood cell count normalized. Two days later her antibiotics were changed to daily intravenous ceftriaxone to complete a seven-day course for possible pneumonia. After being on the ceftriaxone for 24 hours the patient’s fever returned, and the white blood cell count increased to 13.4 k/mcL with 87% being neutrophils. Subsequently, antibiotics were changed back to cefepime. Repeat CSF evaluation was conducted, with CSF analysis again showing benign parameters: lactate 2.0 mmol/L, white blood cells 5 cells/μL, glucose 81 mg/dL and protein 47 mg/dL. However, the Gram stain of the CSF now showed Gram-negative bacilli.
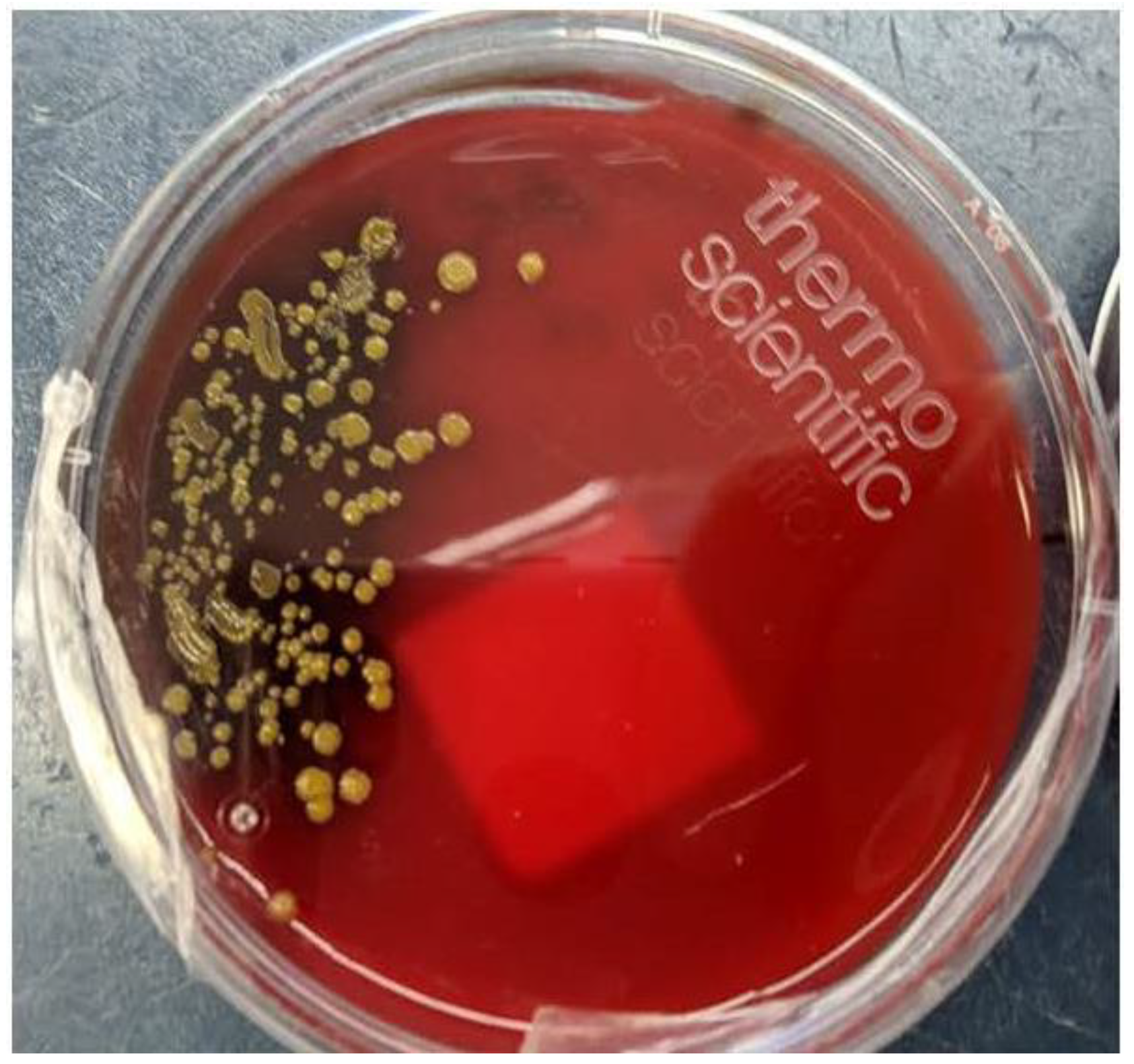
Therefore, cefepime was continued at 2 grams IV q 8 hours and fever improved within 48 hours as did her white blood cell count. As well, yellow colonies started to grow on the CSF blood agar plate (
Figure 2). Since she had bacterial growth from her CSF culture, her EVD was changed. Identification of
S. paucimobilis was then made with antibiotic susceptibilities seen in
Table 1. After three days of intravenous cefepime therapy, the patient defervesced and the altered mental status improved. Two days later, after a clamping trial proved no further evidence of raised intracranial pressure, her EVD was removed. She completed a two-week course of intravenous cefepime and was transferred to rehab for one month and then was subsequently discharged home. Twelve months later, she does not have any further evidence of recurrence of her ventriculitis.
Discussion
Sphingomonas spp. are aerobic non-fermenting Gram-negative bacteria that are widely distributed in both terrestrial, aquatic environments and commonly found in drinking water [
8]. These bacteria can live with low nutrient concentrations and metabolize a wide variety of carbon sources allowing them to live in man-made environments [
8].
Sphingomonas spp. rarely cause clinical infections outside of nosocomial infections and in immunocompromised hosts in which
S. paucimobilis is the most common species implicated [
8,
9,
10].
S. paucimobilis has a single polar flagellum with slow motility and classically produces yellow colonies on agar plates (
Figure 2). Even though the incidence of
S. paucimobilis infections is low, heightened awareness about this pathogen is needed given it is an emerging pathogen.
S. paucimobilis is a unique Gram-negative bacillus in that it lacks lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and instead possesses sphingoglycolipid [
8]. The absence of LPS likely has clinical ramifications in disease presentation given the presence of LPS causes significant inflammatory responses by stimulating pattern recognition receptors [
11]. However, sphingoglycolipid also has been implicated in stimulating mononuclear cells to secrete cytokines which is likely why our patient had systemic immune response even despite the lack of LPS [
12]. However, Gram-negative ventriculitis usually presents with significant derangement of the CSF parameters since LPS is present. In this case, the lack of LPS may be the reason for the absence of changes in these markers. This led to clinicians to not treat her for ventriculitis despite classic symptoms which included fever and altered mental status, resulting in temporary worsening of these symptoms. The clinical decline caused repeat CSF evaluation in which her Gram stain and culture then showed
S. paucimobilis, reinforcing the need to repeat cultures in face of antibiotic transition failure. Nonetheless, since
S. paucimobilis is an emerging pathogen, further research into the different innate immune responses that occur with Gram negative rods that possess LPS and bacteria that do not would be beneficial so clinicians can be cognizant of differences in disease presentations and diagnostic testing.
Also unique to
S. paucimobilis are its high levels of resistance to aztreonam, variable levels of resistance to piperacillin/tazobactam, and potential intrinsic resistance to colistin [
13,
14]. While the resistance mechanisms of this bacterium have yet to be fully elucidated, colistin resistance has been seen in several other
Sphingomonas species, implying that there may be some intrinsic resistance to colistin [
3]. The sensitivity of our isolate (
Table 1) reinforces that aztreonam and piperacillin/tazobactam resistance can be observed with this bacterium. As well, the worsening of symptoms while on ceftriaxone likely represent that this clinical isolate was not susceptible to this antibiotic. However, this claim is limited because susceptibility testing for this antibiotic was not conducted. Consequently, we treated our patient with two weeks of intravenous cefepime therapy as is the recommended duration for Gram-negative ventriculitis [
3]. While further studies are needed to better clarify the resistance mechanisms of
S. paucimobilis, cefepime, ceftazidime and carbapenems are suggested therapeutics to treat
S. paucimobilis infections.
To our knowledge this is the first reported case of an EVD-associated
S. paucimobilis causing nosocomial ventriculitis in an immunocompetent host. Most cases of
S. paucimobilis infections are secondary to bacteremia caused by contaminated medical solutions [
9,
10]. This likely occurs because
S. paucimobilis can pass through 0.2 μm filters, which are used for terminal sterilization of numerous medical products [
8,
10]. Consequently, several solutions have been shown to have been contaminated with this bacterium, including fentanyl, distilled water, and hemodialysis fluids [
9,
10,
15]. In the only other case that has reported
S. paucimobilis meningitis, the patient was immunocompromised and on hemodialysis, which may have led to her infection. In our case, the source of
S. paucimobilis ventriculitis is not known given the lack of bacteremia. As well, no other cases with this bacterium have been seen in our neurosurgical intensive care unit over the past two years and she was not getting solutions infused through her EVD nor was she getting dialysis. However, given the prolonged use of her EVD, this likely placed her at increased risk for this bacterium to colonize the EVD forming biofilms on the device to then infect her ventricles. This claim is supported by studies correlating the risk of ventriculitis associated with prolonged EVD use [
3,
4,
5]. In this case, the patient likely had a
S. paucimobilis biofilm infection on her EVD causing low concentrations of planktonic bacteria to be present in her ventricles leading to difficultly in culturing this bacterium. While the exact source of her
S. paucimobilis infection is unknown, this bacterium can reside in a wide variety of environments and thus clinicians should have heightened awareness for this pathogen’s potential to cause a wide variety of infections in immunocompromised and immunocompetent hosts.