Abstract
Introduction: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a thrombotic microangiopathy associated with severe ADAMTS13 deficiency that can be potentially fatal if not treated in a timely manner. Case report: A 49-year-old previously healthy woman was admitted with a 3-month history of thoracoabdominal pain and headache associated with loss of appetite, emesis, nocturnal diaphoresis, and unintentional loss of 10 kg. On admission she presented anemia, thrombocytopenia, schistocytes in peripheral blood smear, and ADAMTS13 in 1.4%. Due to laboratory findings a diagnosis of TTP was established, and plasma exchange therapy and steroid pulses were started, with resolution of hematological alterations. Within the studies to determine etiology of TTP, pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) was found, neoplastic and autoimmune pathologies were excluded. The tetraconjugated treatment was initiated with optimal tolerance. Conclusions: Upon clinical suspicion of TTP, plasma exchange therapy should be initiated urgently; infectious, neoplastic, or autoimmune pathologies can be triggers; in this case, pulmonary TB was confirmed.
Introduction
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare, potentially fatal disorder associated with an inherited or, more commonly, acquired deficiency of the plasma metalloprotease ADAMTS13, which cleaves the von Willebrand factor (VWF) into smaller fragments. ADAMTS13 deficiency (activity <10%) results in inadequate cleavage of VWF, causing an accumulation of large VWF multimers in the plasma, which, by mechanical effects, are deposited in the microvasculature, conditioning platelet aggregation, and multiorgan microvascular thrombosis, contributing to the development of thrombocytopenia, non-immune hemolytic anemia, and organ damage.[1]
ADAMTS13 deficiency can be primary, due to genetically intrinsic deficiency, with clinical manifestations during childhood or gestation. Secondary or acquired forms result from extrinsic triggers (autoimmune disorders, drugs, infections, bone marrow transplantation) that cause the generation of circulating autoantibodies against ADAMTS13, which is the most frequent form of presentation in adults; however, some of these factors do not lead to ADAMTS13 deficiency but a thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) that is caused by a different (non-ADAMTS13) mechanism (e.g., bone marrow transplantation-associated TMA).[2]
Tuberculosis (TB) has been associated with multiple hematological alterations such as monocytosis, leukocytosis, anemia, and pancytopenia as well as autoimmune phenomena such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis and systemic lupus erythematosus.[3] The association between TTP and TB is extremely rare, with very few cases reported in the literature.[4,5,6] Here, we present the case of an immunocompetent patient with pulmonary TB who presented with TTP, with the purpose of raising awareness of TB in the differential diagnosis of TTP.
Case report
A 49-year-old female, previously healthy, with only history of mother diagnosed with gastric cancer. She presented with a 3-month history of thoracoabdominal cramping pain predominantly in the epigastrium, which worsened with ingestion and was associated with loss of appetite, emesis, nocturnal diaphoresis, and an unintentional weight loss of 10 kg. A week prior, she had reported progressive chest tightness up to intensity 10/10, not associated with physical activity, accompanied by intermittent holocranial headache of intensity 7/10, without alteration of consciousness or motor or sensory symptoms, and the appearance of multiple ecchymoses on the upper limbs and thighs in the absence of trauma. She decided to consult the emergency department because of worsening abdominal pain and headaches.
On admission, she was pale, normotensive, and tachycardic, with adequate oxygen saturation and multiple ecchymoses of the upper limbs of approximately 3×3 centimeters (cm) and a single ecchymosis of 8×3 cm in the left thigh, with no other relevant findings on physical examination. Paraclinical tests at admission (Table 1) showed normocytic normochromic anemia and severe thrombocytopenia, indirect hyperbilirubinemia, normal transaminases, amylase, creatinine, urea nitrogen, and alkaline phosphatase. Total abdominal ultrasonography, cranial computed axial tomography (CT) and electrocardiography showed no alterations. In view of these findings, further studies were performed (Table 1), finding schistocytes in the peripheral blood smear, negative direct Coombs test, and elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Studies for disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), ELISA for HIV, and autoimmunity profile (Table 2) were normal, and ADAMTS13 levels were requested, which were 1.4%, confirming TTP, even though an assay for ADAMTS13 inhibitory antibodies was not performed, due to non-availability of the test.

Table 1.
Initial paraclinical tests.

Table 2.
Additional studies.
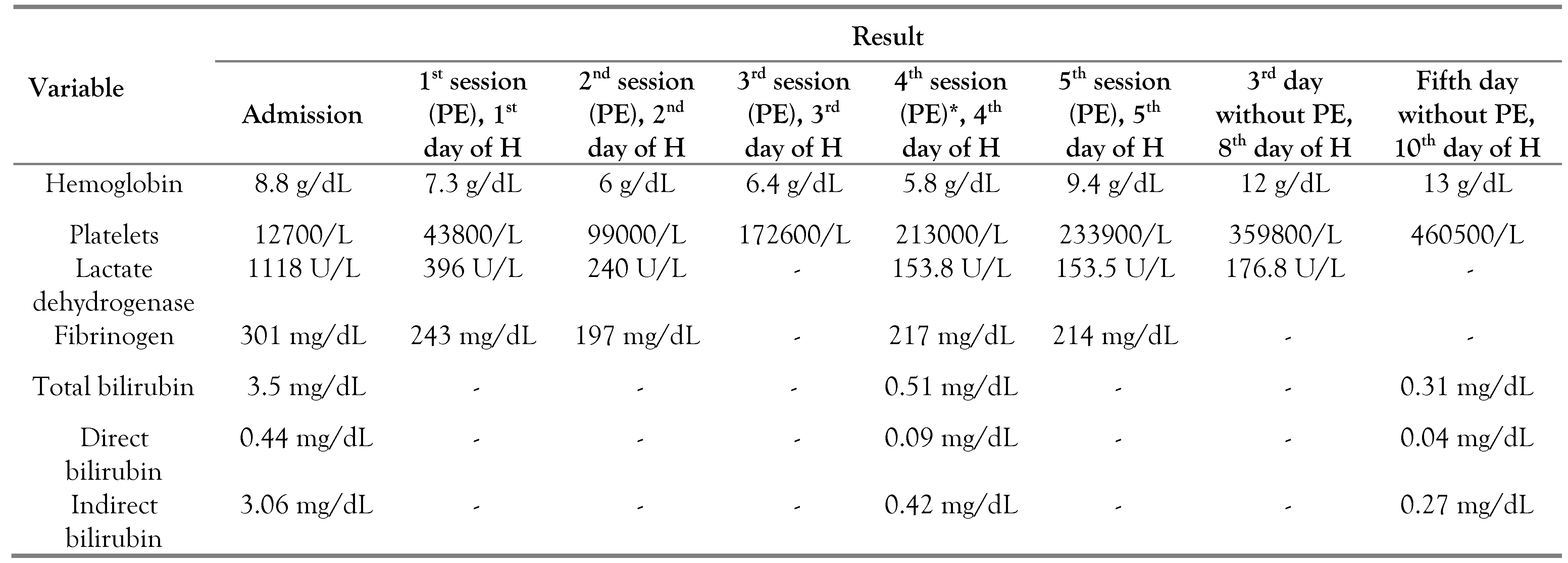
Therapeutic plasma exchange (five sessions) and pulse steroid therapy with 500 mg of methylprednisolone for three days were started on the first day of hospitalization. She presented a mild allergic reaction to plasma, for which steroids, diphenhydramine, and clemastine were administered, with improvement and tolerance in subsequent sessions. The follow-up LDH levels and complete blood counts after each plasmapheresis session are shown in Table 3. Due to symptomatic anemia, she required transfusion of two units of packed red blood cells with adequate post-transfusion performance.

Table 3.
Timeline of laboratory parameters during hospitalization.
Due to weight loss, CT scans of the chest and abdomen were performed on the second day of hospitalization, documenting findings of pulmonary granulomatous disease (Figure 1). She underwent fibrobronchoscopy plus bronchoalveolar lavage (FBC + BAL) the next day due to the findings on chest CT scan.
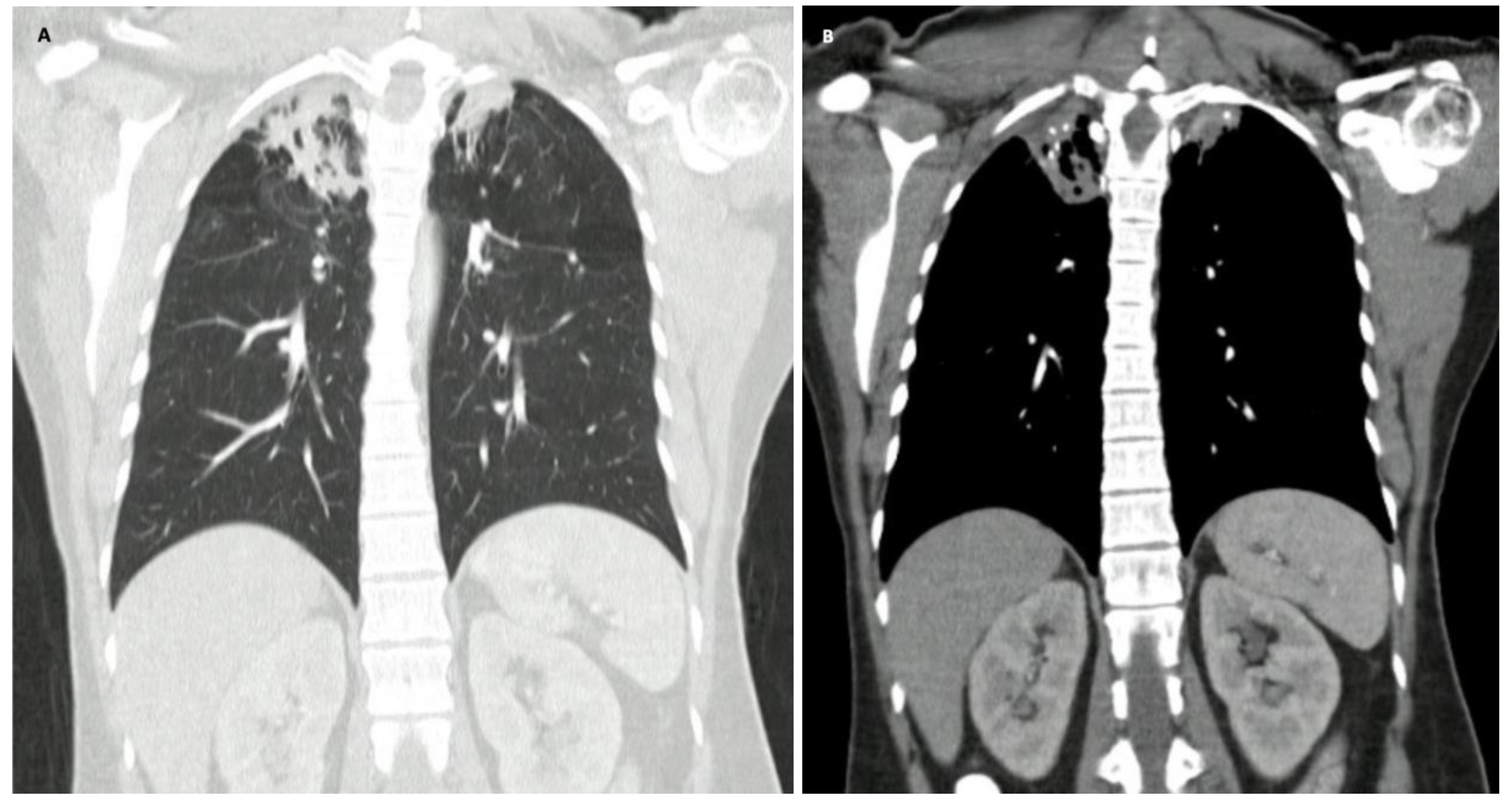
Figure 1.
Computed tomography of the chest. A: Frontal view, pulmonary window, showing multiple opacities with signs of volume loss and distortion of the pulmonary architecture in the apical segment of the right upper lobe and apical segment of the left upper lobe, which are compatible with pulmonary granulomatous disease. B: Frontal view, mediastinal window, many calcifications, bronchiectasis and adjacent parenchymal bands can be observed in the apical segment of the right upper lobe and apical segment of the left upper lobe.
FBC + BAL detected positive polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis with GeneXpert positivity without resistance to rifampicin, findings compatible with pulmonary TB, and tetraconjugate management (rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol) was initiated on the fourth day of hospitalization, and steroids were suspended.
The patient completed five cycles of plasma exchange with normalization of platelet count and normal LDH for 5 days; after 3 days without therapeutic plasma exchange, she had normal ADAMTS13 control (82.3%), fulfilling recovery criteria, and without evidence of early relapse, therefore it was decided to suspend plasma exchange, continuing with tetraconjugate. Blood count and liver profile were normal, with no evidence of toxicity due to tetraconjugate; therefore, hospital discharge was granted on the tenth day of hospitalization.
At the time of her discharge, she was prescribed a 2 months scheme of tetraconjugate for 56 doses from Monday to Saturday, followed by 4 months with isoniazid and rifampicin to complete 112 doses from Monday to Saturday. At the time of writing this report, she completed 56 doses of the first phase of the scheme and was on the 47th dose of the second phase of the scheme. During her follow-up she has not presented any adverse reaction, with normal blood count, liver profile and renal function. The patient denied any TB contact, and persons living with the patient were ruled out for infection, however she resides in Colombia, which is an endemic country for TB.
Discussion
TTP is a rare form of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), characterized by the simultaneous appearance of thrombocytopenia, non-immune microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and organ ischemia, particularly affecting the brain, heart, gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, with an estimated annual prevalence of 2.17 cases per million. TTP is a consequence of a deficiency of ADAMTS13, a plasma metalloprotease that is responsible for cleaving VWF into smaller fragments; thus, its decrease will cause large VWF multimers to persist and accumulate in the circulation, leading to dysregulated platelet adhesion and aggregation, resulting in excessive formation of microthrombi. These disseminated microthrombi consume platelets, leading to thrombocytopenia, mechanically destroy red blood cells passing through microvessels partially occluded by platelet aggregates, producing schistocytes, hemolysis, and occlusion of the microcirculation, causing organ ischemia.[1]
Depending on the cause of ADAMTS13 deficiency, TTP is divided into congenital (inherited) and acquired TTP. Congenital TTP is defined as a severe persistent deficiency of ADAMTS13 caused by pathogenic biallelic mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene. Acquired TTP is in the vast majority of cases immune-mediated (iTTP), where the reduced ADAMTS13 activity is caused by autoantibodies, which inhibit the enzyme or increase its clearance. Anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies are mostly of the IgG class, but also IgA and IgM have been reported in up to 20% of patients with iTTP. iTTP is classified into two subcategories: primary iTTP, which occurs without any apparent associated disorder, and secondary iTTP, when an associated condition can be identified.[1,7] Finally, there is a small subgroup categorized as non-immune-mediated acquired TTP, as occurs in cases of sepsis, where multiple proteases such as thrombin, plasmin, and granulocyte elastase degrade ADAMTS13. Liver damage associated with sepsis could be an additional mechanism that contributes to the decrease in ADAMTS13 activity since this enzyme is synthesized in the liver.[8]
Laboratory diagnosis of TTP is based on the demonstration of ADAMTS13 activity of less than 10%. Subsequent to this result, it is advisable to evaluate autoantibodies directed against ADAMTS13 to distinguish acquired TTP from congenital TTP, as management varies.[7] This distinction is important in children and obstetric patients because congenital TTP occurs more frequently in these patients. It should be noted that congenital TTP can be discovered in adults because of infections as they are a well-known trigger for acute disease episodes in congenital TTP, since infections through inflammation and endothelial alterations lead to an increased secretion of VWF, causing acute disease in the face of absent or severely reduced ADAMTS13 activity. However, in adults, up to 90% of the cases of TTP are immune-mediated.[8,9]
Acquired TTP can be triggered by various conditions, including autoimmune diseases, malignant neoplasms, and infections.[8] The pathogens with the highest number of reports are HIV, hepatitis C, and the influenza virus. The mechanisms involved in the loss of tolerance and the subsequent development of autoantibodies against ADAMTS13 following infection in patients with TTP are unknown, therefore, it is likely that both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the development of TTP. The development of autoimmunity in the context of infections could be explained by the mechanism of “molecular mimicry”, where similarities between pathogen and self-peptides result in the activation of autoreactive T or B cells in genetically susceptible individuals.[10] The possible association between TB and TTP described in this case report could indicate the existence of molecular mimicry between the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and some peptides of the ADAMTS13 molecule, promoting a cross-reactive autoimmune response. Furthermore, TB may stimulate self-reactive T or B cells that contribute to the development of TTP; a possible explanation for this is the excessive cell death, because apoptosis of infected cells (a well documented phenomenon in TB) has been shown to stimulate self-reactive T or B cells prompting autoimmunity phenomena such as the generation of autoantibodies. Also, TB can trigger acute disease episodes in congenital TTP by direct endothelial injury.[3,9]
As TTP can be life-threatening, once it is suspected or diagnosed, management should be initiated as soon as possible. Prior to the development of effective therapies, the mortality of TTP was up to 90%; however, it has decreased markedly, particularly with the advent of plasma exchange, with a current mortality estimated to be around 4 to 32%.[8] Immunosuppression with steroids has been proposed as a first-line adjuvant to plasma exchange; recently, caplacizumab, an inhibitor of the interaction between VWF and platelets, has been shown to shorten recovery time and decrease relapse rate. Rituximab is frequently added to the first-line therapy in cases of acquired TTP; for refractory cases, the use of cyclosporine A, N-acetylcysteine, bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and splenectomy has been described.[7] In secondary TTP with documentation of the cause, it should be treated if applicable.
The case presented had an excellent response to steroids and plasma exchange, with a rapid improvement in platelet count and control of hemolysis. We suspect there is an association of TB with the TTP observed in our patient because other differential diagnoses of TTP were reasonably ruled out, and because it was an iTTP despite the fact that we did not measure anti-ADAMTS13 antibodies which would allow to differentiate this case definitively form secondary TTP caused by the systemic inflammation and endothelial damage often associated with infections, because the patient had an excellent response to plasma exchange therapy and corticosteroid pulses, which is characteristic of iTTP, and iTTP is the most frequent type of TTP observed in the age group of our patient.
Conclusions
Coexistence of TB and TTP is rare. TTP is a potentially fatal entity, and treatment initiated quickly improves survival. The use of the Plasmic Score is useful to guide such treatment. A complete clinical history is key to establishing possible triggers, such as in the case presented here. Treating co-adjuvant causes is fundamental.
Author Contributions
KC and JSG contributed to the initial draft of the manuscript. KC and OMCA contributed to the clinical care of the patient. KC and OMCA contributed to the manuscript critical revision and the final approval. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors – none to declare.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report and its associated images.
References
- Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Coppo, P.; Lämmle, B.; Moake, J.L.; Miyata, T.; Vanhoorelbeke, K. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017, 3, 17020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.R.; de Groot, R.; Scully, M.A.; Crawley, J.T.B. Pathogenicity of anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies in acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. EBioMedicine. 2015, 2, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belyaeva, I.V.; Kosova, A.N.; Vasiliev, A.G. Tuberculosis and autoimmunity. Pathophysiology. 2022, 29, 298–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano, V.; Bontadini, A.; Falsone, G.; et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with primary tuberculosis. Infection. 1995, 23, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamatsu, H.; Teramura, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Yoshida, K. [Case of chronic kidney failure with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura due to miliary tuberculosis]. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi. 1998, 87, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, H.F.; Stavile, R.N.; Correa, M.; Gutiérrez, M.M.; Kicillof, S.; Boschero, F. [Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and tuberculosis: A rare association (Spanish)]. Medicina (B. Aires). 2015, 75, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sukumar, S.; Lämmle, B.; Cataland, S.R. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. J Clin Med. 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.; Bridwell, R.E.; Manchanda, S.; Gottlieb, M. Evaluation and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in the emergency department. J Emerg Med. 2021, 61, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dorland, H.A.; Taleghani, M.M.; Sakai, K.; et al. Hereditary TTP Registry. The International Hereditary Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Registry: key findings at enrollment until 2017. Haematologica. 2019, 104, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghmouchi, A.; Graça, N.A.G.; Voorberg, J. Emerging Concepts In Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Front Immunol. 2021, 12, 757192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2023.