Abstract
Introduction: The severity and spread of tuberculosis, a major burden, can be prevented by more rapid and accurate laboratory diagnosis. The purpose of this study is to systematically explore candidate serum proteins in patients with Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection for further application as novel biomarkers. Methods: Our study was performed in two major steps: screening of the literature for potential biomarkers, and then validation of their levels in patients and controls. Many serum/plasma proteins previously reported to be abnormally expressed in patients with tuberculosis between 2012 and 2021 were comprehensively assembled. The biological role in tuberculosis was also predicted for each using the bioinformatics tool STRING. Candidate proteins found to have the same expression in other related diseases were excluded. Subsequently, the serum level of the candidate serum/plasma protein that met the aforementioned criteria was validated by sandwich ELISA; diagnostic performance was analysed by the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC). Results: From 103 collected serum/plasma proteins, coronin-1A was found to have abnormal expression only in patients with tuberculosis and was associated with tuberculosis. In addition, the validation of coronin-1A in the serum of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis revealed a higher level than in that of healthy individuals. Furthermore, the area under the ROC curve for diagnostic power of coronin-1A was 0.866, with high sensitivity and specificity at a cut-point of approximately 52.7 ng/mL. Conclusions: We concluded that the level of serum coronin-1A might serve as a novel biomarker for alternative laboratory examination to effectively distinguish patients with tuberculosis from those with other related diseases and healthy individuals.
Introduction
Tuberculosis is established as a critical infectious disease that continues to be a major health burden worldwide by causing a large number of deaths and an increase in new cases. In Thailand, the prevalence of tuberculosis is high, with 0.12 million cases reported and the number of new cases increasing continually each year. The tuberculosis situation in Thailand until now has exhibited the inefficiency of treatment and poor control of the disease epidemic [1]. The pathogenesis of tuberculosis is caused by direct infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis spread from patients with tuberculosis via airborne droplet transmission or co-infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). The M. tuberculosis infection primarily causes disease to the lung, with pulmonary tuberculosis accounting for approximately 70% of cases. After inhalation of aerosol containing M. tuberculosis, this microorganism can enter pulmonary alveoli and replicate inside alveolar macrophages to form a granulomatous structure. After the failure of host immunity, the microorganism can come out of granuloma, destroying organ tissues and leading to functional damage of several organs; lung lesions are a common feature in patients [2].
Nevertheless, disease severity and the spread of tuberculosis in patients are controlled by appropriate treatment dependent on rapid and accurate laboratory examinations for differential diagnosis from other diseases. Prolonged duration of pulmonary tuberculosis in more than 40% of patients is found to result in increased transmission and spread to close contacts. Moreover, the delay of laboratory diagnosis can lead to poor prognosis and late treatment in up to 25% of patients. Presently, pulmonary tuberculosis is diagnosed and disease severity followed using several laboratory investigations such as sputum microscopy with acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear, mycobacterial culture for confirmation of AFB, molecular amplification for nucleic acid detection and drug susceptibility testing. The appropriate treatment strategy in patients with tuberculosis requires the combination of these aforementioned laboratory investigations for accurate diagnosis because of the limitations of each technique. AFB microscopy is less sensitive, microorganisms grow slowly in mycobacterial culture, and molecular detection also requires the expertise of technicians and may not distinguish between live and dead organisms [3].
It is thus possible that exploration of other novel methods or molecules from patients’ specimens could provide effective diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. Previous studies have attempted searches and demonstrated that the serum/plasma of patients with tuberculosis contains many important molecules, especially proteins that are altered compared to healthy individuals or those with other diseases [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. Although some altered serum/plasma proteins have been previously reported, the prediction of their biological role in tuberculosis, expression validation in patients’ serum, and diagnostic power remain rarely addressed. Hence, this study aimed to systemically explore and identify the ability of altered serum proteins to serve as novel biomarkers. The data in this study may support the further effective diagnosis and treatment of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis.
Methods
Retrieval of proteomics data
Previous data of serum/plasma proteins in patients with tuberculosis, reporting the fold-change level compared to healthy individuals, were retrieved from all published articles cited in PubMed and ScienceDirect databases between 2012 and 2021. The terms for searching in databases were ‘serum protein of tuberculosis, plasma protein of tuberculosis, or proteomics data of tuberculosis’. All assembled serum/plasma proteins were defined from previous proteomics mass spectrometry data as having significant alteration in patients with active and/or latent phases of tuberculosis infection compared to healthy individuals.
Bioinformatics analysis
Global network analysis relative to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database was applied to predict the biological functions involved in tuberculosis of the altered serum/plasma proteins assembled from the aforementioned published articles. Briefly, the gene symbols of all proteins were submitted to the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Gene/Proteins (STRING), version 11.0 (https://string-db.org/). This global network analysis was carried out using the setting of a medium stringency/confidence level (score ≥ 0.400) based on the physical protein interactions from the literature combined with the database of curated biological pathway knowledge.
Criteria for selection of candidate biomarkers
All eligible serum/plasma proteins which had a biological role in tuberculosis as identified by STRING biological analysis were further screened for a specific expression pattern in tuberculosis by performing a literature search with previous data. We specified that the altered (increased/decreased) level of these candidate novel serum/plasma proteins should only be found in patients with tuberculosis, not those with other respiratory diseases that have signs or symptoms similar to pulmonary tuberculosis, including pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer, lung injury, influenza, and COVID-19.
Recruitment of subjects and ethics
The participants included 25 patients with tuberculosis who were diagnosed with active or latent phase disease in the tuberculosis clinic of Dokkhamtai Hospital, Phayao, Thailand. Additionally, healthy individuals who had no illness, no congenital diseases, and no chronic diseases, especially pulmonary disorders, were used as the controls. The number of participants in this study was calculated from the disease prevalence of pulmonary tuberculosis in Phayao province, Thailand; the proportion of patients (aged 20-60 years old) was 120/100,000. All patients and controls provided written informed consent prior to participation and the research ethics were approved by the University of Phayao Human Ethics Committee, Thailand (UPHEC; approval no. 1.3/001/64) in concordance with international guidelines including the Declaration of Helsinki, the Belmont Report, and ICH Good Clinical Practice.
Collection of serum samples
Blood samples from all patients and controls were collected from the median cubital vein using the standard venipuncture with an aseptic technique. The samples from each participant were then withdrawn into vacutainer tubes containing a clot activator (Becton Dickinson, USA) and serum was separated by centrifugation at 1,800 × g for 5 min. Finally, individual serum samples were carefully collected, aliquoted, and stored at −80 °C until use.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
The concentrations of coronin-1A in serum samples of patients with tuberculosis and healthy controls were detected using a human double antibody sandwich ELISA kit (Abcam, UK) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, 50 µL of serum samples and coronin-1A standard at various concentrations were added to the appropriate well of a microplate. Then, 50 µL of antibody cocktail (capture and detected antibodies) were also immediately added to each well and incubated for 1 h. These wells were subsequently washed in triplicate with washing buffer. Subsequently, 100 µL of TMB substrate was added to each well and incubated at 25 °C in the dark for 10 min. Finally, 100 µL of stop solution was added to each well and the absorbance at a wavelength of 450 nm was determined using a TriStar2 LB 942 multimode plate reader (Berthold Technologies, Germany).
Statistical analysis
Quantitative data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Comparison between the two examined groups was examined by unpaired Student’s t test. Diagnostic performance was analyzed by the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC). All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS, version 25 (IBM; North Castle, NY, USA); a p value less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results
Proteomics data in tuberculosis patients
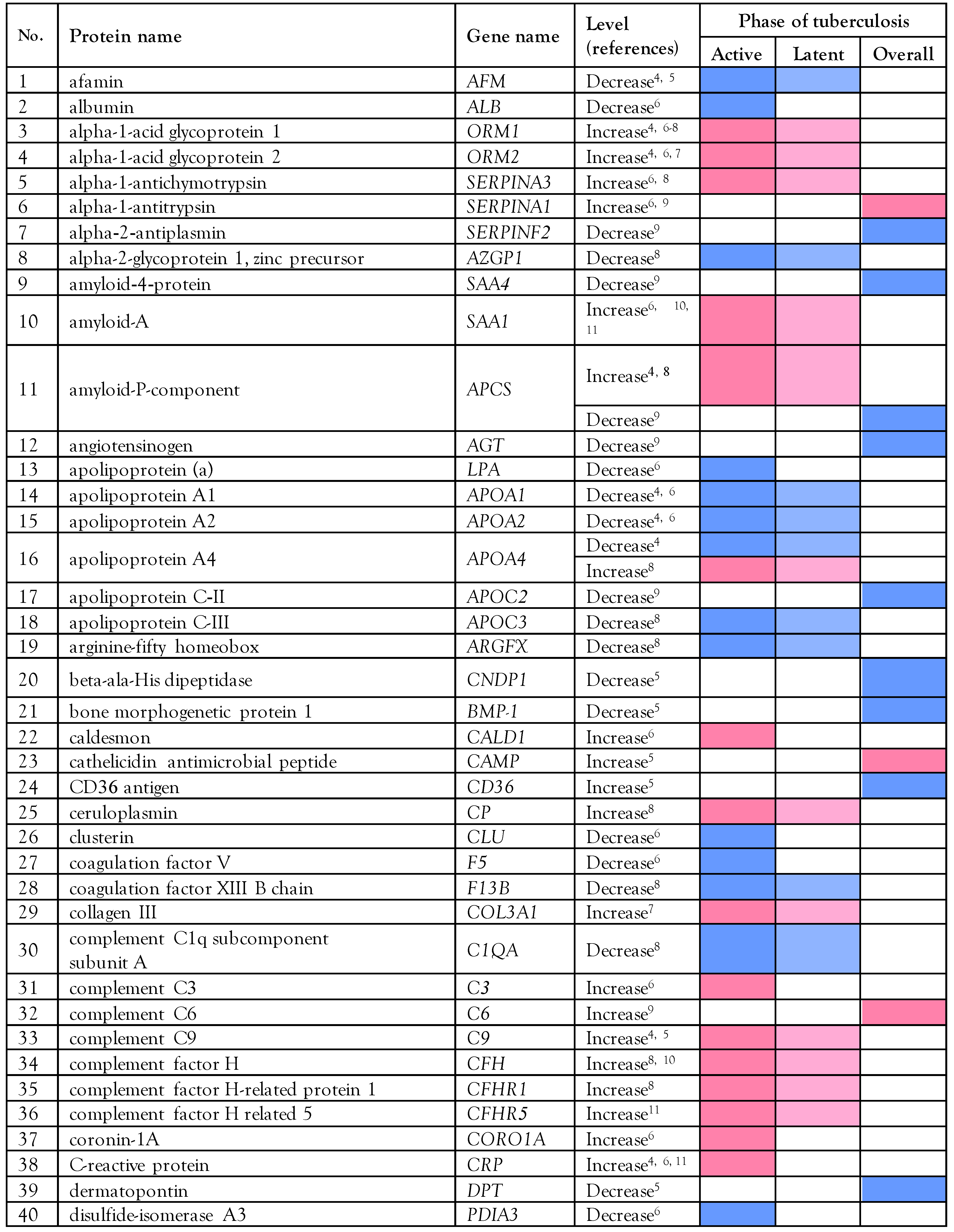
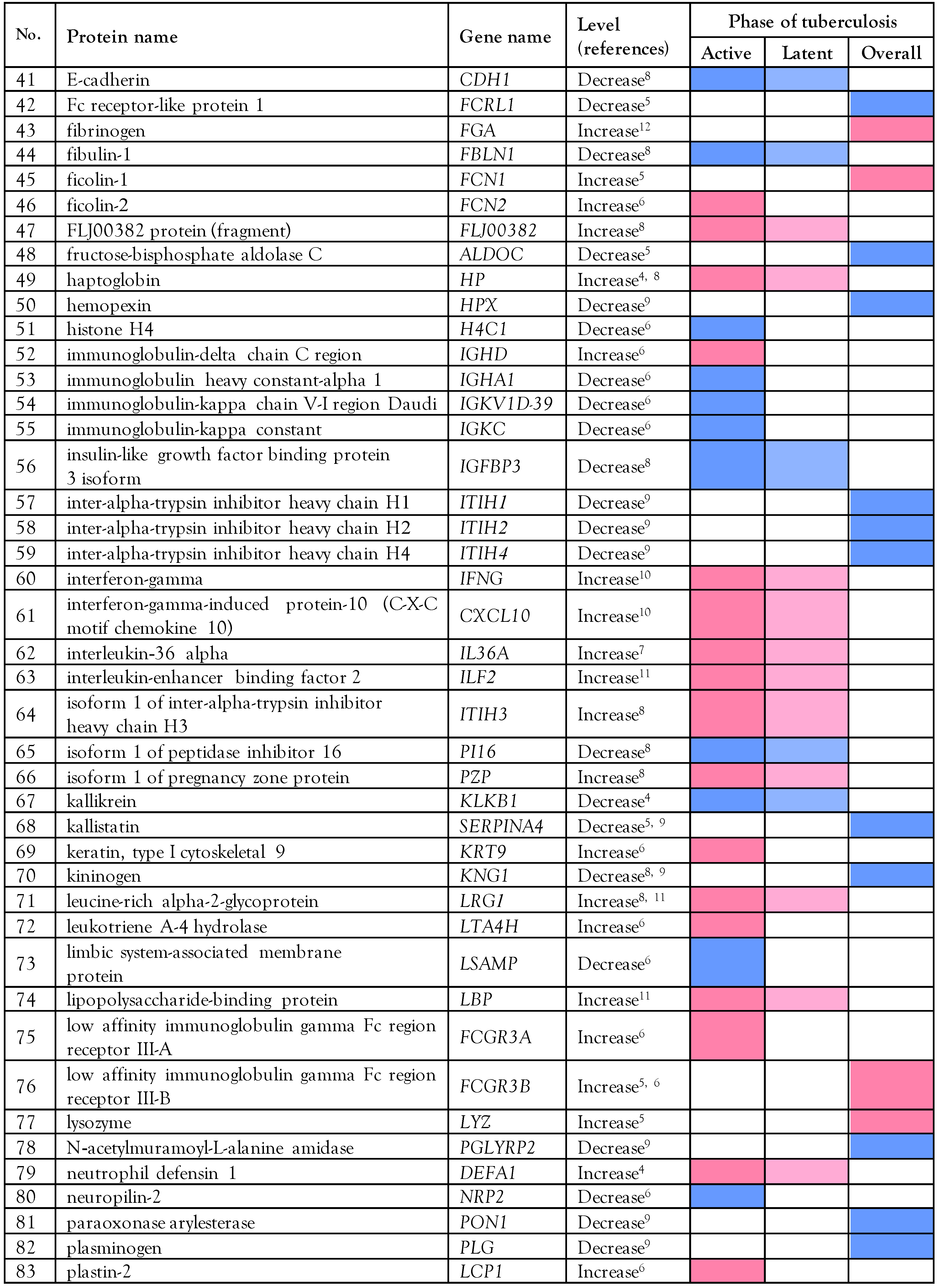
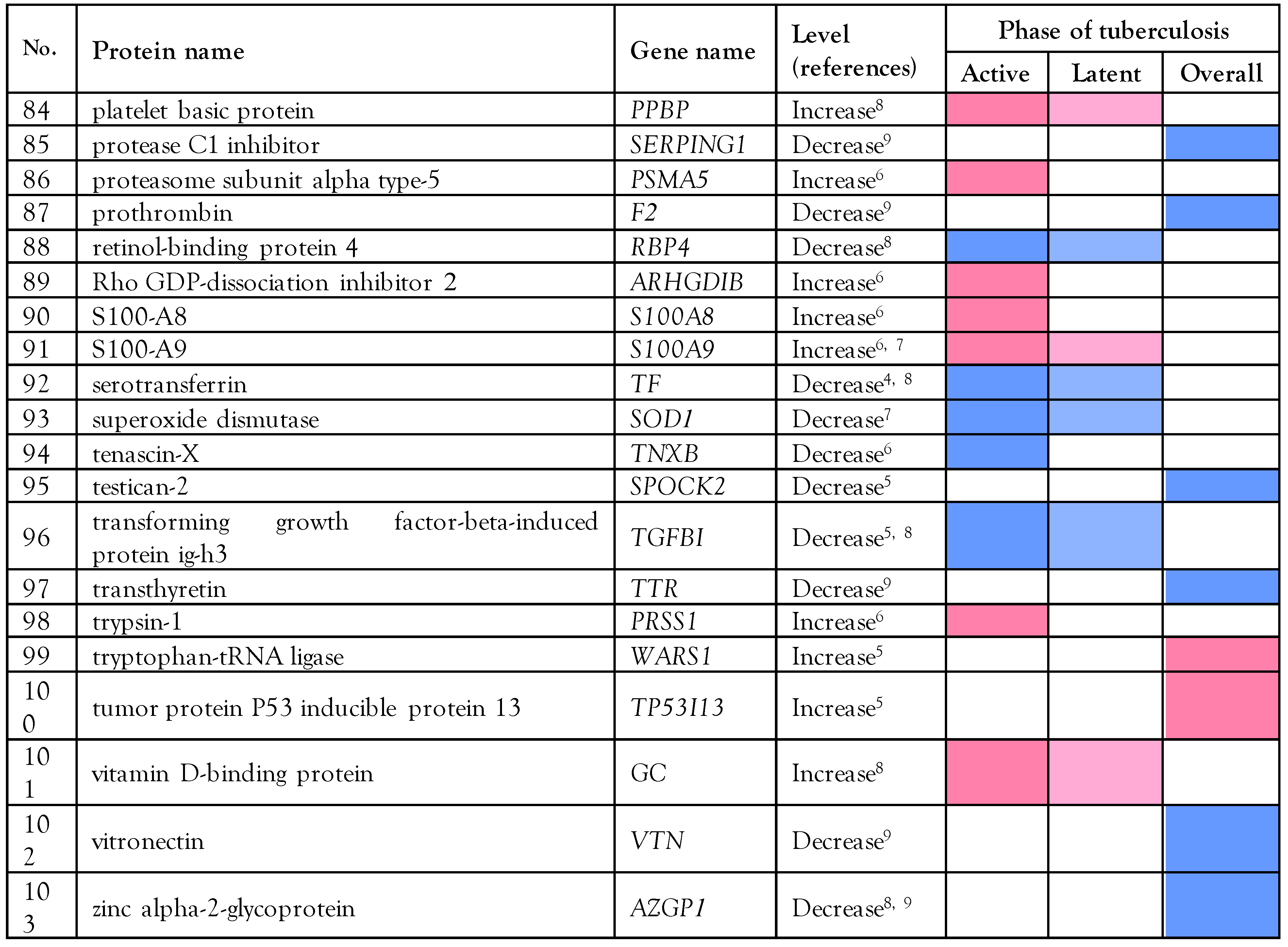
The literature search of PubMed and ScienceDirect that retrieved data from 9 previous proteomics studies [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. established that the levels of 103 serum/plasma proteins are altered in patients with M. tuberculosis infection (active, latent, or overall state) compared to healthy individuals based on statistical fold-change. Fifty-three decreased proteins and 48 elevated proteins have been found in the serum/plasma of patients with tuberculosis; for two proteins, both decreased and increased levels have been reported, as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
List of proteomic data found in serum/plasma of patients with tuberculosis compared with healthy controls, retrieved from all published articles cited in PubMed and Science Direct database from 2012 to 2021.
Biological analysis of the altered serum/plasma proteins
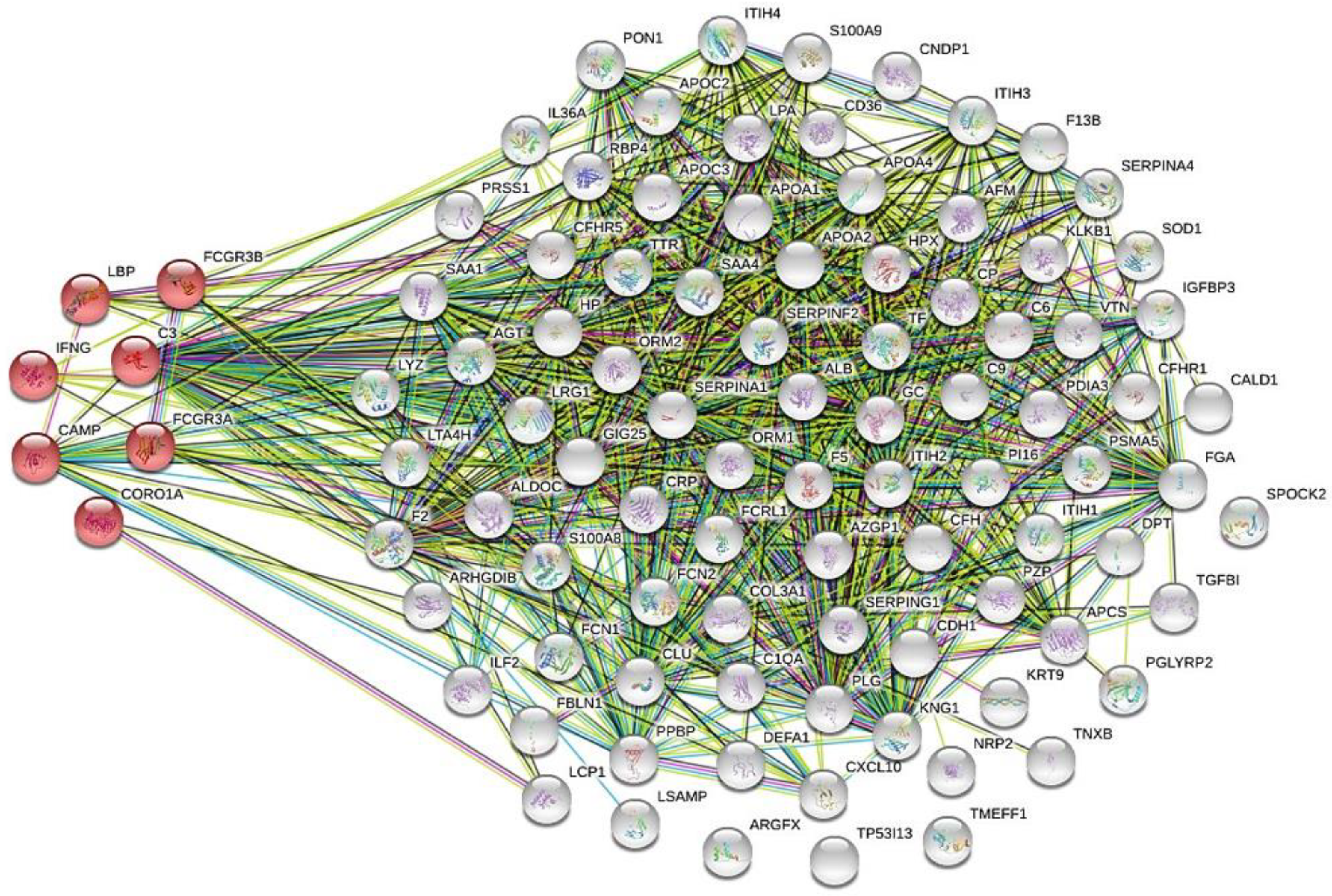
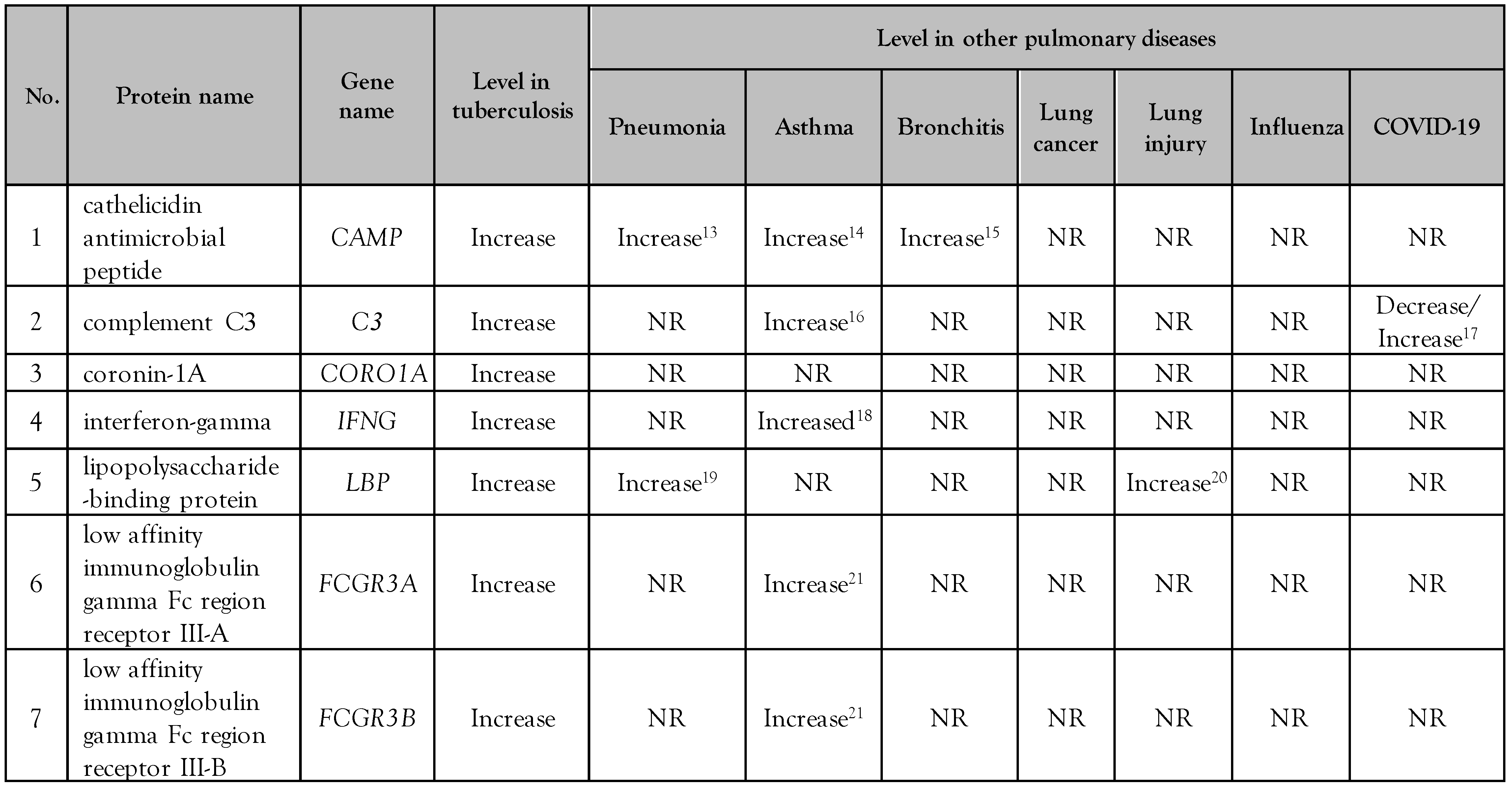
The data of KEGG pathways created by the STRING proteome network for all 103 aforementioned proteins revealed that cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP), complement C3 (C3), coronin-1A (CORO1A), interferon-gamma (IFNG), lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), low-affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-A (FCGR3A), and low-affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-B (FCGR3B) have a close association with tuberculosis (Figure 1).
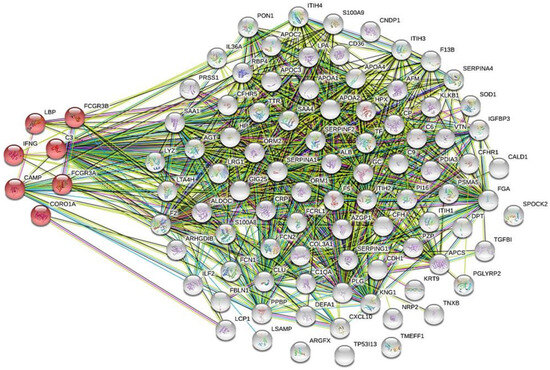
Figure 1.
The biological role in tuberculosis of 103 collected serum/plasma proteins was predicted by global network analysis relative to the KEGG database using the bioinformatics tool STRING, version 11 (http://string-db.org). Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP), complement C3 (C3), coronin-1A (CORO1A), interferon-gamma (IFNG), lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP), low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-A (FCGR3A), and low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-B (FCGR3B). afamin (AFM), albumin (ALB), alpha-2-antiplasmin (SERPINF2), alpha-2-glycoprotein 1, zinc precursor (AZGP1), amyloid-4-protein(SAA4), angiotensinogen (AGT), apolipoprotein (a) (LPA), apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1), apolipoprotein A2 (APOA2), apolipoprotein C-II (APOC2), apolipoprotein C-III (APOC3), arginine-fifty homeobox (ARGFX), beta-ala-His dipeptidase (CNDP1), bone morphogenetic protein 1 (BMP-1), clusterin (CLU), coagulation factor V (F5), coagulation factor XIII B chain (F13B), complement C1q subcomponent subunit A (C1QA), dermatopontin (DPT), disulfide-isomerase A3 (PDIA3), E-cadherin (CDH1), Fc receptor-like protein 1 (FCRL1), fibulin-1 (FBLN1), fructose-bisphosphate aldolase C (ALDOC), hemopexin (HPX), histone H4 (H4C1), immunoglobulin heavy constant-alpha 1 (IGHA1), immunoglobulin-kappa chain V-I region Daudi (IGKV1D-39), immunoglobulin-kappa constant (IGKC), insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 isoform (IGFBP3), inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H1 (ITIH1), inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H2 (ITIH2), inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 (ITIH4), isoform 1 of peptidase inhibitor 16 (PI16), kallikrein (KLKB1), kallistatin (SERPINA4), kininogen (KNG1), limbic system-associated membrane protein (LSAMP), N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase (PGLYRP2), neuropilin-2 (NRP2), paraoxonase arylesterase (PON1), plasminogen (PLG), protease C1 inhibitor (SERPING1), prothrombin (F2), retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4), serotransferrin (TF), superoxide dismutase (SOD1), tenascin-X (TNXB), testican-2 (SPOCK2), transforming growth factor-beta-induced protein ig-h3 (TGFBI), transthyretin (TTR), vitronectin (VTN), and zinc alpha-2-glycoprotein (AZGP1), alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 (ORM1), alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 (ORM2), alpha-1-antichymotrypsin (SERPINA3), alpha-1-antitrypsin (SERPINA1), amyloid-A (SAA1), caldesmon (CALD1), CD36 antigen (CD36), ceruloplasmin (CP), collagen III (COL3A1), complement C6 (C6) complement C9 (C9), complement factor H (CFH), complement factor H-related protein 1 (CFHR1), complement factor H related 5 (CFHR5), C-reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen (FGA), ficolin-1 (FCN1), ficolin-2 (FCN2), FLJ00382 protein (fragment) (FLJ00382), haptoglobin (HP), immunoglobulin-delta chain C region (IGHD), interferon-gamma-induced protein-10 (C-X-C motif chemokine 10) (CXCL10), interleukin-36 alpha (IL36A), interleukin-enhancer binding factor 2 (ILF2), isoform 1 of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H3 (ITIH3), isoform 1 of pregnancy zone protein (PZP), keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 (KRT9), leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein (LRG1), leukotriene A-4 hydrolase (LTA4H), lysozyme (LYZ), neutrophil defensin 1 (DEFA1), plastin-2 (LCP1), platelet basic protein (PPBP), proteasome subunit alpha type-5 (PSMA5), Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 2 (ARHGDIB), S100-A8 (S100A8), S100-A9 (S100A9), trypsin-1 (PRSS1), tryptophan-tRNA ligase (WARS1), tumor protein P53 inducible protein 13 (TP53I13), vitamin D-binding protein (GC), amyloid-P-component (APCS), and apolipoprotein A4 (APOA4).
Selection of serum/plasma proteins as candidate biomarkers
Those serum/plasma proteins in patients with tuberculosis which had a biological function associated with M. tuberculosis infection were selected to serve as the candidate biomarkers for specific diagnosis by following defined criteria, including only being encountered in tuberculosis, not in other respiratory and pulmonary diseases with similar signs/symptoms, including pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer, lung injury, influenza, and SARS-CoV-2. A search of data from previous reports [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21] demonstrated that levels of CAMP, C3, IFNG, LBP, FCGR3A, FCGR3B are altered (increased or decreased) in patients with tuberculosis to the same degree as in the aforementioned related diseases. The level of coronin-1A (CORO1A), however, was found to increase only in patients with tuberculosis, not in those with other respiratory and pulmonary diseases (Table 2). Therefore, coronin-1A (CORO1A) was indicated to have properties based on the aforementioned criteria and may also serve as a novel biomarker for specific diagnosis in tuberculosis patients.

Table 2.
List of the altered serum/plasma proteins found in patients with tuberculosis and other diseases including pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer, lung injury, influenza, and COVID-19.
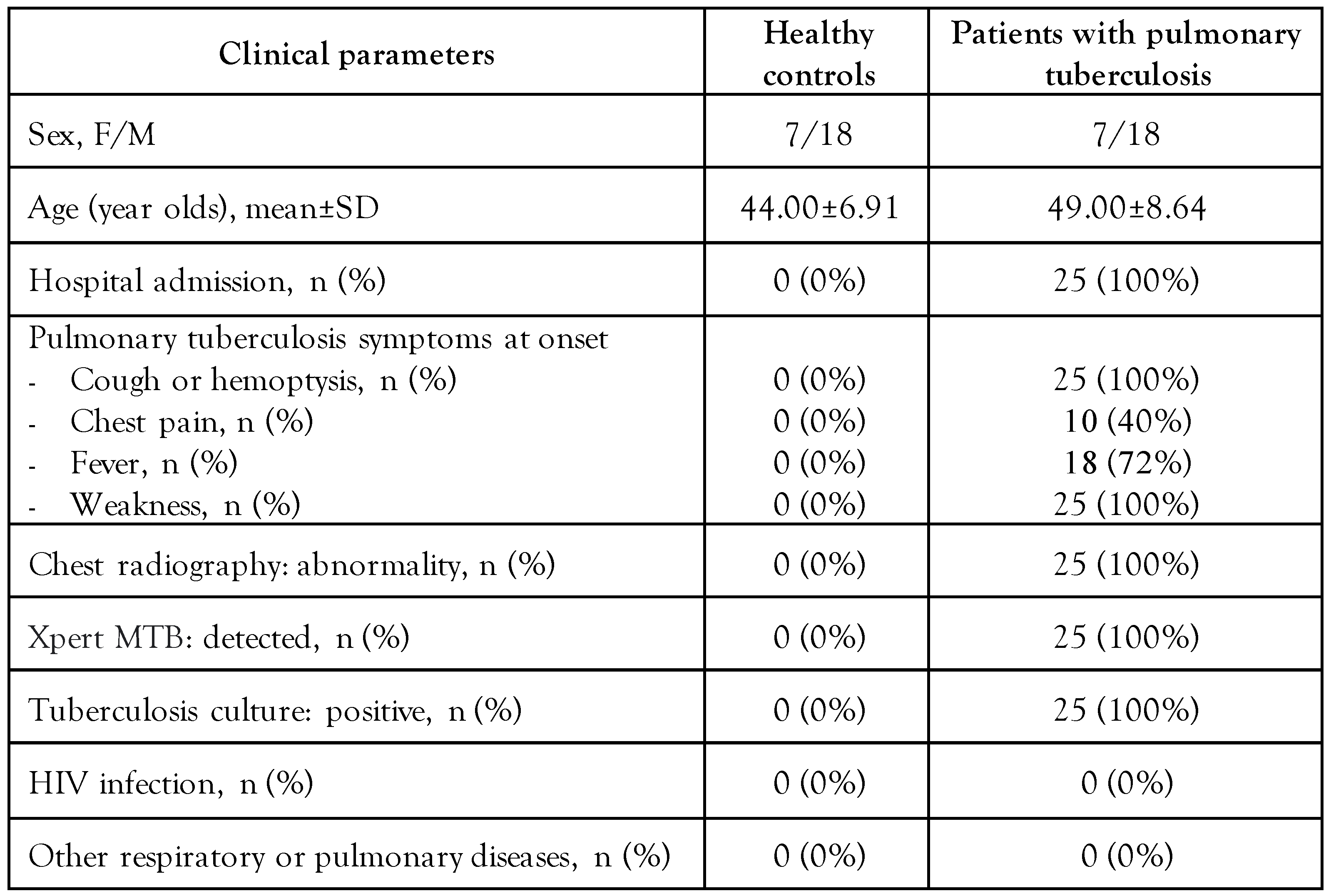
Demographic data of the patients
In all patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, the disease was detected by Xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) and tuberculosis culture. Age- and sex-matched healthy participants who had no illness, history of illness, or clinical manifestations of cognitive and chronic diseases, especially M. tuberculosis infection, and other respiratory and pulmonary diseases, were selected as matching comparative controls. The demographic information and disease status at the time of the study of healthy controls and patients with pulmonary tuberculosis are summarized in Table 3. The data demonstrate that there were no significant differences in terms of sex (female/male) and age between the healthy control group (7/18, 37 to 51 years old) and the pulmonary tuberculosis test group (7/18, 40 to 58 years old). All of the patients were admitted to hospital, had symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis at onset (cough or hemoptysis, chest pain, fever, and weakness), abnormal chest X-ray, and were infected with M. tuberculosis. Moreover, none of the patients or healthy participants had HIV infection or other related respiratory or pulmonary diseases (pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer, lung injury, influenza, and SARS-CoV-2).

Table 3.
Demographic characteristics of healthy controls and patients with pulmonary tuberculosis.
Validation of serum coronin-1A level
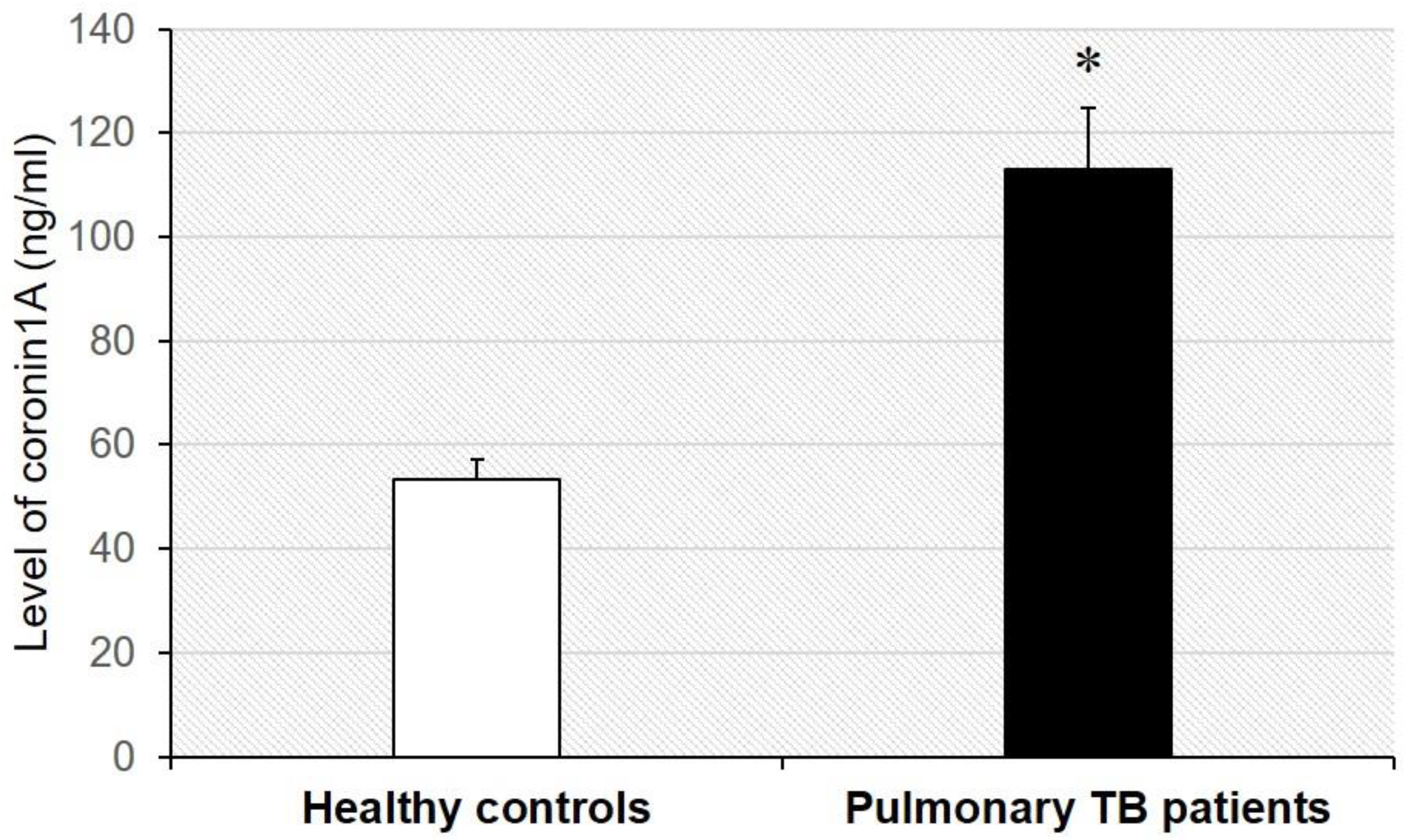
The concentration of coronin-1A in the serum of patients with tuberculosis was compared to that in healthy controls by ELISA with specific capture and detection of antibodies specific to human coronin-1A. The serum of patients with tuberculosis was found to have a statistically significantly higher (p < 0.001) coronin-1A concentration (113.01 ± 11.66 mg/dL) than that of heathy controls (53.23 ± 4.00 ng/mL)—Figure 2.
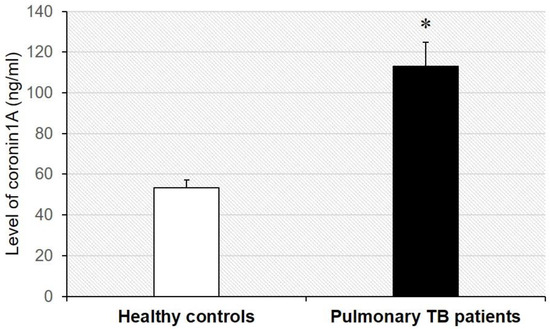
Figure 2.
The level of coronin-1A in serum of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (n = 25) and healthy controls (n = 25) was validated with capture and detection of antibodies specific to human coronin-1A based on sandwich ELISA. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of the data obtained from 25 independent experiments. * p < 0.05 vs. healthy control.
Diagnostic ability of serum coronin-1A level
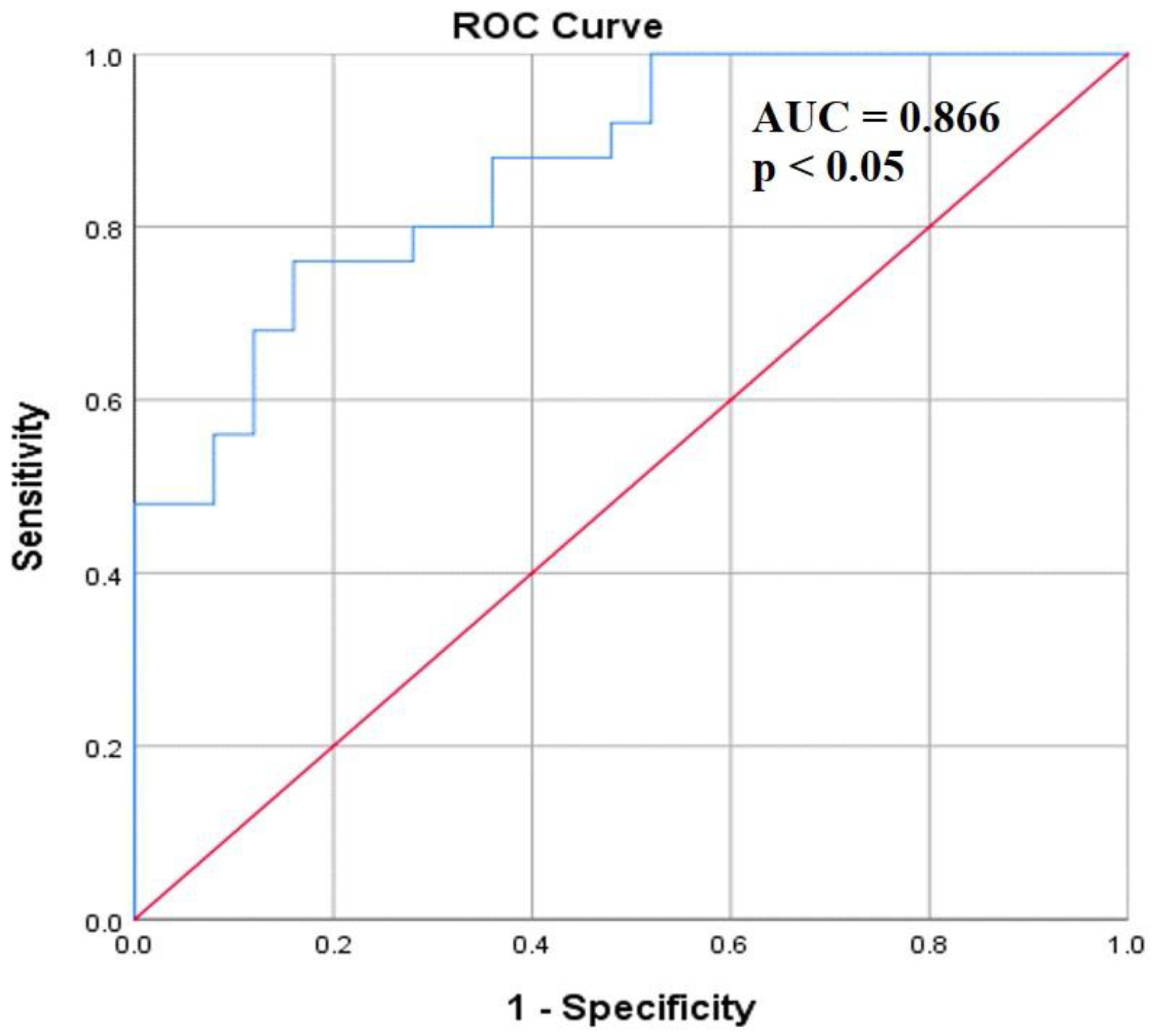
Evaluation of the diagnostic ability of serum coronin-1A level was carried out by analyzing the AUC of the ROC. Analysis of the ROC showed an AUC for the coronin-1A level of 0.866 (95% confidence interval; CI = 0.769–0.962, p < 0.001) in serum samples of tuberculosis patients compared to healthy controls. Moreover, the cut-off of serum coronin-1A level was identified by the optimal value that gave the highest sensitivity and specificity, to further distinguish tuberculosis patients from healthy controls. Our data exhibited that a serum coronin-1A concentration of 52.7 ng/mL had a yield of 92%sensitivity and 52% specificity, respectively (Figure 3).
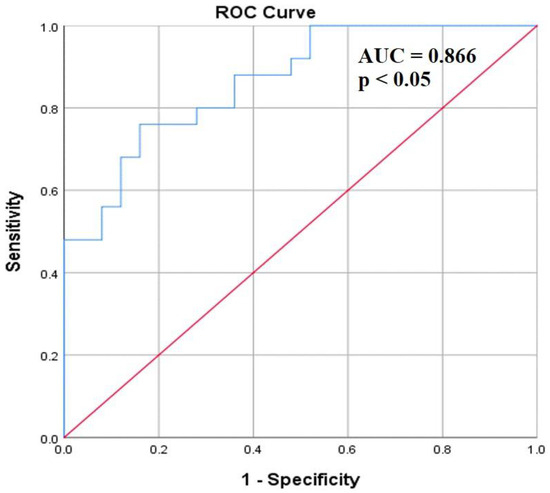
Figure 3.
ROC curve analysis for investigating diagnostic value of serum coronin-1A in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis (n = 25) and healthy controls (n = 25).
Discussion
KEGG is a useful database of bioinformatics pathways dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, etc. for bioinformatics research of several omics studies, systems biology, and drug development. Moreover, as KEGG pathways store more systematic information on gene functions, this database is widely used thus for enrichment analysis platforms. From the results, we identified seven candidate proteins and performed a further literature search to determine which might exhibit alterations specific to pulmonary tuberculosis rather than other respiratory and pulmonary diseases with similar signs/symptoms, including pneumonia, asthma, bronchitis, lung cancer, lung injury, influenza, and SARS-CoV-2. We found that the level of coronin-1A was increased only in tuberculosis, not in these aforementioned important diseases (Table 2), suggesting that coronin-1A could be applied as a candidate biomarker in the further validation of serum level in patients with tuberculosis.
Coronin-1A, gene name CORO1A, is a member of the coronin family of proteins which are important actin regulators through direct binding to the F-actin cytoskeleton. Moreover, the localization of coronin-1A with actin is found in various immune cells, including in the phagocytic cups of neutrophils and macrophages, and leading edge of T cells for supporting phagocytosis, chemotaxis, and cell activation, respectively [22]. Coronin-1A has previously been reported to be localized in mycobacterial phagosomes and the survival of M. tuberculosis in macrophages can also be prevented by coronin-1A gene silencing or depletion, indicating an important role of coronin-1A for bacterium survival in phagocytic cells [23]. Moreover, the level of coronin-1A has been identified by mass spectrometry to be significantly altered in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis compared to controls [24]. Based on previous and present data, the serum level of coronin-1A in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis was validated by sandwich ELISA. The participating patients with tuberculosis and healthy individuals had no significant differences of the crucial clinical parameters of sex, age, HIV infection, and other respiratory or pulmonary diseases related to tuberculosis (Table 3). The results of ELISA testing revealed that serum coronin-1A was markedly increased in the patients as compared to controls (Figure 2). Our findings are consistent with previous data that show an increased coronin-1A expression of mRNA level in the whole blood of tuberculosis patients [25].
The increased level of coronin-1A in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis was subsequently applied to analyze diagnostic power by ROC curve analysis. Coronin-1A level with a cut-off point of approximately 52.7 ng/mL was found to have high sensitivity (92%). Moreover, the AUC for discrimination of patients with tuberculosis from healthy controls was 0.866 with 95% CI = 0.769–0.962 (Figure 3), representing the low variability at each and every point of sensitivity and specificity (high true positive rate) on the ROC curve. These data indicate that coronin-1A is a reliable serum marker for diagnosis of patients with tuberculosis, and possibly could serve as a novel biomarker to be further developed in a supportive laboratory investigation, to provide more accurate diagnosis of patients. However, the present study had limitations for obtaining a larger spectrum of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis with various states of disease, including active pulmonary, active extra-pulmonary, and latent infection, because there have been confined cases of patients with tuberculosis in Thailand. From our results, an increased level of serum coronin-1A specific to patients with tuberculosis is associated with the process of M. tuberculosis infection, suggesting the ability of this protein to be applied as an alternative method of laboratory diagnosis for pulmonary tuberculosis. Additionally, the increased level of coronin-1A in the serum of patients with tuberculosis might provide beneficial information for the potential management of disease severity as well as both prevention and treatment, which is the translational medical development of M. tuberculosis infection. Furthermore, the data in this study can be used as a guideline for functional studies to better understand the underlying mechanisms of pathogenesis and/or disease severity in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis.
Conclusions
The serum coronin-1A level of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis was found to be increased compared to that of healthy individuals, involved in M. tuberculosis infection, and specific to the patients by using a systematic review-based approach of serum/plasma proteome data in tuberculosis, integrative bioinformatics analysis, and biomarker validation, respectively. In addition, a cut-off of serum coronin-1A of approximately 52.7 ng/mL could discriminate patients with pulmonary tuberculosis from healthy controls with high sensitivity and specificity. Taken together, these results indicate that the level of serum coronin-1A could be used as a novel biomarker for further supporting diagnosis specific to patients with tuberculosis.
Author Contributions
SK designed the research question and experiments, SK and OP performed all experiments and analyzed data. SK drafted the original manuscript. Both authors read, edited and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research project was supported by the Thailand Science Research and Innovation Fund and the University of Phayao Unit of Excellence research grant from University of Phayao, Thailand (grant no. FF65-RIM137 and FF65-UoE011).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors recognize and thank all participants in this study including pulmonary patients and healthy individuals. Moreover, the authors would like to thank the School of Allied Health Sciences, University of Phayao, Thailand for providing the needed laboratory equipment and facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors—none to declare.
References
- Fukunaga, R.; Glaziou, P.; Harris, J.B.; Date, A.; Floyd, K.; Kasaeva, T. Epidemiology of tuberculosis and progress toward meeting global targets-worldwide, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021, 70, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Garra, A.; Redford, P.S.; McNab, F.W.; Bloom, C.I.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Berry, M.P. The immune response in tuberculosis. Annu Rev Immunol 2013, 31, 475–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, D.; Motallebirad, T.; Ghaffari, K.; Shojaei, H. Mycobacteriosis and tuberculosis: Laboratory diagnosis. Open Microbiol J 2018, 12, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, J.; Estevez, O.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; et al. Serum proteomics of active tuberculosis patients and contacts reveals unique processes activated during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groote, M.A.; Sterling, D.G.; Hraha, T.; et al. Discovery and validation of a six-marker serum protein signature for the diagnosis of active pulmonary tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol 2017, 55, 3057–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wei, L.L.; Shi, L.Y.; et al. Screening and identification of five serum proteins as novel potential biomarkers for cured pulmonary tuberculosis. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 15615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Pan, L.; Han, F.; et al. Proteomic profiling for plasma biomarkers of tuberculosis progression. Mol Med Rep 2018, 18, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Pan, L.; Jia, H.; et al. Label-free quantitative proteomics identifies novel plasma biomarkers for distinguishing pulmonary tuberculosis and latent infection. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Han, M.; Choi, Y.S.; et al. Proteomic profiling of serum from patients with tuberculosis. Ann Lab Med 2014, 34, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Morris, T.C.; Hoggart, C.J.; Chegou, N.N.; et al. Evaluation of host serum protein biomarkers of tuberculosis in sub-saharan Africa. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 639174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay-Baquero, D.J.; White, C.H.; Walker, N.F.; et al. Comprehensive plasma proteomic profiling reveals biomarkers for active tuberculosis. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e137427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, T.; Wei, L.; et al. The discovery and identification of a candidate proteomic biomarker of active tuberculosis. BMC Infect Dis 2013, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, K.; Kozłowska, E.; Żelechowska, P.; Brzezińska-Błaszczyk, E. Serum concentrations of antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin LL-37 in patients with bacterial lung infections. Cent Eur J Immunol 2018, 43, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.C.; Xiao, H.Q.; Brown, A.J.; Ritter, C.S.; Schroeder, J. Association of vitamin D and antimicrobial peptide production during late-phase allergic responses in the lung. Clin Exp Allergy 2012, 42, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedik, A.H.; Cakir, E.; Gokdemir, Y.; et al. Cathelicidin (LL-37) and human beta2-defensin levels of children with post-infectious bronchiolitis obliterans. Clin Respir J 2017, 11, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Fattah, M.; El Baz, M.; Sherif, A.; Adel, A. Complement components (C3, C4) as inflammatory markers in asthma. Indian J Pediatr 2010, 77, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherimoghaddam, A.; Rafatpanah, H.; Mansouritorghabeh, H. Elevated levels of C3, C4, and CH50 of the complement system in ICU and non-ICU patients with COVID-19. Health Sci Rep 2022, 5, e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, P.; Mahesh, P.A.; Holla, A.D.; et al. Serum levels of interleukin-13 and interferon-gamma from adult patients with asthma in Mysore. Cytokine 2012, 60, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopstaken, R.M.; Cals, J.W.; Dinant, G.J. Accuracy of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) and fibrinogen compared to C-reactive protein (CRP) in differentiating pneumonia from acute bronchitis in primary care. Prim Care Respir J 2009, 18, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Pérez-Méndez, L.; Espinosa, E.; et al. Serum lipopolysaccharide binding protein levels predict severity of lung injury and mortality in patients with severe sepsis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, R.; Huang, J.; et al. Functional Fcgamma receptor polymorphisms are associated with human allergy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Di Ciano-Oliveira, C.; Grinstein, S.; Trimble, W.S. Coronin function is required for chemotaxis and phagocytosis in human neutrophils. J Immunol 2007, 178, 5769–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, S.; Tsujimura, K.; Koide, Y. Coronin-1a inhibits autophagosome formation around Mycobacterium tuberculosis-containing phagosomes and assists mycobacterial survival in macrophages. Cell Microbiol 2012, 14, 710–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.; Kaiqi, H.; Weiqiang, R.; Junge, Z.; Maybank, S. Large-scale weakly supervised object localization via latent category learning. IEEE Trans Image Process 2015, 24, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Gupta, G.; Biswas, S.; et al. Coronin-1 levels in patients with tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res 2021, 154, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2023.