Seropositivity for Dengue and Leptospira IgM Among Patients with Acute Febrile Illness: An Indicator of Co-Infection?
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
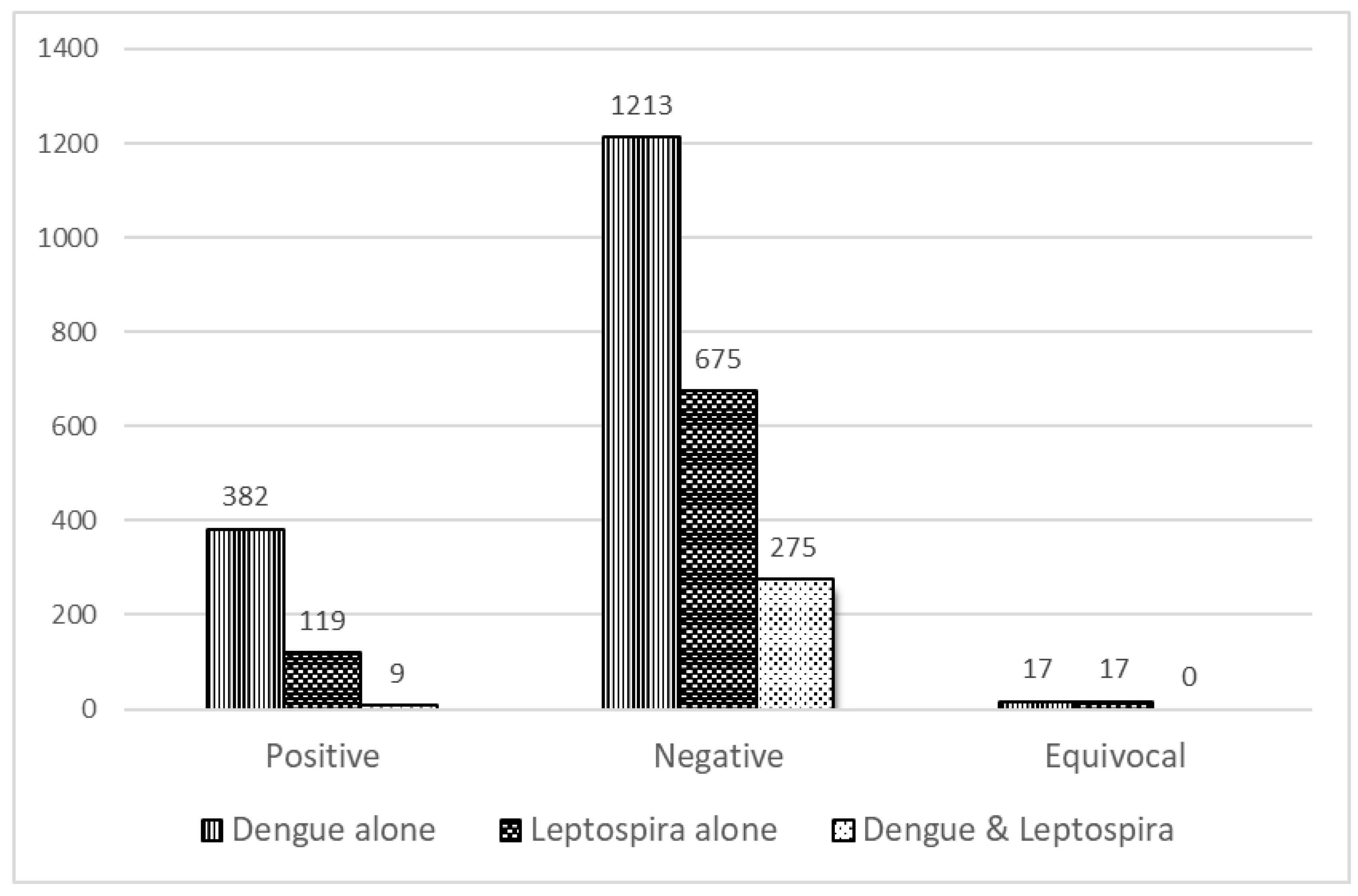
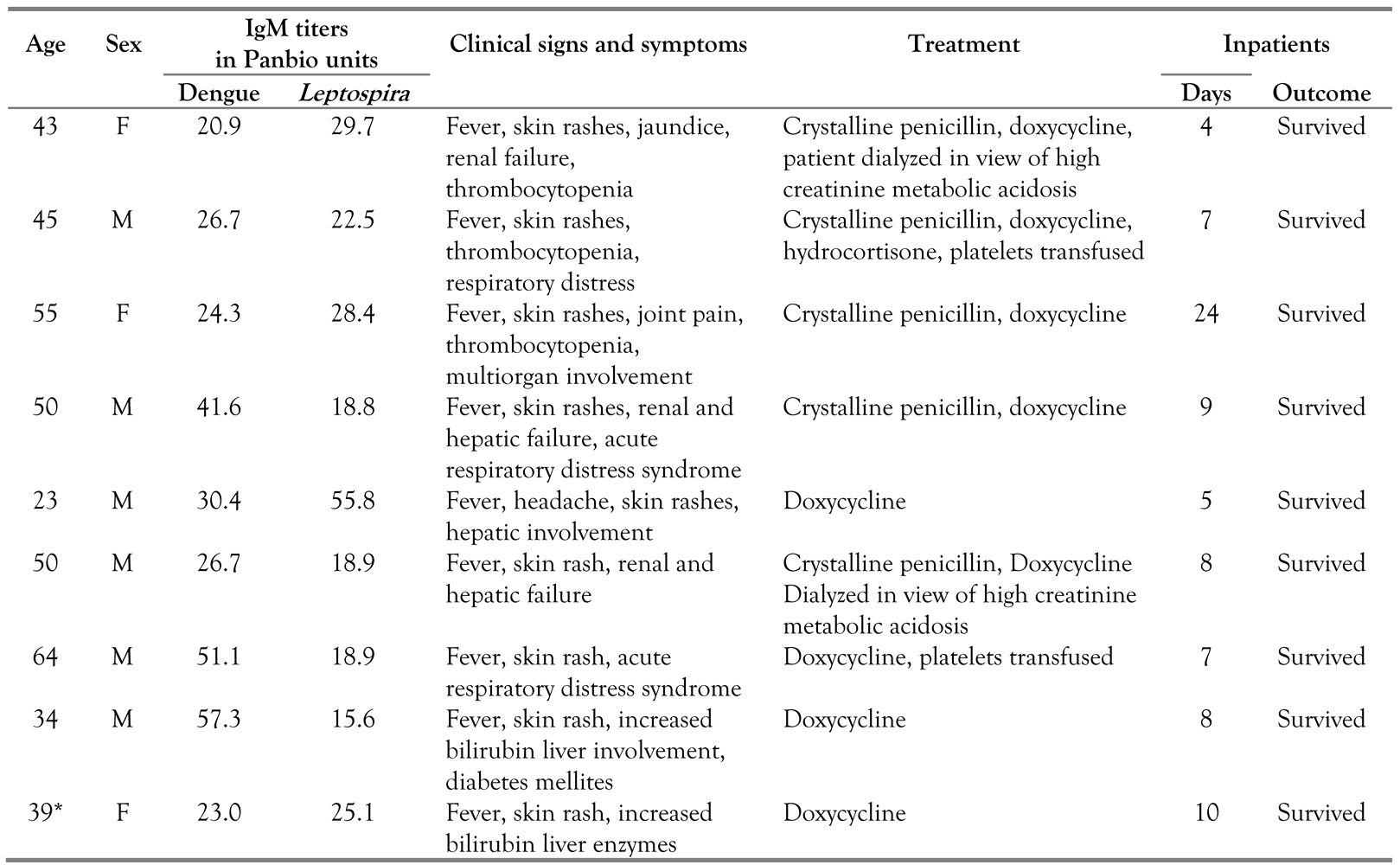
Results
Discussion
Key messages
- Leptospirosis and dengue have mimicking clinical signs and symptoms, which coexist in endemic areas.
- Co-infection with Leptospira and dengue is very difficult to differentiate with serological test in resource poor countries.
- Leptospirosis needs to be differentiated from dengue as the former can be treated with antibiotics, to reduce mortality.
- Suspected co-infection needs to be confirmed by PCR.
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethical approval
Informed consent
References
- Joshi, R.; Colford, J.M., Jr.; Reingold, A.L.; Kalantri, S. Nonmalarial acute undifferentiated fever in a rural hospital in central India: diagnostic uncertainty and overtreatment with antimalarial agents. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2008, 78, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, M.R.; Blair, P.J.; Touch, S.; et al. Infectious Etiologies of acute febrile illness among patients seeking health care in south-central Cambodia. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2012, 86, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshkumar, P.; Murhekar, M.V.; Poornima, V.; et al. Dengue infection in India: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2018, 12, e0006618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme. Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India. Dengue/DHF situation in India. Available online: https://nvbdcp.gov.in/index4.php?lang=1&level=0&lin kid=431&lid=3715 (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; et al. Global morbidity and mortality of leptospirosis: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiva Kumar, S. Indian guidelines for the diagnosis and management of human leptospirosis. In Medicine Update; Muruganathan, A., Ed.; 2013; p. 23-9. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dengue. Testing. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dengue/healthcare-providers/testing/index.html (accessed on 11 May 2020).
- Sushi, K.M.; Sivasangeetha, K.; Kumar, A.S.; et al. Seroprevalence of leptospirosis, enteric fever and dengue in patients with acute febrile illness in Tamil Nadu, India. Indian J Basic Appl Med Res. 2014, 3, 615–623. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.K.; Latha, P.M.; Kalawat, U. Coinfection of leptospirosis and dengue fever at a tertiary care center in South India. Scho Res J. 2012, 2, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Balachandran, V.; Dominic, A.; et al. Serological evidence of leptospirosis and dengue co-infection in an endemic region in South India. Ann Trop Med Public Health. 2012, 5, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holla, R.; Darshan, B.; Pandey, L.; et al. Leptospirosis in coastal south India: a facility based study. Biomed Res Int. 2018, 2018, 1759125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodar, T.; Dias, M.; Mani, R.; et al. Clinical and laboratory profile of dengue viral infections in and around Mangalore, India. Indian J Med Microbiol 2017, 35, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, M.; Daniel, D.; Prakash, J.A.J. Determination of cut-off for Leptospira immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in south India. Int J Sci Study. 2018, 6, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Sengvilaipaseuth, O.; Chanthongthip, A.; et al. Comparison of two commercial ELISA kits for the detection of anti-dengue IgM for routine dengue diagnosis in Laos. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2019, 4, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandeniya, C.L.; Ralapanawa, D.M.P.U.K.; Jayalath, W.; Kularatne, S.A.M. Atypical manifestations of dengue infection due to co-infection with either hepatitis A or leptospirosis: two case reports. Sri Lankan J Infect Dis. 2015, 5, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, A.C.; Souza, N.C.S.; Figueiredo, W.M.; et al. Cross reactivity of commercial anti-dengue immunoassays in patients with acute Zika virus infection. J Med Virol. 2017, 89, 1477–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Kodan, P.; Baruah, K.; Soneja, M.; Biswas, A. Zika virus in India: past, present and future. QJM. 2019, hcz273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.R.; Shieh, W.J. Leptospirosis associated with outbreak of acute febrile illness and pulmonary haemorrhage, Nicaragua, 1995. The Epidemic Working Group at Ministry of Health in Nicaragua. Lancet. 1996, 347, 535–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdinc, F.S.; Koruk, S.T.; Hatipoglu, C.A.; Kinikli, S.; Demiroz, A.P. Three cases of anicteric leptospirosis from Turkey: mild to severe complications. J Infect. 2006, 52, e45–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, S.; Maheshwari, A. Atypical manifestations of dengue. Trop Med Int Health. 2007, 12, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, D.T.; Thao le, T.T.; Hien, T.T.; et al. Liver involvement associated with dengue infection in adults in Vietnam. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010, 83, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.S.; Bujang, M.A. The clinical features and outcomes of acute liver failure associated with dengue infection in adults: a case series. Braz J Infect Dis. 2013, 17, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.R.; Unnikrishnan, D.; Satish, B.; Sahadulla, M.I. Acute renal failure in dengue fever in the absence of bleeding manifestations or shock. Infect Dis Clin Pract. 2005, 13, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratima, P.T.; Irfan, K.J.; Shivanna, S.; Yatish, B.; Joy, R. Hepatic dysfunction and acute renal failure requiring haemodialysis in dengue hemorrhagic fever-a rare complication. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2013, 2, 4725–4728. [Google Scholar]
- Jose, L.R.; Sumana, M.N. Early diagnosis of leptospirosis using conventional techniques: A study in a tertiary care hospital, Mysore, South Karnataka, India. Int J Adv Res. 2014, 2, 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.; Singhal, L.; Sethi, S.; Ratho, R.K. Leptospirosis coexistent with dengue fever: a diagnostic dilemma. J Glob Infect Dis. 2013, 5, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, A.; Gnanapragash, N.; Ranasinghe, G.; Ragunathan, M.K. Fatal co-infection with leptospirosis and dengue in a Sri Lankan male. BMC Res Notes. 2015, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Libraty, D.H.; Myint, K.S.; Murray, C.K.; et al. A comparative study of leptospirosis and dengue in Thai children. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2007, 1, e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meguins, L.C.; Medeiro Júnior, H.O. Leptospirosis and dengue co-infection in a Brazilian Amazon patient. Rev Pan-Amazônica Saúde 2010, 1, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.G.; Vickers, I.E.; Salas, R.A.; Smikle, M.F. Leptospirosis in suspected cases of dengue in Jamaica, 2002-2007. Trop Doct. 2010, 40, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dircio Montes Sergio, A.; González Figueroa, E.; María Saadia, V.G.; et al. Leptospirosis prevalence in patients with initial diagnosis of dengue. J Trop Med. 2012, 2012, 519701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Name of investigation | Normal range | Mean ± standard deviation | Median |
|---|---|---|---|
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate | 1-10 mm/1st hour | 39.7±24.7 | 40 |
| White blood cell count | 4-10 ×103 cells/ mm3 | 12.1±10.4 | 12.0 |
| Platelet count | 150-400 ×103 cells/mm3 | 82.0±48.9 | 107.0 |
| Serum bilirubin | 0.2-1.1 mg/dL | 4.5±6.7 | 1.5 |
| Serum creatinine | 0.4-1.4 mg/dL | 5.1±3.0 | 3.6 |
| Blood urea | 15-40 mg/dL | 74.3±77.0 | 65 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 5-40 IU/L | 110±83.6 | 75 |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 5-40 IU/L | 132±108.9 | 90 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 40-129 IU/L | 164.6±56.8 | 140 |
| Dengue IgM antibodies | <9 Panbio units* | 33.6±13.2 | 27.0 |
| Leptospira IgM antibodies | <9 Panbio units* | 26.0 ±12.2 | 22 |
© GERMS 2021.
Share and Cite
Dhanashree, B.; Shenoy, S. Seropositivity for Dengue and Leptospira IgM Among Patients with Acute Febrile Illness: An Indicator of Co-Infection? Germs 2021, 11, 155-162. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1253
Dhanashree B, Shenoy S. Seropositivity for Dengue and Leptospira IgM Among Patients with Acute Febrile Illness: An Indicator of Co-Infection? Germs. 2021; 11(2):155-162. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1253
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhanashree, Biranthabail, and Shalini Shenoy. 2021. "Seropositivity for Dengue and Leptospira IgM Among Patients with Acute Febrile Illness: An Indicator of Co-Infection?" Germs 11, no. 2: 155-162. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1253
APA StyleDhanashree, B., & Shenoy, S. (2021). Seropositivity for Dengue and Leptospira IgM Among Patients with Acute Febrile Illness: An Indicator of Co-Infection? Germs, 11(2), 155-162. https://doi.org/10.18683/germs.2021.1253




