Abstract
Non-persistent endocrine disrupting chemicals (npEDCs) can affect multiple organs and systems in the body. Whether npEDCs can accumulate in the human brain is largely unknown. The major aim of this pilot study was to examine the presence of environmental phenols and parabens in two distinct brain regions: the hypothalamus and white-matter tissue. In addition, a potential association between these npEDCs concentrations and obesity was investigated. Post-mortem brain material was obtained from 24 individuals, made up of 12 obese and 12 normal-weight subjects (defined as body mass index (BMI) > 30 and BMI < 25 kg/m2, respectively). Nine phenols and seven parabens were measured by isotope dilution TurboFlow-LC-MS/MS. In the hypothalamus, seven suspect npEDCs (bisphenol A, triclosan, triclocarban and methyl-, ethyl-, n-propyl-, and benzyl paraben) were detected, while five npEDCs (bisphenol A, benzophenone-3, triclocarban, methyl-, and n-propyl paraben) were found in the white-matter brain tissue. We observed higher levels of methylparaben (MeP) in the hypothalamic tissue of obese subjects as compared to controls (p = 0.008). Our findings indicate that some suspected npEDCs are able to cross the blood–brain barrier. Whether the presence of npEDCs can adversely affect brain function and to which extent the detected concentrations are physiologically relevant needs to be further investigated.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, industrial progress has introduced exposure to a huge number of new synthetic chemicals—e.g., environmental phenols and parabens such as bisphenol A (BPA), triclosan (TCS), and benzophenone-3 (BP-3)—that can be found in a wide variety of commercial products including plastics, packaged food and drinks, personal care products, and pharmaceuticals [1,2]. Humans are exposed to these chemicals via ingestion, inhalation, dermal contact, and perinatal transmission (i.e., placenta, breast milk) [3,4,5], and the exposure is ubiquitous in western populations [5,6,7,8,9]. Some environmental phenols and parabens are labeled as non-persistent endocrine disrupting chemicals (npEDCs) because of their known or suspected adverse effects on endocrine and metabolic regulation [10,11] and quick metabolism and excretion from the body [2]. However, traces of these npEDCs have recently been detected in human adipose tissue, liver, and brain [12,13,14,15].
Since the early 1980s, the prevalence of obesity has more than doubled worldwide, to 600 million obese adults in 2014 [16]. This increase is reaching epidemic proportions, and can no longer be solely explained by genetic predisposition, increased caloric intake, and lack of physical activity [17]. Accumulating evidence from epidemiological studies suggests involvement of npEDCs in the increased prevalence of obesity [18,19,20,21,22]. Also, the obesogenic properties of npEDCs are supported by functional and in vitro studies [17].
While a lot of research concerning npEDCs and obesity has been done over the years, very little is known about its presence in and potential effects on the human brain. Energy balance consists of complex homeostatic mechanisms involving both peripheral organs and the brain [23], with the hypothalamus playing a central role in the regulation of energy expenditure, metabolism, and nutrient partitioning [24]. Because the hypothalamus receives information through circulating metabolites and hormones, and is therefore susceptible to a wide variety of hormones [24], it is plausible that some EDCs have the potential to infiltrate there and interfere with the physiological processes. Recently, exposure to low doses of BPA in zebrafish has been shown to increase hypothalamic neurogenesis [25]. In rodents, perinatal exposure to BPA has been shown to disrupt the signaling of multiple regulatory hormones, including leptin and insulin [26], very likely through developmental programming of the hypothalamic melanocortin system, permanently remodeling the neurobiology of metabolic homeostasis [27].
As it is only partly protected by the blood–brain barrier (BBB) [28], the hypothalamic exposure to npEDCs is expected to differ from BBB-protected brain regions, such as the white-matter tissue [28]. Although there are some indications of npEDCs presence in human brain tissue [13], information on the distribution of npEDCs in the human brain is not available yet. The major aim of this pilot study was to examine the presence of environmental phenols and parabens in two distinct brain regions, the hypothalamus and white-matter tissue. In addition, we also investigated a potential association between these npEDCs concentrations and obesity.
2. Methods
We used frozen hypothalamic and white-matter brain tissue material obtained from The Netherlands Brain Bank (NBB), Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Amsterdam (open access: www.brainbank.nl). All material was collected from donors whose written informed consent for a brain autopsy and the use of their brain material and clinical information regarding research purposes had been obtained by the NBB [29]. Hypothalamus samples came from 24 individuals (Table S1), 12 of whom were normal-weight controls and 12 were obese individuals (cases) (body mass index (BMI) < 25 kg/m2 and BMI > 30 kg/m2, respectively) that were matched for sex, age, clinical diagnosis, and Braak stage of Alzheimer’s progression [30]. Additional white-matter lipid-enriched brain tissue was collected from five of the above-mentioned matched case-control pairs. All procedures were performed in accordance with national and institutional guidelines and with the ethical guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Seven parabens (methyl paraben (MeP), ethyl paraben (EtP), iso-propyl paraben (i-PrP), n-propyl paraben (n-PrP), iso-butyl paraben (i-BuP), n-butyl paraben (n-BuP) and benzyl paraben (BzP)) and nine phenols (BPA, TCS, triclocarban (TCC), BP-3, 2,4-dichlorophenol (2.4-DCP), 2,5-dichlorophenol (2.5-DCP), 2,4,5-trichlorophenol (2.4.5-TCP), 2-phenylphenol (2-PP) and 4-phenylphenol (4-PP)) were analyzed by means of TurboFlow-LC-MS/MS at Department of Growth and Reproduction, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen with a recently developed method for adipose tissue [12]. Sample weights varied between 44.7 mg and 118.9 mg, and all chemicals, solutions, and laboratory wares were checked for contamination before use. All samples were processed as described previously [12]. In short, samples were analyzed in batches including standards for calibration curves, unknown samples, two blanks, and two control samples (a pool of human fatty tissues) spiked at low and high levels.
Descriptive statistics (mean, Standard Deviation (SD), median, percentiles, minimum and maximum) of the npEDCs were calculated for a total population and stratified by status. The compounds detected in >50% of the samples (BPA and MeP) were included in further analysis, in which concentrations below the limit of detection (LOD) were replaced by LOD/√2. The correlation between BPA and MeP levels and age, body weight, BMI, and other parameters was examined using Spearman’s rho test. Differences between groups were statistically evaluated by the unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction or by the Wilcoxon matched paired signed-rank test. Tests were two-tailed. The level of a nominal significance was set at p < 0.05. Optimal sample sizes were calculated using NCSS PASS software version 11.0 [31,32], assuming that the observed means and standard deviations were representative of the target population. We furthermore assumed a normal distribution of BPA levels, and normal distribution of paired differences in BPA levels between hypothalamus and white-matter tissue. Statistical analysis was conducted with SPSS (version 22 for Windows, SPSS Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA). Graphs were computed with GraphPad Prism software for Windows, Version 5 (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
3. Results
In this study, we included hypothalamic and white-matter brain tissues post mortem obtained from 12 obese and 12 normal-weight control subjects. The study population consisted mainly of women (67%) and the mean age was 74 years old. There were no differences in sex, age, and brain weight between cases and controls (Table S2). A descriptive analysis of the npEDCs measured is presented, for both hypothalamus and white-matter, in Table 1. Out of the nine phenols and seven parabens analyzed, three phenols (BPA, TCS, and TCC) and four parabens (MeP, EtP, n-PrP, and BzP) were detected in the hypothalamus (Figure 1A), while in white-matter brain tissue we found three phenols (BPA, BP-3, and TCC) and two parabens (MeP and n-PrP) (Figure 1B). Of the 24 hypothalamic samples, BPA was detectable above LOD in 23 samples, MeP in 15 samples, EtP in 3 samples, and n-PrP in 5 samples. BPA, TCC, and MeP were detectable in respectively 9, 2, and 3 of the 12 white-matter samples. Furthermore, TCS, TCC, and BzP were detected in single hypothalamus samples, while BP-3 and n-PrP were detectable in single white-matter samples (Table 1). The ranges of some npEDCs in brain tissues were wide, with the largest spread in the concentration found for BPA in both hypothalamus and white-matter (between 0.32 and 26.62 ng/g and between 0.30 and 3.32 ng/g, respectively), for MeP in hypothalamus (ranging between 0.06 and 1.16 ng/g) and for TCC in white-matter tissue (ranging between 1.45 and 5.95 ng/g).

Table 1.
Phenols and parabens (ng/g) in hypothalamus and white-matter brain tissues.
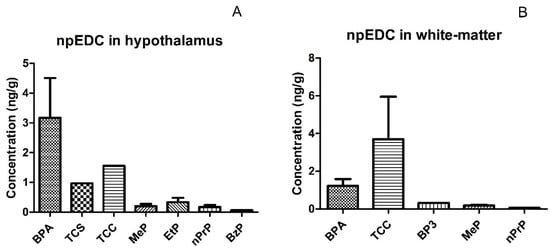
Figure 1.
Measured concentrations (mean ± SD) of npEDC in hypothalamus, n = 24 (A) and white-matter brain tissue, n = 12 (B). Abbreviations: BPA: bisphenol A; BP-3: benzophenone-3; TCC: triclocarban; TCS: triclosan; MeP: methylparaben; EtP: ethylparaben; npEDCs: non-persistent endocrine disrupting chemicals; n-PrP: n-propylparaben; BzP: benzylparaben; SD: standard deviation.
We observed a trend towards a positive correlation between BPA and MeP levels in the hypothalamus (correlation coefficient r = 0.37, p = 0.078) (Figure 2), with BPA concentrations being significantly higher than those of MeP (median: 0.68 vs. 0.09 ng/g, p = 0.038, respectively).
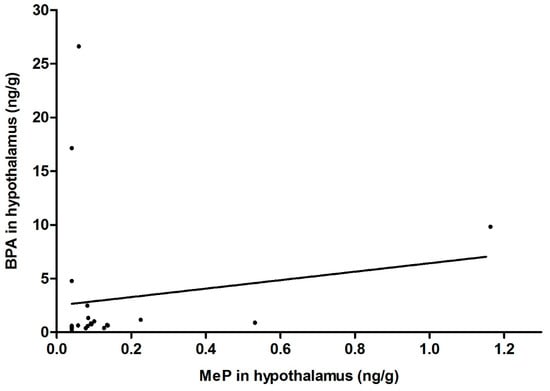
Figure 2.
Correlation between BPA and MeP concentrations in the hypothalamus (Spearman correlation coefficient r = 0.37, p = 0.078).
No differences were observed between hypothalamic and white-matter brain regions in terms of BPA or MeP levels (Table 2). A similar trend was observed in both controls and obese individuals with slightly but not significantly higher BPA levels in white-matter tissue than was found in the hypothalamus in the obese group, while an opposite pattern was found in controls (white-matter vs. hypothalamus; median (mean ± SD): 1.01 (1.23 ± 0.89) vs. 0.54 (0.87 ± 0.92) ng/g, p = 0.62, in obese, and 0.38 (1.00 ± 1.32) vs. 0.59 (4.65 ± 7.23) ng/g, p = 0.63, in controls) (Figure 3). The BPA concentrations were similar for obese and normal-weight individuals in both hypothalamus and white-matter tissues (obese vs. controls; median (mean ± SD): in white-matter 1.01 (1.23 + 0.89) vs. 0.38 (1.00 + 1.32) ng/g, p = 0.81, and in the hypothalamus 0.71 (1.59 ± 2.66) vs. 0.63 (4.49 ± 8.46) ng/g, p = 0.79) (Table 2, Figure 4A). We detected a significantly higher MeP concentration in the hypothalamus of obese individuals as compared with controls (median (mean ± SD): 0.08 (0.18 ± 0.31) vs. 0.05 (0.10 ± 0.14), p = 0.008) (Table 2, Figure 4B).

Table 2.
Descriptive analysis of detected npEDC (ng/g) in hypothalamus and white-matter brain tissue by obesity status.
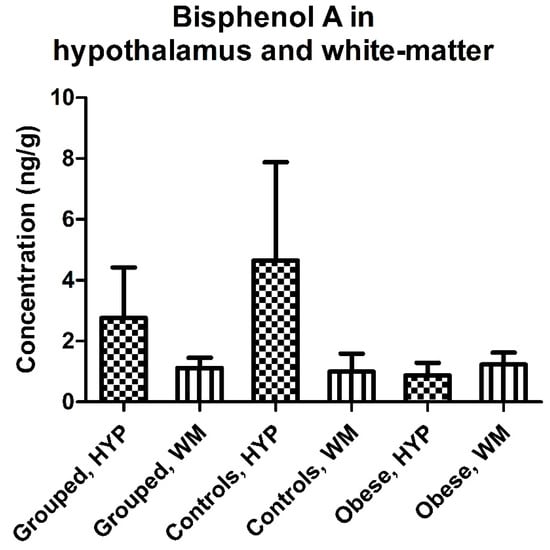
Figure 3.
Concentrations (mean ± SD) of bisphenol A (BPA) in hypothalamus and white-matter brain tissue in all paired samples combined, controls, and obese cases.
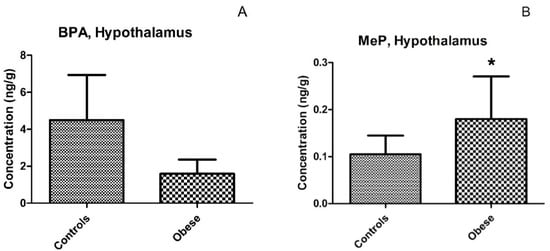
Figure 4.
Concentrations (mean ± SD) of bisphenol A (BPA) (A) and methyl paraben (MeP) (B) in paired hypothalamus tissues from controls (n = 12) and obese individuals (n = 12). *- p < 0.05.
Finally, we found no correlation between BPA or MeP levels and age, body weight, BMI, and brain weight, in both hypothalamic and white-matter tissue (data not shown).
4. Discussion
The detection of seven common environmental chemicals all suspected to be npEDCs—including BPA, TCS, TCC, MeP, EtP, nPrP and BzP—in the hypothalamus indicate the ability of these chemicals to infiltrate the hypothalamus with the potential to cause adverse health effects. In the white-matter brain tissue, five npEDCs (BPA, TCC, BP3, MeP, and nPrP) were detected, suggesting that some of the phenols and parabens might be able to cross the BBB barrier. Also, such a difference between the examined brain regions in terms of npEDC exposure may be explained by the BBB’s protection of white-matter, which is lacking for parts of the hypothalamus, as well as by the relatively high vascularity of the hypothalamus, due to its central role in the receiving of multiple hormonal signals [24].
Two npEDCs have previously been detected in human brain tissue [13]. Geens et al. reported BPA concentrations in brain tissue with a median of 0.57 ng/g [13], showing similar levels as in the present pilot study (0.68 ng/g in hypothalamus and 0.82 ng/g in white-matter). TCS was also measured in 1 (0.23 ng/g) out of 11 brain samples [13], while we detected TCS in one single hypothalamic sample (0.97 ng/g). To our knowledge, no other study has reported npEDC distribution in either human hypothalamus or white-matter brain tissues. In brain tissue samples, we observed a wide concentration range for BPA, MeP, and TCC, suggesting inter-individual differences in the exposure and/or its metabolism and excretion. Previous studies have also reported a high variability in concentrations for BPA in adipose tissue (ranges: 1.80–12.01 ng/g [14], 1.12–12.28 ng/g [13], and <the limit of quantification (LOQ)–20.9 ng/g [15]) and for MeP in adipose tissue (range: <LOQ–22.3 ng/g [15]), but not for BPA in brain (range: <LOD–2.36 ng/g [13]). The variation in individual npEDC exposure may be the result of a number of factors, including sex, age, disease status, and lifestyle. In the current study, the limited number of available brain samples and the modest collection of data did not yield evidence for such correlations.
We observed brain region-specific presence of some npEDCs that were detected only in the hypothalamus (TCS, EtP, and BzP) or white-matter tissue (BP-3). This suggests that the hypothalamus and the white-matter are susceptible to different npEDCs, and that the various npEDCs differ in terms of their ability to cross the BBB and/or a potential to accumulate in lipophilic brain tissue. In our study sample, we found no evidence for a difference in BPA concentration between hypothalamic and white-matter regions, neither when the data was stratified by obesity status. Determining whether or not there is a preferential accumulation of npEDCs that are able to cross the BBB in specific regions of the brain requires further investigation.
Since the hypothalamus is a major regulator of body weight [24,28], and some EDCs have been previously associated with obesity [11,17,18,21], we hypothesized that obese individuals might have higher levels of some EDCs compared to normal-weight individuals. We found significant association between higher levels of MeP measured in hypothalamus in obese individuals compared to the levels measured in normal-weight individuals. Although recent animal and in vitro studies have reported the obesogenic properties of MeP [33,34], from the present study design it is not possible to determine to which extent the detected relationship contributes to the development of obesity. For BPA, no significant differences between obese and normal-weight subjects were observed in terms of the chemical concentrations in both hypothalamus and white-matter tissue (p > 0.7). This could be due to the relatively small sample size, caused by the limited availability of post mortem brain material from obese individuals and well-matched controls as well as due to the above-mentioned high inter-individual variability in BPA levels. Assuming that the observed distribution in the hypothalamic BPA concentration between obese individuals and controls is representative of a target population, a sample size of 32 cases and 32 controls is required to find a significant difference of the same magnitude (i.e., such a sample size will provide 81% power to detect an observed difference with a significance level of 0.05 using a two-sided two-sample t-test).
Note that many individuals included in the present study were elderly and/or suffered from neurological disorders. Since age and neurodegenerative disorders can alter the BBB properties and permeability [35], we cannot exclude a potential confounding effect of these factors on the npEDC levels detected in the brain tissues. Follow-up studies in wider populations are warranted to clarify these questions and to assess the clinical relevance of our findings.
Finally, the detection of npEDCs in the hypothalamus raises important questions about their potential adverse effects on the metabolism. Previously, a strong association between the serum level of BPA and circulating adiponectin, leptin, and the gut-hormone ghrelin has been reported in humans, suggesting BPA interference with hormonal regulation of hunger and satiety [36]. How the presence of BPA and other npEDCs in the major center of metabolic regulation [24] is altering the physiological processes remains to be determined.
5. Conclusions
This study shows—for the first time—the distribution of three environmental phenols and four parabens, assumed to be non-persistent, in the human hypothalamus, indicating their ability to infiltrate, and their potential to accumulate in the brain region responsible for the regulation of metabolism. A smaller number of these chemicals were also detected in white-matter tissues, indicating that the BBB hinders access of chemicals to white-matter lipid fraction. Our results also suggest a possible relationship between MeP levels in the hypothalamus and obesity. Further research is needed to determine to which degree npEDCs might disrupt the normal physiological processes and functioning of the brain.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/14/9/1059/s1, Table S1: Clinicopathological details of the subjects with available hypothalamic material (n = 24), Table S2: Basic characteristics of the study population.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge The Netherlands Brain Bank at The Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience for providing us with the brain material and patient information. We thank our colleagues Chris Thio for statistical advice and Wilma Verweij for critical reading and editing of the manuscript. Jana V. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk is supported by a Diabetes Funds Junior Fellowship from the Dutch Diabetes Research Foundation (project no. 2013.81.1673). This work was supported by the National Consortium for Healthy Ageing (NCHA) (NCHA NGI Grant 050-060-810), and the European Union’s Seventh Framework program (FP7/2007-2013) through the BioSHaRE-EU (Biobank Standardization and Harmonization for Research Excellence in the European Union) project, grant agreement 261433, and by the Danish Center on Endocrine Disrupters and the International Center for Research and Research Training in Endocrine Disruption of Male Reproduction and Child Health (EDMaRC).
Author Contributions
Jana V. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk conceived, designed, and implemented the study. Hanne Frederiksen helped with the design and the implementation of the study, and coordinated and performed the measurements. Thomas P. van der Meer and Jana V. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk analyzed and interpreted the data and drafted the paper. Francisco Artacho-Cordón and Hanne Frederiksen contributed to the interpretation of the data and critically revised the article for important intellectual content. Dick F. Swaab, Dicky Struik, Konstantinos C. Makris, and Bruce H. R. Wolffenbuttel acquired the data and/or provided the study materials. All authors provided critical revision of the manuscript and helped with data interpretation and manuscript preparation. Jana V. van Vliet-Ostaptchouk and Hanne Frederiksen contributed equally to the work. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zoeller, R.T.; Brown, T.R.; Doan, L.L.; Gore, A.C.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Soto, A.M.; Woodruff, T.J.; Vom Saal, F.S. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and public health protection: A statement of principles from The Endocrine Society. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Valentin-Blasini, L.; Ye, X. Trends in exposure to chemicals in personal care and consumer products. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, A.L.; Baduel, C.; Toms, L.M.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Hobson, P.; Broomhall, S.; Mueller, J.F. Use of pooled samples to assess human exposure to parabens, benzophenone-3 and triclosan in Queensland, Australia. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, E.J.; Halden, R.U. Plastics and environmental health: The road ahead. Rev. Environ. Health 2013, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Fourth National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals, Updated Tables; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015; Volume 1, p. 1075.
- Frederiksen, H.; Jensen, T.K.; Jorgensen, N.; Kyhl, H.B.; Husby, S.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Main, K.M.; Juul, A.; Andersson, A.M. Human urinary excretion of non-persistent environmental chemicals: An overview of Danish data collected between 2006 and 2012. Reproduction 2014, 147, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewalque, L.; Pirard, C.; Charlier, C. Measurement of urinary biomarkers of parabens, benzophenone-3, and phthalates in a Belgian population. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 649314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefre de Renzy-Martin, K.; Frederiksen, H.; Christensen, J.S.; Boye Kyhl, H.; Andersson, A.M.; Husby, S.; Barington, T.; Main, K.M.; Jensen, T.K. Current exposure of 200 pregnant Danish women to phthalates, parabens and phenols. Reproduction 2014, 147, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boberg, J.; Taxvig, C.; Christiansen, S.; Hass, U. Possible endocrine disrupting effects of parabens and their metabolites. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, I.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Scarlett, A.; Henley, W.E.; Depledge, M.; Wallace, R.B.; Melzer, D. Association of urinary bisphenol A concentration with medical disorders and laboratory abnormalities in adults. JAMA 2008, 300, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artacho-Cordon, F.; Arrebola, J.P.; Nielsen, O.; Hernandez, P.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Fernandez, M.F.; Andersson, A.M.; Olea, N.; Frederiksen, H. Assumed non-persistent environmental chemicals in human adipose tissue; matrix stability and correlation with levels measured in urine and serum. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geens, T.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Distribution of bisphenol-A, triclosan and n-nonylphenol in human adipose tissue, liver and brain. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.F.; Arrebola, J.P.; Taoufiki, J.; Navalón, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Pulgar, R.; Vilchez, J.L.; Olea, N. Bisphenol-A and chlorinated derivatives in adipose tissue of women. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K. Accumulation of 19 environmental phenolic and xenobiotic heterocyclic aromatic compounds in human adipose tissue. Environ. Int. 2015, 78, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: A pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1377–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Heindel, J.J.; vom Saal, F.S.; Blumberg, B.; Bovolin, P.; Calamandrei, G.; Ceresini, G.; Cohn, B.A.; Fabbri, E.; Gioiosa, L.; Kassotis, C.; et al. Parma consensus statement on metabolic disruptors. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbre, P.D. Endocrine disruptors and obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Blumberg, B.; Cave, M.; Machtinger, R.; Mantovani, A.; Mendez, M.A.; Nadal, A.; Palanza, P.; Panzica, G.; Sargis, R.; et al. Metabolism disrupting chemicals and metabolic disorders. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heindel, J.J.; Newbold, R.; Schug, T.T. Endocrine disruptors and obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janesick, A.S.; Blumberg, B. Obesogens: An emerging threat to public health. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 214, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasande, L.; Attina, T.M.; Blustein, J. Association between urinary bisphenol A concentration and obesity prevalence in children and adolescents. JAMA 2012, 308, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegelman, B.M.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 2001, 104, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Harrold, J.A.; Cutler, D.J. The hypothalamus and the regulation of energy homeostasis: Lifting the lid on a black box. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinch, C.D.; Ibhazehiebo, K.; Jeong, J.H.; Habibi, H.R.; Kurrasch, D.M. Low-dose exposure to bisphenol A and replacement bisphenol S induces precocious hypothalamic neurogenesis in embryonic zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angle, B.M.; Do, R.P.; Ponzi, D.; Stahlhut, R.W.; Drury, B.E.; Nagel, S.C.; Welshons, W.V.; Besch-Williford, C.L.; Palanza, P.; Parmigiani, S.; et al. Metabolic disruption in male mice due to fetal exposure to low but not high doses of bisphenol A (BPA): Evidence for effects on body weight, food intake, adipocytes, leptin, adiponectin, insulin and glucose regulation. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, H.; Patterson, Z.R.; Abizaid, A. Perinatal exposure to low-dose bisphenol-A disrupts the structural and functional development of the hypothalamic feeding circuitry. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaab, D.F. The Human Hypothalamus. Basic and Clinical Aspects. Part I: Nuclei of the Hypothalamus. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Chapter 11. [Google Scholar]
- Klioueva, N.M.; Rademaker, M.C.; Dexter, D.T.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Seilhean, D.; Streichenberger, N.; Schmitz, P.; Bell, J.E.; Ironside, J.W.; Arzberger, T.; et al. BrainNet Europe’s Code of Conduct for brain banking. J. Neur. Transm. 2015, 122, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machin, D.; Campbell, M.; Fayers, P.; Pinol, A. Sample Size Tables for Clinical Studies, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science: Malden, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.; Chen, X.; Whitener, R.J.; Boder, E.T.; Jones, J.O.; Porollo, A.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L. Effects of parabens on adipocyte differentiation. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Kennedy, R.C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, C.L.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L. Differential effects on adiposity and serum marker of bone formation by post-weaning exposure to methylparaben and butylparaben. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 21957–21968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, F.; Sousa, J.C.; Sousa, N.; Palha, J.A. Blood-brain-barriers in aging and in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronn, M.; Lind, L.; Orberg, J.; Kullberg, J.; Soderberg, S.; Larsson, A.; Johansson, L.; Ahlstrom, H.; Lind, P.M. Bisphenol A is related to circulating levels of adiponectin, leptin and ghrelin, but not to fat mass or fat distribution in humans. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).