The Development of a Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Method for Apixaban Quantification in Dried Plasma Spots in Parallel Reaction Monitoring Mode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Experimental Procedures
2.3.1. Preparation of Calibration Standards and Validation Samples
2.3.2. Sample Preparation and Extraction Procedures
2.4. Assay Validation
2.4.1. Linearity
2.4.2. Accuracy
2.4.3. Recovery and the Matrix Effect
2.4.4. Stability
3. Results
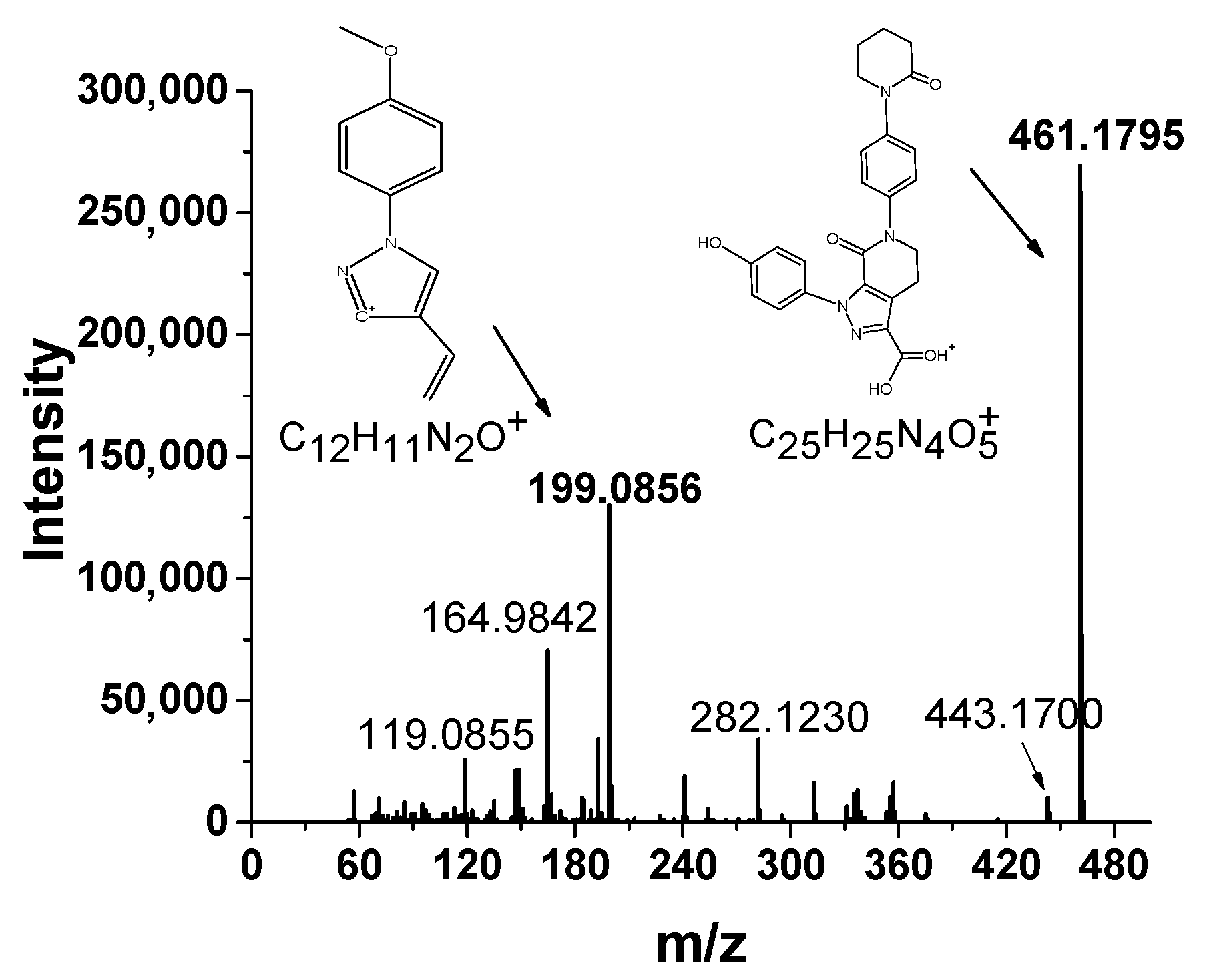
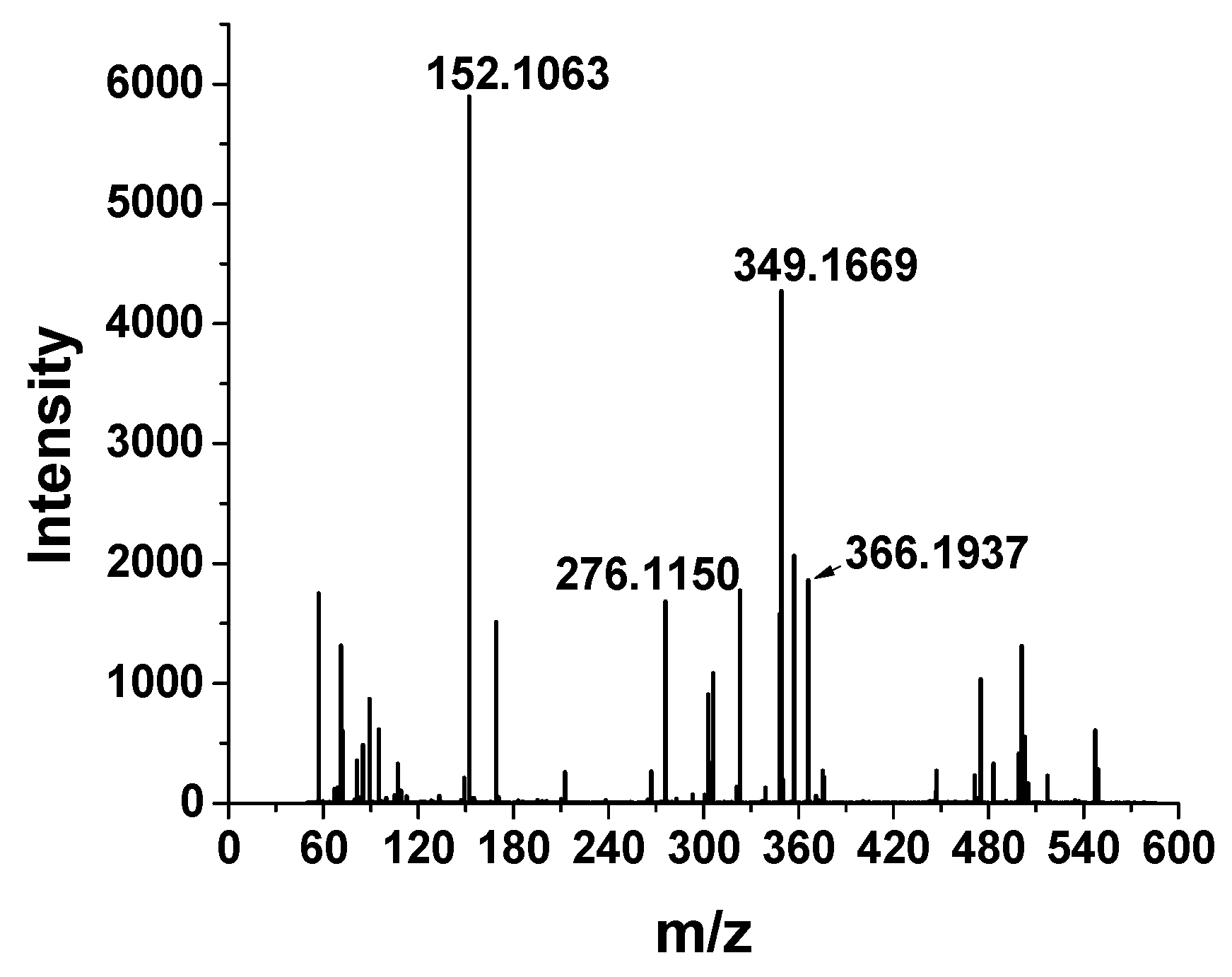
3.1. The HRMS Method
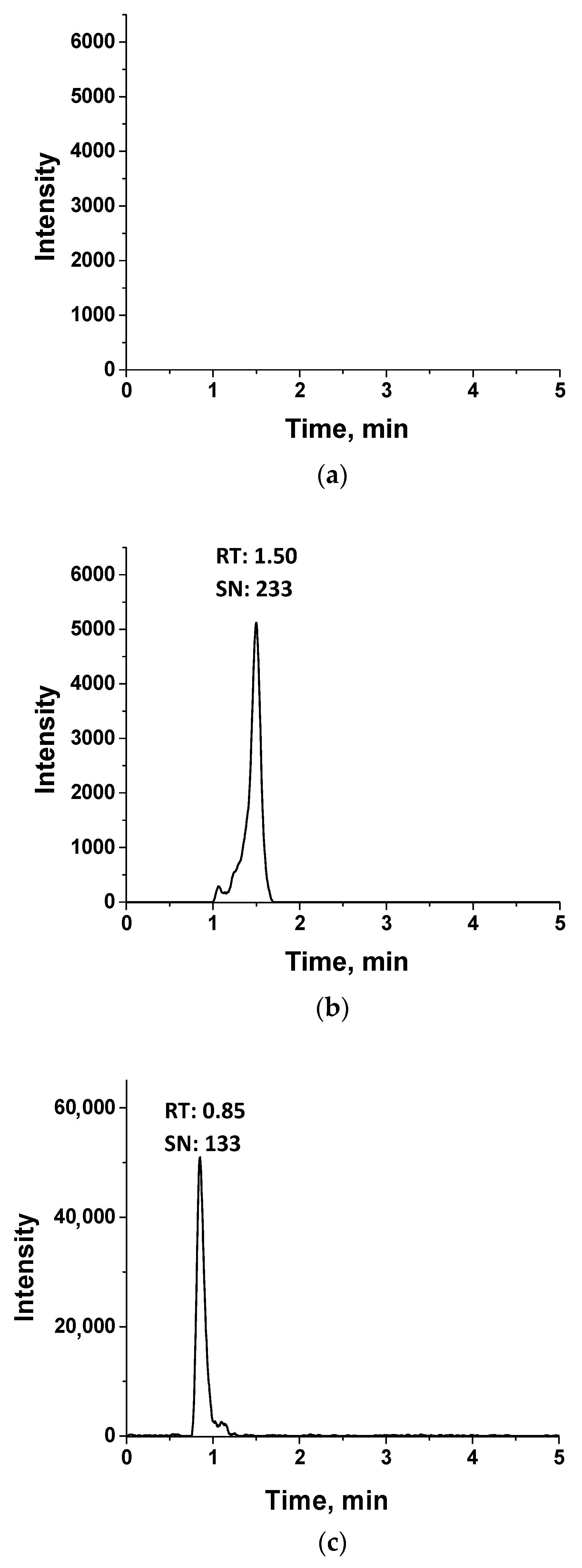
3.2. The Extraction Procedure
3.3. Linearity
3.4. Accuracy
3.5. Recovery and the Matrix Effect
3.6. Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wieland, E.; Shipkova, M. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Drug Monitoring of Direct-Acting Oral Anticoagulants: Where Do We Stand? Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-C.; Kim, T.-E.; Shin, K.-H. Quantification of apixaban in human plasma using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 27, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for Stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursley, J.; Shen, J.X.; Schuster, A.; Dang, O.T.; Lehman, J.; Buonarati, M.H.; Song, Y.; Aubry, A.-F.; Arnold, M.E. LC-MS/MS determination of apixaban (BMS-562247) and its major metabolite in human plasma: An application of polarity switching and monolithic HPLC column. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layeeq, M.; Baig, A.; Ali, S.A. A Validated LC-MS/MS Method for the Estimation of Apixaban in Human Plasma. J. App. Pharma. Sci. 2017, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Delavenne, X.; Mismetti, P.; Basset, T. Rapid determination of apixaban concentration in human plasma by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: Application to pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 78–79, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffel, J.; Verhamme, P.; Potpara, T.S.; Albaladejo, P.; Antz, M.; Desteghe, L.; Haeusler, K.G.; Oldgren, J.; Reinecke, H.; Roldan-Schilling, V.; et al. The 2018 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1330–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, R.-S.; Lin, S.-Y.; Peng, Y.-F.; Chao, H.-C.; Tsai, I.-L.; Lin, Y.-T.; Liao, H.-W.; Tang, S.-C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Jeng, J.-S. Using the PCI-IS Method to Simultaneously Estimate Blood Volume and Quantify Nonvitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant Concentrations in Dried Blood Spots. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2511–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-L.; Lou, D.; Zhang, D.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.-J. Determination of rivaroxaban, apixaban and edoxaban in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS method. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2016, 42, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, S.; Cattaneo, D.; Pignatelli, P.; Perrone, V.; Pastori, D.; Radice, S.; Violi, F.; Clementi, E. Validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of dabigatran, rivaroxaban and apixaban in human plasma. Bioanalysis 2016, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gous, T.; Couchman, L.; Patel, J.P.; Paradzai, C.; Arya, R.; Flanagan, R.J. Measurement of the Direct Oral Anticoagulants Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban, and Rivaroxaban in Human Plasma Using Turbulent Flow Liquid Chromatography With High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Ther. Drug Monit. 2014, 36, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmakuri, C.K.; Prasad, C.; Patil, R.S.; Dharani, K. Method development and validation of selective and highly sensitive method for determination of apixaban in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, K.I.; Huppertz, A.; Müller, O.J.; Rizos, T.; Tilemann, L.; Haefeli, W.E.; Burhenne, J. Simultaneous quantification of direct oral anticoagulants currently used in anticoagulation therapy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 148, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesen, M.H.J.; Blaich, C.; Streichert, T.; Michels, G.; Müller, C. Paramagnetic micro-particles as a tool for rapid quantification of apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban in human plasma by UHPLC-MS/MS. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavik, L.; Jacova, J.; Friedecky, D.; Ulehlova, J.; Tauber, Z.; Prochazkova, J.; Hlusi, A.; Palova, M. Evaluation of the DOAC-Stop Procedure by LC-MS/MS Assays for Determining the Residual Activity of Dabigatran, Rivaroxaban, and Apixaban. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 25, 1076029619872556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Yuan, L.; Ji, Q.C.; Mangus, H.; Song, Y.; Frost, C.; Zeng, J.; Aubry, A.-F.; Arnold, M.E. “Center punch” and “whole spot” Bioanalysis of apixaban in human dried blood spot samples by UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 988, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, N.; Lad, R.; Barfield, M. Dried blood spots as a sample collection technique for the determination of pharmacokinetics in clinical studies: Considerations for the validation of a quantitative bioanalytical method. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1557–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tse, F.L.S. Dried blood spot sampling in combination with LC-MS/MS for quantitative analysis of small molecules. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Park, J.-H.; Long, N.P.; Kim, D.-D.; Kwon, S.W. Simultaneous determination of cardiovascular drugs in dried blood spot by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis Bernieh, S.T. LC-HRMS Analysis of Dried Blood Spot Samples For Assessing Adherence to Cardiovascular Medications. J. Bioanal. Biomed. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, T.; Spooner, N.; Barfield, M. Ensuring the collection of high-quality dried blood spot samples across multisite clinical studies. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelbroek, P.M.; van der Heijden, J.; Stolk, L.M.L. Dried blood spot methods in therapeutic drug monitoring: Methods, assays, and pitfalls. Ther. Drug Monit. 2009, 31, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, A.L.; Kushnir, M.M.; Clarke, N.J. Mass Spectrometry. In Principles and Applications of Clinical Mass Spectrometry: Small Molecules, Peptides, and Pathogens Edited by Nader Rifai, A. Rita Horvath, Carl T. Wittwer, Andy Hoofnagle; Rifai, N., Horvath, A.R., Wittwer, C., Hoofnagle, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 33–65. ISBN 9780128160633. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Kerns, E.H. LC/MS applications in drug development. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1999, 18, 187–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfgartner, G.; Varesio, E.; Tschäppät, V.; Grivet, C.; Bourgogne, E.; Leuthold, L.A. Triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometer for the analysis of small molecules and macromolecules. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl-Zeng, J.; Lange, V.; Ossola, R.; Eckhardt, K.; Krek, W.; Aebersold, R.; Domon, B. High sensitivity detection of plasma proteins by multiple reaction monitoring of N-glycosites. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Du, Z.; Jiang, H. HRMS for the quantification of xenobiotics in biological samples. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1939–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponzetto, F.; Boccard, J.; Nicoli, R.; Kuuranne, T.; Saugy, M.; Rudaz, S. UHPLC-HRMS Analysis for Steroid Profiling in Serum (Steroidomics). Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1738, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauniyar, N. Parallel Reaction Monitoring: A Targeted Experiment Performed Using High Resolution and High Mass Accuracy Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28566–28581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.C.; Russell, J.D.; Bailey, D.J.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J. Parallel reaction monitoring for high resolution and high mass accuracy quantitative, targeted proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, A.; Noble, W.S.; Wolf-Yadlin, A. Technical advances in proteomics: New developments in data-independent acquisition. F1000. Fac. Res. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, K.I.; Huppertz, A.; Meid, A.D.; Müller, O.J.; Rizos, T.; Tilemann, L.; Haefeli, W.E.; Burhenne, J. Dried-Blood-Spot Technique to Monitor Direct Oral Anticoagulants: Clinical Validation of a UPLC-MS/MS-Based Assay. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9395–9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, S.; Dyrkorn, R.; Spigset, O.; Hegstad, S. Quantification of Apixaban, Dabigatran, Edoxaban, and Rivaroxaban in Human Serum by UHPLC-MS/MS-Method Development, Validation, and Application. Ther. Drug Monit. 2018, 40, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secrétan, P.-H.; Sadou-Yayé, H.; Aymes-Chodur, C.; Bernard, M.; Solgadi, A.; Amrani, F.; Yagoubi, N.; Do, B. A comprehensive study of apixaban’s degradation pathways under stress conditions using liquid chromatography coupled to multistage mass spectrometry. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35586–35597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenova, L.V.; Koval, V.V.; Chernonosov, A.A. Optimization of the Extraction Procedure of Apixaban from Dried Rat Plasma Spots. JPRI 2020, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernonosov, A.A. Quantification of Warfarin in Dried Rat Plasma Spots by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. 2016, 2016, 6053295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Concentration, ng/mL | Interday (n = 18) | Intraday (n = 12) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % bias | % RSD | % bias | % RSD | |
| 40 | 5.0 | 9.6 | 6.1 | 3.0 |
| 200 | 3.4 | 5.9 | 5.7 | 5.2 |
| 350 | 8.3 | 4.4 | 7.1 | 3.9 |
| Concentration, ng/mL | Recovery, % | Matrix Effect, % | Efficiency, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 69.7 | 99.3 | 69.2 |
| 200 | 73.5 | 89.3 | 65.6 |
| 350 | 85.1 | 102.2 | 87.0 |
| Concentration, ng/mL | 0 h | 5 h | 24 h | 48 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % bias | % RSD | % bias | % RSD | % bias | % RSD | % bias | % RSD | |
| 30 | 11.0 | 13.2 | 3.2 | 10.5 | 10.9 | 15.4 | 11.8 | 17.2 |
| 200 | −2.6 | 6.6 | −1.8 | 7.4 | −2.0 | 7.9 | −5.9 | 6.7 |
| 350 | 10.1 | 8.6 | 6.8 | 12.7 | 7.1 | 9.8 | 8.3 | 8.8 |
| Concentration, ng/mL | 1 day | 7 days | 21 days | 35 days | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % bias | % RSD | % bias | % RSD | % bias | % RSD | % bias | % RSD | |
| 20 °C | ||||||||
| 30 | −5.5 | 4.6 | 9.6 | 13.0 | 3.6 | 9.6 | −6.2 | 24.1 |
| 200 | −7.0 | 4.9 | −6.7 | 5.9 | −5.2 | 10.8 | −11.3 | 5.7 |
| 350 | −7.3 | 8.3 | −11.3 | 11.0 | −8.8 | 7.3 | −34.4 | 8.5 |
| 4 °C | ||||||||
| 30 | −5.5 | 4.6 | −62.4 | 20.1 | −53.3 | 17.0 | −29.6 | 13.5 |
| 200 | −7.0 | 4.9 | −16.1 | 3.8 | −10.4 | 6.7 | −16.6 | 12.9 |
| 350 | −7.3 | 8.3 | 3.9 | 9.4 | 10.9 | 10.9 | −3.1 | 2.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chernonosov, A.; Aksenova, L.; Koval, V. The Development of a Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Method for Apixaban Quantification in Dried Plasma Spots in Parallel Reaction Monitoring Mode. Processes 2021, 9, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030450
Chernonosov A, Aksenova L, Koval V. The Development of a Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Method for Apixaban Quantification in Dried Plasma Spots in Parallel Reaction Monitoring Mode. Processes. 2021; 9(3):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030450
Chicago/Turabian StyleChernonosov, Alexander, Liliya Aksenova, and Vladimir Koval. 2021. "The Development of a Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Method for Apixaban Quantification in Dried Plasma Spots in Parallel Reaction Monitoring Mode" Processes 9, no. 3: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030450
APA StyleChernonosov, A., Aksenova, L., & Koval, V. (2021). The Development of a Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometric Method for Apixaban Quantification in Dried Plasma Spots in Parallel Reaction Monitoring Mode. Processes, 9(3), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9030450






