Extraction of Type I Collagen from Tilapia Scales Using Acetic Acid and Ultrafine Bubbles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
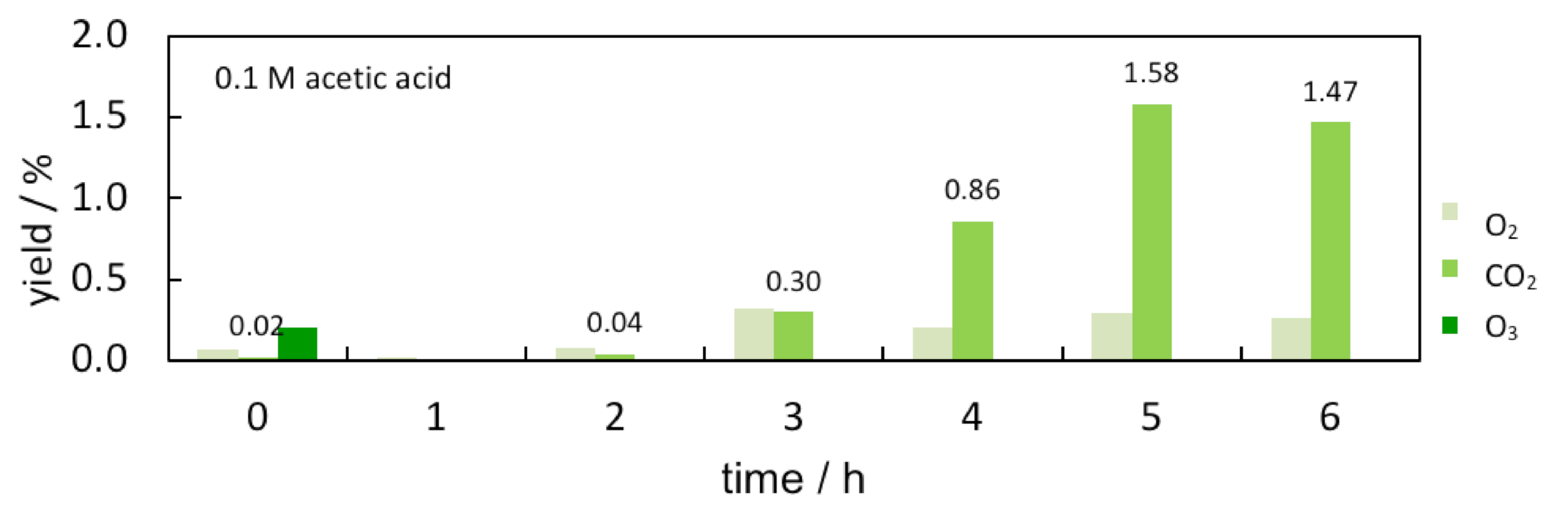
2.2. Extraction of Collagen from Fish Scales
2.3. SDS-PAGE of Extracted Collagen Samples
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Soluble Collagen Using the Sirius Red Total Collagen Detection Kit
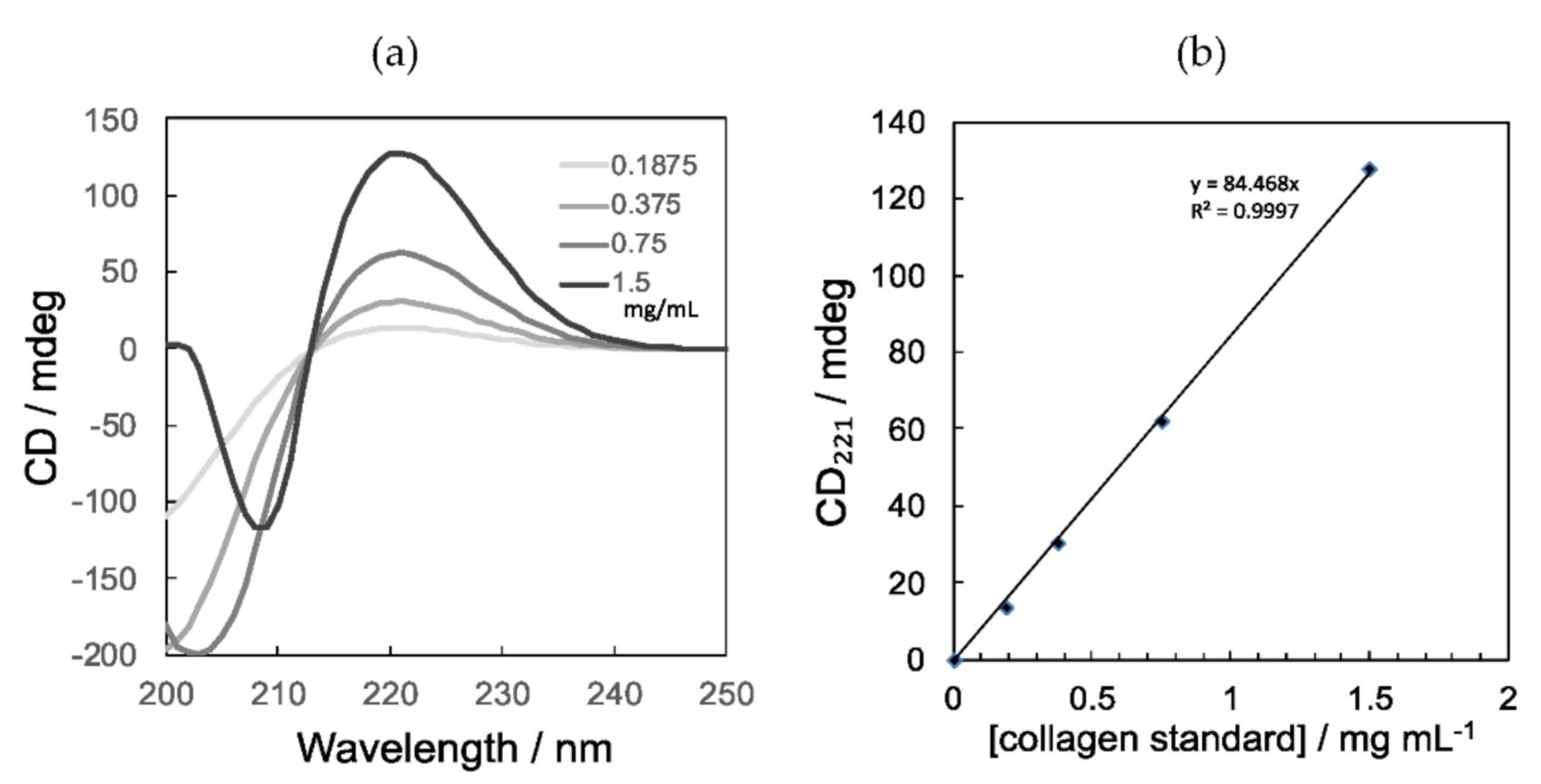
2.5. Circular Dichroism Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
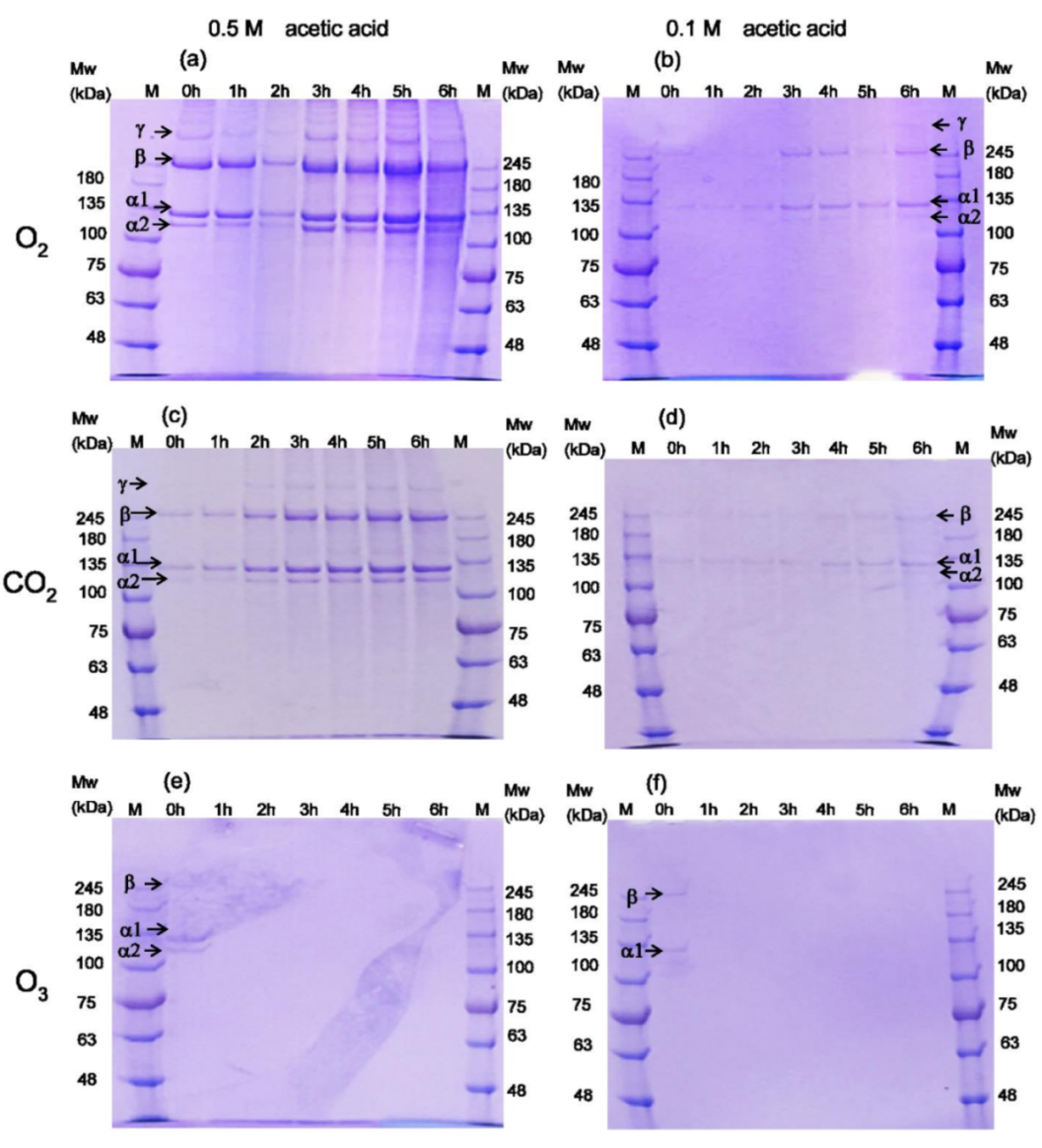
3.1. Analysis of Collagen by SDS-PAGE Profiles
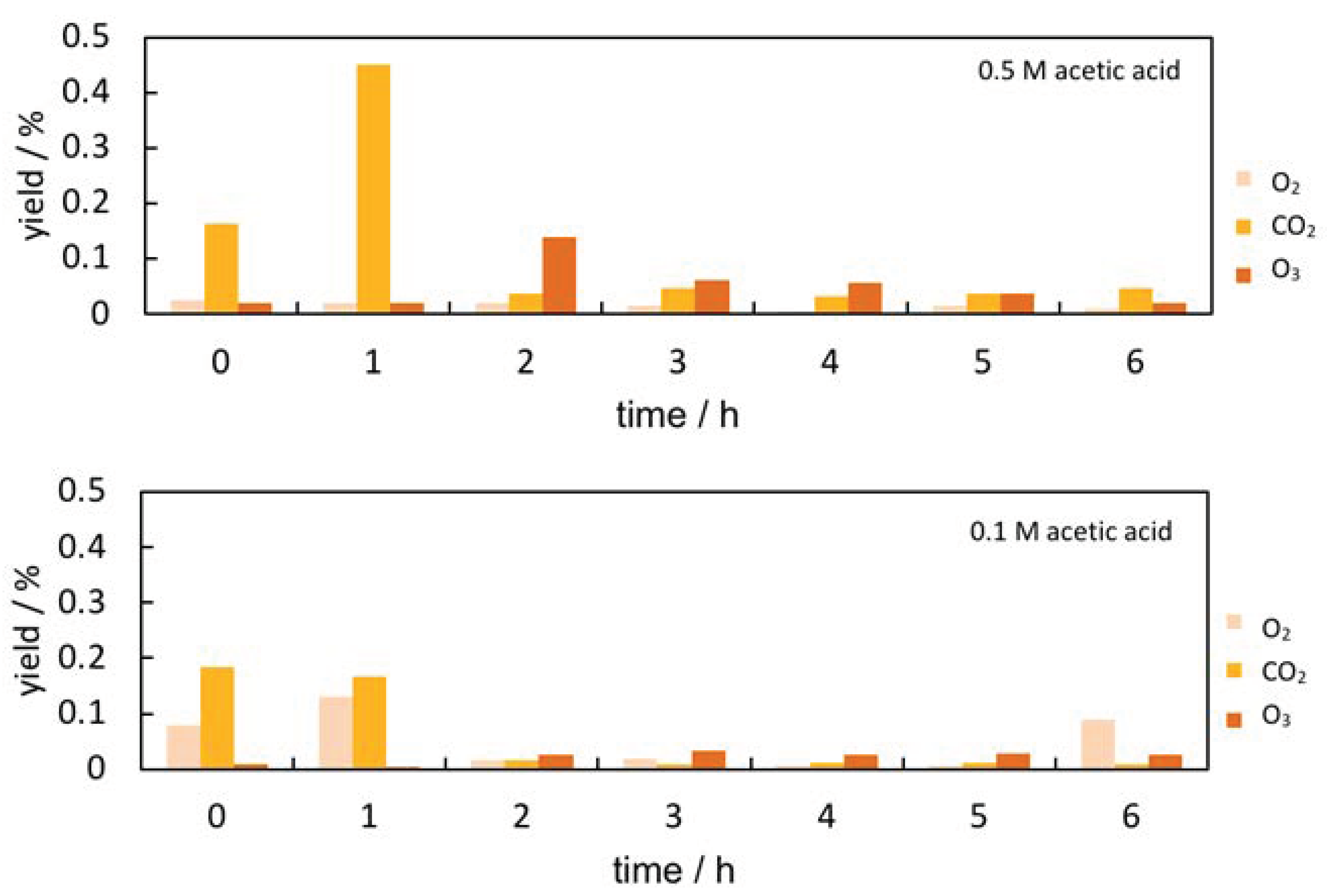
3.2. Evaluation of Collagen Extraction Rate Using the Sirius Red Total Collagen Detection Kit
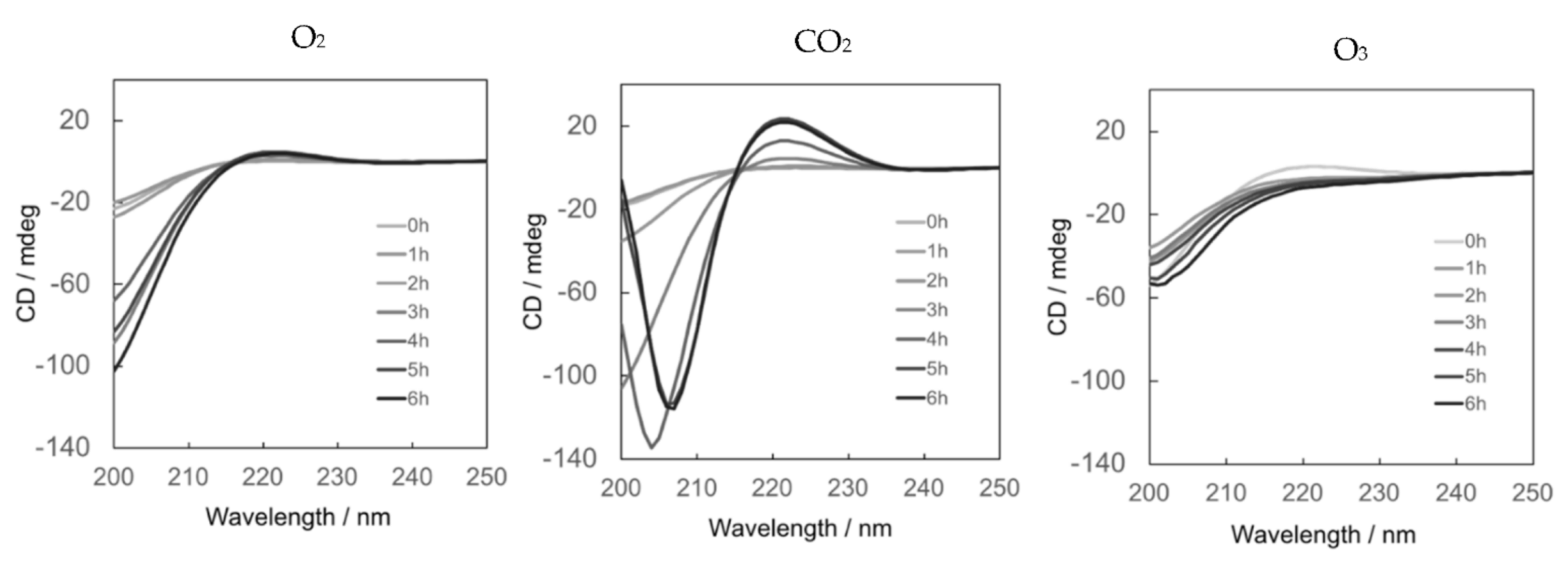
3.3. Yield of Collagen from Tilapia Fish Scales Determined by CD Spectral Change
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walker, C.; Mojares, E.; del Río Hernández, A. Role of extracellular matrix in development and cancer progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Baumstark, M.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Addad, S.; Exposito, J.-Y.; Faye, C.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Lethias, C. Isolation, Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Jellyfish Collagen for Use in Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gauza-Włodarczyk, M.; Kubisz, L.; Mielcarek, S.; Włodarczyk, D. Comparison of thermal properties of fish collagen and bovine collagen in the temperature range 298–670 K. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Nieves, D.; Chaikof, E.L. Collagen and elastin biomaterials for the fabrication of engineered living tissues. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenteau-Bareil, R.; Gauvin, R.; Berthod, F. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1863–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovell, C.R.; Smolenski, K.A.; Duance, V.C.; Light, N.D.; Young, S.; Dyson, M. Type I and III collagen content and fibre distribution in normal human skin during ageing. Br. J. Dermatol. 1987, 117, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Goldstein, E.L.; Turner, A.S.; Les, C.M.; Orr, B.G.; Fisher, G.J.; Welch, K.B.; Rothman, E.D.; Banaszak Holl, M.M. Type I collagen D-spacing in fibril bundles of dermis, tendon, and bone: Bridging between nano- and micro-level tissue hierarchy. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9503–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kew, S.J.; Gwynne, J.H.; Enea, D.; Abu-Rub, M.; Pandit, A.; Zeugolis, D.; Brooks, R.A.; Rushton, N.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. Regeneration and repair of tendon and ligament tissue using collagen fibre biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3237–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiku, M.L.; Madhan, B. Preserving the longevity of long-lived type II collagen and its implication for cartilage therapeutics. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.L.; Marques, A.L.P.; Martins, E.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Cosmetic potential of marine fish skin collagen. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tziveleka, L.-A.; Ioannou, E.; Tsiourvas, D.; Berillis, P.; Foufa, E.; Roussis, V. Collagen from the Marine Sponges Axinella cannabina and Suberites carnosus: Isolation and Morphological, Biochemical, and Biophysical Characterization. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berillis, P. Marine Collagen: Extraction and Applications. In Research Trends in Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Microbiology; SM Group: Dover, DE, USA, 2015; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky, B.; Thiagarajan, G.; Madhan, B.; Kar, K. Triple-helical peptides: An approach to collagen conformation, stability, and self-association. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veit, G.; Kobbe, B.; Keene, D.R.; Paulsson, M.; Koch, M.; Wagener, R. Collagen XXVIII, a novel von Willebrand factor A domain-containing protein with many imperfections in the collagenous domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 3494–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricard-Blum, S.; Ruggiero, F. The collagen superfamily: From the extracellular matrix to the cell membrane. Pathol. Biol. 2005, 53, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, H.; Lista, A.; Siekapen, M.M.; Ghaari-Bohlouli, P.; Nie, L.; Alimoradi, H.; Shavandi, A. Fish Collagen: Extraction, characterization and applications for biomaterials engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, T.A.; Kim, D.W. Applications of porcine dermal collagen (ENDURAGen) in facial plastic surgery. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 15, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, T.; Takahashi, A.; Ito, K.; Uetake, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Inagaki, N.; Nakata, M.; Imanishi, Y.; Sato, K. Amount of collagen in the meat contained in Japanese daily dishes and the collagen peptide content in human blood after ingestion of cooked fish meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, B.; Bernhardt, A.; Heinemann, S.; Stachel, I.; Meyer, M.; Gelinsky, M. Biomimetically mineralized salmon collagen scaffolds for application in bone tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jithendra, P.; Merlin Rajam, A.; Kalaivani, T.; Baran Mandal, A.; Rose, C. Preparation and characterization of aloe vera blended collagen-chitosan composite scaffold for tissue engineering applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7291–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, R.O.; Alves, A.L.; Carvalho, D.N.; Martins, E.; Oliveira, C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Acid and enzymatic extraction of collagen from Atlantic cod (Gadus Morhua) swim bladders envisaging health-related applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylingo, R.; Mania, S.; Panek, A.; PiÄtek, R.; PawÅowicz, R. Isolation and Characterization of Acid Soluble Collagen from the Skin of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus), Salmon (Salmo salar) and Baltic Cod (Gadus morhua). J Biotechnol. Biomater. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Thuy, L.T.; Okazaki, E.; Osako, K. Isolation and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from the scales of marine fishes from Japan and Vietnam. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues Menezes, M.d.L.L.; Ribeiro, H.L.; da Silva Abreu, F.d.O.M.; de Andrade Feitosa, J.P.; de Sá Moreira de, S.; Filho, M. Optimization of the collagen extraction from Nile tilapia skin (Oreochromis niloticus) and its hydrogel with hyaluronic acid. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 189, 110852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Yi, R.; Gao, R.; He, J. Release kinetics of tilapia scale collagen I peptides during tryptic hydrolysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, N.; Wang, T. Extraction and characterization of pepsin-solubilized collagen from snakehead (Channa argus) skin: Effects of hydrogen peroxide pretreatments and pepsin hydrolysis strategies. Process Biochem. 2019, 76, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-K.; Ham, Y.-K.; Shin, D.-M.; Kim, H.-W.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, Y.-B.; Choi, Y.-S. Extraction of crude gelatin from duck skin: Effects of heating methods on gelatin yield. Polut. Sci. 2020, 99, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.-W.; Yu, S.-J.; Cho, S.-M.; Lee, Y.-B.; Kim, S.-B. Extraction optimization and properties of collagen from yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) dorsal skin. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.O.; Martins, E.; Carvalho, D.N.; Alves, A.L.; Oliveira, C.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Collagen from Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) skins extracted using CO2 acidified water with potential application in healthcare. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alheshibri, M.; Qian, J.; Jehannin, M.; Craig, V.S.J. A history of nanobubbles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11086–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.Q.; Truong, P.N.H.; Zitzmann, K.; Nguyen, K.T. Effects of ultrafine bubbles on gram-negative bacteria: Inhibition or selection? Langmuir 2019, 35, 13761–13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Liao, G.-Y. Degradation of antibiotic tetracycline by ultrafine-bubble ozonation process. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola, C.M.; Camila, A.M.; Ana, C.; Marlon, O.; Diego, S.; Robin, Z.; Beatriz, G.; Cristina, C. Functional textile finishing of type I collagen isolated from bovine bone for potential healthtech. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.C.; Barros, A.A.; Aroso, I.M.; Fassini, D.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Extraction of collagen/gelatin from the marine demosponge Chondrosia reniformis (Nardo, 1847) using water acidified with carbon dioxide—Process optimization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6922–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürck, J.; Heissler, S.; Geckle, U.; Ardakani, M.F.; Schneider, R.; Ulrich, A.S.; Kazanci, M. Resemblance of electrospun collagen nanofibers to their native structure. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1562–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputo, I.; Lepretti, M.; Scarabino, C.; Esposito, C.; Proto, A. An acetic acid-based extraction method to obtain high quality collagen from archeological bone remains. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hou, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagen extracted from the skin of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liang, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Yao, X.; Konno, K. Properties of collagen from skin, scale and bone of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Food Chem. 2009, 112, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gistelinck, C.; Gioia, R.; Gagliardi, A.; Tonelli, F.; Marchese, L.; Bianchi, L.; Landi, C.; Bini, L.; Huysseune, A.; Witten, P.E.; et al. Zebrafish Collagen Type I: Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of the Major Structural Protein in Bone and Skin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.-T.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, X.-R.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Gelatin and Antioxidant Peptides from Gelatin Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) Scales: Preparation, Identification and Activity Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marotta, M.; Martino, G. Sensitive spectrophotometric method for the quantitative estimation of collagen. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, L.C.; Cossermelli, W.; Brentani, R. Differential staining of collagens type I, II and III by Sirius Red and polarization microscopy. Arch. Histol. Jpn. 1978, 41, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lattouf, R.; Younes, R.; Lutomski, D.; Naaman, N.; Godeau, G.; Senni, K.; Changotade, S. Picrosirius Red Staining: A Useful Tool to Appraise Collagen Networks in Normal and Pathological Tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, P.; Arribas, S.M.; de Pablo, A.L.L.; González, M.C.; Abderrahim, F.; Condezo-Hoyos, L. A simple dot-blot-Sirius red-based assay for collagen quantification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 6863–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qin, S. Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Yi, R.; Xu, N.; Gao, R.; Hong, B. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from scales and skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, M.J.; Martins, E.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Extraction and Characterization of Collagen from Elasmobranch Byproducts for Potential Biomaterial Use. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Short Biography of Author
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuwahara, J. Extraction of Type I Collagen from Tilapia Scales Using Acetic Acid and Ultrafine Bubbles. Processes 2021, 9, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020288
Kuwahara J. Extraction of Type I Collagen from Tilapia Scales Using Acetic Acid and Ultrafine Bubbles. Processes. 2021; 9(2):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020288
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuwahara, Junko. 2021. "Extraction of Type I Collagen from Tilapia Scales Using Acetic Acid and Ultrafine Bubbles" Processes 9, no. 2: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020288
APA StyleKuwahara, J. (2021). Extraction of Type I Collagen from Tilapia Scales Using Acetic Acid and Ultrafine Bubbles. Processes, 9(2), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020288





