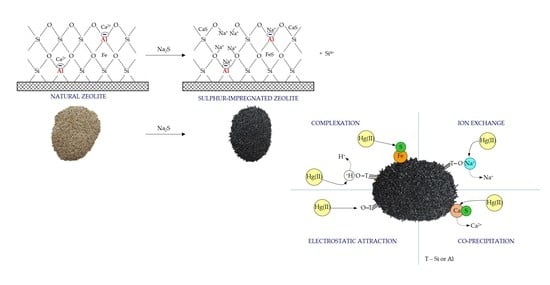
Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
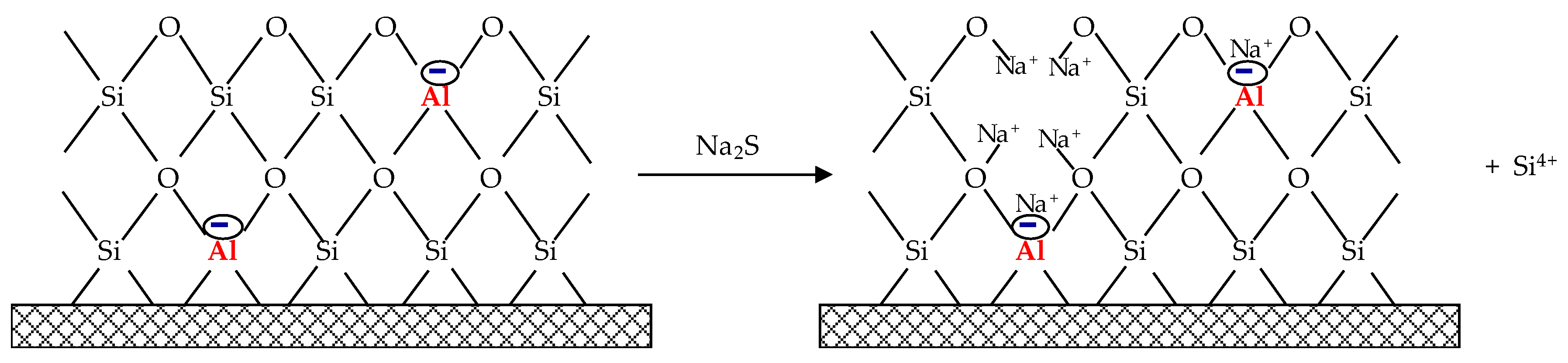
2.1. Sorbent Preparation
2.2. Sorbent Characterization
2.3. Batch Sorption Experiment
2.4. Leaching Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
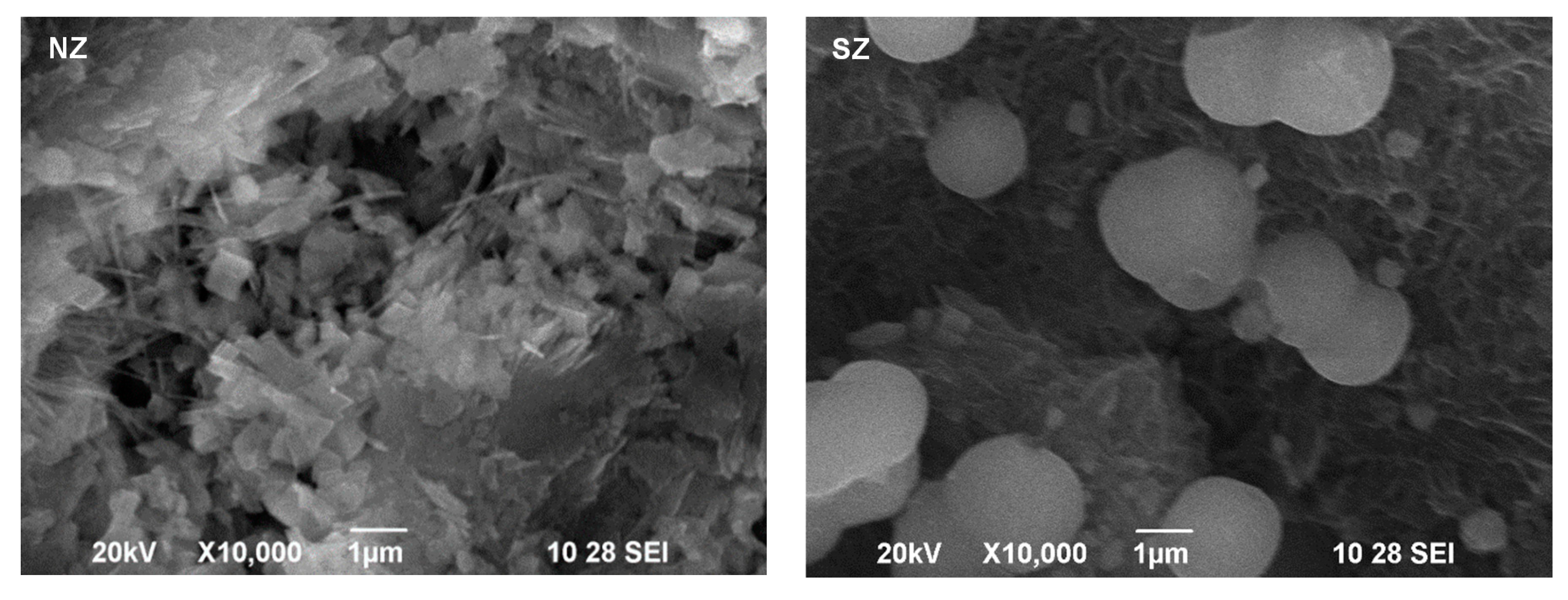
3.1. Mineralogical and Physico-Chemical Characterization of Sorbents
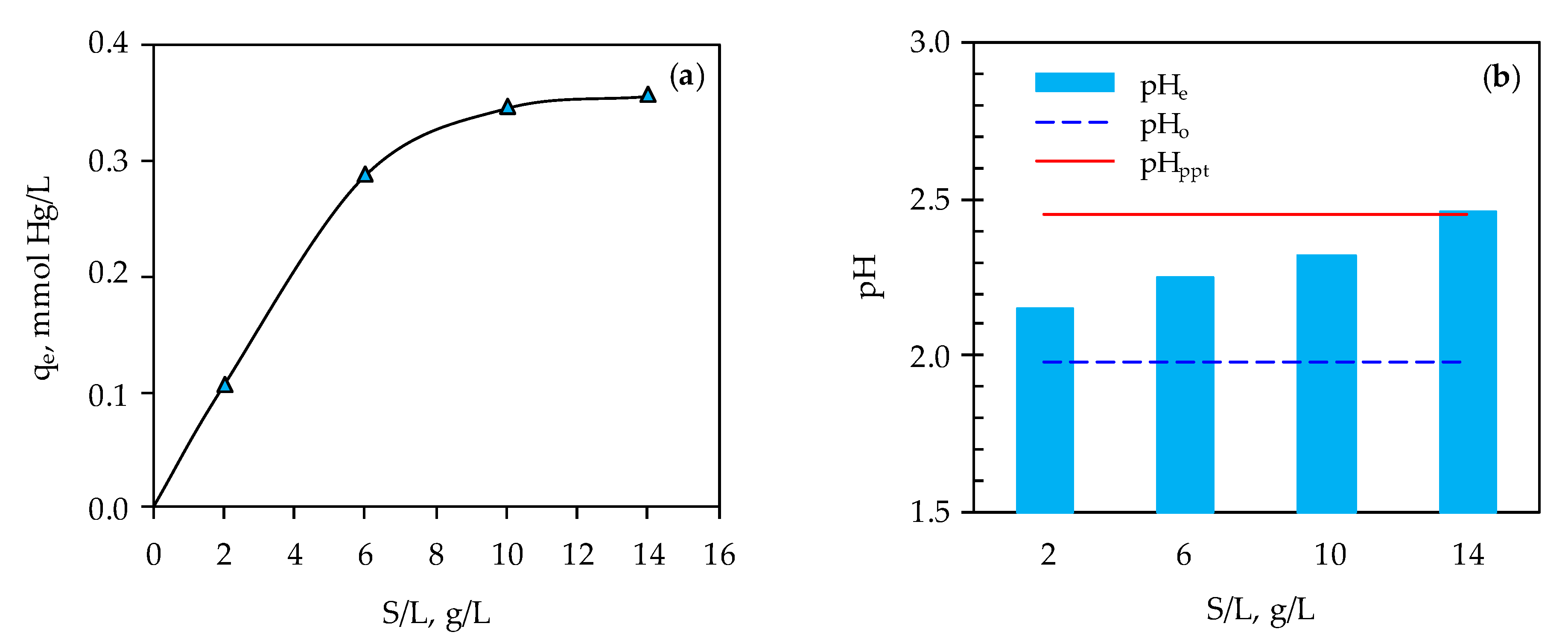
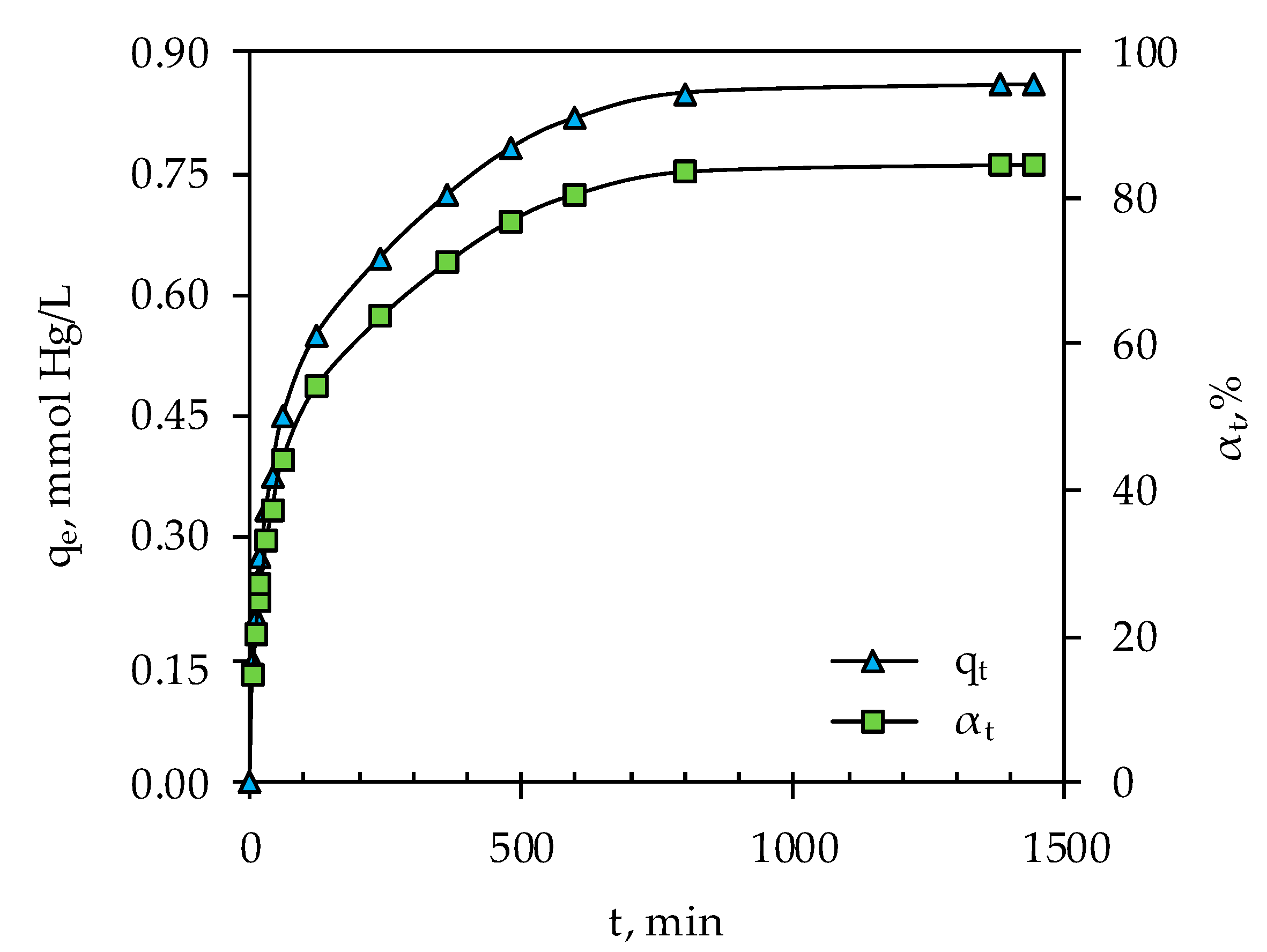
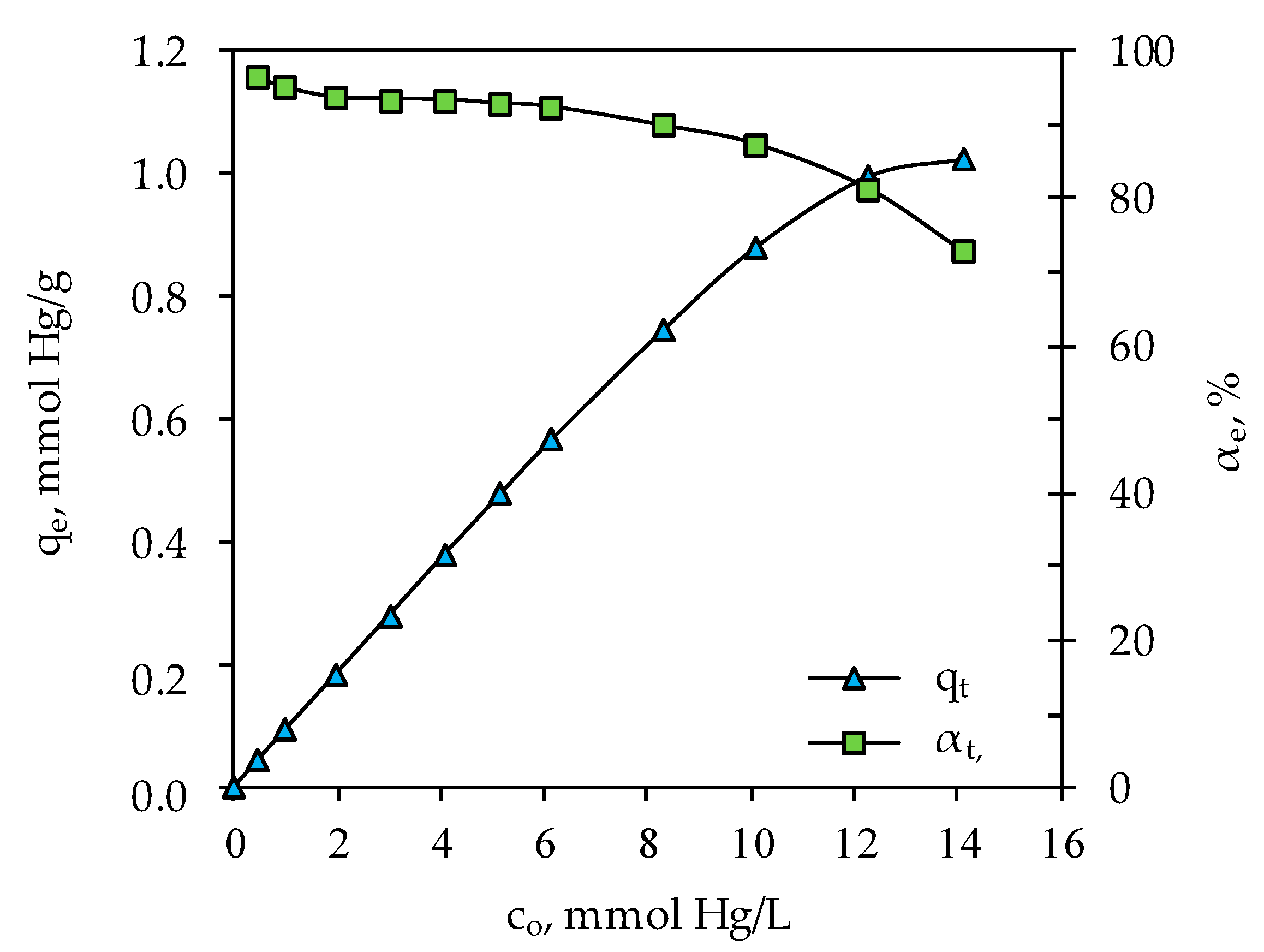
3.2. Determination of Optimal Mercury Sorption Parameters
3.3. Characterization of the Mercury-Saturated Sulfur-Impregnated Zeolite
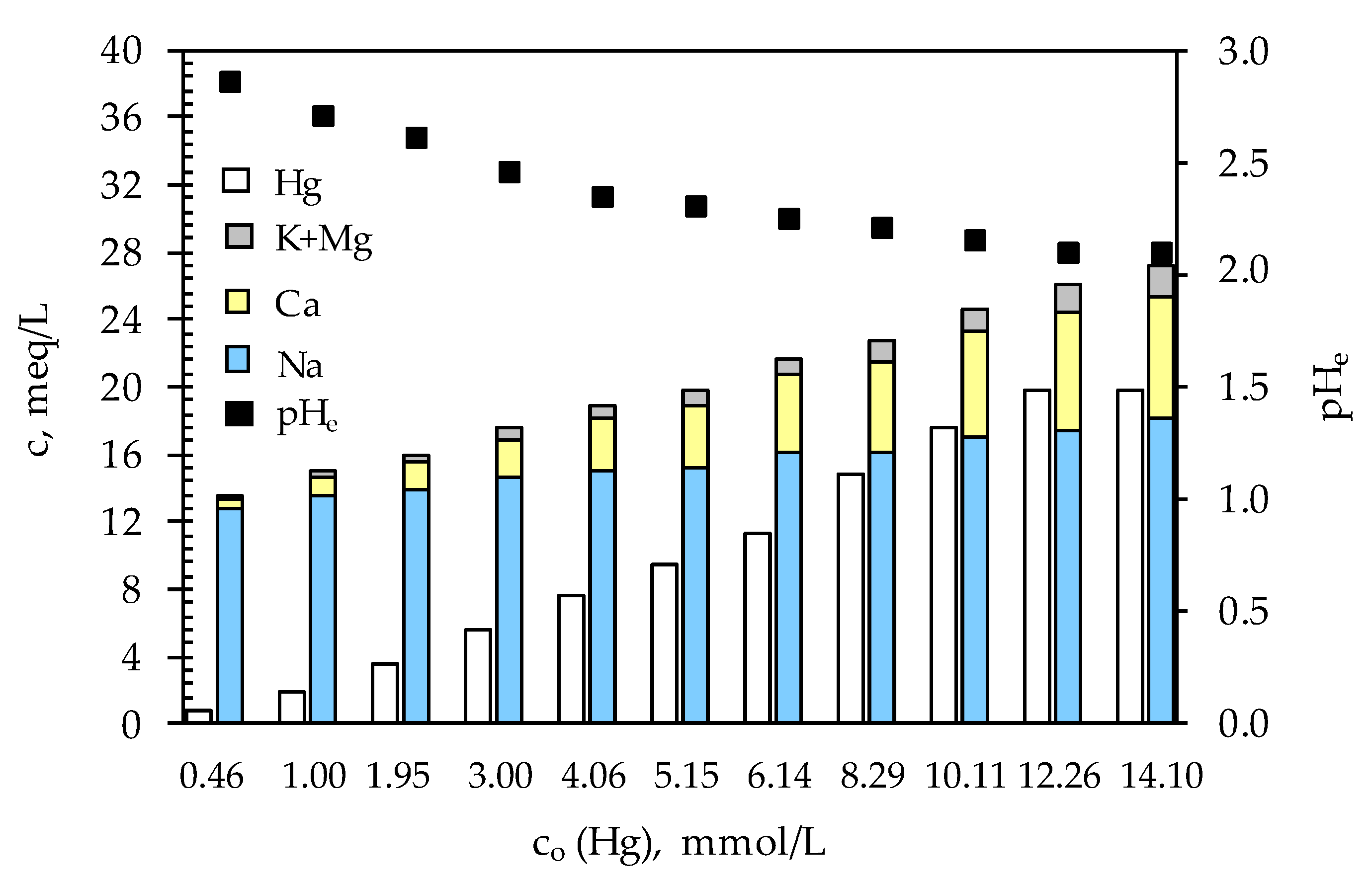
3.4. Leaching Properties of the Mercury-Saturated Sulfur-Impregnated Zeolite
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hay, R.L.; Sheppard, R.A. Occurrence of zeolites in Sedimentary Rocks: An Overview: Occurrence, properties, application. In Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications; Bish, D.L., Ming, D.W., Eds.; Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, R.A.; Hay, R.L. Formation of zeolites in Open Hydrologic Systems: Occurrence, properties, application. In Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications; Bish, D.L., Ming, D.W., Eds.; Virginia Polytechnic Institute & State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, K.; Zabukovec Logar, N.; Šiljeg, M.; Farkaš, M. Natural Zeolites in Water Treatment–How Effective is Their Use. In Water Treatment; Elshorbagy, W., Chowdhury, R.K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, S.; Diaz, E. Basic Zeolites: Structure, Preparation and Environmental Applications. In Handbook of Zeolites: Structure, Properties and Applications; Wong, T.W., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: London, UK, 2009; pp. 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Busca, G. Acidity and basicity of zeolites. A fundamental approach. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 254, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoliva, V.; Saviano, M.; De Luca, S. Zeolites as Acid/basic Solid Catalysts: Recent Synthetic Developments. Catalysts 2019, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, G. Electrical Investigation of the Mechanism of Water Adsorption/Desorption by Natural Clinoptilolite Desiccant Used in Food Preservation. Mater. Proc. 2020, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaby, S. Effect of Water Adsorption on Cation-Surface Interaction Energy in the Na-Mordenite of 5.5:1 Si/Al Ratio. J. Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fischer, M. Structure and bonding of water molecules in zeolite hosts: Benchmarking plane-wave DFT against crystal structure dana. Z. Krist. 2015, 230, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, Y. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misealidis, P. Application of natural zeolites in environmental remediation: A short review. Micropous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 144, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørklund, G.; Dadar, M.; Mutter, J.; Aaseth, J. The toxicology of mercury: Current research and emerging trends. Environ. Res. 2017, 159, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H. Lecture on Methylmercury Poisoning in Minamata (MPM). In Mercury Pollution in Minamata; Springer Briefs in Environmental Science; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 5–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, K.; Cukrowska, E.M.; Coville, N.J. Improved uptake of mercury by sulphur-containing carbon nanotubes. Microchem. J. 2013, 108, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Garcia Bravo, A.; Lagerkvist, A.; Bertilsson, S.; Sjöblom, R.; Kumpiene, J. Sources and remediation techniques for mercury contaminated soil, review. Environ. Int. 2015, 74, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Feng, X.; Anderson, C.W.N.; Xing, Y.; Shang, L. Remediation of mercury contaminated sites—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 221–222, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hou, D.; Cao, Y.; Sik Ok, Y.; Tack, F.M.G.; Rinklebe, J.; O’Connor, D. Remediation of mercury contaminated soil, water, and air: A review of emerging materials and innovative technologies. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105281–105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajima, T.; Sugawara, K. Adsorption behaviors of mercury from aqueous solution using sulfur-impregnated adsorbent developed from coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.S.; Ruiz, S.V.; Granados, D.L.; Santángelo, J.M. Adsorption of Mercury (II) from Liquid Solutions Modified Activated Carbons. Mater. Res. 2010, 13, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.; Da’ana, D.; Abu-Dieyeh, M.; Khraisheh, M. Adsorptive removal of mercury from water by adsorbents derived from daze pits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15327–15340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Vidyarthi, S.R. Enhanced sorption of mercury from compact fluorescent bulbs and contaminated water streams using functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Hua, Y.; Peng, B.; Deng, M.; Yan, N.; Qu, Z. A sulfur-resistant CuS-modified active coke for mercury removal from municipal solid waste incineration flue gas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24831–24839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Xu, N.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, W. Sorption of mercury (II) and atrazine by biochar, modified biochars and biochar based activated carbon in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Liu, M.-H.; Hung, C.-H. Preparation of Sulfurized Powdered Activated Carbon from Waste Tires Using an Innovative Compositive Impregnation Process. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xue, Y.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Long, L. Preparation and characterization of Na2S-modified biochar for nickel removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9887–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelouahab-Reddam, Z.; Wahby, A.; El Mail, R.; Silvestre-Albero1, J.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, R.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A. Activated Carbons Impregnated with Na2S and H2SO4: Texture, Surface Chemistry and Application to Mercury Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.H.; Jia, C.Q. Mercury Removal from Aqueous Solution Using Coke-Derived Sulfur-Impregnated Activated Carbons. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 2716–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asasian, N.; Kaghazchi, T. Sulfurized activated carbons and their mercury adsorption/desorption behavior in aqueous phase. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin-Haile, T.; Olguín, M.T.; Solache-Ríos, M. Removal of mercury ions from mixed aqueous metal solutions by natural and modified zeolitic minerals. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 148, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.-K.; Ahmad, T.; Kim, K.-Y.; Oh, K.-J.; Lee, S.-S. Mercury Adsorption Characteristics of Sulphur-Impregnated Activated Carbon Pellets for the Flue Gas Condition of a Cement-Manufacturing Process. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Hogland, W.; Marques, M.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the modification methods of activated carbon for its water treatment applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 219, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ahmad, N.M.; Cheema, W.A.; Zhu, S. Removal of Hg(II) in aqueous solutions through physical and chemical adsorption principles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 20941–20953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, C.; Bagatin, R.; Tagliabue, M.; Vignola, V. Zeolites and related mesoporous materials for multi-talented environmental solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 166, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Particle Size Analysis-Sieving Analysis-Part 2: Procedure; DIN 66165-2; Deutsches Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 2016.
- Liu, Y.; Khan, A.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, S.; Sun, T.; Liang, D.; Yu, H. Upcycling of Electroplating Sludge to Prepare Erdite-Bearing Nanorods for the Adsorption of Heavy Metals from Electroplating Wastewater Effluent. Water 2020, 12, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinovitch, I.; Debrad-Guedon, J.; Louvrier, J. The Analysis of Silicates; Israel Program for Scientific Translations: Jerusalem, Israel, 1966; pp. 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bohem, H.P. Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon 1994, 32, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Cation-Exchange Capacity of Soils (Ammonium Acetate): Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste. SW-846, Method 9080; US EPA, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- Ievtifieieva, O.A.; Bolotov, V.V.; Kostina, T.A.; Svechnikova, O.M.; Yuschenko, T.I.; Kaminska, N.I.; Kosareva, A.E.; Slobodyanyuk, L.V.; Yashchuk, O.P. Analytical Chemistry (Qualitative Analysis) Part I; Ievtifieieva, O.A., Ed.; Publishing House the CLL Generous Farmstead Plus: Kharkiv, Ukraina, 2014; pp. 120–121. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301527607_Analytical_chemistry_Qualitative_analysis_Part_I_The_manual_for_students_of_higher_schools_O_A_Ievtifieieva_V_V_Bolotov_T_A_Kostina_O_M_Svechnikova_T_I_Yuschenko_N_I_Kaminska_A_E_Kosareva_L_V_Slobodya (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Ugrina, M.; Čeru, T.; Nuić, I.; Trgo, M. Comparative Study of Mercury(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions onto Natural and Iron-Modified Clinoptilolite Rich Zeolite. Processes 2020, 8, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German Standard Procedure for Water, Wastewater and Sediment Testing–Sludge and Sediment. Determination of Leachability; DIN 38414 S4; Institut für Normung: Berlin, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Minceva, M.; Fajagar, R.; Markovska, L.; Meshko, V. Comparative study of Zn2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ removal from water solution using natural clinoptilolitic zeolite and commercial granulated activated carbon. Equilibrium and adsorption. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 2117–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holleman, A.F.; Wiberg, E. Inorganic Chemistry; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 1451–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Mozgawa, W. The influence of some heavy metals cations on the FTIR spectra of zeolites. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 555, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadiş, A.-I.; Perhaiţa, I.; Munteanu, V.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Silipas, D.T.; Mureşan, L.E. Influence of preparative conditions for obtaining ZnS:Mn nanoparticles using ultrasound-assisted precipitation. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavifar, M.; Bahramifar, N.; Younesi, H.; Li, Q. Adsorption of mercury ions from synthetic and real wastewater aqueous solution by functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotube with both amino and thiolated groups. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, C.; Qin, Y.; Liang, J. Preparation of a Stable Nanoscale Manganese Residue-Derived FeS@Starch-Derived Carbon Composite for the Adsorption of Safranine T. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, G.H.; Gao, Q.Q.; Chen, Y.J.; Chen, Z.P.; Xu, Z.S.; Li, W.D. Changes of mineralogical characteristics and osteoblast activities of raw and processed pyrites. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28373–28382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, M.; Ma, C. Study on the oxidation of calcium sulfide using TGA and FTIR. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgawa, W.; Król, M.; Barczyk, K. FT-IR studies of zeolites from different structural groups. CHEMIK 2011, 65, 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- Santona, L.; Cozza, C.; Giuliano, V.; Abbruzzese, C.; Nastro, V.; Melis, P. Thermal and spectroscopic studies of zeolites exchanged with metal cations. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 734, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, V.A.; Antonovich, V.P.; Nevskaja, E.M. Metal Ions Hydrolysis in Dilute Solutions; Atomizad: Moscow, Russia, 1979; pp. 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nies, D.H. The biological chemistry of the transition metal “transportome” of Cupriavidus metallidurans. Metallomics 2016, 8, 481–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blais, J.F.; Djedidi, Z.; Ben Cheikh, R.; Tyagi, R.D.; Mercier, G. Metals Precipitation from Effluents: Review. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2008, 12, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praus, P.; Motáková, M.; Ritz, M. Montmorillonite ion exchanged by mercury (II). Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2012, 9, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Brigatti, M.F.; Colonna, S.; Malferrari, D.; Medici, L.; Poppi, L. Mercury adsorption by montmorillonite and vermiculite: A combined XRD, TG-MS, and EXAFS study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2005, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumayor, M.; Diaz-Somoano, M.; Lopez-Anton, M.A.; Martinez-Tarazona, M.R. Mercury compounds characterization by thermal desorption. Talanta 2013, 114, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, D. Immobilization of Mercury by Carboxymethyl Cellulose Stabilized Iron Sulfide Nanoparticles: Reaction Mechanisms and Effects of Stabilizer and Water Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3986–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, G.; Zheng, N. Effective solidification/stabilisation of mercury-contaminated wastes using zeolites and chemically bonded phosphate ceramics. Waste Manag. Res. 2015, 33, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J. The Applications of Zeolite in Sustainable Binders for Soil Stabilization. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 256–259, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mola-Abasi, H.; Kordtabar, B.; Kordnaeij, A. Effect of Natural Zeolite and Cement Additive on the Strength of Sand. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2016, 34, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
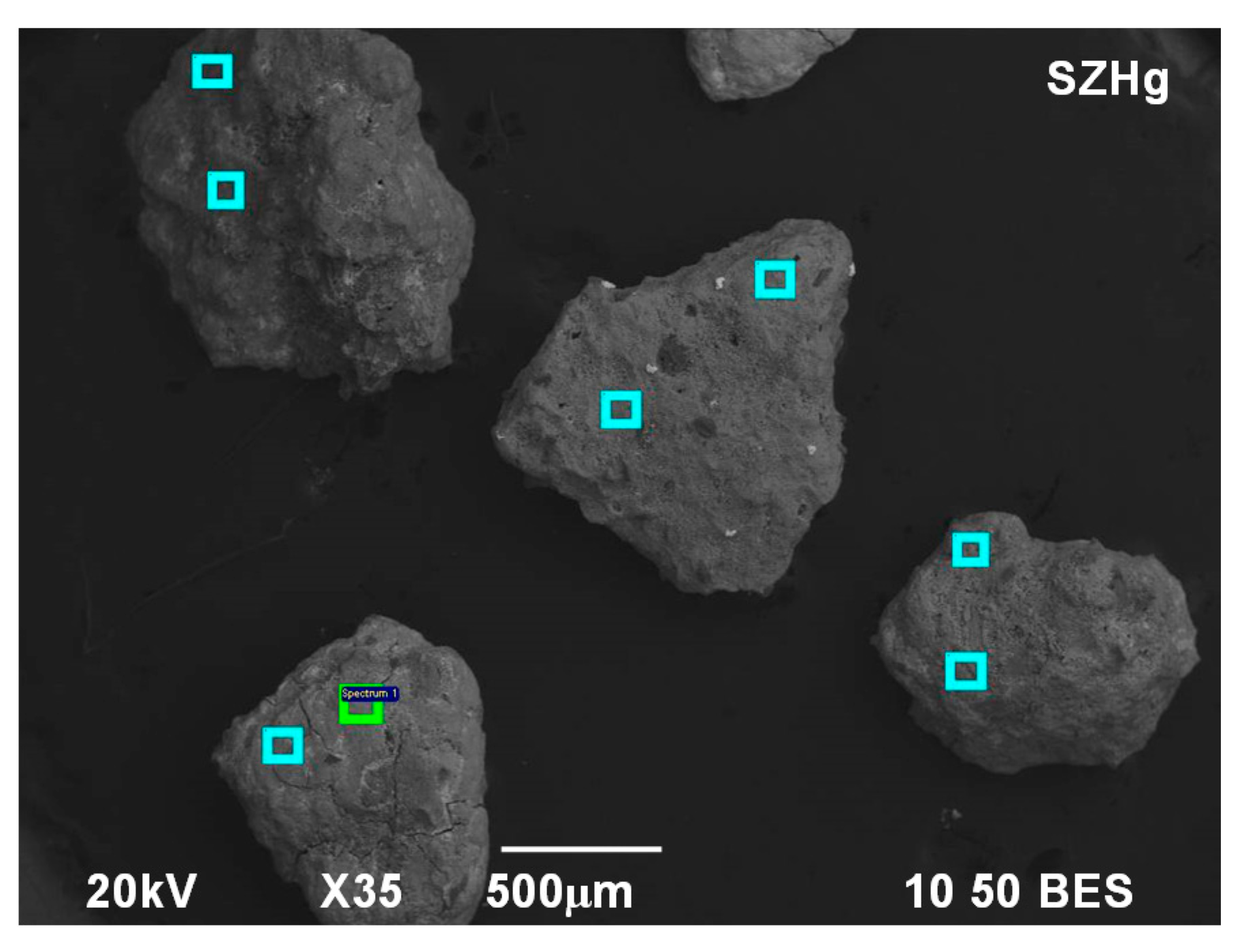
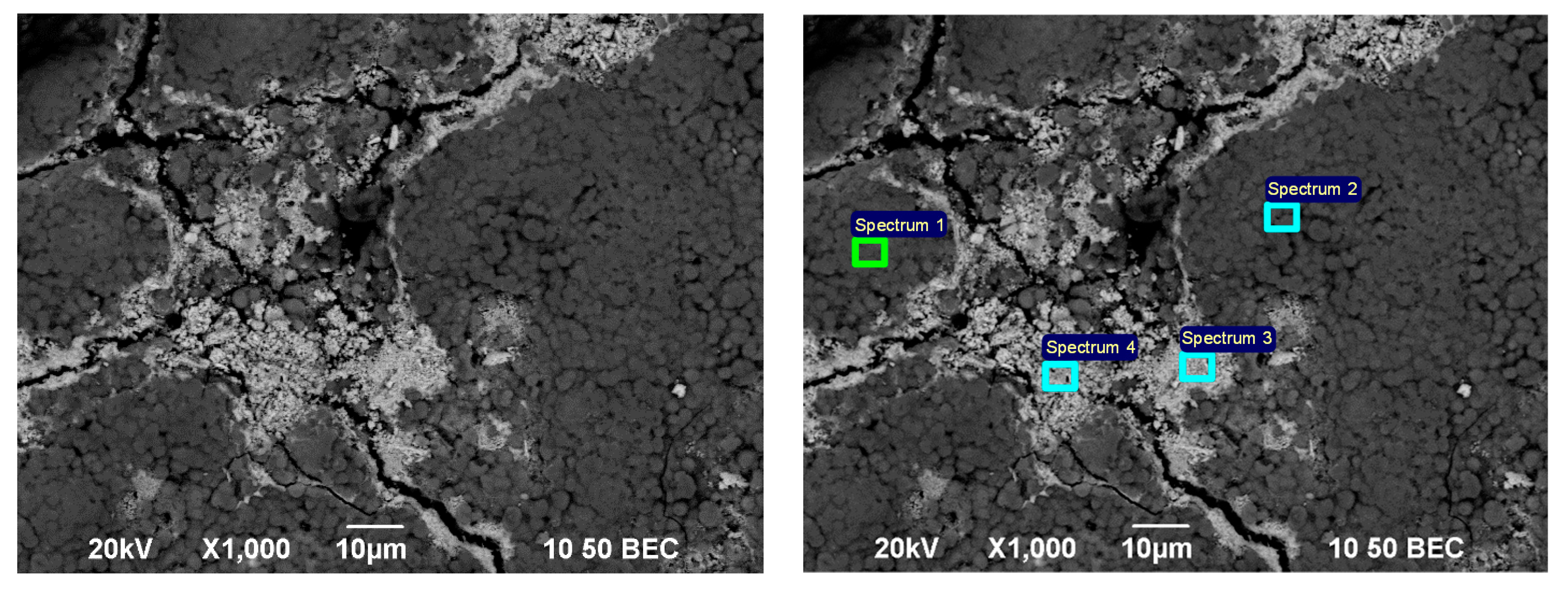
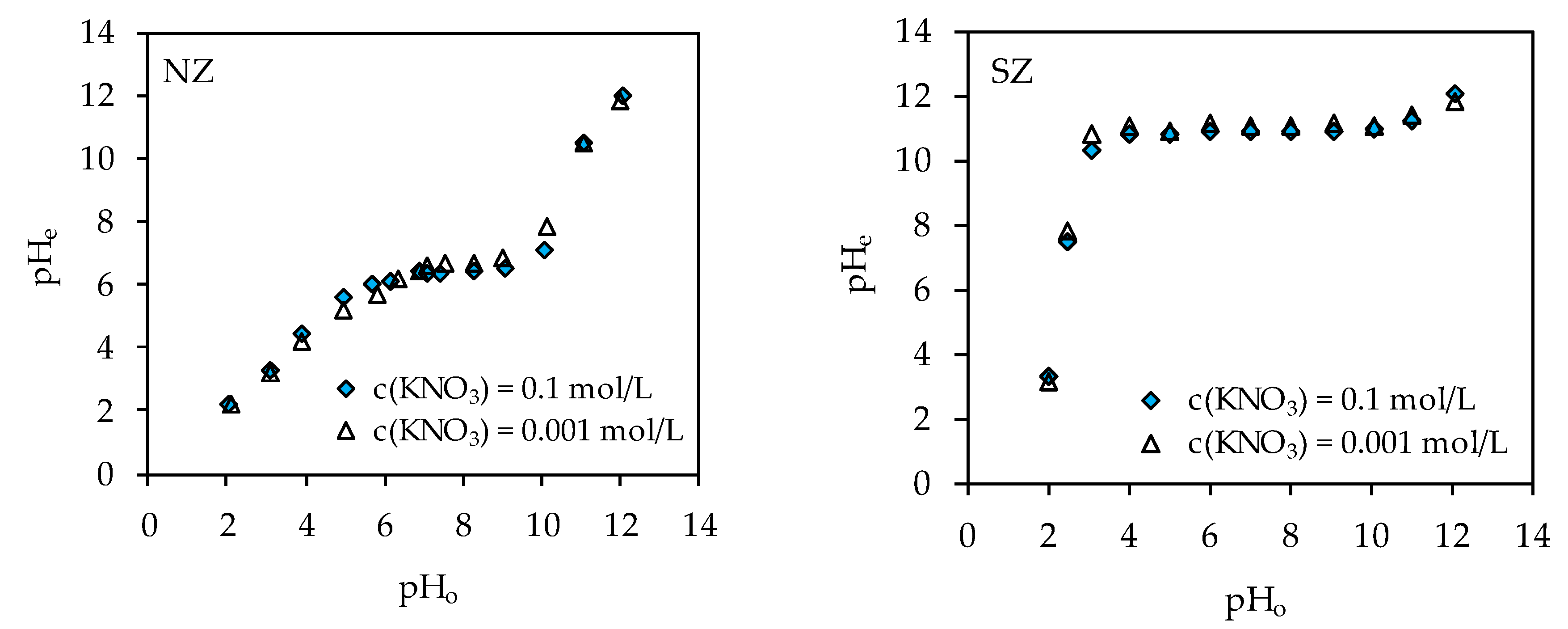


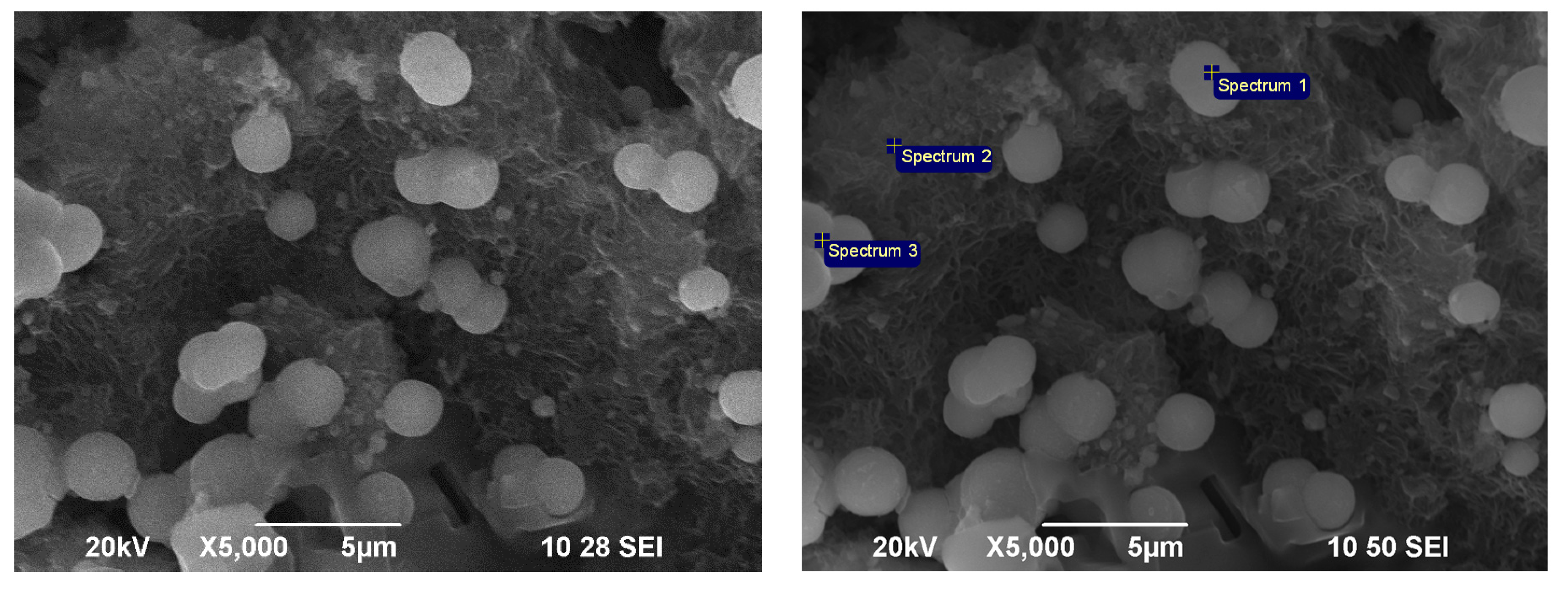


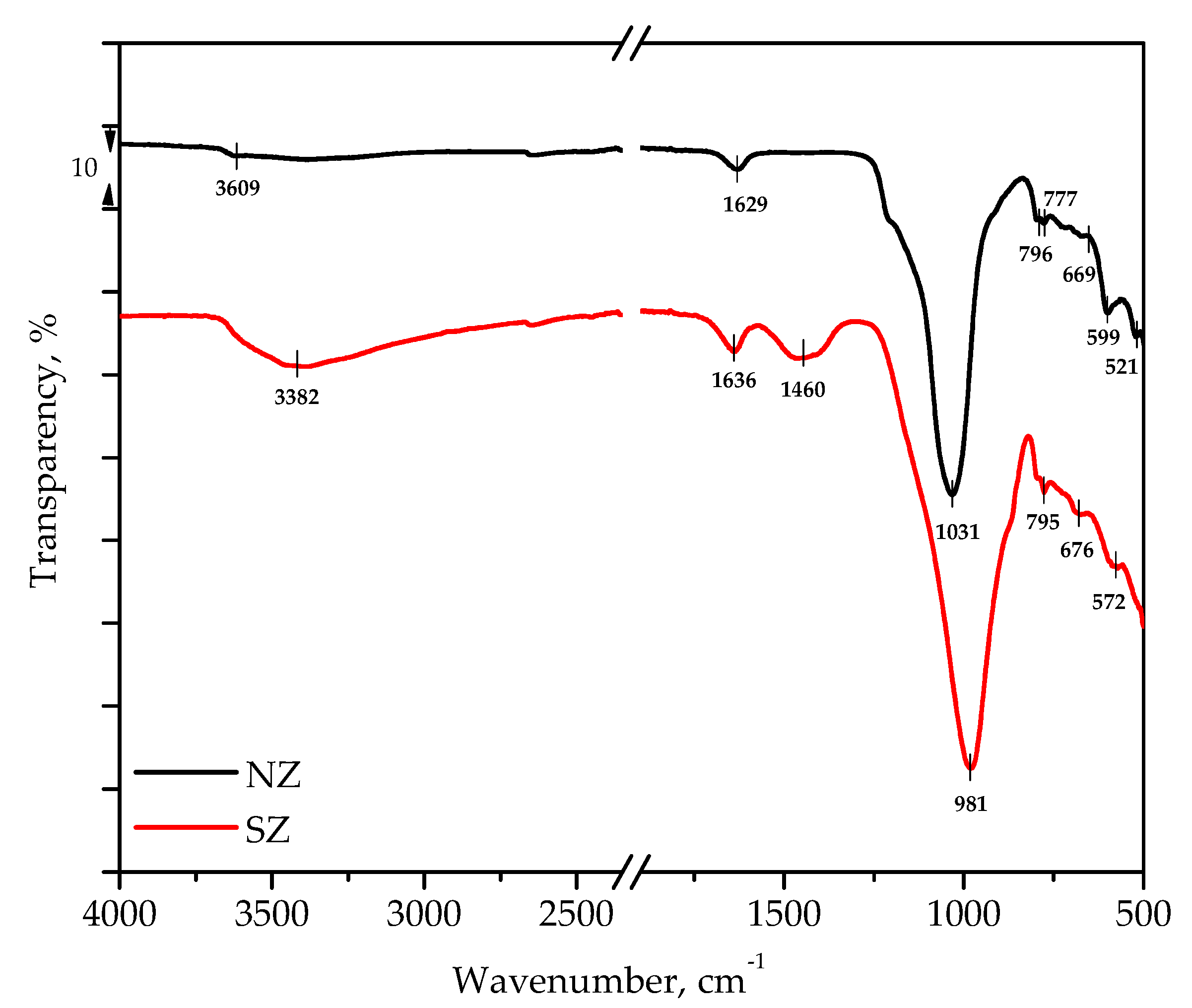
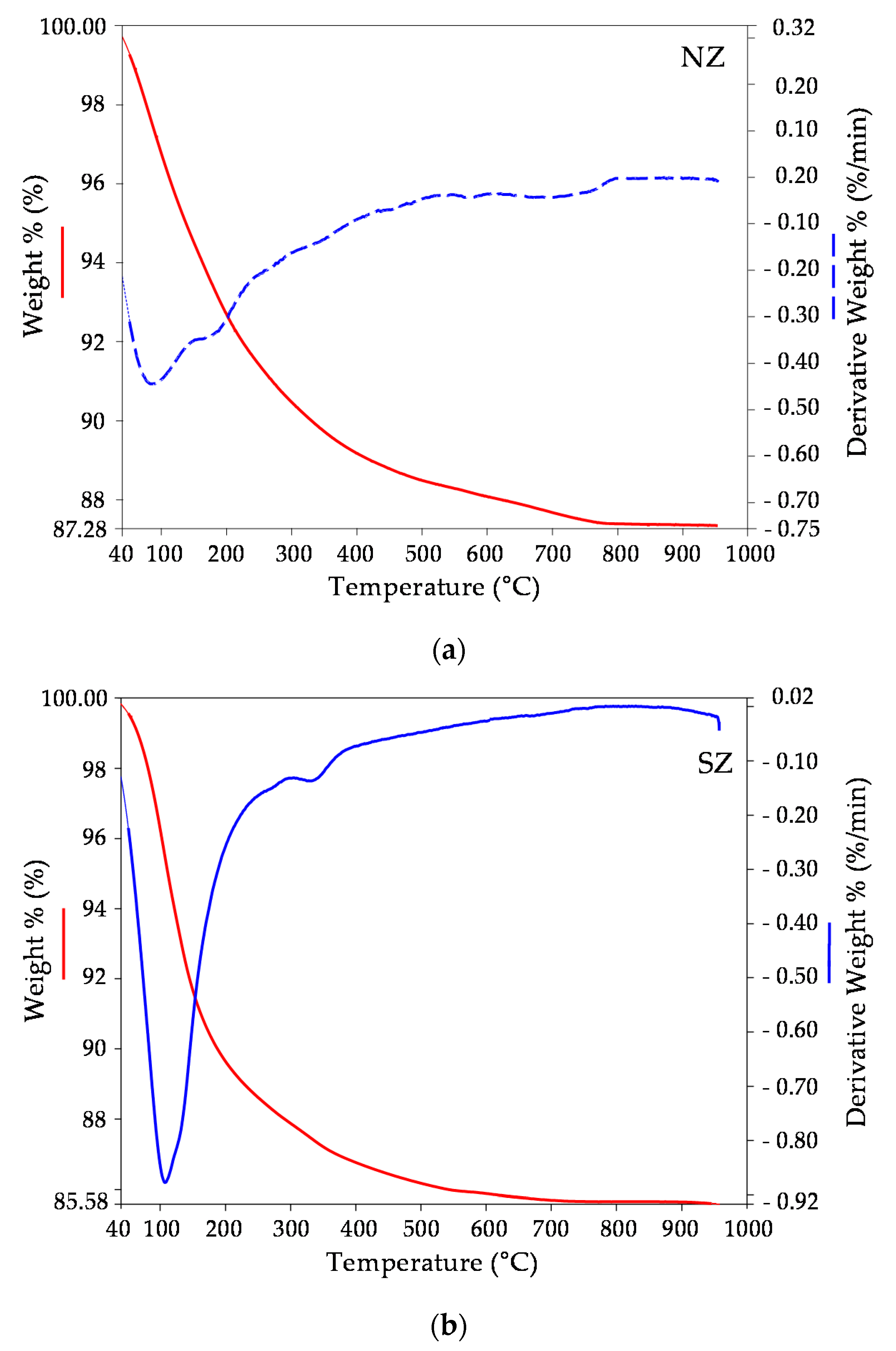
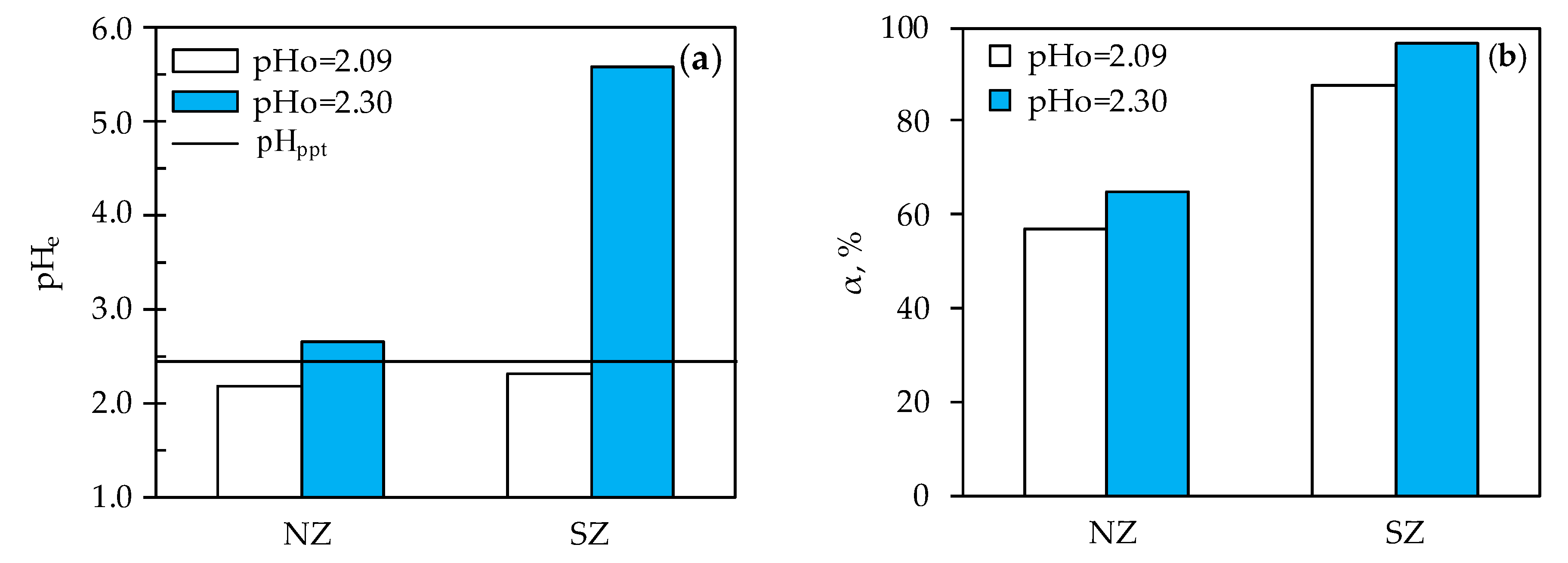


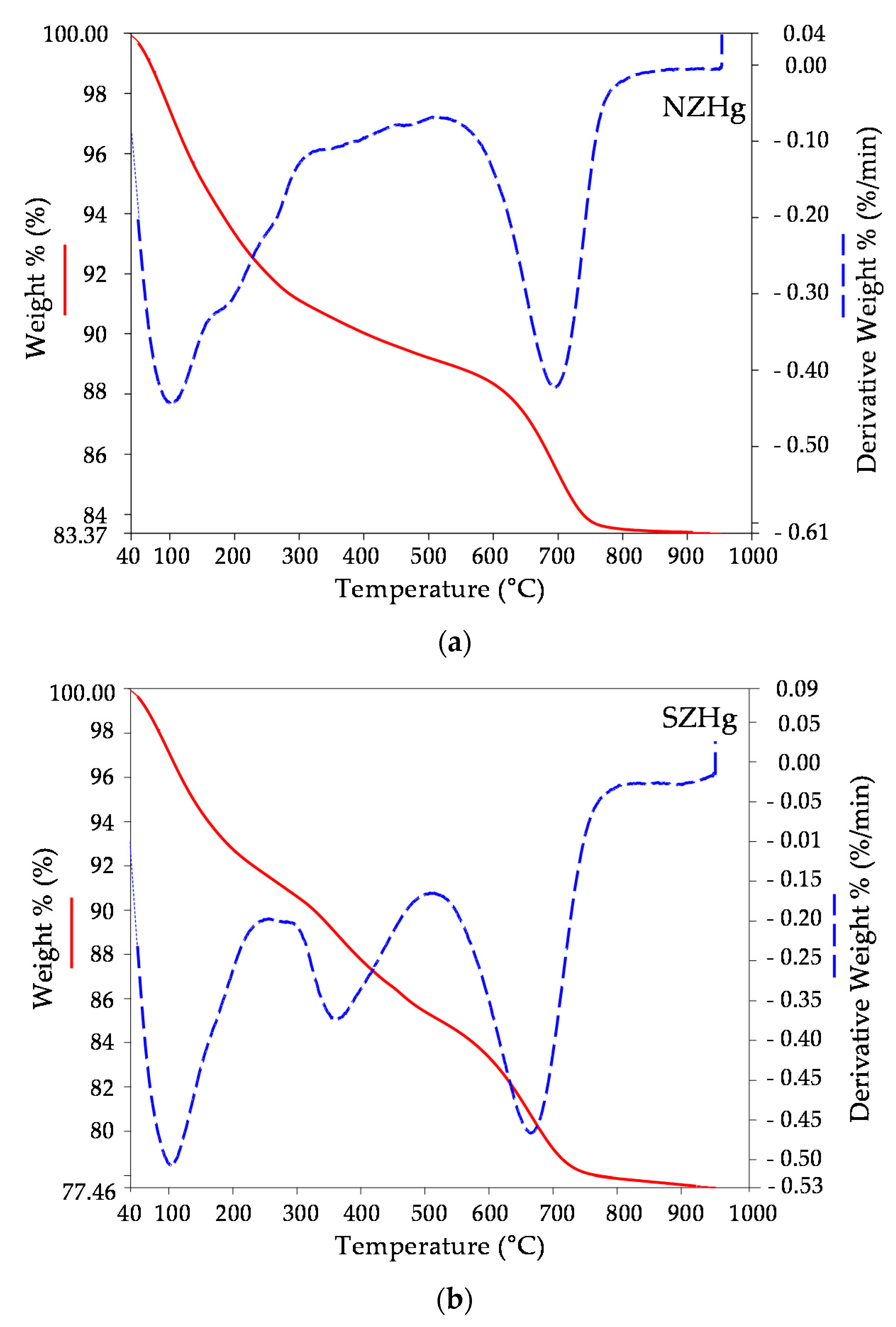
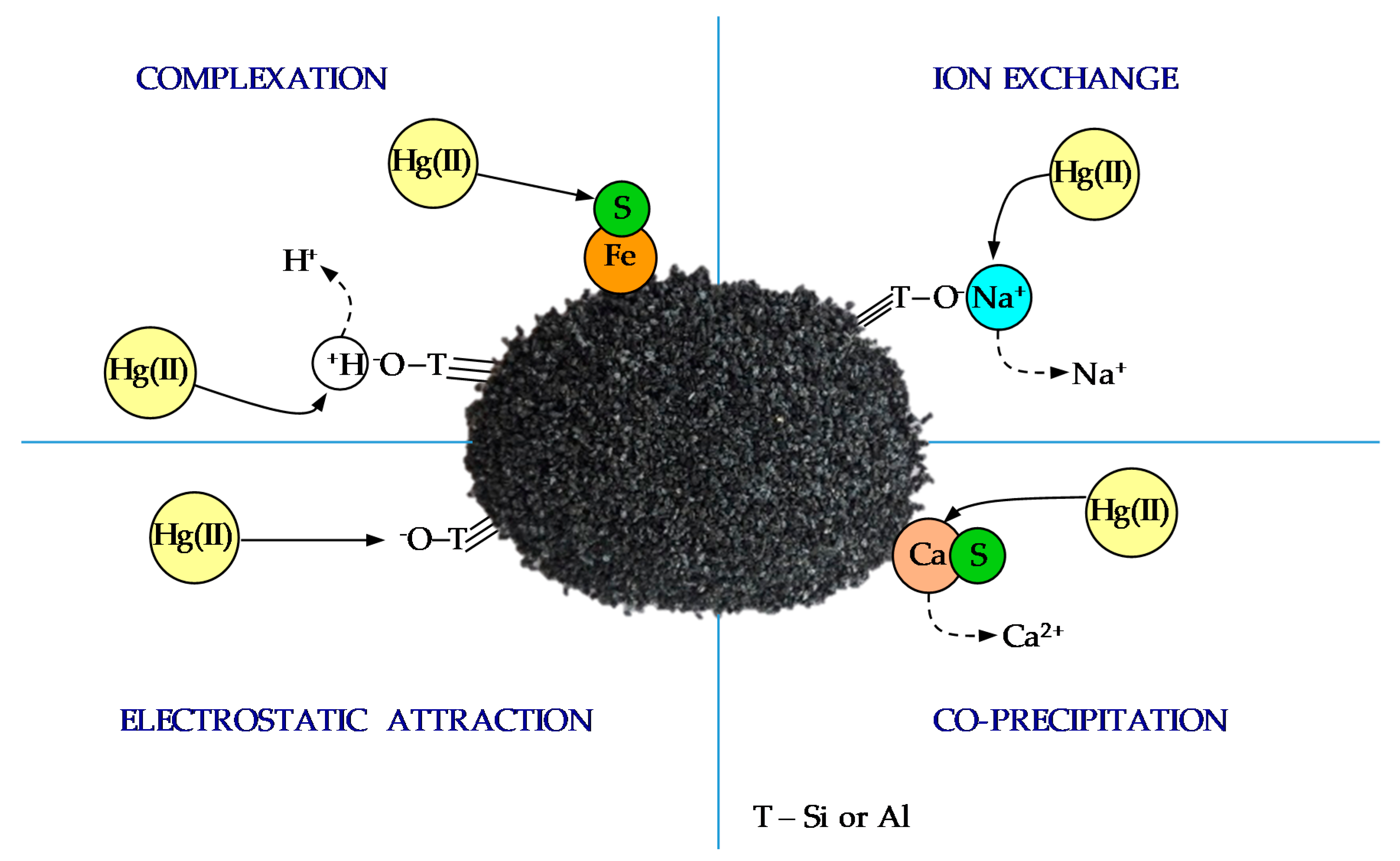
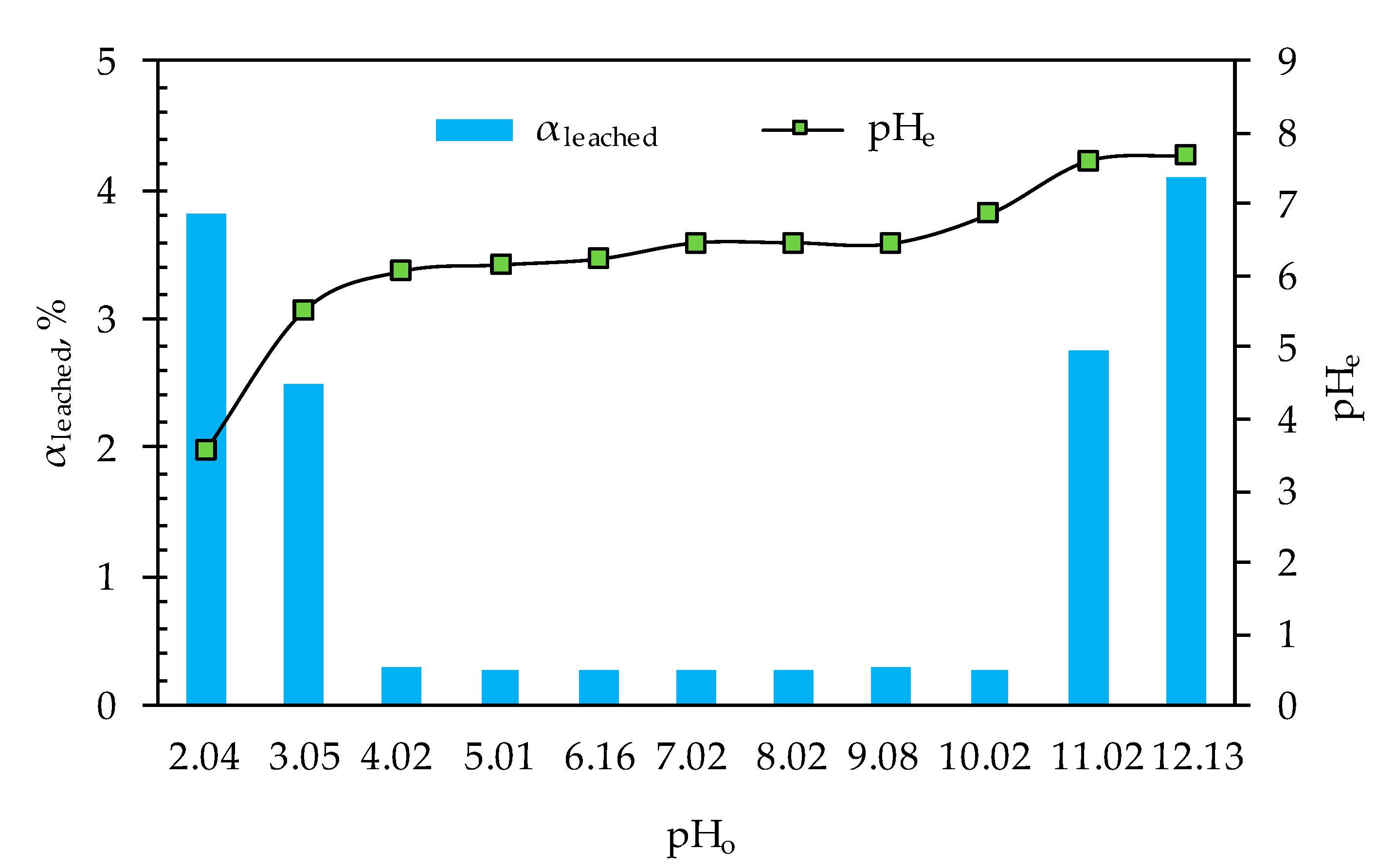
| Sample | Content, wt % | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Na2O | K2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | S | SO3 | Loss of Ignition | |
| NZ | 66.56 | 13.41 | 1.95 | 1.56 | 1.12 | 4.00 | 0.54 | 0.169 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 10.24 |
| SZ | 56.69 | 12.34 | 2.07 | 10.70 | 0.76 | 4.03 | 0.73 | 0.168 | 1.08 | 2.70 | 9.76 |
| Sample | Element Quantity, mmol/g | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | K | Ca | Mg | Al | Si | O | Fe | Ti | S | Si/Al | |
| NZ | 0.503 | 0.238 | 0.713 | 0.134 | 2.630 | 11.077 | 27.80 | 0.244 | 0.021 | 0.100 | 4.21 |
| SZ | 3.454 | 0.161 | 0.719 | 0.181 | 2.420 | 9.435 | 26.14 | 0.259 | 0.021 | 0.674 | 3.89 |
| Sample | Total Acidic Sites (meq/L) | Total Basic Sites (meq/L) | Zeta Potential (pH = 5.82) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NZ | 46.3 | 30.0 | −22.8 |
| SZ | 2.5 | 190.0 | −39.9 |
| Sample | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Radius (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NZ | 19.447 | 0.082 | 1.979 |
| SZ | 12.064 | 0.081 | 1.953 |
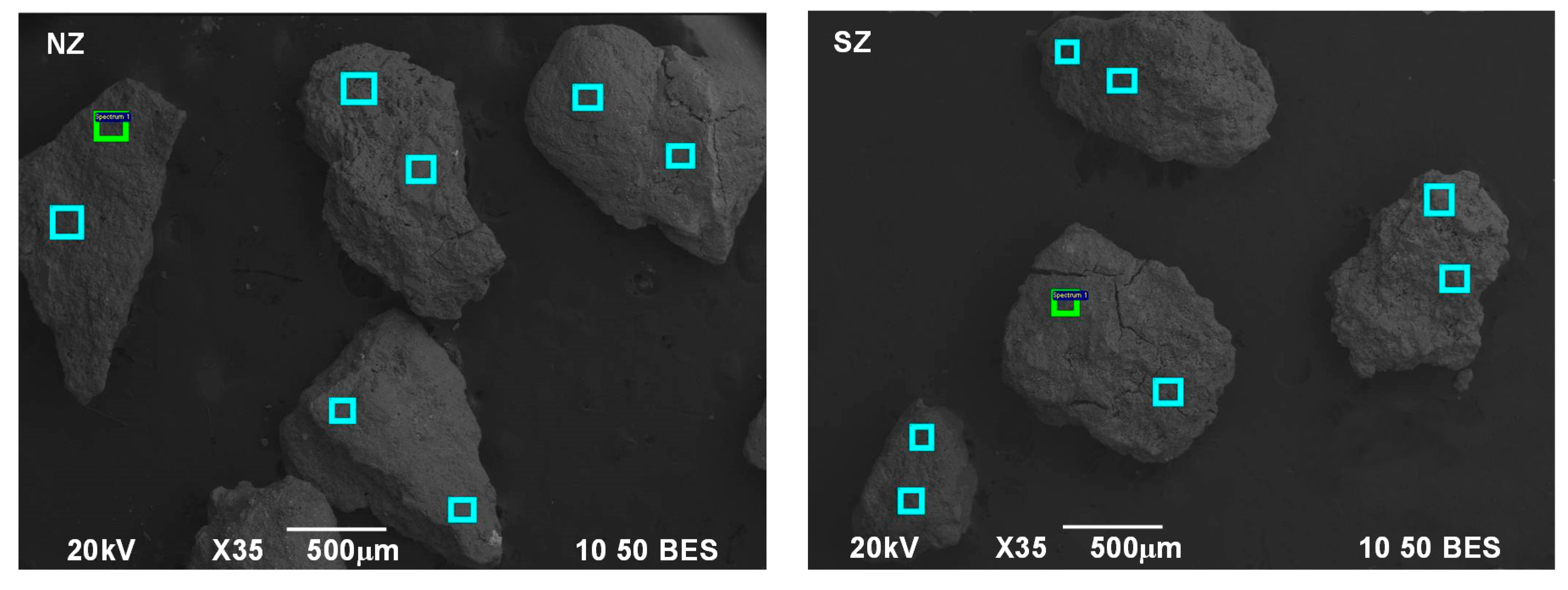
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 59.10 | 0.37 | 0.77 | 6.02 | 30.50 | 1.02 | 2.22 | - |
| Sp 2 | 59.36 | 0.56 | 0.72 | 6.01 | 30.00 | 0.97 | 2.09 | 0.29 |
| Sp 3 | 52.77 | 0.76 | 0.47 | 5.79 | 35.48 | 1.38 | 2.74 | 0.60 |
| Sp 4 | 55.67 | 0.74 | 0.61 | 5.89 | 32.99 | 1.34 | 2.77 | - |
| Sp 5 | 58.61 | 0.38 | 2.01 | 8.37 | 23.37 | 3.65 | 0.48 | 2.59 |
| Sp 6 | 58.14 | 0.41 | 2.11 | 8.35 | 23.44 | 3.46 | 0.53 | 3.11 |
| Sp 7 | 52.91 | 0.45 | 0.64 | 5.89 | 32.40 | 1.25 | 3.00 | 3.46 |
| Sp 8 | 45.00 | - | 0.55 | 6.05 | 33.17 | 1.76 | 4.42 | 7.50 |
| Mean | 55.20 | 0.46 | 0.99 | 6.55 | 30.17 | 1.85 | 2.28 | 2.19 |
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 56.59 | 16.11 | - | 6.51 | 15.80 | 1.43 | 0.33 | 0.80 | 2.43 |
| Sp 2 | 56.15 | 14.36 | 0.34 | 7.34 | 17.50 | 1.03 | 0.41 | 1.58 | 1.29 |
| Sp 3 | 56.32 | 13.21 | 0.50 | 6.62 | 18.68 | 1.02 | 0.43 | 2.12 | 1.10 |
| Sp 4 | 55.03 | 15.18 | - | 7.66 | 16.25 | 1.80 | 0.38 | 0.47 | 3.22 |
| Sp 5 | 55.97 | 15.22 | - | 8.30 | 17.86 | 1.20 | 0.22 | 0.40 | 0.83 |
| Sp 6 | 57.11 | 16.45 | - | 7.77 | 16.64 | 1.13 | 0.34 | - | 0.56 |
| Sp 7 | 59.64 | 19.55 | - | 5.46 | 12.25 | 1.36 | 0.23 | 0.91 | 0.61 |
| Sp 8 | 59.78 | 18.34 | 0.30 | 5.94 | 12.50 | 1.42 | 0.25 | 1.03 | 0.44 |
| Mean | 57.07 | 16.05 | 0.14 | 6.95 | 15.94 | 1.30 | 0.32 | 0.91 | 1.31 |
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 50.85 | 6.67 | 1.10 | 4.43 | 24.68 | 3.32 | 1.11 | 2.49 | 5.35 |
| Sp 2 | 58.98 | 8.71 | 0.70 | 7.00 | 20.11 | 1.36 | 0.34 | 1.88 | 0.93 |
| Sp 3 | 49.02 | 8.07 | 0.50 | 8.44 | 25.67 | 2.03 | 0.70 | 2.75 | 2.83 |
| Element | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | S | K | Ca | Fe | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 34.75 | 1.60 | - | 6.75 | 16.03 | 1.07 | - | 0.34 | - | 39.46 |
| Sp 2 | 38.09 | 2.36 | - | 7.18 | 14.57 | 1.27 | 0.39 | 0.39 | - | 35.75 |
| Sp 3 | 42.84 | 0.48 | 0.58 | 4.09 | 25.85 | 0.63 | 0.37 | 0.70 | - | 24.46 |
| Sp 4 | 41.20 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 4.07 | 24.14 | 1.12 | 0.41 | 0.52 | 0.49 | 27.17 |
| Sp 5 | 45.83 | 0.40 | 0.83 | 4.08 | 17.43 | 1.60 | 0.37 | 0.43 | 4.53 | 24.49 |
| Sp 6 | 50.44 | 0.61 | 0.89 | 4.17 | 22.22 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 0.60 | 4.59 | 14.73 |
| Sp 7 | 43.81 | - | 0.28 | 4.84 | 22.75 | 1.02 | 0.86 | 0.43 | 2.83 | 23.20 |
| Sp 8 | 45.98 | - | 0.32 | 4.85 | 20.26 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.34 | 2.03 | 25.10 |
| Mean | 42.87 | 0.73 | 0.43 | 5.00 | 20.63 | 1.01 | 0.48 | 0.47 | 1.81 | 26.80 |
| Element | O | Na | Al | Si | S | Ca | Fe | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sp 1 | 35.69 | 1.21 | 7.95 | 15.95 | - | 0.29 | - | 38.92 |
| Sp 2 | 39.44 | 1.35 | 8.43 | 16.78 | - | 0.26 | 0.41 | 33.32 |
| Sp 3 | 9.00 | - | 0.52 | 1.53 | 11.50 | - | 1.10 | 76.34 |
| Sp 4 | 10.97 | - | 0.48 | 1.52 | 10.56 | - | 3.35 | 73.12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ugrina, M.; Gaberšek, M.; Daković, A.; Nuić, I. Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2021, 9, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217
Ugrina M, Gaberšek M, Daković A, Nuić I. Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes. 2021; 9(2):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217
Chicago/Turabian StyleUgrina, Marin, Martin Gaberšek, Aleksandra Daković, and Ivona Nuić. 2021. "Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions" Processes 9, no. 2: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217
APA StyleUgrina, M., Gaberšek, M., Daković, A., & Nuić, I. (2021). Preparation and Characterization of the Sulfur-Impregnated Natural Zeolite Clinoptilolite for Hg(II) Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Processes, 9(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9020217