Physicochemical and Nutritional Evaluation of Bread Incorporated with Ayocote Bean (Phaseolus coccineus) and Black Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
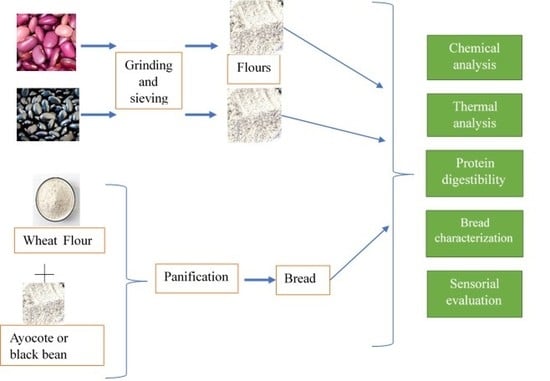
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ayocote Beans and Black Beans
2.2. Flour and Bread Preparation
2.3. Proximal Analysis
2.4. Thermal Properties of Bread Incorporated with Black Bean and Ayocote Bean
2.5. In Vitro Protein Digestibility (IPD)
2.6. Bread Characterization
2.6.1. Color
2.6.2. Specific Volume
2.7. Sensorial Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Beans and Bread Chemical Composition
3.2. Thermal Properties of Bread Incorporated with Black Bean and Ayocote Bean
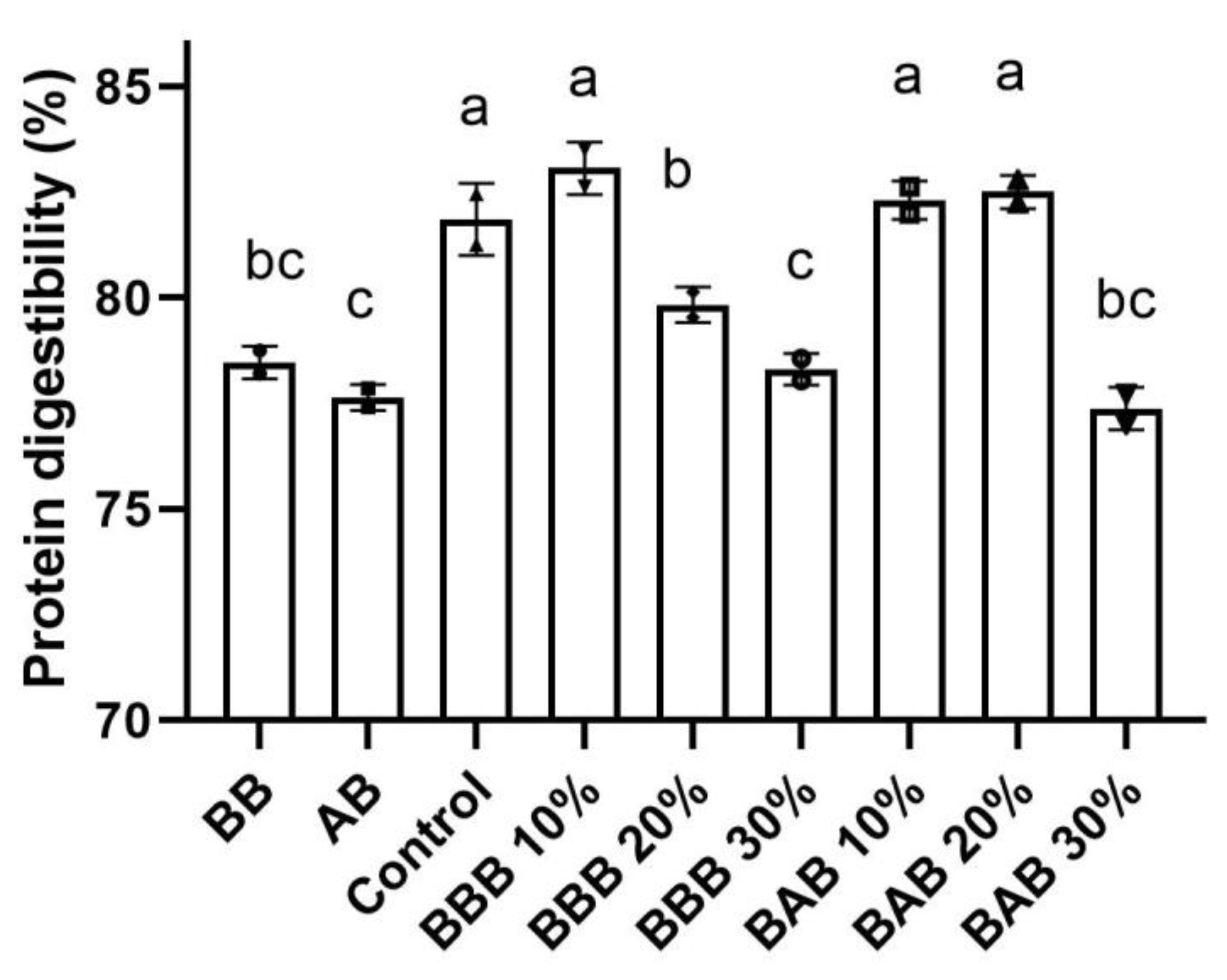
3.3. In Vitro Protein Digestibility
3.4. Bread Characterization
3.4.1. Color
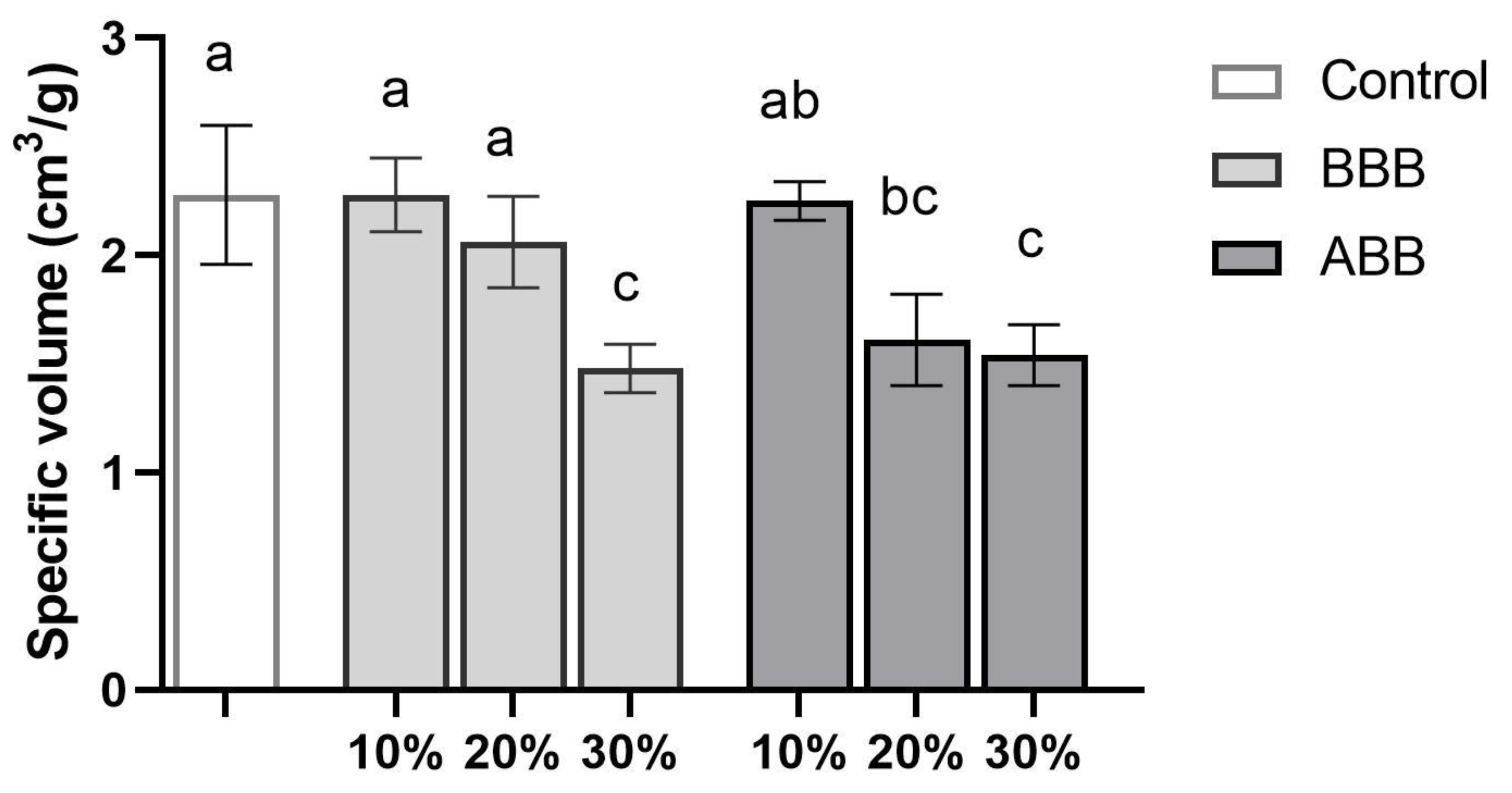
3.4.2. Specific Volume
3.5. Sensorial Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dewettinck, K.; van Bockstaele, F.; Kuhen, F.; Van de Walle, D.; Courtens, T.M.; Gellynck, X. Nutritional value of bread: Influence of processing, food interaction and consumer perception. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 48, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczyk, M.; Kruszewski, M.; Michalowska, D. Effect of Coconut and Chestnut Flour Supplementations on Texture, Nutritional and Sensory Properties of Baked Wheat Based. Molecules 2021, 26, 4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa-Kozak, U.; Drabińska, N.; Baczek, N.; Šimková, K.; Starowicz, M.; Jeliński, T. Application of broccoli leaf powder in gluten-free bread: An innovative approach to improve its bioactive potential and technological quality. Foods 2021, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoehnel, A.; Axel, C.; Bez, J.; Arendt, E.K.; Zannini, E. Comparative analysis of plant-based high-protein ingredients and their impact on quality of high-protein bread. J.Cereal Sci. 2019, 89, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Salazar, R.; Mayek-Pérez, N.; Vargas-Vázquez, M.L.; Hernández-Delgado, S.; Muruaga-Martínez, J. Análisis de la estructura poblacional del frijol Ayocote (Phaseolus coccineus L.) mediane AFLP. Polibotánica 2019, 46, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-López, A.N.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Heredia, J.B.; Baeza-Jiménez, R.; Garcia-Galindo, H.S.; Lopez-Martinez, L.X. Nutritional and bioactive characteristics of Ayocote bean (Phaseolus coccienus L.): An underutilized legume harvested in Mexico. CYTA-J. Food 2019, 17, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Available online: http://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/f961bcd6-85db-405e-af70-3ed044f1b1d7/ (accessed on 29 August 2021).
- Gepts, P. Phaseolus vulgaris (Beans). In Encyclopedia of Genetics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 1444–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Brummer, Y.; Kaviani, M.; Tosh, S.M. Structural and functional characteristics of dietary fibre in beans, lentils, peas and chickpeas. Food Res. Int. 2015, 67, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizkalla, S.W.; Bellisle, F.; Slama, G. Health benefits of low glycaemic index foods, such as pulses, in diabetic patients and healthy individuals. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Rosa-Millán, J.; Heredia-Olea, E.; Perez-Carrillo, E.; Guajardo-Flores, D.; Serna-Saldívar, S.R.O. Effect of decortication, germination and extrusion on physicochemical and in vitro protein and starch digestion characteristics of black beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). LWT 2019, 102, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.T.; Charles, A.L.; Ho, C.T.; Huang, T.C. A novel bread making process using salt-stressed Baker’s yeast. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, S399–S4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Ramos, D.; de Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.D.; Véles-Medina, J.J.; Mariscal-Moreno, R.M. Changes in the thermal and structural properties of maize starch during nixtamalization and tortilla-making processes as affected by grain hardness. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 74, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.W.; Vavak, D.L.; Satterlee, L.D.; Miller, G.A. A Multienzyme Technique for Estimating Protein Digestibility. J. Food Sci. 1977, 42, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa Cárdenas, J.D.; Godinez, M.G.A.; Méndez, N.L.V.; Guzmán, A.L.; Acosta, L.M.F.; González-Hernández, J. Fortificacion y evaluacion de tortillas de nixtamal. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2001, 51, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Tomic, J.; Torbica, A.; Popovic, L.; Rakita, S.; Zivancev, D. Breadmaking potential and proteolytic activity of wheat varieties from two production years with different climate conditions. Food Feed Res. 2015, 42, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, K.A.; Barry-Ryan, C.; Burke, R.; Hussey, K.; McCarthy, S.; Gallagher, E. Effect of pulse flours on the physiochemical characteristics and sensory acceptance of baked crackers. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbas, B.; Machado, N.; Oppolzer, D.; Ferreira, L.; Brites, C.; Rosa, E.A.S.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Comparison of near-infrared (NIR) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopy for the determination of nutritional and antinutritional parameters in common beans. Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, R.; Orúe, E.; Zabalza, M.J.; Grant, G.; Marzo, F. Effect of extrusion cooking on structure and functional properties of pea and kidney bean proteins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.S.M.; Hucl, P. Amino acid composition and in vitro protein digestibility of selected ancient wheats and their end products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2002, 15, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.S.; Talou, T.; Straumite, E.; Sabovics, M.; Kruma, Z.; Saad, Z.; Hijazi, A.; Mera, O. Protein bread fortification with cumin and caraway seeds and by-product flour. Foods 2018, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, F.; Dowell, E.; Sun, X.S. Using Visible and Near-Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy and Differential Scanning Calorimetry to Study Starch, Protein, and Temperature Effects on Bread Staling. Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Ramos, D.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.D.; Véles-Medina, J.J.; Salazar, R. Physicochemical properties of nixtamalized black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flours. Food Chem. 2017, 240, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jongh, H.H.J.; Broerse, K. Application Potential of Food Protein Modification. In Advances in Chemical Engineering, 1st ed.; Nawaz, Naveed, S., Eds.; In TEch: London, UK, 2012; Volume 1, p. 584. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Taylor, C.; Nebl, T.; Ng, K.; Bennett, L.E. Effects of chemicpp. al composition and baking on in vitro digestibility of proteins in breads made from selected gluten-containing and gluten-free flours. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes Almeida Sá, C.B.; Franco, M.Y.M.; Mattar, B.A.C. Food processing for the improvement of plant proteins digestibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 3367–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T.; Álvarez, C.; Bobo, G.; Aguiló-Aguayo, I. Characterization of functional properties of proteins from Ganxet beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L. var. Ganxet) isolated using an ultrasound-assisted methodology. LWT 2018, 98, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazaridou, A.; Duta, D.; Papageorgiou, M.; Belc, N.; Biliaderis, C.G. Effects of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality parameters in gluten-free formulations. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H. Chemistry of gluten proteins. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, M.M.; Díaz, Á.; Gómez, M. Effect of different microstructural features of soluble and insoluble fibres on gluten-free dough rheology and bread-making. J. Food Eng. 2014, 142, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients | Control Bread | Bread with Black Bean | Bread with Ayocote Bean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 10 | 20 | 30 | ||
| Wheat flour | 100 | 90 | 80 | 70 | 90 | 80 | 70 |
| Ayocote flour | - | 10 | 20 | 30 | - | - | - |
| Black bean flour | - | - | - | - | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Yeast | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Milk power | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Sugar | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Salt | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Water | 63 | 63 | 63 | 63 | 63 | 63 | 63 |
| Butter | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Samples | Crude Protein (%) | Ash (%) | Crude Fiber (%) | Crude Fat (%) | Carbohydrates (%) | Energy Value (Kcal/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) flour | 21.06 ± 0.13 | 4.20 ± 0.04 | 3.06 ± 0.07 | 1.68 ± 0.26 | 59.43 ± 1.22 | 342.20 ± 0.12 |
| Ayocote bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.) flour | 23.94 ± 0.36 | 3.70 ± 0.13 | 5.21 ± 0.53 | 1.31 ± 0.02 | 56.36 ± 1.28 | 343.41 ± 0.34 |
| Control bread | 12.60 ± 0.06 d | 0.19 ± 0.01 c | 0.57 ± 0.09 c | 9.63 ± 0.31 b | 52.31 ± 1.43 a | 347.45 ± 0.05 f |
| Bread with black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) | ||||||
| 10% | 14.67 ± 0.12 c | 0.23 ± 0.03 c | 0.71 ± 0.12 c | 11.53 ± 0.35 a | 48.86 ± 1.55 ab | 359.31 ± 0.10 c |
| 20% | 15.23 ± 0.09 bc | 0.27 ± 0.02 b | 0.98 ± 0.17 c | 11.67 ± 0.37 a | 50.70 ± 1.31 ab | 370.71 ± 0.07 b |
| 30% | 15.72 ± 0.06 ab | 0.34 ± 0.07 a | 1.24 ± 0.13 b | 11.90 ± 0.18 a | 49.98 ± 0.35 ab | 372.38 ± 0.09 a |
| Bread with ayocote bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.) | ||||||
| 10% | 14.84 ± 0.10 bc | 0.21 ± 0.04 c | 1.61 ± 0.22 b | 8.62 ± 0.45 c | 50.32 ± 1.18 ab | 341.44 ± 0.35 g |
| 20% | 16.33 ± 0.10 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 b | 2.03 ± 0.45 a | 10.32 ± 0.18 b | 48.20 ± 1.79 b | 355.06 ± 0.08 e |
| 30% | 16.88 ± 0.09 a | 0.39 ± 0.04 a | 2.18 ± 0.28 a | 9.63 ± 0.29 b | 49.47 ± 1.63 ab | 356.43 ± 0.09 d |
| Melting of Retrograded Starch | Starch Gelatinization | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | ToR (°C) | TpR (°C) | TfR (°C) | ΔH (J/g) | To g (°C) | Tpg (°C) | Tf g (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
| Black bean flour | 73.44 | 85.80 | 93.48 | 3.15 | ||||
| Ayocote bean flour | 62.08 | 72.66 | 83.78 | 4.49 | ||||
| Control bread | 45.83 ± 1.87 a | 55.32 ± 0.35 a | 65.65 ± 0.47 a | 0.26 ± 0.08 a | ||||
| Bread with black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) | ||||||||
| 10% | 47.67 ± 2.13 a | 53.55 ± 0.10 b | 62.25 ± 0.21 b | 0.21 ± 0.05 a | 70.93 ± 0.28 bc | 80.03 ± 0.17 b | 86.13 ± 0.22 c | 0.14 ± 0.01 c |
| 20% | 45.33 ± 0.48 a | 53.83 ± 0.35 b | 62.96 ± 0.48 b | 0.28 ± 0.05 a | 67.40 ± 0.39 e | 81.63 ± 0.49 a | 86.46 ± 0.57 c | 0.27 ± 0.05 bc |
| 30% | 73.10 ± 0.54 a | 79.83 ± 0.12 b | 84.51 ± 0.34 d | 0.56 ± 0.08 a | ||||
| Bread with ayocote bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.) | ||||||||
| 10% | 66.72 ± 0.48 d | 74.50 ± 0.12 c | 89.12 ± 0.47 b | 0.18 ± 0.04 c | ||||
| 20% | 72.44 ± 0.44 ab | 73.18 ± 0.23 d | 90.12 ± 0.34 ab | 0.22 ± 0.10 | ||||
| 30% | 70.35 ± 1.01 c | 74.25 ± 0.18 c | 90.17 ± 0.12 a | 0.44 ±0.05 ab | ||||
| Melting of Amylose-Lipid Complexes + Protein Denaturalization | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | ToAMLC+PD (°C) | TpAMLC+PD (°C) | TfAMLC+PD (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
| Black bean flour | 97.70 ± 0.34 | 101.95 ± 0.54 | 106.17 ± 0.32 | 1.65 ± 0.09 |
| Ayocote bean flour | 90.21 ± 0.26 | 96.47 ± 0.41 | 103.02 ± 0.17 | 1.71 ± 0.06 |
| Control bean | 100.05 ± 0.14 b | 106.48 ± 0.47 a | 113.20 ± 0.20 a | 0.78 ± 0.04 d |
| Bread with black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) | ||||
| 10% | 89.28 ± 0.27 e | 105.57 ± 0.45 a | 109.55 ± 0.55 bc | 0.68 ± 0.07 d |
| 20% | 88.25 ± 0.25 f | 102.43 ± 0.60 b | 109.83 ± 0.63 bc | 0.97 ± 0.06 d |
| 30% | 101.97 ± 0.50 a | 106.47 ± 0.27 a | 109.90 ± 0.49 b | 1.38 ± 0.08 c |
| Bread with ayocote bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.) | ||||
| 10% | 94.34 ± 0.56 c | 102.46 ± 0.26 b | 108.12 ± 0.12 cd | 1.48 ± 0.19 c |
| 20% | 95.14 ± 0.34 c | 103.13 ± 0.33 b | 108.63 ± 0.63 bcd | 2.08 ± 0.08 b |
| 30% | 93.17 ± 0.27 d | 103.59 ± 0.97 b | 106.97 ± 1.14 d | 2.50 ± 0.18 a |
| Samples | % | Color | Sensorial Analysis b | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | A* | B* | Odor | Flavor | Texture | Color | ||
| Control | 65.25 ± 0.18 a | 5.07 ± 0.07 a | 15.32 ± 0.07 a | 4.25 ± 0.48 a | 4.15 ± 0.48 a | 4.15 ± 0.63 a | 3.85 ± 0.81 a | |
| Black bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) breads | 10 | 58.57 ± 0.10 d | 2.80 ± 0.05 d | 10.70 ± 0.12 e | 3.80 ± 0.69 ab | 3.80 ± 0.69 a | 3.75 ± 0.71 a | 3.85 ± 0.81 ab |
| 20 | 58.51 ± 0.41 d | 1.95 ± 0.08 e | 8.83 ± 0.14 f | 2.95 ± 0.94 bc | 2.90 ± 0.85 b | 2.50 ± 0.88 b | 2.90 ± 0.78 cd | |
| 30 | 54.56 ± 0.51 e | 1.63 ± 0.08 f | 6.98 ± 0.16 g | 1.85 ± 1.08 d | 1.95 ± 0.88 c | 2.30 ± 0.86 b | 2.05 ± 0.75 e | |
| Ayocote (Phaseolus coccineus L.) breads | 10 | 63.55 ± 0.30 b | 4.72 ± 0.15 b | 14.55 ± 0.24 b | 3.95 ± 0.68 a | 3.79 ± 1.05 a | 3.55 ± 0.71 a | 3.80 ± 0.73 a |
| 20 | 62.51 ± 0.28 c | 4.12 ± 0.01 c | 13.10 ± 0.09 c | 2.20 ± 1.00 cd | 2.45 ± 0.75 bc | 2.35 ± 0.67 b | 3.00 ± 0.65 cd | |
| 30 | 62.26 ± 0.46 c | 3.90 ± 0.05 c | 12.43 ± 0.10 d | 1.80 ± 1.00 d | 2.10 ± 0.78 c | 2.20 ± 0.85 b | 2.55 ± 0.51 de | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mariscal-Moreno, R.M.; Chuck-Hernández, C.; Figueroa-Cárdenas, J.d.D.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O. Physicochemical and Nutritional Evaluation of Bread Incorporated with Ayocote Bean (Phaseolus coccineus) and Black Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Processes 2021, 9, 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101782
Mariscal-Moreno RM, Chuck-Hernández C, Figueroa-Cárdenas JdD, Serna-Saldivar SO. Physicochemical and Nutritional Evaluation of Bread Incorporated with Ayocote Bean (Phaseolus coccineus) and Black Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Processes. 2021; 9(10):1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101782
Chicago/Turabian StyleMariscal-Moreno, Rosa María, Cristina Chuck-Hernández, Juan de Dios Figueroa-Cárdenas, and Sergio O. Serna-Saldivar. 2021. "Physicochemical and Nutritional Evaluation of Bread Incorporated with Ayocote Bean (Phaseolus coccineus) and Black Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris)" Processes 9, no. 10: 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101782
APA StyleMariscal-Moreno, R. M., Chuck-Hernández, C., Figueroa-Cárdenas, J. d. D., & Serna-Saldivar, S. O. (2021). Physicochemical and Nutritional Evaluation of Bread Incorporated with Ayocote Bean (Phaseolus coccineus) and Black Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Processes, 9(10), 1782. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9101782