Performance, Emissions, Combustion and Vibration Analysis of a CI Engine Fueled with Coconut and Used Palm Cooking Oil Methyl Ester
Abstract
1. Introduction
Purpose of Study
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Test Fuels and Engine Operating Conditions
2.2. Test Engine
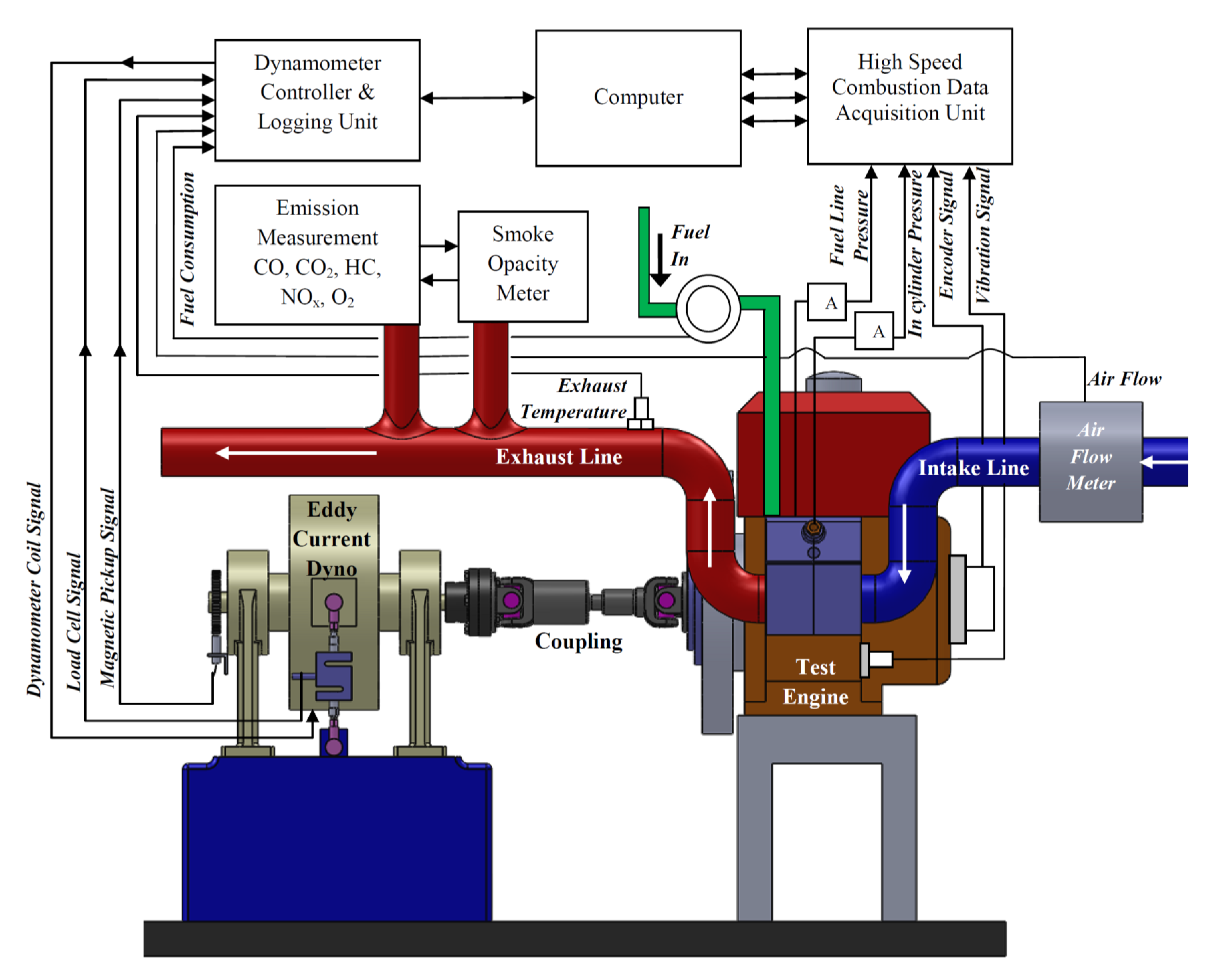
2.3. Test Bed Configuration and Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Engine Performance Characteristics
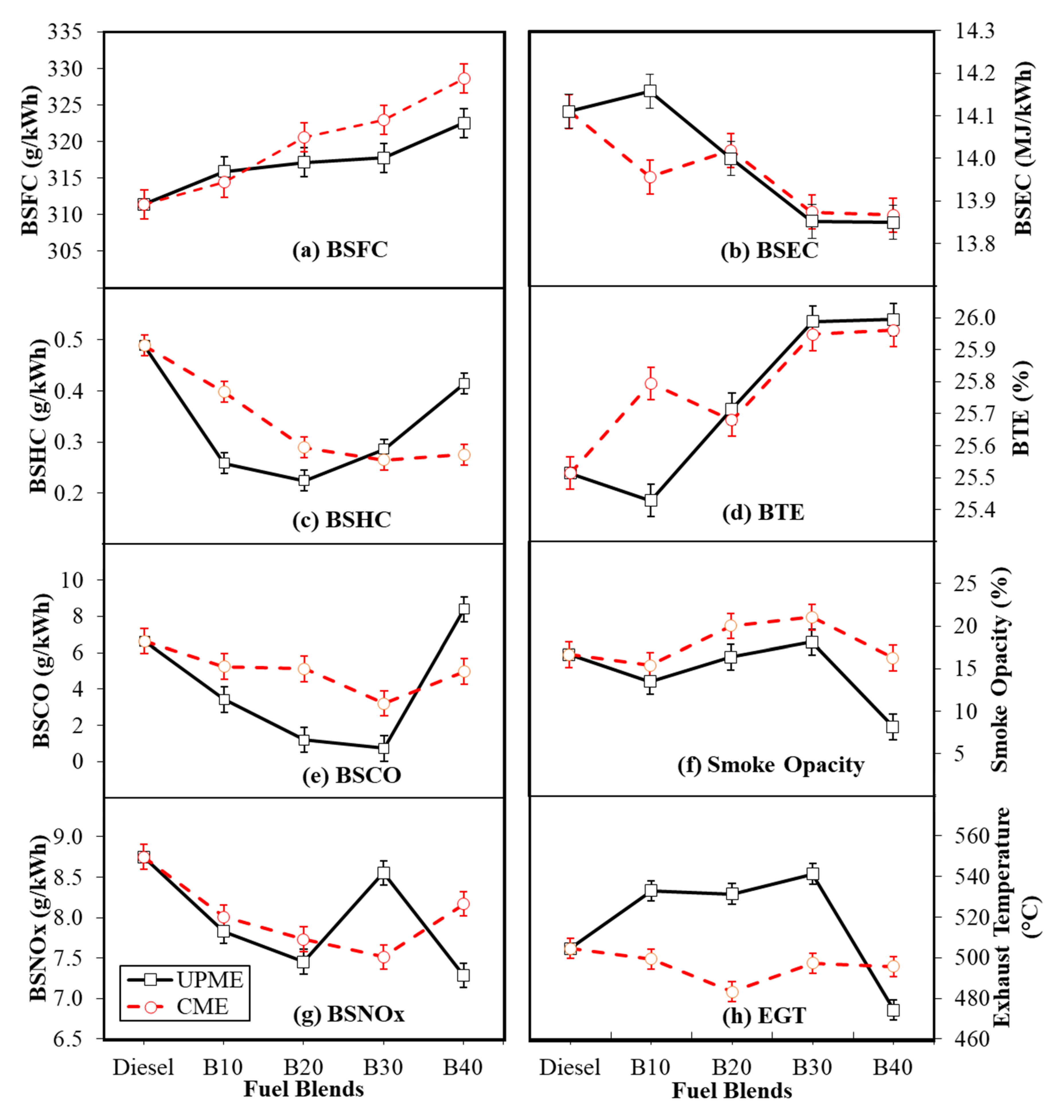
3.1.1. Brake Specific Fuel Consumption
3.1.2. Brake Specific Energy Consumption
3.1.3. Brake Thermal Efficiency
3.2. Exhaust Emissions Characteristics
3.2.1. Brake Specific Hydrocarbon
3.2.2. Brake Specific Carbon Monoxide
3.2.3. Brake Specific Nitrogen Oxide
3.2.4. Smoke Opacity
3.2.5. Exhaust Gas Temperature
3.3. Combustion Characteristics
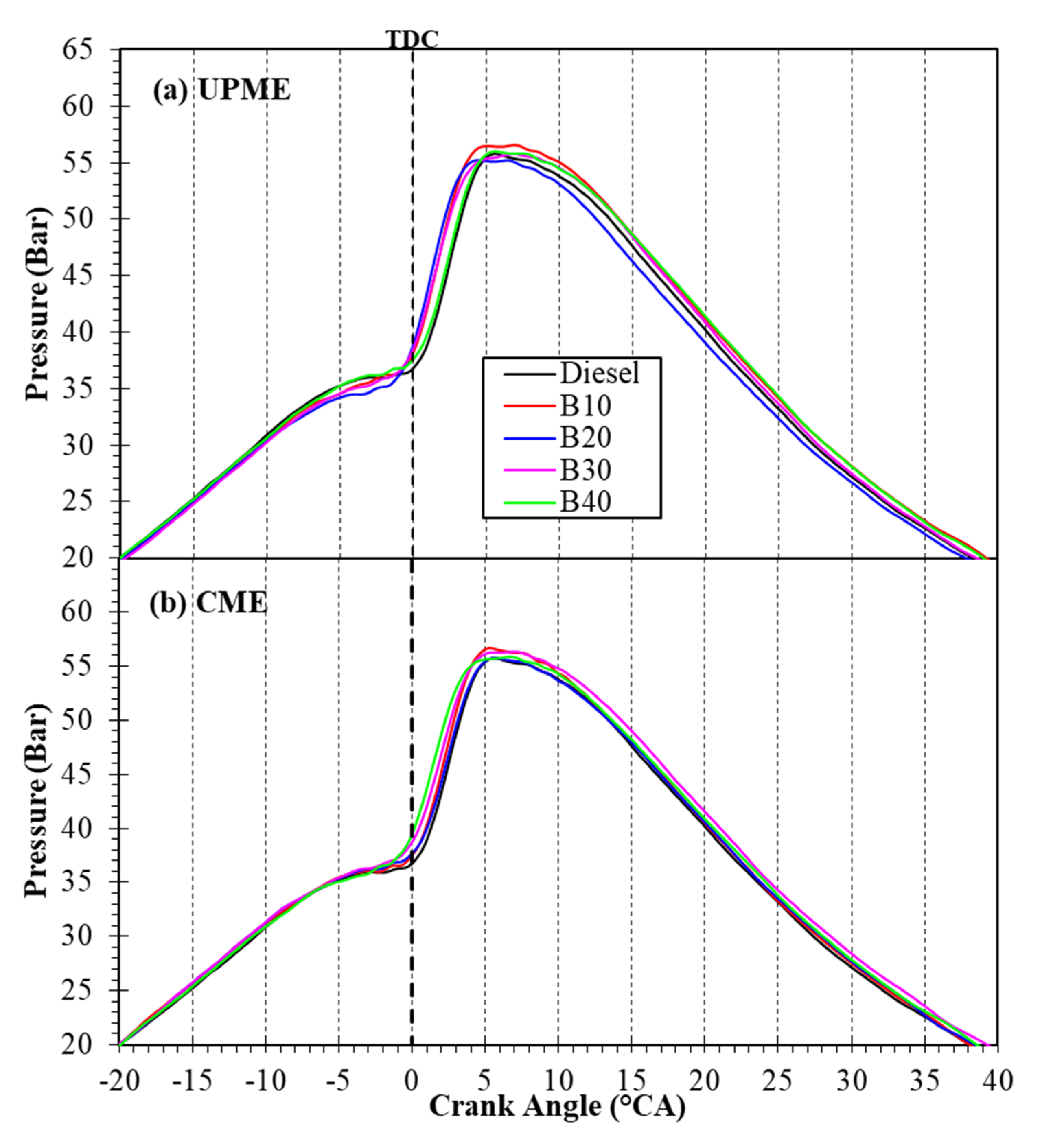
3.3.1. In-Cylinder Combustion Pressure
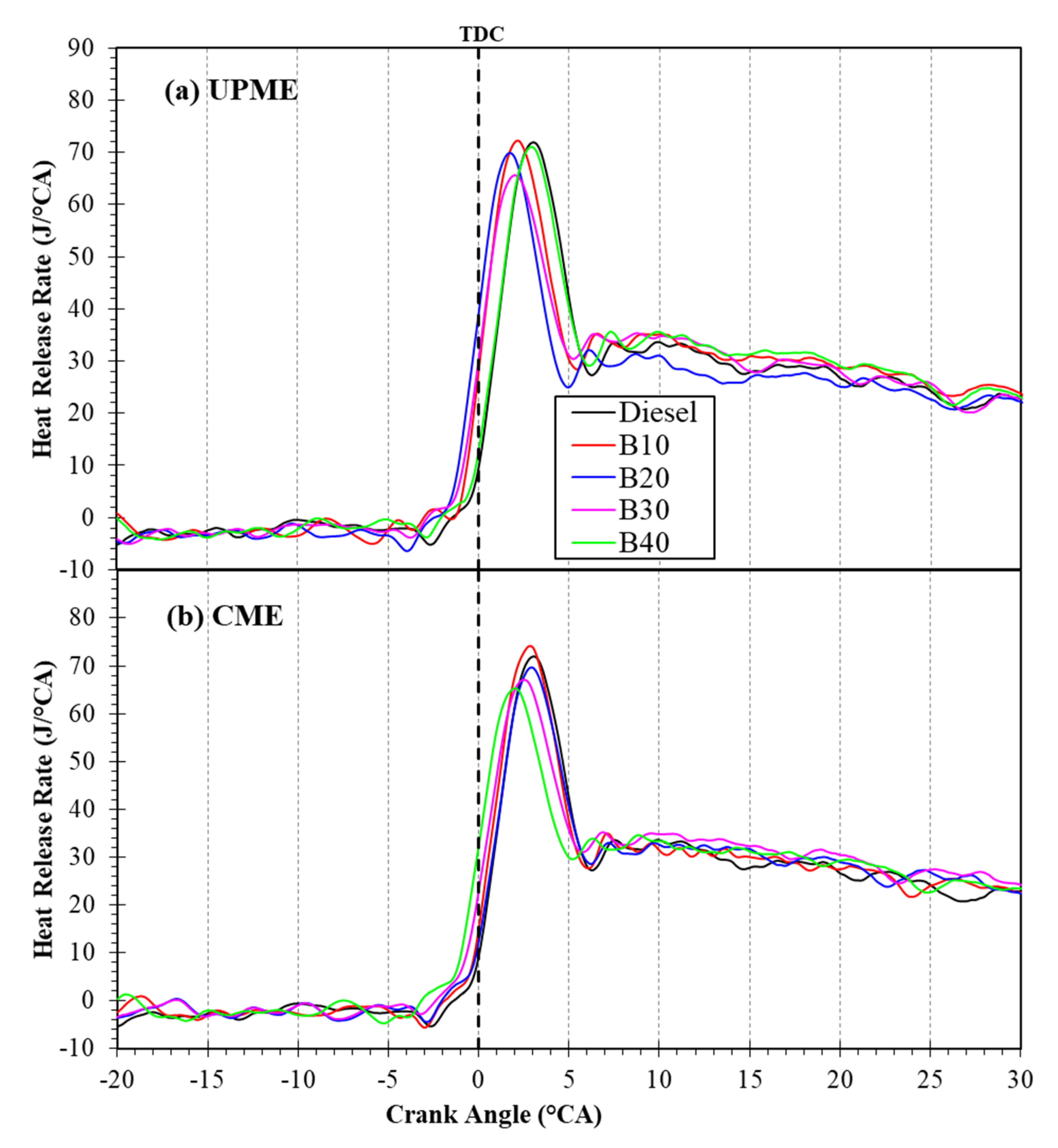
3.3.2. Heat Release Rate
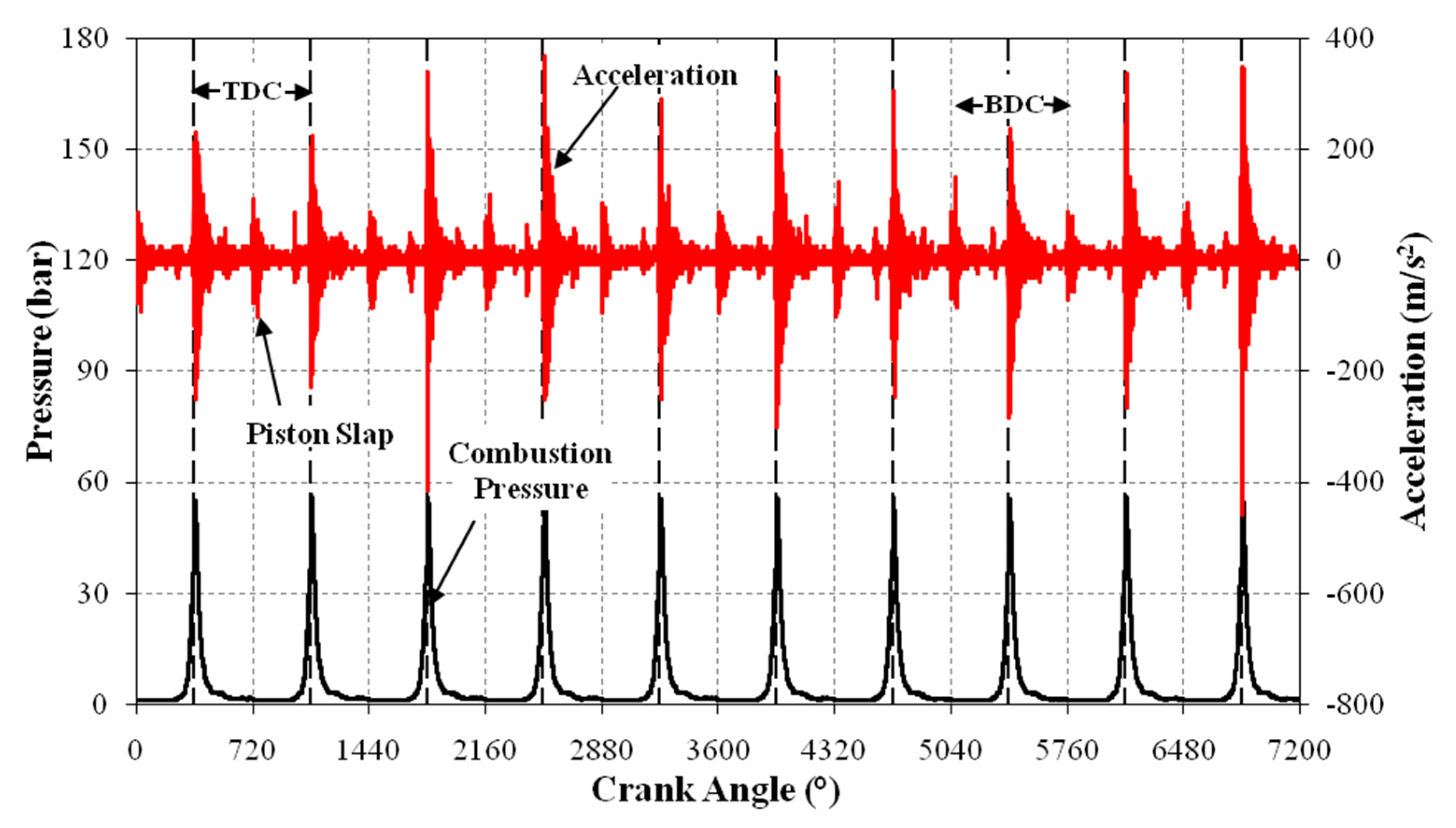
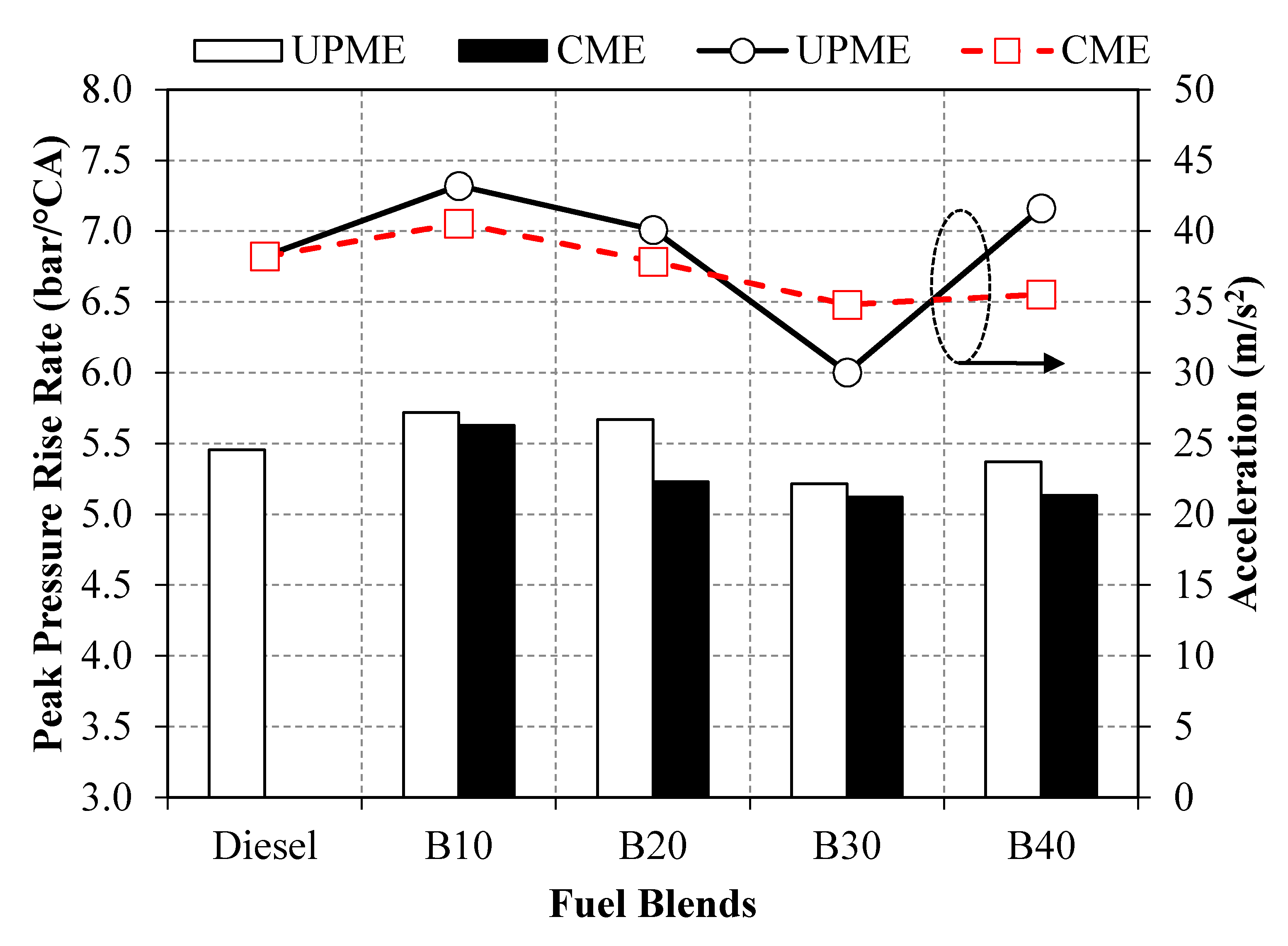
3.4. Vibration Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, Y.C.; Singh, B. Development of biodiesel: Current scenario. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA, USEPA. Sources of Greenhouse Gas Emissions|Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/sources-greenhouse-gas-emissions (accessed on 11 July 2020).
- Graboski, M.S.; McCormick, R.L. Combustion of fat and vegetable oil derived fuels in diesel engines. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1998, 24, 125–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhas, A.S.; Jayaraj, S.; Muraleedharan, C. Use of vegetable oils as I.C. engine fuels—A review. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, M.P.; Dwivedi, G. Impact of ternary blends of biodiesel on diesel engine performance. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, N.; Shrivastava, D.; Shrivastava, V. Experimental investigation of performance and emission characteristics of diesel engine using Jatropha biodiesel with alumina nanoparticles. Int. J. Green Energy 2018, 15, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudul, H.M.; Hagos, F.Y.; Mamat, R.; Adam, A.A.; Ishak, W.F.W.; Alenezi, R. Production, characterization and performance of biodiesel as an alternative fuel in diesel engines—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caresana, F. Impact of biodiesel bulk modulus on injection pressure and injection timing. The effect of residual pressure. Fuel 2011, 90, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szybist, J.P.; Song, J.; Alam, M.; Boehman, A.L. Biodiesel combustion, emissions and emission control. Fuel Process. Technol. 2007, 88, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.J.; Boehman, A.L.; Martin, G.C. An Experimental Investigation of the Origin of Increased NOx Emissions When Fueling a Heavy-Duty Compression-Ignition Engine with Soy Biodiesel. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2009, 2, 789–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.F.E.; Zhing, S.S.; Bilong Bugik, C. Biodiesel unsaturation degree effects on diesel engine NOx emissions and cotton wick flame temperature. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 90, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Yang, W.M.; Chou, S.K.; Chua, K.J. Combustion and emissions characteristics of diesel engine fueled by biodiesel at partial load conditions. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, B.; Raman, A.A.A.; Arandiyan, H. A comprehensive review on properties of edible and non-edible vegetable oil-based biodiesel: Composition, specifications and prediction models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 63, 62–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, M.; Kalam, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Bhuiya, M.M.K.; Mofijur, M. An experimental investigation into biodiesel stability by means of oxidation and property determination. Energy 2012, 44, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, J.G. Performance and Emission Characteristics of CI Engine Fueled by Coconut Oil Methyl Ester. SAE Int. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakpong, P.; Wootthikanokkhan, S. High free fatty acid coconut oil as a potential feedstock for biodiesel production in Thailand. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1682–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, E.; Myo, T.; Hamasaki, K.; Tajima, H.; Kun, Z.R. Diesel Combustion Characteristics of Coconut Oil and Palm Oil Biodiesels. SAE Int. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Yoshida, K.; Shoji, H.; Iijima, A. The Application of Coconut-oil Methyl Ester for Diesel Engine. Soc. Automot. Eng. Jpn. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hajjari, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M.; Ghanavati, H. A review on the prospects of sustainable biodiesel production: A global scenario with an emphasis on waste-oil biodiesel utilization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirvel, S.; Layek, A.; Muthuraman, S. Exploration of waste cooking oil methyl esters (WCOME) as fuel in compression ignition engines: A critical review. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, R.; Kannan, G.R.; Nagarajan, S.; Velmathi, S. Performance Emission and Combustion Characteristics of a Diesel Engine Fueled with Biodiesel Produced from Waste Cooking Oil. SAE Int. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolesi de Araújo, C.D.; de Andrade, C.C.; de Souza e Silva, E.; Dupas, F.A. Biodiesel production from used cooking oil: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, A.M.A.; Hassaneen, A.E. Influence of diesel fuel blended with biodiesel produced from waste cooking oil on diesel engine performance. Fuel 2016, 167, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Bae, C.; Gupta, T. Application of waste cooking oil (WCO) biodiesel in a compression ignition engine. Fuel 2016, 176, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, K.A.; El Morsi, A.K.; Sayed, M.M.; Shaib, A.A.E.; Gad, M.S. Effect of waste cooking-oil biodiesel on performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, K.; Vasudevan, D. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a variable compression ratio engine using methyl esters of waste cooking oil and diesel blends. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3959–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareh, P.; Zare, A.A.; Ghobadian, B. Comparative assessment of performance and emission characteristics of castor, coconut and waste cooking based biodiesel as fuel in a diesel engine. Energy 2017, 139, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, H.; Teoh, Y.; Masjuki, H.; Kalam, M. Impact of coconut oil blends on particulate-phase PAHs and regulated emissions from a light duty diesel engine. Energy 2012, 48, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahan, K.A.; Kano, M. Biodiesel production from palm oil, its by-products, and mill effluent: A review. Energies 2018, 11, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarthy, M.; Saravanan, P.; Gowthaman, M.; Rose, C.; Kamini, N. Enzymatic transesterification for production of biodiesel using yeast lipases: An overview. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullen, J.; Saeed, K. Factors affecting biodiesel engine performance and exhaust emissions—Part II: Experimental study. Energy 2014, 72, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Khan, M.E.; Dubey, A.M.; Pal, A. Performance and emission characteristics of a transportation diesel engine operated with non-edible vegetable oils biodiesel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2016, 8, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfa, B.; Mishra, R.; Zhang, C.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D. Combustion and performance characteristics of CI (compression ignition) engine running with biodiesel. Energy 2013, 51, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, H.G.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Teoh, Y.H. An investigation of the engine performance, emissions and combustion characteristics of coconut biodiesel in a high-pressure common-rail diesel engine. Energy 2014, 69, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.K.; Khan, M.E.; Pal, A.; Ghosh, U. Performance and emission characteristics of a stationary diesel engine fuelled by Schleichera Oleosa Oil Methyl Ester (SOME) produced through hydrodynamic cavitation process. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, M.; Sharma, A.; Dwivedi, G. Performance evaluation of diesel engine using rice bran biodiesel. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, X.J.; Cheung, C.S.; Ning, Z.; Wei, L.; Huang, Z.H. Influence of engine load and speed on regulated and unregulated emissions of a diesel engine fueled with diesel fuel blended with waste cooking oil biodiesel. Fuel 2016, 180, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaramakrishnan, K. Investigation on performance and emission characteristics of a variable compression multi fuel engine fuelled with Karanja biodiesel–diesel blend. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, C.; Gumus, M. Impact of compression ratio and injection parameters on the performance and emissions of a DI diesel engine fueled with biodiesel-blended diesel fuel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2011, 31, 3182–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, O.S.; Pasa, V.M.D.; Belchior, C.R.P.; Sodré, J.R. Physical–chemical properties of waste cooking oil biodiesel and castor oil biodiesel blends. Fuel 2011, 90, 1700–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah, M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Rizwanul Fattah, I.M.; Ashraful, A.M.; Mobarak, H.M. Biodiesel production and performance evaluation of coconut, palm and their combined blend with diesel in a single-cylinder diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhan, S.; Saravanan, N.; Nagarajan, G.; Vedaraman, N. Effect of biodiesel unsaturated fatty acid on combustion characteristics of a DI compression ignition engine. Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapuerta, M.; Herreros, J.M.; Lyons, L.L.; García-Contreras, R.; Briceño, Y. Effect of the alcohol type used in the production of waste cooking oil biodiesel on diesel performance and emissions. Fuel 2008, 87, 3161–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.T.; Zhang, C.H. An experimental study on the performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine fuelled with soybean oil methyl ester. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D: J. Automob. Eng. 2008, 222, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H. Biodiesel from palmoil—An analysis of its properties and potential. Biomass Bioenergy 2002, 23, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utlu, Z.; Koçak, M.S. The effect of biodiesel fuel obtained from waste frying oil on direct injection diesel engine performance and exhaust emissions. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsezen, A.N.; Canakci, M.; Turkcan, A.; Sayin, C. Performance and combustion characteristics of a DI diesel engine fueled with waste palm oil and canola oil methyl esters. Fuel 2009, 88, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armas, O.; Yehliu, K.; Boehman, A.L. Effect of alternative fuels on exhaust emissions during diesel engine operation with matched combustion phasing. Fuel 2010, 89, 438–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcanli, M.; Akar, M.A.; Calik, A.; Serin, H. Using HHO (Hydroxy) and hydrogen enriched castor oil biodiesel in compression ignition engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 23366–23372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwanchareon, P.; Luengnaruemitchai, A.; Jai-In, S. Solubility of a diesel–biodiesel–ethanol blend, its fuel properties, and its emission characteristics from diesel engine. Fuel 2007, 86, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.-Q.; Hu, Z.-Y.; Lou, D.-M.; Li, Z.-J. Exhaust emissions from a light-duty diesel engine with Jatropha biodiesel fuel. Energy 2012, 39, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Nagarajan, G.; Lakshmi Narayana Rao, G.; Sampath, S. Combustion characteristics of a stationary diesel engine fuelled with a blend of crude rice bran oil methyl ester and diesel. Energy 2010, 35, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado, M.P.; Ballesteros, E.; Arnal, J.M.; Gómez, J.; López, F.J. Exhaust emissions from a Diesel engine fueled with transesterified waste olive oil. Fuel 2003, 82, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.L.; Reece, D.L. Emissions Testing with Blends of Esters of Rapeseed Oil Fuel With and Without a Catalytic Converter. SAE Int. 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjumea, P.; Agudelo, J.R.; Agudelo, A.F. Effect of the Degree of Unsaturation of Biodiesel Fuels on Engine Performance, Combustion Characteristics, and Emissions. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Sen, R. Fuel properties, engine performance and environmental benefits of biodiesel produced by a green process. Appl. Energy 2013, 105, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuszkowski, J.; Flaim, K.; Thompson, G. The Effect of Cetane Improvers and Biodiesel on Diesel Particulate Matter Size. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2011, 4, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, R.; Petru, C.; Edward, R.; Gheorghe, M. Fueling an D.I. agricultural diesel engine with waste oil biodiesel: Effects over injection, combustion and engine characteristics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 2158–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.K.; Davies, P.A. Combustion and Emission Characteristics of a Typical Biodiesel Engine Operated on Waste Cooking Oil Derived Biodiesel. SAE Int. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, M. Comprehensive Experimental Investigation of Combustion and Heat Release Characteristics of a Biodiesel (Hazelnut Kernel Oil Methyl Ester) Fueled Direct Injection Compression Ignition Engine. Fuel 2010, 89, 2802–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldhaidhawi, M.; Chiriac, R.; Badescu, V. Ignition delay, combustion and emission characteristics of Diesel engine fueled with rapeseed biodiesel—A literature review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 73, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyukkaya, E. Effects of biodiesel on a DI diesel engine performance, emission and combustion characteristics. Fuel 2010, 89, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, A.; Puhan, S.; Govindan, N. Effect of Unsaturated Fatty Acid Esters of Biodiesel Fuels on Combustion, Performance and Emission Characteristics of a DI Diesel Engine. Int. J. Energy Environ. 2010, 1, 411–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Cheung, C.S.; Huang, Z. Impact of chemical structure of individual fatty acid esters on combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine. Energy 2016, 107, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qate, M.; Pourabdian, M.; Javareshkian, A.; Farzbod, A. A Review of Ignition Delay and Combustion Characteristics of Biodiesel Fueled Diesel Engine. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 390, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Chen, J. Investigation into piston-slap-induced vibration for engine condition simulation and monitoring. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 282, 735–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Z.C.; Mohd Mishani, M.B.; Chong, W.T.; Soon, R.S.; Ong, H.C.; Ismail, Z. Identification of optimum Calophyllum inophyllum bio-fuel blend in diesel engine using advanced vibration analysis technique. Renew. Energy 2017, 109, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzomi, A.L.; Hesterman, D.C.; Stone, B.J. The effect of piston friction on the torsional natural frequency of a reciprocating engine. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 2833–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Alisaraei, A.; Ghobadian, B.; Tavakoli-Hashjin, T.; Mohtasebi, S.S. Vibration analysis of a diesel engine using biodiesel and petrodiesel fuel blends. Fuel 2012, 102, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiatti, G.; Chiavola, O.; Palmieri, F. Vibration and acoustic characteristics of a city-car engine fueled with biodiesel blends. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavola, O.; Chiatti, G.; Arnone, L.; Manelli, S. Combustion Characterization in Diesel Engine via Block Vibration Analysis. SAE Int. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavola, O.; Chiatti, G.; Recco, E. Accelerometer Measurements to Optimize the Injection Strategy. SAE Int. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, P.; Senthilkumar, A. Effects of oxygen enriched combustion on pollution and performance characteristics of a diesel engine. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Combustion Efficiency Impacts of Biofuels. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2009, 31, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Alisaraei, A.; Ghobadian, B.; Tavakoli-Hashjin, T.; Mohtasebi, S.S.; Rezaei-asl, A.; Azadbakht, M. Characterization of engine’s combustion-vibration using diesel and biodiesel fuel blends by time-frequency methods: A case study. Renew. Energy 2016, 95, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Thomas, R.; Gray, C.L. An HCCI Engine: Power Plant for a Hybrid Vehicle. SAE Int. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Properties | Test Method | Diesel | UPME | CME | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon chain length distribution (wt. %) | Gas Chromatograph-Flame Ionization detector (GC-FID) | ||||
| Saturated fatty acid | C 8:0 | - | <0.01 | 10.56 | |
| C 10:0 | - | <0.01 | 8.38 | ||
| C 12:0 | - | 0.69 | 43.11 | ||
| C 14:0 | - | 1.35 | 14.01 | ||
| C 16:0 | - | 38.91 | 7.86 | ||
| C 18:0 | - | 4.75 | 2.84 | ||
| C 20:0 | - | 0.4 | <0.01 | ||
| Monounsaturated fatty acid | C 16:1 | - | 0.48 | <0.01 | |
| C 18:1 | - | 42.27 | 9.7 | ||
| Polyunsaturated fatty acid | C 18:2 | - | 10.42 | 3.51 | |
| C 18:3 | - | 0.76 | <0.01 | ||
| Fatty acid saturation/unsaturation ratio (wt. %/wt. %) | - | 46.1/53.9 | 86.8/13.2 | ||
| Cetane index | ASTM D976 | 52 | 59 | 56 | |
| Flash point, °C | ASTM D93 | 92 | 184 | 162 | |
| Density (40 °C), kg/m3 | ASTM D7042 | 838.4 | 862.35 | 880.5 | |
| Kinematic viscosity (40 °C), mm2/s | ASTM D7042 | 3.815 | 5.199 | 6.692 | |
| Heating value, MJ/kg | ASTM D4809 | 45.31 | 39.74 | 37.85 | |
| Property | Units | UPME | CME | Test Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B10 | B20 | B30 | B40 | B10 | B20 | B30 | B40 | |||
| Heating value | MJ/kg | 44.82 | 44.14 | 43.59 | 42.94 | 44.39 | 43.73 | 42.96 | 42.20 | ASTM D4809 |
| Kinematic viscosity (40 °C) | mm2/s | 3.971 | 3.916 | 4.100 | 4.337 | 4.176 | 4.372 | 4.616 | 4.860 | ASTM D7042 |
| Dynamic viscosity (40 °C) | mPa·s | 3.331 | 3.293 | 3.461 | 3.676 | 3.513 | 3.701 | 3.937 | 4.163 | ASTM D7042 |
| Density (40 °C) | kg/m3 | 838.7 | 841.1 | 844.1 | 847.5 | 841.3 | 846.5 | 852.8 | 856.6 | ASTM D7042 |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Engine model | Single cylinder, water cooled 4-stroke DI diesel |
| Bore | 92 mm |
| Stroke | 96 mm |
| Displacement | 638 cm3 |
| Compression Ratio | 17.7:1 |
| Continuous Rating Output | 10.5 hp @ 2400 rpm |
| 1-Hour Rating Output | 12.0 hp @ 2400 rpm |
| Injection Timing | 17 °BTDC |
| Injection Pressure Connecting Rod Length | 196 bar or 200 kg/cm2 149.5 mm |
| Equipment | Measurement Principle | Component | Measurement Range | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas analyzer | Non-dispersive infrared | Carbon monoxide (CO) | 0–10% Vol. | 0.01% Vol. |
| Non-dispersive infrared | Unburned hydrocarbon (HC) | 0–20,000 ppm Vol. | 1 ppm | |
| Electrochemical | Nitrogen oxides (NOx) | 0–5000 ppm Vol. | 1 ppm | |
| Electrochemical | Oxygen (O2) | 0–25% Vol. | 0.01% Vol. | |
| Calculation | Excess air ratio (λ) | 0–9999 | 0.001 | |
| Smoke opacimeter | Photodiode detector | Opacity (%) | 0–100% | 0.10% |
| Fuel | Start of Injection (SOI) °BTDC | Start of Combustion (SOC) °BTDC | Ignition Delay (°CA) | Pressure | Pressure Rise Rate (dP/dθ) | Heat Release Rate (HRR) | IMEP (Bar) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Value (Bar) | Location °ATDC | Peak Value (Bar/°CA) | Location °ATDC | Peak Value (J/°CA) | Location °ATDC | ||||||
| Diesel | 17 | 1 | 16 | 55.7 | 5.5 | 5.46 | 2.75 | 71.9 | 3 | 5.86 | |
| UPME | B10 | 17.25 | 1.25 | 16 | 56.5 | 7 | 5.72 | 1.75 | 72.2 | 2.25 | 6.37 |
| B20 | 17.25 | 1.75 | 15.5 | 55.2 | 4.5 | 5.67 | 1.5 | 69.9 | 1.75 | 5.87 | |
| B30 | 17.75 | 2 | 15.75 | 55.8 | 7 | 5.21 | 1.75 | 65.7 | 2 | 6.10 | |
| B40 | 17.5 | 2 | 15.5 | 55.9 | 5.75 | 5.37 | 2.5 | 71.0 | 3 | 5.99 | |
| CME | B10 | 17.25 | 1.5 | 15.75 | 56.6 | 5.25 | 5.63 | 2.5 | 74.0 | 2.75 | 5.93 |
| B20 | 17 | 1.75 | 15.25 | 55.8 | 5.5 | 5.23 | 2.5 | 69.6 | 3 | 6.00 | |
| B30 | 17.5 | 2 | 15.5 | 56.3 | 7 | 5.12 | 2 | 67.1 | 2.5 | 6.21 | |
| B40 | 17.5 | 3 | 14.5 | 55.9 | 6.75 | 5.13 | 1.5 | 65.4 | 2 | 6.03 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teoh, Y.H.; How, H.G.; Balakrishnan, N.K.; Le, T.D.; Nguyen, H.T. Performance, Emissions, Combustion and Vibration Analysis of a CI Engine Fueled with Coconut and Used Palm Cooking Oil Methyl Ester. Processes 2020, 8, 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080990
Teoh YH, How HG, Balakrishnan NK, Le TD, Nguyen HT. Performance, Emissions, Combustion and Vibration Analysis of a CI Engine Fueled with Coconut and Used Palm Cooking Oil Methyl Ester. Processes. 2020; 8(8):990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080990
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeoh, Yew Heng, Heoy Geok How, Navaneetha Krishnan Balakrishnan, Thanh Danh Le, and Huu Tho Nguyen. 2020. "Performance, Emissions, Combustion and Vibration Analysis of a CI Engine Fueled with Coconut and Used Palm Cooking Oil Methyl Ester" Processes 8, no. 8: 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080990
APA StyleTeoh, Y. H., How, H. G., Balakrishnan, N. K., Le, T. D., & Nguyen, H. T. (2020). Performance, Emissions, Combustion and Vibration Analysis of a CI Engine Fueled with Coconut and Used Palm Cooking Oil Methyl Ester. Processes, 8(8), 990. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080990






