Residue Char Derived from Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Sludge as Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
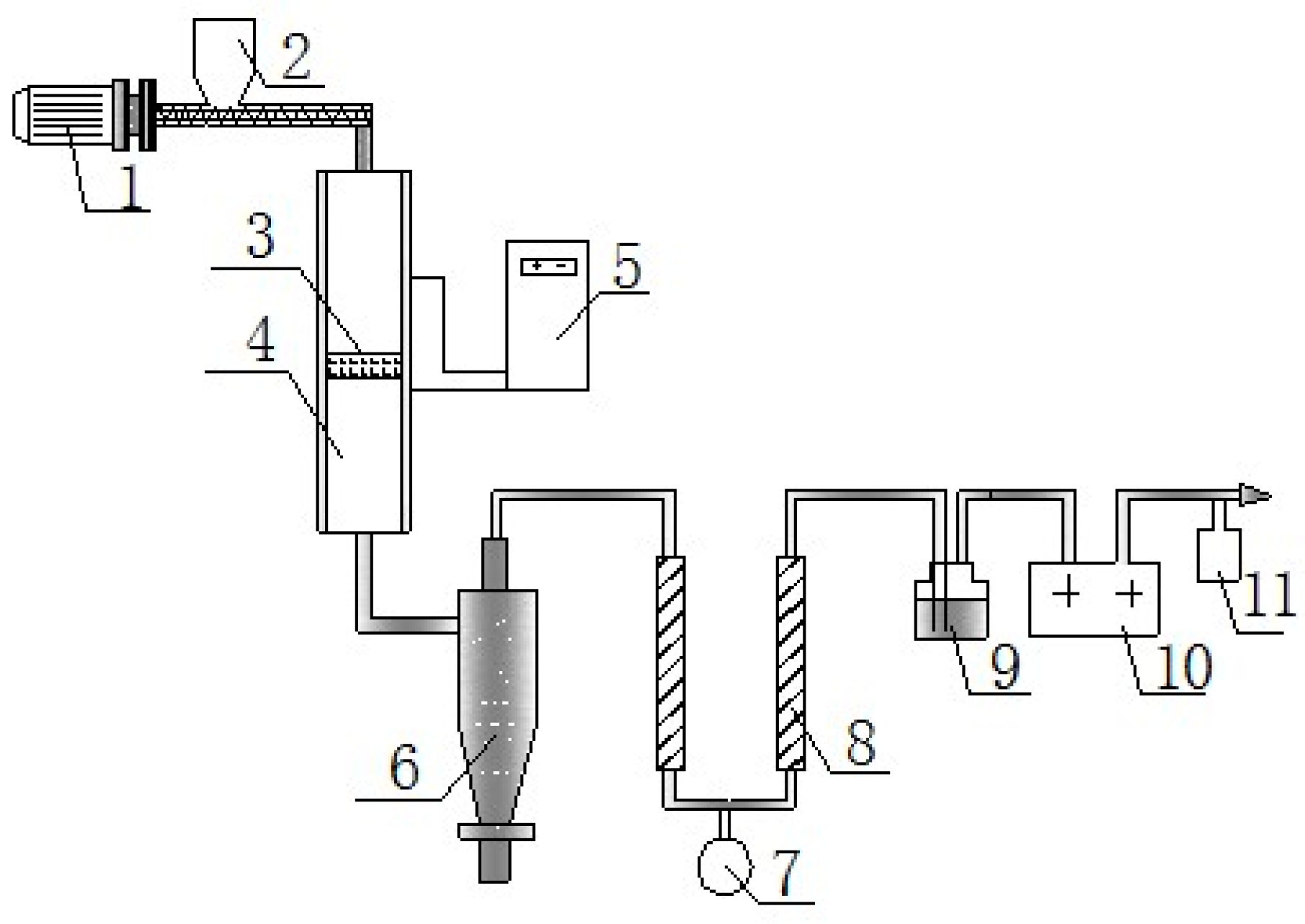
2.1. Preparation of Residue Char
2.2. Adsorption Procedures
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.6. The Apparent Adsorption Activation Energy
3. Results and Discussion
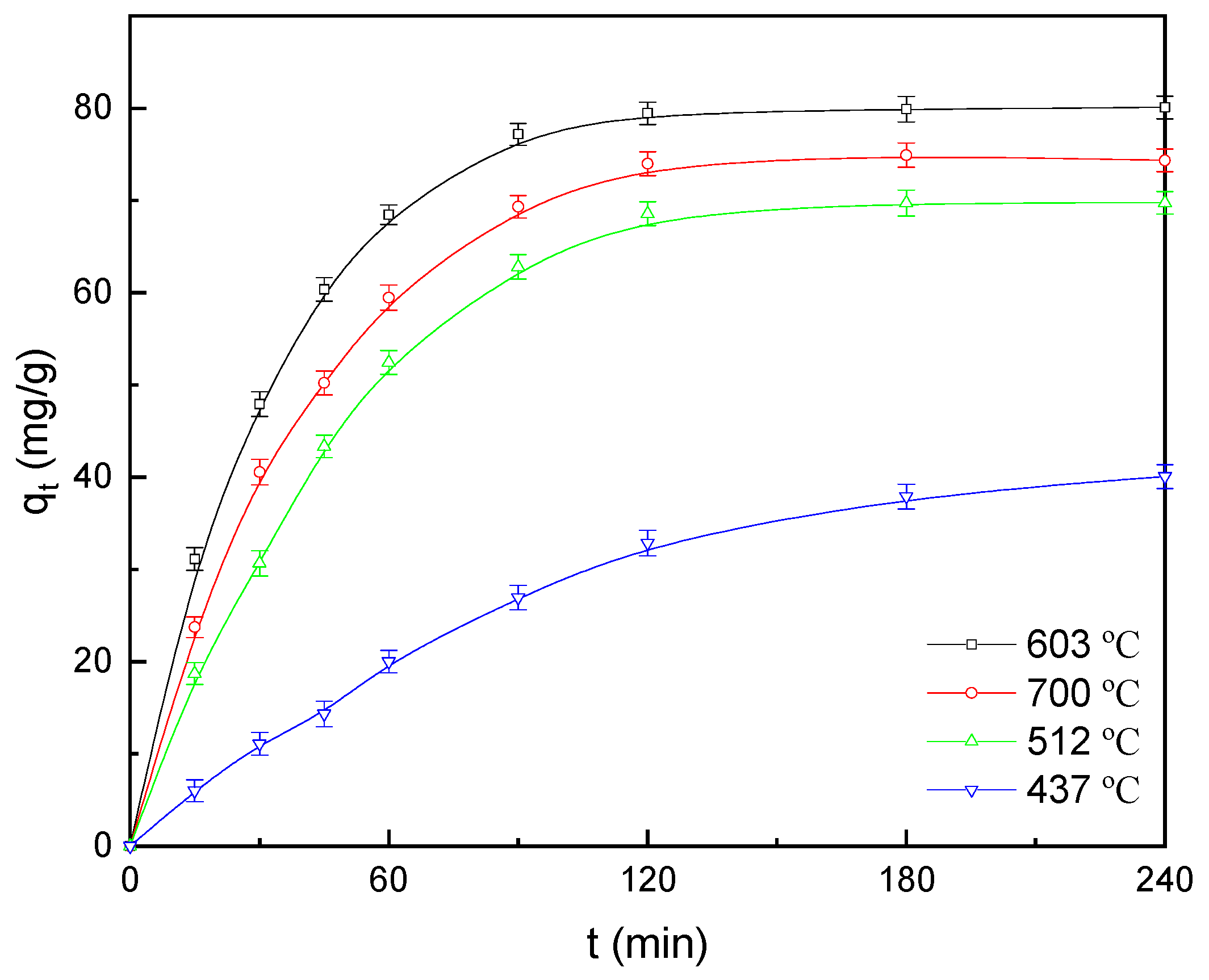
3.1. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature
3.2. Effect of Pyrolysis Time
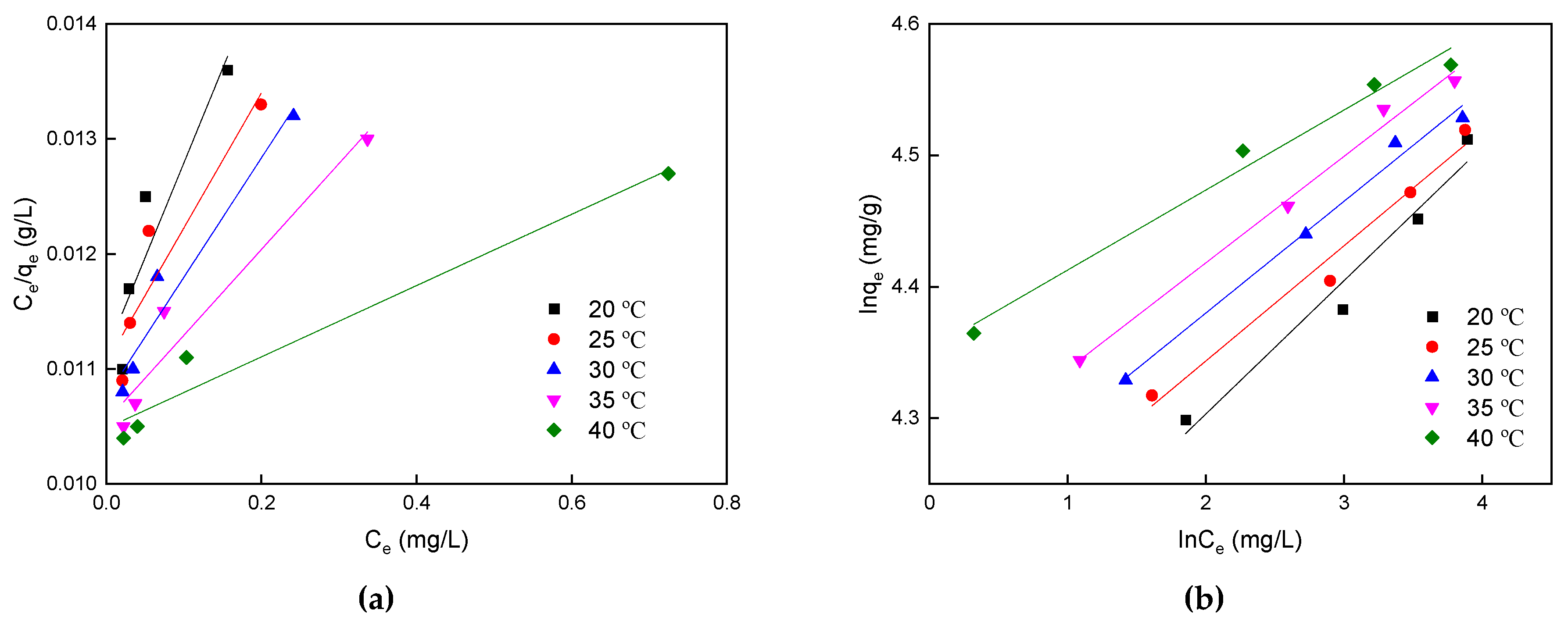
3.3. Equilibrium Isotherms
3.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
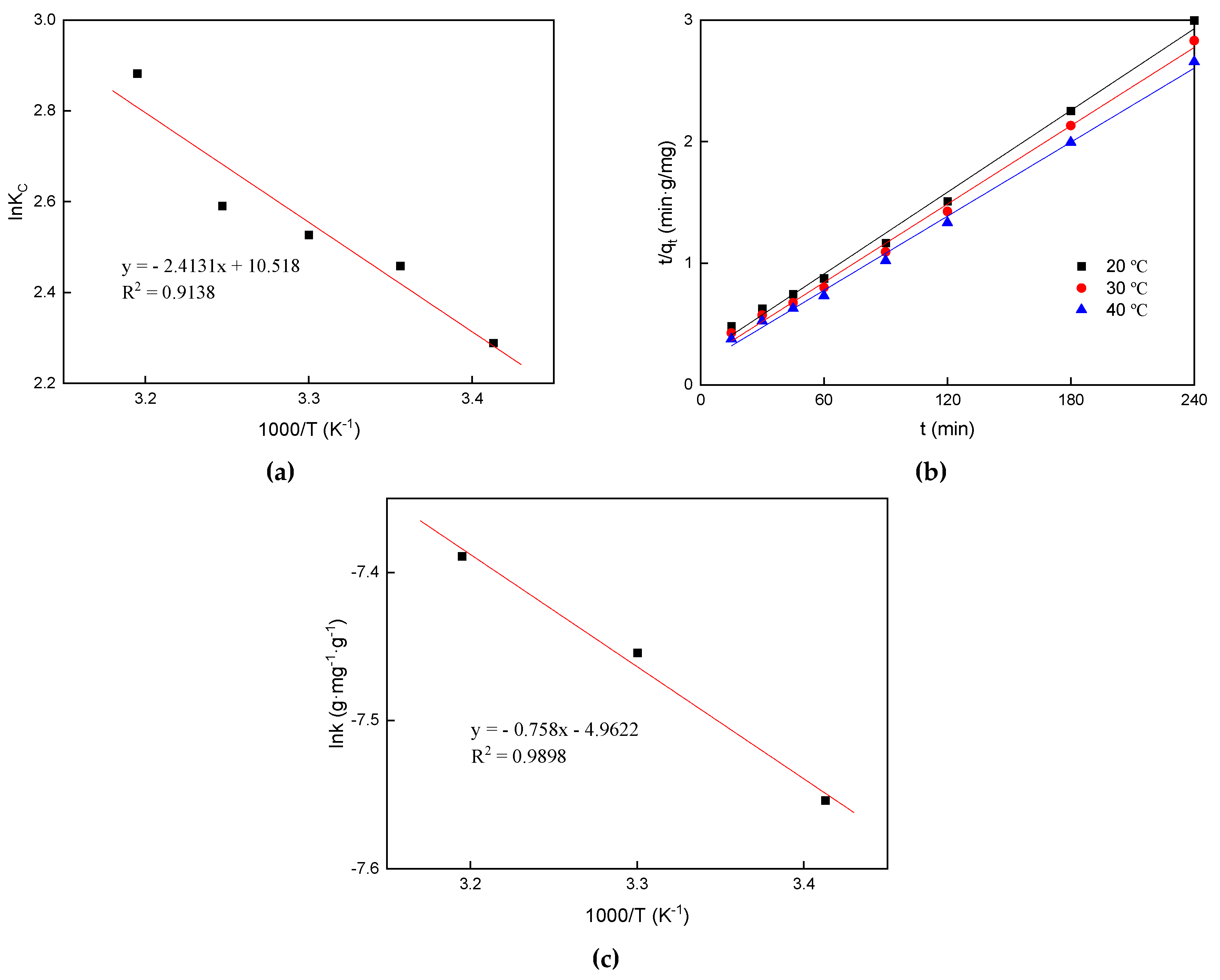
3.5. The Apparent Adsorption Activation Energy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anastopoulos, I.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Fu, J.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Use of nanoparticles for dye adsorption: Review. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, S.; Meng, Z.; Hong, Y.; Lin, C.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y. Graphene-supported biomimetic catalysts with synergistic effect of adsorption and degradation for efficient dye capture and removal. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.F.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.T.; Zhu, H.L. Photooxidation Degradation of Reactive Brilliant Red K-2BP in Aqueous Solution by Ultraviolet Radiation/Sodium Hypochlorite. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2009, 37, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadivelan, V.; Kumar, K.V. Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Ding, Y.H.; Ma, G.Y.; Yang, J.; Zeng, Q.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Xia, D.S.; Zhu, H.L.; An, S.Q. Removal of a Toxic Anthraquinone Dye by Combination of Red Mud Coagulation and Ozonation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2009, 31, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Li, X.; Ruan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Pan, F.; Li, Q.; Xia, D.; Fu, J. Adsorption-photocatalytic degradation of dye pollutant in water by graphite oxide grafted titanate nanotubes. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, B.; Creamer, A.E.; Cao, C.; Li, Y. Adsorption of VOCs onto engineered carbon materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 338, 102–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camu, E.; Pasten, B.; Matus, C.; Ramirez, F.; Ojeda, J.; Aguila, G.; Baeza, P. Simultaneous adsorption of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene and quinoline over Nickel and Boron modified Gamma-Al2O3 adsorbent. Processes 2020, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Carvalho, F.C.; do Nascimento, P.F.; de Souza, M.R.O.; Araujo, A.S. The efficiency of bimodal silica as a carbon dioxide adsorbent for natural gas treatment. Processes 2020, 8, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edet, U.A.; Ifelebuegu, A.O. Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic modeling of the adsorption of phosphates from model wastewater using recycled brick waste. Processes 2020, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolenko, A.; Shevelev, A.; Vikulova, M.; Blagova, T.; Altukhov, S.; Gorokhovsky, A.; Godymchuk, A.; Burmistrov, I.; Offor, P.O. Wastewater treatment from lead and strontium by potassium polytitanates: Kinetic analysis and adsorption mechanism. Processes 2020, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.; Zhu, J.; Huang, W.; Fang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, X.; Liao, K. Preparation of nano-porous carbon-silica composites and its adsorption capacity to volatile organic compounds. Processes 2020, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gargiulo, N.; Peluso, A.; Caputo, D. MOF-based adsorbents for atmospheric emission control: A review. Processes 2020, 8, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; You, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Lv, Y. Fabrication of ultrathin MoS2 nanosheets and application on adsorption of organic pollutants and heavy metals. Processes 2020, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Balsamo, M.; Montagnaro, F. A fractal-based correlation for time-dependent surface diffusivity in porous adsorbents. Processes 2020, 8, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, M.I.; Ibrahim, T.H.; Jumean, F.H.; Sara, Z.A.; Atallah, B.A. Cyclic sequential removal of alizarin red S Dye and Cr(VI) ions using wool as a low-cost adsorbent. Processes 2020, 8, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandaker, T.; Hossain, M.S.; Dhar, P.K.; Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, M.A.; Ahmed, M.B. Efficacies of carbon-based adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture. Processes 2020, 8, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marocco, A.; Dell’Agli, G.; Sannino, F.; Esposito, S.; Bonelli, B.; Allia, P.; Tiberto, P.; Barrera, G.; Pansini, M. Removal of agrochemicals fromwaters by adsorption: A critical comparison among humic-like substances, zeolites, porous oxides, and magnetic nanocomposites. Processes 2020, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, F.; Liu, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, N.; Qiu, Y. Methane adsorption interpreting with adsorption potential and its controlling factors in various rank coals. Processes 2020, 8, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veclani, D.; Tolazzi, M.; Melchior, A. Molecular interpretation of pharmaceuticals’ adsorption on carbon nanomaterials: Theory meets experiments. Processes 2020, 8, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, R.; Ren, B.; Yaseen, M.; Hursthouse, A. Enhancing the removal of Sb (III) from water: A Fe3O4@HCO composite adsorbent caged in sodium alginate microbeads. Processes 2020, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Tian, Y.; Chen, L.; Yin, L.; Zhang, J. Sulfur Transformation during Microwave and Conventional Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrafioti, E.; Bouras, G.; Kalderis, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Biochar production by sewage sludge pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogru, M.; Midilli, A.; Howarth, C.R. Gasification of sewage sludge using a throated downdraft gasifier and uncertainty analysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2002, 75, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Sikarwar, V.S.; He, J.; Dastyar, W.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M. Opportunities and challenges in sustainable treatment and resource reuse of sewage sludge: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 616–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motasemi, F.; Afzal, M.T. A review on the microwave-assisted pyrolysis technique. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ran, C.; Mao, X.; Kang, Q.; Ao, W.; Fu, J.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; et al. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of textile dyeing sludge, and migration and distribution of heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 355, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R. Microwave pyrolysis of oily sludge with activated carbon. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 3139–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Scale-up of microwave heating process for the production of bio-oil from sewage sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 94, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, A.; Menendez, J.A.; Inguanzo, M.; Pis, J.J. Production of bio-fuels by high temperature pyrolysis of sewage sludge using conventional and microwave heating. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimpae, S.; Wongsakulphasatch, S.; Vivanpatarakij, S.; Glinrun, T.; Wiwatwongwana, F.; Maneeprakorn, W.; Assabumrungrat, S. Syngas production from combined steam gasification of biochar and a sorption-enhanced water-gas shift reaction with the utilization of CO2. Processes 2019, 7, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, S. Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 modified biochar and its application in methylene blue removal from aqueous solution. Processes 2019, 7, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolaou, E.; Philippou, K.; Anastopoulos, I.; Pashalidis, I. Copper adsorption by magnetized pine-needle biochar. Processes 2019, 7, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddeeg, S.M.; Tahoon, M.A.; Rebah, F.B. Simultaneous removal of calconcarboxylic acid, NH4+ and PO43− from pharmaceutical effluent using iron oxide-biochar nanocomposite loaded with Pseudomonas putida. Processes 2019, 7, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, W.T.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, Y.Q.; Tsai, C.H.; Chen, W.S.; Chang, Y.T. Enhancing the pore properties and adsorption performance of cocoa pod husk (CPH)-Derived biochars via post-acid treatment. Processes 2020, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Xi, B.; He, X.; Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Ouche, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xue, C. Methane emission reduction enhanced by hydrophobic biochar-modified soil cover. Processes 2020, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, C.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Du, P.; Cui, F.; He, K. Role of extracellular polymeric substances in biosorption of Pb2+ by a high metal ion tolerant fungal strain Aspergillus niger PTN31. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Ofomaja, A.E. Pseudo-second-order model for lead ion sorption from aqueous solutions onto palm kernel fiber. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Wang, C.C. Pseudo-isotherms for the sorption of cadmium ion onto tree fern. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Zhou, J.L.; Wang, J.; Liang, H.; Li, G. Phosphorus elimination from aqueous solution using ‘zirconium loaded okara’ as a biosorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Yang, Y.; Mai, J.; Sun, W.; Zhang, C.; Wei, D.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue onto titanate nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y. Isotherms for the Sorption of Lead onto Peat: Comparison of Linear and Non-Linear Methods. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Mahapatra, K.; Ramteke, D.S.; Paliwal, L.J. Production of activated carbon from sludge of food processing industry under controlled pyrolysis and its application for methylene blue removal. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 95, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, R.; Xu, Q. Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.A.P.; Debacher, N.A.; Downs, A.J.; Cottet, L.; Mello, C.A.D. Removal of methylene blue from colored effluents by adsorption on montmorillonite clay. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 332, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; He, P.-W.; Luo, Y.; Lu, X.; Liang, Y.; Fu, J. Adsorption of Phosphate by Biomass Char Deriving from Fast Pyrolysis of Biomass Waste. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2012, 40, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethaib, S. Effects of microwave absorbers on the products of microwave pyrolysis of oily sludge. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Salema, A.A.; Ani, F.N. Microwave induced pyrolysis of oil palm biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3388–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.N.; Kim, S.C.; Yoshikawa, K. Pyrolysis gasification of dried sewage sludge in a combined screw and rotary kiln gasifier. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.; Dang, F.Q. Biomass-derived highly porous functional carbon fabricated by using a free-standing template for efficient removal of methylene blue. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 154, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Liang, B.; Liu, M.; Xu, X.; Cui, M. Effects of pyrolysis temperature, time and leaf litter and powder coal ash addition on sludge-derived adsorbents for nitrogen oxide. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 125, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franca, A.S.; Oliveira, L.S.; Nunes, A.A.; Alves, C.C. Microwave assisted thermal treatment of defective coffee beans press cake for the production of adsorbents. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.S.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.D. Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lua, A.C. Characterization of chars pyrolyzed from oil palm stones for the preparation of activated carbons. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 1998, 46, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.I.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olu-Owolabi, B.I.; Diagboya, P.N.; Adebowale, K.O. Evaluation of pyrene sorption–desorption on tropical soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Palma, P.R.; Parmigiani, A.; Huber, C.; Guyennon, N.; Viotti, P. Pore-scale simulations of concentration tails in heterogeneous porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 205, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Módenes, A.N.; Hinterholz, C.L.; Neves, C.V.; Sanderson, K.; Trigueros, D.E.G.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Borba, C.E.; Steffen, V.; Scheufele, F.B.; Kroumov, A.D. A new alternative to use soybean hulls on the adsorptive removal of aqueous dyestuff. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 6, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Yac’cob, N.A.N.; Ngadi, N.; Hassan, O.; Inuwa, I.M. From pollutant to solution of wastewater pollution: Synthesis of activated carbon from textile sludge for dye adsorption. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Is the Free Energy Change of Adsorption Correctly Calculated? J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Ma, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qiao, N.; Hu, M.; Ma, H. Adsorption of methylene blue onto Fe3O4/activated montmorillonite nanocomposite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Song, R.; Mao, W.J.; Wang, Q.; An, S.Q.; Zeng, Q.F.; Zhu, H.L. Adsorption of disperse blue 2BLN by microwave activated red mud. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2011, 30, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, M.; Alkan, M.; Demirbaş, Ö.; Özdemir, Y.; Özmetin, C. Adsorption kinetics of maxilon blue GRL onto sepiolite from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 124, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollet, H.; Roels, M.; Lutgen, P.; Van der Meeren, P.; Verstraete, W. Removal of PCBs from wastewater using fly ash. Chemosphere 2003, 53, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ultimate Analysis (%) | Proximate Analysis (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | N | S | Volatile matter | Fixed carbon | Ash |
| 19.7 | 3.2 | 23.2 | 3.4 | 0.5 | 18.4 | 38.6 | 43.1 |
| Pyrolysis temperature (°C) | 437 | 512 | 603 | 600 | 600 | |
| Pyrolysis holding time (min) | 15 | 15 | 15 | 10 | 5 | |
| Pseudo-first order kinetics | qe (mg·g−1) | 47.17 | 96.66 | 84.28 | 69.46 | 56.49 |
| k1 (min−1) | 0.016 | 0.033 | 0.035 | 0.029 | 0.026 | |
| R2 | 0.902 | 0.980 | 0.982 | 0.957 | 0.960 | |
| Pseudo-second order kinetics | qe (mg·g−1) | 66.67 | 86.21 | 89.29 | 84.75 | 74.07 |
| k2 × 10−4 (g·mg−1·min−1) | 1.05 | 2.6 | 5.24 | 3.89 | 4.2 | |
| R2 | 0.977 | 0.984 | 0.995 | 0.988 | 0.982 | |
| Modified pseudo-first order kinetics | qe (mg·g−1) | 52.63 | 125.5 | 122.3 | 95.78 | 77.28 |
| K1 (min−1) | 0.010 | 0.028 | 0.031 | 0.024 | 0.021 | |
| R2 | 0.905 | 0.944 | 0.969 | 0.951 | 0.966 | |
| Intraparticle diffusion model | kp1(g·mg−1·min−0.5) | 3.758 | 8.097 | 9.732 | 10.08 | 9.381 |
| R2 | 0.995 | 0.991 | 0.996 | 0.999 | 0.998 | |
| kp2(g·mg−1·min−0.5) | 1.600 | 0.263 | 0.426 | 0.464 | 0.500 | |
| R2 | 0.968 | 0.918 | 0.698 | 0.832 | 0.968 | |
| Temperature (K) | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/mg·g−1 | KL/L·mg−1 | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | |
| 293 | 90.09 | 0.672 | 0.857 | 60.3 | 0.101 | 0.962 |
| 298 | 90.09 | 0.948 | 0.873 | 64.5 | 0.087 | 0.977 |
| 303 | 92.59 | 1.038 | 0.949 | 67.3 | 0.085 | 0.989 |
| 308 | 95.24 | 1.400 | 0.942 | 70.5 | 0.081 | 0.991 |
| 313 | 95.24 | 3.387 | 0.963 | 77.6 | 0.060 | 0.983 |
| Temperature (K) | KC | ΔG0 (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS0 (J·mol−1·K−1) | ΔH0 (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | 9.860 | −5.57 | 87.45 | 20.30 |
| 298 | 11.68 | −6.09 | ||
| 303 | 12.51 | −6.37 | ||
| 308 | 13.33 | −6.63 | ||
| 313 | 17.85 | −7.50 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, G.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Luo, S.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Fu, J. Residue Char Derived from Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Sludge as Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Processes 2020, 8, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080979
Cheng G, Li Y, Sun L, Luo S, Kyzas GZ, Fu J. Residue Char Derived from Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Sludge as Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Processes. 2020; 8(8):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080979
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Gong, Yazhuo Li, Liming Sun, Siyi Luo, George Z. Kyzas, and Jie Fu. 2020. "Residue Char Derived from Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Sludge as Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions" Processes 8, no. 8: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080979
APA StyleCheng, G., Li, Y., Sun, L., Luo, S., Kyzas, G. Z., & Fu, J. (2020). Residue Char Derived from Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Sludge as Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions. Processes, 8(8), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080979







