Detection of E. coli O157:H7 in Food Using Automated Immunomagnetic Separation Combined with Real-Time PCR
Abstract
1. Introduction
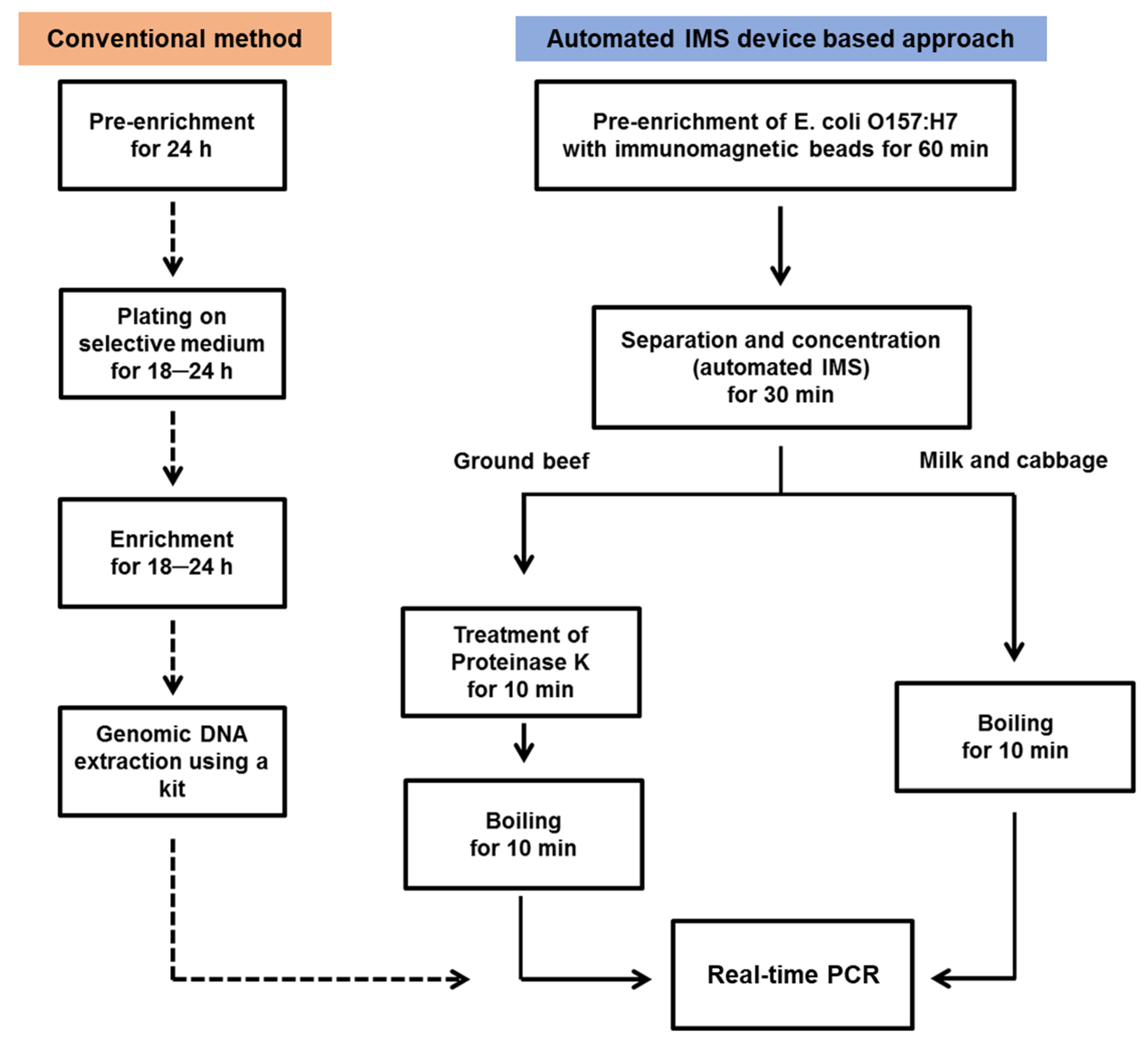
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
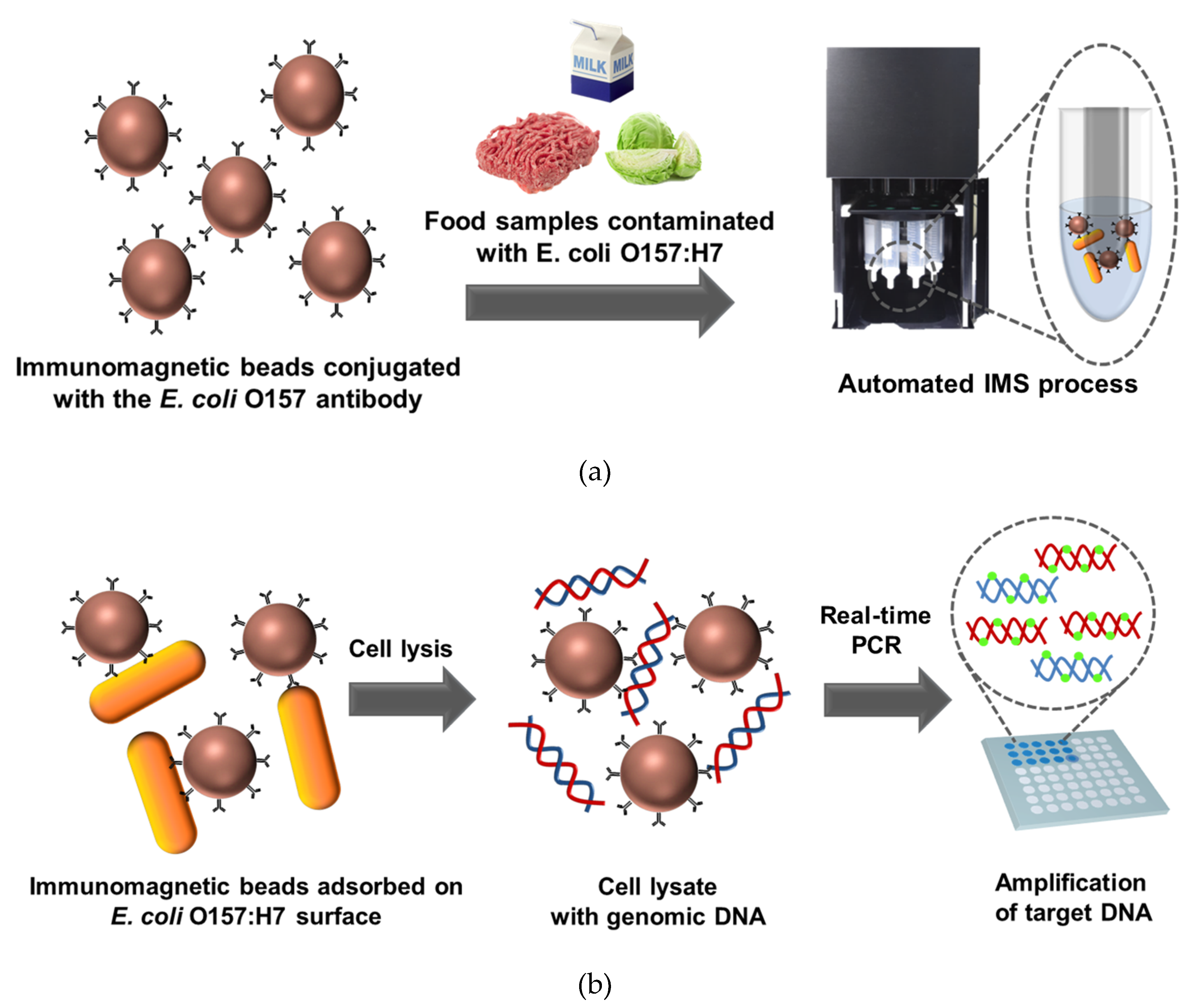
2.2. Preparation of Pathogenic-Bacteria-Contaminated Food Samples and Immunomagnetic Bead Reaction
2.3. Automated IMS Process
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. Recovery Monitoring and Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
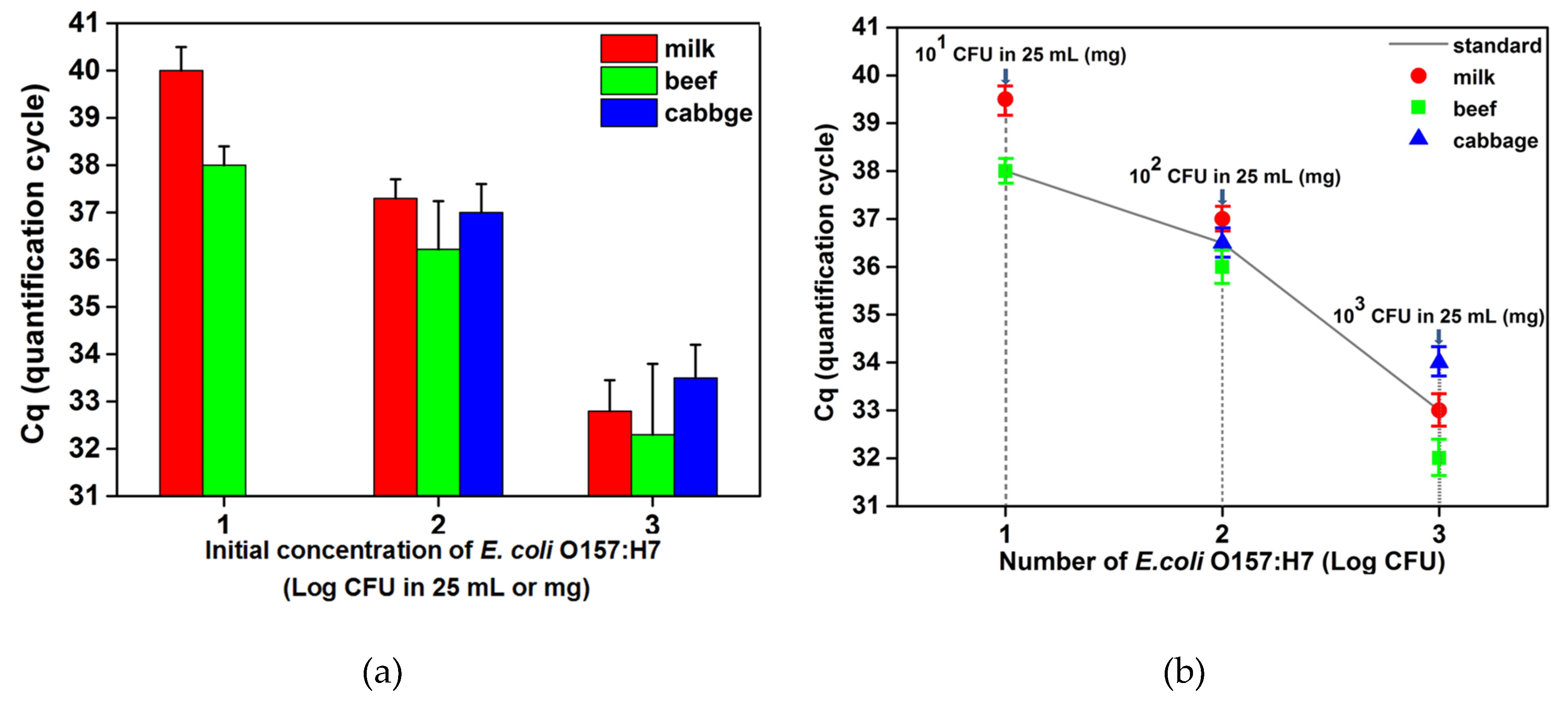
3.1. Establishment of a Standard Curve
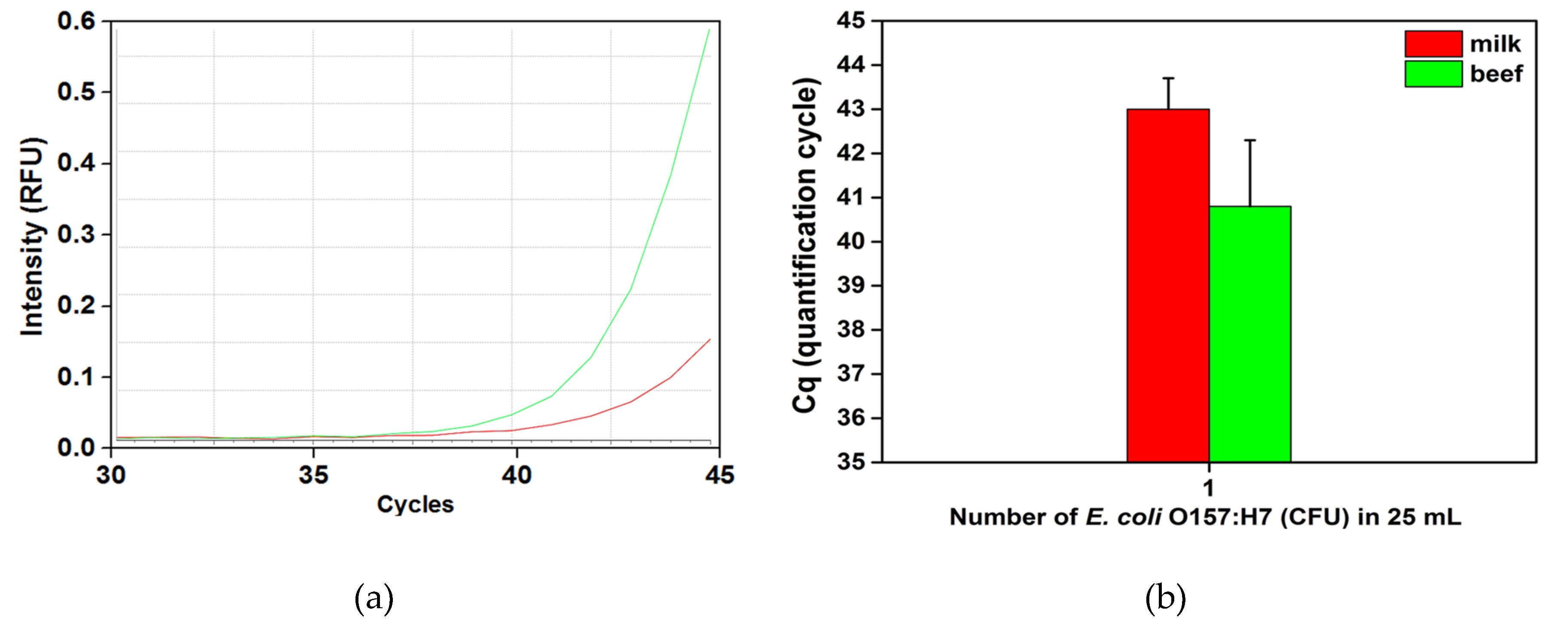
3.2. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 by Automated IMS Combined with Real-Time PCR
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doyle, M.P.; Schoeni, J.L. Isolation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 from retail fresh meats and poultry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 2394–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coia, J.E.; Johnston, Y.; Steers, N.J.; Hanson, M.F. A survey of the prevalence of Escherichia coli O157 in raw meats, raw cow’s milk and raw-milk cheeses in south-east Scotland. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 66, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.P.; Jayarao, B.M.; Almeida, R.A. Disease. Foodborne pathogens in milk and the dairy farm environment: Food safety and public health implications. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2005, 2, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.G.; Shipman, L.D.; Greene, K.D.; Sowers, E.G.; Green, J.H.; Cameron, D.N.; Downes, F.P.; Martin, M.L.; Griffin, P.M.; Ostroff, S.M. Isolation of Escherichia coli serotype O157: H7 and other Shiga-like-toxin-producing E. coli from dairy cattle. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jett, B.D.; Hatter, K.L.; Huycke, M.M.; Gilmore, M.S. Simplified agar plate method for quantifying viable bacteria. Biotechniques 1997, 23, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Kwon, K.Y.; Oh, S.K.; Chang, H.-J.; Chun, H.S.; Choi, S.-W. A multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Bacillus cereus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus in Korean ready-to-eat food. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.F.; Cao, W.W.; Cerniglia, C.E. A universal protocol for PCR detection of 13 species of foodborne pathogens in foods. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 83, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, S.; Oh, S.W. Combination of bacteria concentration and DNA concentration for rapid detection of E. coli O157: H7, L. monocytogenes, and S. Typhimurium without microbial enrichment. LWT 2020, 117, 108609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alía, A.; Andrade, M.J.; Córdoba, J.J.; Martín, I.; Rodríguez, A. Development of a multiplex real-time PCR to differentiate the four major Listeria monocytogenes serotypes in isolates from meat processing plants. Food Microbiol. 2020, 87, 103367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Oh, S.W. Rapid and sensitive detection of E. coli O157: H7 and S. Typhimurium in iceberg lettuce and cabbage using filtration, DNA concentration, and qPCR without enrichment. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Dean-Nystrom, E.A. Detection of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157: H7 by using a multiplex real-time PCR assay for genes encoding intimin and Shiga toxins. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 93, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, O.F.; Poltronieri, P.; Marsigliante, S.; Storelli, C.; Hernández, M.; Rodríguez-Lázaro, D. A filtration-based real-time PCR method for the quantitative detection of viable Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes in food samples. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lantz, P.-G.; Knutsson, R.; Blixt, Y.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Borch, E.; Rådström, P. Detection of pathogenic Yersinia enterocolitica in enrichment media and pork by a multiplex PCR: A study of sample preparation and PCR-inhibitory components. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 45, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogva, H.K.; Rudi, K.; Naterstad, K.; Holck, A.; Lillehaug, D. Application of 5′-nuclease PCR for quantitative detection of Listeria monocytogenes in pure cultures, water, skim milk, and unpasteurized whole milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4266–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, H.A.; Gooding, C.M.; Garrett, S.D.; Lund, B.M.; McKee, R.A. Proteinase inhibition of the detection of Listeria monocytogenes in milk using the polymerase chain reaction. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 18, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossen, L.; Nørskov, P.; Holmstrøm, K.; Rasmussen, O.F. Inhibition of PCR by components of food samples, microbial diagnostic assays and DNA-extraction solutions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1992, 17, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeke, T.; Jenkins, G.R. Influence of DNA extraction methods, PCR inhibitors and quantification methods on real-time PCR assay of biotechnology-derived traits. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, N.; Dillon, H.K.; Vermund, S.H.; Unnasch, T.R. Magnetic bead capture eliminates PCR inhibitors in samples collected from the airborne environment, permitting detection of Pneumocystis carinii DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stals, A.; Baert, L.; Van Coillie, E.; Uyttendaele, M. Extraction of food-borne viruses from food samples: A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 153, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Rogelj, S.; Kieft, T.L. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 by immunomagnetic separation and real-time PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 99, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Mutharasan, R. Review of biosensors for foodborne pathogens and toxins. Sensors Actuat B Chem. 2013, 183, 535–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Lee, G.; Song, X.; Park, S.; Kim, M. Immunoliposome-based immunomagnetic concentration and separation assay for rapid detection of Cronobacter sakazakii. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, M.; Yang, L.; Su, X.-L.; Li, Y. Magnetic nanoparticle-antibody conjugates for the separation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in ground beef. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedio, W.M.; Jinneman, K.C.; Yoshitomi, K.J.; Zapata, R.; Wendakoon, C.N.; Browning, P.; Weagant, S.D. Detection of E. coli O157: H7 in raw ground beef by Pathatrix™ immunomagnetic-separation, real-time PCR and cultural methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 148, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullane, N.R.; Murray, J.; Drudy, D.; Prentice, N.; Whyte, P.; Wall, P.; Parton, A.; Fanning, S. Detection of Enterobacter sakazakii in dried infant milk formula by cationic-magnetic-bead capture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6325–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.-C.; Park, J.Y.; Park, K.; Ok, G.; Jang, H.-J.; Choi, S.-W. An automated system for separation and concentration of food-borne pathogens using immunomagnetic separation. Food Control 2017, 73, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Park, K.; Ok, G.; Chang, H.-J.; Park, T.J.; Choi, S.-W.; Lim, M.-C. Detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 using automated immunomagnetic separation and enzyme-based colorimetric assay. Sensors 2020, 20, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.-C.; Lee, G.-H.; Huynh, D.T.N.; Hong, C.-E.; Park, S.-Y.; Jung, J.-Y.; Park, C.-S.; Ko, S.; Kim, Y.-R. Biological preparation of highly effective immunomagnetic beads for the separation, concentration, and detection of pathogenic bacteria in milk. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liming, S.H.; Bhagwat, A.A. Application of a molecular beacon—Real-time PCR technology to detect Salmonella species contaminating fruits and vegetables. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidic, J.; Vizzini, P.; Manzano, M.; Kavanaugh, D.; Ramarao, N.; Zivkovic, M.; Radonic, V.; Knezevic, N.; Giouroudi, I.; Gadjanski, I. Point-of-need DNA testing for detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors 2019, 19, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, S.A.; Shah, M.A.; Mir, M.M.; Dar, B.N.; Greiner, R.; Roohinejad, S. Microbiological contamination of ready-to-eat vegetable salads in developing countries and potential solutions in the supply chain to control microbial pathogens. Food Control 2018, 85, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Wan, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, E.; Cheng, X.; Du, M. Rapid detection of trace Salmonella in milk and chicken by immunomagnetic separation in combination with a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6067–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Initial Concentration (CFU in 25 mL or g) | Milk | Ground Beef | Cabbage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repetition Number (R/D) | Cq | Repetition Number (R/D) | Cq | Repetition Number (R/D) | Cq | |
| 101 | 5/5 | 40 ± 0.5 | 5/5 | 38 ± 0.4 | 5/0 | None |
| 102 | 5/5 | 37 ± 0.4 | 5/5 | 36 ± 1 | 5/5 | 37 ± 0.6 |
| 103 | 5/5 | 33 ± 0.6 | 5/5 | 32 ± 1.5 | 5/5 | 34 ± 0.7 |
| Initial Concentration | Milk | Ground Beef | Cabbage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repetition Number (R/D) | Cq | Repetition Number (R/D) | Cq | Repetition Number (R/D) | Cq | |
| <10 colonies in 25 mL or g | 5/3 | 43 ± 0.7 | 5/2 | 41 ± 1.5 | 5/0 | None |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.Y.; Lim, M.-C.; Park, K.; Ok, G.; Chang, H.-J.; Lee, N.; Park, T.J.; Choi, S.-W. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 in Food Using Automated Immunomagnetic Separation Combined with Real-Time PCR. Processes 2020, 8, 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080908
Park JY, Lim M-C, Park K, Ok G, Chang H-J, Lee N, Park TJ, Choi S-W. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 in Food Using Automated Immunomagnetic Separation Combined with Real-Time PCR. Processes. 2020; 8(8):908. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080908
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Ji Young, Min-Cheol Lim, Kisang Park, Gyeongsik Ok, Hyun-Joo Chang, Nari Lee, Tae Jung Park, and Sung-Wook Choi. 2020. "Detection of E. coli O157:H7 in Food Using Automated Immunomagnetic Separation Combined with Real-Time PCR" Processes 8, no. 8: 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080908
APA StylePark, J. Y., Lim, M.-C., Park, K., Ok, G., Chang, H.-J., Lee, N., Park, T. J., & Choi, S.-W. (2020). Detection of E. coli O157:H7 in Food Using Automated Immunomagnetic Separation Combined with Real-Time PCR. Processes, 8(8), 908. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080908






