Abstract
Although hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe, it is not possible to find it in its purest state in nature. In this study, two-stage experimentation was carried out. The first stage was hydrogen production. The second stage was an electrochemical process to hydrogenate soybean oil in a PEM fuel cell. In the fist stage a Zirfon Perl UTP 500 membrane was used in an alkaline hydrolizer of separated gas to produce hydrogen, achieving 9.6 L/min compared with 5.1 L/min, the maximum obtained using a conventional membrane. The hydrogen obtained was used in the second stage to feed the fuel cell hydrogenating the soybean oil. Hydrogenated soybean oil showed a substantial diminished iodine index from 131 to 54.85, which represents a percentage of 58.13. This happens when applying a voltage of 90 mV for 240 min, constant temperature of 50 °C and one atm. This result was obtained by depositing 1 mg of Pt/cm in the cathode of the fuel cell. This system represents a viable alternative for the use of hydrogen in energy generation.
1. Introduction
Electrolyzers are an essential part of the so-called “hydrogen economy” as transformers and devices for storing primary energy and replacing fossil fuels. As conventional electrolyzers are designed for operation at fixed process conditions, the implementation of fluctuating and highly intermittent renewable energy is challenging [1]. In recent years, different technologies have been developed to produce fuels based on several sources of animals and plants. Vegetable seed oils for the production of non-fossil fuels are an alternative that has been developed in Southeast Asia. Through transesterification, the achieved conversion yields of sunflower oil reached efficiency of 78.3% at a temperature of 660 °K over ZnCl as the catalyst [2].
By means of rapeseed oil hydrogenation tests [3], they studied the performances with cobalt and molybdenum catalysts with an initial hydrogen pressure of 1.10 MPa and reaction temperature in the range of 200 °C to 400 °C, for 6 and 180 min. In addition, at the temperature of 400 °C and 120 with min of reaction duration, the hydrocarbon yield approached 92% in the presence of a catalyst, while in the absence of the catalyst this value approached 85%. Moreover, they carried out tests on oils of jatropha, palm and canola, by means of hydroprocessing on sulfur-based NiMo and NiW catalysts supported by SAPO-11; they obtained results for all the catalysts—40% of diesel and 40% aviation kerosene [3], and the remaining 20% were lighter hydrocarbons from gasoline range. Lu et al. [4] produced biohydrogen diesel (BHD) and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) by hydrotreating vegetable oils on NiMo-based catalysts in a high-pressure, fixed-base flow reaction system at 350 °C under 4 MPa hydrogen. In processes that combine selective transesterification and hydrogenation biodiesel was produced from hemp (cannabis sativa L.) [5], where a series of alkaline earth metal oxides and copper oxides supported by alkaline earth metals were tested as catalysts. SrO supported 10% by weight by CuO showed superior catalytic activity for transesterification with a biodiesel yield of 96% and hydrogenation with a reduced iodine value of 113.
Zirfon
In Zirfon, the addition of ZrO to the polysulfone matrix results in a high wettability, which is, of course, of the highest importance in systems where H and O are being evolved. The separator is very stable in concentrated potassium hydroxide (KOH) solutions at elevated temperatures [6,7,8,9]. The standard type of Zirfon separator is a microporous organo-mineral material, pore size 0.15 ± 0.05 m and the crystallite size of cubic ZrO is 8 nm, containing 85 wt% of a hydrophilic ZrO powder with a high specific surface area (22 m/g) to assure an optimum wettability and 15 wt% polysulfone (PSF) which gives the material its mechanical strength [10]. A commercially available product of this type of separator is denoted as Zirfon PERL UTP 500(AGFA). In the datasheet of the manufacturer, a thickness of approximately 500 ± 50 m, a porosity of 50 ± 10% and pores of approximately 0.15 ± 0.05 m diameter were reported [3]. Initially, the Zirfon separator was developed for use in alkaline water electrolysis, where it was an alternative for asbestos. In the “classical” alkaline water electrolysis technology, the asbestos diaphragm limits the working temperature of the cell up to 90 °C [11]. In addition, the commercial porous separator Zirfon, which is composed of 85 wt% zirconia nanoparticles and 15 wt% polysulfone, exhibits a satisfactory bubble point pressure performance of approximately 2.5 bar and ionic resistance of 0.3 cm. However, the Zirfon PERL separator exhibits a high hydrogen permeability value of 20 × 10 mole cm bar sec due to its large average pore size of 130 nm, resulting in a limited dynamic range of the electrolyzer [12]. Furthermore, with Zirfon as the separator and NaOH as the electrolyte, the shortest distances between electrodes, the best system performance and the resistance increased with longer distances [11]. One of the advantages of the Zirfon membrane concerning the Nafion membrane, is that it allows one to significantly reduce the amount of raw material required for its manufacturing. It can be sintered under controlled conditions to achieve the appropriate microporosity that enables the flow of fluids (electrolyte) but not that of gas bubbles generated in the electrolyzer. These materials have the required chemical resistance. The thicknesses of the Zirfon membranes are less than the widths of conventional layers, which represents a significant saving in the number of raw materials needed to obtain it and also allows the energy necessary to carry out alkaline electrolysis to be generally lower than that required with conventional membranes, and that the process is more efficient [13].
On the other hand, hydrogenation is a process that increases the melting point of the final product, transforming oils into fats and increasing its oxidative stability, eliminating linoleic acids, mainly responsible for the deterioration of the product by oxidation. Basically, it consists of a chemical process in which the oils are transformed into solid fats by adding hydrogen at high pressures and temperatures, generally in the presence of a catalyst. This process converts unsaturated fatty acids into saturated ones. This transformation, besides changing the nature of fatty acids, also changes the position within the molecules of the double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids and makes them produce their different trans isomers produced by hydrogenation. Several processes have been developed out of biodiesel generation from vegetable oils by hydrogen transfer to their fatty esters, a base of methanol, or additional glycerol as the supply of hydrogen for corn reduction and soybean oils to >80% oleate. The cost of an iridium catalyst is mitigated by its recovery by means aqueous extraction. The process may be further boosted with a supporting iron-based catalyst for complete saturation of all olefins. Preparatory procedures are established for synthesis and separation of methyl esters from hydrogenated fatty acids, allowing instant access to improved biofuels [4]. Hydrogenation of soybean oil in the liquid phase has been studied using Cu-Zn-Al catalysts with silica supports and Cu-Zn-Al [14]. Indeed, biodiesel has been achieved by means of simultaneous transesterification and partial hydrogenation of soybean oil on Cu catalysts in supercritical methanol at 320 °C and 20 MPa, despite the absence of hydrogen gas [15].
Besides, electrochemical hydrogenation of soybean oil is useful for decreasing the amount of unwanted trans fatty acid isomers in an oil product; electrochemical hydrogenation in a PEM reactor with water as a feed anode; and either Pd or Pt as the catalytic cathode. Some edible oil processors prefer to evaluate a hydrogenated oil product based on the sum of tranisomers and 18-carbon saturated fatty acids. There are many studies of other seed types. Nevertheless, there are not many cases of electrochemical hydrogenation processes of soybean oil [16]. On the other hand, polymer membrane electrolyzers (PEM) are considered as the most promising long-term option; currently, they are ideal for small or medium-scale applications, such as car power or smaller applications, where the unit may be used to produce hydrogen using a renewable energy supply, such as solar energy [16,17]. These electrolyzers may benefit greatly from the technical development that is being carried out on PEM fuel cells and their mass production. Some models of PEM electrolyzers are currently on the market, despite being a newly created technology compared to alkaline electrolyzers. The efficiency of PEM electrolyzers is expected to be as high as 94%, but for now, this is somewhat hypothetical. PEM electrolyzers work efficiently for renewable energy systems where the energy supply is highly variable. PEM electrolyzers are generally more suitable for small power plants, especially those with a variable output, while alkaline electrolyzers are clearly better for large power plants that are connected to the power grid. Currently, there are developments in electrocatalysts for zero gap alkaline water electrolyzers and hydroxide transport membranes for such cells [18,19].
Highly pressurized electrolyzers production is intended to increase overall energy efficiency by eliminating mechanical compression. However, in-depth modeling of electrolyzers suggests that atmospheric pressure electrolysis is electrically efficient if parasitic energy consumption and gas losses are incorporated in both cases. In addition, reversible cell voltage increases with increasing pressures. Likewise, the activation of the electrode and the ohmic losses, the leakage current and the inevitable heat losses increase the electrolysis voltage beyond the thermo-neutral voltage. Consequently, removing heat from the cell becomes essential; thus, the expected gas loss at several operating pressures is incorporated to reveal the energy consumption that may occur in practice [20,21,22,23].
2. Experimental Development
2.1. Experimental Procedure
All reagents used were analytical grade. The aqueous solutions were prepared with MilliQ plus treated water of 11 M cm resistivity. To determine 100% soybean oil unsaturation from the Nutrioli brand, the iodine index was determined by obtaining the Hanus reagent (Merck); for evaluation of samples, 99.99% sodium thiosulfate (NaSO) and reactive ACS grade starch were used as indicators, both of Sigma-aldrich brand.
In the hydrolyzer, reagent grade 90% KOH (Sigma-Aldrich) has been used as a raw material electrolyte with a Zirfon Perl UTP 500 membrane (AGFA) as the separator between anode and cathode compartment, and plates have been made of 316 L by San Luis steels.
Soybean oil partial electrochemical hydrogenation was carried out in 25 cm fuel cell (PEM) with a deposit of platinum-carbon 20% (Sigma-Aldrich) over the Nafion 117 membrane of Sigma-Aldrich (charge: Pt 1 mg cm) as the electrocatalyst on both cathode and anode sides.
2.2. Design of Separate Gas Electrolyzer and Oil Hydrogenation PEM Reactor
The hydrogen separation process from KOH was done throughout the alkaline electrolyzer of separated gases. Figure 1 shows the alkaline hydrolyzer was made up of a stack of six stainless steel plates; each one was cut in a circular section with a diameter of 11.28 cm. Plate 1—cathode, plate 6—anode and intermediate plates—neutrals.
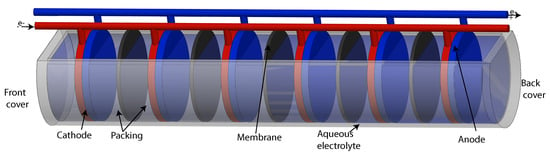
Figure 1.
Principle of a bipolar electrolyzer design.
Interleaved to stainless steel plates were added six circular Zirfon plates with a diameter of 11.28 cm; between each Zirfon plate and stainless steel plate, a 3 mm thick neoprene gasket was added, with an outer diameter of 12.5 cm and the internal diameter of 11.28 cm, obtaining an active area of 100 cm as a result.
Potassium hydroxide electrolyte was used. This system was assembled into several components to make it work correctly; see Figure 2.
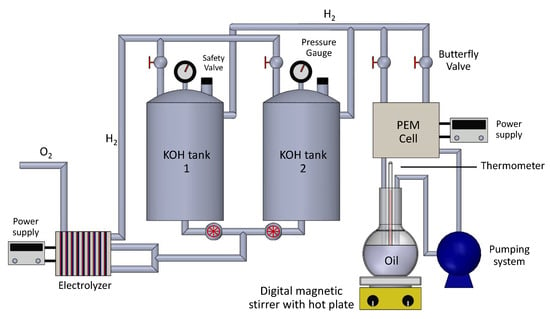
Figure 2.
Hydrogen generation system and hydrogenation electrolyzer.
In Figure 2, the hydrogen generation system and hydrogenation electrolyzer received by gravity through 2 hoses (Truper 1/2″) through which KOH was pumped. End plates were connected to DC source (BK Precision 36 V, 40 A, 1.44 kW, programmable), adding 12, 14 and 16 V. Hydrogen and oxygen obtained are led to the KOH storage tanks. The KOH storage system is made up of two PVC pipes (ID 40, 5″) 50 cm in length. Through the lower part of the storage system, it is supplied with KOH in solutions of 25% and 30% by weight, and at 50 °C to the electrolyzer. The top part of this system receives hydrogen and oxygen from the electrolyzer. Each storage system has a manometer (MT, with glycerin from 0 to 10 bar), a safety valve (OEM, 1/4″, up to 142 Psi) and an electrical resistance of 1000 W for heat input. Gases flows from the electrolyzer to the KOH storage systems were regulated by valves (DEPOT MX, 1/2″) at the top of storage system where the hydrogen was located, connected to fuel cell by means of a pneumatic hose (6 mm polyurethane tubing). The PEM type fuel cell was manufactured using the Nafion 117 membrane, activated in 3% sulfuric acid, with distilled water and 3% hydrogen peroxide. Two blocks of carbon paper were covered, by means of blow-drying technique, with catalytic ink made with: 50 mg of Pt/C Vulcan, 5 mL of liquid Nafion and 12 mL of isopropyl alcohol. The ink was mixed in mechanical stirrer (ARGOLAB MIX, 60 W) and added to the two blocks of carbon paper of 5 × 5 cm. Later, the electron collecting plates were built with 316L stainless steel and serpentine type geometry. The channels were 1 × 1 mm, generating an active area of 25 cm. The potential applied to the fuel cell was 90 mV. Soybean oil storage system was built with a 200 mL matrass, and a perforated stopper; 100 mL soybean oil was added to the storage system; it was connected to a peristaltic pump (no brand, model G528. 0–150 mL/min), by means of 6 mm polyurethane tubing pneumatic hose; the output of peristaltic pump with a flow rate of 20 mL/min was connected to fuel cell anode whose output was connected to soybean oil storage system, and this storage system has an electrical resistance of 1000 W, for the addition of heat to the soybean oil to keep it at 50 °C.
2.3. Chemical Analysis
To determine total soybean unsaturation, Hanus’ volumetric method was used. This method involves the iodine index technique in vegetable fats and oils, in which 0.15 g of soybean oil is placed in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer matrass and dissolved with stirring in 15 mL of a chloroform; then, 25 mL of the reagent of Hanus is added, and covered with aluminum foil; and after 60 min, 10 mL of 15% potassium iodide is added, followed by 100 mL of distilled water and 2 mL of 15% starch indicator. Excess unreacted iodine is titrated with a standard 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate (NaSO) solution and continued until the blue color disappears (note spent milliliters). Finally, the blank is run in the same way as a sample without soybean oil, and the milliliters spent during titration are noted.
Iodine number calculation:
where:
- I is the iodine number;
- m is the sample mass (g);
- is the volume of sodium thiosulfate expended in blank titration (mL);
- is the volume of sodium thiosulfate expended in sample titration (mL);
- N is the normality of the sodium thiosulfate sample (eq/L), and iodine constant with the value of 0.1269.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrogen Production in a Separate Gas Electrolyzer
The test results using an alkaline electrolyzer are shown below.
Figure 3a shows the results obtained in hydrolyzer from Figure 2 to achieve H with 25% KOH obtaining 1.175 L/min with constantly supplying 12 V at 90 min, and as voltage increased at 14 V, 4.0 L/min was obtained. However, the highest flow result with 25% KOH was 8.5 L/min at 16 V.
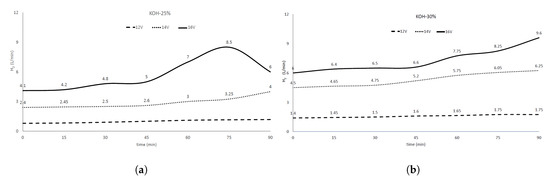
Figure 3.
(a) H2 production (L/min) vs. time (min) at different potentials 12, 14 and 16 V, ambient pressure and temperature 50 °C. KOH at: (a) 25% and (b) 30% by weight.
Tests were performed with higher KOH concentrations and potentials, but the amount of hydrogen collected was negligible. The highest H flow of all tests was obtained at 30% (KOH) electrolyte concentration, as seen in Figure 3b, showing a similar behavior to Figure 3a under the same pressure and temperature conditions. When using the 12, 14 and 16 V potentials, H flow was increased from 1.75 to 6.25 L/min until obtaining 9.61 L/min at same time, respectively. Therefore, in order to amount of hydrogen to be greater in this system, a 30% KOH concentration and a maximum voltage of 16 V are recommended. Regarding the above, the literature is scarce.
The potential of the electrolyzer at a temperature of 50 °C is calculated as follows:
where the value of is 0.401 V. In the case of the cathode
where the value of is 0.83 V. In the case of the global
The potential of the electrolyzer under standard conditions is obtained with:
The corrected power of the cell for 50 °C is obtained using the Nernst equation
and is calculated with K, , , and . The cell power is calculated by replacing in Equation (6):
Thus, E = −1.2762 V. The electrical charge calculation Q(c) for an volume of 9.6 was the best performance of with 30% KOH; see Figure 3b.
Theoretical power = (1096.24 A)(1.2762 V) = 1399.02 W
For the calculation of cell efficiency for a volume of 9.6 , we supplied: I = 2.5 A, V = 18 V, t = 60 s and real power = (2.5 A)(18 V)(60 s) = 2700 .
Therefore, %cell efficiency = × 100 = 51.81%
3.2. Iodine Index Results
In Figure 4, after conducting a large number of experiments, nine tests in progressive order were chosen to observe the increase in soybean oil hydrogenation as the trials progress.
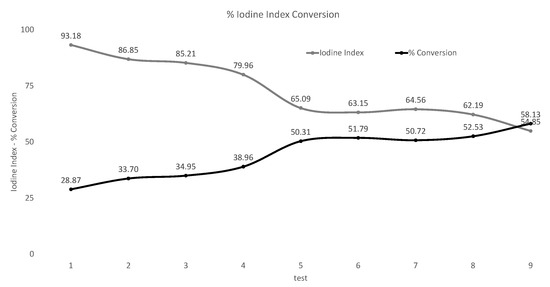
Figure 4.
Iodine index conversion.
There was an iodine number in the first test of 93.18, which represents a conversion of 28.87% of that obtained from the iodine number of non-generated soybean oil (131), and nine obtained an iodine number of 54.85, which represents a conversion from 58.13.
Figure 5 represents the degree of establishment of soybean oil from the chosen experimental tests, which also specifies the duration time and voltage to which each sample was subjected.
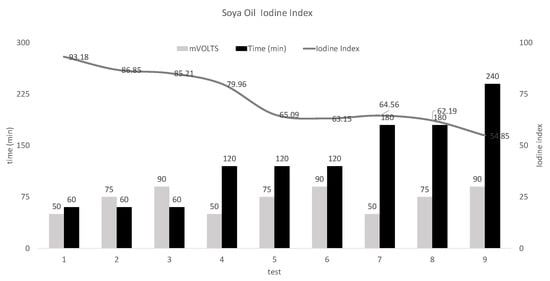
Figure 5.
Percentage of iodine index vs. time and mV.
Thus, in the first three tests, the constant time was 60 min, where the best result was obtained by reducing the iodine index of the non-generated sample from 131 to 85.21 of the hydrogenated sample, supplying 90 mV to the PEM cell.
For samples 4, 5 and 6, the constant time was increased to 120 min, thereby obtaining a better result when decreasing, compared with the untreated sample up to an iodine index value of 65.09 of the hydrogenated sample at the voltage of 90 mV. For samples 7, 8 and 9, the constant time was first increased to 180 min and finally up to 240 min whereby the best iodine index result of 54.85 was obtained, which represented a reduction of 58.85 from the value of 131 of the non-generated soybean oil supplying a voltage of 90 mV, a constant temperature of 50 °C, a pressure atmosphere in all tests and a flow of 20 mL/min.
The previous results may be compared with those reported by [16], wherein soybean oil was partially hydrogenated in the electrochemical reactor with a proton exchange membrane (PEM) composed of a Pd cathode and a Pt anode attached to opposite surfaces of the membrane of cation exchange (Nafion 117) with H gas as the anode feed and soybean oil at the cathode. The reactor was operated at a moderate temperature of 70 °C, under 1 atm, for 30 mL/min, thereby reducing the iodine number from 132 to 92; therefore, there was an improvement of 30.3% [16] vs. 58.85% reduction in this investigation, as well as a 50 °C temperature operation in our process. This improvement may be attributed to the use of Pt at the cathode, the mg per cm of the Pt catalyst attached to 5 × 5 cm carbon paper blocks and the flow used.
4. Conclusions
Partially hydrogenated soybean oil has been made in an electrochemical PEM reactor with H gas-powered anode. The PEM reactor was operated in a semi-batch mode at a moderate temperature of 50 °C and 1 atm of pressure using commercial grade soybean oil, such as cathode feed. The performance or conversion rate of oil hydrogenation tends to increase with voltage and time, with a range of 28.87 to 58.13 hydrogenation.
Hydrogen obtained in the electrolyzer of separate gases at a concentration of 25% by weight of KOH and 12 V is sufficient for the hydrogenation of soybean oil in this PEM reactor.
Subsequent tests on the alkaline electrolyzer of separate gases using higher KOH concentrations and higher voltage indicate higher hydrogen production, which can be used for larger electrolyzers or hydrogen storage for other uses such as hybrid vehicle fuel.
The maximum production so far of hydrogen obtained in the separate gas electrolyzer was at a concentration of 30% by weight of KOH and 16 V, and it was 9.6 mL/min. This represents a 16%-higher balue relative to the target value in the operating conditions.
The theoretical maximum production calculated, taking into account the maximum experimental operating conditions in the separate gas electrolyzer at a concentration of 30% by weight of KOH and 16 V, was 11.51 L/min. It is essential to mention that in similar works, the value of each of the different properties depends on the composition of the material but also changes reversibly, driven by the reaction [16].
The difference between experimental and theoretical results was due to this being the first time this technique was used with the Zirfon membrane, a new layer on the market compared to Nafion, and therefore it is necessary to fine-tune that technique with the original product entreating.
It is known that the theoretical results with the experimental results will always have a difference in the losses that occur in the time taken to dry the hydrogen in the filter for drying the used equipment, and that stays in the entire line of the material because it is KOH wet with water. When passing through the dryer, stagnation in the flow is generated, and when the difference is output, they are not taken into account in a theoretical calculation, but they are given at the time of performing the experimental part [16].
Based on the theoretical results obtained from applying the corresponding formulas, it was estimated that the maximum hydrogen production gained was 11.51 L/min at 23.5 A, 23 A, 16 V and 50 °C temperature, with KOH at 30% by weight. In the experimental results obtained in carrying out the corresponding hydrogen production tests, it was observed that the maximum hydrogen production received was 9.6 L/min at 23.5 A, 16 V and 50 °C temperature, with KOH at 30% by weight. The percentage difference between hydrogen obtained theoretically with that obtained experimentally was approximately 19%. It can be concluded than electrochemical problems that rely heavily on notions of solid-state physics for proper clarification are best grouped into electrochemical physics, in analogy with chemical physics.
5. Future Works
Performing cell stack at the industrial level; the stack prototypes are currently being made at the pilot plant level. The membrane is new; therefore, it is expensive; in consequence, we must seek to optimize costs, because the percentage is very high in terms of value. In addition, the wear of the Nafion membranes is higher than that of the Zirfon membrane, which will allow efficient hydrogen production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.E.E.V.; Data curation, D.L.O., and M.A.Z.A.; Analysis, R.G.G.; Investigation, J.E.E.V., J.R.R., R.G.G., M.A.Z.A., and P.J.P.K.; Methodology, R.G.G., M.A.Z.A., P.J.P.K., and J.R.R.; Project administration, J.R.R. and M.A.Z.A.; Resources, D.L.O.; Validation, J.E.E.V., R.G.G., P.J.P.K.; Writing, J.R.R.; Writing—original draft, J.R.R., and M.A.Z.A.; Writing—review and editing, D.L.O., and M.A.Z.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Vice Rectory National of Research of Universidad del Valle de México, CONACYT, and PRODEP.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Vice-Direction of Research of the UVM for the support provided in carrying out the research work. The authors thank Miguel Angel Cruz Pérez for support in the translation of the work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| Potential under standard conditions (potentials are tabulated for different reduction reactions) | |
| Potential cathode energy | |
| Potential Anode Energy | |
| E | Corrected cell potential |
| R | Gas constant in J/mole K |
| T | Absolute temperature (Kelvin scale) |
| n | Amount of mole of electrons involved in the reaction |
| F | Faraday’s constant in C/mole |
| Q | Reaction ratio in the Nernst equation. |
| Electrical charge calculation in C/min |
References
- Brauns, J.; Turek, T. Alkaline Water Electrolysis Powered by Renewable Energy: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DemirbaŞ, A. Fuel conversional aspects of palm oil and sunflower oil. Energy Sources 2003, 25, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.; Adriansens, W.; Leysen, R. Zirfon: A new separator for Ni-H {sub 2} batteries and alkaline fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1996, 21, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Cherepakhin, V.; Kapenstein, T.; Williams, T.J. Upgrading biodiesel from vegetable oils by hydrogen transfer to its fatty esters. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5749–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, W.; You, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, S. The influence of manufacturing parameters and adding support layer on the properties of Zirfon® separators. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.; Adriansens, W.; Moreels, J.; Leysen, R. Evaluation of the Zirfon® separator for use in alkaline water electrolysis and Ni-H2 batteries. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, V.M.; Tasic, G.S.; Maksic, A.D.; Saponjic, D.P.; Miulovic, S.M.; Kaninski, M.P.M. Raising efficiency of hydrogen generation from alkaline water electrolysis–Energy saving. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 12369–12373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Zhang, D. Recent progress in alkaline water electrolysis for hydrogen production and applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojić, D.L.; Marčeta, M.P.; Sovilj, S.P.; Miljanić, Š.S. Hydrogen generation from water electrolysis—possibilities of energy saving. J. Power Sources 2003, 118, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.H.; Leysen, R.; Beckers, H.; Moreels, J.P.; Claes, A. The influence of manufacturing parameters on the properties of macroporous Zirfon® separators. J. Porous Mater. 2008, 15, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Rana, B.S.; Kumar, R.; Sibi, M.; Sinha, A.K. Diesel and aviation kerosene with desired aromatics from hydroprocessing of jatropha oil over hydrogenation catalysts supported on hierarchical mesoporous SAPO-11. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 490, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, P.; Kuypers, S.; Genne, I.; Leysen, R.; Mewis, J.; Vankelecom, I.; Jacobs, P. Polysulfone- ZrO2 Surface Interactions. The Influence on Formation, Morphology and Properties of Zirfon-Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7425–7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevda, S.; Dominguez-Benetton, X.; Vanbroekhoven, K.; Sreekrishnan, T.; Pant, D. Characterization and comparison of the performance of two different separator types in air—Cathode microbial fuel cell treating synthetic wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasarti, A.; Segobia, D.; Apesteguia, C.; Santoro, F.; Zaccheria, F.; Ravasio, N. Selective hydrogenation of soybean oil on copper catalysts as a tool towards improved bioproducts. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Bae, S.Y.; Kim, Y.C. Biodiesel production from highly unsaturated feedstock via simultaneous transesterification and partial hydrogenation in supercritical methanol. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2013, 82, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintauro, P.; Gil, M.P.; Warner, K.; List, G.; Neff, W. Electrochemical hydrogenation of soybean oil with hydrogen gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 6188–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K.; Lalvani, S. Low temperature soybean oil hydrogenation by an electrochemical process. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletcher, D.; Li, X. Prospects for alkaline zero gap water electrolysers for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 15089–15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darjat, D.; Sulistyo, S.; Triwiyatno, A.; Sudjadi; Kurniahadi, A. Designing Hydrogen and Oxygen Flow Rate Control on a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Simulator Using the Fuzzy Logic Control Method. Processes 2020, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Watson, S.; Infield, D. Comparison of electrical energy efficiency of atmospheric and high-pressure electrolysers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2006, 31, 1964–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Gong, X.; Guo, Z. The intensification technologies to water electrolysis for hydrogen production—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaiz-Moretón, H.; Jove, E.; Casteleiro-Roca, J.L.; Quintián, H.; López García, H.; Benítez-Andrades, J.A.; Novais, P.; Calvo-Rolle, J.L. Bioinspired Hybrid Model to Predict the Hydrogen Inlet Fuel Cell Flow Change of an Energy Storage System. Processes 2019, 7, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Durán, A.; Martínez-Sibaja, A.; Rodríguez-Jarquin, J.P.; Posada-Gómez, R.; González, O.S. PEM Fuel Cell Voltage Neural Control Based on Hydrogen Pressure Regulation. Processes 2019, 7, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).