Design and Construction of pH-Selective Self-Lytic Liposome System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Purification of the Membrane Lytic Polypeptides
2.2. Preparation of Liposomes
2.3. Calcein Leakage Assay
2.4. Liposome-Accessibility Assay
2.5. CD Measurements
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
2.7. Zeta Potential Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design of Melittin-Mimetic Lytic Polypeptides and Their Retro-Analogs
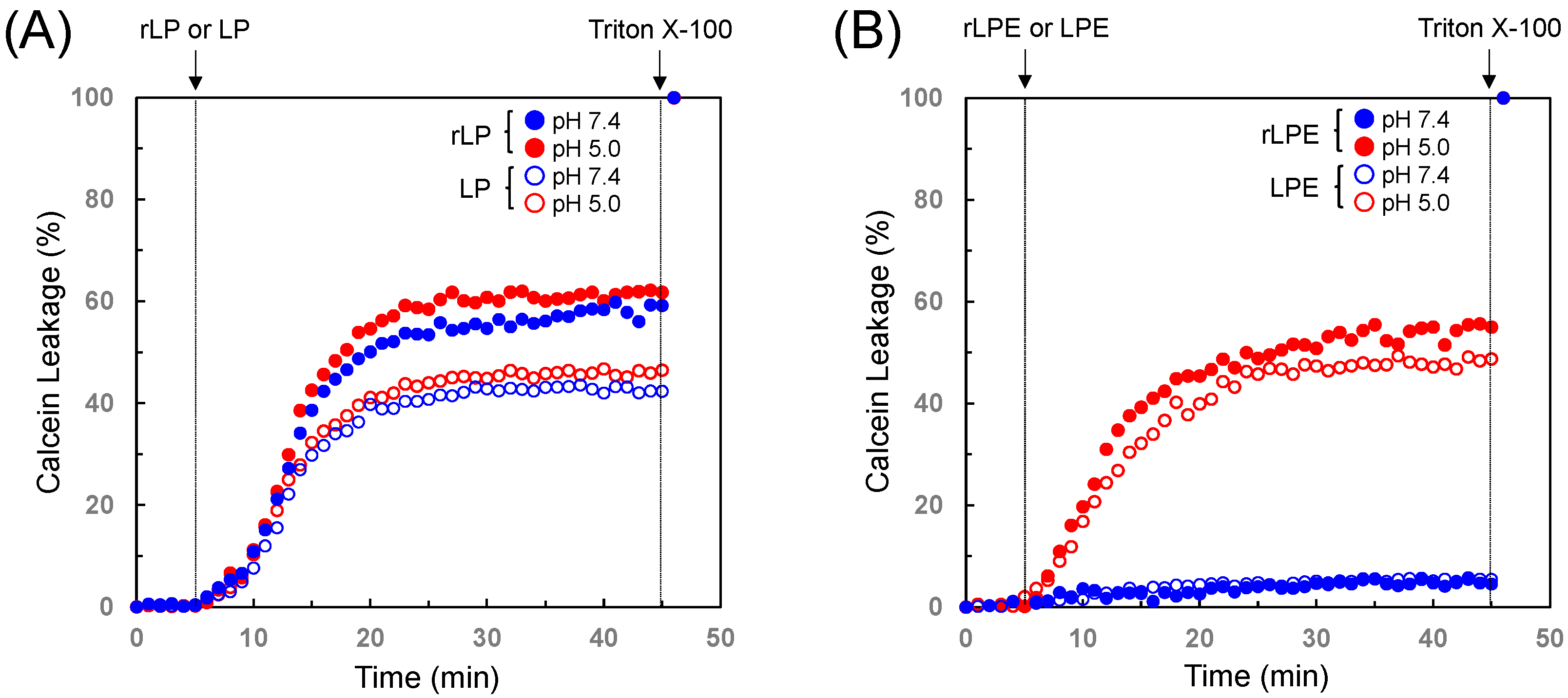
3.2. Membrane Lytic Properties of the Designed Polypeptides
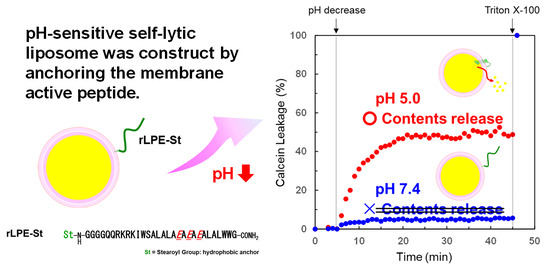
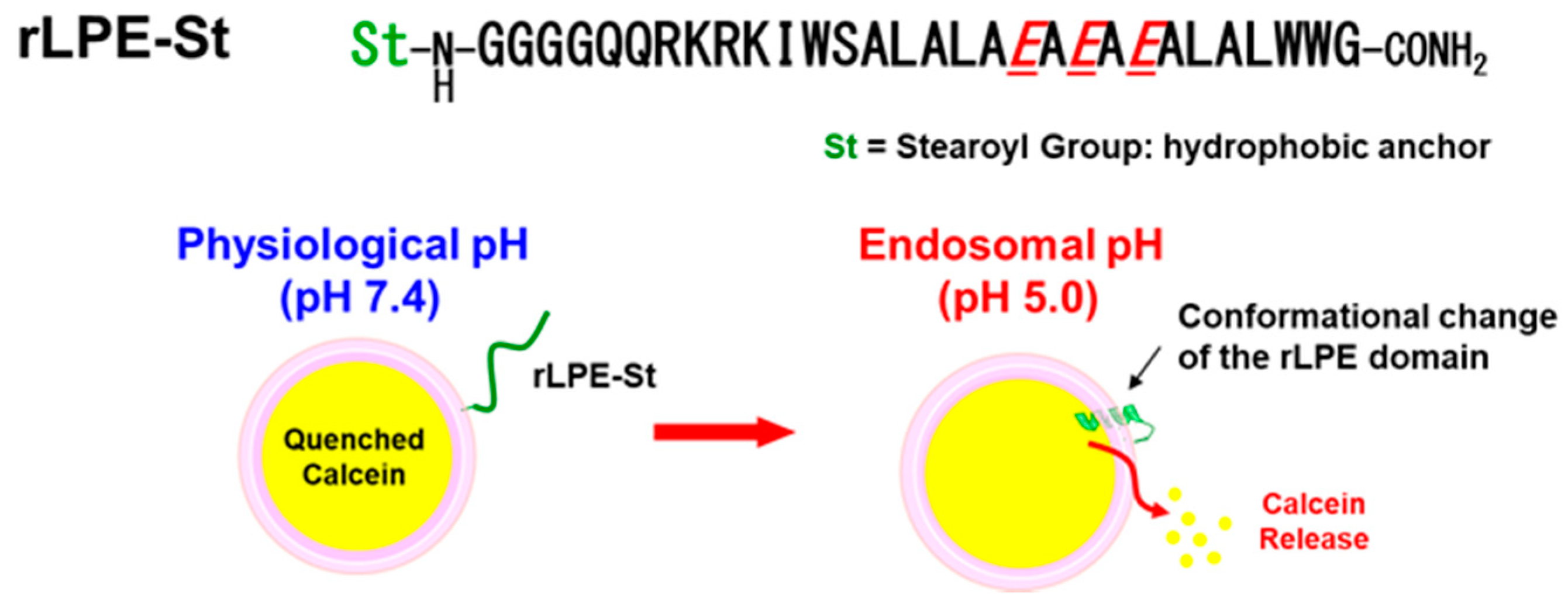
3.3. Design of Acidic-pH-Selective Membrane Lytic Polypeptide Conjugate
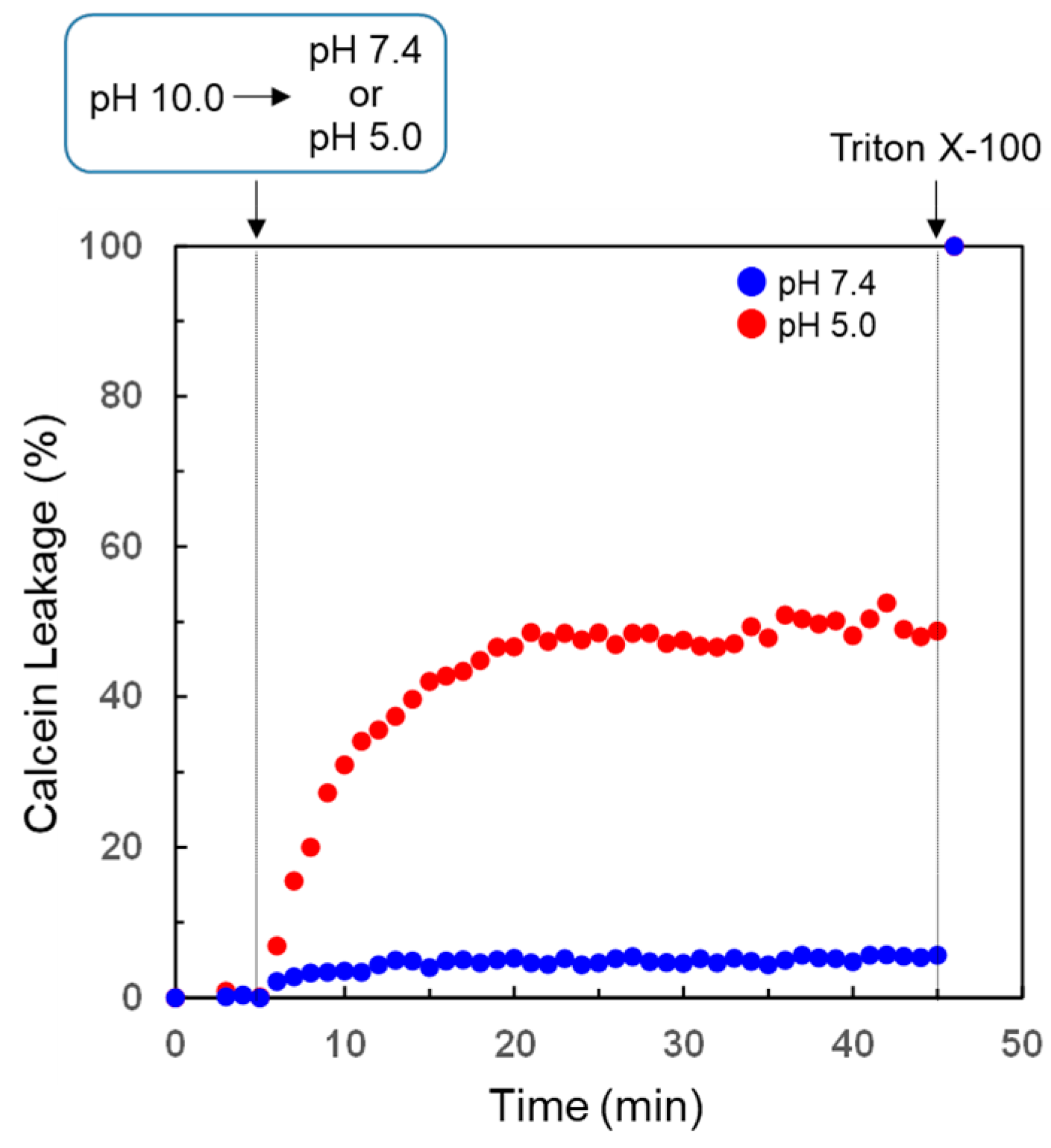
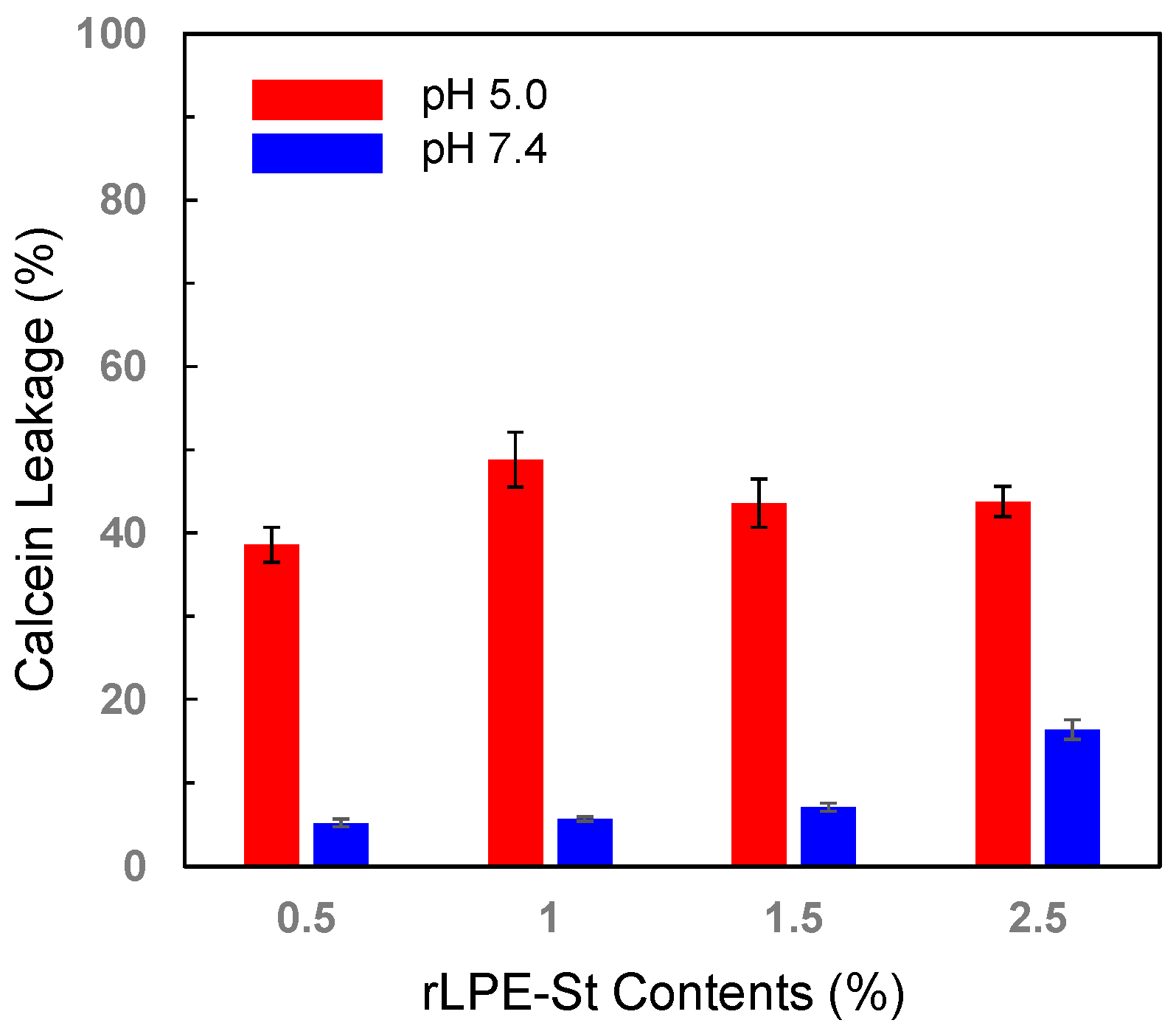
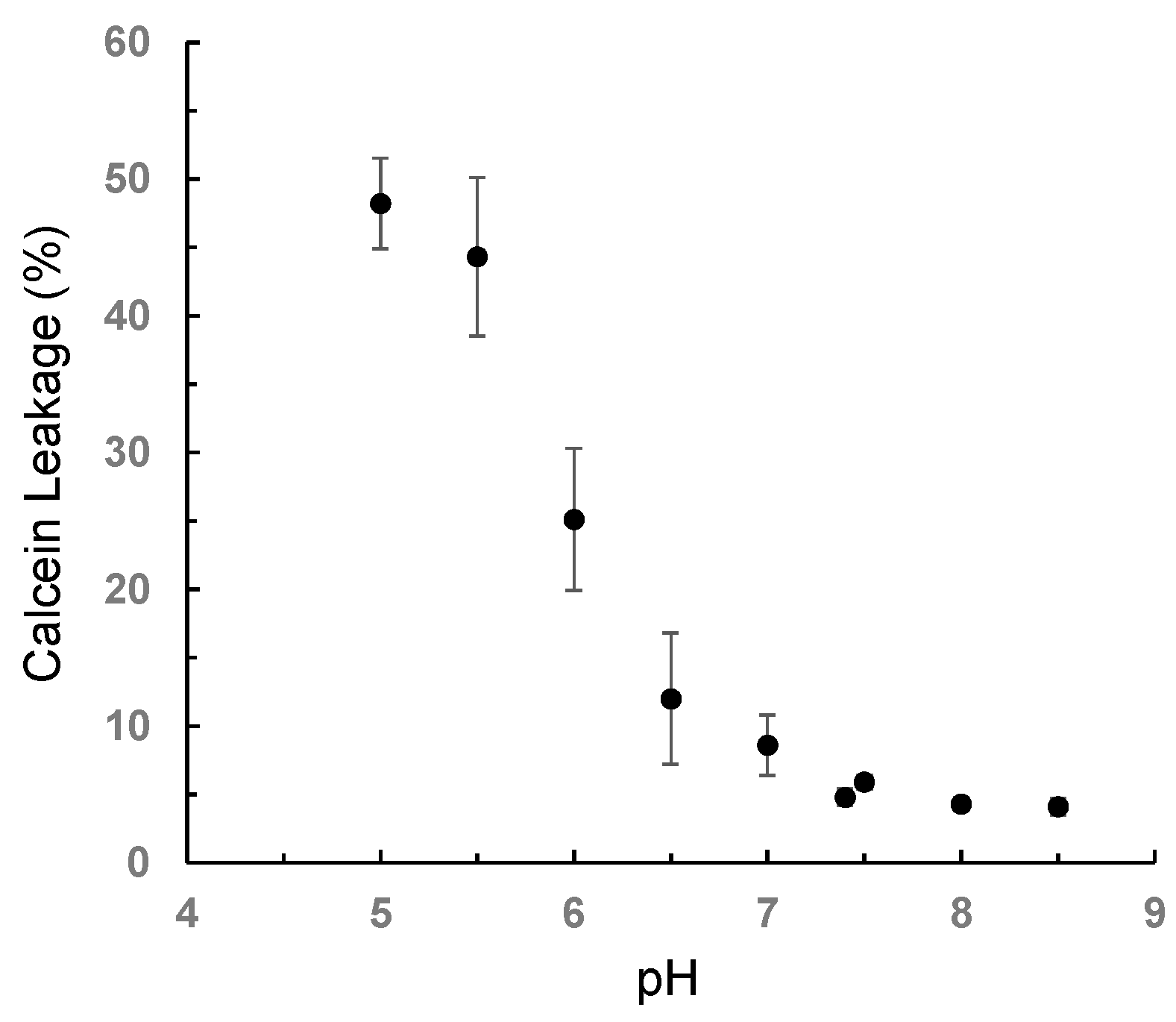
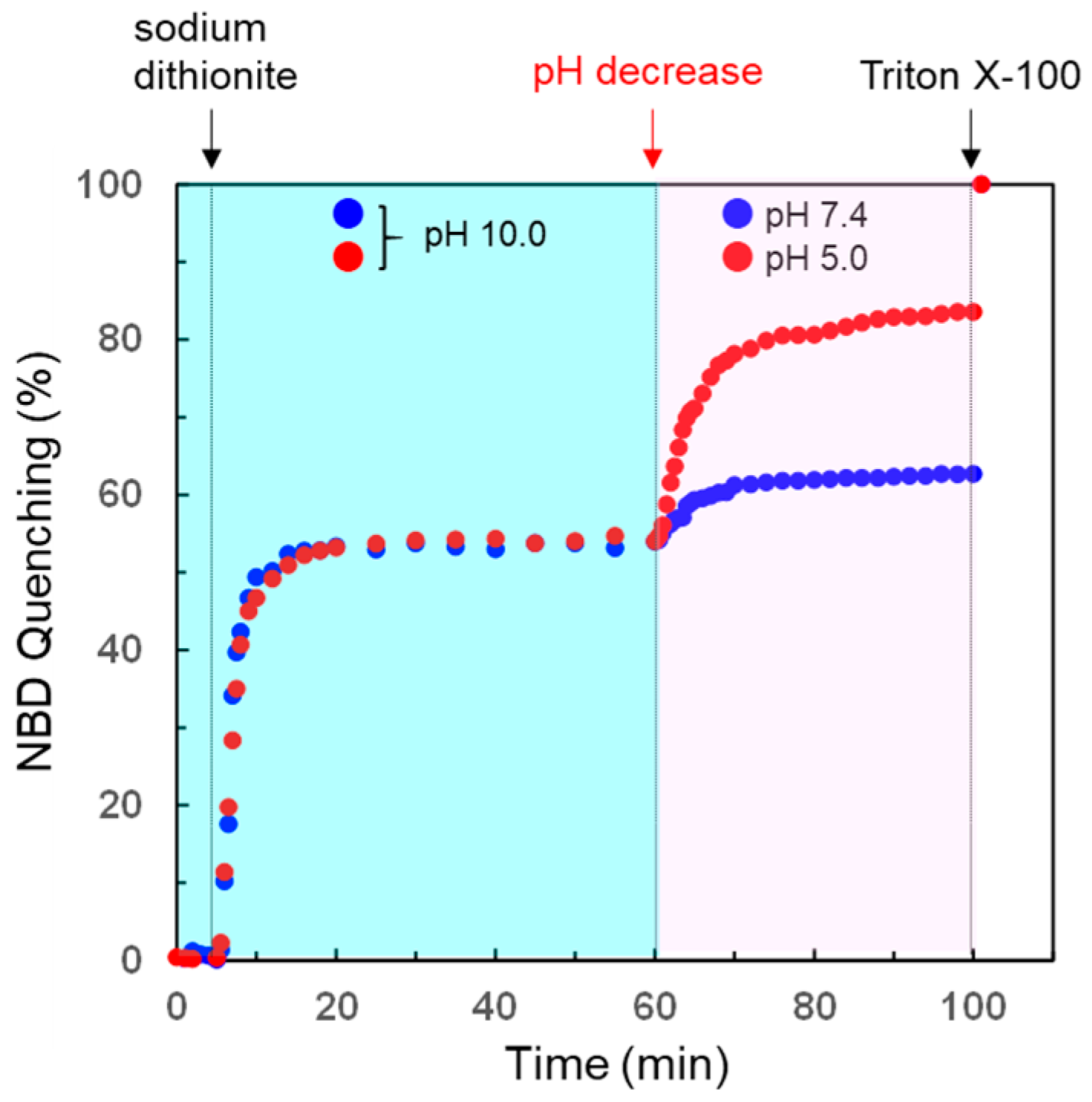
3.4. pH-Selective Lytic Properties of the rLPE-St Anchoring Liposomes
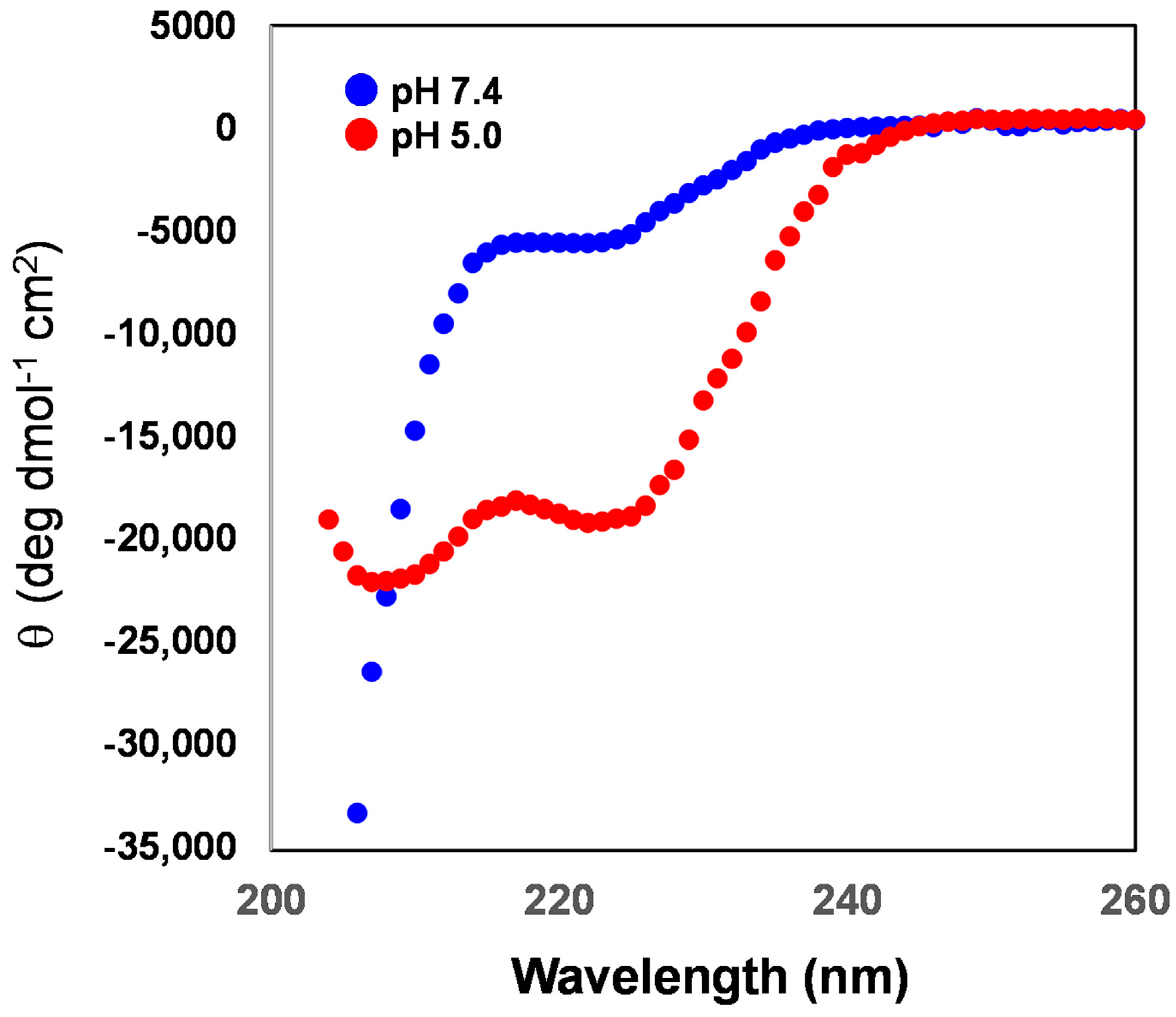
3.5. Secondary Structure of the rLPE Segment Anchored into the Liposomal Membranes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bangham, A.; Standish, M.M.; Watkins, J.C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J. Mol. Biol. 1965, 13, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, A.D. Properties and uses of lipid vesicles: An overview. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1978, 308, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, J.S.; Rana, P.A.C.; Bhandari, D.A.K. Liposome: Methods of preparation and applications. Int. J. Pharm. Stud. Res. 2012, 3, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rideau, E.; Dimova, R.; Schwille, P.; Wurm, F.R.; Landfester, K. Liposomes and polymersomes: A comparative review towards cell mimicking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8572–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papahadjopoulos, D.; Allen, T.M.; Gabizon, A.; Mayhew, E.; Matthay, K.; Huang, S.K.; Lee, K.; Woodle, M.C.; Lasic, D.D.; Redemann, C.; et al. Sterically stabilized liposomes: Improvements in pharmacokinetics and antitumor therapeutic efficacy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11460–11464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, K. Intracellular Targeting Delivery of Liposomal Drugs to Solid Tumors Based on EPR Effects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardone, R.A.; Casavola, V.; Reshkin, S.J. The role of disturbed pH dynamics and the Na+/H+ exchanger in metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swietach, P.; Vaughan-Jones, R.D.; Harris, A.L.; Hulikova, A. The Chemistry, Physiology and Pathology of pH in Cancer. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2014, 369, 20130099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Such, G.K.; Yan, Y.; Johnston, A.P.; Gunawan, S.T.; Caruso, F. Interfacing materials science and biology for drug carrier design. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2278–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macháček, M.; Carter, K.A.; Kostelanský, F.; Miranda, D.; Seffouh, A.; Ortega, J.; Šimůnek, T.; Zimčík, P.; Lovell, J.F. Binding of an amphiphilic phthalocyanine to pre-formed liposomes confers light-triggered cargo release. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 7298–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Lazenby, R.A.; Yuan, Z.; White, R.J.; Park, Y.C. Effect of laser irradiation on reversibility and drug release of light-activatable drug-encapsulated liposomes. Langmuir 2020, 36, 3573–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, R.; Wan, A.; Liu, X.; Jin, H. Intracellular fluorescent thermometry and photothermal-triggered drug release developed from gold nanoclusters and doxorubicin dual-loaded liposomes. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1546–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ueda, M.; Hirose, T.; Ito, Y. Spontaneous Formation of Gating Lipid Domain in Uniform-Size Polypeptide Vesicles for Controlled Release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17956–17961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reja, R.M.; Khan, M.; Singh, S.K.; Misra, R.; Shiras, A.; Gopi, H.N. pH sensitive coiled coils: A strategy for enhanced liposomal drug delivery. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5139–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, F.S.; Wang, X.; Dorrani, M.; Karjoo, Z.; Hatefi, A. A recombinant biopolymeric platform for reliable evaluation of the activity of pH-responsive amphiphile fusogenic peptides. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanz, S.Z.; Shu, N.S.; Qian, J.; Christman, N.; Kranz, P.; An, M.; Grewer, C.; Qiang, W. Protonation-driven membrane insertion of a pH-low insertion peptide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12376–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Akishiba, M.; Iwata, I.; Murata, K.; Mizuno, S.; Kawano, K.; Imanishi, M.; Sugiyama, F.; Futaki, S. Optimizing charge switching in membrane lytic peptides for endosomal release of biomacromolecules. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwada, A.; Mizuno, M.; Hashimoto, J. pH-Dependent membrane lysis by using melittin-inspired designed peptides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 6281–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegh, D.Y.; Mackay, S.M.; Tan, E.W. Pulsatile release from pH triggered imidazoline switchable surfactant liposomes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56859–56866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lei, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, H. Dual-sensitive on–off switch in liposome bilayer for controllable drug release. Langmuir 2019, 35, 5213–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Seo, C.H.; Hahm, K.-S.; Park, Y. Reversed sequence enhances antimicrobial activity of a synthetic peptide. J. Pept. Sci. 2011, 17, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvvadi, P.; Vunnam, S.; Rotondi, K.S.; Merrifield, R.B. Synthetic melittin, its nantio, retro, and retroenantio isomers, and selected chimeric analogs: Their antibacterial, hemolytic, and lipid bilayer action. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8989–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Liang, R.; Zheng, X.; Chen, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, B.; Yan, X.; Wang, R. Stearylated antimicrobial peptide melittin and its retro isomer for efficient gene transfection. Bioconjugate Chem. 2013, 24, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzgunes, N.; Straubinger, R.M.; Baldwin, P.A.; Friend, D.S.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Proton-induced fusion of oleic acid-phosphatidylethanolamine liposomes. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klocek, G.; Schulthess, T.; Shai, Y.; Seelig, J. Thermodynamics of melittin binding to lipid bilayers: Aggregation and pore formation. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 2586–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, K.P.; Irudayam, S.J.; Berkowitz, M.L. Melittin creates transient pores in a lipid bilayer: Results from computer simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 5031–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauson, A.J.; He, J.; Wimley, W.C. Gain-of-function analogues of the pore-forming peptide melittin selected by orthogonal high-throughput screening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12732–12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckl, M.; Claessensa, M.M.A.E.; Subramaniam, V. Kinetic measurements give new insights into lipid membrane permeabilization by α-synuclein oligomers. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.A.; Bhattacharya, S. Transverse membrane asymmetry in model phospholipid bilayers: NBD-Phosphatidylethanolamine and the separation of flip from flop. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8688–8689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Gong, Y.; Bong, D. Lipid membrane adhesion and fusion driven by designed, minimally multivalent hydrogen-bonding lipids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16919–16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Fa, K.; Liu, H.; Waigh, T.A.; McBain, A.; Lu, J.R. Hydrophobic control of the bioactivity and cytotoxicity of de novo-designed antimicrobial peptides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34609–34620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kashiwada, A.; Namiki, K.; Mori, H. Design and Construction of pH-Selective Self-Lytic Liposome System. Processes 2020, 8, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121526
Kashiwada A, Namiki K, Mori H. Design and Construction of pH-Selective Self-Lytic Liposome System. Processes. 2020; 8(12):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121526
Chicago/Turabian StyleKashiwada, Ayumi, Kana Namiki, and Haruka Mori. 2020. "Design and Construction of pH-Selective Self-Lytic Liposome System" Processes 8, no. 12: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121526
APA StyleKashiwada, A., Namiki, K., & Mori, H. (2020). Design and Construction of pH-Selective Self-Lytic Liposome System. Processes, 8(12), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8121526