Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Pine Wood Sawdust Mixed with Activated Carbon for Bio-Oil and Bio-Char Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Proximate Analysis
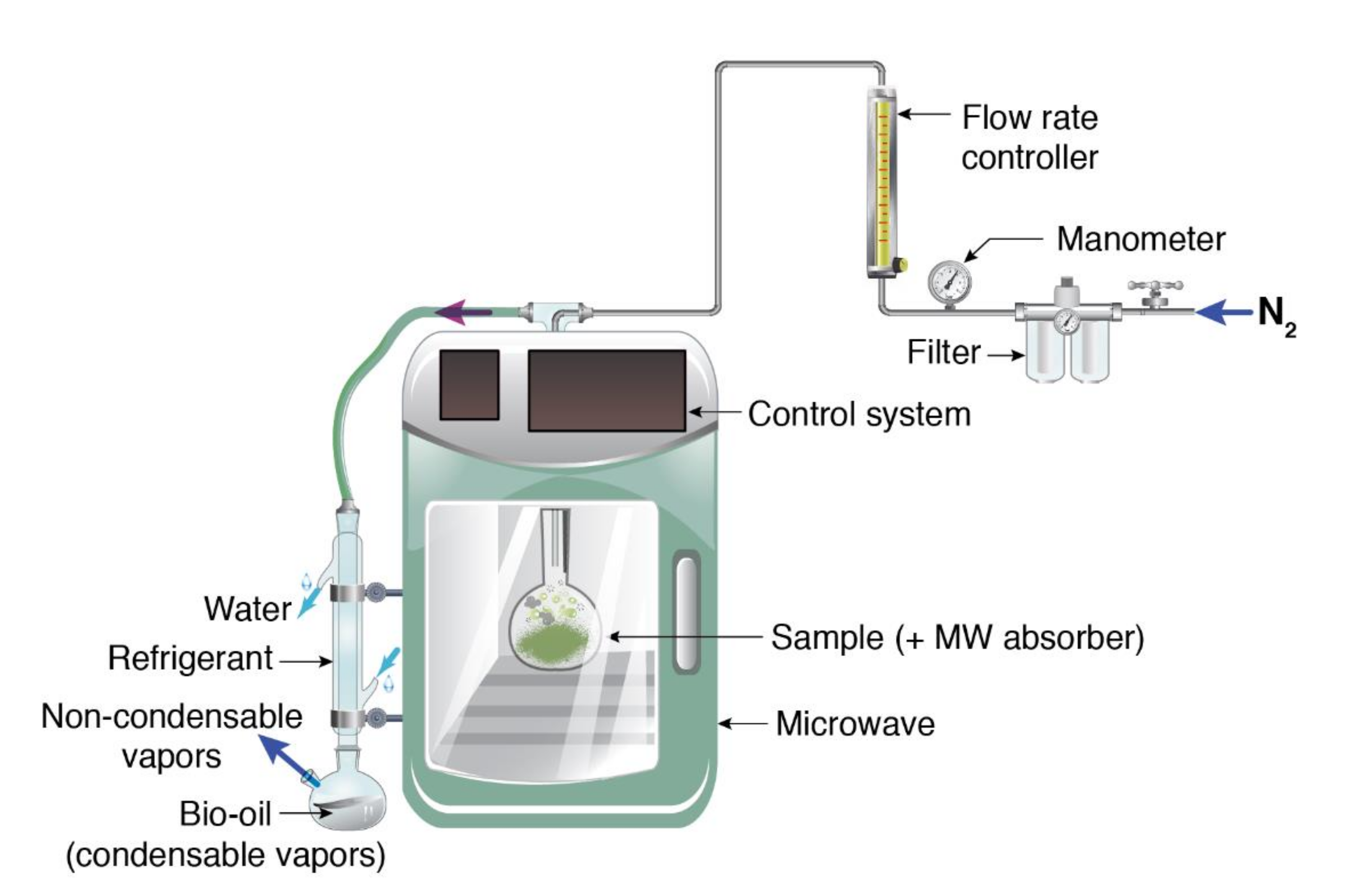
2.3. Pyrolysis Process
2.4. Chromatographic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
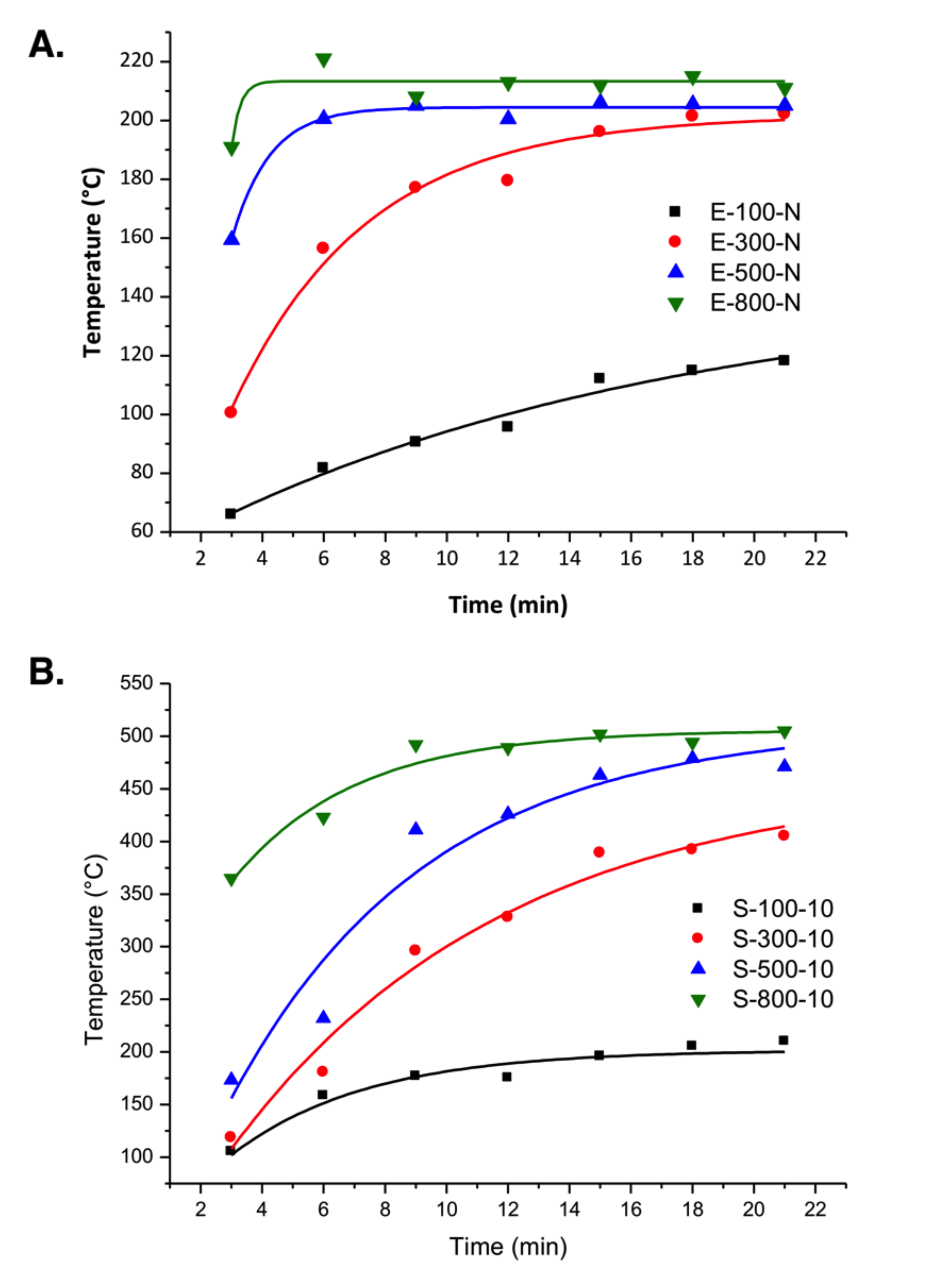
3.1. Temperature Profiles
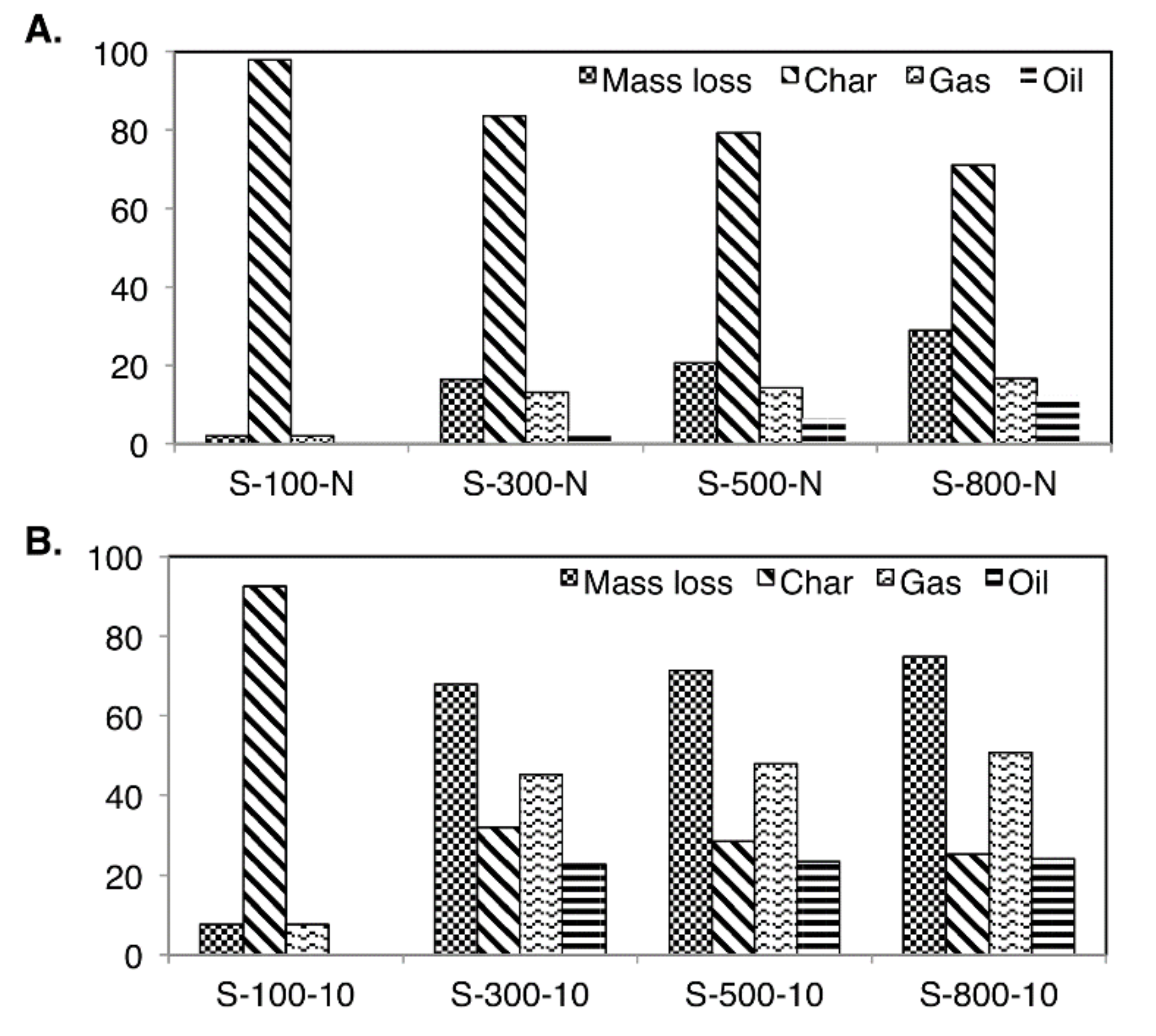
3.2. Pyrolysis Products’ Yields
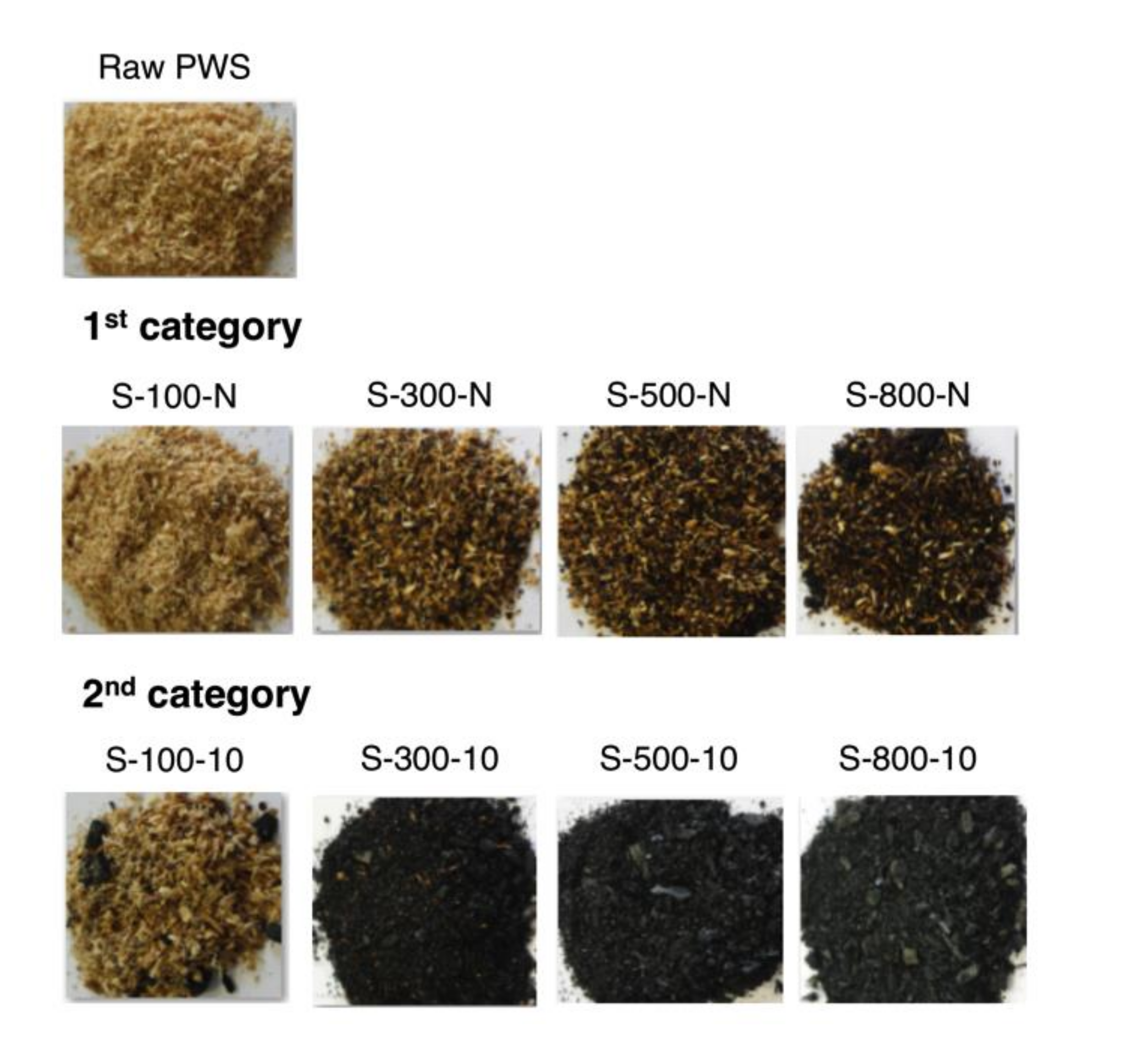
3.3. Characterization of the Solid Fraction
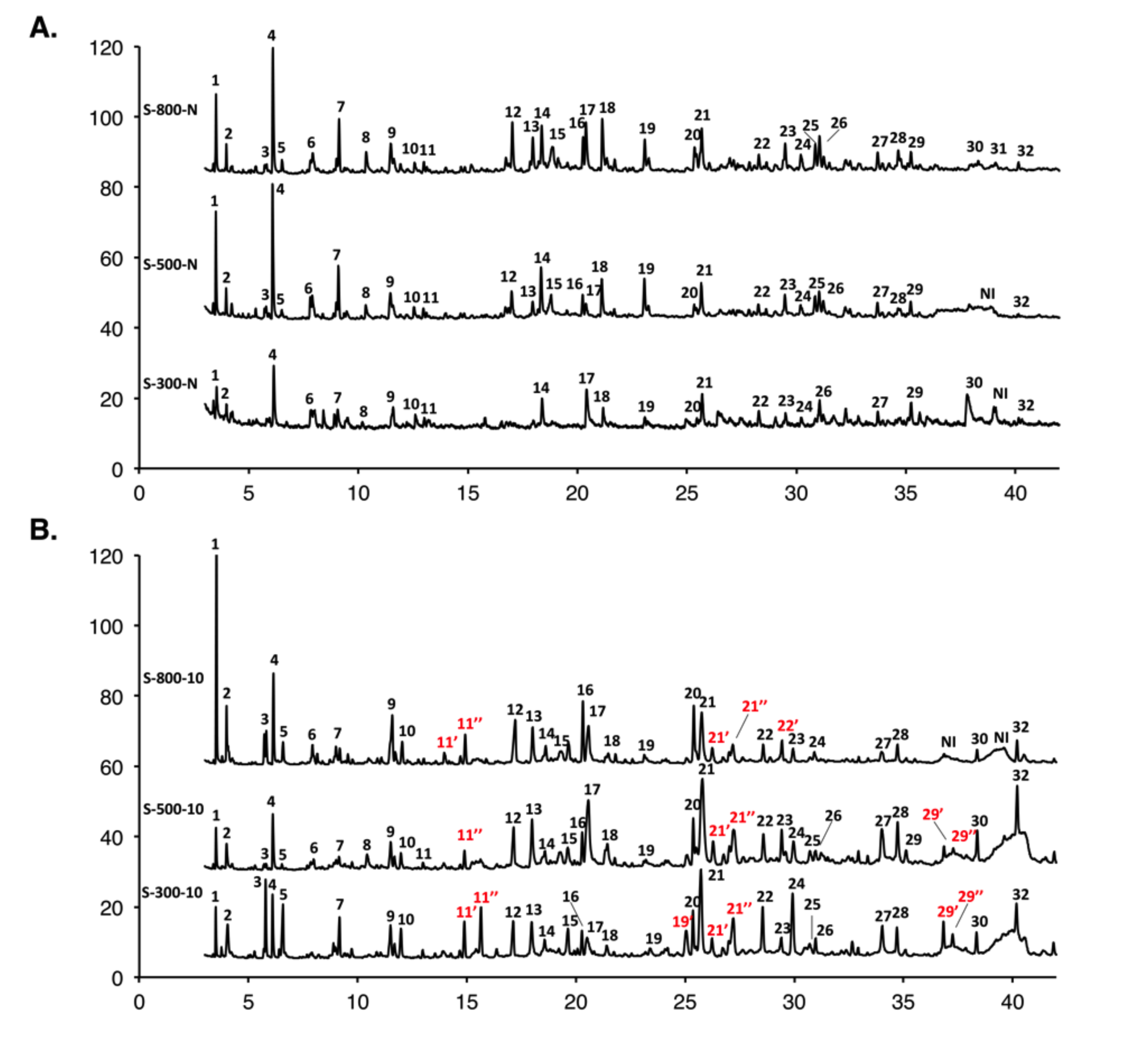
3.4. GC-MS Characterization of the Liquid Fraction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajpai, P. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Biofuel Production; Springer: Singapore, 2016; ISBN 978-981-10-0686-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mašek, O.; Budarin, V.; Gronnow, M.; Crombie, K.; Brownsort, P.; Fitzpatrick, E.; Hurst, P. Microwave and slow pyrolysis biochar—Comparison of physical and functional properties. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 100, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salema, A.A.; Ani, F.N. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of oil palm shell biomass using an overhead stirrer. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 96, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Microwave-assisted catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass for bio-oil production using chemical vapor deposition modified HZSM-5 catalyst. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrera-Lorenzo, N.; Fuente, E.; Bermúdez, J.M.; Suárez-Ruiz, I.; Ruiz, B. Conventional and microwave pyrolysis of a macroalgae waste from the Agar-Agar industry. Prospects for bio-fuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 151, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, A.; Menéndez, J.A.; Fernández, Y.; Pis, J.J.; Nabais, J.M.V.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Carrott, M.M.L.R. Conventional and microwave induced pyrolysis of coffee hulls for the production of a hydrogen rich fuel gas. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2007, 79, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Chiueh, P.-T.; Kuan, W.-H.; Lo, S.-L. Microwave pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass: Heating performance and reaction kinetics. Energy 2016, 100, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanik, J.; Stahl, R.; Troeger, N.; Sinag, A. Pyrolysis of algal biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 103, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Qian, L.; Liu, R.; Chen, M.; Yan, J.; Hu, Q. Lead adsorption by biochar under the elevated competition of cadmium and aluminum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, B.A.; Kim, C.S.; Ellis, N.; Bi, X. Microwave-assisted catalytic pyrolysis of switchgrass for improving bio-oil and biochar properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazargan, A.; Rough, S.L.; McKay, G. Compaction of palm kernel shell biochars for application as solid fuel. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 70, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Fan, L.; Duan, D.; Ruan, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L. Production of hydrocarbon-rich bio-oil from soapstock via fast microwave-assisted catalytic pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 125, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernik, S.; Bridgwater, A.V. Overview of applications of biomass fast pyrolysis oil. Energy Fuels 2004, 18, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Chiueh, P.-T.; Kuan, W.-H.; Lo, S.-L. Effects of lignocellulosic composition and microwave power level on the gaseous product of microwave pyrolysis. Energy 2015, 89, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzini, A.; Madi, H.; Chiodo, V.; Papurello, D.; Maisano, S.; Santarelli, M.; Van Herle, J. Dealing with fuel contaminants in biogas-fed solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) and molten carbonate fuel cell (MCFC) plants: Degradation of catalytic and electro-catalytic active surfaces and related gas purification methods. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 61, 150–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, M.R.B.; Salinas Gutiérrez, J.M.; Meléndez Zaragoza, M.J.; López Ortiz, A.; Collins-Martínez, V. Optimal slow pyrolysis of apple pomace reaction conditions for the generation of a feedstock gas for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 23232–23237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.; Chase, H.A. A Review on waste to energy processes using microwave pyrolysis. Energies 2012, 5, 4209–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hayward, D.O. Applications of microwave dielectric heating in environment-related heterogeneous gas-phase catalytic systems. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2006, 359, 3421–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marland, S.; Merchant, A.; Rowson, N. Dielectric properties of coal. Fuel 2001, 80, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, J.E.; Wheeler, R.R. Temperature dependent complex permittivities of graphitized carbon blacks at microwave frequencies between 0.2 and 26 GHz. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.H.; Ting, T.H.; Wang, G.P.; Yang, C.C.; Tsai, C.W. Synthesis and microwave electromagnetic characteristics of bamboo charcoal/polyaniline composites in 2–40 GHz. Synth. Met. 2008, 158, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwater, J.E.; Wheeler, R.R. Complex permittivities and dielectric relaxation of granular activated carbons at microwave frequencies between 0.2 and 26 GHz. Carbon 2003, 41, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, C.R.; Hoff, R.; Mărculescu, C.; Boldor, D. Investigation of microwave-assisted pyrolysis of biomass with char in a rectangular waveguide applicator with built-in phase-shifting. Appl. Energy 2020, 259, 114217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sabbarwal, S.; Mishra, P.K.; Upadhyay, S.N. Thermal degradation kinetics of sugarcane leaves (Saccharum officinarum L.) using thermo-gravimetric and differential scanning calorimetric studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgovnikov, G.I. Dielectric Properties of Wood and Wood-Based Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Gholizadeh, M. Biomass pyrolysis: A review of the process development and challenges from initial researches up to the commercialisation stage. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 39, 109–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Menéndez, J.A.; Arenillas, A.; Cot, J. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of biomass feedstocks: The way forward? Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5481–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, D.; Darr, M.; Shah, A.; Potter, B.; Zimmerman, J. Effects of torrefaction process parameters on biomass feedstock upgrading. Fuel 2012, 91, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukios, E.G. Progress in thermochemical, solid-state refining of biofuels—From research to commercialization. In Advances in Thermochemical Biomass Conversion; Bridgwater, A.V., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 1678–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Li, A.; Quan, C.; Du, L.; Duan, Y. TG–FTIR and Py–GC/MS analysis on pyrolysis and combustion of pine sawdust. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 100, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, G.; Ronsse, F.; Venderbosch, R.; Duren, R.; van Kersten, S.R.A.; Prins, W. Effect of biomass ash in catalytic fast pyrolysis of pine wood. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 168–169, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bhowmick, G.; Sarmah, A.K.; Sen, R. Production and characterization of a value added biochar mix using seaweed, rice husk and pine sawdust: A parametric study. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, K.; Ganesh, A. Heating value of biomass and biomass pyrolysis products. Fuel 1996, 75, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, G.R.; Richards, G.N. Thermal synthesis and pyrolysis of a xylan. Carbohydr. Res. 1991, 218, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh, F.; McGinnis, G.D.; Philpot, C.W. Thermal degradation of xylan and related model compounds. Carbohydr. Res. 1972, 25, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antal, M.J.; Leesomboon, T.; Mok, W.S.; Richards, G.N. Mechanism of formation of 2-furaldehyde from d-xylose. Carbohydr. Res. 1991, 217, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.K.; Gu, S.; Bridgwater, A.V. Study on the pyrolytic behaviour of xylan-based hemicellulose using TG–FTIR and Py–GC–FTIR. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2010, 87, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.K.; Gu, S. The mechanism for thermal decomposition of cellulose and its main products. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6496–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Yang, X.; Dong, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X. Influence of pyrolysis temperature and time on the cellulose fast pyrolysis products: Analytical Py-GC/MS study. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 92, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, D.J.; Bridgwater, A.V.; Elliott, D.C.; Meier, D.; de Wild, P. Lignin fast pyrolysis: Results from an international collaboration. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2010, 88, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windt, M.; Meier, D.; Marsman, J.H.; Heeres, H.J.; Koning, S. de Micro-pyrolysis of technical lignins in a new modular rig and product analysis by GC-MS/FID and GC × GC-TOFMS/FID. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 85, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.T.; Virk, P.S. Modeling of Lignin Thermolysis. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murwanashyaka, J.N.; Pakdel, H.; Roy, C. Step-wise and one-step vacuum pyrolysis of birch-derived biomass to monitor the evolution of phenols. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2001, 60, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.P.; Kim, C.S. Lignin depolymerization and conversion: A review of thermochemical methods. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Lei, H.; Wang, L.; Bu, Q.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Julson, J.; Ruan, R. Biofuel production and kinetics analysis for microwave pyrolysis of Douglas fir sawdust pellet. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 94, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effendi, A.; Gerhauser, H.; Bridgwater, A.V. Production of renewable phenolic resins by thermochemical conversion of biomass: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2092–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestos, C.; Chorianopoulos, N.; Nychas, G.-J.E.; Komaitis, M. RP-HPLC analysis of the phenolic compounds of plant extracts. investigation of their antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Kim, K.H.; Brown, R.C. Catalytic pyrolysis of individual components of lignocellulosic biomass. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Pang, S.; de Miguel Mercader, F.; Torr, K.M. The effect of biomass pretreatment on catalytic pyrolysis products of pine wood by Py-GC/MS and principal component analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 138, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-X.; Cao, J.-P.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Liu, T.-L.; Wei, F.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Wei, X.-Y. Study on pine sawdust pyrolysis behavior by fast pyrolysis under inert and reductive atmospheres. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 125, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Higher heating value (MJ/kg) | 16.6 |
| Density of particles (g/cm3) | 0.113 |
| Proximate analysis (wt.%): | |
| Moisture Volatile matter Fixed carbon Ash | 9 81.1 9.7 0.2 |
| Sample | HHV (MJ/kg) | AshC (wt.%) | VMC (wt.%) | FCC (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw PWS | 16.6 | 0.2 | 81.1 | 9.7 | |
| 1st category | S-100-N | 17.7 | 0.3 | 80.9 | 14.8 |
| S-300-N | 19.4 | 0.5 | 77.4 | 22.1 | |
| S-500-N | 19.4 | 0.7 | 73.7 | 25.6 | |
| S-800-N | 22.8 | 0.6 | 69.6 | 29.8 | |
| 2nd category | S-100-10 | 21.5 | 0.4 | 74.4 | 25.2 |
| S-300-10 | 29.3 | 1.7 | 19.6 | 78.7 | |
| S-500-10 | 30.2 | 6.1 | 15.8 | 78.1 | |
| S-800-10 | 30.3 | 10.0 | 10.8 | 79.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khelfa, A.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Koubaa, M.; Vorobiev, E. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Pine Wood Sawdust Mixed with Activated Carbon for Bio-Oil and Bio-Char Production. Processes 2020, 8, 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111437
Khelfa A, Rodrigues FA, Koubaa M, Vorobiev E. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Pine Wood Sawdust Mixed with Activated Carbon for Bio-Oil and Bio-Char Production. Processes. 2020; 8(11):1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111437
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhelfa, Anissa, Filipe Augusto Rodrigues, Mohamed Koubaa, and Eugène Vorobiev. 2020. "Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Pine Wood Sawdust Mixed with Activated Carbon for Bio-Oil and Bio-Char Production" Processes 8, no. 11: 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111437
APA StyleKhelfa, A., Rodrigues, F. A., Koubaa, M., & Vorobiev, E. (2020). Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Pine Wood Sawdust Mixed with Activated Carbon for Bio-Oil and Bio-Char Production. Processes, 8(11), 1437. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111437






