Classification, Force Deformation Characteristics and Cooking Kinetics of Common Beans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Common Beans Classification
2.2.1. Cooking of Beans
2.2.2. Subjective Cookability Evaluation
2.2.3. Objective Cookability Evaluation
2.3. Bean Texture Measurement
2.4. Bean Softening Experiments
2.4.1. Soaking
2.4.2. Cooking in Salt
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Kinetics of Bean Softening
3. Results and Discussion
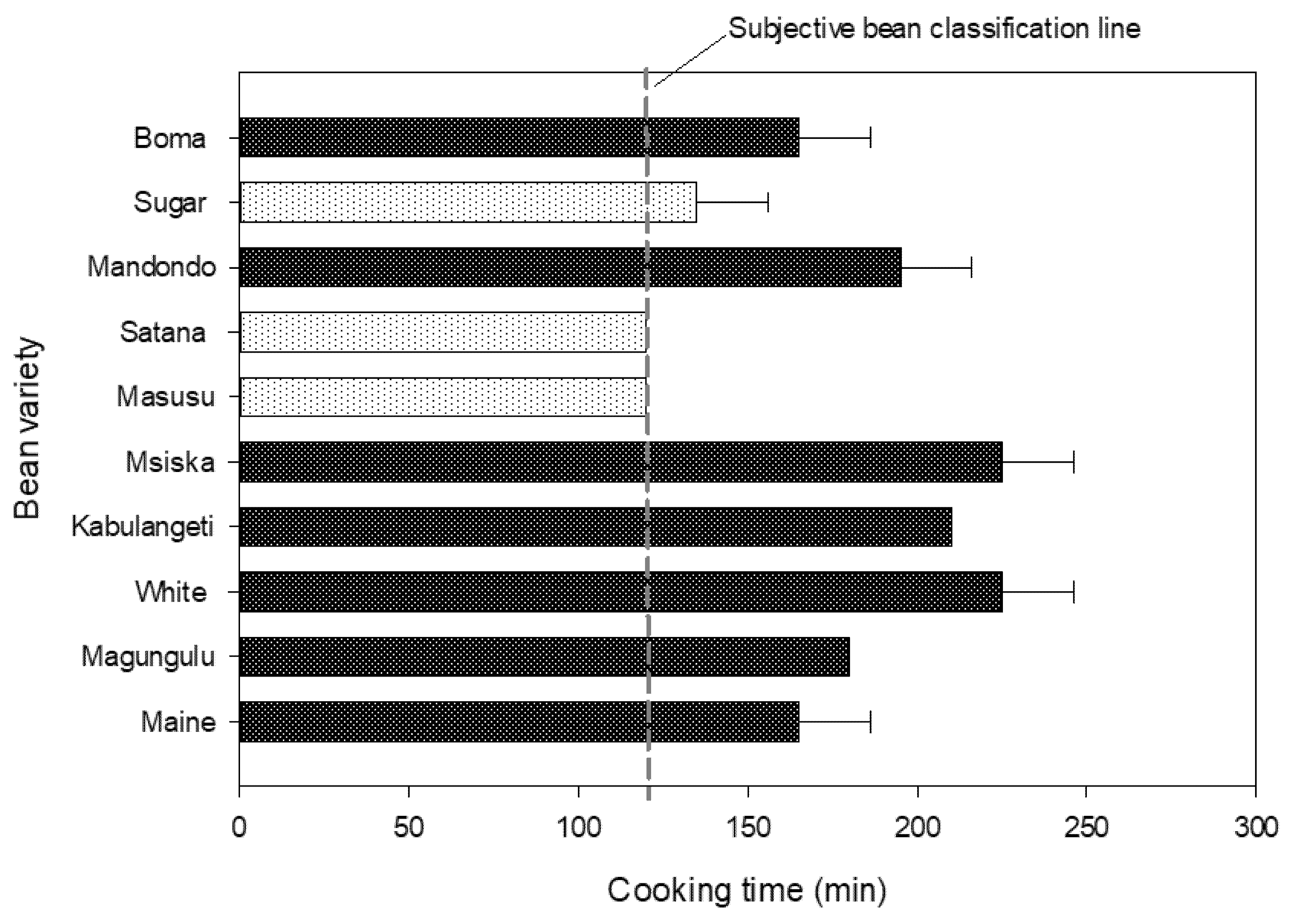
3.1. Bean Classification
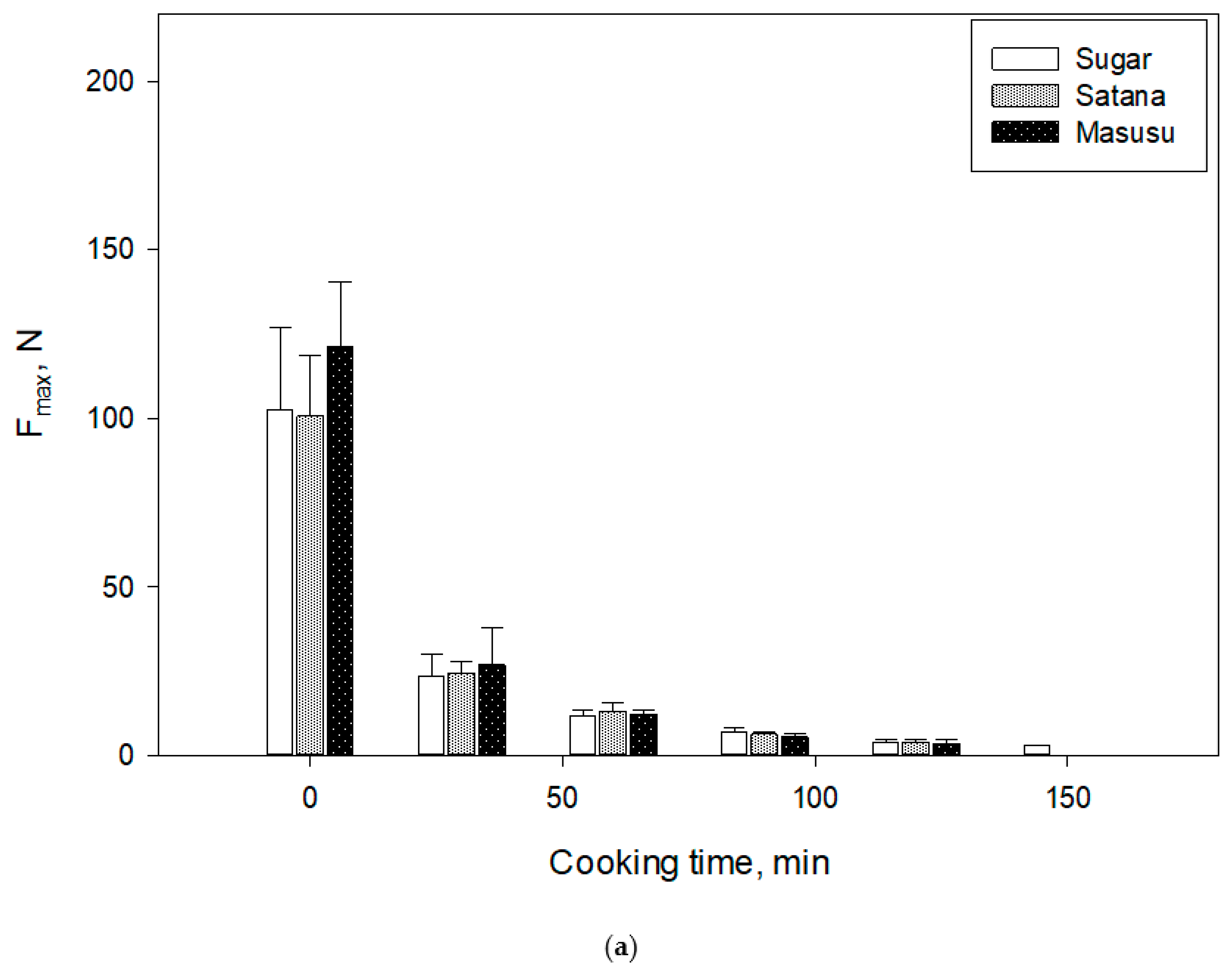
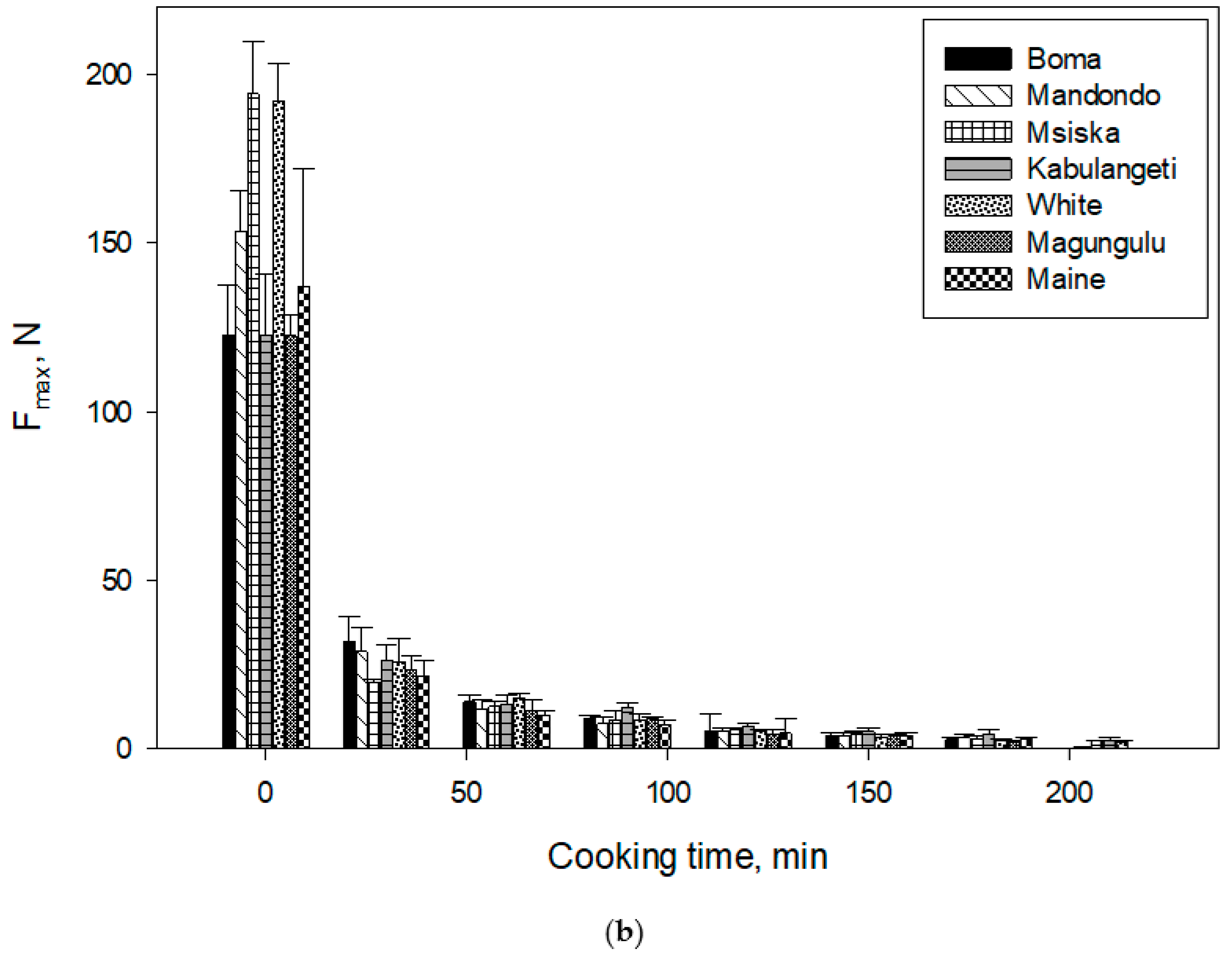
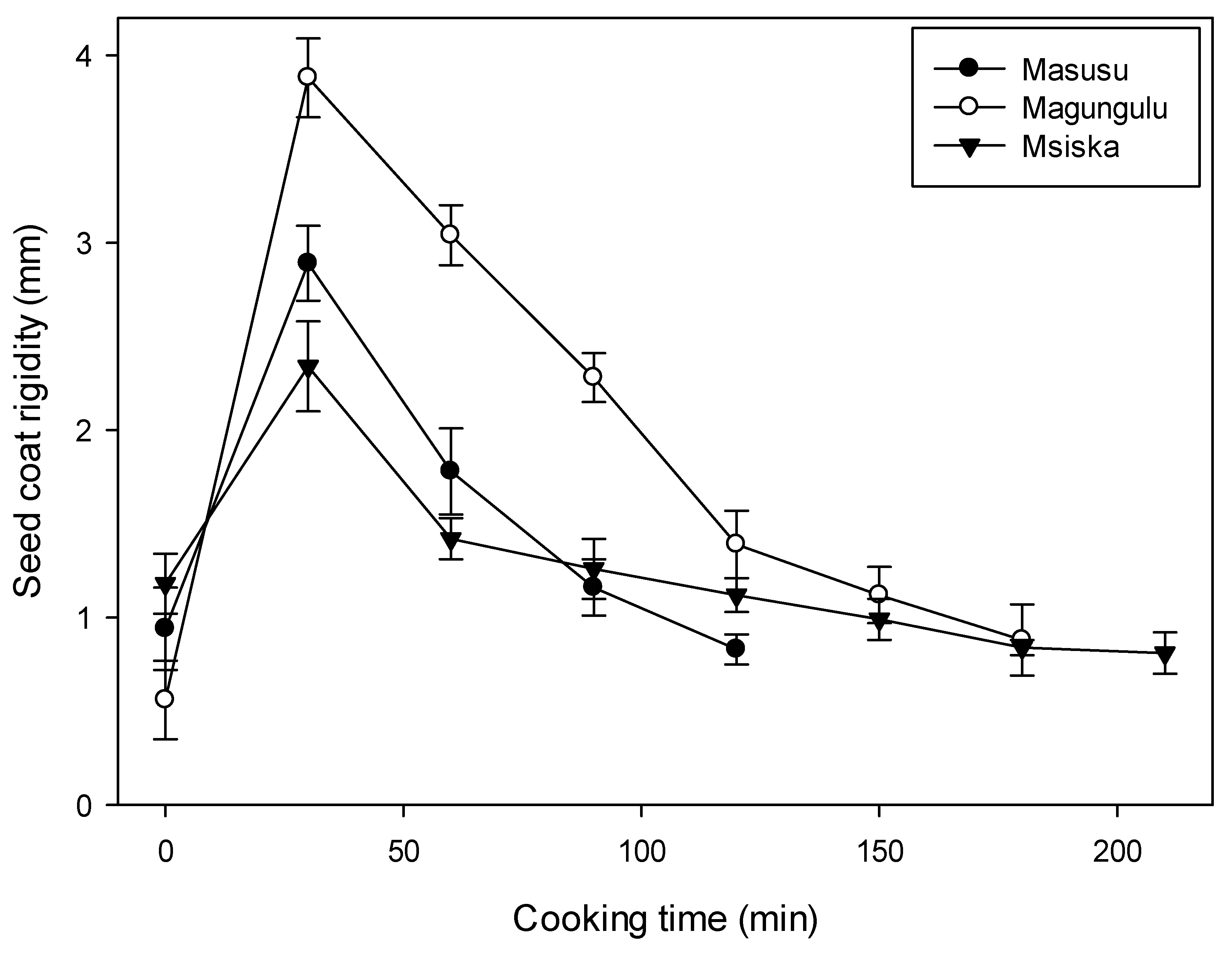
3.2. Bean Structure Deformation during Cooking
3.3. Modeling Bean Texture as a Function of Time
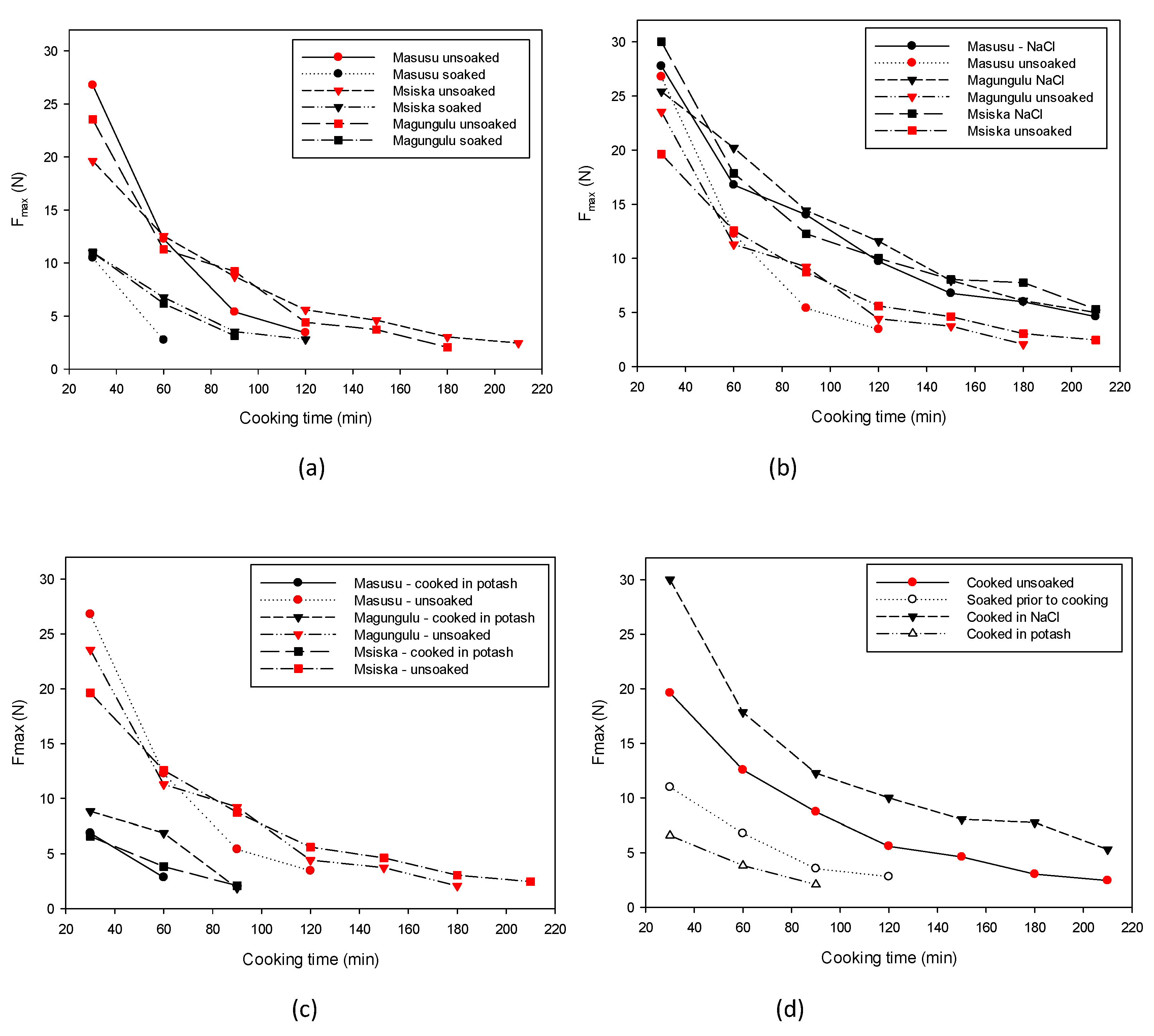
3.4. Softening Techniques and Their Impact during Cooking
3.4.1. Effect of Soaking on the Texture of Common Beans
3.4.2. Effect of Salt Addition on Texture Profile during Cooking
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anton, A.A.; Ross, K.A.; Beta, T.; Fulcher, R.G.; Arntfield, S.D. Effect of pre-dehulling treatments on some nutritional and physical properties of navy and pinto beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Öner, M.D.; Bayram, M. Effect of soaking and ultrasound treatments on texture of chickpea. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebersax, M.A.; Ruengsakulrach, S.; Occea, L.G. Strategies and procedures for processing dry beans. J. Food Tech. 1991, 44, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Nyakuni, G.A.; Kikafunda, J.K.; Muyonga, J.H.; Kyamuhangire, W.M.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Ugen, M. Chemical and nutritional changes associated with the development of the hard-to-cook defect in common beans. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 59, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiga, T.M.; Lajolo, F.M.; Filisetti, T.M.C.C. Changes in the cell wall polysaccharides during storage and hardening of beans. Food Chem. 2004, 84, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscoso, W.; Bourne, M.C.; Hood, L.F. Relationships Between the Hard-to-Cook Phenomenon in Red Kidney Beans and Water Absorption, Puncture Force, Pectin, Phytic Acid, and Minerals. Int. J. Food Sci. 1984, 49, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Kyriakidis, N.B.; Margaris, I. Phytase–phytate–pectin hypothesis and quality of legumes cooked in calcium solutions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincks, M.J.; Stanley, D.W. Lignification: Evidence for a role in hard-to-cook beans. J. Food Biochem. 1987, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuma, N.; Hammerschmidt, R.; Uebersax, M.A.; Ruengsakulrach, S.; Bennink, M.R.; Hosfield, G.L. Storage Induced Changes of Phenolic Acids and the Development of Hard-To-Cook in Dry Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris var. Seafarer). J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujolà, M.; Farreras, A.; Casañas, F. Protein and starch content of raw, soaked and cooked beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, M.; Misra, N.N.; Mahadevan, K.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound assisted hydration of navy beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de León, L.F.; Elías, L.G.; Bressani, R. Effect of salt solutions on the cooking time, nutritional and sensory characteristics of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). Food Res. Int. 1992, 25, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowen, A.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Frias, J.; Oliveira, J. Influence of pre-blanching on the water absorption kinetics of soybeans. J. Food Eng. 2007, 78, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Cichy, K.A.; Harte, J.B.; Kelly, J.D.; Ng, P.K. Effects of extrusion cooking on the chemical composition and functional properties of dry common bean powders. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, R.; Aguirre, A.; Marzo, F. Effects of extrusion and traditional processing methods on antinutrients and in vitro digestibility of protein and starch in faba and kidney beans. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.; Orúe, E.; Marzo, F. Effects of extrusion and conventional processing methods on protein and antinutritional factor contents in pea seeds. Food Chem. 1998, 63, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoroge, D.M.; Kinyanjui, P.K.; Chigwedere, C.M.; Christiaens, S.; Makokha, A.O.; Sila, D.N.; Hendrickx, M.E. Mechanistic insight into common bean pectic polysaccharide changes during storage, soaking and thermal treatment in relation to the hard-to-cook defect. Food Res. Int. 2016, 81, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinyanjui, P.K.; Njoroge, D.M.; Makokha, A.O.; Christiaens, S.; Ndaka, D.S.; Hendrickx, M. Hydration properties and texture fingerprints of easy- and hard-to-cook bean varieties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 3, 9–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindiola, O.L.; Seib, O.A.; Hoseney, R.C. Accelerated development of hard-to-cook state in beans. Cereal Foods World 1986, 31, 14. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos Siqueira, B.; Vianello, R.P.; Fernandes, K.F.; Bassinello, P.Z. Hardness of carioca beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as affected by cooking methods. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 54, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, I.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M. Effect of canning process on texture of Faba beans (Vicia Faba). Food Chem. 2008, 106, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaei, S.M.; Masoumi, A.A.; Roshan, H. Analysis of water absorption of bean and chickpea during soaking using Peleg model. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2016, 15, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWatters, K.H.; Chinnan, M.S.; Phillips, R.D.; Beuchat, L.R.; Reid, L.B.; Mensa-Wilmot, Y.M. Functional, Nutritional, Mycological, and Akara-making Properties of Stored Cowpea Meal. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, S.E.; Mcminn, W.A.; Magee, T.R.; Richardson, P.S. Effect of processing conditions on the water absorption and texture kinetics of potato. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, J.; Mohammadi, N. Effect of temperature on hydration kinetics of sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum L.). J. Food Eng. 2009, 91, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, A.C.; Augusto, P.E.D. From the sigmoidal to the downward concave shape behavior during the hydration of grains: Effect of the initial moisture content on Adzuki beans (Vigna angularis). Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Adhikari, B.; Panozzo, J.; Aldred, P. Water uptake and its impact on the texture of lentils (Lens culinaris). J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Ghannam, N. Interpretation of the force deformation curves of soaked red kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.W.; Aguilera, J.M. A review of textural defects in cooked reconstituted legumes—The influence od structure and composition. J. Food Biochem. 1985, 9, 277–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefa-Dedeh, S.; Stanley, D.W. The relationship of microstructure of cowpeaa to water absorption and dehulling properties. Cereal Chem. 1979, 56, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Sefa-Dedeh, S.; Stanley, D.W. Textural implications of the microstructure of legumes. Food Technol. 1979, 33, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Peleg, M. An Empirical Model for the Description of Moisture Sorption Curves. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 1216–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharanagat, V.S.; Kansal, V.; Kumar, K. Modeling the effect of temperature on the hydration kinetic whole moong grain. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefa-Dedeh, S.; Stanley, D.W.; Voisey, P.W. Effects of soaking time and cooking conditions on texture and microstructure of cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata). J. Food Sci. 1978, 43, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressani, R. Grain quality of common beans. Food Rev. Int. 1993, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 3-Parameter Model | 2-Parameter Model | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bean Cultivar | Fe | Fd | KF | R2 | RMSE (%) | F0 | KF | R2 | RMSE (%) |
| Boma | 4.39 | 103.8 | 0.0428 | 0.999 | 12.5 | 107.8 | 0.0367 | 0.991 | 14.5 |
| Sugar | 4.33 | 104.0 | 0.0574 | 0.998 | 3.3 | 108.0 | 0.0463 | 0.990 | 8.9 |
| Mandondo | 3.66 | 104.7 | 0.0459 | 0.998 | 10.4 | 107.9 | 0.0404 | 0.991 | 18.4 |
| Satana | 4.22 | 104.1 | 0.0538 | 0.997 | 4.5 | 107.1 | 0.0445 | 0.990 | 8.5 |
| Masusu | 3.61 | 104.7 | 0.0584 | 0.998 | 3.9 | 108.7 | 0.0427 | 0.994 | 4.8 |
| Msiska | 4.56 | 102.9 | 0.0424 | 0.994 | 14.7 | 107.9 | 0.0498 | 0.978 | 29.7 |
| Kabulangeti | 4.12 | 102.1 | 0.0514 | 0.994 | 9.2 | 107.5 | 0.0405 | 0.975 | 22.4 |
| White | 4.39 | 103.6 | 0.0486 | 0.994 | 10.4 | 107.6 | 0.0409 | 0.984 | 14.7 |
| Magungulu | 4.43 | 103.4 | 0.0549 | 0.996 | 12.8 | 107.9 | 0.0455 | 0.986 | 16.1 |
| Maine | 4.05 | 103.6 | 0.0537 | 0.999 | 11.8 | 108.1 | 0.0490 | 0.988 | 10.2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwofie, E.M.; Mba, O.I.; Ngadi, M. Classification, Force Deformation Characteristics and Cooking Kinetics of Common Beans. Processes 2020, 8, 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101227
Kwofie EM, Mba OI, Ngadi M. Classification, Force Deformation Characteristics and Cooking Kinetics of Common Beans. Processes. 2020; 8(10):1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101227
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwofie, Ebenezer M., Ogan I. Mba, and Michael Ngadi. 2020. "Classification, Force Deformation Characteristics and Cooking Kinetics of Common Beans" Processes 8, no. 10: 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101227
APA StyleKwofie, E. M., Mba, O. I., & Ngadi, M. (2020). Classification, Force Deformation Characteristics and Cooking Kinetics of Common Beans. Processes, 8(10), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101227