A Review of the Use of Eutectic Solvents, Terpenes and Terpenoids in Liquid–liquid Extraction Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Application of Eutectic Solvents in Liquid–liquid Extraction
- Separation of solutes from oils and biodiesel.
- Separation of hydrocarbons.
- Separation of alcohols from hydrocarbons.
- Separation of value-added compounds.
- Formation of Aqueous Biphasic Systems (ABS) using eutectic solvents.
- Separation of organic compounds using hydrophobic eutectic solvents (HES).
- Separation of metals using hydrophobic eutectic solvents (HES).
- Development of analytical methods using eutectic solvents.
2.1. Eutectic Solvents in Liquid–liquid Extraction Processes
2.1.1. Separation of Organic Compounds from Oils and Biodiesel
2.1.2. Separation of Aromatic, Sulfur or Nitrogen Hydrocarbons from Alkanes
| Solute | Raffinate | Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzene | n-Hexane | Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide + ethylene glycol | 2012 | [50] |
| Benzene and Ethylacetate | n-Hexane | Choline chloride + lactic acid Choline chloride + glycerol | 2013 | [53] |
| Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene and m-Xylene | n-Octane | Tetrabutylammonium bromide + sulfolane | 2014 | [54] |
| Benzene, Toluene or Pyridine | n-Hexane | Choline chloride + glucose | 2016 | [55] |
| Benzene | n-Hexane | (Tetramethylammonium chloride, tetraethylammonium chloride, tetrabutylammonium chloride, or tetrahexylammonium chloride) + (ethylene glycol or glycerol) | 2017 | [56] |
| Benzene | Cyclohexane | Tetrabutylammonium bromide + (sulfolane or triethylene glycol) Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide + (triethylene glycol or 1,2 propanediol) Choline chloride + triethylene glycol | 2017 | [57] |
| Benzene, Toluene | Cyclohexane, n-Heptane | N-ethylpyridinium bromide + (N-formyl morpholine or levulinic acid) | 2019 | [58] |
| Benzene, Cyclohexane | Thiophene, Hexadecane | Choline chloride + (monoethylene glycol, diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, monoethanolamine, diethanolamine; or triethanolamine) | 2019 | [59] |
| Toluene | n-Heptane | Tetrabutylphosphonium bromide + (ethylene glycol or sulfolane) | 2012 | [51] |
| Toluene | n-Heptane | Ethyltriphenylphosphonium iodide + (ethylene glycol or sulfolane) | 2013 | [52] |
| Toluene | n-Heptane | (Choline chloride, benzylcholinium chloride or tetrabutylammonium chloride) + levulinic acid | 2016 | [60] |
| Toluene, Quinoline | n-Heptane | Methyltriphenyl phosphonium bromide + (ethyleneglycol or glycerol) | 2016 | [61] |
| Toluene | n-Octane | Choline chloride + malonic acid | 2018 | [62] |
| Toluene | n-Hexane, n-Heptane | Choline chloride + Phenol | 2019 | [63] |
| Ethylbenzene | n-Octane | Tetrabutylammonium bromide + (pyridine and/or ethylene glycol) | 2015 | [64] |
| Ethylbenzene | Styrene | Tetrabutyl ammonium bromide + (ethylene glycol diethylene glycol or triethylene glycol) | 2019 | [65] |
| Benzene, Toluene, Ethylbenzene, Xylene | Reformer and Pyrolysis Gasolines | Choline chloride + (ethylene glycol, glycerol, levulinic acid, phenylacetic acid, malonic acid or urea) | 2018 | [66] |
| Solute | Raffinate | Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyridine Toluene | n-Hexane | Choline chloride + urea Choline chloride + glycerol | 2016 | [82] |
| Pyridine Benzothiazole | n-Hexane n-Heptane | Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide + ethylene glycol | 2019 | [83] |
| Pyridine | n-Hexane n-Heptane n-Octane | Binary: (Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide + glycerol) Ternary: (Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide + glycerol + ethylene glycol) | 2020 | [84] |
| Quinoline Indoline | n-Heptane Toluene | Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide + ethylene glycol | 2017 | [86] |
| Quinoline | n-Heptane (Molecular Simulation) | Methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide + ethylene glycol | 2018 | [87] |
| Tetralin | n-Dodecane | Tetrabutylphosphonium bromide + (Propionic Acid, Formic acid, or Levulinic acid) | 2020 | [85] |
2.1.3. Separation of Alcohols from Hydrocarbons
| Solute | Raffinate | Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methanol | Toluene n-Heptane | Choline chloride + malic acid | 2017 | [90] |
| Methanol Ethanol | Benzene | Choline chloride + (ethylene glycol, levulinic acid or 1,2-propanediol) | 2018 | [91] |
| Ethanol | n-Heptane | Choline chloride + (glycerol, levulinic acid or ethylene glycol) | 2013 | [88] |
| Ethanol | n-Hexane n-Heptane | Choline chloride + (glycolic acid or lactic acid) | 2015 | [89] |
| Ethanol | Methyl ethyl ketone | (Choline chloride or tetramethylammonium chloride) + glycerol | 2016 | [92] |
| Ethanol | n-Hexane n-Heptane n-Octane | Choline chloride + (urea or 1,2-propanediol) Tetrabutylammonium bromide + levulinic acid | 2017 | [93] |
| Ethanol | n-Hexane | Choline chloride + (oxalic acid or malonic acid) | 2017 | [94] |
| Ethanol | n-Hexane n-Heptane | Binary: Choline chloride + 1,2-propanediol) Ternary: Choline chloride + (1,2-propanediol + water) | 2018 | [95] |
| Ethanol | Dimethyl carbonate | Choline chloride + (glycerol, ethylene glycol, urea or malonic acid) | 2019 | [96] |
| Ethanol n-Propanol n-Butanol | Ethyl acetate n-Propylacetate n-Butylacetate | Choline chloride + malonic acid | 2018 | [97] |
| Ethanol n-Propanol n-Butanol | (Ethyl, propyl or butyl)acetate (Ethyl, propyl or butyl)propionate | Choline chloride + glutaric acid | 2019 | [98] |
| Phenol Cresol | n-Hexane, Toluene p-Xylene | Choline chloride, triethylamine hydrochloride or ethylamine hydrochloride to form eutectic solvents | 2012 | [99] |
| Phenol, o,m,p-Cresol | Coal tar | Imidazole to form eutectic solvents | 2015 | [100] |
| Cresols | n-Hexane | Imidazole to form eutectic solvents | 2016 | [101] |
| Phenol | Toluene | Choline chloride, triethylethanaminium chloride or trimethylmethanaminium chloride to form eutectic solvents | 2016 | [102] |
2.1.4. Separation of Value-Added Compounds
| Solute | Raffinate | Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Tocopherol | β-Tocopherol | Choline chloride + (levulinic acid or 1,4-butanediol) with other liquid phase formed by (n-heptane + ethanol) | 2017 | [103] |
| Chloromycetin Thiamphenicol | Milk | Choline chloride + glycerol with other liquid phase formed by chloroform | 2017 | [105] |
| Vitamin E | Red Palm Biodiesel | Potassium carbonate + glycerol | 2018 | [106] |
| Partition of: Coumarin, β-Ionone, β-Carotene and α-Tocopherol | Menthol + levulinic acid with other liquid phase formed by (n-heptane + methanol) | 2019 | [104] | |
| Monosaccharides and Amino Acids | Kelp | Two phases using hydrophilic and hydrophobic eutectic solvents. Hydrophilic: Choline chloride + (caffeic acid and/or glycerol) Hydrophobic: Tetrabutylammonium chloride + (octanoic acid and/or decanoic acid) | 2020 | [107] |
2.1.5. Aqueous Biphasic Systems (ABS) with Eutectic Solvents to Separate Organic Compounds
2.1.6. Extraction of Organic Compounds with Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents (HES)
| Solute | Raffinate | Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volatile fatty acids | Water | Quaternary ammonium salts + decanoic acid | 2015 | [130] |
| Caffeine Tryptophan Isophthalic acid Vanillin | Water | DL-Menthol + (pyruvic acid, acetic acid, L-lactic acid or lauric acid) | 2015 | [14] |
| Pesticides | Water | DL-Menthol + natural organic acids Tetrabutylammonium chloride + natural organic acids | 2017 | [133] |
| Bisphenol A | Water | Fatty acids combined: octanoic acid, nonanoic acid, decanoic acid and dodecanoic acid | 2018 | [135] |
| Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin | Water | Quaternary ammonium salts + (hexanoic acid, octanoic acid, decanoic acid, n-butyl alcohol, cyclohexanol, 1-octanol, 1-dodecanol or 1-dodecanol) | 2018 | [136] |
| Ethanol 1-Propanol 1-Butanol | Water | DL-Menthol + dodecanoic acid | 2018 | [137] |
| Ethanol 1-Propanol 1-Butanol | Water | DL-Menthol + (decanoic acid or dodecanoic acid) | 2018 | [138] |
| Tyrosol Phenols | Olive oil mill wastewater | DL-Menthol + (octanoic acid or dodecanoic acid) | 2019 | [139] |
| N,N-Diethyl-4-nitroaniline Chloranilic acid Dyes | Water | 10 Binary eutectic solvents formed by: menthol, camphor, borneol, thymol and trans-sobrerol | 2019 | [16] |
| Pyrethroids | Tea beverages and fruit juices | Hexafluoroisopropanol as hydrogen-bond donor and L-carnitine or betaine as hydrogen-bond acceptor | 2019 | [140] |
| Acetic acid Propionic acid Butyric acid Valeric acid | Water | (DL-Menthol or thymol) + octanoic acid | 2019 | [26] |
| Volatile fatty acids | Water | Trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO) + (dodecanoic acid or dihexylthiourea) | 2019 | [131] |
| 2-Chlorophenol o-Cresol Phenol | Water | (DL-Menthol, Thymol or dodecanoic acid) + (octanoic acid or decanoic acid) | 2019 | [141] |
| Trace phenolic compounds | Large volume water | Binary or ternary mixtures of carboxylic acids (C8, C9, C10, C11 and C12). | 2019 | [142] |
| Bisphenol A | Water | Menthol or quaternary ammonium salts + (octanoic acid or decanoic acid) | 2020 | [143] |
| Carbamazepine | Water | Menthol + (formic acid or acetic acid) | 2020 | [144] |
| Pesticides: Bifenthrin, Deltamethrin, Fenpropathrin Permethrin Tetramethrin | Water | DL-Menthol + (thymol, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid or sesamol) | 2020 | [134] |
| Adipic acid Levulinic acid Succinic acid | Water | Trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO) + (decanoic acid or dodecanoic acid) | 2020 | [132] |
| Phenolic Compounds | Beverage samples | DL-Menthol + carboxylic acids (C8, C9, C10, C11 and C12). | 2020 | [145] |
| Phenol 2-Chlorophenol 2-Nitrophenol | Water | Menthol + (thymol or octanoic acid) Thymol + octanoic acid | 2020 | [27] |
2.1.7. Extraction of Metals with Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents (HES)
2.1.8. Predictive Methods in Liquid–liquid Extraction with Eutectic Solvents
2.1.9. Correlation of Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Using Eutectic Solvents
2.1.10. Simulation of Liquid–Liquid Extraction Processes with Eutectic Solvents
2.2. General Overview of the Use of Eutectic Solvents in the Development of Analytical Methods by Liquid–Liquid Extraction
3. Application of Terpenes and Terpenoids in Extraction Processes
- Agricultural products
- Microalgae
- Aqueous streams
- Others
3.1. Extraction from Agricultural Products with Terpenes and Terpenoids
3.2. Extraction from Microalgae with Terpenes and Terpenoids
| Solute Extracted | Microalgae | Terpene/Terpenoid as Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipids | Chlorella vulgaris | Limonene, α-pinene, p-cymene | 2012 | [246] |
| Lipids | Nannochloropsis oculata and Dunaliella salina | Limonene, α-pinene, p-cymene | 2013 | [247] |
| Lipids | Spirulina, Phormidium sp., Anabaena planctonica and Stigeoclonium sp. | Limonene | 2014 | [249] |
| Carotenoids | Neochloris oleoabundans | Limonene | 2013 | [250] |
| Phenolic compounds | Zonaria tournefortii | Eucalyptol | 2018 | [251] |
3.3. Extraction from Aqueous Solutions with Terpenes and Terpenoids
3.4. Other Applications in Extraction of Terpenes and Terpenoids
3.5. Predictive Methods in Extraction with Terpenes and Terpenoids
3.6. Correlation of Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Using Terpenes and Terpenoids
3.7. Simulation of Liquid–Liquid Extraction Processes with Terpenes and Terpenoids
4. Conclusions and Future Outlook of the Use of Eutectic Solvents, Terpenes and Terpenoids in Liquid–Liquid Extraction Processes
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhatib, I.I.I.; Bahamon, D.; Llovell, F.; Abu-Zahra, M.R.M.; Vega, L.F. Perspectives and guidelines on thermodynamic modelling of deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 298, 112183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Schaeffer, N.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Phenolic hydrogen bond donors in the formation of non-ionic deep eutectic solvents: The quest for type V DES. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10253–10256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.A.; Baeza, A.; Chinchilla, R.; Guillena, G.; Pastor, I.M.; Ramón, D.J. Deep Eutectic Solvents: The Organic Reaction Medium of the Century. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 2016, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruß, C.; König, B. Low melting mixtures in organic synthesis–An alternative to ionic liquids? Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2969–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Kroon, M.C. Low-transition-temperature mixtures (LTTMs): A new generation of designer solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 3074–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Jayakumar, N.S. New horizons in the extraction of bioactive compounds using deep eutectic solvents: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 979, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; van Spronsen, J.; Witkamp, G.-J.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural deep eutectic solvents as new potential media for green technology. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 766, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Friesen, J.B.; McAlpine, J.B.; Lankin, D.C.; Chen, S.N.; Pauli, G.F. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Properties, Applications and Perspectives. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, A.; Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Martins, M.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents–Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; van Spronsen, J.; Kroon, M.C.; Gallucci, F.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Tuinier, R. A Search for Natural Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Natural Components. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Florindo, C.; Iff, L.C.; Coelho, M.A.Z.Z.; Marrucho, I.M. Menthol-based Eutectic Mixtures: Hydrophobic Low Viscosity Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.A.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Tunable Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Monocarboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8836–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Silva, L.P.; Schaeffer, N.; Abranches, D.O.; Maximo, G.J.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Greener Terpene–Terpene Eutectic Mixtures as Hydrophobic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 17414–17423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwenger Chhandak Basu, S.; Zwenger, S.; Basu, C. Plant Terpenoids: Applications and Future Potentials. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2008, 3, 1–007. [Google Scholar]
- Kirk-Othmer. Chemical Technology of Cosmetics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boutekedjiret, C.; Vian, M.A.; Chemat, F. Terpenes as Green Solvents for Natural Products Extraction. In Alternative Solvents for Natural Products Extraction. Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 205–219. [Google Scholar]
- Vovers, J.; Smith, K.H.; Stevens, G.W. Bio-Based Molecular Solvents; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128054437. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kunz, W.; Chemat, F. From Petroleum to Bio-Based Solvents: From Academia to Industry. In Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology; Li, Y., Chemat, F., Eds.; Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 51–87. ISBN 978-981-13-3809-0. [Google Scholar]
- Espino, M.; de los Ángeles Fernández, M.; Gomez, F.J.V.; Silva, M.F. Natural designer solvents for greening analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 76, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, L.I.N.; Baião, V.; da Silva, W.; Brett, C.M.A. Deep eutectic solvents for the production and application of new materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Row, K.H. Development of deep eutectic solvents applied in extraction and separation. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 3505–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) for Phenolic Compounds Extraction: Overview, Challenges and Opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Llorente, D.; Bengoa, A.; Pascual-Muñoz, G.; Navarro, P.; Águeda, V.I.; Delgado, J.A.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; García, J.; Larriba, M. Sustainable Recovery of Volatile Fatty Acids from Aqueous Solutions Using Terpenoids and Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 16786–16794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Llorente, D.; Cañada-Barcala, A.; Muñoz, C.; Pascual-Muñoz, G.; Navarro, P.; Santiago, R.; Ismael Águeda, V.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; García, J.; Larriba, M. Separation of phenols from aqueous streams using terpenoids and hydrophobic eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S.C.; Fernandes, J.O. Extraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jung, D.; Park, K. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of organic and inorganic analytes from aqueous environments. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś, P.; Słupek, E.; Gębicki, J. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents in microextraction techniques–A review. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Cullis, P.M.; Gibson, M.J.; Harris, R.C.; Raven, E. Extraction of glycerol from biodiesel into a eutectic based ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; ALNashef, I.M. Using Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Removal of Glycerol from Palm Oil-Based Biodiesel. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 3349–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayyan, M.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. A novel technique for separating glycerine from palm oil-based biodiesel using ionic liquids. Fuel Process. Technol. 2010, 91, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Methyl Triphenyl Phosphunium Bromide for the Removal of Glycerol from Palm-Oil-Based Biodiesel. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C.; Shahbaz, K.; Rashmi, W.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; Alnashef, I.M. Removal of glycerol from palm oil-based biodiesel using new ionic liquids analogues. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 10, 98–111. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Eutectic solvents for the removal of residual palm oil-based biodiesel catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israyandi, Z.; Mulia, K. Optimization process condition for deacidification of palm oil by liquid–liquid extraction using NADES (Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent). AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1823, 020107. [Google Scholar]
- Zahrina, I.; Nasikin, M.; Krisanti, E.; Mulia, K. Deacidification of palm oil using betaine monohydrate-based natural deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulia, K.; Nasikin, M.; Krisanti, E.A.; Zahrina, I. Deacidification of Palm Oil Using Betaine Monohydrate-Carboxylic Acid Deep Eutectic Solvents: Combined Extraction and Simple Solvent Recovery. Processes 2020, 8, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Hadi, N.; Ng, M.H.; Choo, Y.M.; Hashim, M.A.; Jayakumar, N.S. Performance of Choline-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Extraction of Tocols from Crude Palm Oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Zhang, M.; Tan, T.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, H. Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for phenolic compounds from model oil. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11749–11752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Clemente, A.; Summo, C.; Pasqualone, A.; Caponio, F. Towards green analysis of virgin olive oil phenolic compounds: Extraction by a natural deep eutectic solvent and direct spectrophotometric detection. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradiso, V.M.; Squeo, G.; Pasqualone, A.; Caponio, F.; Summo, C. An easy and green tool for olive oils labelling according to the contents of hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol derivatives: Extraction with a natural deep eutectic solvent and direct spectrophotometric analysis. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullaikah, S.; Wibowo, N.D.; Wahyudi, I.M.G.E.D.; Rachimoellah, M. Deacidification of Crude Rice Bran Oil (CRBO) to Remove FFA and Preserve γ-Oryzanol Using Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES). Mater. Sci. Forum. 2019, 964, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Esteban, J.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M. Deterpenation of Citrus Essential Oils Using Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M. Alkanediol-based deep eutectic solvents for isolation of terpenoids from citrus essential oil: Experimental evaluation and COSMO-RS studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Alam, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Huang, D.; Hu, K.; Chen, H.; Yuan, Z. One-step production of biodiesel from wet and unbroken microalgae biomass using deep eutectic solvent. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Antonije Košćak, M.; Kosir, D.; Milosavljević, N.; Parlov Vuković, J.; Magić, L. The influence of animal fat type and purification conditions on biodiesel quality. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Petračić, A.; Parlov Vuković, J.; Husinec, L. From Coffee to Biodiesel—Deep Eutectic Solvents for Feedstock and Biodiesel Purification. Separations 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Liquid–liquid equilibria for the ternary system (phosphonium based deep eutectic solvent–benzene–hexane) at different temperatures: A new solvent introduced. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2012, 314, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.O.; Bagh, F.S.G.; Alnashef, I.M. Phase equilibria of toluene/heptane with tetrabutylphosphonium bromide based deep eutectic solvents for the potential use in the separation of aromatics from naphtha. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2012, 333, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, M.A.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.O.; Ghareh Bagh, F.S.; Alnashef, I.M. Phase equilibria of toluene/heptane with deep eutectic solvents based on ethyltriphenylphosphonium iodide for the potential use in the separation of aromatics from naphtha. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 65, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.S.B.; Francisco, M.; Jimeno, G.; de Dios, S.L.G.; Kroon, M.C. Liquid–liquid equilibrium data for the systems {LTTM + benzene + hexane} and {LTTM+ethyl acetate+hexane} at different temperatures and atmospheric pressure. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 360, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyono, S.; Hizaddin, H.F.; Alnashef, I.M.; Hashim, M.A.; Fakeeha, A.H.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Separation of BTEX aromatics from n-octane using a (tetrabutylammonium bromide + sulfolane) deep eutectic solvent–experiments and COSMO-RS prediction. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17597–17606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Athirah, N.A.; Candieiro, F.J.M.; Lal, B. Phase Behavior of Ternary Mixtures {Aliphatic Hydrocarbon + Aromatic Hydrocarbon + Deep Eutectic Solvent}: A Step Forward toward “Greener” Extraction Process. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; Gerlach, T.; Scheepers, D.; Kroon, M.C.; Smirnova, I. Experimental determination of the LLE data of systems consisting of {hexane + benzene + deep eutectic solvent} and prediction using the Conductor-like Screening Model for Real Solvents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2017, 104, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, Z.; Wazeer, I.; Mulyono, S.; El-blidi, L.; Hashim, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Efficient removal of benzene from cyclohexane-benzene mixtures using deep eutectic solvents–COSMO-RS screening and experimental validation. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2017, 104, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Sun, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, F.; Liu, W. Effective separation of aromatic hydrocarbons by pyridine-based deep eutectic solvents. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 3138–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Mohammadi, B. Liquid–Liquid Equilibria for Benzene/Thiophene + Cyclohexane/Hexadecane + Deep Eutectic Solvents: Data and Correlation. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 3904–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, A.S.L.; Oliveira, F.S.; Kurnia, K.A.; Marrucho, I.M. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Azeotrope Breakers: Liquid–Liquid Extraction and COSMO-RS Prediction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5640–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.K.; Dehury, P.; Paul, S.; Banerjee, T. Evaluation of Deep Eutectic Solvent for the selective extraction of toluene and quinoline at T = 308.15 K and p = 1 bar. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2016, 423, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarov, A.A.; Smirnov, M.A.; Sokolova, M.P.; Toikka, A.M. Liquid–liquid Equilibrium Data for the System N-Octane + Toluene + DES at 293.15 and 313.15 K and Atmospheric Pressure. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2018, 52, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, A.; Haghbakhsh, R.; Raeissi, S. Experimental Investigation of Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Toluene + Heptane or Toluene + Hexane Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 3811–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizaddin, H.F.; Sarwono, M.; Hashim, M.A.; Alnashef, I.M.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Coupling the capabilities of different complexing agents into deep eutectic solvents to enhance the separation of aromatics from aliphatics. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 84, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyono, S.; Hizaddin, H.F.; Wazeer, I.; Alqusair, O.; Ali, E.; Ali Hashim, M.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Liquid–liquid equilibria data for the separation of ethylbenzene/styrene mixtures using ammonium-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 135, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larriba, M.; Ayuso, M.; Navarro, P.; Delgado-Mellado, N.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M.; García, J.; Rodríguez, F. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents in the Dearomatization of Gasolines. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Salleh, Z.; Ali, E.; Khan, R.; Hashim, M.A. Separation of aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons using deep eutectic solvents: A critical review. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Xun, S.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H. One-pot extraction combined with metal-free photochemical aerobic oxidative desulfurization in deep eutectic solvent. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2464–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A. Synthesis and application of magnetic deep eutectic solvents: Novel solvents for ultrasound assisted liquid–liquid microextraction of thiophene. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrag, S.E.E.; Rodriguez, N.R.; Nashef, I.M.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Siepmann, J.I.; Kroon, M.C.; Peters, C.J. Separation of Thiophene from Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Using Tetrahexylammonium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extracting Agents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 2911–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrag, S.E.E.; Adeyemi, I.; Rodriguez, N.R.; Nashef, I.M.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Kroon, M.C.; Peters, C.J. Effect of the Type of Ammonium Salt on the Extractive Desulfurization of Fuels Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrag, S.E.E.; Pototzki, C.; Rodriguez, N.R.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Kroon, M.C.; Held, C.; Sadowski, G.; Peters, C.J. Oil desulfurization using deep eutectic solvents as sustainable and economical extractants via liquid–liquid extraction: Experimental and PC-SAFT predictions. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2018, 467, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Baker, G.A.; Wagle, D.V.; Ravula, S.; Zhang, Q. Tuning Task-Specific Ionic Liquids for the Extractive Desulfurization of Liquid Fuel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Al-Murshedi, A.Y.M.; Alshammari, O.A.O.; Harris, R.C.; Kareem, J.H.; Qader, I.B.; Ryder, K. Thermodynamics of phase transfer for polar molecules from alkanes to deep eutectic solvents. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gano, Z.S.; Mjalli, F.S.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; AlNashef, I.M. Desulfurization of liquid fuel via extraction with imidazole-containing deep eutectic solvent. Green Process. Synth. 2017, 6, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, R.D.; Kroon, M.C. Extraction of benzothiazole and thiophene from their mixtures with n-heptane using tetrahexylammonium bromide-based deep eutectic solvents as extractive denitrogenation and desulfurization agents. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2018, 477, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjalli, F.S.; Ahmed Rahma, W.S.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Al-Hashmi, A.A. Superior liquid fuel desulfurization through emulsification solvent extraction using polymeric-based eutectic solvents. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ani, Z.; Al Wahaibi, T.; Mjalli, F.S.; Al Hashmi, A.; Abu-Jdayil, B. Flow of deep eutectic solvent-simulated fuel in circular channels: Part II—Extraction of dibenzothiophene. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 119, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, B.; Qi, Z. Screening deep eutectic solvents for extractive desulfurization of fuel based on COSMO-RS model. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2018, 125, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, D.V.; Zhao, H.; Deakyne, C.A.; Baker, G.A. Quantum Chemical Evaluation of Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extractive Desulfurization of Fuel. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7525–7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, R.D.; AlNashef, I.M.; Kroon, M.C. Removal of 2-and 3-methylthiophene from their mixtures with n-heptane using tetrahexylammonium bromide-based deep eutectic solvents as extractive desulfurization agents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 125, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, A.; Rogošić, M.; Slivar, A.; Žuteg, B. Separation of Hydrocarbons by Means of Liquid–liquid Extraction with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2016, 34, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrag, S.E.E.; Alli, R.D.; Kroon, M.C. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium Measurements for the Extraction of Pyridine and Benzothiazole from n -Alkanes Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 4882–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrag, S.E.E.; Darwish, A.S.; Adeyemi, I.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Kroon, M.C.; AlNashef, I.M. Extraction of pyridine from n-alkane mixtures using methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide-based deep eutectic solvents as extractive denitrogenation agents. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2020, 517, 112622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Extractive separation of tetralin-dodecane mixture using tetrabutylphosphonium bromide-based deep eutectic solvent. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2020, 149, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.K.; Paul, S.; Banerjee, T. Liquid Liquid Equilibria measurements for the extraction of poly aromatic nitrogen hydrocarbons with a low cost Deep Eutectic Solvent: Experimental and theoretical insights. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.K.; Mohan, M.; Banerjee, T.; Paul, S.; Goud, V.V. Molecular Dynamic Simulations for the Extraction of Quinoline from Heptane in the Presence of a Low-Cost Phosphonium-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 4006–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, F.S.; Pereiro, A.B.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Deep eutectic solvents as extraction media for azeotropic mixtures. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; Molina, B.S.; Kroon, M.C. Aliphatic+ethanol separation via liquid–liquid extraction using low transition temperature mixtures as extracting agents. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2015, 394, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuksanović, J.; Todorović, N.M.; Kijevčanin, M.L.; Šerbanović, S.P.; Radović, I.R. Experimental investigation and modeling of thermophysical and extraction properties of choline chloride + DL-malic acid based deep eutectic solvent. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 1287–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazeer, I.; Hizaddin, H.F.; El Blidi, L.; Ali, E.; Hashim, M.A.; Hadj-Kali, M.K. Liquid–Liquid Equilibria for Binary Azeotrope Mixtures of Benzene and Alcohols Using Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.R.; Ferre Guell, J.; Kroon, M.C. Glycerol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extractants for the Separation of MEK and Ethanol via Liquid–Liquid Extraction. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2016, 61, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Hizaddin, H.F.; Wazeer, I.; El blidi, L.; Mulyono, S.; Hashim, M.A. Liquid–liquid separation of azeotropic mixtures of ethanol/alkanes using deep eutectic solvents: COSMO-RS prediction and experimental validation. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarov, A.A.; Smirnov, M.A.; Sokolova, M.P.; Popova, E.N.; Toikka, A.M. Choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents as extraction media for separation of n-hexane–ethanol mixture. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuksanović, J.; Kijevčanin, M.L.; Radović, I.R. Effect of water addition on extraction ability of eutectic solvent choline chloride+ 1,2-propanediol for separation of hexane/heptane+ethanol systems. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1477–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, D.; Diao, B.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y. Choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents selection and liquid–liquid equilibrium for separation of dimethyl carbonate and ethanol. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarov, A.A.; Smirnov, M.A.; Toikka, A.M.; Prikhodko, I.V. Study of Deep Eutectic Solvent on the Base Choline Chloride as Entrainer for the Separation Alcohol–Ester Systems. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2018, 63, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarov, A.; Prikhodko, I.; Shner, N.; Sadowski, G.; Held, C.; Toikka, A. Liquid–Liquid Equilibria for Separation of Alcohols from Esters Using Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Experimental Study and Thermodynamic Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 6049–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.; Hou, Y.; Wu, W.; Guo, W.; Peng, W.; Marsh, K.N. Efficient separation of phenols from oils via forming deep eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2398–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Li, C.; Zhuang, X.; Cao, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, S. The new liquid–liquid extraction method for separation of phenolic compounds from coal tar. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 266, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, T.; Wang, H.; Dai, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, S. Thermodynamics Study on the Separation Process of Cresols from Hexane via Deep Eutectic Solvent Formation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8848–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Ji, Y.; Yao, C.; Niu, M.; Wu, W. Phase equilibria of phenol + toluene + quaternary ammonium salts for the separation of phenols from oil with forming deep eutectic solvents. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2016, 429, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Weinberger, M.E.; Minceva, M. Computational solvent system screening for the separation of tocopherols with centrifugal partition chromatography using deep eutectic solvent-based biphasic systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1491, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, F.; Minceva, M. A water-free solvent system containing an L-menthol-based deep eutectic solvent for centrifugal partition chromatography applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1587, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, T.; Row, K.H. Deep eutectic solvents for the purification of chloromycetin and thiamphenicol from milk. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manurung, R.; Hutauruk, G.R.; Arief, A. Vitamin E extraction from red palm biodiesel by using K2CO3 based deep eutectic solvent with glycerol as hydrogen bond donor. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1977, 020011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Row, K.H. Air Assisted Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction (AA-DLLME) Using Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Isolation of Monosaccharides and Amino Acids from Kelp. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aqueous biphasic systems: A boost brought about by using ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4966–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ding, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, K. Deep eutectic solvents as novel extraction media for protein partitioning. Analyst 2014, 139, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, N.; Wen, Q. A green deep eutectic solvent-based aqueous two-phase system for protein extracting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 864, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Huang, Y.; Wen, Q.; Ding, X. Development of green betaine-based deep eutectic solvent aqueous two-phase system for the extraction of protein. Talanta 2016, 152, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, H.; Tavares, D.J.P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Are Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Deep Eutectic Solvents Ternary or Quaternary Systems? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Wen, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Ternary and binary deep eutectic solvents as a novel extraction medium for protein partitioning. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 8196–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.-W.; Zong, Y.; Xiao, Y.-X. Hexafluoroisopropanol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent/Salt Aqueous Two-Phase Systems for Extraction of Anthraquinones from Rhei Radix et Rhizoma Samples. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4267–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Sosa, F.H.B.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. Study of the pseudo-ternary aqueous two-phase systems of deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride:sugars) + K2HPO4 + water. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Passos, H.; Lima, Á.S.; Mafra, M.R.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Is It Possible To Create Ternary-like Aqueous Biphasic Systems with Deep Eutectic Solvents? ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9402–9411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Sha, X.; Chao, Y.; Chen, G.; Han, C.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q. Green aqueous biphasic systems containing deep eutectic solvents and sodium salts for the extraction of protein. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49361–49367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Wen, Q.; Yang, Q. Aqueous biphasic systems containing PEG-based deep eutectic solvents for high-performance partitioning of RNA. Talanta 2017, 170, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farias, F.O.; Passos, H.; Sanglard, M.G.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. Designer solvent ability of alcohols in aqueous biphasic systems composed of deep eutectic solvents and potassium phosphate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 200, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Wang, R.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Tan, Z. Enantioselective Extraction of Phenylalanine Enantiomers Using Environmentally Friendly Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Processes 2018, 6, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, W.; Ni, R.; Meng, J.; Zhou, Y. A novel aqueous biphasic system formed by deep eutectic solvent and ionic liquid for DNA partitioning. Talanta 2018, 189, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, P. Aqueous biphasic systems formed by deep eutectic solvent and new-type salts for the high-performance extraction of pigments. Talanta 2018, 181, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, F.O.; Passos, H.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Mafra, M.R. pH Effect on the Formation of Deep-Eutectic-Solvent-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 16917–16924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Ni, R.; Liu, Z.; Xu, F. Development of different deep eutectic solvent aqueous biphasic systems for the separation of proteins. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14116–14125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnasamy, S.K.; Rajendran, D.S.; Balaraman, H.B.; Viswanathan, G. Functional deep eutectic solvent-based chaotic extraction of phycobiliprotein using microwave-assisted liquid–liquid micro-extraction from Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis) and its biological activity determination. Algal Res. 2019, 44, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Xu, W.; Ni, R.; Meng, J.; Zhou, Y. Development of deep eutectic solvent-based aqueous biphasic system for the extraction of lysozyme. Talanta 2019, 202, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, Y.; Ding, H.; Peng, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Chang, H.; Jiang, W.; Chen, G.; Han, C.; Zhu, W. High Efficient Extraction of Tryptophan Using Deep Eutectic Solvent-based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 81, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Deive, F.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Álvarez, M.S. Towards the use of eco-friendly solvents as adjuvants in remediation processes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Xu, P.; Wang, Y. Aqueous biphasic systems formed by hydrophilic and hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for the partitioning of dyes. Talanta 2020, 213, 120839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as water-immiscible extractants. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bruinhorst, A.; Raes, S.; Maesara, S.A.; Kroon, M.C.; Esteves, A.C.C.; Meuldijk, J. Hydrophobic eutectic mixtures as volatile fatty acid extractants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 216, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveiro, E.; González, B.; Domínguez, Á. Extraction of adipic, levulinic and succinic acids from water using TOPO-based deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Branco, L.C.C.; Marrucho, I.M.M. Development of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for extraction of pesticides from aqueous environments. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2017, 448, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Hussin, S.A.; Varanusupakul, P.; Shahabuddin, S.; Yih Hui, B.; Mohamad, S. Synthesis and characterization of green menthol-based low transition temperature mixture with tunable thermophysical properties as hydrophobic low viscosity solvent. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 308, 113015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Romero, L.; Rintoul, I.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. From Phase Change Materials to Green Solvents: Hydrophobic Low Viscous Fatty Acid–Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Dai, Y.; Row, K.H. Evaluation of fatty acid/alcohol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as media for extracting antibiotics from environmental water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 7325–7336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Banerjee, T. Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Lower Alcohols Using Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent: Experiments and COSMO-SAC Predictions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Mohan, M.; Goud, V.V.; Banerjee, T. Operational Strategies and Comprehensive Evaluation of Menthol Based Deep Eutectic Solvent for the Extraction of Lower Alcohols from Aqueous Media. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16920–16932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldo, M.; Cicci, A.; Sed, G.; Sapone, V.; Bravi, M. Detoxification of Olive Mill Wastewaters by Liquid–liquid Extraction with Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 74, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Yu, L.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Deng, Z.; Xiao, Y. Hexafluoroisopropanol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of pyrethroids in tea beverages and fruit juices. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sas, O.G.; Castro, M.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Removing phenolic pollutants using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Xun, C.; Yang, Y. A green deep eutectic solvents microextraction coupled with acid-base induction for extraction of trace phenolic compounds in large volume water samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Monteiro, N.V.; Ribeiro, B.D.; Branco, L.C.C.; Marrucho, I.M.M. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for purification of water contaminated with Bisphenol-A. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, A.G.; Kurtulbaş, E.; Toprakçı, İ.; Şahin, S. Menthol-based deep eutectic solvent for the separation of carbamazepine: Reactive liquid–liquid extraction. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Y. Acid-base-governed deep eutectic solvent-based microextraction combined with magnetic solid-phase extraction for determination of phenolic compounds. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Parmentier, D.; Dietz, C.H.J.T.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Tuinier, R.; Kroon, M.C. Removal of alkali and transition metal ions from water with hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11987–11990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, N.; Martins, M.; Neves, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J. Sustainable hydrophobic terpene-based eutectic solvents for the extraction and separation of metals. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8104–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmore, M.; McCourt, É.N.; Connolly, F.; Nockemann, P.; Swadźba-Kwaśny, M.; Holbrey, J.D. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Incorporating Trioctylphosphine Oxide: Advanced Liquid Extractants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 17323–17332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Conceica¸, J.H.; Martins, M.A.; Neves, M.C.; Pérez-Sánchez, G.; Gomes, J.R.B.; Papaiconomou, N.; Coutinho, J.A. Non-ionic hydrophobic eutectics–Versatile solvents for tailored metal separation and valorisation. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukomska, A.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Domańska, U. Liquid–liquid extraction of cobalt(II) and zinc(II) from aqueous solutions using novel ionic liquids as an extractants. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, R.; Du, Y.; Luo, F.; Yan, H.; Sun, L. Dehydration of 1-Butanol with a Deep Eutectic Solvent by Liquid–Liquid Extraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaee, S.; Daneshfar, A. Magnetic deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of hexanal and heptanal in edible oils followed by gas chromatography–Flame ionization detection. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4162–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çabuk, H.; Yılmaz, Y.; Yıldız, E. A vortex-assisted deep eutectic solvent-based liquid–liquid microextraction for the analysis of alkyl gallates in vegetable oils. Acta Chim. Slov. 2019, 66, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrone, V.; Genovese, S.; Carlucci, M.; Tiecco, M.; Germani, R.; Preziuso, F.; Epifano, F.; Carlucci, G.; Taddeo, V.A. A green deep eutectic solvent dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction (DES-DLLME) for the UHPLC-PDA determination of oxyprenylated phenylpropanoids in olive, soy, peanuts, corn and sunflower oil. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R. A green ultrasonic-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for the HPLC-UV determination of ferulic, caffeic and cinnamic acid from olive, almond, sesame and cinnamon oil. Talanta 2016, 150, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Qin, Y.; Yu, J. A simple and green ultrasonic-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction technique based on deep eutectic solvents for the HPLC analysis of sesamol in sesame oils. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4184–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Yu, J.; Bi, Y. A Green Ultrasonic-Assisted Liquid–liquid Microextraction Based on Deep Eutectic Solvent for the HPLC-UV Determination of TBHQ in Edible Oils. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3209–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zong, B.; Yu, J.; Bi, Y. Ultrasonic-Assisted Liquid–liquid Microextraction Based on Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent for the HPLC-UV Determination of Tert-Butylhydroquinone from Soybean Oils. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, K.; Chen, J.; Yu, J. Ascorbic acid and choline chloride: A new natural deep eutectic solvent for extracting tert-butylhydroquinone antioxidant. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Tang, W.; Row, K.H. Characterization of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Phenolics. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 2177–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Xia, M.; Lu, H.; Shi, H.; Sun, D.; Hou, B.; Jia, L.; Li, D. Deep eutectic solvent-based liquid–liquid microextraction for the HPLC-DAD analysis of bisphenol A in edible oils. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 306, 112881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebi, A.; Samadi, M.; Tavakoli, H.R.; Parastouei, K. Homogenous liquid–liquid extraction followed by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the extraction of some antibiotics from milk samples before their determination by HPLC. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Vortex assisted deep eutectic solvent (DES)-emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction of trace curcumin in food and herbal tea samples. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Unal, Y.; Elik, A. Towards green analysis of curcumin from tea, honey and spices: Extraction by deep eutectic solvent assisted emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction method based on response surface design. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A 2020, 37, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazmandegan-Shamili, A.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Moghadam, M.R.; Saeidi, M. Temperature-controlled liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for the simultaneous determination of diazinon and fenitrothion in water and fruit juice samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M. Novel hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for vortex assisted dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction of two auxins in water and fruit juice samples and determination by high performance liquid chromatography. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R.; Aghanassab, M. Deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mohebbi, A.; Nemati, M. Stir bar sorptive extraction combined with deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction: Application in simultaneous derivatisation and extraction of acidic pesticides. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Meng, Z.; Qian, H.; Zhang, S.; Lu, R.; Gao, H.; Zhou, W. Extraction of benzoylurea pesticides from tea and fruit juices using deep eutectic solvents. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1140, 121995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Based on Acid–Base-Induced Deep Eutectic Solvents for Determination of β-Carotene and Lycopene in Fruit Juices. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mayor, Á.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. A green and simple procedure based on deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of phthalates from beverages. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 125798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Volodina, N.; Nechaeva, D.; Gagarinova, S.; Bulatov, A. Deep eutectic solvents as a new kind of dispersive solvent for dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 38146–38149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Volodina, N.; Nechaeva, D.; Gagarinova, S.; Bulatov, A. An automated homogeneous liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for the HPLC-UV determination of caffeine in beverages. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, J.; Jia, H.; Zhang, H. Liquid–liquid microextraction of synthetic pigments in beverages using a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mohebbi, A.; Tofigh Gharamaleki, V.; Abbaspour, M.; Sorouraddin, S.M. Low temperature-induced homogeneous liquid–liquid extraction and ternary deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography in the assessment of multiclass pesticide residues in cucumbers. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 12453–12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Sohrabi, H.; Mohebbi, A.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Combination of a modified quick, easy, cheap, efficient, rugged and safe extraction method with a deep eutectic solvent based microwave-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction: Application in extraction and preconcentration of multiclass pestic. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Abbaspour, M.; Kazemian, R. Synthesis of a green high density deep eutectic solvent and its application in microextraction of seven widely used pesticides from honey. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1603, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastpour, N.; Khandaghi, J.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Mogaddam, M.R.A. Deep eutectic solvent-based QuEChERS method combined with dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for extraction of benzoylurea insecticides in cabbage leaves samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Nemati, M.; Alizadeh Nabil, A.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Preparation of ferrofluid from toner powder and deep eutectic solvent used in air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction: Application in analysis of sixteen polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urine and saliva samples of tobacco smokers. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saei, A.; Javadi, A.; Mogaddam, M.R.A.; Mirzaei, H.; Nemati, M. Determination of three antibiotic residues in hamburger and cow liver samples using deep eutectic solvents based pretreatment method coupled with ion mobility spectrometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jin, Y.; Jung, D.; Park, K.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. In situ formation of thymol-based hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents: Application to antibiotics analysis in surface water based on liquid–liquid microextraction followed by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 460730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Ma, W.; Row, K.H. Preconcentration and Determination of Chlorophenols in Wastewater with Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Using Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Ao, Y.-T.; Ding, W.-H. Determination of microcystins in water samples by deep eutectic solvent-based vortex-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38669–38676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diuzheva, A.; Balogh, J.; Jekő, J.; Cziáky, Z. Application of liquid–liquid microextraction for the effective separation and simultaneous determination of 11 pharmaceuticals in wastewater samples using high-performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2870–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Adeli, M.; Noormohammadi, F. Deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid micro-extraction for extraction of malachite green and crystal violet in water samples prior their determination using high performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Yang, Y. Emulsification liquid–liquid micro-extraction based on natural deep eutectic solvent for (triarylmethane) dyes determination. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 3617–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R.; Feriduni, B. Simultaneous synthesis of a deep eutectic solvent and its application in liquid–liquid microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from aqueous samples. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47990–47996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś, P.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as “green” extraction media for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1570, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yang, S. Air-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on a new hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for the preconcentration of benzophenone-type UV filters from aqueous samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Lu, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Gao, H. Deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of ultraviolet filters in water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1516, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhu, G. Air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating deep eutectic solvent for the analysis of ultraviolet filters in water samples by high performance liquid chromatography with the aid of response surface methodology. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1618, 460876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Dai, E. A Deep Eutectic Solvent as an Extraction Solvent to Separate and Preconcentrate Parabens in Water Samples Using in situ Liquid–liquid Microextraction. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deen, A.K.; Shimizu, K. Deep eutectic solvent as a novel disperser in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplet (DLLME-SFOD) for preconcentration of steroids in water samples: Assessment of the method deleterious impact on the e. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 103988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezeli, T.; Daneshfar, A.; Sahraei, R. Emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent: An extraction method for the determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and seven polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1425, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Hong, K.; Li, X.; Ge, F.; Tang, Y. Freezing temperature controlled deep eutectic solvent dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic droplets for rapid determination of benzoylureas residual in water samples with assistance of metallic salt. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56528–56536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Qiao, K.; Li, X.; Yang, M.; Zhang, S.; Lu, R.; Li, J.; Gao, H.; Zhou, W. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the solidification of deep eutectic solvent for the determination of benzoylureas in environmental water samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamei, N.; Ezoddin, M.; Abdi, K. Air assisted emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for preconcentration of methadone in water and biological samples. Talanta 2017, 165, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, T. Emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvents: An extraction method for the determination of sulfonamides in water samples. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 4747–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, T. Comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents for pretreatment determination of sulfonamides from aqueous environments. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 5901–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Lv, Y.; Liu, L.; Row, K.H.; Zhu, T. Synthesis and characterization of deep eutectic solvents (five hydrophilic and three hydrophobic) and hydrophobic application for microextraction of environmental water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7489–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbana, J.V.; de Oliveira, L.H.; Paveglio, G.C.; Trindade, M.A.G. Narrowing the interface between sample preparation and electrochemistry: Trace-level determination of emerging pollutant in water samples after in situ microextraction and electroanalysis using a new cell configuration. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 275, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the simultaneous enantiomeric analysis of five β-agonists in the environmental samples. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2828–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś, P.; Fernandes, A.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Sample preparation procedure using extraction and derivatization of carboxylic acids from aqueous samples by means of deep eutectic solvents for gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1555, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matong, J.; Mpupa, A.; Nomngongo, P. Ultrasound Assisted-Homogeneous Liquid–liquid Phase Microextraction based on Deep Eutectic Solvents and Ethyl Acetate for Preconcentration of Selected Organochlorine Pesticides in Water Samples. Eurasian J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomai, P.; Lippiello, A.; D’Angelo, P.; Persson, I.; Martinelli, A.; Di Lisio, V.; Curini, R.; Fanali, C.; Gentili, A. A low transition temperature mixture for the dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of pesticides from surface waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1605, 360329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouyban, A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Afshar Mogaddam, M.R. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of deep eutectic solvent droplets for analysis of pesticides in farmer urine and plasma by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1124, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidi, S.M.; Hadjmohammadi, M.R. Hydrophobic borneol-based natural deep eutectic solvents as a green extraction media for air-assisted liquid–liquid micro-extraction of warfarin in biological samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1621, 461030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugbienyo, L.; Shishov, A.; Garmonov, S.; Moskvin, L.; Andruch, V.; Bulatov, A. Flow method based on liquid–liquid extraction using deep eutectic solvent for the spectrofluorimetric determination of procainamide in human saliva. Talanta 2017, 168, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishov, A.; Gerasimov, A.; Nechaeva, D.; Volodina, N.; Bessonova, E.; Bulatov, A. An effervescence-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent decomposition: Determination of ketoprofen and diclofenac in liver. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J. A hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent-based vortex-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with HPLC for the determination of nitrite in water and biological samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounr, R.A.; Tuzen, M.; Khuhawar, M.Y. Ultrasound assisted deep eutectic solvent based on dispersive liquid liquid microextraction of arsenic speciation in water and environmental samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 242, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, A.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Baig, J.A.; Afridi, H.I. Developed a modified liquid–liquid micro-extraction method for the preconcentration of cadmium in groundwater samples of aquifers at different depth in a coal mining area. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorouraddin, S.M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Okhravi, T. Development of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent using as complexing agent and extraction solvent: Application for extraction of heavy metals. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2995–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpa, Ç.; Albayati, S.; Yahya, M. Effervescence-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for preconcentration and FAAS determination of copper in aqueous samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2018, 98, 938–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Tuzen, M.; Citak, D.; Uluozlu, O.D.; Mendil, D.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I. Separation and preconcentration of trivalent chromium in environmental waters by using deep eutectic solvent with ultrasound-assisted based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 291, 111299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habila, M.A.; Alabdullkarem, E.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Thiomalic acid/ferric chloride-based deep eutectic solvent for microextraction of chromium in natural water samples prior to FAAS analysis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmohammad, M.; Faraji, M.; Jafarinejad, S. Extraction of chromium (VI) in water samples by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent and determination by UV–Vis spectrophotometry. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.S.; Rahnama, R.; Zakeri, M.; Jamali, M.R. Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on green type solvents—“deep eutectic solvents”—for highly selective separation and efficient preconcentration of nickel in water samples. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2019, 16, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, K.; Ezoddin, M.; Pirooznia, N. Temperature-controlled liquid–liquid microextraction using a biocompatible hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent for microextraction of palladium from catalytic converter and road dust samples prior to ETAAS determination. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panhwar, A.H.; Tuzen, M.; Kazi, T.G. Ultrasonic assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method based on deep eutectic solvent for speciation, preconcentration and determination of selenium species (IV) and (VI) in water and food samples. Talanta 2017, 175, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Elik, A.; Gürkan, R. Monitoring of some trace metals in honeys by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after ultrasound assisted-dispersive liquid liquid microextraction using natural deep eutectic solvent. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorouraddin, S.M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Dastoori, H. Development of a dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method based on a ternary deep eutectic solvent as chelating agent and extraction solvent for preconcentration of heavy metals from milk samples. Talanta 2020, 208, 120485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidi, S.; Alavi, L. Novel and Rapid Deep Eutectic Solvent (DES) Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Microextraction (HLLME) with Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (FAAS) Detection for the Determination of Copper in Vegetables. Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 2092–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishov, A.; Terno, P.; Moskvin, L.; Bulatov, A. In-syringe dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using deep eutectic solvent as disperser: Determination of chromium (VI) in beverages. Talanta 2020, 206, 120209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorouraddin, S.M.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Dastoori, H.; Okhravi, T. Development of an air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction method based on a ternary solidified deep eutectic solvent in extraction and preconcentration of Cd(II) and Zn(II) ions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounr, R.A.; Tuzen, M.; Khuhawar, M.Y. Novel ultrasonic-assisted deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for determination of vanadium in food samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry: A multivariate study. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibollahi, M.H.; Karimyan, K.; Arfaeinia, H.; Mirzaei, N.; Safari, Y.; Akramipour, R.; Sharafi, H.; Fattahi, N. Extraction and determination of heavy metals in soil and vegetables irrigated with treated municipal wastewater using new mode of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on the solidified deep eutectic solvent followed by GFAAS. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panhwar, A.H.; Tuzen, M.; Deligonul, N.; Kazi, T.G. Ultrasonic assisted deep eutectic solvent liquid–liquid microextraction using azadipyrromethene dye as complexing agent for assessment of chromium species in environmental samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezoddin, M.; Lamei, N.; Siami, F.; Abdi, K.; Karimi, M.A. Deep Eutectic Solvent Based Air Assisted Ligandless Emulsification Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Preconcentration of Some Heavy Metals in Biological and Environmental Samples. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidipally, P.K.; Liu, S.X. First approach on rice bran oil extraction using limonene. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2004, 106, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.X.; Mamidipally, P.K. Quality Comparison of Rice Bran Oil Extracted with d-Limonene and Hexane. Cereal Chem. J. 2005, 82, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virot, M.; Tomao, V.; Ginies, C.; Chemat, F. Total Lipid Extraction of Food Using d-Limonene as an Alternative to n-Hexane. Chromatographia 2008, 68, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virot, M.; Tomao, V.; Ginies, C.; Visinoni, F.; Chemat, F. Green procedure with a green solvent for fats and oils’ determination. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1196–1197, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertouche, S.; Tomao, V.; Hellal, A.; Boutekedjiret, C.; Chemat, F. First approach on edible oil determination in oilseeds products using alpha-pinene. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2013, 25, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fine, F.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Abert-Vian, M.; Carre, P.; Pages, X.; Chemat, F. Evaluation of alternative solvents for improvement of oil extraction from rapeseeds. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicaire, A.-G.; Abert Vian, M.; Fine, F.; Carré, P.; Tostain, S.; Chemat, F. Experimental approach versus COSMO-RS assisted solvent screening for predicting the solubility of rapeseed oil. OCL 2015, 22, D404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yara-Varón, E.; Selka, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Balcells, M.; Canela-Garayoa, R.; Bily, A.; Touaibia, M.; Chemat, F. Solvent from forestry biomass. Pinane a stable terpene derived from pine tree byproducts to substitute n-hexane for the extraction of bioactive compounds. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 6596–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madji, S.; Hilali, S.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Tenon, M.; Bily, A.; Laguerre, M.; Chemat, F. Para-Menthane as a Stable Terpene Derived from Orange By-Products as a Novel Solvent for Green Extraction and Solubilization of Natural Substances. Molecules 2019, 24, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemat-Djenni, Z.; Ferhat, M.A.; Tomao, V.; Chemat, F. Carotenoid Extraction from Tomato Using a Green Solvent Resulting from Orange Processing Waste. J. Essent. Oil Bear. Plants 2010, 13, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filly, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.-S.; Lemasson, Y.; Roy, C.; Fernandez, X.; Chemat, F. Extraction of aroma compounds in blackcurrant buds by alternative solvents: Theoretical and experimental solubility study. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filly, A.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Fernandez, X.; Chemat, F. Alternative solvents for extraction of food aromas. Experimental and COSMO-RS study. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva Bermejo, D.; Angelov, I.; Vicente, G.; Stateva, R.P.; Rodriguez García-Risco, M.; Reglero, G.; Ibañez, E.; Fornari, T. Extraction of thymol from different varieties of thyme plants using green solvents. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillet, S.; Tomao, V.; Ruiz, K.; Chemat, F. Green procedure using limonene in the Dean–Stark apparatus for moisture determination in food products. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 674, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertouche, S.; Tomao, V.; Ruiz, K.; Hellal, A.; Boutekedjiret, C.; Chemat, F. First approach on moisture determination in food products using alpha-pinene as an alternative solvent for Dean–Stark distillation. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazhdannikov, A.E.; Kornaukhova, L.M.; Rodionov, V.I.; Pankrushina, N.A.; Shults, E.E.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Popov, S.A.; Chemat, F. Selecting a Green Strategy on Extraction of Birch Bark and Isolation of Pure Betulin Using Monoterpenes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6281–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejoye Tanzi, C.; Abert Vian, M.; Ginies, C.; Elmaataoui, M.; Chemat, F. Terpenes as Green Solvents for Extraction of Oil from Microalgae. Molecules 2012, 17, 8196–8205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejoye Tanzi, C.; Abert Vian, M.; Chemat, F. New procedure for extraction of algal lipids from wet biomass: A green clean and scalable process. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmakani, M.-T.; Mendiola, J.A.; Rezaei, K.; Ibáñez, E. Pressurized limonene as an alternative bio-solvent for the extraction of lipids from marine microorganisms. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2014, 92, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Herrero, M.; Urreta, I.; Mendiola, J.A.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E.; Suárez-Alvarez, S. Optimization of clean extraction methods to isolate carotenoids from the microalga Neochloris oleoabundans and subsequent chemical characterization using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4607–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamiche, S.; Bouzidi, N.; Daghbouche, Y.; Badis, A.; Garrigues, S.; de la Guardia, M.; El Hattab, M. Eucalyptol-based green extraction of brown alga Zonaria tournefortii. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 10, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gironi, F.; Gonzalez Farias, I.; Lamberti, L. Liquid–liquid Equilibria for the Water + Ethanol + Citral and Water + Ethanol + Limonene Systems at 293 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1995, 40, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cháfer, A.; Muñoz, R.; Burguet, M.C.; Berna, A. The influence of the temperature on the liquid–liquid equlibria of the mixture limonene + ethanol + H2O. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2004, 224, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cháfer, A.; de la Torre, J.; Muñoz, R.; Burguet, M.C. Liquid–liquid equlibria of the mixture linalool+ethanol+water at different temperatures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2005, 238, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramajo de Doz, M.B.; Cases, A.M.; Díaz, P.A.; Sólimo, H.N. (Liquid + Liquid) Equilibria for Water + Ethanol + Citral Multicomponent System at 303.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Li, H. Mutual Solubilities of Terpene in Methanol and Water and Their Multicomponent Liquid−Liquid Equilibria. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2005, 50, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tamura, K. Ternary and quaternary (liquid + liquid) equilibria for (water + ethanol + α-pinene, + β-pinene or + limonene) and (water + ethanol + α-pinene + limonene) at the temperature 298.15K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2005, 38, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tamura, K. Ternary liquid–liquid equilibria for (water + terpene + 1-propanol or 1-butanol) systems at the temperature 298.15K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2008, 263, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tamura, K. (Ternary liquid + liquid) equilibria for (water + acetone + α-pinene or β-pinene or limonene) mixtures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2010, 42, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Fu, W.; Tamura, K. Liquid–Liquid Phase Behaviors of Geraniol in Aqueous Alcohol Mixtures. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2012, 57, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Tamura, K. Ternary (liquid + liquid) equilibria for β-citronellol in aqueous alcohol at different temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2012, 53, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, C.; Ma, X.; Feng, Y. Liquid–liquid Equilibria for Linalool in Aqueous Alcohol Mixtures. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 634–638, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.M.; Koshima, C.C.; Capellini, M.C.; Carvalho, F.H.; Aracava, K.K.; Gonçalves, C.B.; Rodrigues, C.E.C. Liquid–liquid equilibrium data for the system limonene + carvone + ethanol + water at 298.2K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 360, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, H.; Yan, Y.; Han, Y. Liquid–liquid Equillibria for the (Water + Methanol + Citral) System at 283.15 and 313.15 K. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 634–638, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Han, Y.; Huang, C.; Yang, C. (Liquid + liquid) equilibria for (water + 1-propanol or acetone + β-citronellol) at different temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2015, 86, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, Z.; Wan, L.; Huang, C.; Zhang, T.; Fang, Y. (Liquid + liquid) equilibria of four alcohol–Water systems containing 1,8-cineole at T = 298.15 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 101, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Li, H.; Huang, C.; Feng, Y.; Chu, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, W.; Qin, Y.; Sun, D.; Fang, Y. Influence of the temperature on the (liquid + liquid) phase equilibria of (water + 1-propanl + linalool or geraniol). J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 109, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wan, L.; Chu, G.; Tan, W.; Liu, B.; Qin, Y.; Feng, Y.; Sun, D.; Fang, Y. (Liquid + liquid) extraction of phenols from aqueous solutions with cineole. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2016, 107, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreza, N.; Naghdi, T. d -Limonene as a green bio-solvent for dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of β-cyclodextrin followed by spectrophotometric determination. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.A.; Goushjuii, L. Study of menthol as a green extractant in dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction; application in extraction of phthalate esters from pharmaceutical products. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, K.; Bouju, E.; Suchet, P.; Berthod, A. Use of Limonene in Countercurrent Chromatography: A Green Alkane Substitute. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4644–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedovici, A.; Udrescu, S.; David, V. Use of a green (bio) solvent-limonene-as extractant and immiscible diluent for large volume injection in the RPLC-tandem MS assay of statins and related metabolites in human plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikakhtari, H.; Vagi, L.; Choi, P.; Liu, Q.; Gray, M.R. Solvent screening for non-aqueous extraction of Alberta oil sands. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 91, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
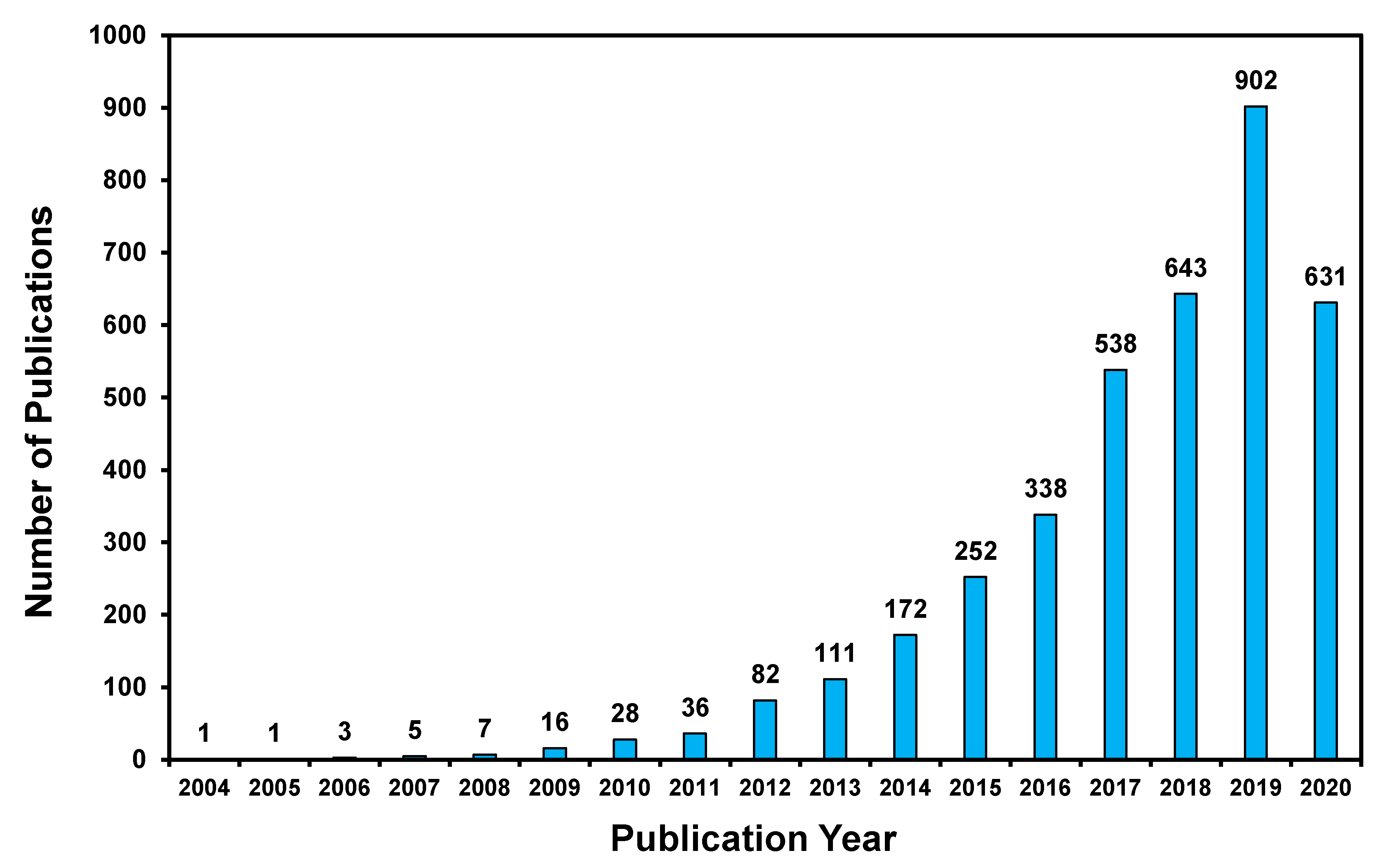
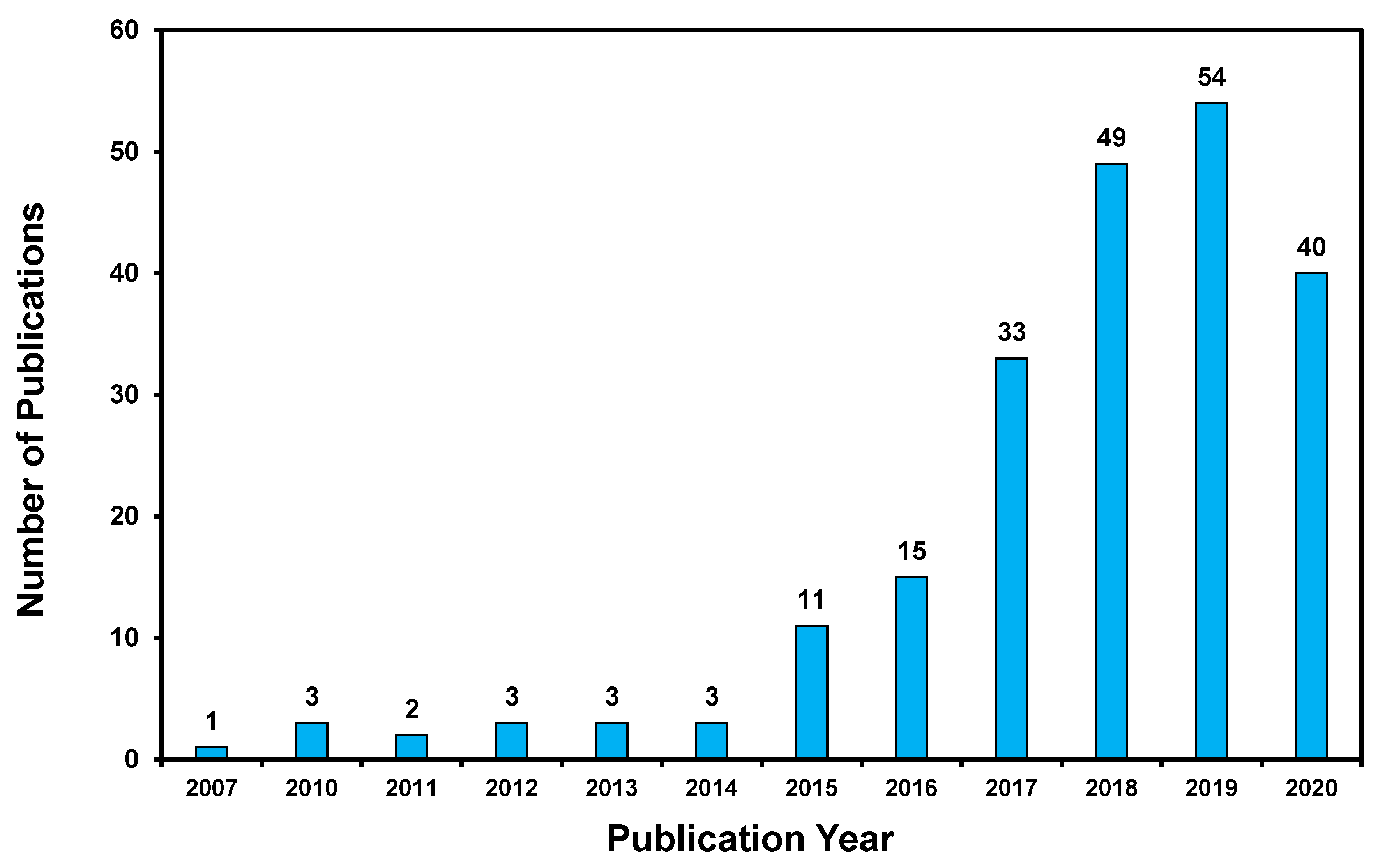
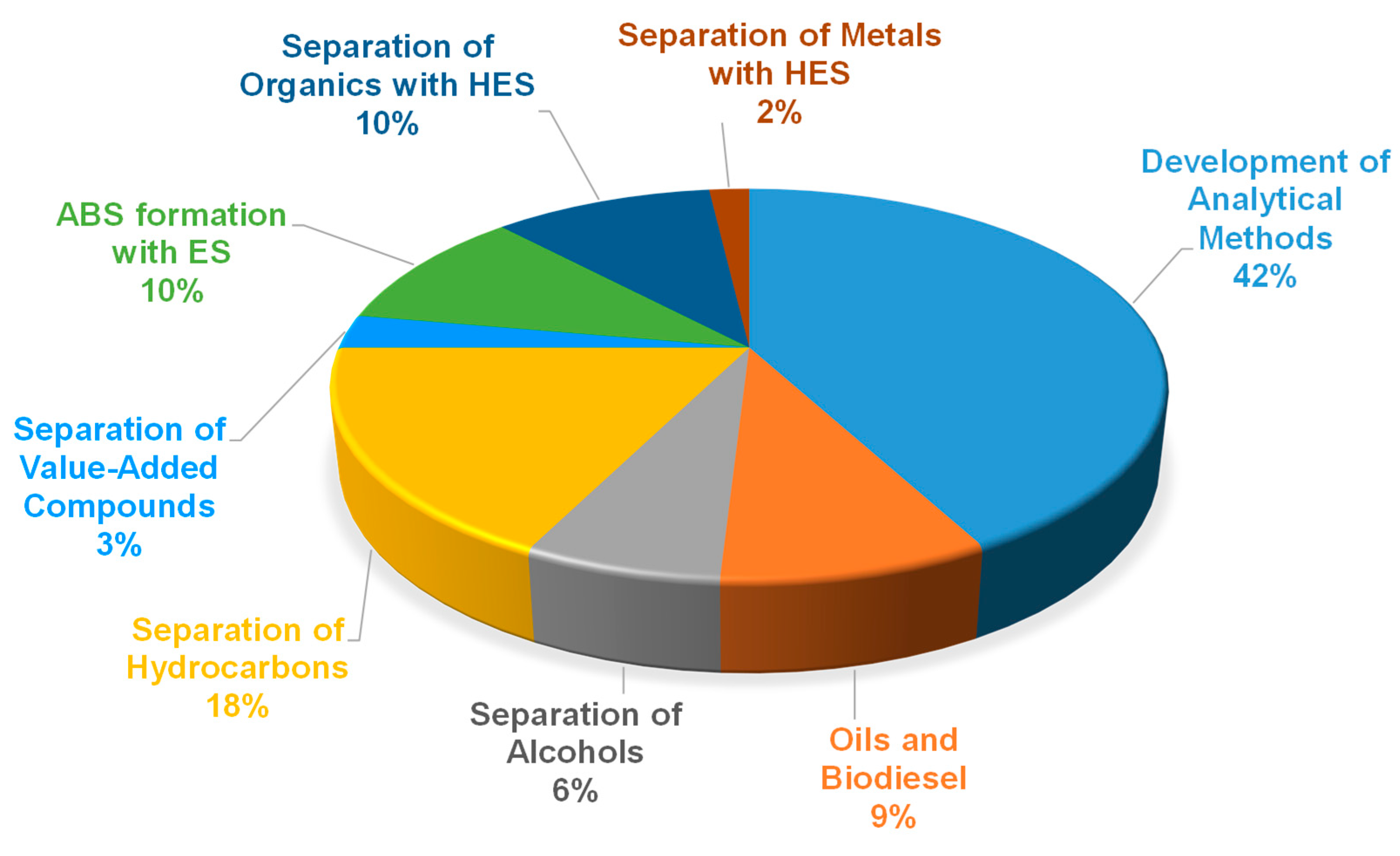
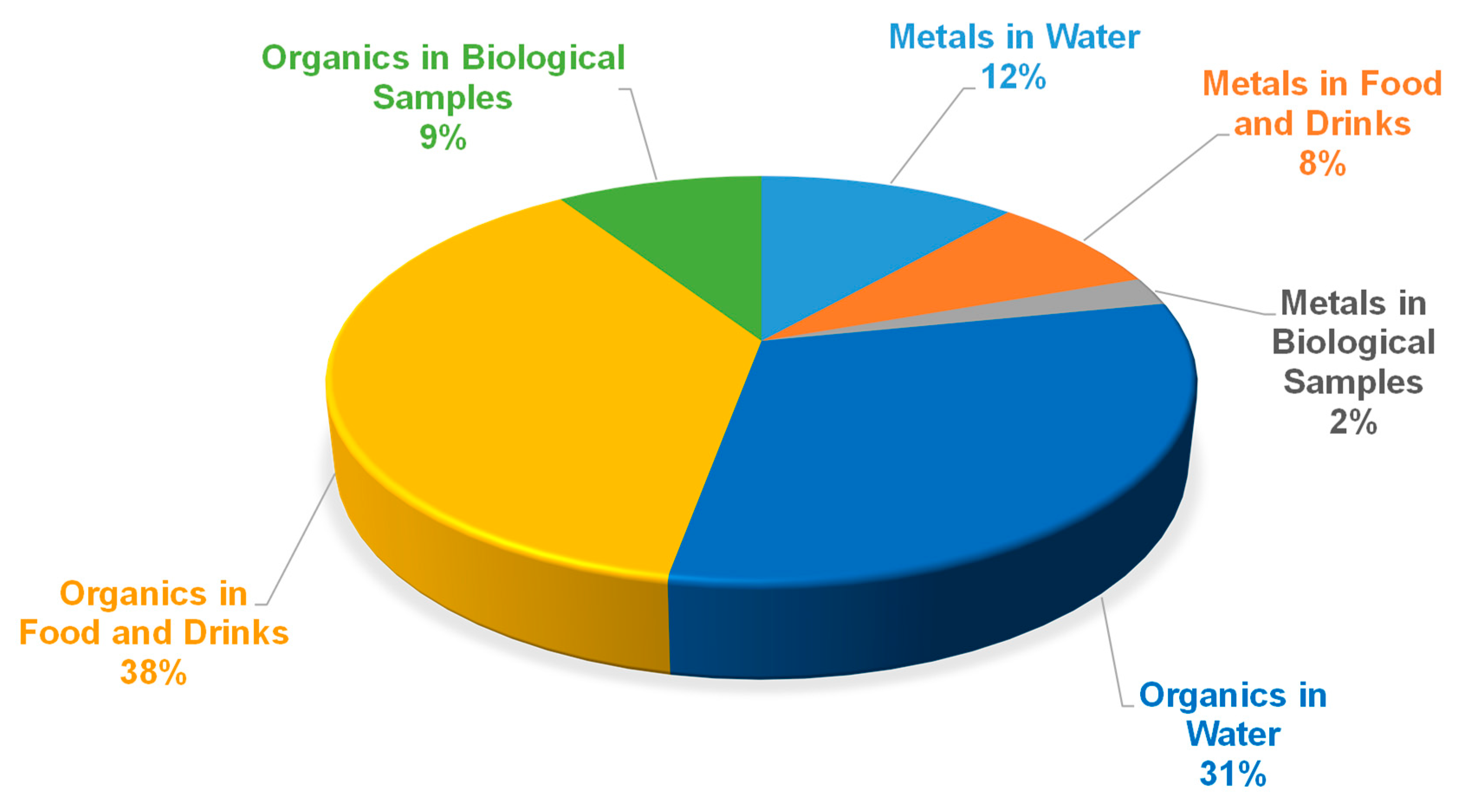
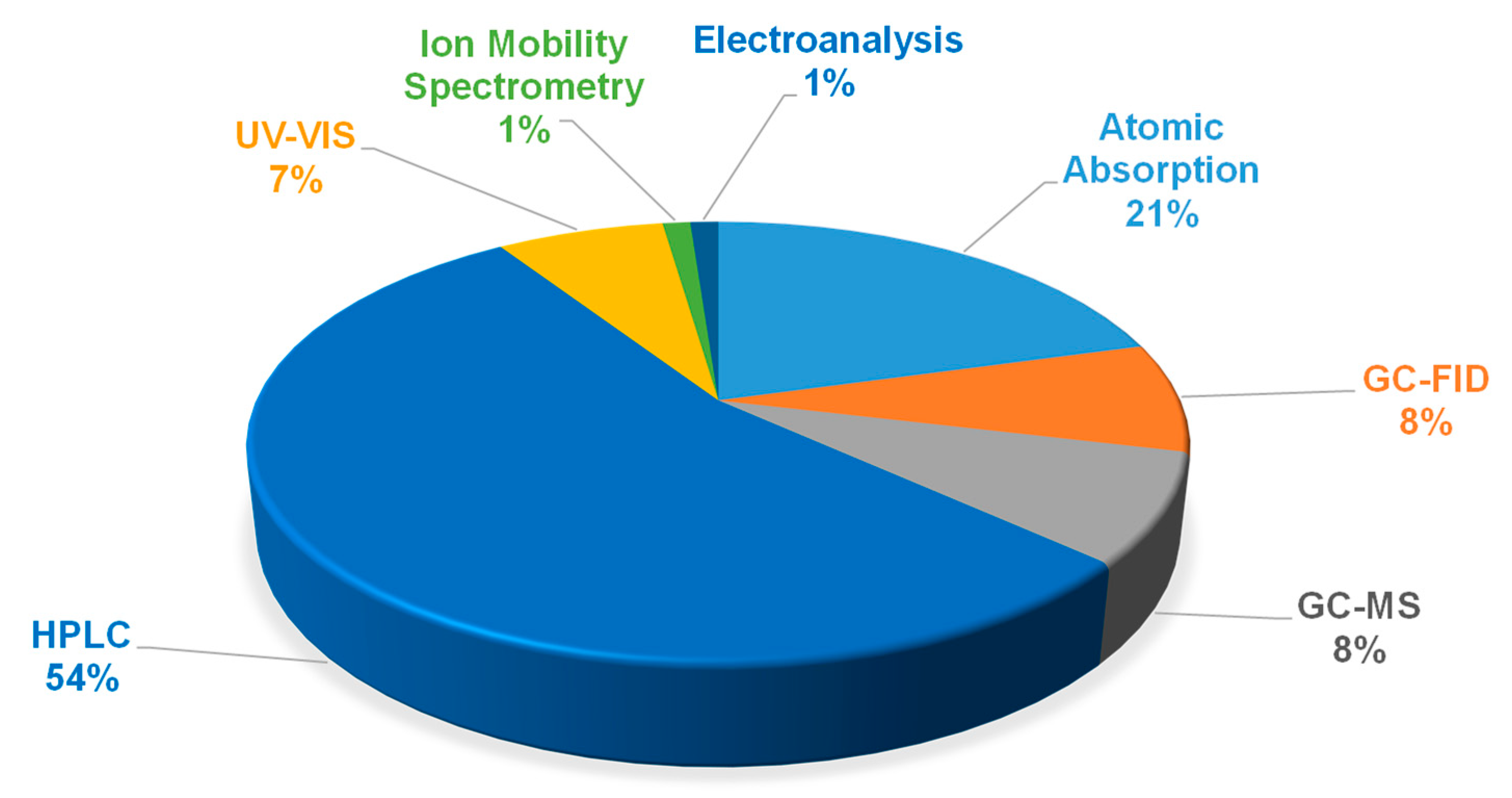
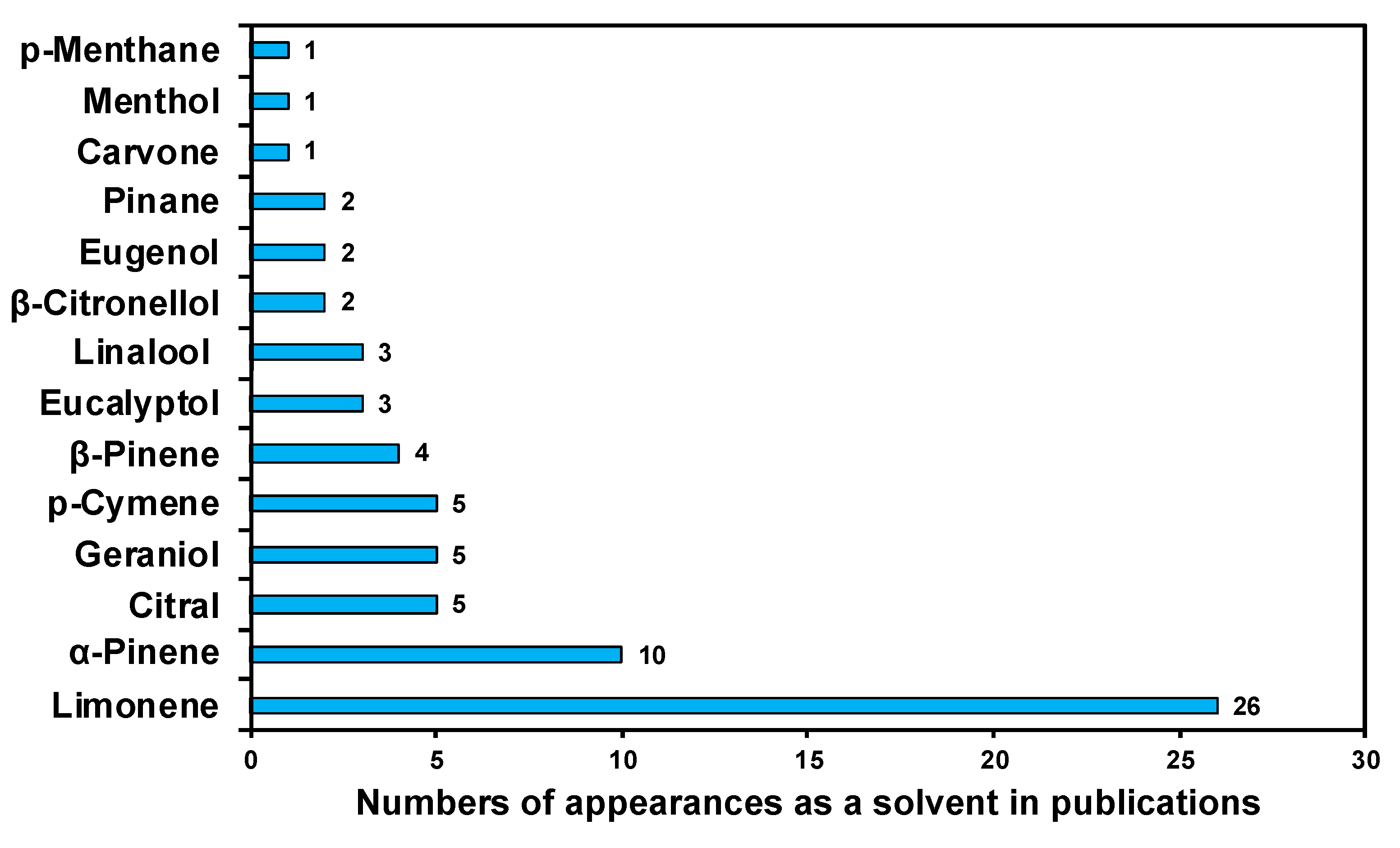
| Solute | Raffinate | Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerol | Biodiesel | Quaternary ammonium salts + glycerol | 2007 | [31] |
| Glycerol | Palm Oil-Biodiesel | Choline chloride (ChCl) + ethylene glycol ChCl + 2,2,2-trifluoroacetamide | 2010 | [32] |
| Glycerol | Palm Oil-Biodiesel | ChCl + glycerol | 2010 | [33] |
| Glycerol | Palm Oil-Biodiesel | Methyl triphenyl phosphonium bromide + (glycerol, ethylene glycol or triethylene glycol) | 2011 | [34] |
| Glycerol | Palm Oil-Biodiesel | Ternary ES: ChCl + glycerol + ethylene glycol | 2015 | [35] |
| KOH | Palm Oil-Biodiesel | 9 ES based on ChCl and 9 ES based on methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide (MTPB) | 2011 | [36] |
| Palmitic Acid | Palm Oil | Betaine monohydrate + propionic acid | 2017 | [37] |
| Palmitic acid, β-Carotene, α-tocopherol | Palm Oil | Binary ES: Betaine monohydrate + (glycerol or propylene glycol) Ternary ES: Betaine monohydrate + (propylene glycol + glycerol) or (propylene glycol + propionic acid) or (glycerol + propionic acid) | 2018 | [38] |
| Palmitic Acid | Palm Oil | Betaine monohydrate + propionic acid Betaine monohydrate + acetic acid | 2020 | [39] |
| Tocols | Palm Oil | ChCl + acetic acid ChCl + malonic acid ChCl + citric acid | 2015 | [40] |
| Phenol, p-Cresol, β-naphthol | Model Oil | ChCl + ethylene glycol ChCl + glycerol ChCl + urea MTPB + ethylene glycol | 2014 | [41] |
| Hydroxybenzoic acid, Protocathecuic acid, Vanillic acid, Tyrosol, p-Coumaric acid, Caffeic acid, Apigenin, Pinoresinol | Virgin Olive Oil | Lactic acid + glucose + water (mole ratio 6:1:6) | 2016 | [42] |
| Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol derivatives | Olive Oil | Lactic acid + glucose + water (mole ratio 3:1:3) | 2019 | [43] |
| Free Fatty Acids | Crude Rice Bran Oil | ChCl + ethylene glycol, ChCl + glycerol, ChCl + Urea, ChCl + Oxalic acid, and Betaine Monohydrate + Glycerol | 2019 | [44] |
| Terpenes | Citrus Essential Oils | ChCl + glycerol ChCl + (1,3-butanediol, 2,3-butanediol, 1,2-propanediol or 1,3-propanediol) | 2018–2019 | [45,46] |
| Solute | Raffinate | Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiophene | n-Heptane | Choline chloride + phenol + FeCl4 Choline chloride + ethylene glycol + FeCl4 | 2017 | [69] |
| Thiophene | n-Hexane n-Octane | Tetrahexylammonium bromide + (ethylene glycol or glycerol) | 2017 | [70] |
| Thiophene | n-Hexane | (Tetraethylammonium chloride or methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide) + (ethylene glycol or glycerol) | 2018 | [71] |
| Thiophene | n-Hexane n-Octane | (Tetraethylammonium chloride, tetrahexylammonium bromide or methyltriphenylphosphonium bromide) + (ethylene glycol or glycerol) | 2018 | [72] |
| Thiophene Benzothiophene Dibenzothiophene 4,6-dimethyl-dibenzothiophene | n-Octane n-Dodecane | Choline chloride + glycerol Choline acetate + glycerol | 2016 | [73] |
| Thiophene Benzothiophene Dibenzothiophene | n-Decane | Choline chloride + 1,5-pentandiol Choline chloride + glycerol | 2017 | [74] |
| Thiophene Dibenzothiophene | Fuel | Tetrabutylammonium bromide + imidazole | [75] | |
| Thiophene Benzothiazole | n-Heptane | Tetrahexylammonium bromide + (ethylene glycol or glycerol) | 2018 | [76] |
| Thiophene Dibenzothiophene | Model Oil | Tetrabutylammonium bromide + polyethylene glycol | 2019 | [77] |
| Dibenzothiophene | Cyclohexane p-Xylene | Choline chloride + 2CnH2n+1COOH, n = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4) | 2015 | [68] |
| Dibenzothiophene | Fuel | Tetrabutylammonium bromide + polyethylene glycol 200 | 2017 | [78] |
| Dibenzothiophene | n-Octane | Screening with 49 eutectic solvents | 2018 | [79] |
| Dibenzothiophene Benzothiophene | Fuel (Molecular Simulation) | Choline chloride + urea Choline chloride + ethylene glycol | 2018 | [80] |
| 2,3-Methylthiophene | n-Heptane | Tetrahexylammonium bromide + (ethylene glycol or glycerol) | 2018 | [81] |
| Solute | Eutectic Solvent | Salt or Polymer | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine serum albumin | Choline chloride + (urea or methylurea) (Tetramethylammonium chloride or tetrapropylammonium bromide) + urea | K2HPO4 | 2014 | [109] |
| Bovine serum albumin Trypsin | Choline chloride + (ethylene glycol, glycerol, D-glucose, D-sorbitol) | K2HPO4 | 2015 | [110] |
| Bovine serum albumin Trypsin Ovalbumin | Betaine + (urea, methylurea, D- glucose, D-sorbitol, ethylene glycol or glycerol) | K2HPO4 K3PO4 | 2016 | [111] |
| Textile dyes: Sudan III and PB 29 | Choline chloride + (carboxylic acids or urea) | Poly(propylene) glycol 400 | 2016 | [112] |
| Bovine serum albumin | Binary: Tetramethylammonium chloride (TMAC) + (urea, glycerol, ethylene glycol or D-(+)-glucose). Ternary: TMAC + glycerol + (urea, ethylene glycol, D-(+)-glucose or D- sorbitol) | K2HPO4 | 2016 | [113] |
| Anthraquinones | (Choline chloride, decyltrimethylammonium bromide, dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide or tetradecyltrimethylammonium bromide) + hexafluoroisopropanol | Na2SO4 K2HPO4 Na2HPO4 (NH4)2SO4 KH2PO4 | 2017 | [114] |
| Gallic acid | Choline chloride + sugars: (D-glucose, D-fructose or saccharose) | K2HPO4 | 2017 | [115] |
| Phenolic compounds Amino-acids, Alkaloids | Choline chloride + glucose | Poly(propylene)glycol 400 | 2017 | [116] |
| Bovine serum albumin Papain | Choline chloride + PEG (molar ratio of 20:1) | NaH2PO4 Na2CO3 Na3C6H5O7 | 2017 | [117] |
| RNA | (Tetrabutylammonium chloride, tetrabutylammonium bromide, tetraethylammonium chloride or tetraethylammonium bromide) + PEG polymers | Na2CO3 NaH2PO4 Na2SO4 K2HPO4 Sodium citrate | 2017 | [118] |
| Phenolic compounds Amino-acids, Alkaloids | Choline chloride + (ethanol, n-propanol 1,2-propanediol or ethylene glycol) | K2HPO4 | 2018 | [119] |
| Phenylalanine Enantiomers | Choline chloride + (urea, lactic acid or sorbitol) Betaine + (urea, glucose or glycol) | 11 salts, being the optimal: K3PO4 | 2018 | [120] |
| DNA from bovine blood | (Tetrabutylammonium bromide or betaine) + (PPG 400, D- (+)-glucose, sucrose, D-sorbitol or xylitol) | Na2CO3 K2HPO4 NaH2PO4 Sodium citrate | 2018 | [121] |
| Pigments: Amaranth. Sunset yellow FCF, Sudan Ⅲ. | Tetrabutylammonium bromide + polypropylene glycol 400 | 12 salts, including Na2CO3 and Na2SO4 | 2018 | [122] |
| Gallic acid Caffeine L-tryptophan | Tetrabutylammonium chloride + (ethanol or n-propanol) | K3C6H5O7 or K3C6H5O7/ C6H8O7 buffers | 2018 | [123] |
| Proteins from porcine pancreas | (L-proline or lysine) + (glycerol, ethylene glycol, D-sorbitol or xylitol) | Tetrabutyl-ammonium chloride + PPG 400 | 2019 | [124] |
| Phycobiliprotein from Spirulina | (Glucose, fructose, sucrose, maltose or xylose) + glycerol | Na2SO4 Na2CO3 K2HPO4 PEG 6000 | 2019 | [125] |
| Lysozime from chicken egg white | (Tetrabutylammonium bromide or benzyltributylammonium bromide) + carboxylic acids | Na2SO4 | 2019 | [126] |
| Thyptophan | Choline chloride + polyethylene glycol 2000 | Na2CO3 K2HPO4 NaH2PO4 Sodium citrate | 2019 | [127] |
| Dyazo Dyes | Choline chloride + urea | Triton X-100 surfactant | 2020 | [128] |
| Dyes: Tartrazine Methylene blue Sudan Ⅲ | Hydrophilic: Choline chloride + (glycerol, glucose, malonic acid or urea) Hydrophobic: (Decyl trimethyl ammonium chloride, dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride or tetradecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride) + hexafluoroisopropanol. Tetrabutylammonium bromide + polypropylene glycol 400 | - | 2020 | [129] |
| Metals Extracted | Raffinate | Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li, Na, K, Co, Ni, Mn, Zn and Cu chlorides | Water | Decanoic acid + lidocaine in a 2:1, 3:1 and 4:1 molar ratio | 2016 | [146] |
| Cu, Fe, Mg, Ca, Cr, Mn, Co and Ni | Mildly acidic solutions | (Menthol or thymol) + (C8, C10, C12, C14, C16 and C18) carboxylic acids | 2018 | [147] |
| Uranyl nitrate | Aqueous acid | Trioctylphosphine oxide (TOPO) + Phenol | 2018 | [148] |
| Pd, Pt, Cu, Co, Ni, Cr and Fe | HCl media | Thymol + trioctylphosphine oxide Trioctylphosphine oxide + capric acid Hydrocinnamic acid + capric acid | 2020 | [149] |
| Co and Zn | Water | [BMPYR][NTf2] + 2-methyl-2-butanol [HMPYR][Cl] + 1-decanol or [NBz1,1,18][BTMPP] + lactic acid | 2020 | [150] |
| Solute Extracted | Agricultural Product | Terpene/Terpenoid as Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipids | Rice bran | Limonene | 2004 | [230] |
| Lipids | Rice bran | Limonene | 2005 | [231] |
| Lipids | Olive seeds | Limonene | 2008 | [232,233] |
| Lipids | Peanuts, soy and sunflower seeds | α-Pinene | 2013 | [234] |
| Lipids | Rapeseed | Limonene, α-pinene, p-cymene | 2014 | [235] |
| Lipids | Rapeseed | Limonene, p-cymene | 2015 | [236] |
| Lipids, aromas, carotenoids | Caraway seed, carrot, rapeseed | Pinane | 2016 | [237] |
| Lipids, aromas, carotenoids, water | Caraway seed, carrot, rapeseed | p-Menthane | 2019 | [238] |
| Carotenoids | Tomato | Limonene | 2010 | [239] |
| Aromas | Blackcurrant bud | α-Pinene | 2014 | [240] |
| Aromas | Caraway seed | α-Pinene | 2015 | [241] |
| Aromas | Thyme | Limonene | 2015 | [242] |
| Water (Moisture determination) | Onion, garlic, minced meat, carrots, rosemary, mozzarella, mint, leeks and sage leaves | Limonene | 2010 | [243] |
| Water (Moisture determination) | Onion, garlic, carrot, leeks, olive, caraway and coriander seeds | α-Pinene | 2012 | [244] |
| Betulin | Birch bark | Limonene, pinane and turpentine | 2018 | [245] |
| Solute | Raffinate | Terpene/Terpenoid as Solvent | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Water | Limonene, citral | 1995 | [252] |
| Ethanol | Water | Limonene | 2004 | [253] |
| Ethanol | Water | Linalool | 2005 | [254] |
| Ethanol | Water | Citral | 2007 | [255] |
| Methanol | Water | Limonene, α-pinene, β-pinene | 2005 | [256] |
| Ethanol | Water | Limonene, α-pinene, β-pinene | 2005 | [257] |
| 1-Butanol, 1-propanol | Water | Limonene, α-pinene, β-pinene | 2008 | [258] |
| Acetone | Water | Limonene, α-pinene, β-pinene | 2010 | [259] |
| Ethanol, methanol | Water | Geraniol | 2012 | [260] |
| Ethanol, methanol | Water | β-Citronellol | 2012 | [261] |
| Ethanol, methanol | Water | Linalool | 2013 | [262] |
| Ethanol | Water | Limonene, carvone | 2013 | [263] |
| Methanol | Water | Citral | 2013 | [264] |
| Acetone, 1-propanol | Water | β-Citronellol | 2015 | [265] |
| 1-Butanol, ethanol, methanol, 1-propanol | Water | Eucalyptol | 2016 | [266] |
| 1-Propanol | Water | Linalool, geraniol | 2016 | [267] |
| Phenol, p-cresol | Water | Eucalyptol | 2016 | [268] |
| β-Cyclodextrin | Pharmaceutical wastewaters | Limonene | 2016 | [269] |
| Acetic, propionic, butyric and valeric acids | Water | Citral, eugenol, geraniol | 2019 | [26] |
| Phenol, 2-chlorophenol, 2-nitrophenol | Water | Citral, eugenol, geraniol linalool | 2020 | [27] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Llorente, D.; Cañada-Barcala, A.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Águeda, V.I.; García, J.; Larriba, M. A Review of the Use of Eutectic Solvents, Terpenes and Terpenoids in Liquid–liquid Extraction Processes. Processes 2020, 8, 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101220
Rodríguez-Llorente D, Cañada-Barcala A, Álvarez-Torrellas S, Águeda VI, García J, Larriba M. A Review of the Use of Eutectic Solvents, Terpenes and Terpenoids in Liquid–liquid Extraction Processes. Processes. 2020; 8(10):1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101220
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Llorente, Diego, Andrés Cañada-Barcala, Silvia Álvarez-Torrellas, Vicente Ismael Águeda, Juan García, and Marcos Larriba. 2020. "A Review of the Use of Eutectic Solvents, Terpenes and Terpenoids in Liquid–liquid Extraction Processes" Processes 8, no. 10: 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101220
APA StyleRodríguez-Llorente, D., Cañada-Barcala, A., Álvarez-Torrellas, S., Águeda, V. I., García, J., & Larriba, M. (2020). A Review of the Use of Eutectic Solvents, Terpenes and Terpenoids in Liquid–liquid Extraction Processes. Processes, 8(10), 1220. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8101220








