Abstract
In this study, we attempted the preparation of gac oil-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) by the high-speed homogenization method using Naterol SE solid lipid, a cosmetic self-emulsifying base, and surfactant and investigated the effects of different conditions on the characteristics of the resulting nanoparticles. The suspensions containing 5% active agents (gac-oil, w/w) were dispersed in a surfactant concentration of 5% (w/w) (Span 80:Tween 80 ratio of 28:72 w/w) and 2.5% (w/w) of solid lipid (Naterol SE) concentration. Suitable conditions for hot homogenization were 13,000 rpm, 60 min and 60 °C for speed, time and temperature, respectively. The suitable conditions for the subsequent cold homogenization were 25 min of homogenization time and 5 °C of temperature. The results showed that the mean size of SLNs-gac oil was 107 nm (measured by laser diffraction spectrometry, LDS), and dried size of SLNs-gac oil ranged from 50 to 80 nm (measured by transmission electron microscope, TEM). In addition, the study investigated the impact of gac oil content on the particle size of SLNs-gac oil and its stability under different storage conditions of UV radiation and storage temperature. At high storage temperatures, the color changes (ΔE) of the samples were more profound in comparison to that at the low storage temperature. The ΔE value of the blank sample (SLN-FREE gac-oil) was higher than that of the Gac oil-loaded SLNs samples (SLN-gac oil).
1. Introduction
In Vietnam, gac fruit (Momordica Cocochinensis Spreng) has been used as a functional food, providing vitamin A to children and pregnant, breastfeeding women and serving as an important ingredient in traditional medicine [1,2]. However, the most valuable features of gac fruits are the high levels of β-carotene and lycopene, vitamin E, and unsaturated fatty acids contained in gac arils [3,4,5]. To be specific, the β-carotene compound in gac fruit aril is 1.8 times and 15 times higher than that in cod liver and carrots respectively [6,7]. Lycopene content was observed to be 70 times higher than that in tomatoes [7,8]. In addition, the presence of lipid in gac oil also facilitates the digestion of carotenoids into the human body [9,10,11]. At present, it has been demonstrated that β-carotene and lycopene consumption are linked to reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and many types of cancer such as lung, breast, stomach, and prostate [12,13]. The incorporation of carotenoids extracted from gac oil into edible products and cosmetics is therefore a prevailing trend. However, the major obstacle when utilizing gac oil in the manufacturing of cosmetics and functional foods is to protect the carotenoids contained in the oil, as this compound could easily decompose under oxidation agents including temperature, light and oxygen.
Nanoparticles have been used as a solution for the effective encapsulation of antioxidants and oxidation-susceptible compounds, mainly due to their many advantages over other delivery systems and colloidal carriers, including reduced size, large surface area and surface modification potential. Nanoparticles are also biodegradable, non-toxic and highly stable, enabling them to be stored for an extended period [14]. Furthermore, nanoparticles have recently been discovered to be controllably incorporable into polymeric vesicles, affording opportunities to organize nanoparticles into different structures to suit specific needs [15]. In applications in functional food, nanostructured materials could contribute to nano-chemoprevention and maintenance of bioactivity, thus enhancing the absorption of the drug in cell monolayers. For instance, Hu et al. (2013) successfully encapsulated (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) in nanoparticles prepared from caseinophosphopeptide and chitosan, showing excellent encapsulation efficiency, antioxidant activity and absorption in HepG2 cancer cells [16]. In another application, Li et al. (2018) attempted the synthesis of silica-dye nanoporous materials using ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and utilized the synthesized composite spheres in the detection of trimethylamine N-Oxide in urine [17]. The results indicated a strong colorimetric responsiveness of the nanoparticles against trimethylamine N-Oxide, even at a very low concentration.
Among many types of nano-carriers, solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) are proven ideal for the encapsulation of highly lipophilic bioactive compounds [18], drugs or antioxidants [19,20,21]. SLNs comprise spherical lipid particles with a nanometer size range of 50–1000 nm [22,23] and are capable of facilitating the dissolution of poorly water-soluble compounds and controlling the release effectively [24]. Some typical compounds utilizing SLN encapsulation include rosmarinic acid [25], β -carotene [26,27] and vitamin D3 [28]. For β-carotene, it was shown that the compound could be successfully loaded into SLNs and retained for 1 month [29]. This was supported by Helgason et al. (2009) who found that SLNs encapsulating β-carotene could maintain their stability in the 21 days before the degradation of β-carotene occurred [27]. In terms of particle size, Effat et al. (2011) also successfully fabricated Coenzyme Q10 loaded SLNs by using a high-pressure homogenization method and showed that the average particle size of the resulted SLNs was from 50 nm to 100 nm [30].
Given the considerable potential of gac oil and the aforementioned suitability of SLNs in practical applications; this study, for the first time, attempts the encapsulation of carotenoids in gac oil into SLNs using Naterol SE. In addition, the influence of difference conditions on the properties of the gac oil-loaded SLNs was investigated and the stability of gac oil-loaded SLNs will be tested under different storage conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Gac oil was extracted from gac arils peeled from Vietnamese gac fruits. Naterol SE (glycerol stearate (and) ceteareth-20 (and) ceteareth-12 (and) cetearyl alcohol (and) cetyl palmitate) was purchased from Cognis Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG Care Chemicals (Monheim, Germany). All other chemicals including Tween 80 and Span 80 were supplied by Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Preparation of Gac Oil-Loaded SLNs
SLNs containing gac oil were prepared by hot high-speed homogenization followed by cold high-speed homogenization. Homogenization was performed at homogenization speed at 13,000 rpm. The ratio of gac oil: Naterol SE: Tween 80: Span 80: water was 5: 2.5: 3.6: 1.4: 87.5, according to the previously described procedure [9]. In the hot homogenization stage, the oil phase (including gac-oil and SLNs) was stirred for 15 min at the appropriate temperature until the homogeneous solution was formed, while the water phase (including span 80, tween 80 and water) was also heated at the same time. The oil phase and aqueous phase were then mixed together at 75 °C and homogenized at high speed to form a micro-emulsion. In the cold homogenization stage, the temperature of micro-emulsion was cooled down to 0–5 °C by being placed into an ice bath. Then, different mixtures were prepared at different times and speeds of homogenization.
2.3. Effect of Homogenization Conditions on Particle Size Distribution
An experimental investigation regarding the effect of temperature and time was attempted by performing single factor experiments with varying temperatures and times of homogenization. The temperature of hot homogenization varies from 40 to 90 °C. Time of hot homogenization varies from 30 to 120 min. Selected periods of cold homogenization were 5, 10, 20, 30, and 40 min.
The size distribution and median size of gac oil-loaded SLNs were measured by using a laser diffraction spectrometry (LDS) scattering instrument (Horiba LA920, Kyoto, Japan). All analyses were performed in auto-measuring mode at 25 °C and the results were presented as the average value of triplicate samplings. The shape and internal matrix of individual nanoparticles were characterized by using a transmission electron microscope with a camera (JEOL TEM 1010, Peabody, MA, USA).
2.4. Effect of Gac Oil Content and Total Oil Phase on Particle Size Distribution
Optimized conditions from the RSM were then used to perform a single factor experiment to investigate into the effects of different gac oil content and total oil phase on particle size and size distribution. Gac oil content varies from 5% to 8%(w/w), and total oil phase content varies from 7.5% to 15%.
2.5. Carotenoids Entrapment Efficiency (EE%)
After homogenization of the product with suitable conditions. Carotenoids were analyzed for stability before and after assimilation of SLNs, by HPLC analysis (column C18, columnar solvent system (IPA:MET 2:98)). The carotenoid stability of SLNs (%EE) was measured by the following formula [23].
where WSLN-DG and WDG (mg/g) are the carotenoid content in Gac oil loaded SLNs (SLN-gac oil) and gac oil, respectively.
%EE = (WSLN-Gac oil/WGac oil) × 100
2.6. Stability of Gac Oil-Loaded SLNs
To assess the stability of the gac oil-loaded SLNs, we conducted sensitivity experiments with different temperature (45 °C, room temperature and 10 °C) and UV light exposure.
In parallel, a blank sample (SLN-FREE), a solid lipid suspension without gac oil, was prepared as a reference sample for a comparison of the stability of SLNs.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Hot Homogenization Temperature
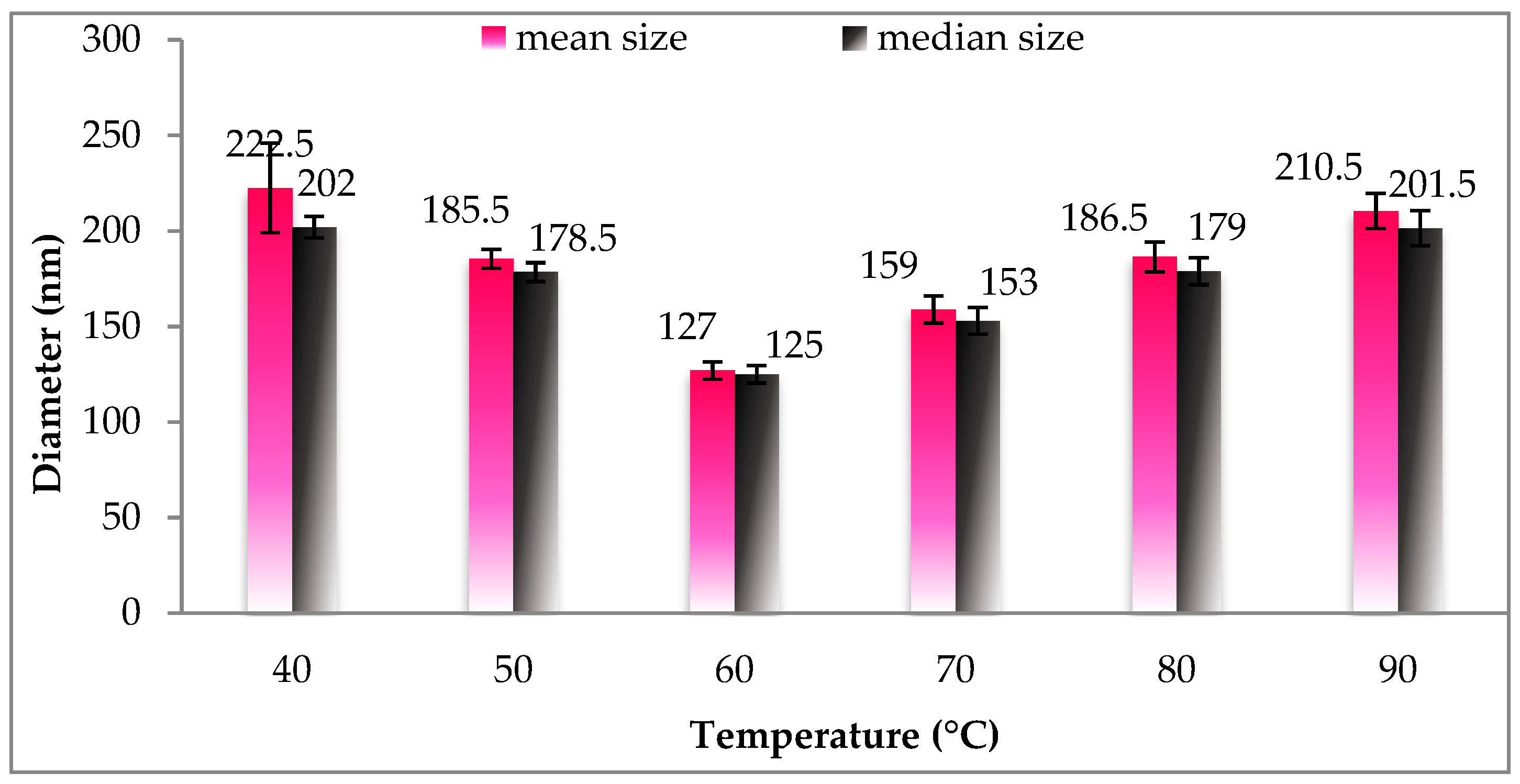
Figure 1 displays the different effects of temperature on particle size and size distribution of gac oil-loaded SLNs. Evidently, SLNs achieved the smallest mean size and were uniformly distributed in size at temperature of 60 °C. The declining size of the particles relative to temperature could be explained by the higher supply of energy to the system that both assisted the breaking down of droplet emulsion to smaller droplets and prevented particle aggregation. The size-declining range of 40–60 °C coincides with the melting temperature range of the Naterol SE (49–52 °C), causing the homogeneity of the emulsion, and, in turn, reduced particle size. However, as the temperature increased, small emulsion droplets were more likely to collide and coagulate, resulting in an increase in droplet size. Therefore, a hot homogenization temperature of 60 °C was used for further experiments.
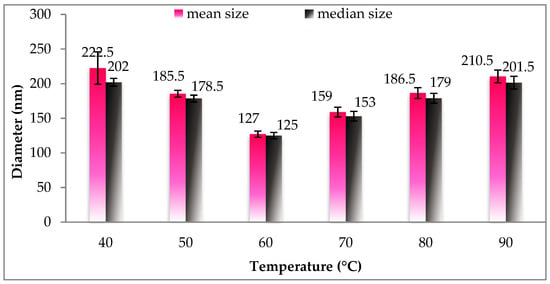
Figure 1.
Size distribution of Gac oil-loaded SLNs at different temperatures of hot homogenization. SLNs: Solid lipid nanoparticles.
3.2. Effect of Hot Homogenization Time
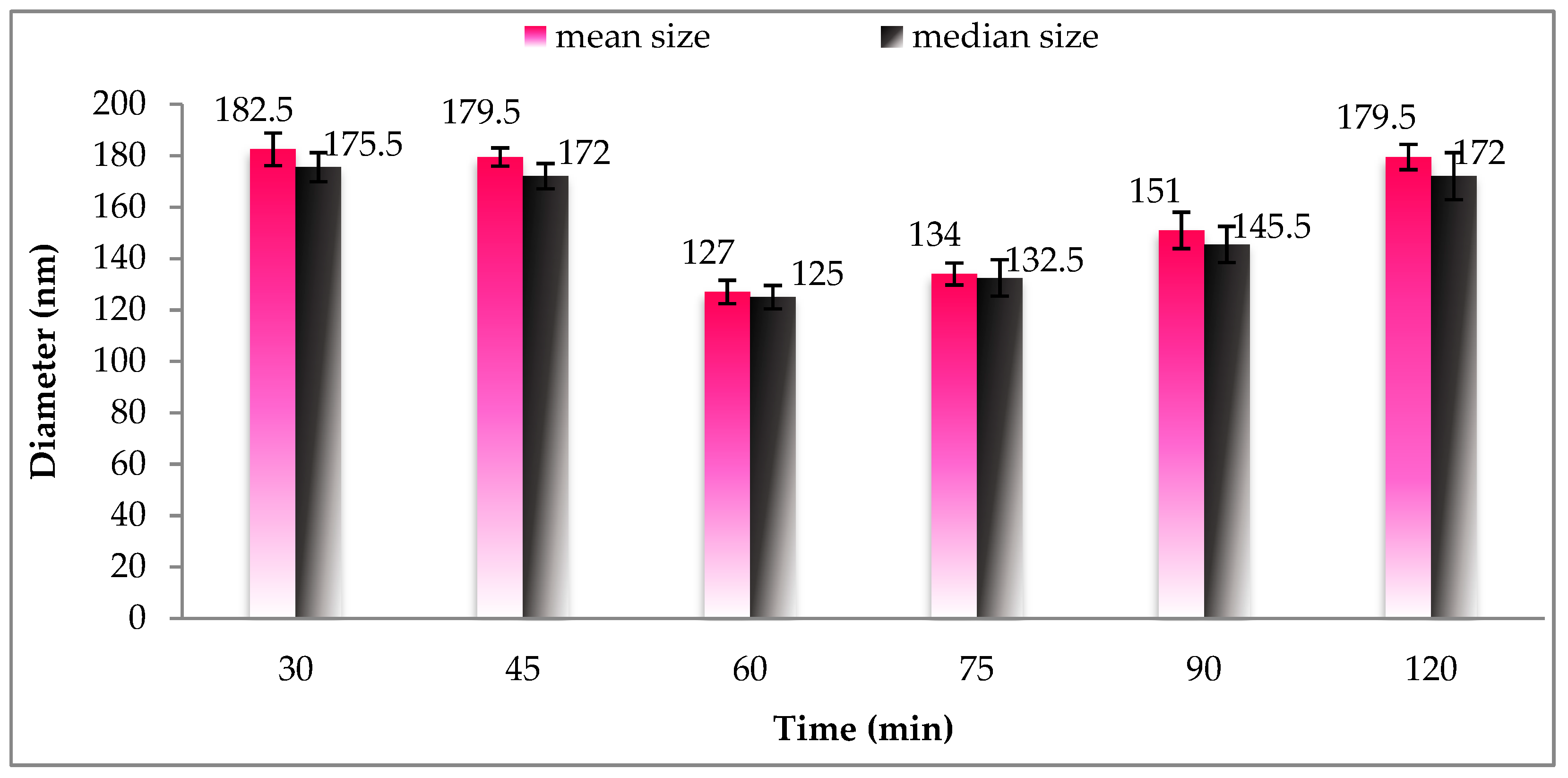
Figure 2 displays variations in the diameter of the particle with respect to homogenization time. Based on Figure 2, the particle size of all analyzed samples was less than 200 nm and achieved high distribution uniformity. As the homogenization time increased from 30 to 60 min, the SLN-carotenoid particle size tended to decrease from 182.5 to 127 nm. The explanation for the decline could be two-fold. First, it is possible that prolonged homogenization time was needed to reduce the particle size. Second, longer homogenization time is associated with greater energy accumulation, which subsequently breaks down and prevents the aggregation of particles.
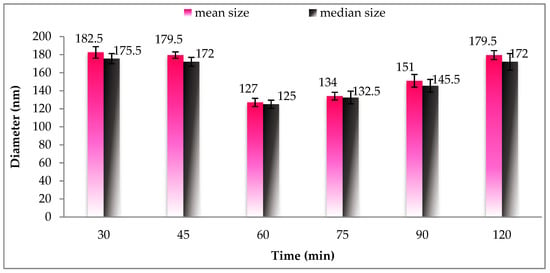
Figure 2.
Size distribution of gac oil-loaded SLNs at different times of hot homogenization.
From 60 to 120 min, particle size increased from 126–176 nm, indicating that the excess energy supply tend to cause particles to collide, leading to increased size. Therefore, we select 60 min as the appropriate time for hot homogenization.
3.3. Effect of Cold Homogenization Time
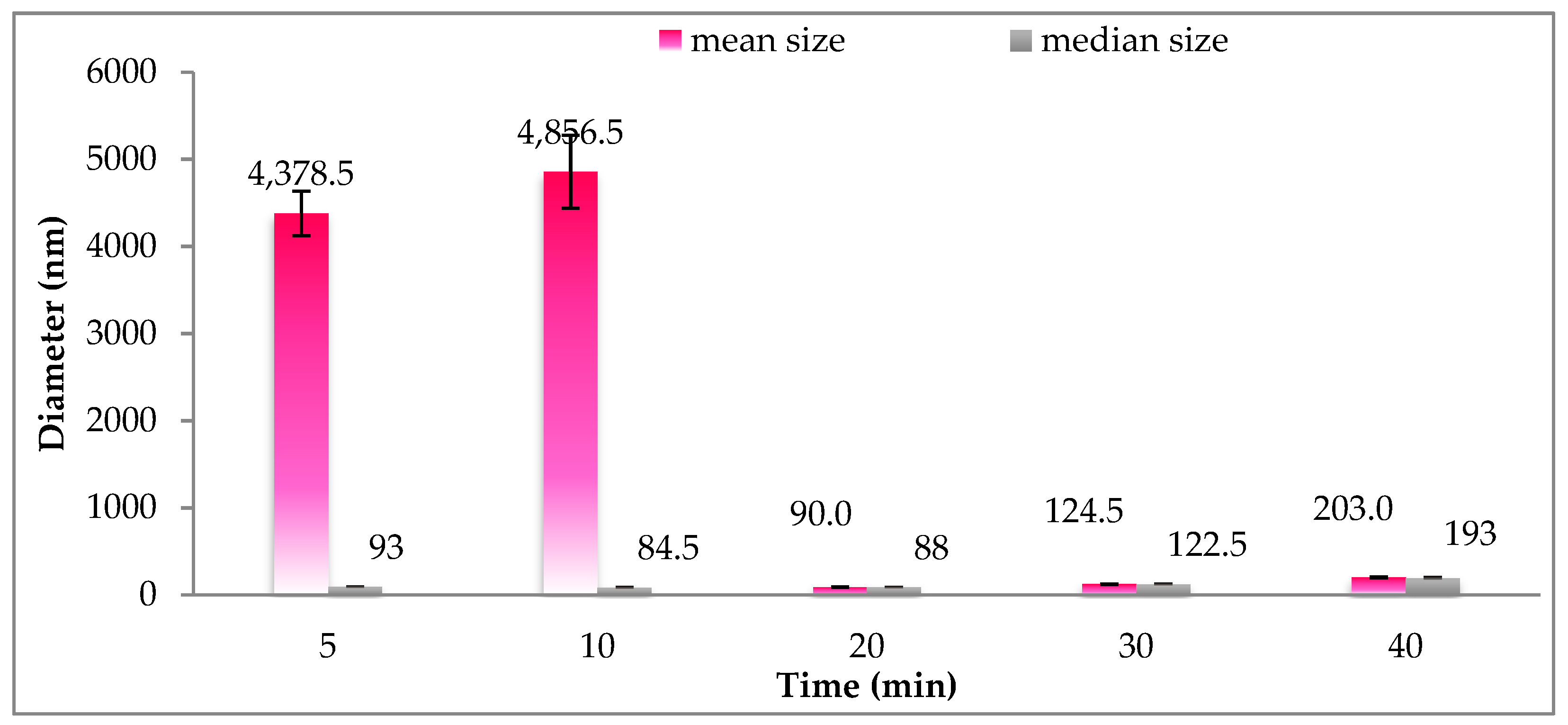
Figure 3 displays the effects of cold homogenization time on particle size and size distribution. At first glance, it is shown that the size of particles was large and strikingly heterogenous at 5 and 10 min, as demonstrated by the difference between mean size (4375.5 and 4856.5 nm) and median size (93 and 84.5 nm). The disuniformity of the particle size could be attributable to the insufficient energy required to break down the particles. From 20 to 40 min of cold homogenization time, the particle distribution was smaller and more uniform. The smallest particle size was achieved at 20 min of cold homogenization time, where the size increased thereafter with prolonged homogenization time. This trend could be explained by the solidification of SLNs at a low temperature, aggregating particles and therefore increasing particle size. Therefore, a cold homogenization time of 20 min was selected as the appropriate time for cold homogenization.
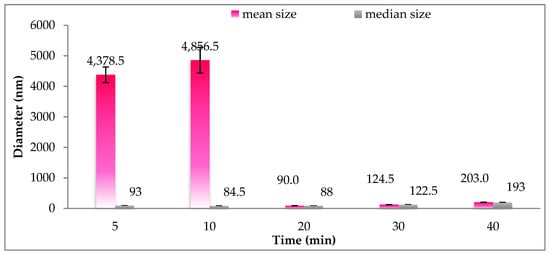
Figure 3.
Size distribution of gac oil-loaded SLNs at different times of cold homogenization.
3.4. Effects of Total Oil Phase Content on Nanoparticle Size
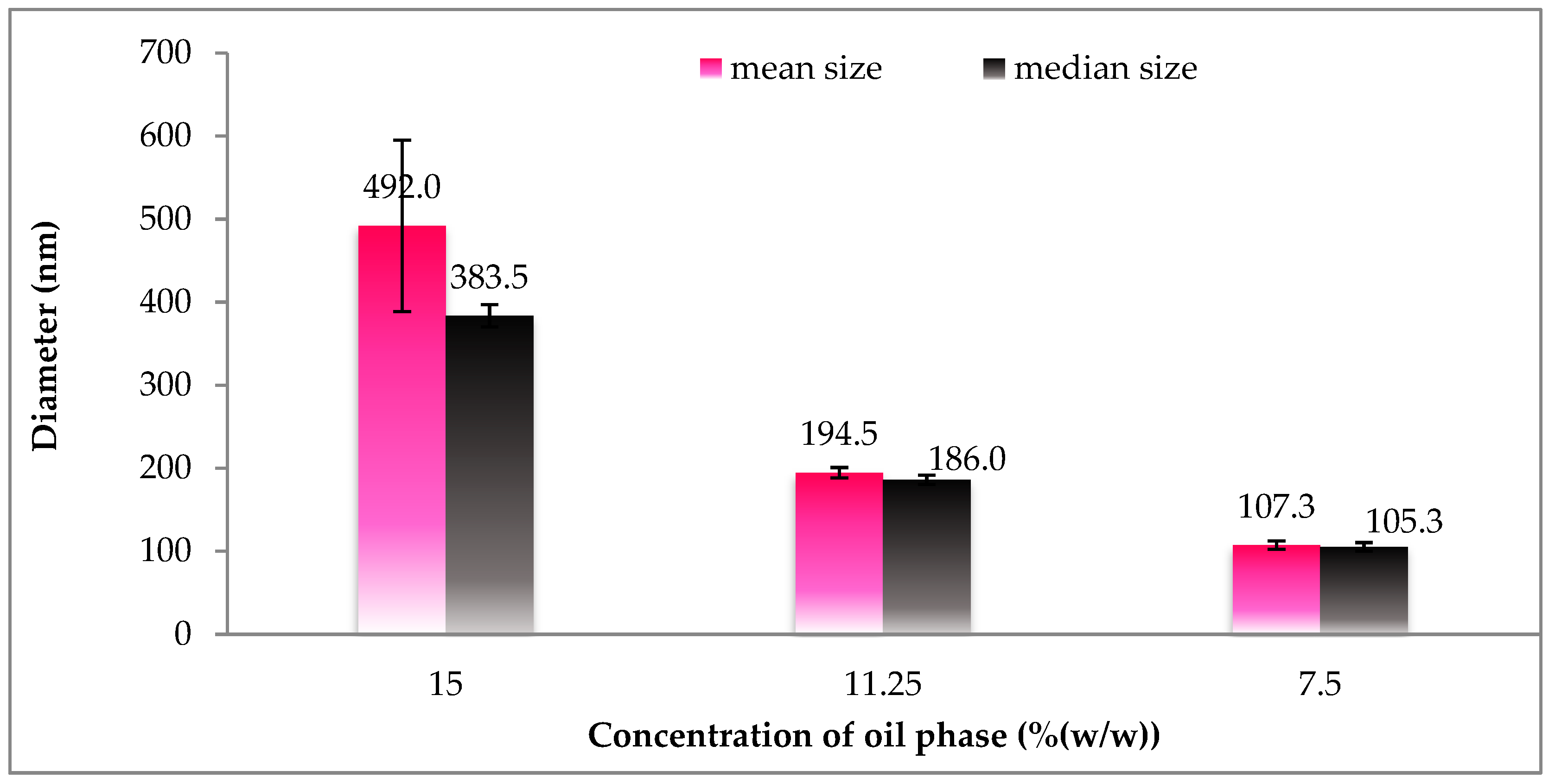
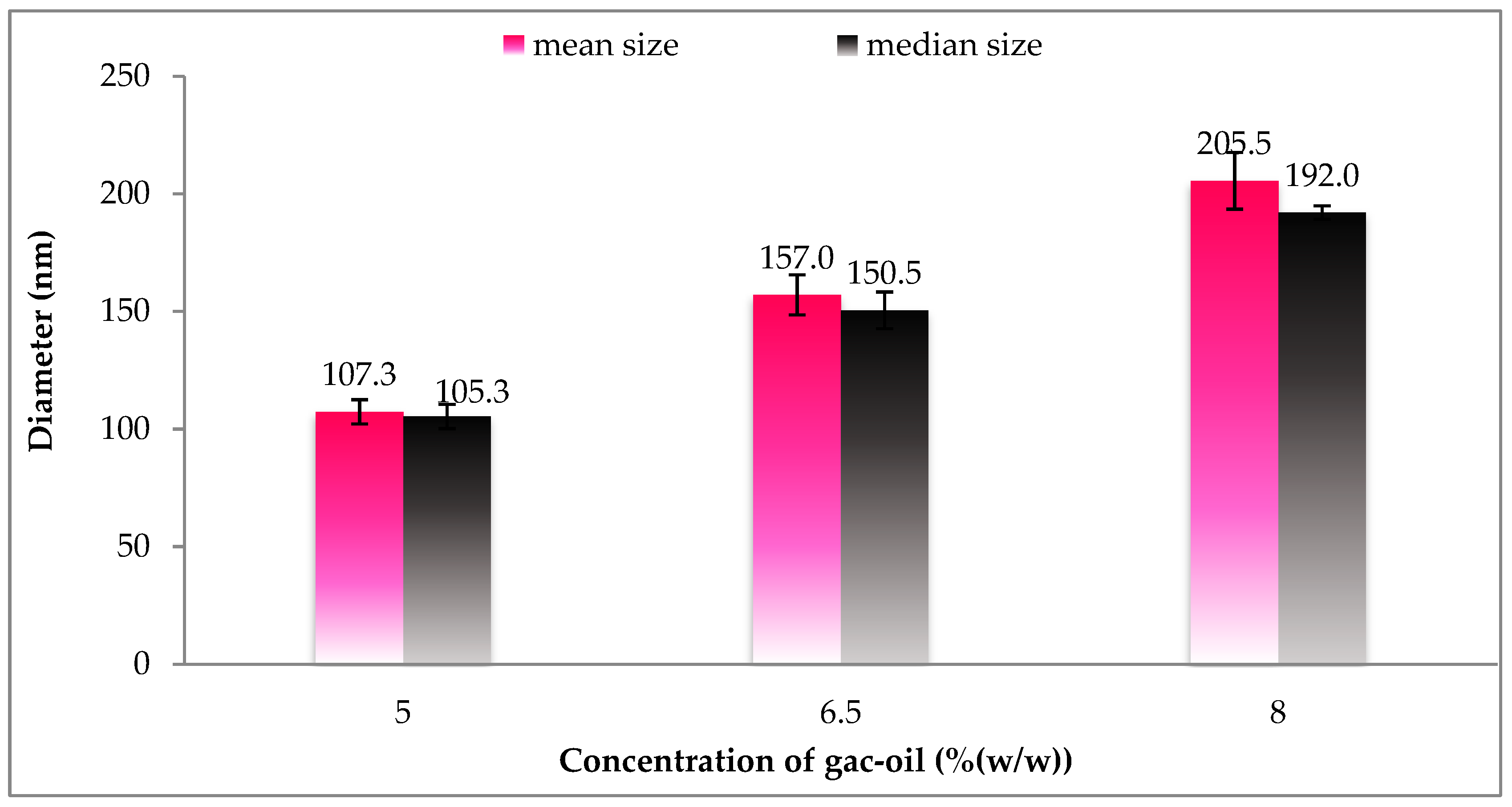
Figure 4 displays the size and size distribution of particles with regards to different oil phase concentrations. Accordingly, the size distribution of SLNs was found to be most uniform and achieved the smallest diameter at a concentration of 7.5%. The proportionality of size of particle relative to concentration could be explained by the imbalance of the suspension caused by the lack of surfactant agents in response to increased oil phase concentration. Subsequently, at the given oil phase concentration of 7.5%, different gac oil ratios in the oil phase and associated particle size are reported in Figure 5. Although particle size is positively associated with Gac oil concentration, increased gac oil concentration also boosts the active components (Carotenoids) in the suspension.
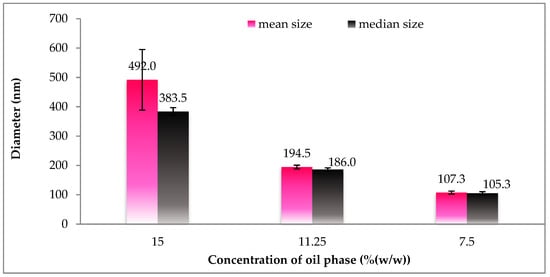
Figure 4.
Size distribution of gac oil-loaded SLNs at different oil phase concentrations.
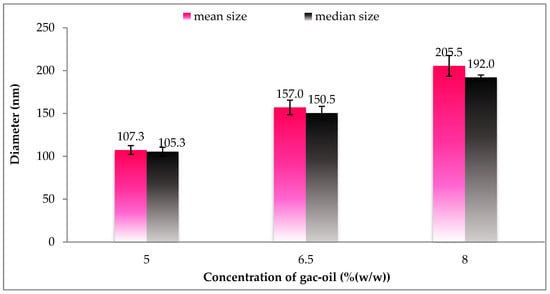
Figure 5.
Size distribution of gac oil-loaded SLNs at different gac-oil concentrations.
3.5. Laser Diffraction Spectrometry (LDS) of Gac Oil-Loaded SLNs
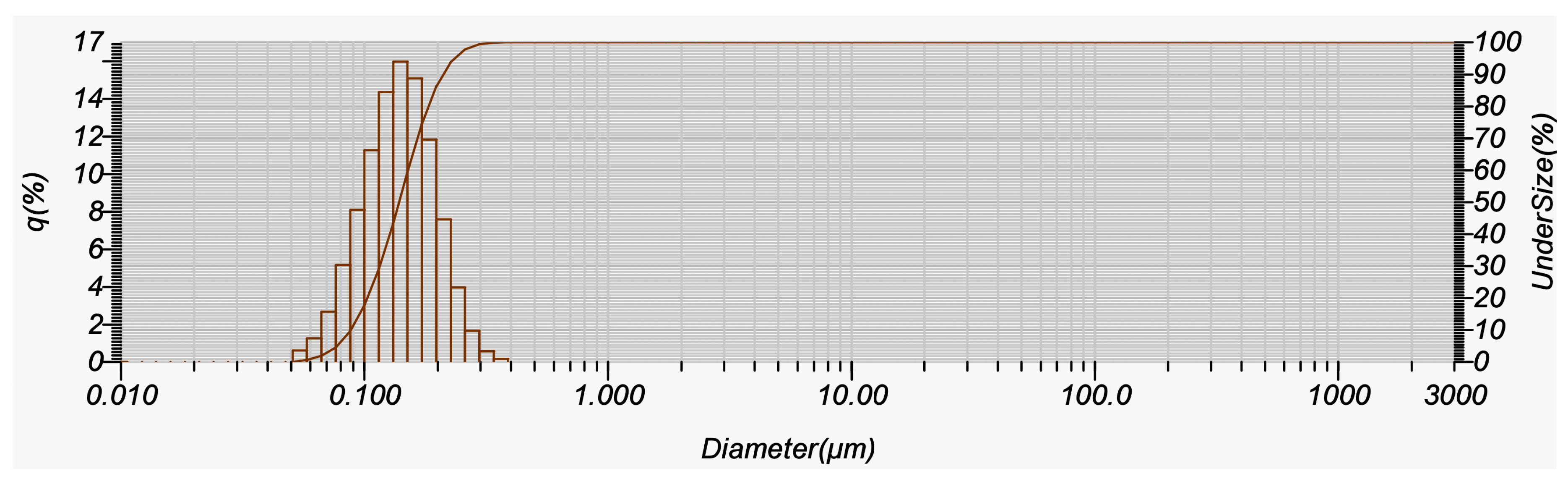
Based on the particle size distribution chart, the gac oil-loaded SLNs system had a fairly uniform distribution, which is indicated by the symmetry of two tails from the mean size of 107 nm (Figure 6).
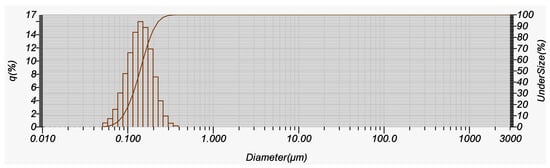
Figure 6.
Distribution chart (LDS size) of SLN-gac oil.
3.6. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) of Gac Oil-Loaded SLNs
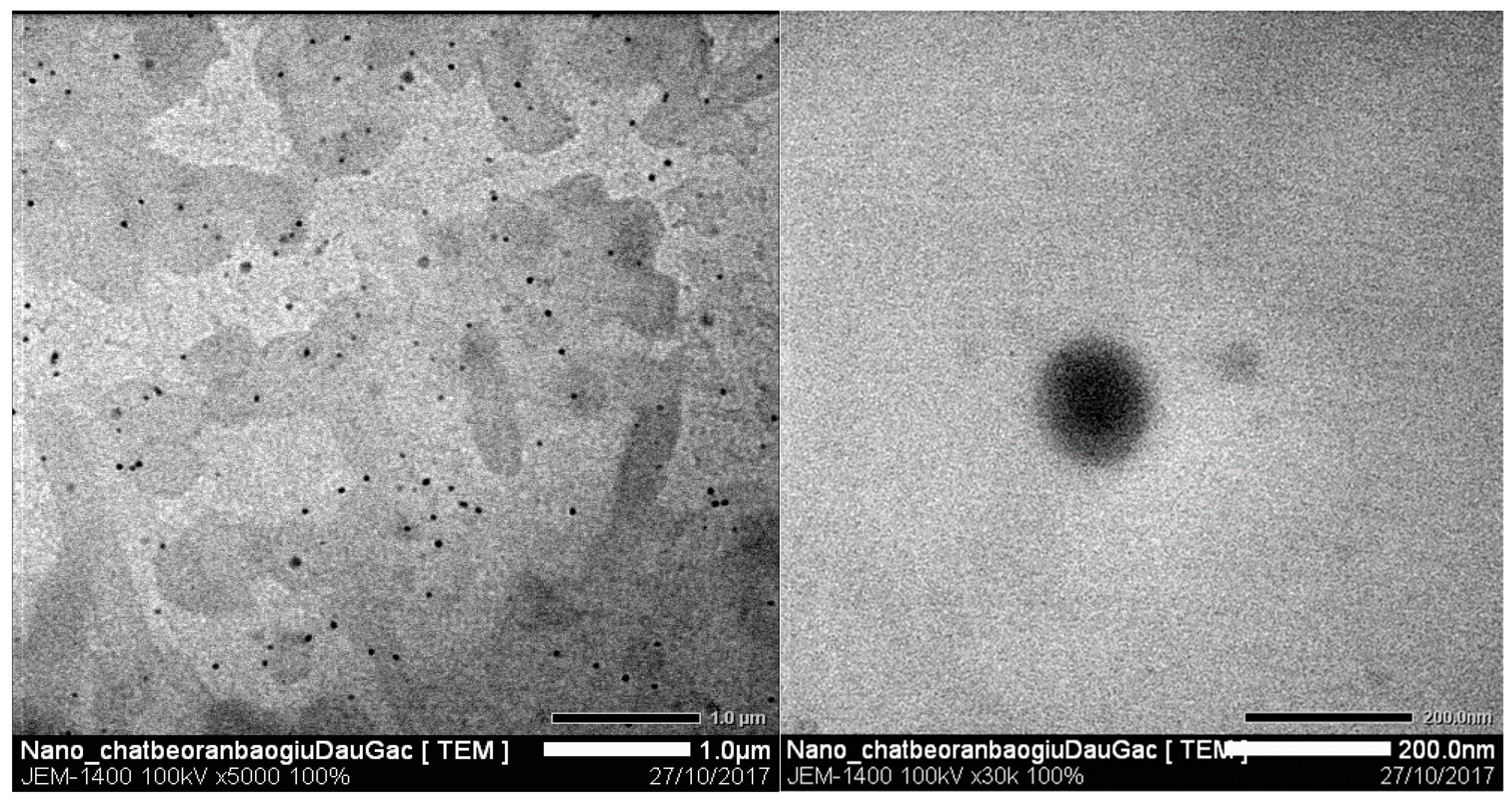
Figure 7 shows the shape and size of solid lipid nanoparticles containing gac oil produced by TEM. In general, gac oil-loaded SLNs were spherical in shape and had a dried size of about 115 nm. The structure of particles was relatively uniform and matrix.
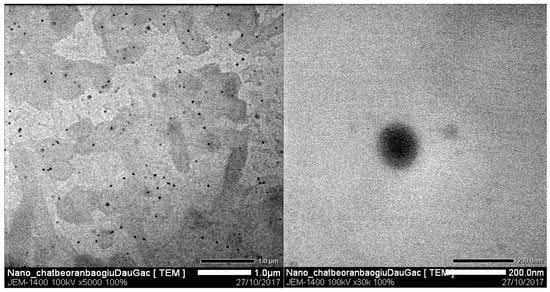
Figure 7.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of gac oil-loaded SLNs.
3.7. Stability of Gac Oil-Loaded SLNs
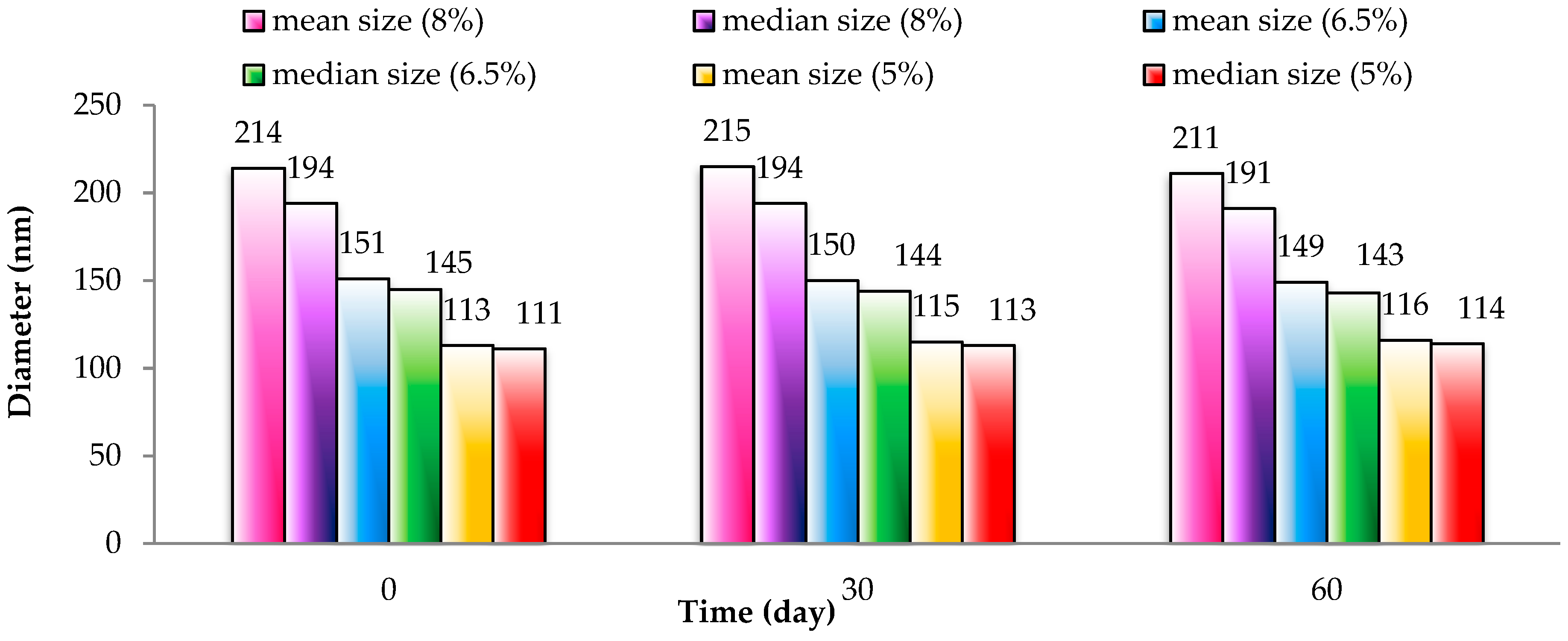
Figure 8 displays the particle size of SLNs corresponding to different gac oil concentrations in three storage periods including 0, 30 and 60 days. Overall particle size and distribution size of gac oil-loaded SLNs was relatively stable over time. After 60 days of storage, the 5%, 6.5% and 8% gac-oil sample only exhibited marginal size deviation, indicating that the sample had no phase separation or deposition. This result shows excellent size stability of SLN containing gac oil, which is promising for wider applications.
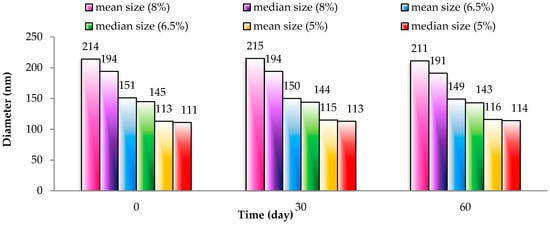
Figure 8.
Changes in particle size by the time storage of 5%, 6.5% and 8% gac-oil.
3.8. Stability of Carotenoids in SLNs
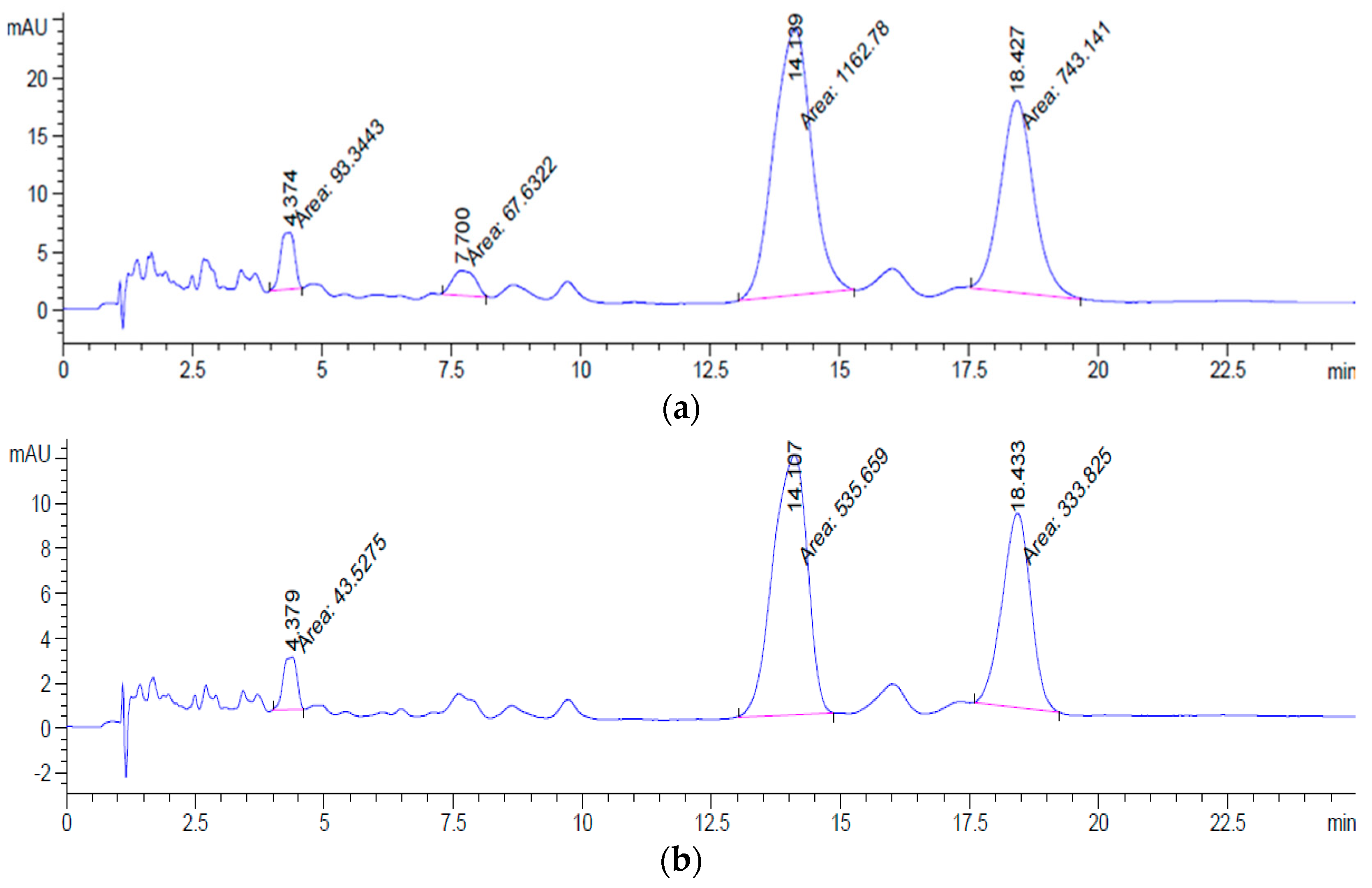
Based on the HPLC spectrum of Figure 9 performed at the wavelength of 450 nm, it is shown that the sample of gac oil exhibited four peaks with a total peak area of 2066.8958. In addition, peak location in the SLNs-gac oil spectrum is similar to that in the reference spectrum. Compared to the gac oil spectrum, the peak area in the SLNs-gac oil spectrum witnessed a substantial loss. This suggests that the process of encapsulation has resulted in the degradation of carotenoids. Based on Equation (1), the result of the stabilization of carotenoids in SLNs (%EE) after homogenization is about 44%.
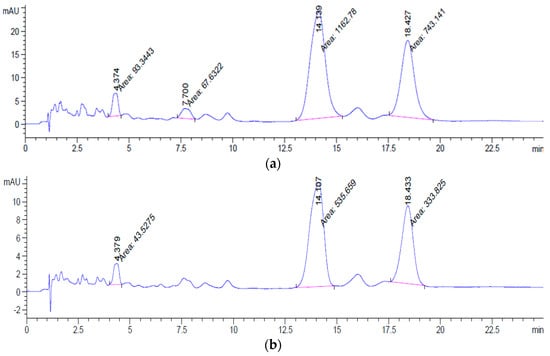
Figure 9.
The HPLC spectrum (a) gac-oil and (b) SLNs-gac oil.
3.9. Effects of Storage Temperature on Gac Oil-Loaded SLNs Stability
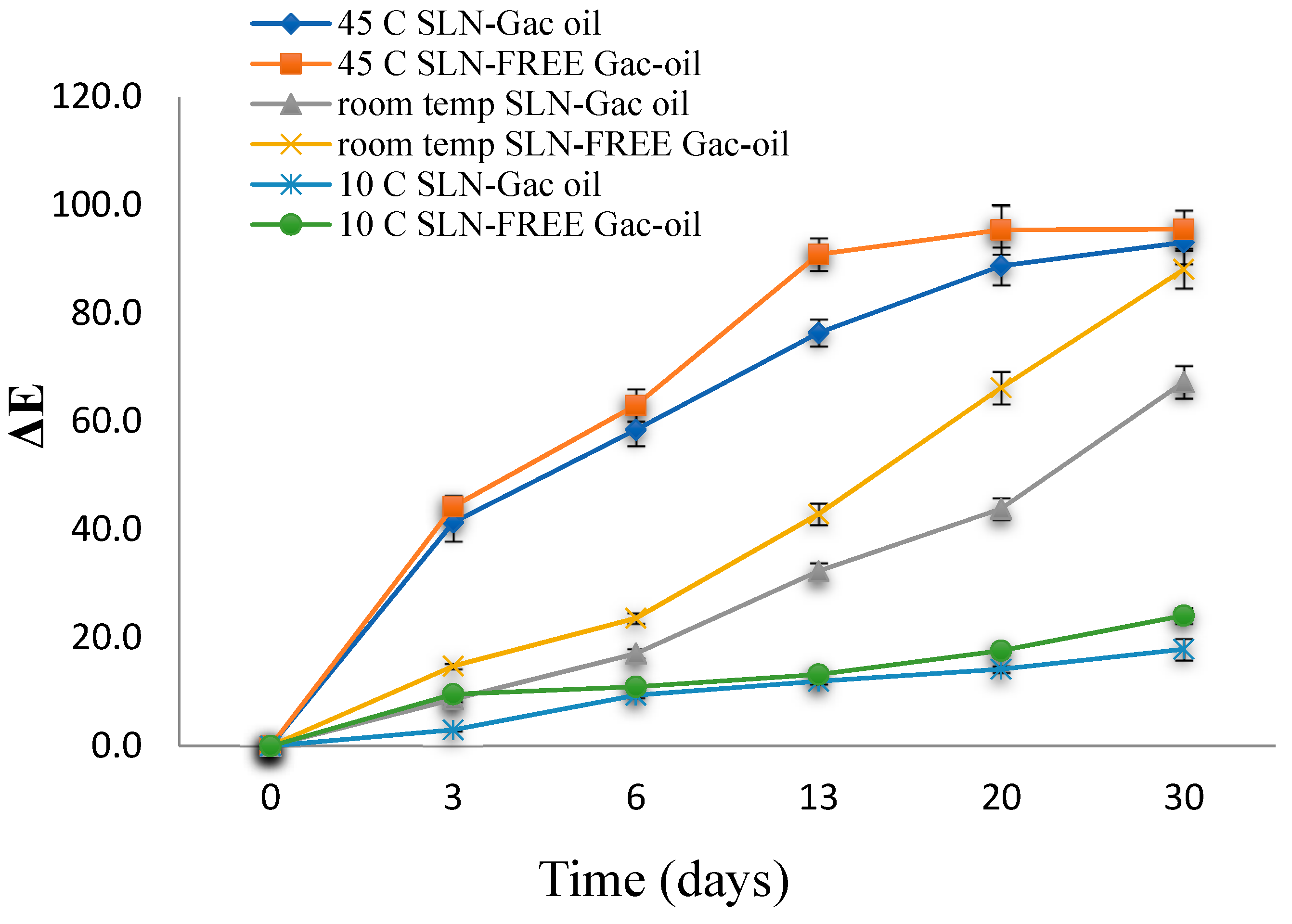
SLN-FREE samples were analyzed for color as demonstrated in Figure 10. In general, color change was recognized with increased storage time, and the change was stable and least profound at samples stored at 10 °C. In addition, in comparison with SLC-FREE samples, SLCs-gac oil samples exhibited less drastic color change, suggesting protective efficacy of SLNs. Therefore, the sample should be preserved at a temperature of 10 °C.
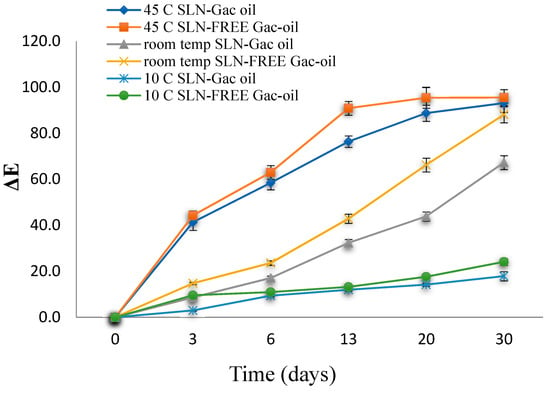
Figure 10.
Effects of different temperatures on ΔE values of samples.
3.10. Effects of UV Light on Gac Oil-Loaded SLNs Stability
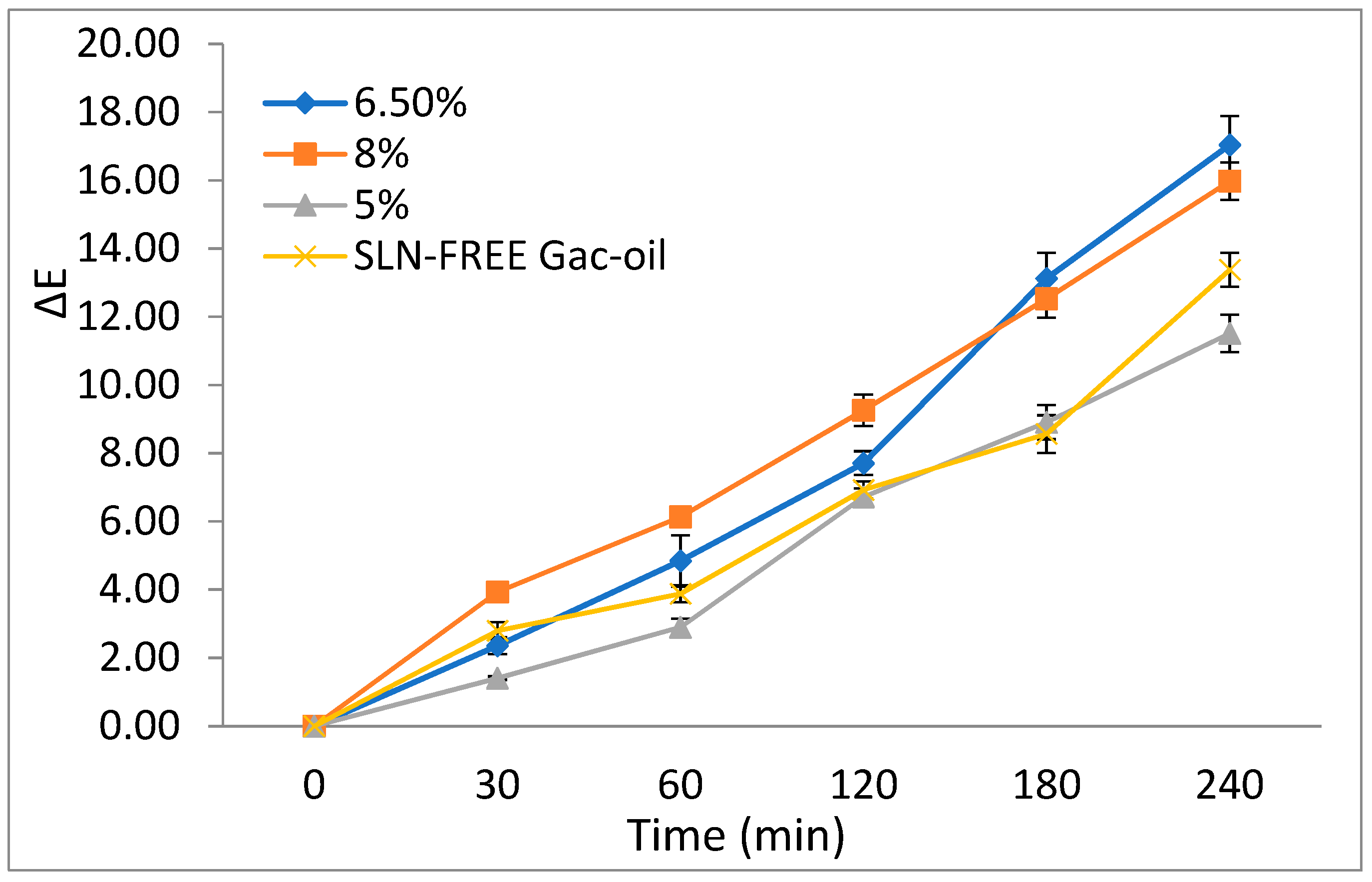
Figure 11 displays the trends of the color measure with regard to the UV exposure period. Accordingly, the UV exposure period had a significant effect on the color change of all the samples, which is demonstrated by the increasing ΔE trend. The gac oil-loaded SLNs experienced higher color change in comparison with other samples, indicating that SLN exhibited protective effects against oxidation degradation.
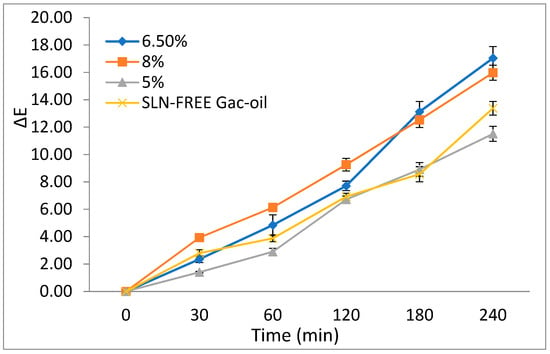
Figure 11.
Effects of UV light on ΔE values of the samples including 8% gac oil-loaded SLNs, 6.5% gac oil-loaded SLNs, 5% gac oil-loaded SLNs and SLN-FREE gac oil.
4. Conclusions
The present study has shown that the encapsulation of carotenoids by SLNs using Naterol SE is feasible and practical. The suspensions containing 5% gac-oil (w/w) were dispersed in a surfactant of 5%(w/w) (Span 80:Tween 80 ratio of 28:72 w/w) and 2.5% (w/w) of Naterol SE concentration. At a hot homogenization temperature of 60 °C, hot homogenization time of 60 min and cold homogenization time of 25 min, the obtained particle size was averaged at approximately 107 nm with a homogenous size distribution. Through TEM examination, nanoparticles were observed to be spherical and had uniform structure. Increasing the oil phase concentration in the suspension resulted in an increase of particle size. The SLNs-gac oil particles were shown to be stable against the temperature and UV light exposure. In addition, a storage temperature of 10 °C is recommended to limit the color change in the suspension.
Author Contributions
Investigation, H.C.M. and T.S.V.N.; Supervision, T.H.N.L. and L.G.B.; Writing—original draft, H.C.M.; Writing—review & editing, D.C.N.
Funding
This work was funded by Ministry of Education and Training, Vietnam (B2016-NLS-04).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere thank for Organic Chemistry Laboratory, Department of Chemical Engineering, Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology and Chemistry Technology Laboratory, Nong Lam University, Ho Chi Minh City for providing facilities and Ministry of Education and Training of Vietnam for sponsoring this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gonçalves, A.; Estevinho, B.N.; Rocha, F. Microencapsulation of vitamin A: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasa-Saracibar, B.; Estella-Hermoso de Mendoza, A.; Guada, M.; Dios-Vieitez, C.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Lipid nanoparticles for cancer therapy: State of the art and future prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, H.; Kieu, N.T.; Kuze, N.; Tomisaka, K.; Van Chuyen, N. Carotenoid pigments in GAC fruit Momordica cochinchinensis SPRENG). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2479–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, B.K.; Turner, C.; Chapman, M.H.; McKeon, T.A. Fatty acid and carotenoid composition of gac (Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng) fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kha, T.C.; Nguyen, M.H.; Roach, P.D.; Parks, S.E.; Stathopoulos, C. Gac fruit: Nutrient and phytochemical composition, and options for processing. Food Rev. Int. 2013, 29, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, L.T.; Franke, A.A.; Custer, L.J.; Murphy, S.P. Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng. (gac) fruit carotenoids reevaluated. J. Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.H.; Hanh, P.T.; Osorio-Puentes, F.J.; Waché, Y. Stability of carotenoid extracts of gấc (Momordica cochinchinensis) towards cooxidation—Protective effect of lycopene on β-caroten. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2252–2257. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J. Lycopene in Tomatoes: Chemical and Physical Properties Affected by Food Processing. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2000, 20, 293–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.J.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Nguyen, M.L.; Cooper, D.A.; Eldridge, A.L.; Schwartz, S.J.; White, W.S. Carotenoid bioavailability is higher from salads ingested with full-fat than with fat-reduced salad dressings as measured with electrochemical detection. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnlein, H.V. Karat, pulque, and gac. Three shining stars in the traditional food galaxy. Nutr. Nev. 2004, 62, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unlu, N.Z.; Bohn, T.; Clinton, S.K.; Schwartz, S.J. Carotenoid absorption from salad and salsa by humans is enhanced by the addition of avocado or avocado oil. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Rao, A.V. Tomato lycopene and its role in human health and chronic diseases. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2000, 163, 739–744. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.; Dan, H.; Wu, R.; Meng, W.; Liu, N.; Jin, X.; Zhou, M.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Q. Lycopene: Features and potential significance in the oral cancer and precancerous lesions. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, G.; Li, L.B.; Lou, H.X. Enhancement of gastrointestinal absorption of quercetin by solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Cont. Release 2009, 133, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xie, D. Nanoparticle encapsulation in vesicles formed by amphiphilic diblock copolymers. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 7840–7847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Ting, Y.; Zeng, X.; Huang, Q. Bioactive Peptides/Chitosan Nanoparticles Enhance Cellular Antioxidant Activity of (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Suslick, K.S. Ultrasonic Preparation of Porous Silica-Dye Microspheres: Sensors for Quantification of Urinary Trimethylamine N -Oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 15820–15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlke, K.; Behsnilian, D.; Mayer-Miebach, E.; Weidler, P.G.; Greiner, R. Edible solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) as carrier system for antioxidants of different lipophilicity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyaboonchai, W.; Tungpradit, W.; Plianbangchang, P. Formulation and characterization of curcuminoids loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.N.Q.; Bach, L.G.; Nguyen, T.D.; Le, N.T.H. Efficient Method for Preparation of Rutin Nanosuspension Using Chitosan and Sodium Tripolyphosphate Crosslinker. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.C.; Le, T.T.T.; Diep, T.T.; Le, T.H.N.; Nguyen, D.T.; Bach, L.G. Development of Soild Lipid Nanoparticles of Gac (Momordica cocochinensis Spreng) Oil by Nano-Emulsion Technique. Asian J. Chem. 2018, 30, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carla, V. The size of solid lipid nanoparticles: An interpretation from experimental design. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 84, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- DongZhi, H. The production and characteristics of soilid nanoparticles (SLNs). Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Garud, A.; Singh, D.; Garud, N. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs): Method, characterization and applications. Int. Curr. Pharm. J. 2012, 1, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.A.; Madureira, A.R.; Gomes, A.M.; Sarmento, B.; Pintado, M.M. Optimization of the production of solid Witepsol nanoparticles loaded with rosmarinic acid. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 115, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentschel, A.; Gramdorf, S.; Müller, R.H.; Kurz, T. β-Carotene-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, N1–N6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgason, T.; Awad, T.S.; Kristbergsson, K.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J.; Weiss, J. Impact of Surfactant Properties on Oxidative Stability of β-Carotene Encapsulated within Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8033–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Pezeshki, A.; Mesgari Abbasi, M.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Vitamin D3-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers as a Potential Approach for Fortifying Food Beverages; in Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 7, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.R. Nanocarrier Technologies: Frontiers of Nanotherapy, 1st ed.; Springer: Heidelberg, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Effat, S.F.; Saman, A.N.; Zahra, T. Novel formulation and evaluation of a Q10-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle cream: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).