Preparation and Characterization of Porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3/PbO2 Electrodes for the Removal of Chloride Ions in Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Electrode Preparation
2.3. Electrode Characterization
2.4. Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Chloride Ions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
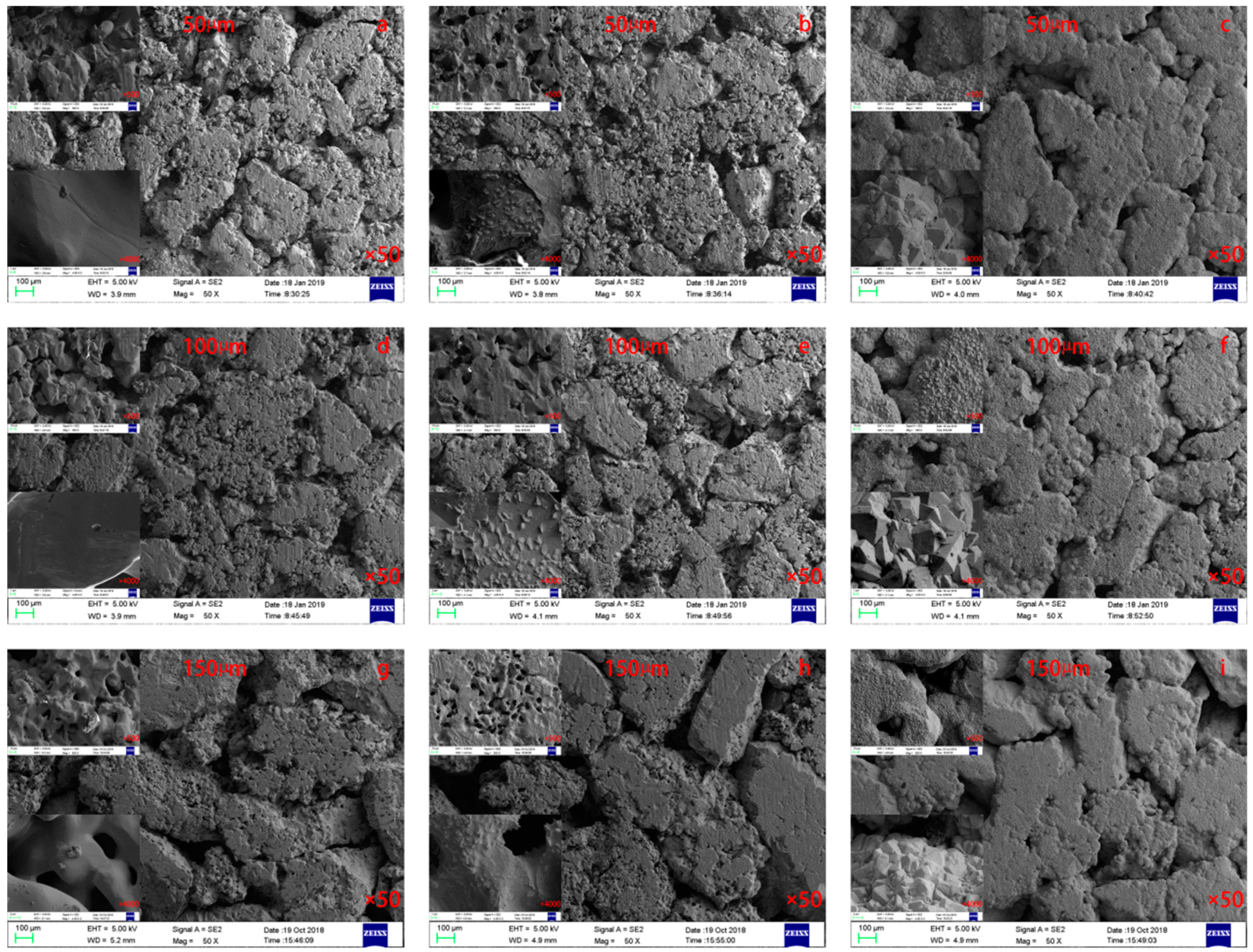
3.1.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Characterization
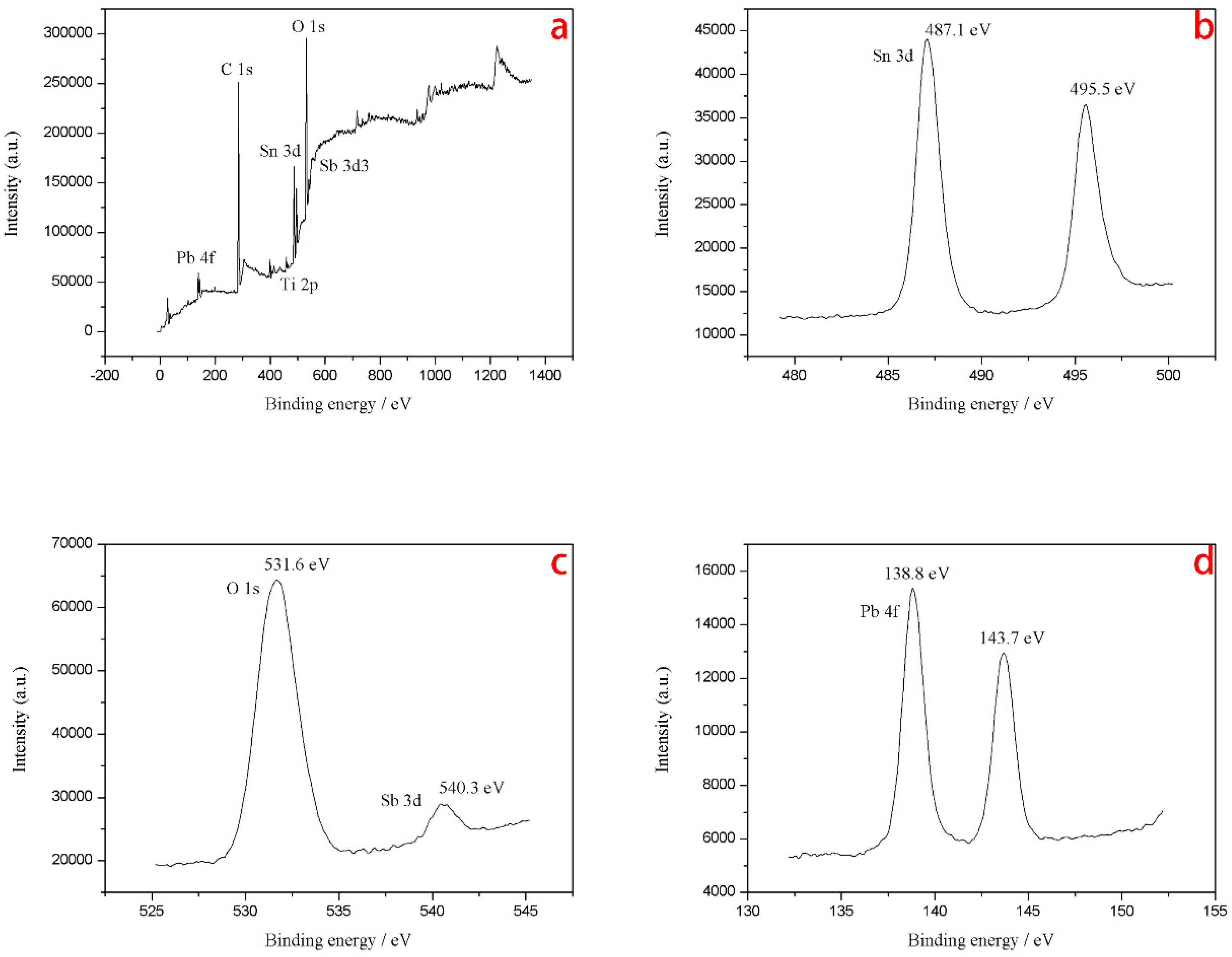
3.1.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectrometer (XPS) Characterization
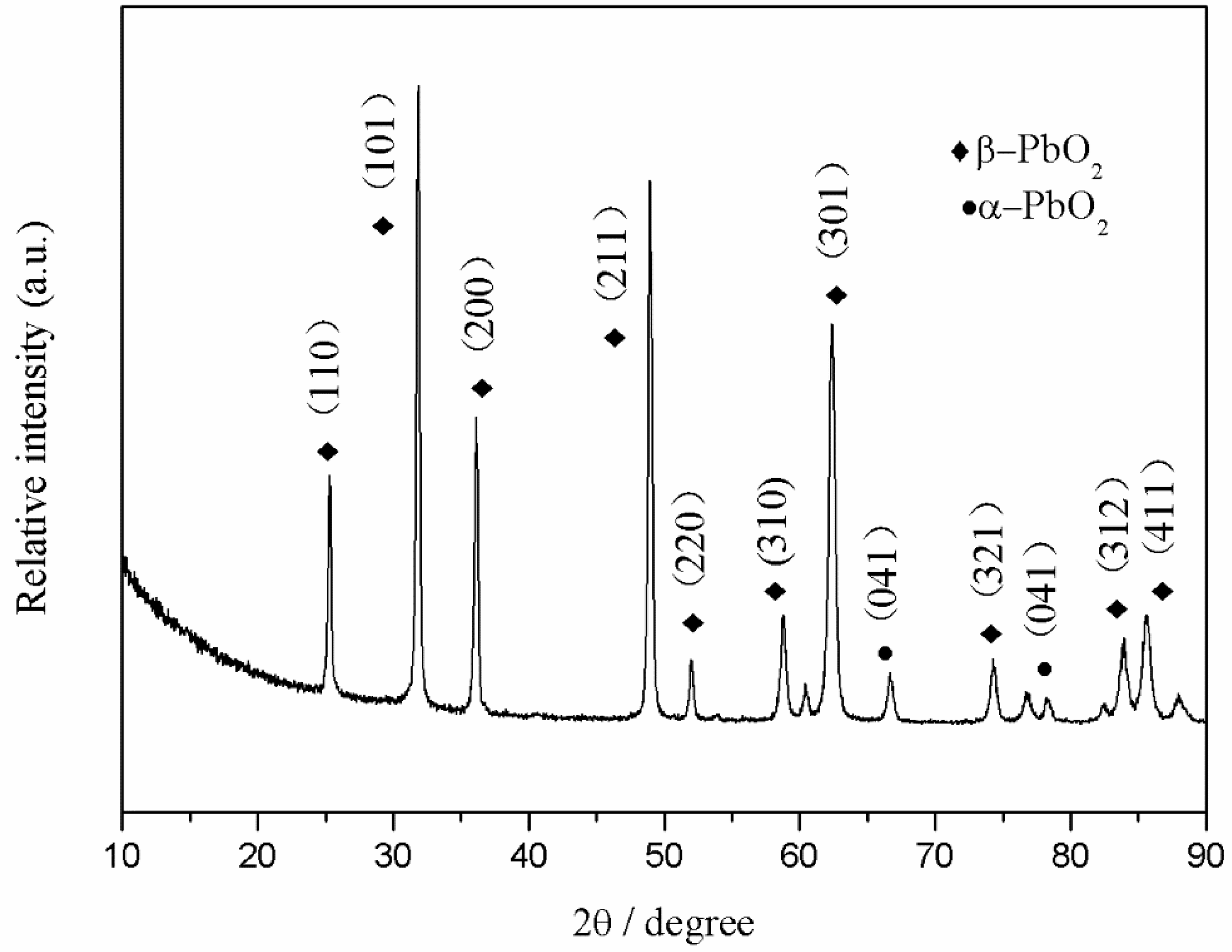
3.1.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Characterization
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization
3.2.1. Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV) Curves
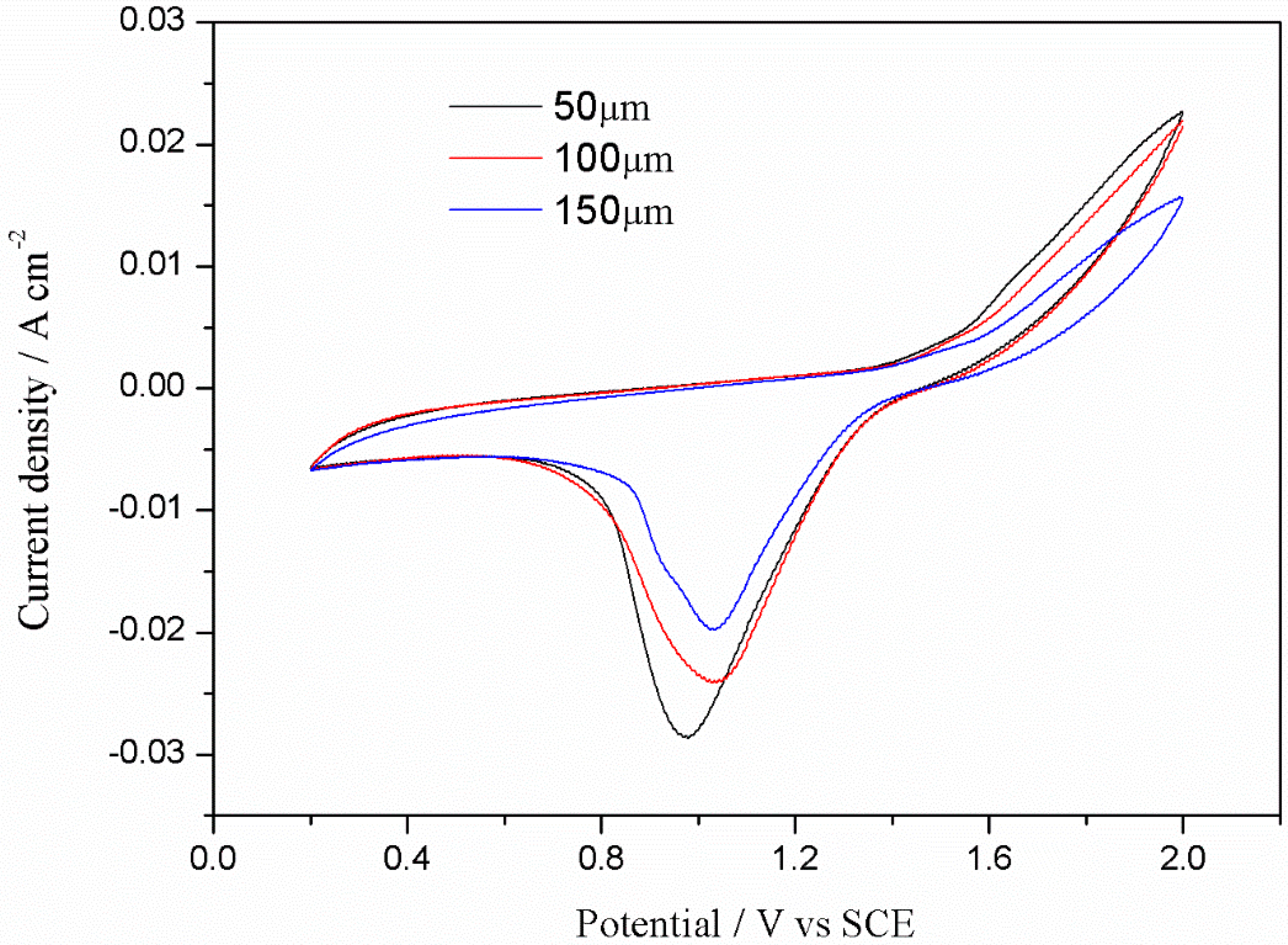
3.2.2. Cyclic Voltammetry
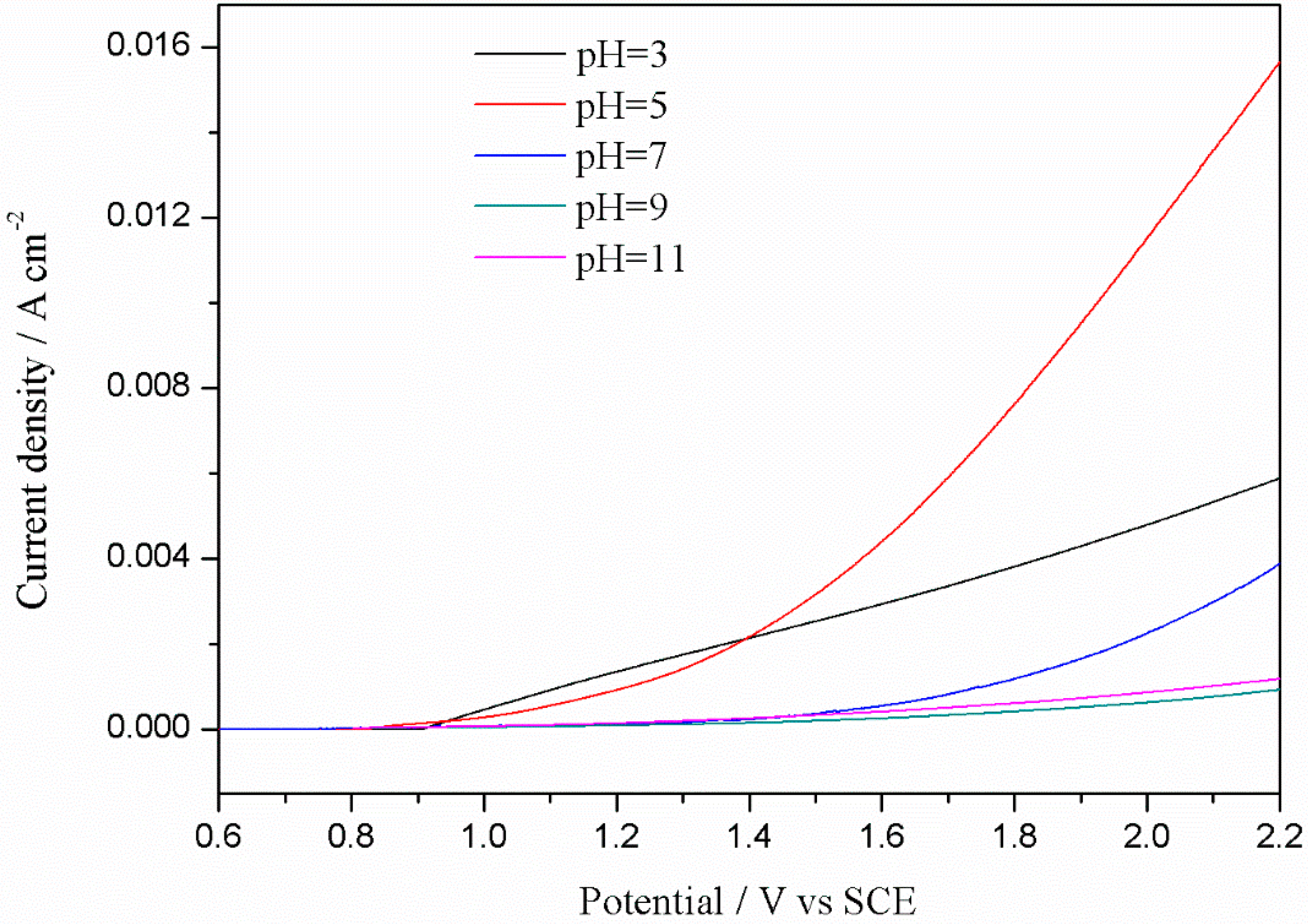
3.2.3. Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV) Curves in Different pH Solutions
3.3. Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Chloride Ions
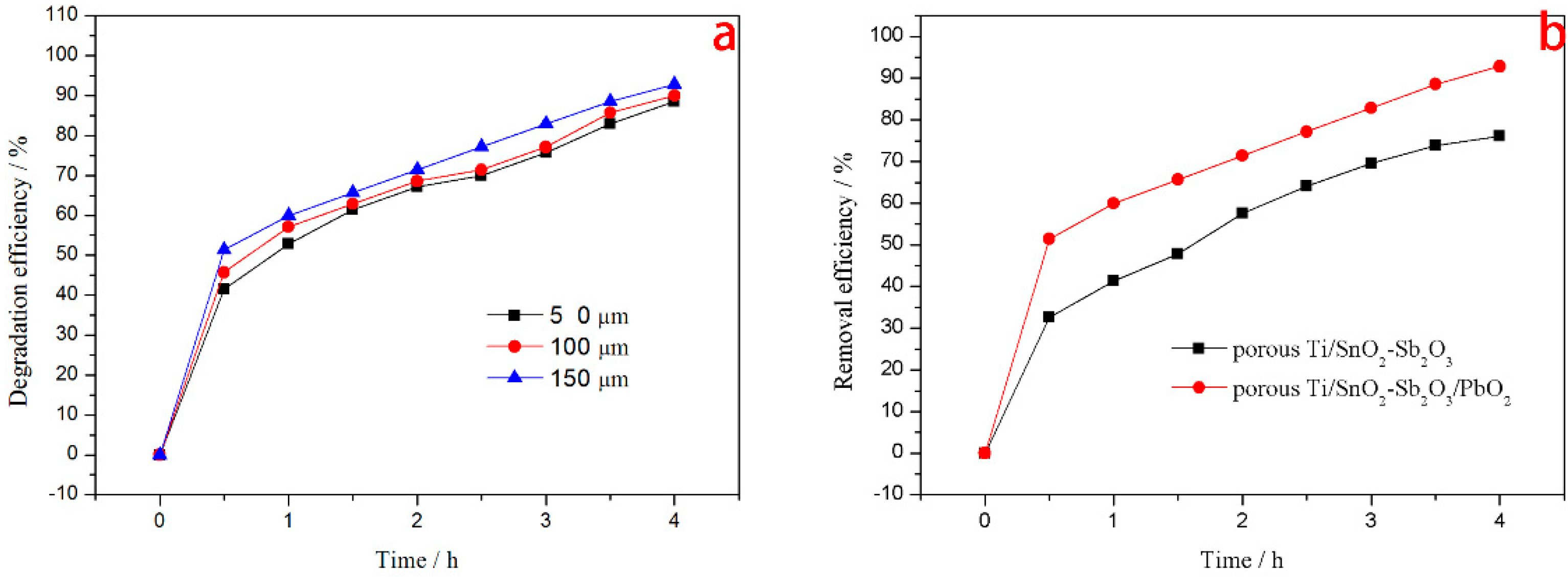
3.3.1. Effect of Pore Size
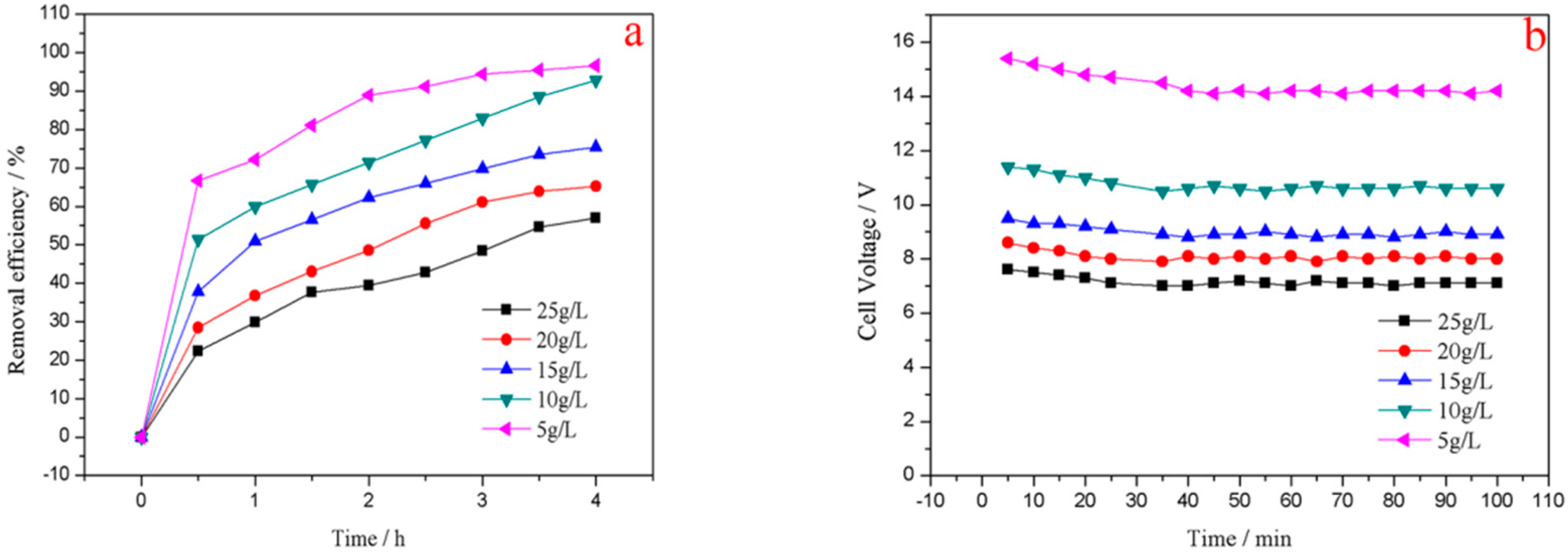
3.3.2. Effect of Initial NaCl Concentration
3.3.3. Effect of Current Density
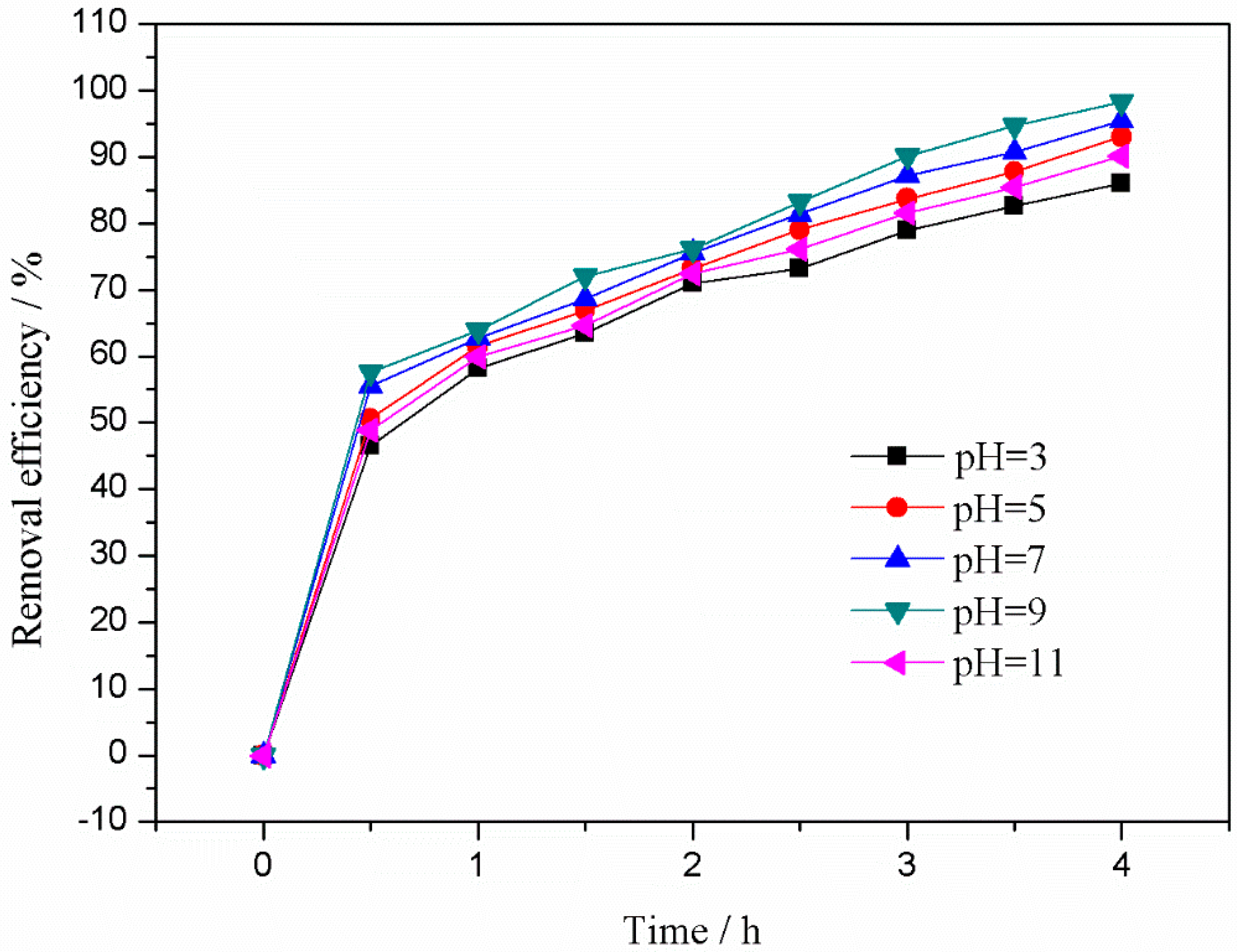
3.3.4. Effect of Initial pH
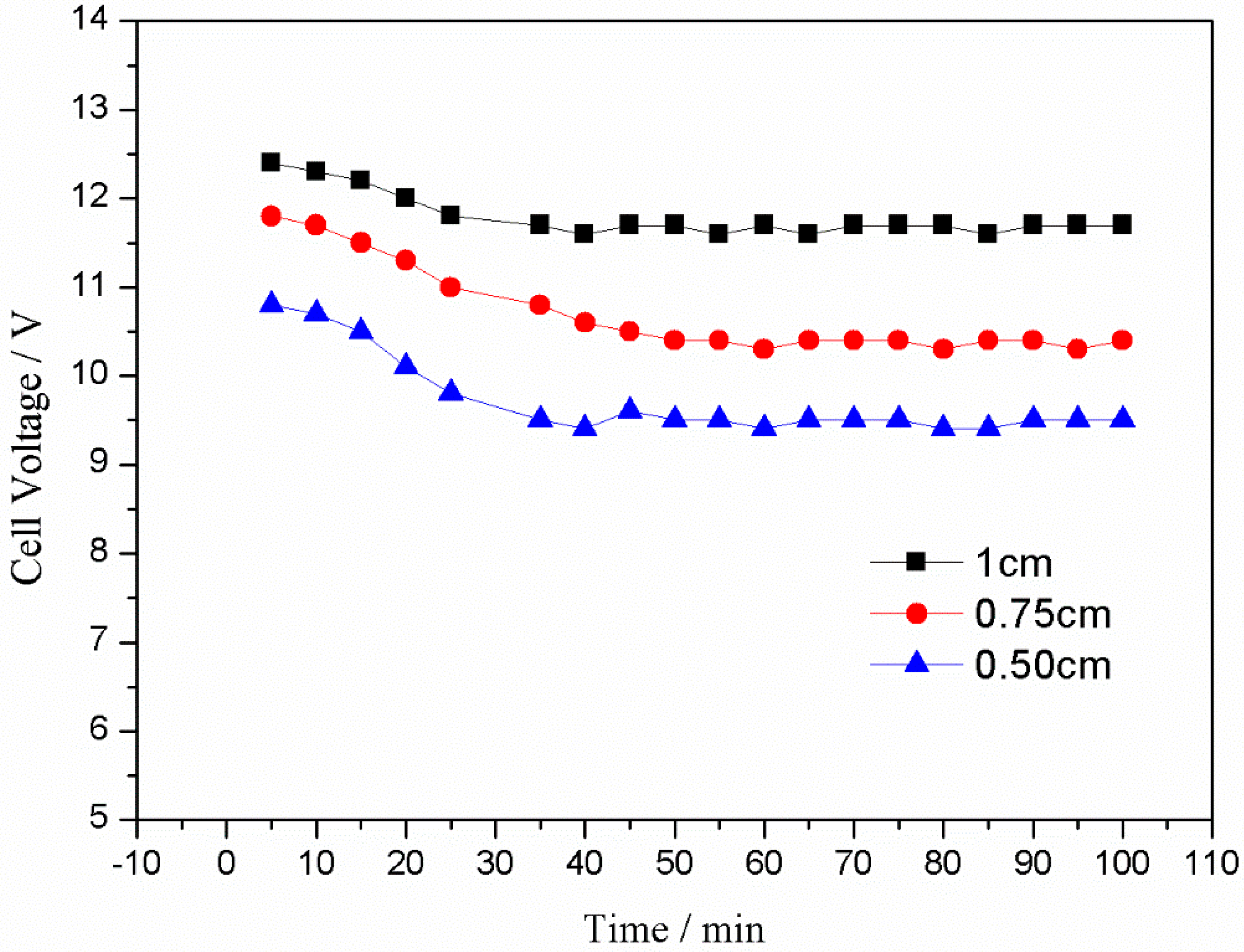
3.3.5. Effect of Electrode Plate Spacing
3.3.6. Number of Cycles
3.3.7. Mechanism of Removing Chloride Ions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, L.; Li, G.P.; Li, Y.Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L.Q.; Dong, Y.; Ma, C.Y. Electrolysis-electrodialysis process for removing chloride ion in wet flue gas desulfurization wastewater (DW): Influencing factors and energy consumption analysis. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 123, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, A.; Batchelor, B. Chloride removal from recycled cooling water using ultra-high lime with aluminum process. Water Environ. Res. 2002, 74, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolard, C.R.; Irvine, R.L. Biological treatment of hypersaline wastewater by a biofilm of halophific bacteria. Water Environ. Res. 1994, 66, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyrides, I.; Stuckey, D.C. Saline sewage treatment using a submerged anaerobic membrane reactor (SAMBR): Effects of activated carbon addition and biogas-sparging time. Water Res. 2009, 43, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walha, K.; Amar, R.B.; Firdaous, L.; Quéméneur, F.; Jaouen, P. Brackish groundwater treatment by nanofiltration, reverse osmosis and electrodialysis in tunisia: Performance and cost comparison. Desalination 2007, 207, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, K. New nanopore zeolite membranes for water treatment. Desalination 2010, 251, 176–180. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, W.A. Fundamentals of zero liquid discharge system design. Power 2011, 155, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Sun, P.D.; Gu, Z.Y.; Du, H.G.; Pang, X.J.; Tao, X.H.; Xu, R.F.; Xu, L.L. Removal of chloride ion from aqueous solution by ZnAl-NO3 layered double hydroxides as anion-exchanger. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Long, J.Y.; Jiang, D.Q.; Liu, J.; Li, S.J.; Qi, J.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Gong, J.; et al. Simultaneous removal of thallium and chloride from a highly saline industrial wastewater using modified anion exchange resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.X.; Li, Y.N.; Bradley, P.L. A review of reverse osmosis membrane fouling and control strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tang, J.Y.; Zhou, X.Z.; Li, J.S.; Sun, X.Y.; Shen, J.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Han, W.Q. Electrochemical degradation of pyridine by Ti/SnO2-Sb tubular porous electrode. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Lin, H.; Liang, S.T.; Xie, R.Z.; Lv, S.H.; Niu, J.F.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.Y. A reactive electrochemical filter system with an excellent penetration flux porous Ti/SnO2-Sb filter for efficient contaminant removal from water. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 13933–13944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Li, Q.; Tao, D.J.; Cui, H.; Xu, X.T.; Ding, L.; Sun, L.; Zhai, J.P. The synthesis and characterization of Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3/PbO2 electrodes: The influence of morphology caused by different electrochemical deposition time. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.Y.; Feng, Y.J.; Liu, J.F. Preparation and properties of Ti/SnO2-Sb2O5 electrodes by electrodeposition. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4920–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xing, J.T.; Chen, D.H.; Bai, Z.L.; Xia, Y.S. Study on the performance of an improved Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3/PbO2 based on porous titanium substrate compared with planar titanium substrate. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26530–26539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xing, J.T.; Chen, D.H.; Jin, D.Y.; Shen, J. Electrochemical degradation of Musk ketone in aqueous solutions using a novel porous Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3/PbO2 electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 775, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.T.; Chen, D.H.; Zhao, W.; Peng, X.L.; Bai, Z.L.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhao, X.X. Preparation and characterization of a novel porous Ti/SnO2-Sb2O3-CNT/PbO2 electrode for anodic oxidation of phenol wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53504–53513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.R.; Lu, H.Y.; Lin, H.B.; Huang, W.M.; Li, H.D.; Lu, J.; Cui, T. Boron doped diamond electrodes based on porous Ti substrate. Mater. Lett. 2012, 83, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.; Fujishima, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hashimoto, K. Detection of active oxidative species in TiO2 photocatalysis using the fluorescence technique. Electrochem. Commun. 2000, 2, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Lin, H.B.; Kong, H.S.; Lu, H.Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, T.T. High energy density PbO2/activated carbon asymmetric electrochemical capacitor based on lead dioxide electrode with three-dimensional porous titanium substrate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 17153–17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neodo, S.; Rosestolato, D.; Ferro, S.; De Battisti, A. On the electrolysis of dilute chloride solutions: Influence of the electrode material on Faradaic efficiency for active chlorine, chlorate and perchlorate. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 80, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duirk, S.E.; Desetto, L.M.; Davis, G.M. Transformation of Organophosphorus Pesticides in the Presence of Aqueous Chlorine: Kinetics, Pathways, and Structure−Activity Relationships. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2335–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.P.; Duirk, S.E.; Tarr, J.C.; Collette, T.W. Monitoring the speciation of aqueous free chlorine from pH 1 to 12 with Raman spectroscopy to determine the identity of the potent low-pH oxidant. Appl. Spectrosc. 2006, 60, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, K.; Peng, J.; Chen, P.; Gu, W.; Luo, Y.; Yu, P. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3/PbO2 Electrodes for the Removal of Chloride Ions in Water. Processes 2019, 7, 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7100762
Xu K, Peng J, Chen P, Gu W, Luo Y, Yu P. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3/PbO2 Electrodes for the Removal of Chloride Ions in Water. Processes. 2019; 7(10):762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7100762
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Kangdong, Jianghua Peng, Pan Chen, Wankai Gu, Yunbai Luo, and Ping Yu. 2019. "Preparation and Characterization of Porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3/PbO2 Electrodes for the Removal of Chloride Ions in Water" Processes 7, no. 10: 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7100762
APA StyleXu, K., Peng, J., Chen, P., Gu, W., Luo, Y., & Yu, P. (2019). Preparation and Characterization of Porous Ti/SnO2–Sb2O3/PbO2 Electrodes for the Removal of Chloride Ions in Water. Processes, 7(10), 762. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7100762



