Second-Order Symmetric Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method for Transient Heat Conduction Problems with Initial Discontinuity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Transient Heat Conduction Problem
3. SO-SSPH Method
3.1. SPH Method
3.2. SO-SSPH Method
4. Numerical Analysis
4.1. Truncation Error
4.2. Numerical Accuracy
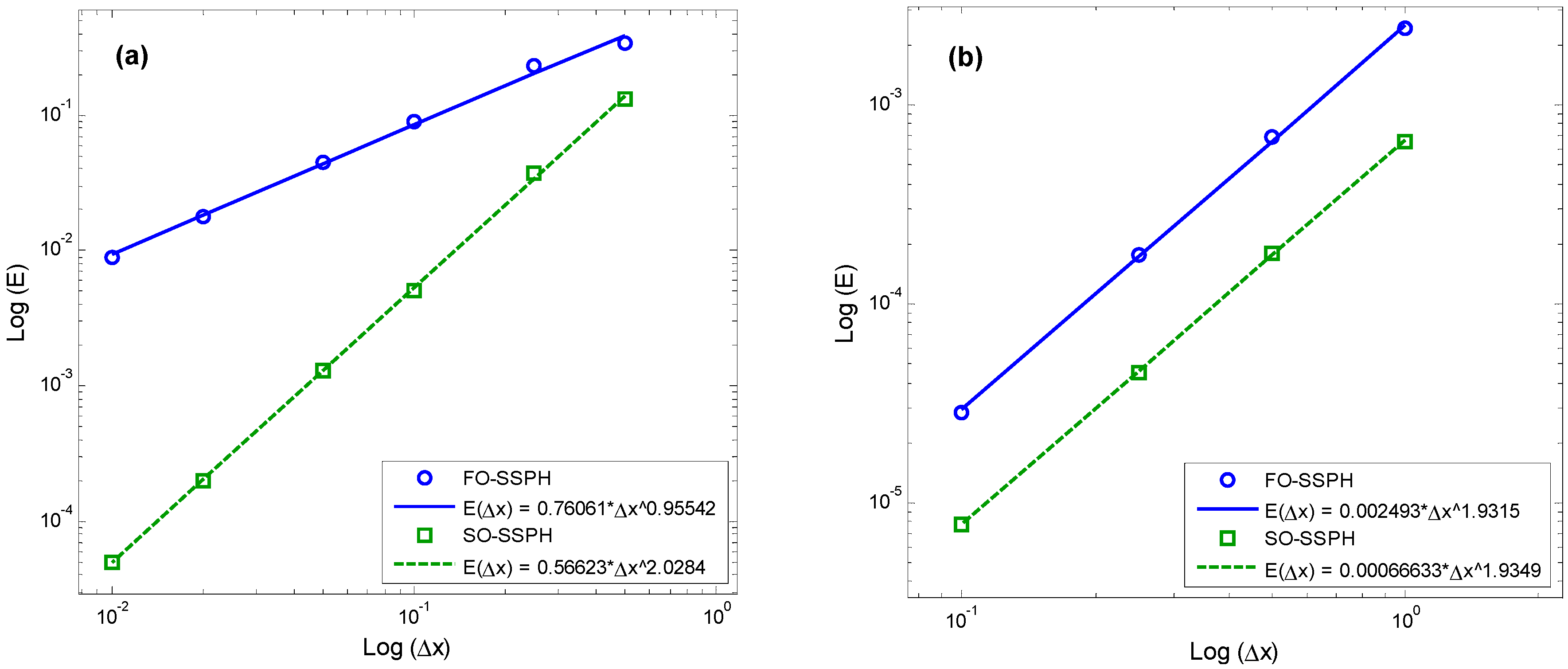
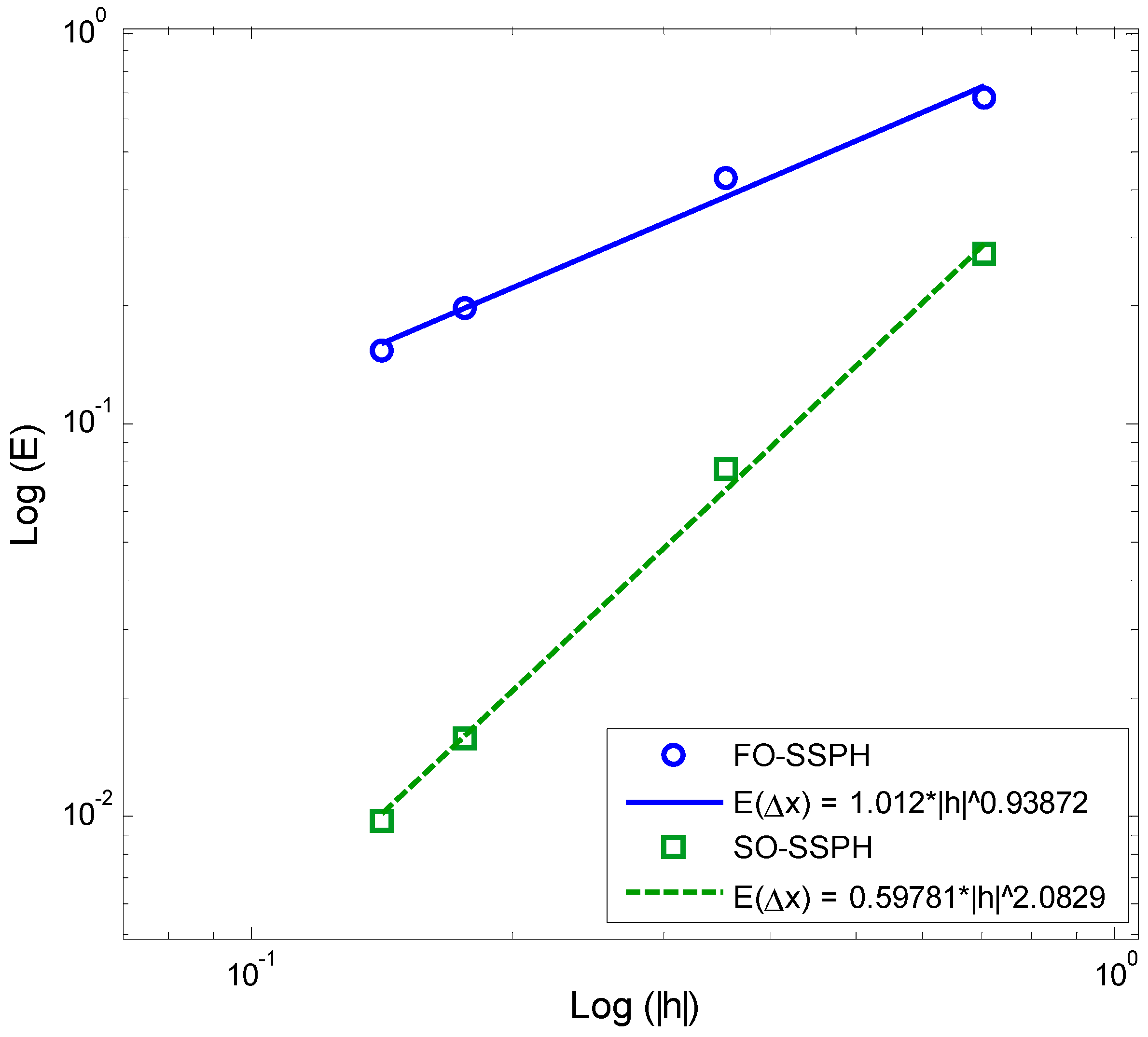
4.3. Convergence Rate
4.4. Stability Analysis
5. Numerical Experiments
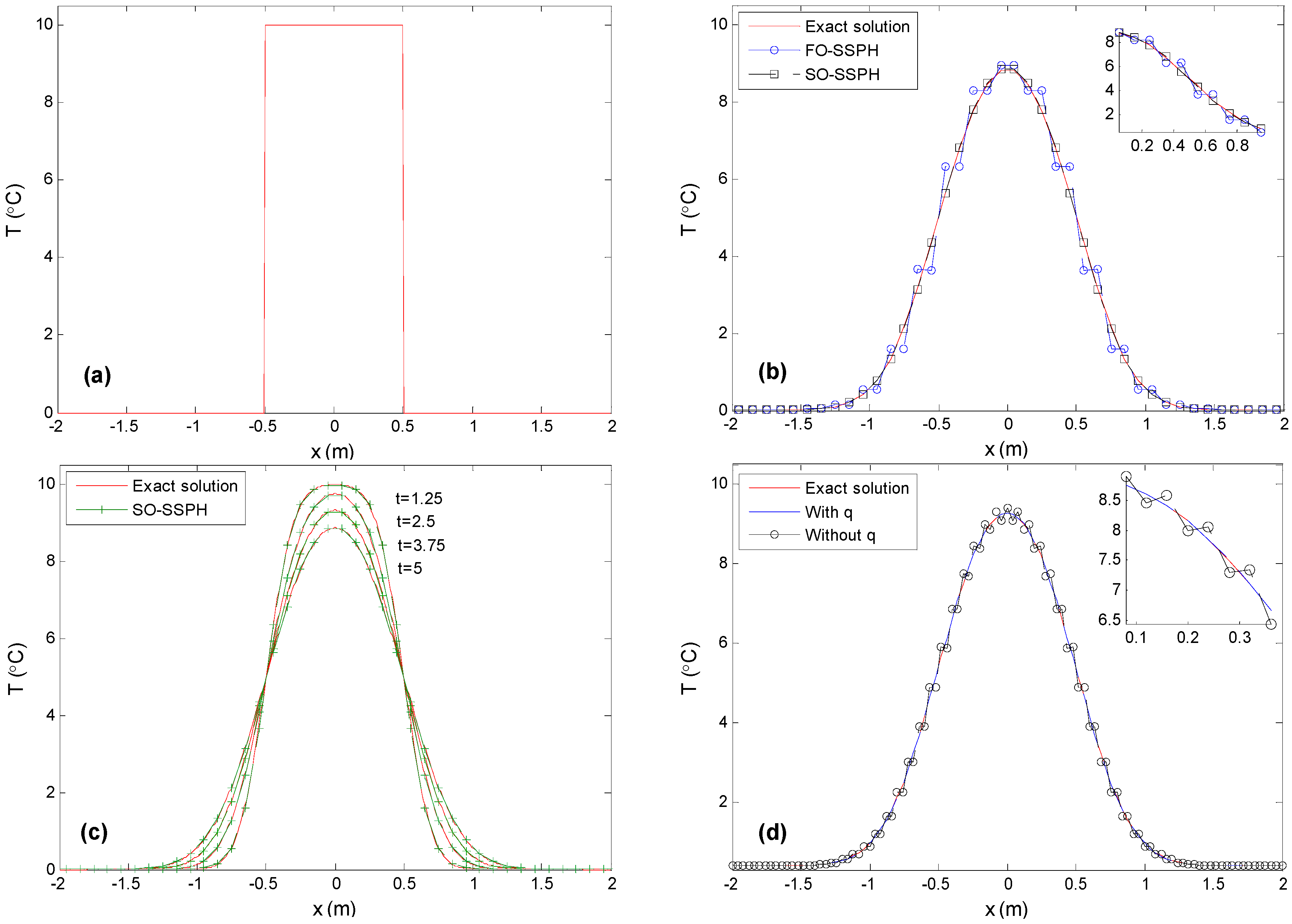
5.1. One-Dimensional Case
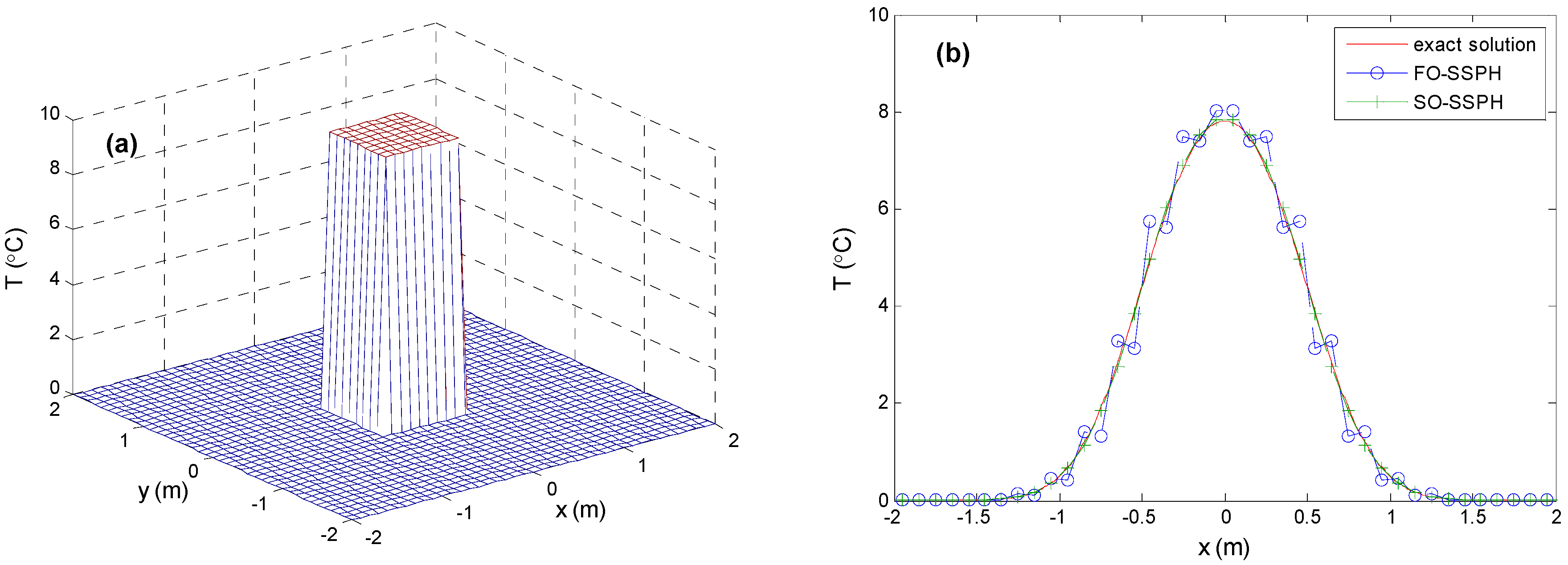
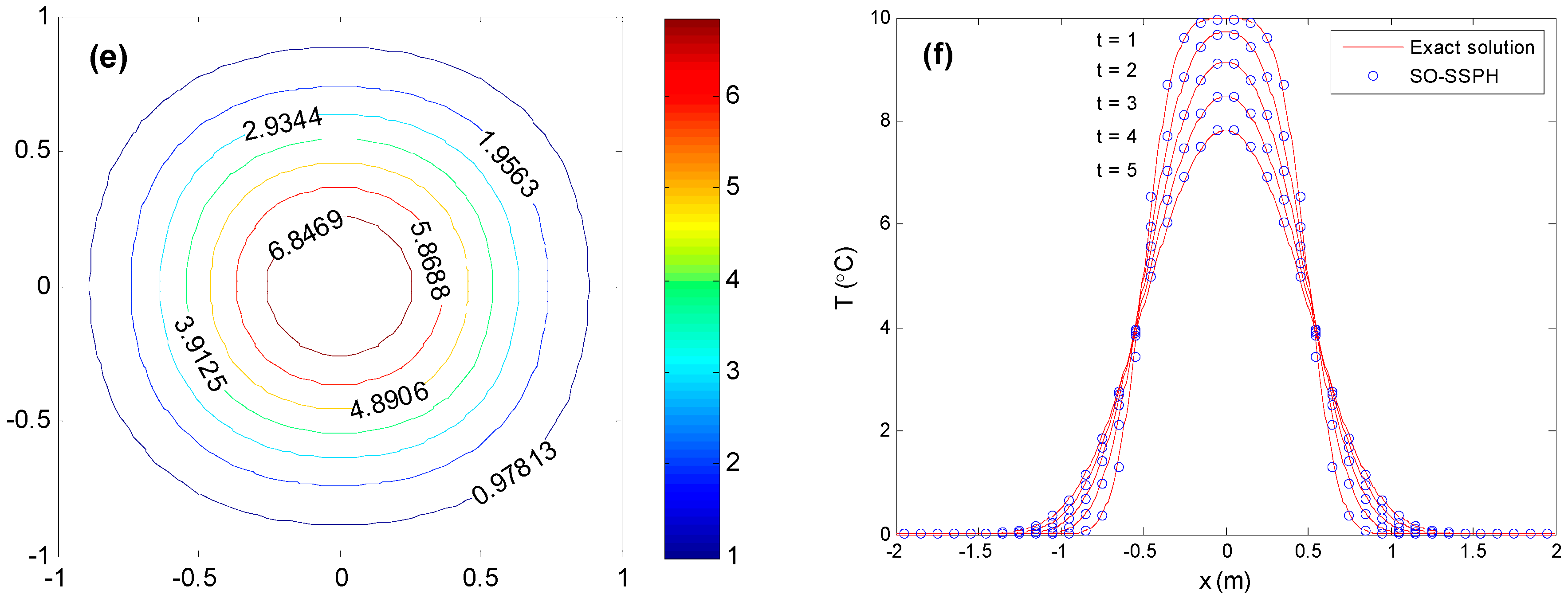
5.2. Two-Dimensional Case
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Abbreviations | |
| CSPM | corrective smoothed particle method |
| DNS | direct numerical simulation |
| EFG | element-free Galerkin |
| FDM | finite difference methods |
| FEM | finite element methods |
| FO-SSPH | first-order symmetric smoothed particle hydrodynamics |
| FTCS | forward time central space |
| FVM | finite volume methods |
| LBM | lattice Boltzmann method |
| MLSPH | moving least squares particle hydrodynamics |
| MSPH | modified smoothed particle hydrodynamics |
| NHT | Numerical Heat Transfer |
| SO-SSPH | second-order symmetric smoothed particle hydrodynamics |
| SPH | smoothed particle hydrodynamics |
| Symbols | |
| bT | heat source on the boundary |
| cp | material specific heat capacity |
| E | numerical error |
| erf | error function |
| G | amplification factor |
| G0 | source term |
| h | smoothing length |
| h | vector of particle distance |
| i | imaginary unit |
| kx | thermal conductivity coefficients in x direction |
| ky | thermal conductivity coefficients in y direction |
| n | unit normal vector on the boundary |
| q | heat flux |
| T | temperature |
| T0 | initial temperature distribution |
| T1 | boundary temperature |
| TE | truncation error |
| Te | exact temperature |
| Tn | numerical temperature |
| v | column vector of the wave number in the Fourier analysis method |
| W | kernel function |
| Wk | compactly supported function |
| αx | coefficients of ∂f/∂x |
| αy | coefficients of ∂f/∂y |
| βx | coefficients of ∂2f/∂x2 |
| βy | coefficients of ∂2f/∂y2 |
| Dirichlet boundary of the domain | |
| Neumann boundary of the domain | |
| Δt | time step |
| ΔVj | volume of j th particle |
| Δx | particle distance in x direction |
| Δy | particle distance in y direction |
| κx | kx/ρcp, m2/s |
| κy | ky/ρcp, m2/s |
| ρ | material density |
| Ω | computational domain |
| approximation operator | |
| kernel gradient |
References
- Tao, W.Q. Numerical Heat Transfer, 2nd ed.; Xi’an Jiaotong University Press: Xi’an, China, 2003; pp. 10–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.P.; Chen, C.L. Hybrid differential transform and finite difference method to solve the nonlinear heat conduction problem. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2008, 13, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.W.; Nithiarasu, P.; Seetharamu, K.N. Fundamentals of the Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chicheste, UK, 2004; pp. 38–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Rui, X. Nonlinear heat conduction equation solved with Lattice Boltzmann method. Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 27, 699–704. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.V.; Sandeep, K.; Prakash, R. Meshless EFG method in transient heat conduction problems. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2003, 21, 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.R.; Liu, M.B. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH): An overview and recent development. Arch. Comput. Meth. Eng. 2010, 17, 25–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.R.; Liu, M.B. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics: A Mesh-free Particle Method; World Scientific: Singapore, 2003; pp. 26–52. [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan, J.J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 30, 543–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1703–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its diverse applications. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2012, 44, 323–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.B.; Li, S.M. On the modeling of viscous incompressible flows with smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2016, 28, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.M.; Sun, P.N.; Ming, F.R.; Colagrossi, A. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications in fluid-structure interactions. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2017, 29, 187–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswog, S. Astrophysical smooth particle hydrodynamics. New Astron. Rev. 2009, 53, 78–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springel, V. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics in astrophysics. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 48, 391–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belytschko, T.; Krongauz, Y.; Dolbow, J.; Gerlach, C. On the completeness of meshfree methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1998, 43, 785–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.K.; Beraun, J.E.; Carney, T.C. A corrective smoothed particle method for boundary value problems in heat conduction. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1999, 46, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.M.; Batra, R.C. Modified smoothed particle hydrodynamics method and its application to transient problems. Comput. Mech. 2004, 34, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilts, G.A. Moving least squares particle hydrodynamics I. Consistency and stability. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2015, 44, 1115–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, L.B. A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron. J. 1977, 82, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Jhon, M.S.; Halow, J.S.; Van Osdol, J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: Applications to heat conduction. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2003, 153, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookshaw, L. A method of calculating radiative heat diffusion in particle simulation. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 1985, 6, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Miyama, S.; Sekiya, M. Numerical simulation of viscous flow by smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1994, 92, 939–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaniotis, A.K.; Poulikakos, D.; Koumoutsakos, P. Remeshed smoothed particle hydrodynamics for the simulation of viscous and heat conducting flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2002, 182, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, P.W. Modeling confined multi-material heat and mass flows using SPH. Appl. Math. Model. 1998, 22, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, P.W.; Monaghan, J.J. Conduction modeling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1999, 148, 227–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubelgas, M.; Springel, V.; Dolag, K. Thermal conduction in cosmological SPH simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 351, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, R.; Yildiz, M.; Dost, S. Modeling transient heat transfer using SPH and implicit time integration. Numer. Heat Transf. B 2007, 51, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Sousa, A.C.M. SPH numerical modeling for ballistic-diffusive heat conduction. Numer. Heat Transf. B 2006, 50, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Sousa, A.C.M. Effective thermal conductivity of heterogeneous multi-component materials: An SPH implementation. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 43, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, R.; Manzari, M.T. Error estimation in smoothed particle hydrodynamics and a new scheme for second derivatives. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 61, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francomano, E.; Paliaga, M. Highlighting numerical insights of an efficient SPH method. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 339, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Ouyang, J.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J.L. The first order symmetric SPH method for transient heat conduction problems. Acta Phys. Sin. 2010, 60, 090206. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, W.P.; Feng, G.L.; Dong, W.J.; Li, J.P. Comparison with solution of convection-diffusion by several difference schemes. Acta Phys. Sin. 2004, 53, 3258–3264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Prieto, F.U.; Muñoz, J.J.B.; Corvinos, L.G. Application of the generalized finite difference method to solve the advection-diffusion equation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2011, 235, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, J.J.; Ureña, F.; Gavete, L. Solving parabolic and hyperbolic equations by the generalized finite difference method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2007, 209, 208–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L. A Course in Computational Fluid Dynamics; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 32–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmin, D.; Möller, M. Algebraic Flux Correction I. Scalar Conservation Laws. In Flux-Corrected Transport; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 185–203. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, A.R.; Griffiths, D.F. The Finite Difference Method in Partial Differential Equations; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 76–78. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Δx (m) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.5 | |
| FO-SSPH | 0.0089 | 0.0178 | 0.0445 | 0.0898 | 0.2297 | 0.3381 |
| SO-SSPH | 0.0013 | 0.0051 | 0.0379 | 0.1303 | ||
| Method | Δx (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| FO-SSPH | 0.0024 | |||
| SO-SSPH | ||||
| Method | Δx = Δy (m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 | |
| FO-SSPH | 0.1548 | 0.1974 | 0.4263 | 0.6867 |
| SO-SSPH | 0.0098 | 0.0159 | 0.0773 | 0.2719 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Xing, Y.; Hou, Q.; Lu, W. Second-Order Symmetric Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method for Transient Heat Conduction Problems with Initial Discontinuity. Processes 2018, 6, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6110215
Song Z, Xing Y, Hou Q, Lu W. Second-Order Symmetric Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method for Transient Heat Conduction Problems with Initial Discontinuity. Processes. 2018; 6(11):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6110215
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhanjie, Yaxuan Xing, Qingzhi Hou, and Wenhuan Lu. 2018. "Second-Order Symmetric Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method for Transient Heat Conduction Problems with Initial Discontinuity" Processes 6, no. 11: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6110215
APA StyleSong, Z., Xing, Y., Hou, Q., & Lu, W. (2018). Second-Order Symmetric Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Method for Transient Heat Conduction Problems with Initial Discontinuity. Processes, 6(11), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6110215





