Extending Applications of High-Pressure Homogenization by Using Simultaneous Emulsification and Mixing (SEM)—An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Coalescence and agglomeration can occur at higher volume fractions of the disperse phase (e.g., in dairy homogenization) [10,15]. In general, coalescence is more likely to occur in high-pressure homogenizers compared to rotor-stator-systems because of the high energy input at extremely short residence times [16].
- Emulsifiers need to meet specific criteria such as fast adsorption kinetics in order to fulfill their purpose in high-pressure homogenizers [17]. Some of the emulsifiers typically used in the food industry (biopolymers or proteins), for example, are heat- or pressure sensitive [1,7] which complicates the production of emulsions at higher temperatures.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. High-Pressure Homogenization
2.2. Mixing
3. Developments in High-Pressure Homogenization
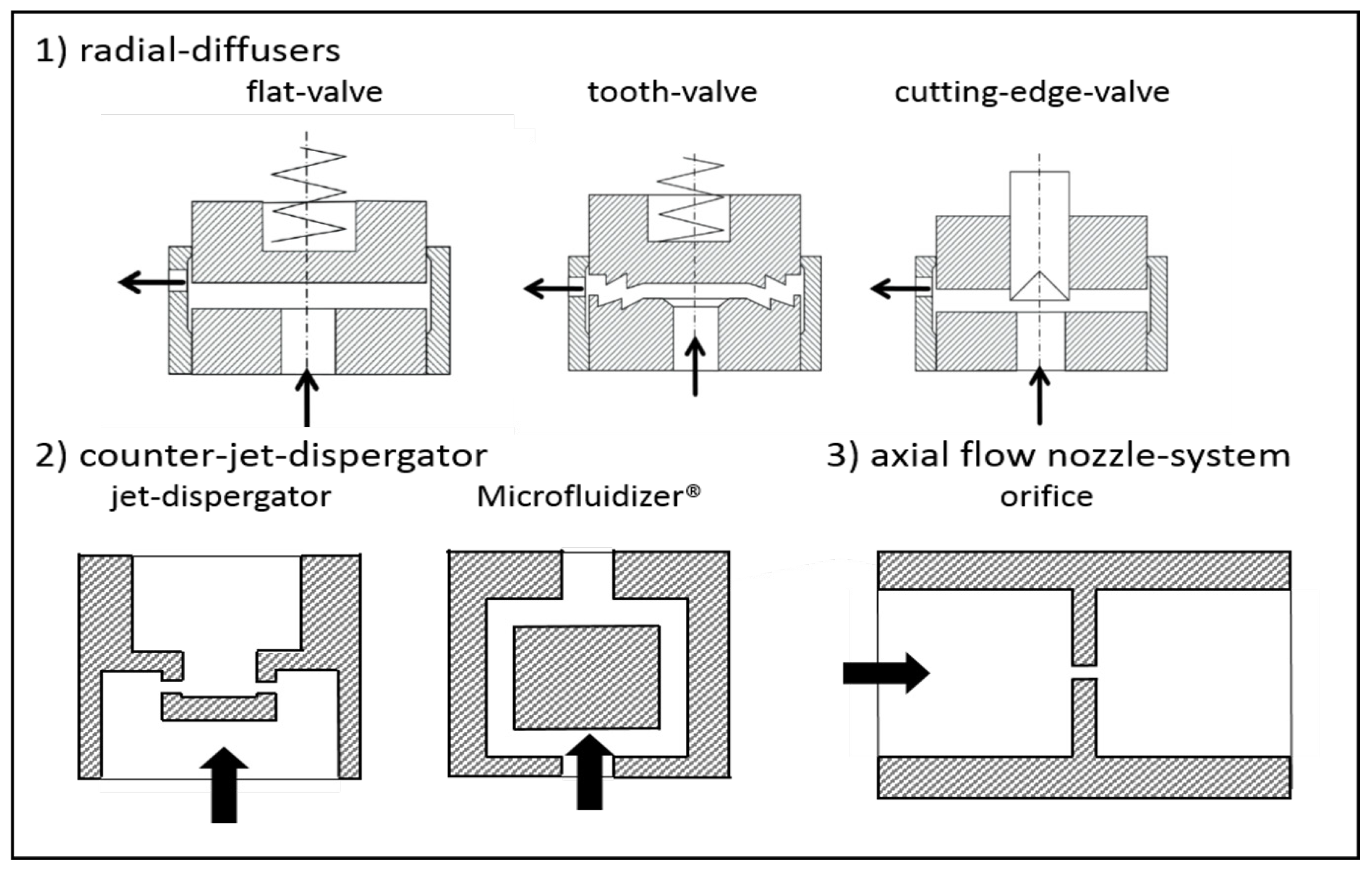
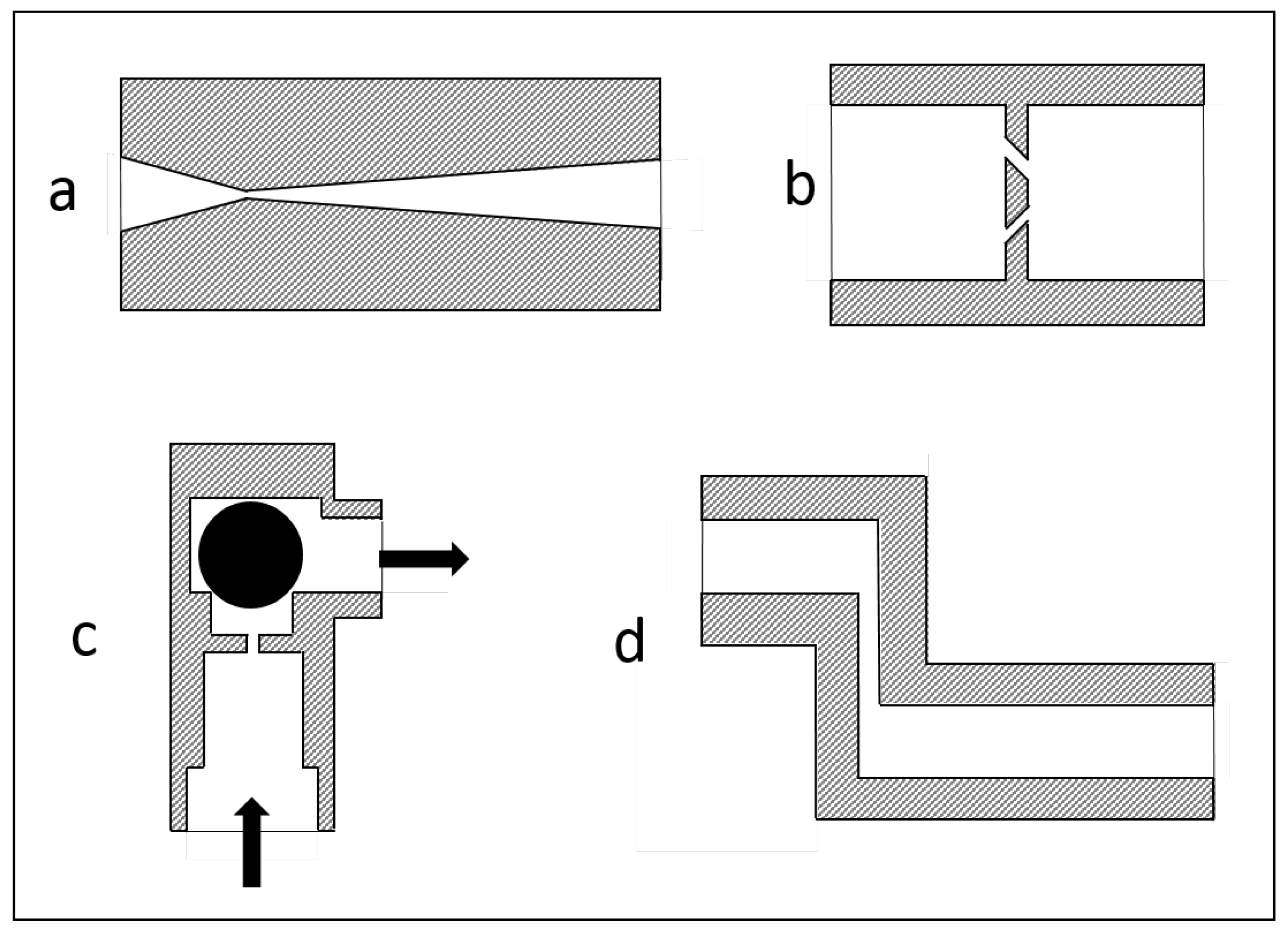
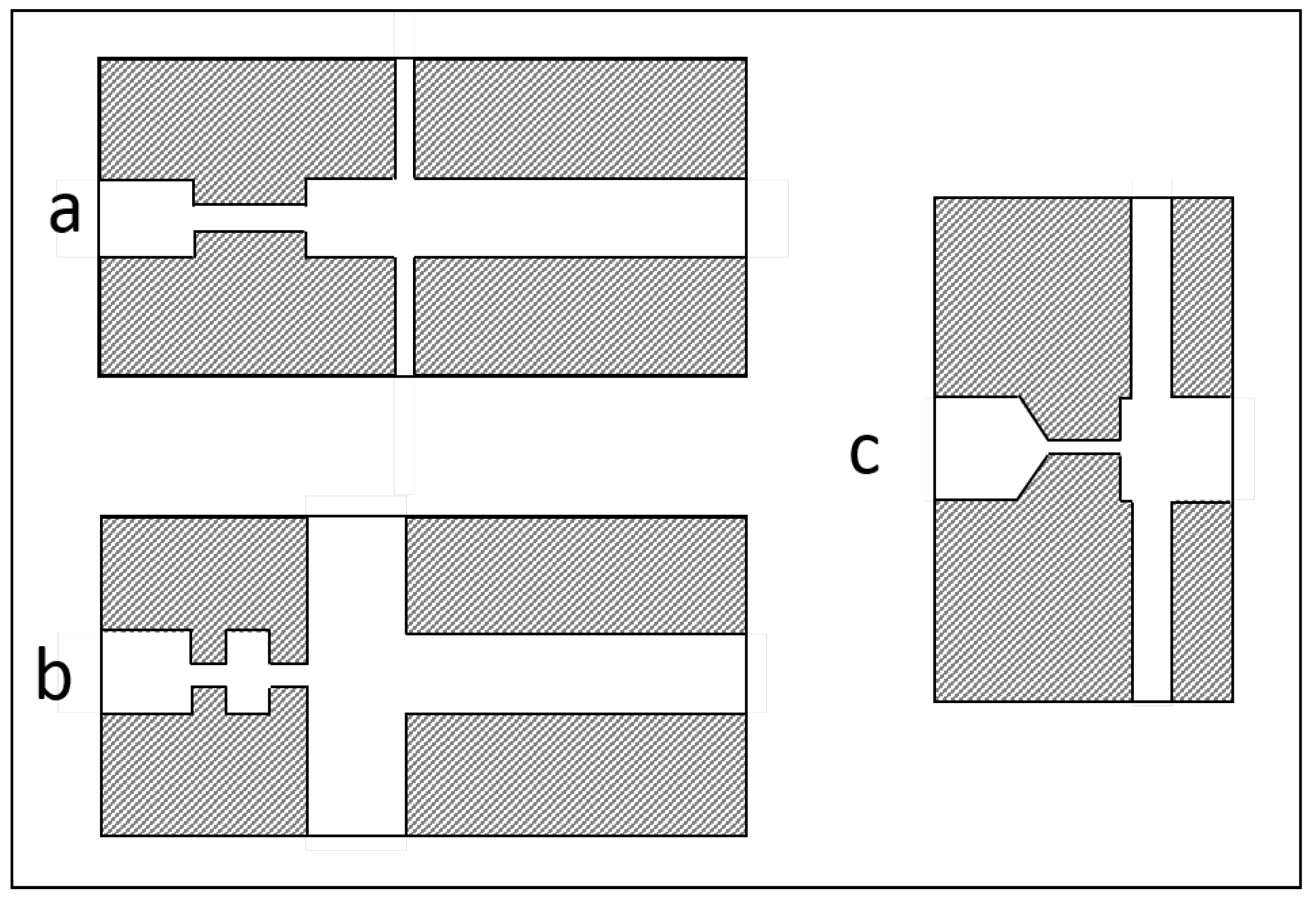
3.1. Geometrical Modifications of the Disruption Valve
3.2. Inserting a Second Homogenization Step
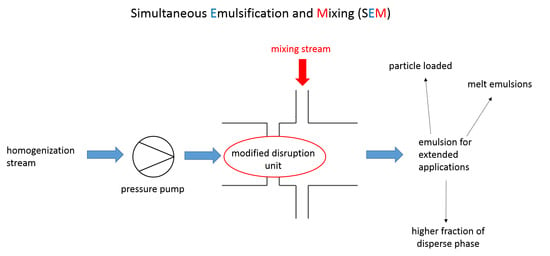
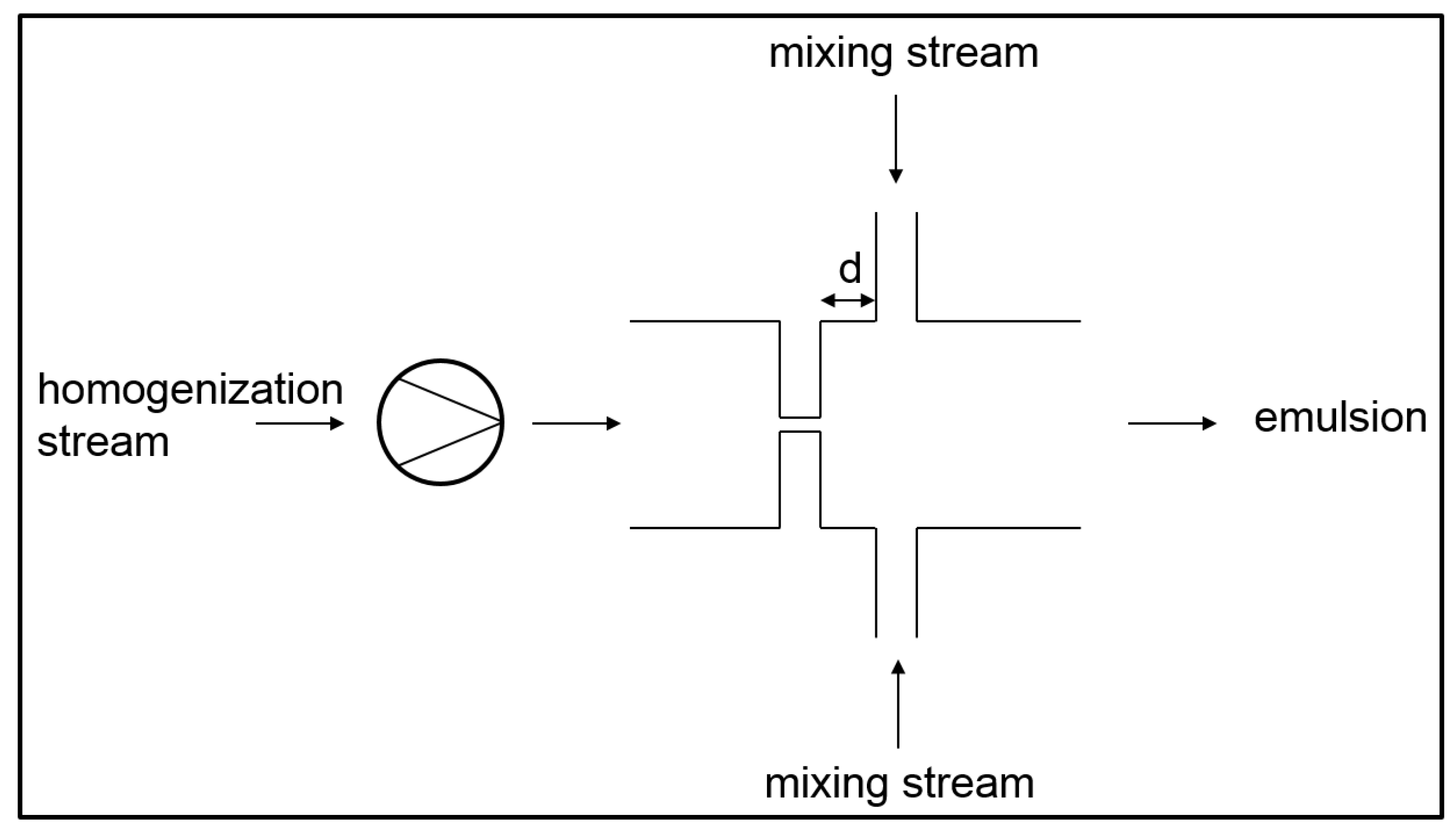
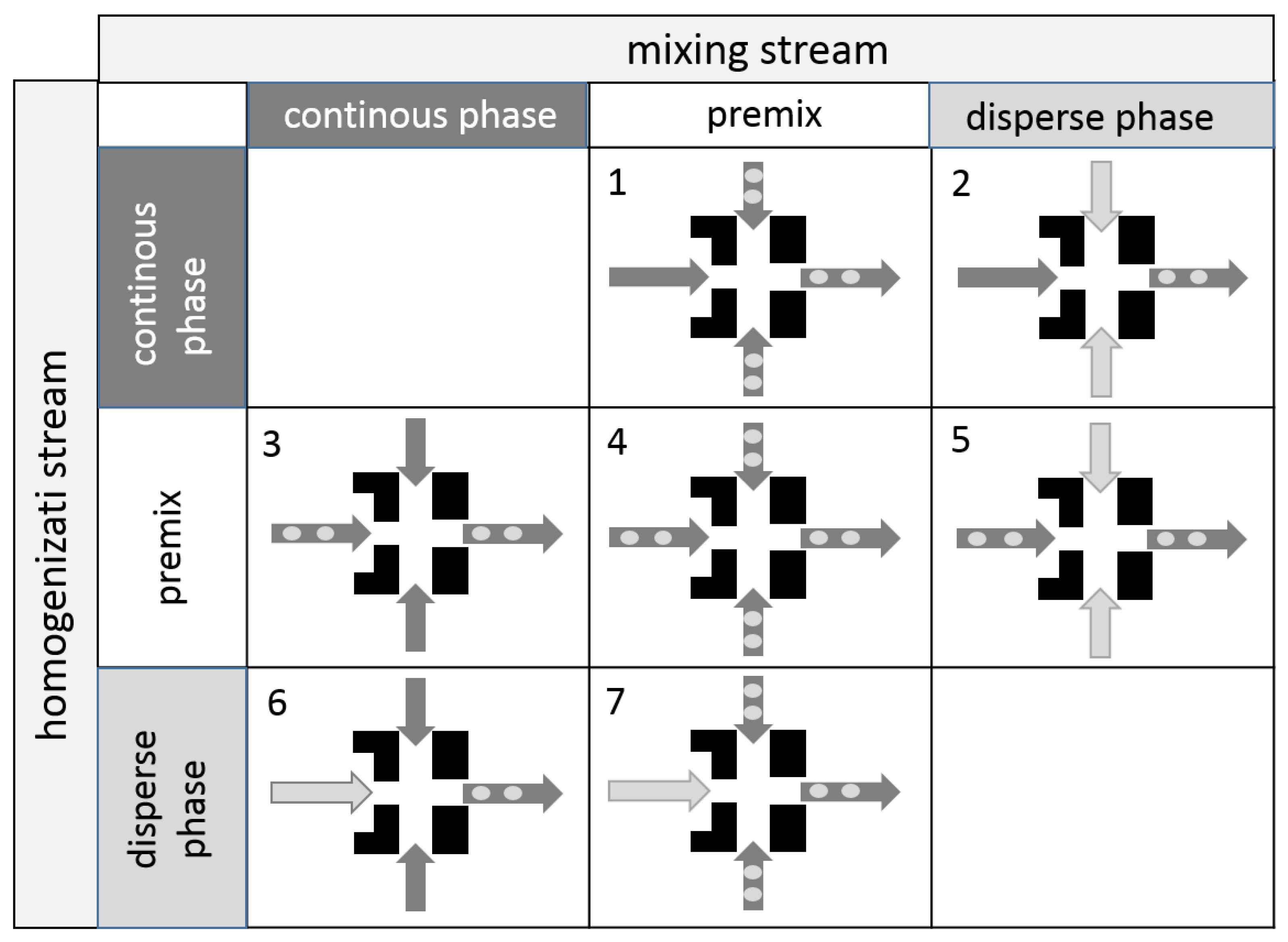
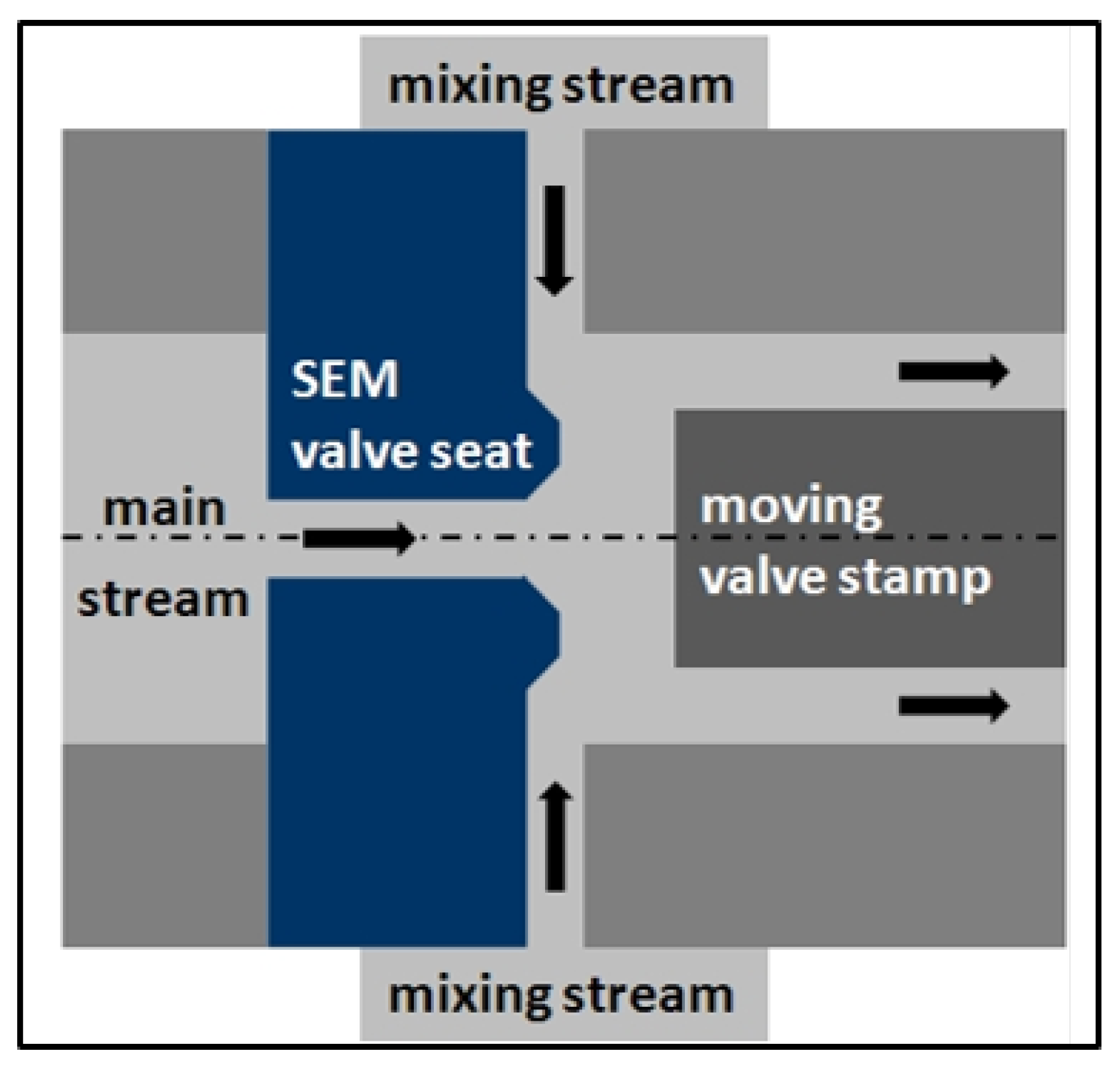
3.3. Simultaneous Emulsifying and Mixing
- In the operational modes 2 and 6, pure phases are mixed in the micromixer. Primary droplets are produced due to the turbulent current after the orifice. These operational modes can also be referred to as simultaneous primary emulsification and mixing (SpEM).
- In the operational modes 1, 3, and 4, the already existing droplets of the premixes are disrupted into smaller droplets. These operational modes can also be referred to as simultaneous homogenization and mixing (SHM).
- In the operational modes 5 and 7, primary and secondary droplet breakup occurs since both pure disperse phase and emulsion premix are inserted into the homogenizer.
4. Applications of SEM Homogenization
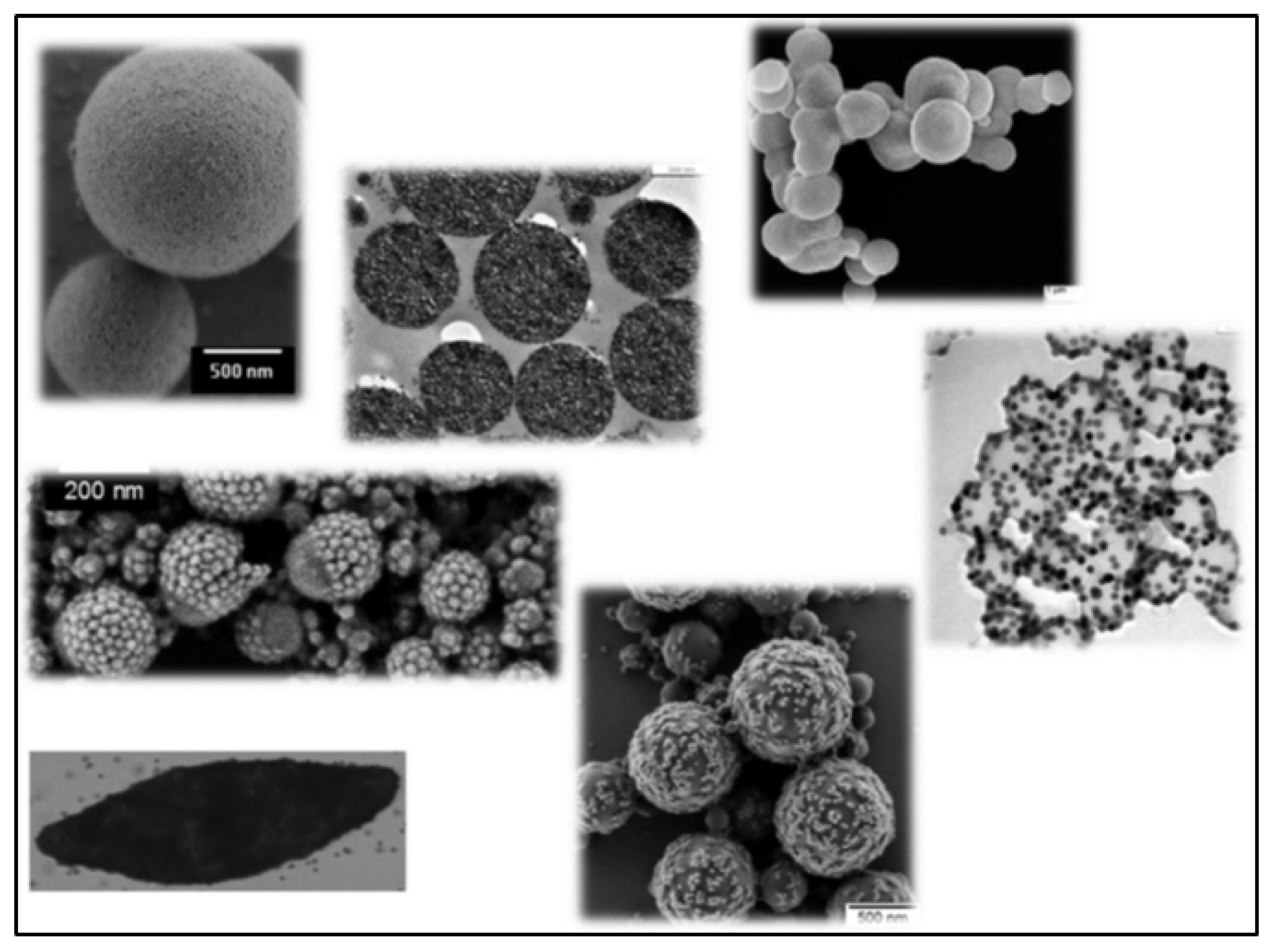
4.1. Preparation of Hybrid Nanoparticles
4.2. Particle Stabilized Emulsions
4.3. Dairy Homogenization
4.4. Melt Emulsification
4.5. SEM Process for Research Purposes
4.6. Economical Interest
5. Summary and Outlook
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santana, R.; Perrechil, F.; Cunha, R. High- and low-energy emulsifications for food applications: A focus on process parameters. Food Eng. Rev. 2013, 5, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, S.; Wagner, G.; Urban, K.; Ulrich, J. High-pressure homogenization as a process for emulsion formation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2004, 27, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Tesch, S.; Freudig, B. Emulgieren in Hochdruckhomogenisatoren. In Emulgiertechnik; Köhler, K., Schuchmann, H.P., Eds.; Behrs Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, K.; Aguilar, F.A.; Hensel, A.; Schubert, K.; Schubert, H.; Schuchmann, H.P. Design of a Microstructured System for Homogenization of Dairy Products with High Fat Content. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2007, 30, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, G.; Wagner, G.; Viardot, K.; Ulrich, J. Zur Herstellung von Feinemulsionen mittels Hochdruckdispergiereinheiten. Chem. Ing. Technik 2001, 73, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floury, J.; Legrand, J.; Desrumaux, A. Analysis of a new type of high pressure homogeniser. Part B. Study of droplet break-up and recoalescence phenomena. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Hensel, A.; Kraut, M.; Schuchmann, H.P. Melt emulsification—Is there a chance to produce particles without additives? Particuology 2011, 9, 506–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stang, M.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Schubert, H. Emulsification in High-Pressure Homogenizers. Eng. Life Sci. 2001, 4, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiebaud, M.; Dumay, E.; Picart, L.; Guiraud, J.P.; Cheftel, J.C. High-pressure homogenisation of raw bovine milk. Effects on fat globule size distribution and microbial inactivation. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Karasch, S.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Kulozik, U. Energiesparende Homogenisierung von Milch mit etablierten sowie neuartigen Verfahren. Chem. Ing. Technik 2008, 80, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchmann, H.P. Advances in Hydrodynamic Pressure Processing for Enhancing Emulsification and Dispersion. In Innovative Food Processing Technologies: Extraction, Separation, Component Modification and Process Intensification; Knoerzer, K., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; Number 302; pp. 387–412. [Google Scholar]
- Hecht, L.L.; Schlender, M.; Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Abrasion in high-pressure homogenization orifices: A new method to quantify the impact of particle loaded fluids. Wear 2012, 289, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, C.; Schuchmann, H.P. Materialschonendes Hochdruckdispergieren mit dem High Pressure Post Feeding (HPPF)-System. Chem. Ing. Technik 2008, 80, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, C.; Schuchmann, H.P. High pressure for dispersing and deagglomerating nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2007, 30, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudig, B. Herstellen von Emulsionen und Homogenisieren von Milch in modifizierten Lochblenden; Universität Karlsruhe (TH): Karlsruhe, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schuchmann, H.P.; Danner, T. Emulgieren: Mehr als nur Zerkleinern. Chem. Ing. Technik 2004, 76, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Schlender, M.; Schuchmann, H.P. Hochdruckemulgieren—Neue Prozesse und Produkte. Process 2011, 7/8, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, K. Simultanes Emulgieren und Mischen; Logos Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Simultanes Emulgieren und Mischen. Chem. Ing. Technik 2012, 84, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulin, A. Appareil et Procédé pour la Stabilisation du Lait. Patent Brecet 295596, 23 May 1899. [Google Scholar]
- Schuchmann, H.P. Tropfenaufbruch und Energiedichtekonzept beim mechanischen Emulgieren. In Emulgiertechnik; Köhler, K., Schuchmann, H.P., Eds.; Behrs Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schuchmann, H.P.; Karbstein, N.; Hecht, L.L.; Gedrat, M.; Köhler, K. High-Pressure Homogenization for the Production of Emulsions. In Industrial High Pressure Applications, Processes, Equipment and Safety; Eggers, R., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag: Weinheim, Germany, 2012; pp. 97–118. [Google Scholar]
- Karbstein, H. Untersuchungen zum Herstellen und Stabilisieren von Öl-in-Wasser-Emulsionen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Karlsruhe, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Klinksiek, B.; Koglin, B. Herstellung von Pharmazeutischen oder Kosmetischen Dispersionen. Patent EP0101007 B1, 11 May 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.J.; Lagace, A.P. Apparatus for Forming Emulsions. U.S. Patent 4,533,254, 6 August 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Stang, M. Zerkleinern und Stabilisieren von Tropfen Beim Mechanischen Emulgieren; Universität Karlsruhe (TH): Karlsruhe, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Tesch, S. Charakterisieren Mechanischer Emulgierverfahren: Herstellen und Stabilisieren von Tropfen als Teilschritte beim Formulieren von Emulsionen; Universität Karlsruhe (TH): Karlsruhe, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar, F.A.; Köhler, K.; Schubert, H.; Schuchmann, H.P. Herstellen von Emulsionen in einfachen und modifizierten Lochblenden: Einfluss der Geometrie auf die Effizienz der Zerkleinerung und Folgen für die Maßstabsvergrößerung. Chem. Ing. Technik 2008, 80, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, K.; Schuch, A.; Schuchmann, H.P. Influence of flow conditions in high pressure orifices on droplet disruption of O/W emulsions. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2014, 37, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, K.; Crowther, F.E.; Cierpka, C.; Hecht, L.L.; Kähler, C.J.; Schuchmann, H.P. Investigations on the characterization of laminar and transitional flow conditions after high pressure homogenization orifices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 18, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelemen, K.; Gepperth, S.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.-J.; Schuchmann, H.P. On the visualization of droplet deformation and breakup during high-pressure homogenization. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2015, 19, 1139–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, M. Mischtechnik, Aufgaben und Bedeutung. In Mischen und Rühren: Grundlagen und Moderne Verfahren; Kraume, M., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kraume, M.; Merz, C.; Henzler, H.-J. Continuous Mixing of Fluids. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kraume, M. (Ed.) Mischen und Rühren. Grundlagen und Moderne Verfahren; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005.
- Pravinata, L.; Akhtar, M.; Bentley, P.J.; Mahatnirunkul, T.; Murray, B.S. Preparation of alginate microgels in a simple one step process via the Leeds Jet Homogenizer. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgaud, I.; Dickinson, E.; Nelson, P.V. An Improved High-Pressure Homogenizer for Making Fine Emulsions on a Small-Scale. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1990, 25, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladisavljevic, G. Emulgieren mit mikrostrukturierten Systemen. In Emulgiertechnik; Köhler, K., Schuchmann, H.P., Eds.; Behrs Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2012; pp. 253–290. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, L.; McClements, D. Extending Emulsion Functionality: Post-Homogenization Modification of Droplet Properties. Processes 2016, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floury, J.; Bellettre, J.; Legrand, J.; Desrumaux, A. Analysis of a new type of high pressure homogeniser: A study of the flow pattern. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, F.A.; Freudig, B.; Schuchmann, H.P. Herstellen von Emulsionen in Hochdruckhomogenisatoren mit modifizierten Lochblenden. Chem. Ing. Technik 2004, 76, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschiolik, G.; Roeder, R.-T.; Lengfeld, K. Druckhomogenisator. Patent DE19530247 A1, 20 February 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Forschungskreis der Ernährungsindustrie e. V. Energiesparende und Schonende Homogenisierung von Milch und Auswirkungen auf die Textur von Milchprodukten; AiF FV 14073 N; FEI: Bonn, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Forschungskreis der Ernährungsindustrie e. V. Entwicklung einer Verbesserten Düse zum Hochdruckhomogenisieren und -Emulgieren; AiF FV 12405 N; FEI: Bonn, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann, M.; Schuler, T.; Uzunogullari, P.; Winkler, C.A.; Gerlinger, W.; Sachweh, B.; Schuchmann, H.P. Influence of mixing on the precipitation of zinc oxide nanoparticles with the miniemulsion technique. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 81, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudig, B.; Tesch, S.; Schubert, H. Herstellen von Emulsionen in Hochdruckhomogenisatoren—Teil 2: Bedeutung der Kavitation für die Tropfenzerkleinerung. Chem. Ing. Technik 2002, 74, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlender, M.; Minke, K.; Spiegel, B.; Schuchmann, H.P. High-pressure double stage homogenization processes: Influences of plant setup on oil droplet size. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 131, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzhals, H.A.; Reuter, H. Untersuchungen über die physikalisch-technischen Vorgänge beim Homogenisieren von Milch in Hochdruck-Homogenisiermaschinen. Chem. Ing. Technik 1979, 51, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, S. The theory of high-pressure homogenization. In Emulsions and Nanosuspensions for the Formulation of Poorly Soluble Drugs; Benita, S., Bohm, B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Freudig, B.; Tesch, S.; Schubert, H. Production of emulsions in high-pressure homogenizers—Part II: Influence of Cavitation on Droplet Breakup. Eng. Life Sci. 2003, 6, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, J.H.; Niemann, S.; Richter, C.; Gothsch, T.; Kwade, A.; Büttgenbach, S.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Multiple orifices in customized microsystem high-pressure emulsification: The impact of design and counter pressure on homogenization efficiency. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, H.G. Food and Bio Process Engineering: Dairy Technology; 109 Tables, 5th ed.; A. Kessler: München, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, G.E. Zur Emulsionsherstellung in Blendensystemen; Universität Bremen: Bremen, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Karasch, S.; Kulozik, U. Hochdruckhomogenisierung von Milch mit modifizierten Lochblenden im Vergleich zu konventionellen Flachventilen. Chem. Ing. Technik 2008, 80, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempa, L.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Schubert, H. Drip-reducing and drip coalescence in mechanical emulsifying with high pressure homogenisers. Chem. Ing. Technik 2006, 78, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, L.L.; Merkel, T.; Schoth, A.; Köhler, K.; Wagner, C.; Muñoz-Espí, R.; Landfester, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Emulsification of particle loaded droplets with regard to miniemulsion polymerization. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Aguilar, F.A.; Hensel, A.; Schubert, H.; Schuchmann, H.P. Design of a Micro-Structured System for the Homogenization of Dairy Producs at High Fat Content—Part III: Influence of Geometric Parameters. Chem. Eng. Techol. 2009, 32, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Aguilar, F.A.; Hensel, A.; Schubert, K.; Schubert, H.; Schuchmann, H.P. Design of a Microstructured System for the Homogenization of Dairy Products at High Fat Content Part II: Influence of Process Parameters. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2008, 31, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, K.; Santana, A.S.; Braisch, B.; Preis, R.; Schuchmann, H.P. High pressure emulsification with nano-particles as stabilizing agents. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlender, M.; Schuchmann, H.P. Fortschritte bei der Milchhomogenisation. Food Lab 2014, 2014, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Tiarks, F.; Landfester, K.; Anonietti, M. Encapsulation of carbon black by miniemulsion polymerization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiert, N.; Landfester, K. Encapsulation of organic pigment particles via miniemulsion polymerization. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu, S.; Novat, C.; Graillat, C.; Guyot, A.; Bourgeat-Lami, E. Encapsulation of an organic phthalocyanine blue pigment into polystyrene latex particles using a miniemulsion polymerization. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitzi, D.B. Thin-Film Deposition of Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3283–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossmeyer, T.; Guse, B.; Besnard, I.; Bauer, R.E.; Mullen, K.; Yasuda, A. Gold nanoparticle/polyphenylene dendrimer composite films: Preparation and vapor-sensing properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Yang, D.; Hu, J.H.; Yang, W.L.; Wang, C.C.; Lu, J.Q. Preparation of monodispersed hybrid nanospheres with high magnetite content from uniform Fe3O4 clusters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 339, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Rudzinski, W.E. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashita, M.; Tanaka, M.; Kokubo, T.; Inoue, Y.; Yao, T.; Hamada, S.; Shinjo, T. Preparation of ferrimagnetic magnetite microspheres for in situ hyperthermic treatment of cancer. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechthold, N.; Tiarks, F.; Willert, M.; Landfester, K.; Antonietti, M. Miniemulsion polymerization: Applications and new materials. Macromol. Symp. 2000, 151, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Zhou, S.X.; Weng, Y.M.; Wu, L.M. Synthesis of SiO2/polystyrene nanocomposite particles via miniemulsion polymerization. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenmark, L.; Polpanich, D.; Thiramanas, R.; Tangboriboonrat, P. Preparation of superparamagnetic polystyrene-based nanoparticles functionalized by acrylic acid. Macromol. Res. 2012, 20, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeat-Lami, E.; Farzi, G.A.; David, L.; Putaux, J.L.; Mckenna, T.F.L. Silica Encapsulation by Miniemulsion Polymerization: Distribution and Localization of the Silica Particles in Droplets and Latex Particles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6021–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconu, G.; Paulis, M.; Leiza, J.R. High solids content waterborne acrylic/montmorillonite nanocomposites by miniemulsion polymerization. Macromol. React. Eng. 2008, 2, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.D.; Dai, C.A.; Chiu, W.Y. Nucleation Mechanism and Morphology of Polystyrene/Fe3O4 Latex Particles via Miniemulsion Polymerization Using AIBN as Initiator. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, S.U. Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, W. Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and ‘suspensions’ (observations on surface-membranes, bubbles, emulsions, and mechanical coagulation). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (1854–1905) 1903, 72, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveyard, R.; Binks, B.P.; Clint, J.H. Emulsions stabilised solely by colloidal particles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100, 503–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braisch, B.; Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Wolf, B. Preparation and Flow Bahaviour of Oil-In-Water Emulsions Stabilised by Hydrophilic Silica Particles. Chem. Eng. Techol. 2009, 32, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P.; Geurts, T.J.; Noomen, A.; Jellema, A.; van Boekel, A.J.S. Dairy Technology: Principles of Milk Properties and Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Schlender, M.; Köhler, K.; Schuchmann, H.P. Neue Technologie ermöglicht Energieeinsparungen beim Hochdruckhomogenisieren. Rundsch. Fleischhygiene Lebensmittelüberwachung 2014, 66, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Abramov, S.; Ruppik, P.; Schuchmann, H. Crystallization in Emulsions: A Thermo-Optical Method to Determine Single Crystallization Events in Droplet Clusters. Processes 2016, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchmann, H.P.; Köhler, K. Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Dispersion und Vorrichtung Hierzu. Patent DE102009009060 B3, 12 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Runde, M. Oral correspondence: Mixolutions engineering, Frankfurt. 2016. [Google Scholar]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gall, V.; Runde, M.; Schuchmann, H.P. Extending Applications of High-Pressure Homogenization by Using Simultaneous Emulsification and Mixing (SEM)—An Overview. Processes 2016, 4, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040046
Gall V, Runde M, Schuchmann HP. Extending Applications of High-Pressure Homogenization by Using Simultaneous Emulsification and Mixing (SEM)—An Overview. Processes. 2016; 4(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleGall, Vanessa, Marc Runde, and Heike P. Schuchmann. 2016. "Extending Applications of High-Pressure Homogenization by Using Simultaneous Emulsification and Mixing (SEM)—An Overview" Processes 4, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040046
APA StyleGall, V., Runde, M., & Schuchmann, H. P. (2016). Extending Applications of High-Pressure Homogenization by Using Simultaneous Emulsification and Mixing (SEM)—An Overview. Processes, 4(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr4040046