Decomposition Behavior of Bisphenol A Under Subcritical Water Conditions: A Response Surface Methodology Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Hydrothermal Decomposition Procedure and Product Recovery
2.3. Analytical Methods
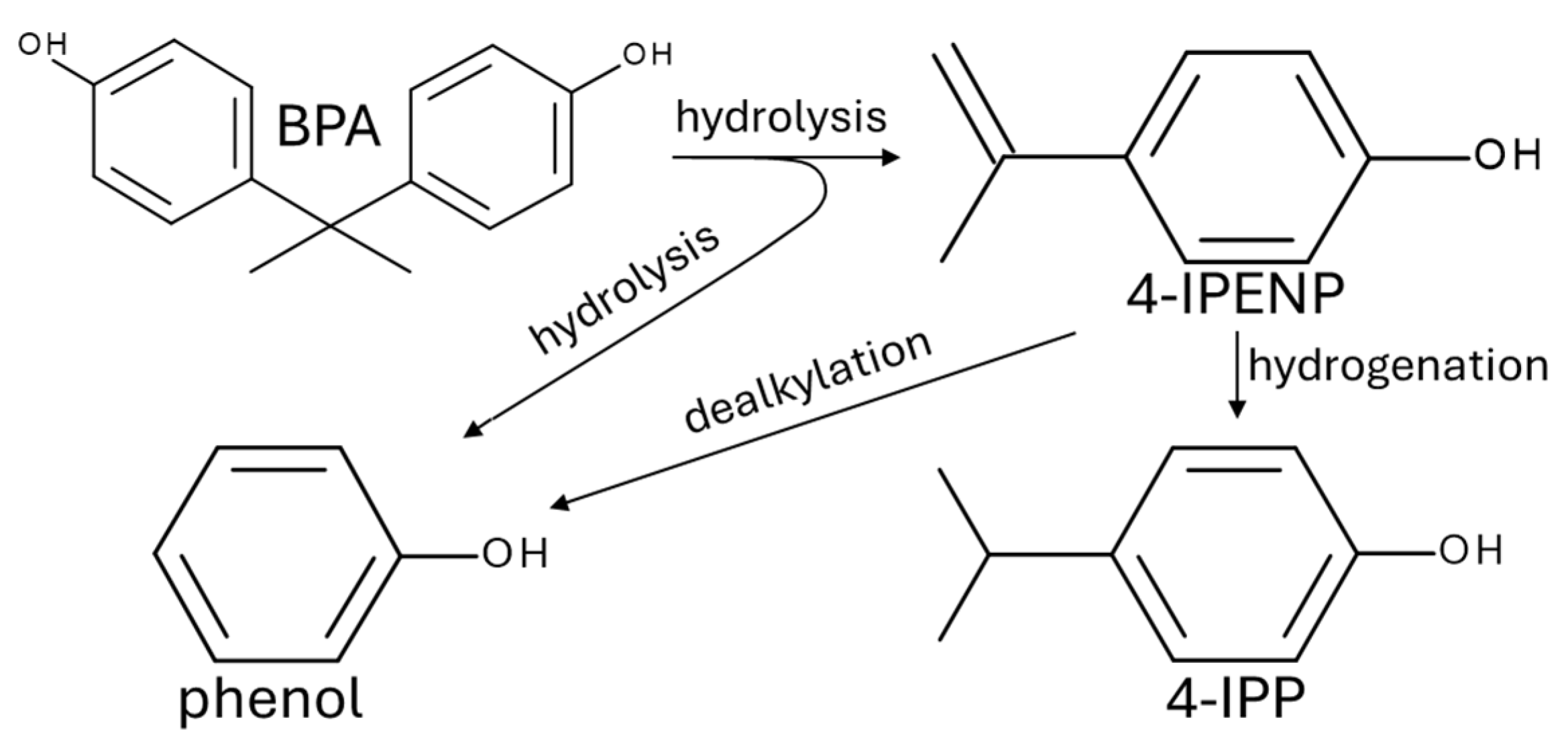
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Product Recovery
3.2. DEE-Phase Composition
3.3. Total Carbon Content in Water-Soluable Phase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PC | Polycarbonate |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| 4-IPENP | 4-Isopropenylphenol |
| 4-IPP | 4-Isopropylphenol |
| TC | Total carbon |
| DEE | Diethyl ether |
| RSM | Response Surface Method |
Appendix A
| Experiment # | T (°C) | t (min) | Water-to-Material Ratio (mL/g) | γ(DEE) (%) | γ(aq) (%) | TC (g/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | ||||
| 1 | 250 | 5 | 10 | 95.2 | 94.8 | 2.0 | 1.9 | 2.91 | 2.46 |
| 2 | 250 | 17.5 | 5 | 93.3 | 94.1 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.75 | 3.06 |
| 3 | 250 | 17.5 | 15 | 94.6 | 94.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 3.42 | 3.64 |
| 4 | 250 | 30 | 10 | 93.4 | 93.4 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 4.32 | 4.25 |
| 5 | 300 | 5 | 5 | 94.5 | 94.9 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 3.00 | 2.68 |
| 6 | 300 | 5 | 15 | 95.0 | 94.9 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 3.03 | 3.25 |
| 7 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 92.2 | 92.8 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 3.24 | 3.86 |
| 8 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 92.4 | 92.8 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 4.40 | 3.86 |
| 9 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 93.0 | 92.8 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.50 | 3.86 |
| 10 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 92.7 | 92.8 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 3.41 | 3.86 |
| 11 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 93.6 | 92.8 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 4.67 | 3.86 |
| 12 | 300 | 30 | 15 | 92.1 | 90.8 | 3.2 | 3.3 | 5.16 | 5.04 |
| 13 | 300 | 30 | 5 | 90.0 | 90.8 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 4.32 | 4.47 |
| 14 | 350 | 5 | 10 | 92.5 | 92.0 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 5.05 | 5.39 |
| 15 | 350 | 17.5 | 15 | 88.7 | 88.7 | 5.0 | 4.8 | 6.74 | 6.57 |
| 16 | 350 | 17.5 | 5 | 88.0 | 88.7 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 5.98 | 6.00 |
| 17 | 350 | 30 | 10 | 85.4 | 85.3 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 7.36 | 7.18 |
| Experiment # | T (°C) | t (min) | Water-to-Material Ratio (mL/g) | γ(BPA) (%) | γ(4-IPENP) (%) | γ(4-IPP) (%) | γ(phenol) (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | ||||
| 1 | 250 | 5 | 10 | 79.8 | 77.4 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 5.0 | 2.6 |
| 2 | 250 | 17.5 | 5 | 47.1 | 51.5 | 6.8 | 6.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 6.1 | 7.2 |
| 3 | 250 | 17.5 | 15 | 51.2 | 51.5 | 11.3 | 10.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 8.3 | 6.4 |
| 4 | 250 | 30 | 10 | 39.1 | 36.9 | 8.2 | 9.7 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 7.2 | 10.3 |
| 5 | 300 | 5 | 5 | 31.2 | 32.1 | 15.1 | 14.8 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 13.3 | 14.3 |
| 6 | 300 | 5 | 15 | 33.3 | 32.1 | 17.0 | 18.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 12.3 | 13.5 |
| 7 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 14.2 | 15.2 | 21.0 | 21.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 21.3 | 24.0 |
| 8 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 16.5 | 15.2 | 22.7 | 21.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 25.0 | 24.0 |
| 9 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 15.5 | 15.2 | 20.6 | 21.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 26.4 | 24.0 |
| 10 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 15.5 | 15.2 | 22.0 | 21.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 24.6 | 24.0 |
| 11 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 | 12.7 | 15.2 | 20.9 | 21.4 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 22.8 | 24.0 |
| 12 | 300 | 30 | 15 | 11.3 | 9.9 | 18.4 | 17.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 21.3 | 21.2 |
| 13 | 300 | 30 | 5 | 9.5 | 9.9 | 14.0 | 13.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 24.2 | 22.1 |
| 14 | 350 | 5 | 10 | 6.0 | 8.8 | 24.1 | 22.6 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 26.2 | 26.4 |
| 15 | 350 | 17.5 | 15 | 4.0 | 1.1 | 21.6 | 21.9 | 1.4 | 1.3 | 29.4 | 30.2 |
| 16 | 350 | 17.5 | 5 | 4.1 | 1.1 | 16.5 | 17.9 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 31.0 | 31.0 |
| 17 | 350 | 30 | 10 | 2.5 | 4.9 | 15.8 | 15.7 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 35.0 | 34.1 |
| T (°C) | k (mol∙L−1∙min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 250 | 0.0326 | 0.9872 |
| 275 | 0.0484 | 0.9241 |
| 300 | 0.0695 | 0.8686 |
| 325 | 0.1216 | 0.8767 |
| 350 | 0.2159 | 0.9097 |
| Ea (kJ/mol) | 50.6 | 0.9761 |
| ln(A) (min−1) | 8.1 |
References
- Nayanathara Thathsarani Pilapitiya, P.G.C.; Ratnayake, A.S. The World of Plastic Waste: A Review. Clean. Mater. 2024, 11, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi Kalali, E.; Lotfian, S.; Entezar Shabestari, M.; Khayatzadeh, S.; Zhao, C.; Yazdani Nezhad, H. A Critical Review of the Current Progress of Plastic Waste Recycling Technology in Structural Materials. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 40, 100763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiounn, T.; Smith, R.C. Advances and Approaches for Chemical Recycling of Plastic Waste. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 58, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Grand, D.G.; Bendler, J.T. (Eds.) Handbook of Polycarbonate Science and Technology; Plastics Engineering; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA; Basel, Switzerland, 2000; ISBN 978-0-8247-9915-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhan, L.; Xie, B.; Gao, B. Products Derived from Waste Plastics (PC, HIPS, ABS, PP and PA6) via Hydrothermal Treatment: Characterization and Potential Applications. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 742–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, K. 5.16—Polycarbonates. In Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference; Matyjaszewski, K., Möller, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 363–376. ISBN 978-0-08-087862-1. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, C.M. Bisphenol A: Understanding the Controversy. Workplace Health Saf. 2016, 64, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengstler, J.G.; Foth, H.; Gebel, T.; Kramer, P.-J.; Lilienblum, W.; Schweinfurth, H.; Völkel, W.; Wollin, K.-M.; Gundert-Remy, U. Critical Evaluation of Key Evidence on the Human Health Hazards of Exposure to Bisphenol A. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2011, 41, 263–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, A.; Katoh, K.; Tagaya, H. Monomer Recovery of Waste Plastics by Liquid Phase Decomposition and Polymer Synthesis. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmer Pedersen, T.; Conti, F. Improving the Circular Economy via Hydrothermal Processing of High-Density Waste Plastics. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.A.; Shaver, M.P. Depolymerization within a Circular Plastics System. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 2617–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakou, E.V.; Achilias, D.S. Recent Advances in Polycarbonate Recycling: A Review of Degradation Methods and Their Mechanisms. Waste Biomass Valorization 2013, 4, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, R.; Zenda, K.; Hatakeyama, K.; Yui, K.; Funazukuri, T. Reaction Kinetics of Hydrothermal Depolymerization of Poly(Ethylene Naphthalate), Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate), and Polycarbonate with Aqueous Ammonia Solution. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grause, G.; Tsukada, N.; Hall, W.J.; Kameda, T.; Williams, P.T.; Yoshioka, T. High-Value Products from the Catalytic Hydrolysis of Polycarbonate Waste. Polym. J. 2010, 42, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagaya, H.; Katoh, K.; Kadokawa, J.; Chiba, K. Decomposition of Polycarbonate in Subcritical and Supercritical Water. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 64, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vom Saal, F.S.; Myers, J.P. Bisphenol A and Risk of Metabolic Disorders. JAMA 2008, 300, 1353–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.G.; Jo, E.Y.; Park, S.M.; Jeon, H.W.; Ko, K.B. Degradation of Bisphenol A by UV/H2O2 Oxidation in Aqueous Solution Containing Nitrate and Alkalinity. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gözmen, B.; Oturan, M.A.; Oturan, N.; Erbatur, O. Indirect Electrochemical Treatment of Bisphenol A in Water via Electrochemically Generated Fenton’s Reagent. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3716–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yun, J.; Zhang, H.; Si, J.; Fang, X.; Shao, L. Degradation of Bisphenol A by Ozonation in Rotating Packed Bed: Effects of Operational Parameters and Co-Existing Chemicals. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Costa, M.J.; Araújo, J.V.S.; Moura, J.K.L.; da Silva Moreno, L.H.; Pereira, P.A.; da Silva Santos, R.; Moura, C.V.R. A Brief Review of Detection and Removal of Bisphenol A in Aqueous Media. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Lara, M.A.; Calero, M.; Ronda, A.; Iáñez-Rodríguez, I.; Escudero, C. Adsorptive Behavior of an Activated Carbon for Bisphenol A Removal in Single and Binary (Bisphenol A—Heavy Metal) Solutions. Water 2020, 12, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, S.; Kabay, N.; Yüksel, M. Removal of Bisphenol A (BPA) from Water by Various Nanofiltration (NF) and Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.; Wu, X.; Tang, K.H.D.; Li, R. Microbial Degradation of Bisphenol A—A Mini-Review. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2025, 43, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razia, S.; Hadibarata, T.; Lau, S.Y. A Review on Biodegradation of Bisphenol A (BPA) with Bacteria and Fungi under Laboratory Conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 195, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, A.; Pedroso, G.B.; Kuriyama, S.N.; Fidalgo-Neto, A.A. Subcritical and Supercritical Water for Chemical Recycling of Plastic Waste. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 25, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, H.; Takesue, M.; Smith, R.L. Green Chemical Processes with Supercritical Fluids: Properties, Materials, Separations and Energy. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2011, 60, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; 1. Paperback; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-0-19-850698-0. [Google Scholar]
- Benmakhlouf, N.; Outili, N.; García-Jarana, B.; Sánchez-Oneto, J.; Portela, J.R.; Jeguirim, M.; Meniai, A.-H. Applications of Supercritical Water in Waste Treatment and Valorization: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boel, M.J.; Wang, H.; AL Farra, A.; Megido, L.; González-LaFuente, J.M.; Shiju, N.R. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Plastics: A Survey of the Effect of Reaction Conditions on the Reaction Efficiency. React. Chem. Eng. 2024, 9, 1014–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Lin, C.; Pan, Z. Stability of Bisphenol A in High-Temperature Water in Fused Silica Capillary Reactor. Huagong Xuebao/CIESC J. 2011, 62, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Fang, Y. Stability of BPA in Near Critical Water. In Proceedings of the 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Adschiri, T.; Shibata, R.; Arai, K. Phenol Recovery by BPA Tar Hydrolysis in Supercritical Water. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 1997, 40, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.E.; Felczak, C.A.; Savage, P.E. Synthesis of P-Isopropenylphenol in High-Temperature Water. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.E.; Savage, P.E. Kinetics and Mechanism of P-Isopropenylphenol Synthesis via Hydrothermal Cleavage of Bisphenol A. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 4724–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Bai, B.; Wei, W.; Chen, Y.; Ge, Z.; Shi, J. Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Polycarbonate (PC) Plastics in Sub-/Supercritical Water and Reaction Pathway Exploration. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 7039–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolnik, M.; Knez, Ž.; Škerget, M. Sub- and Supercritical Water for Chemical Recycling of Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 233, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corson, B.B.; Heintzelman, W.J.; Schwartzman, L.H.; Tiefenthal, H.E.; Lokken, R.J.; Nickels, J.E.; Atwood, G.R.; Pavlik, F.J. Preparation of Vinylphenols and Isopropenylphenols. J. Org. Chem. 1958, 23, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, T.L.-K.; Matsumura, Y. Kinetics Analysis of Phenol and Benzene Decomposition in Supercritical Water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2014, 87, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Hassani, S.; Derakhshani, M. Phenol. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 871–873. ISBN 978-0-12-386455-0. [Google Scholar]
- Takahata, K.; Taniguchi, K.; Fujimoto, T. Process for Separation of Alkylphenols by Azeotropic Distillation. European Patent EP0013133B1, 12 January 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, A.G.; Mammucari, R.; Foster, N.R. A Review of Subcritical Water as a Solvent and Its Utilisation for the Processing of Hydrophobic Organic Compounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, X.; Yuan, T.; Shen, Z. Decomposition of 15 Aromatic Compounds in Supercritical Water Oxidation. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Experiment # | T (°C) | t (min) | Water-to-Material Ratio (mL/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 250 | 5 | 10 |
| 2 | 250 | 17.5 | 5 |
| 3 | 250 | 17.5 | 15 |
| 4 | 250 | 30 | 10 |
| 5 | 300 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 300 | 5 | 15 |
| 7 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 |
| 8 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 |
| 9 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 |
| 10 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 |
| 11 | 300 | 17.5 | 10 |
| 12 | 300 | 30 | 15 |
| 13 | 300 | 30 | 5 |
| 14 | 350 | 5 | 10 |
| 15 | 350 | 17.5 | 15 |
| 16 | 350 | 17.5 | 5 |
| 17 | 350 | 30 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Irgolič, M.; Čolnik, M.; Škerget, M. Decomposition Behavior of Bisphenol A Under Subcritical Water Conditions: A Response Surface Methodology Approach. Processes 2026, 14, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010053
Irgolič M, Čolnik M, Škerget M. Decomposition Behavior of Bisphenol A Under Subcritical Water Conditions: A Response Surface Methodology Approach. Processes. 2026; 14(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrgolič, Mihael, Maja Čolnik, and Mojca Škerget. 2026. "Decomposition Behavior of Bisphenol A Under Subcritical Water Conditions: A Response Surface Methodology Approach" Processes 14, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010053
APA StyleIrgolič, M., Čolnik, M., & Škerget, M. (2026). Decomposition Behavior of Bisphenol A Under Subcritical Water Conditions: A Response Surface Methodology Approach. Processes, 14(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr14010053








