Abstract
To address the sustainability challenges faced by the machinery manufacturing industry, this study establishes an emergy-based evaluation framework that integrates four dimensions—economic, social, ecological, and sustainability—to comprehensively assess the sustainability of mechanical manufacturing systems. An empirical study was conducted on the balance shaft housing manufacturing system of AH Axle Co., Ltd. Results reveal that the system exhibits a relatively low net emergy yield ratio (NEYR), with an emergy investment ratio (EIR) of 2.27 and an improved emergy sustainable index (IESI) of 0.44, indicating poor social benefits and weak long-term sustainability. However, through the optimization of finishing and casting processes, the emergy waste rate (EWR) decreased from 12.96% to 9.86%, substantially enhancing overall sustainability. This study not only provides a novel perspective and practical tool for sustainability assessment in mechanical manufacturing systems but also offers significant theoretical and practical implications for promoting green transformation and sustainable development across the industry.
1. Introduction
The mechanical manufacturing industry constitutes the backbone of the global industrial system and a key driver of national economic growth, exerting a pivotal influence [1]. The mechanical manufacturing industry not only provides technical equipment for the national economy and defense construction, but it is also an important pillar of the national industrial system. Its maturity is widely regarded as a benchmark for a nation’s scientific, technological, and industrial prowess. Globally—particularly across Asia—governments prioritize the machinery sector as a strategic frontier for economic advancement. During the 1960s–1970s, the South Korean government made bold investments in four key industries: shipbuilding, refining and petrochemicals, automobiles, and semiconductors, ultimately forming a highly developed heavy industry [2,3,4]. Japan’s industrial robots, machine tools, and automotive industries are at the forefront of the world. Switzerland has demonstrated astonishing strength in both confidential machine tools and textile machinery and is known as the hidden champion of the world [5]. The United States is a leader in the fields of construction machinery, agricultural machinery, machine tools, and instrumentation. Its domestic Caterpillar company is the world’s largest supplier of construction machinery and mining equipment. As a global powerhouse in the mechanical industry, Germany has demonstrated outstanding strength in high-end machine tools, metallurgical equipment, railway equipment, printing equipment, and agricultural machinery. According to data from the China Statistical Yearbook [6], the operating revenue of China’s large-scale machinery industry reached 31.5 trillion yuan, and the industrial scale has innovated to new heights.
The mechanical industry is one of the industries with high energy consumption [7]. However, due to the complexity and diversity of energy consumption processes, a large amount of energy is wasted, resulting in low efficiency and high energy consumption in the mechanical manufacturing industry [8]. Moreover, due to the use of non-renewable energy resources by most manufacturing units, these resources generate a large amount of waste in the process of causing various types of pollution, which not only exacerbates the excessive consumption of limited resources in human society but also has a significant negative impact on environmental quality [9]. Research shows that the combination of sustainable manufacturing practices and circular economy capabilities can reduce the harmful impact of their operations on the environment [10]. Developing the machinery manufacturing industry not only promotes economic growth but also faces multiple challenges, such as resource consumption, environmental pollution, and social responsibility. With the continuous development of the social economy, the demand for the mechanical manufacturing market is increasing day by day, and the industry scale is gradually expanding. The environmental protection and sustainable development situation and tasks it faces are becoming more urgent and arduous. How to reduce resource consumption and environmental pollution in the mechanical manufacturing industry, and achieve sustainable development of the industry, has become an important topic for both the theoretical and business communities at home and abroad to explore. Therefore, it is urgent to adopt scientific and reasonable methods to comprehensively evaluate the sustainability of mechanical manufacturing systems and implement effective optimization strategies based on this evaluation to promote the green transformation and sustainable development of the industry.
2. Literature Review
2.1. The Connotation of Sustainable Manufacturing
With the increasing demand for environmental protection and maintenance, coupled with pressure from stakeholders, the manufacturing industry is transitioning toward sustainable manufacturing—a new and complex manufacturing system paradigm constructed from a sustainability perspective [11], which can provide technology and management solutions [12] in manufacturing enterprises, enabling them to produce products with minimal environmental impact [13], achieve waste minimization, resource efficiency, pollution prevention, energy-saving manufacturing processes, and scrap management [14], achieve the expected goals of reducing costs, improving environmental impact, and employee well-being [15]. It has emerged as a global imperative for achieving the integrated goals of economic viability, environmental protection, and social responsibility [16]. Sustainable manufacturing has become a global and societal goal.
2.2. System and Method for Sustainability Evaluation of Mechanical Manufacturing Systems
Amid global manufacturing transformation, the sustainability assessment of mechanical manufacturing systems has garnered significant attention. Cai et al. [17] analyzed the energy perspective of the mechanical manufacturing industry. On one hand, they reviewed and analyzed the performance certification of the mechanical manufacturing industry, proposed methods for developing energy performance certification, and on the other hand, proposed a new method for setting multi-objective energy benchmarks based on energy prediction and comprehensive evaluation to promote energy management and energy efficiency improvement in the mechanical manufacturing industry. Liu et al. [18] proposed an evaluation model for the quality of remanufactured products and put forward suggestions to promote the high-quality development of the remanufacturing industry from the relationship between social losses, functional limitations, and quality losses. Hidimoglu et al. [19] used the AHP framework to evaluate and rank the innovation standards for sustainable development in the mechanical manufacturing industry, ranking them from multiple aspects such as economic standards, product-related environment, market, and process-related environment. Yang et al. [20] constructed a sustainability evaluation index system for mechanical production processes from economic and environmental perspectives and used the emergy analysis method to evaluate the sustainability of mechanical production processes. Sun et al. [21] measured and evaluated sustainable processing systems from the perspectives of energy, resources, and environment. Xu et al. [22] evaluated sustainable manufacturing performance from the perspectives of manufacturers, customers, and government stakeholders. Some scholars have selected different indicators from the dimensions of environment, economy, and society to construct a sustainable evaluation index system for manufacturing systems [23,24]. On this basis, combined with the Triple Bottom Line concept (TBL) [25], the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) [26] management model, Green Lean Six Sigma (GLSS) framework [27], and full lifecycle [28] evaluation methods are adopted to comprehensively assess the sustainability of manufacturing systems. Scholars have established evaluation systems from different perspectives and used different methods for evaluation, providing a reference for this article. However, evaluating the sustainability of mechanical manufacturing systems requires accounting for input-output resources, and a unified measurement standard is necessary.
2.3. Pathways to Sustainable Implementation in Mechanical Manufacturing Systems
In the process of continuously exploring the sustainability improvement of mechanical manufacturing systems, scholars have proposed implementation plans from different perspectives. Hasrulnizam et al. [29] believed that overall equipment efficiency (OEE) measures can improve productivity by identifying and eliminating significant losses in the manufacturing industry, and the implementation of OEE can help advance the achievement of sustainability goals in the manufacturing industry. Liu et al. [30,31] studied the remanufacturing system and found that it can promote the sustainable development of the remanufacturing industry by designing data-driven intelligent control systems and reprocessing waste parts. Xia et al. [32] used the automotive engine manufacturing system as an example to demonstrate an energy efficiency technology that includes machine, system, and lifecycle levels. They proposed a layered sustainable development goal for energy-saving manufacturing, ultimately achieving energy efficiency optimization. Additive manufacturing is considered an effective path for sustainable development in the manufacturing industry. Alimuzzaman et al. [33] studied metal additive manufacturing processes and proposed the sustainability of manufacturing parts from the use of cutting fluids. May et al. [34] called for the adoption of standardized methods and attention to energy management to optimize the energy efficiency of additive manufacturing processes, thereby improving the sustainability of modern manufacturing. Lodha et al. [35] believed that combining AM with recycling can bring significant environmental and economic advantages. The combination of AI and AM with sustainable design and manufacturing processes is crucial for achieving outstanding sustainable performance [36]. Hybrid manufacturing (HM) is seen as a way to achieve more sustainable production as a process. Sefene et al. [37] believed that the introduction of hybrid additive manufacturing (HAM) technology in the manufacturing industry can minimize manufacturing costs, improve the mechanical properties, and surface quality of products. The application of artificial intelligence technology can improve the production efficiency and accuracy of mechanical manufacturing, enhance the flexibility and adaptability of production lines, and promote the industrial upgrading of mechanical manufacturing [38].
In summary, scholars have conducted extensive research on the sustainability of mechanical manufacturing systems and achieved good results. However, there are still some shortcomings in current research: (1) Although the manufacturing process contributes greatly to energy consumption and harmful substance emissions, most sustainability evaluations conducted in the field of mechanical manufacturing focus on the product or industry level, while there is more research on additive manufacturing at the process level; (2) When conducting system sustainability evaluation, it is necessary to account for various resources input and output. However, due to the inconsistency of units such as material flow, energy flow, and capital flow, there is a lack of unified measurement standards in the accounting process; (3) Less consideration has been given to the free resources provided by nature, such as solar and wind energy, and the impact of resource consumption on the natural environment has been overlooked.
To address these gaps, this study proposes to introduce emergy theory into the sustainable evaluation of mechanical manufacturing systems. On the basis of fully considering the resources provided by nature, this method converts various inputs and outputs of energy in the system into a unified unit of measurement for objective evaluation of the contribution of various resources to the system. This method has been widely recognized and applied by scholars due to its scientific, objective, and easy to operate nature. It is mainly used for the sustainability evaluation of various systems such as regional economy [39,40], agriculture [41,42], ocean [43], and electricity [44]. In the field of mechanical manufacturing, the emergy method has also been applied to environmental impact analysis and sustainability assessment [21,45]. This study constructs a sustainability evaluation index system based on emergy from four aspects: economy, society, ecology, and sustainability. Taking the balanced shaft shell manufacturing system as an example, the method is applied and practiced to verify its effectiveness.
The research focuses on the key link of mechanical manufacturing technology, introduces the concept of emergy, converts the energy flow, logistics, and monetary flow in the mechanical manufacturing system into a unified emergy for accounting, simplifies the evaluation process of complex systems, and more intuitively and clearly reveals the inherent connections and dynamic balance between various elements; When constructing emergy indicators to evaluate the sustainability of mechanical manufacturing systems, the contribution of various free natural resources and the potential impact of waste generated during system operation on the environment were fully considered, which broadened the scope and depth of the evaluation and made the evaluation results more comprehensive and objective. Through the sustainable evaluation of mechanical manufacturing systems, this study accurately analyzes their energy consumption, material consumption, and environmental impact, and proposes targeted optimization strategies and improvement plans. This not only helps to improve the energy efficiency and environmental performance of the manufacturing system but also provides a practical and feasible path for the sustainable development of the entire mechanical manufacturing system. It has important theoretical and practical guidance significance for promoting industry transformation and upgrading, as well as achieving green manufacturing.
The organizational structure of this article is as follows. The first and second sections are the introduction and literature review, while the third section describes the research methods and indicator system construction, including emergy theory, emergy flow diagram construction, data collection, processing, and emergy measurement, establishing an emergy evaluation indicator system. The fourth section validates the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method using the balance axle housing manufacturing system of AH Axle Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China). as a case study, and discusses the results. The fifth section proposes processing technology optimization based on the analysis results to reduce the use of raw materials in the production process and lower waste emissions. The sixth section summarizes the main conclusions and contributions, as well as the research shortcomings and prospects.
3. Research Methods and Indicator System Construction
3.1. Emergy Theory
The emergy theory was originally proposed by the famous American ecologist Howard T. Odum in the late 1980s as a new ecological and economic value measurement system and systematic analysis method. This method takes solar emergy as the benchmark, its basic unit is the solar joule (sej), converts various types of energy and non-flowing forms of energy in the studied object, such as material flow, capital flow, etc., into a unified solar emergy [46,47], processes and analyzes the data, and then constructs a system emergy evaluation index to evaluate the sustainable development performance of the system. It provides a common scale and systematic analysis method for people to analyze various ecological cycles within the system.
3.2. Emergy Flow Diagram Construction
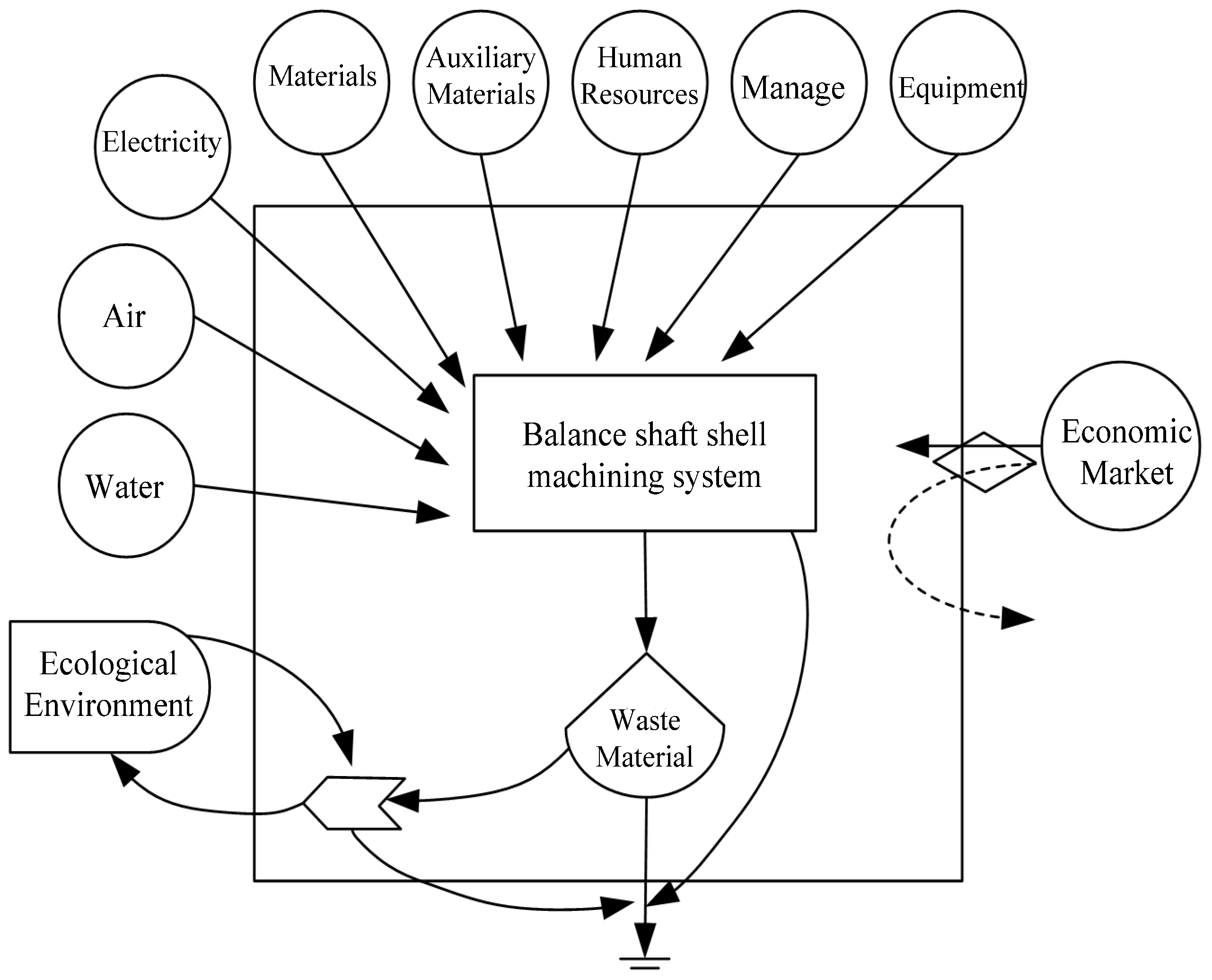
To conduct emergy analysis, the first step is to define the boundary of the system scope, list the main energy sources of the system, clarify the basic structure of the system, the interrelationships inside and outside the system, and the direction of the main ecological flow. Combining the characteristics of different systems, draw corresponding emergy flow diagrams. Taking the balanced shaft shell processing system as an example, its input resources include renewable resources R (e.g., solar energy, rainwater, wind, etc., from nature), non-renewable resources N (e.g., thermal power, diesel fuel and coke), purchased resources F (e.g., materials, auxiliary materials, labor, equipment, and management costs required for production). The output resources are the balanced shaft shell finished products P that are put into the economic market, and the waste W generated during production. The emergy flow diagram is shown in Figure 1.
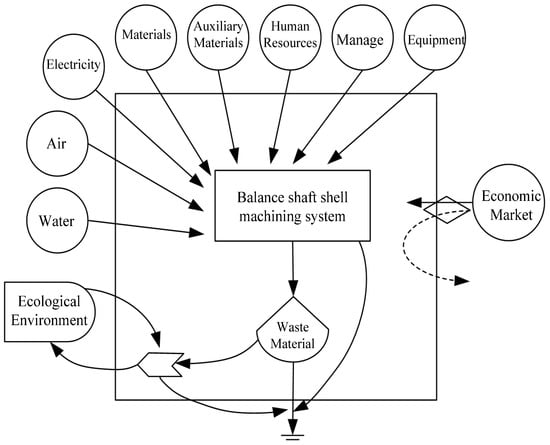
Figure 1.
Emergy flow structure diagram of balance shaft shell manufacturing system.
3.3. Data Collection, Processing and Emergy Measurement
Through field research, various data inputs and outputs of the manufacturing system are collected, and the raw data are processed and classified accordingly. The energy flow, material flow, and capital flow of different categories are uniformly converted into solar emergy units for emergy measurement. The fundamental equation for emergy calculation is as follows:
where i is the total number of resource types used in the mechanical manufacturing system; represents the solar emergy of the i-th resource; represents the emergy conversion rate of the i-th resource; and represents the quantity of different units of resources (mass g or energy J). In this paper, EMi refers to the solar emergy of the i-th resource within one day.
Based on the emergy measurement results, the emergy of each input and output of the mechanical manufacturing system can be summarized to update resource EMR, purchase resource EMF, finished product EMP, and waste EMW generated during the production process.
3.4. Establish an Emergy Evaluation Indicator System
The emergy evaluation indicator system is the main basis for conducting systematic analysis, comparative research, and drawing conclusions. Based on the characteristics of the manufacturing system, the following indicators are developed to evaluate the sustainability of the manufacturing system.
3.4.1. Economic Benefit Index
Net Emergy Yield Ratio (NEYR): The ratio of the net emergy generated by a manufacturing system through effective conversion and utilization of resources during its operating cycle to the initial input emergy. Among them, net emergy output refers to the output after deducting factors such as waste disposal, non-production performance consumption, and environmental losses. The calculation formula is:
NEYR can not only measure the production efficiency of manufacturing systems but also evaluate the net contribution of the system to the economy and energy utilization efficiency, indicating the efficiency of energy production and utilization, and demonstrating the competitiveness of economic activities. The higher NEYR, the higher the production efficiency of the system, indicating that industrial production has high economic benefits and competitiveness.
3.4.2. Social Benefit Index
Emergy Investment Ratio (EIR): The ratio of investment input from the economic system to free investment input from other ecosystems (primarily referring to the natural world). Calculation formula:
This index can quantify the corresponding emergy required to develop and utilize each unit of natural resources in the manufacturing process. It reflects the complexity and cost of resource conversion within the manufacturing system and serves as an important metric for evaluating the degree of economic development and sustainable development capability of the system. The lower EIR indicates higher dependence on natural resources and lower economic development levels.
3.4.3. Ecological Benefit Index
(1) Improved Environmental Load Rate (IELR). The traditional environmental load factor is the ratio of the emergy of all non-renewable resources (such as fossil fuels) actually invested by the system to the emergy of all renewable resources (such as solar and wind energy). In industrial production systems, there will be some emissions of pollutants, which will inevitably cause significant pressure on the surrounding environment. Based on this, we have improved the traditional environmental load factor by adding consideration for pollutant emissions, so that this indicator takes into account both resource consumption and environmental pollution and can more accurately reflect the actual impact of production activities on the environment. The calculation formula is:
IELR serves as a good warning. The higher the IEILR of a manufacturing system, the higher its dependence on non-renewable resources, and the greater the environmental pressure caused by the pollutants generated by the system. This dual-pressure warning effect helps decision-makers to have a more comprehensive understanding of the environmental risks of system operation and to stop the system in a timely manner.
(2) Emergy Waste Rate (EWR): The ratio of the emergy of waste emitted during mechanical processing to the total emergy of input.
This indicator aims to directly reflect the depth of resource utilization within the mechanical processing system and the optimization level of waste conversion into renewable resources. The lower the value, the higher the degree of circular management and utilization, and the enterprise has achieved the maximization of resource utilization and the minimization of waste generation.
3.4.4. Improved Emergy Sustainable Index
Improved emergy sustainable index (IESI) is measured by comparing the emergy output rate with the system environmental load rate. In order to further enhance the comprehensiveness and accuracy of the evaluation, an improved sustainable development index has been introduced based on the previously improved environmental load rate. The calculation formula is:
This index takes into account the negative impact of the generation and emission of atmospheric pollutants on the environment. The higher the IESI value of the system, the stronger its sustainable development capability. If the IESI value falls between 1 and 5, it indicates that the system has medium-term sustainability. If the IESI value is greater than 5, it indicates that the system has long-term sustainability.
4. Sustainability Evaluation of Mechanical Manufacturing Systems
4.1. Case Background
AH Axle Co., Ltd. is an automotive parts manufacturer with a long history and rich cultural heritage. After decades of unremitting efforts, it has become one of the manufacturers of semi-trailer axles and special axles with the most innovative and development capabilities in China. Drawing on scholars’ use of emergy theory to evaluate the ecological sustainability of manufacturing systems [19,29], this study focuses on the 2918ADZ-130 balance shaft shell processing system independently developed by the company. Combining relevant knowledge of emergy theory, the economic and ecological sustainability of the production process are evaluated.
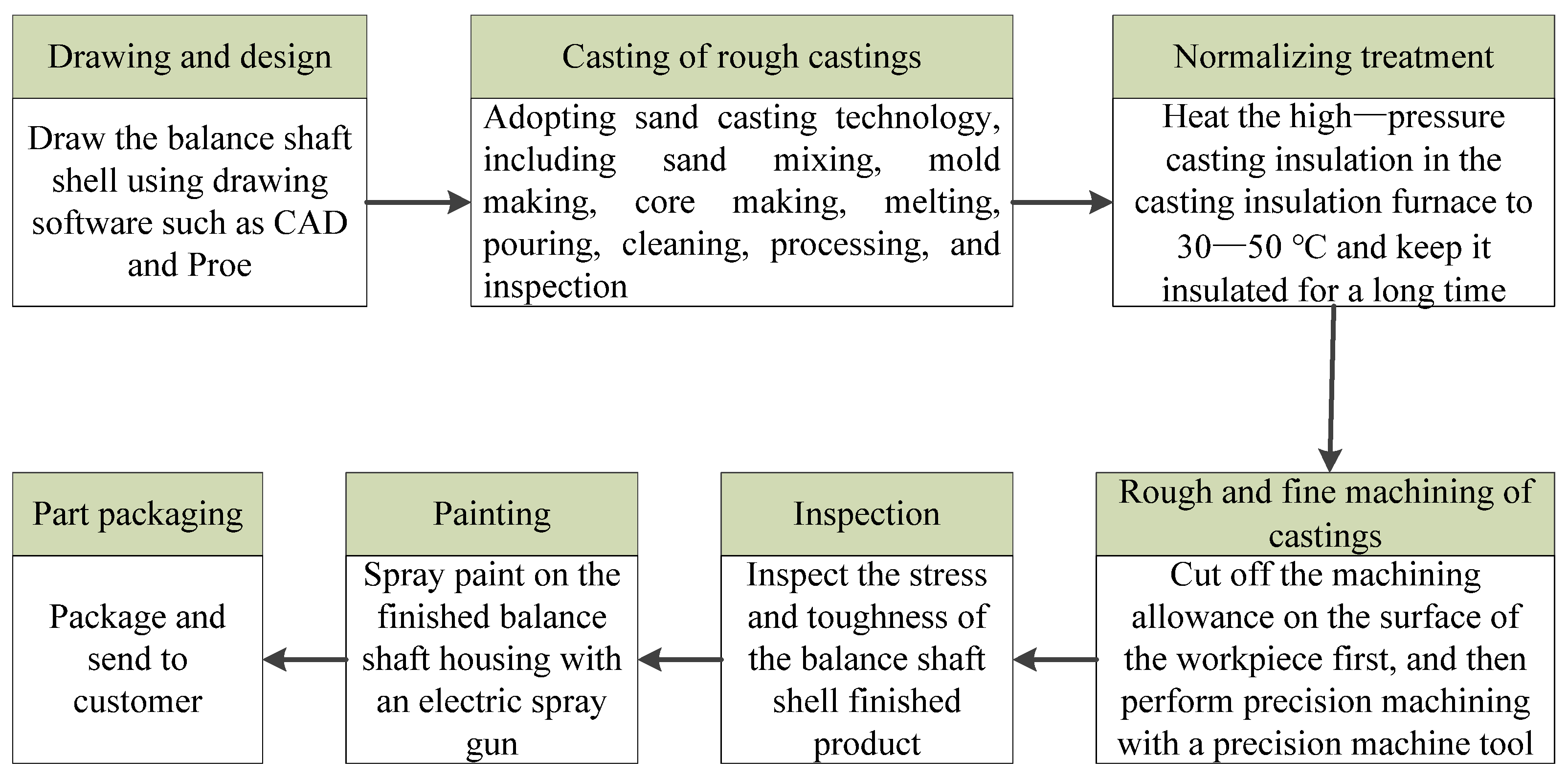
According to field research, the balance shaft housing processing system of the 2918ADZ-130 model independently developed by the company was collected. The entire production process comprises the following stages: drawing and design, casting of rough castings, normalizing treatment, rough and fine machining of castings, inspection, painting, and part packaging. The production process is shown in Figure 2. Among them, due to the large-scale production of balanced shaft shell castings, sand casting is selected as the casting process, which mainly includes sand mixing, mold making, core making, melting, pouring, cleaning, processing, and inspection. The equipment parameters and cost energy consumption used in the main process of rough and fine machining are shown in Table 1.
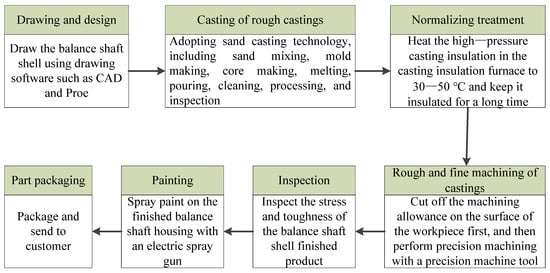
Figure 2.
Production process of balance shaft shell.

Table 1.
Parameters and emergy consumption of machining equipment.
4.2. Data Collection and Processing
Based on field research conducted by A Axle Co., Ltd., collect raw input and output data of the system for one day, and calculate the emergy flow rate through emergy conversion rate. Table 2 shows the emergy analysis table of the system.

Table 2.
Emergy analysis of balance shaft process system.
According to the emergy analysis table of the balance shaft shell processing technology, it can be concluded that:
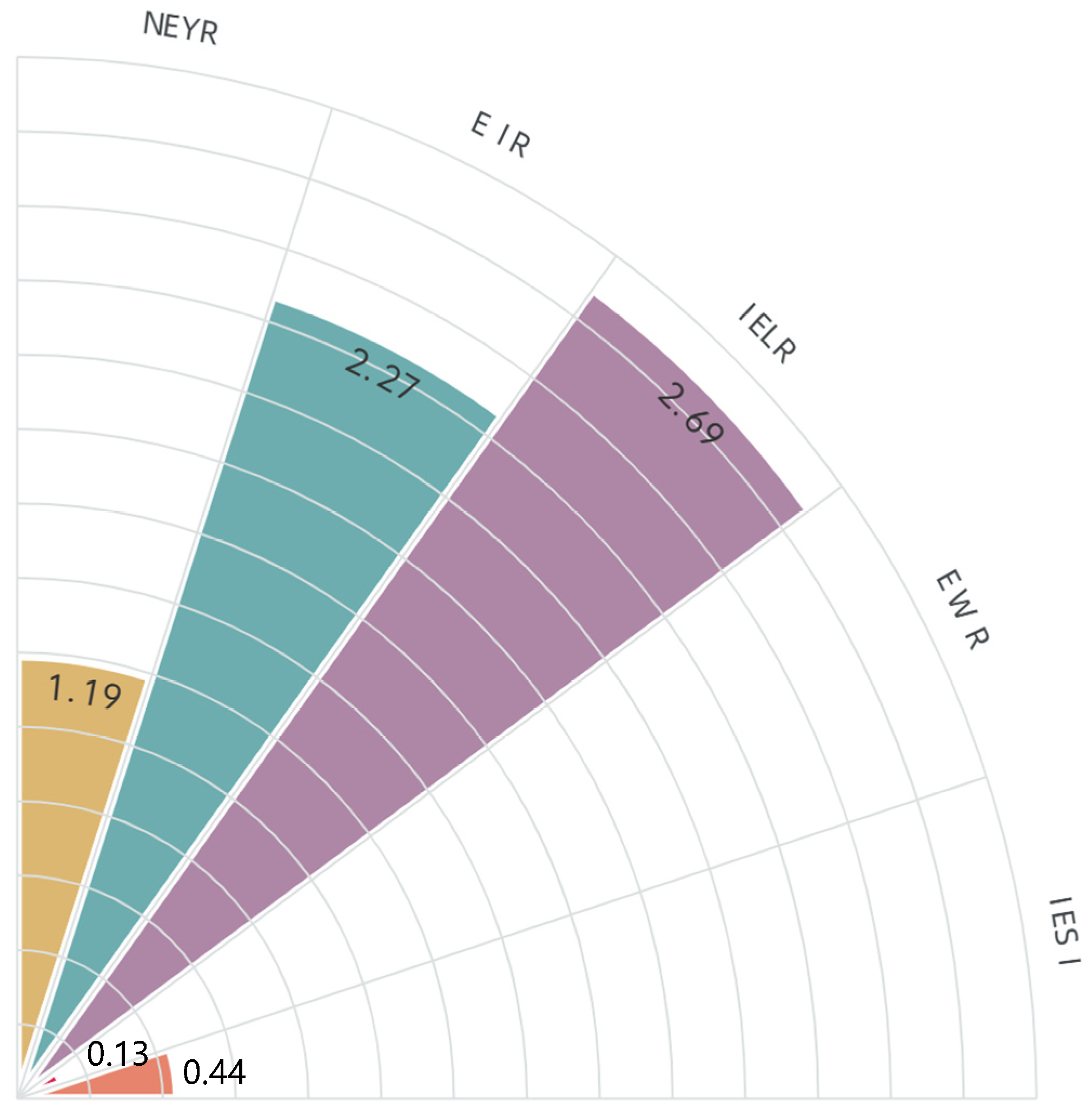
The emergy of the renewable resources in this manufacturing system is 1.92 × 1017; the non-renewable resources’ emergy is 6.67 × 1013; the purchased emergy is 4.36 × 1017; the waste emergy is 8.15 × 1016; and the total output emergy is 6.08 × 1017. Based on the energy evaluation indicators of the manufacturing system constructed in the third section, the sustainability evaluation indicators of the balance shaft shell manufacturing system are obtained as shown in Figure 3.
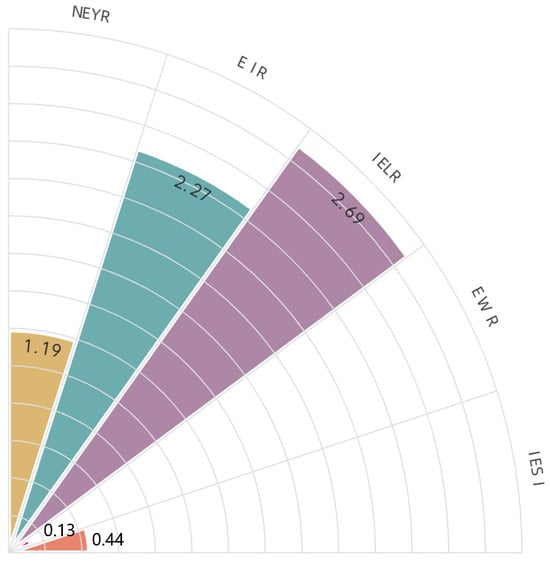
Figure 3.
Sustainability evaluation of balance shaft shell manufacturing system.
4.3. Results and Analysis
The indicators show that NEYR of the company’s processing system is relatively low, with average production efficiency and economic competitiveness. The reason for the low NEYR based on process analysis is that the processing system has invested too much emergy, especially in equipment and manpower. Among them, the precision machining time of the shaft shell is much longer than other processes, so the primary task to improve the production efficiency of the balanced shaft shell machining system is to improve the precision machining efficiency and reduce emergy input.
The EIR of the system is 2.27, indicating that the social benefits brought by the system are not significant, and there are too many renewable resources invested in the processing system, especially the input of industrial water is too large. Meanwhile, the material usage cost and coating cost in the casting process also have a significant impact on the emergy investment rate. By reducing the emergy input of industrial water resources, strengthening the recycling of industrial water, changing the casting process pouring method, coating pouring method, and riser improvement, the cost of material use and production can be reduced, and EIR can be increased.
From EWR and IELR, the overall ecological benefits of the system are good, with less waste emissions, but there is still room for further reduction. The pollution output during the casting stage is the highest, especially wastewater and waste residue. The emergy output of wastewater is as high as 3.58 × 1016, accounting for 44% of the total waste emergy output. Waste emissions in precision machining processes account for 35% of all waste emissions, mainly consisting of various waste liquids.
IESI of the system is 0.44, indicating that the balance shaft manufacturing system is not sustainable in the long run.
5. Sustainability Optimization and Improvement of Mechanical Manufacturing Systems
Based on the above analysis, this article proposes two processing technology optimizations to reduce the use of raw materials in the production process and lower waste emissions.
5.1. Optimization of Precision Processing Technology
In the precision machining process, due to the large selection of original parameters, the removal rate of raw materials is relatively high, which exacerbates equipment wear and waste discharge. The problem of long processing hours also reduces production efficiency. This article mainly aims to solve this problem by reasonably reducing machining parameters without affecting the size of the workpiece. The parameters and corresponding changes before and after optimization are shown in Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 3.
Comparison of finish-machining parameters before and after optimization.

Table 4.
Performance metrics before and after finish-machining optimization.
The emergy input of cutting fluid in the precision machining process of the balance shaft is 1.95 × 1016, which accounts for a large proportion in this process. The discharge emergy of its waste liquid accounts for 60% of all waste liquids, and technical optimization has been carried out for this. One approach is to adopt dry machining technology, which can still achieve a yield of over 95% without using cutting fluid or coolant, achieving zero discharge of cutting waste liquid. The second is the precision cutting and processing technology of low-temperature balanced cold air. In the precision cutting and processing technology of low-temperature balanced shaft shell, a very small amount of organic vegetable oil that has not been oxidized by high temperature is used instead of its coolant to provide low-temperature cold air (−10~−100 °C) for cutting and processing. This technology achieves zero use and zero emission of coolant.
5.2. Casting Process Optimization
The original casting process used closed pouring, which had problems such as unstable steel filling, high defect rate, and non-recyclable waste liquid. The cost of using ordinary risers is relatively high, and the yield of workpieces is also low, with the occurrence of riser cracks. The long pouring time results in a significant discharge of pouring waste liquid. Artificial coatings result in waste and low efficiency of coatings. Regarding the above issues, optimization was carried out as shown in Table 5, and the optimization results are shown in Table 6.

Table 5.
Comparison of casting parameters before and after optimization.

Table 6.
Performance metrics before and after casting optimization.
5.3. Post-Optimization Simulation and Assessment
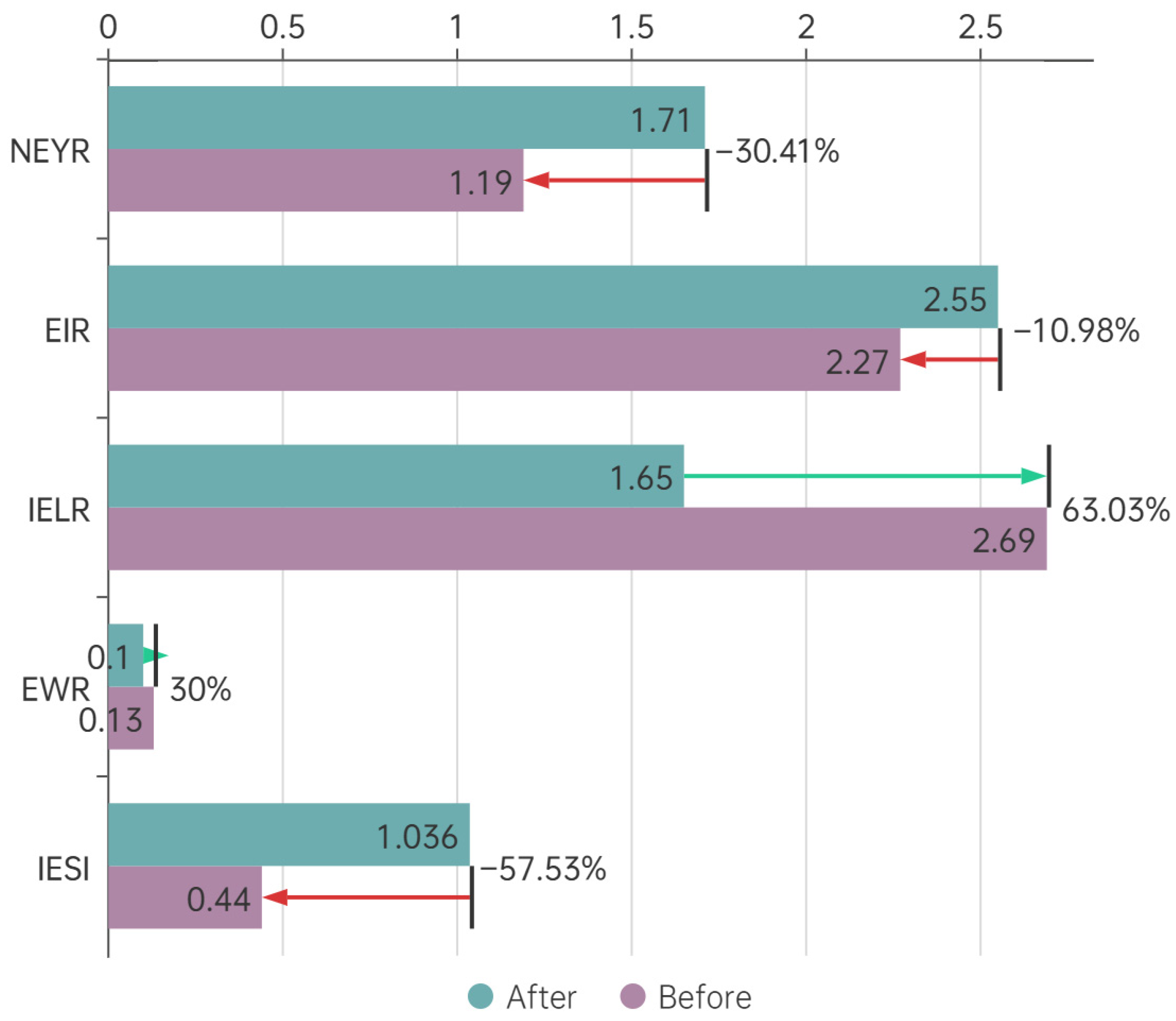
Some processes machines have replaced manual labor, which can reduce emergy input in certain situations. After optimization, some process machines have replaced manual labor, resulting in standardized production processes that greatly improve work efficiency. The optimized production process and precise operation can reduce energy waste and material waste, achieve lean production, and thus save a lot of emergy input. Although the equipment’s emergy has slightly increased, the energy and material costs have decreased throughout the entire processing process, and the production hours have also been relatively reduced. The use of new machines has also reduced the difficulty of management, and the emergy consumption per unit product is usually lower than that of low-speed production lines with a large amount of manual labor. In addition, high-efficiency machines avoid energy consumption in the working environment required by humans. The emergy evaluation indicators of the system before and after optimization are shown in Figure 4.
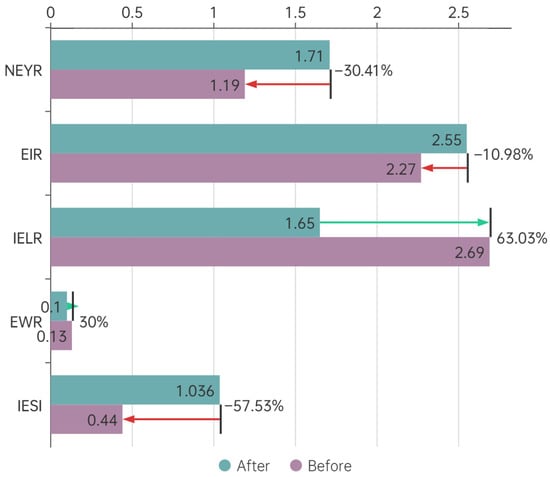
Figure 4.
Changes in various emergy evaluation indicators before and after optimization.
From the perspective of sustainable development of enterprises, the optimized manufacturing system has demonstrated significant improvements in both environmental and economic benefits. EWR has decreased from 12.96% to 9.86%, indicating a reduction in waste output and a significant improvement in resource utilization efficiency; IELR has decreased to 1.65, reflecting a reduction in the system’s pressure on the environment and better environmental performance; NEYR has jumped from 1.19 to 1.71, which not only enhances the production capacity of enterprises, but also directly improves the added value and market competitiveness of products; EIR has increased from 2.27 to 2.55, indicating the optimization of resource allocation by enterprises. Based on the improvement of the above indicators, IESI has also increased, and in the medium term, it basically has the ability for sustainable development.
6. Conclusions
Driven by the economic wave of the new era, the mechanical manufacturing industry is moving from a traditional extensive model to an intensive development model. In the context of the increasing emphasis on global sustainable development strategy and environmental protection, promoting the healthy, stable, and sustainable development of the machinery manufacturing industry is not only an inevitable requirement for the development of the national economy, but also a key factor in promoting the harmonious coexistence of nature and economy.
The study focuses on the daily manufacturing system of the 2918AD-130 special axle balance housing independently developed and produced by AH Axle Co., Ltd. The sustainability evaluation and optimization of its manufacturing system were conducted based on the research method of emergy theory. Through optimized data simulation analysis, both EWR and IELR have been reduced, and the IESI of the system has also been improved. In the medium term, it has the ability for sustainable development. This achievement verifies the effectiveness and practicality of emergy theory in optimizing mechanical processing technology. The research not only brings considerable economic benefits to AH Axle Co., Ltd., but also has great significance for the ecological environment.
Considering the cost input, this study optimized the production process by fully utilizing existing production equipment and achieved certain results. Although the current optimization has enabled the system to have sustainable development capabilities in the medium term, further exploration of new energy introduction pathways and efficient waste recycling strategies is needed to ensure its long-term sustainability. This is not only the key direction of future research in this topic but also the necessary path to promote the transformation of the entire mechanical manufacturing industry towards a greener, low-carbon, and circular development model. Therefore, we will further study the recycling of cutting waste liquid, waste residue, and other waste materials, as well as the industrial and policy coordination of waste recycling, in order to further enhance the sustainability of the mechanical manufacturing industry system.
Author Contributions
Y.W.: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, project administration, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review, and editing. X.S.: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, project administration, writing—original draft, writing—review, and editing. Y.Z.: project administration, writing—review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge that this study was funded by the following projects: Key Projects of Philosophy and Social Sciences in Universities in Anhui Province, No. 2024AH053175, No.2022AH051357; Anhui Province Social Science Innovation and Development Project, No. 2023CX023; Suzhou City Social Science Innovation and Development Project, No. 2025CX003; Provincial New Professional Quality Improvement Project, No. 2023xjzlts069; Suzhou University Research Platform Project, No. 2024PTPY05; Suzhou University Teaching Innovation Team, No.szxy2024cxtd02; Suzhou University Doctoral Research Initiation Fund Project, No. 2023BSK035, No. 2023BSK036, No. 2023BSK037.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Anonymous. Innovation and service: Essentials lead to great success—A visit to some Swiss textile machinery manufacturers and testing company. China Text. Lead. 2008, 5, 16+18+20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.-Y. The Korean Shipbuilding Industries: Retrospect and Prospect. J. Marit. Bus. 2015, 30, 79–115. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.Y. Comparative Study of Automobile Industry Competitive Strength between China and Korea. Glob. Bus. Adm. Rev. 2011, 8, 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.H. Behaviors of Korean Government on High-Tech Industries and Illuminations to China. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Redkva, O. Methodological prerequisites for ensuring the economic security of the machine-building complex of Ukraine. Econ. Ecol. Soc. 2022, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yadegari, M.J.; Martucci, A.; Biamino, S.; Ugues, D.; Montanaro, L.; Fino, P.; Lombardi, M. Aluminum laser additive manufacturing: A review on challenges and opportunities through the lens of sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Liu, F.; Xie, J.; Zhou, X. An energy management approach for the mechanical manufacturing industry through developing a multi-objective energy benchmark. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 132, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, N.A.; Sindhwani, R.; Kumar, R.; Mathiyazhagan, K. Identifying the drivers and barriers for the implementation of sustainable manufacturing. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2024, 48, 532–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquah, I.S.K.; Quaicoe, J.; Gatsi, J.G. Modelling circular economy capabilities and sustainable manufacturing practices for environmental performance: Assessing linear and non-linear effects. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 205, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminuddin, A.S.A.; Nawawi, M.K.M.; Mohamed, N.M.Z.N. Analytic network process model for sustainable lean and green manufacturing performance indicator. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1613, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bilge, P.; Badurdeen, F.; Seliger, G.; Jawahir, I.S. A novel manufacturing architecture for sustainable value creation. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, R.M.; Vinodh, S.; Dhanasekaran, S. State-of-art review on strategies, tools and indicators of sustainable manufacturing. Int. J. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2021, 40, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rashid, S.H.; Sakundarini, N.; Ariffin, R.; Ramayah, T. Drivers for the adoption of sustainable manufacturing practices: A Malaysia perspective. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2017, 4, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewiadomski, P.; Stachowiak, A. Identification of barriers to sustainable manufacturing implementation—The perspective of manufacturers of parts and components for agricultural transport. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Palaniappan, M.; Alsaleh, N.; Kumar, D.T.; Elfar, A.A.; Pinto, M.C.B.; Torres, A.M. Decision analysis on sustainable manufacturing practices: Cross-country perspective. Ann. Oper. Res. 2025, 345, 277–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Liu, C.H.; Lai, K.H.; Li, L.; Cunha, J.; Hu, L.K. Energy performance certification in mechanical manufacturing industry: A review and analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 186, 415–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Quantitative evaluation model of the quality of remanufactured product. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 7413–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidimoglu, M.B.; Feyzioglu, A.; Haliloglu, H.; Gok, A.E. Prioritizing sustainability innovation in machinery manufacturing: A multi-criteria decision-making case study. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, C.X.; Wang, C. An emergy-based sustainability method for mechanical production process—A case study. Processes 2022, 10, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.M.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, J.Q.; Gao, M.D.; Shen, X.H. A novel method of sustainability evaluation in machining processes. Processes 2019, 7, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Murugesan, T.M.; Elfar, A.A.A.; Durairaj, M.P.R. Evaluation of sustainable manufacturing performance—A case illustration with multistakeholder perspective. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 458, 142368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickcha, B.; Callychurn, D.S.; Hurreeram, D.K. Developing a sustainability index for Mauritian manufacturing companies. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.A.; Darras, B.; Kishawy, H.A. Towards sustainability assessment of machining processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; He, N.; Wei, Z.; Gupta, M.K.; Khan, A.M. A novel quantifiable approach of estimating energy consumption, carbon emissions and cost factors in manufacturing of bearing steel based on triple bottom-line approach. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 36, e00593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bezerra Araujo, J.; de Gores Oliveira, J.F. Towards a balanced scoreboard for assessing manufacturing process sustainability. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Manag. 2012, 13, 198–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, R.; Kaswan, M.S.; Garza-Reyes, J.A.; Antony, J.; Cross, J. Green Lean Six Sigma for improving manufacturing sustainability: Framework development and validation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selicati, V.; Cardinale, N.; Dassisti, M. The interoperability of exergy and life cycle thinking in assessing manufacturing sustainability: A review of hybrid approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasrulnizzam Wan Mahmood, W.; Abdullah, I.; Fauadi, M.H.F.M. Translating OEE measure into manufacturing sustainability. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 761, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cai, W.; Zhang, C.; Jia, S.; Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; Hu, L. Data-driven intelligent control system in remanufacturing assembly for production and resource efficiency. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 3531–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Cai, W. Data-driven remanufacturability evaluation method of waste parts. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 4587–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.B.; An, X.X.; Yang, H.Q.; Jiang, Y.M.; Xu, Y.H.; Zheng, M.M.; Pan, E.R. Efficient energy use in manufacturing systems—Modeling, assessment, and management strategy. Energies 2023, 16, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimuzzaman, S.M.; Jahan, M.P.; Rakurty, C.S.; Rangasamy, N.; Ma, J.F. Cutting fluids in metal AM: A review of sustainability and efficiency. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 106, 51–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, G.; Psarommatis, F. Maximizing energy efficiency in additive manufacturing: A review and framework for future research. Energies 2023, 16, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, S.; Song, B.; Park, S.I.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, S.W.; Park, H.W.; Choi, S.K. Sustainable 3D printing with recycled materials: A review. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 5481–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Aftab, J.; Tyll, L. The influence of artificial intelligence and additive manufacturing on sustainable manufacturing practices and their effect on performance. Sustain. Futures 2025, 10, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefene, E.M.; Hailu, Y.M.; Tsegaw, A.A. Metal hybrid additive manufacturing: State-of-the-art. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 7, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.M. The application of artificial intelligence technology in mechanical manufacturing and automation. Scalable Comput. Pract. Exp. 2024, 25, 5383–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Zhang, P.Y.; Pang, B. Process and mechanism of agricultural irrigation benefit allocation coefficient based on emergy analysis—A case study of Henan, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Bian, Y.T.; Ji, G.X. Assessing the sustainability of China’s coastal regions: A perspective on local coupling and telecoupling. Ecol. Model. 2024, 501, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, X.X.; Zhang, C.X.; Liu, F. Assessment and suggestions on sustainable development of regional ecological economy based on emergy theory: A case study of Henan Province. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Y.L.; Liu, C.H.; Xu, G.W.; Guo, Y.X.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y. Sustainability of regional agro-ecological economic system based on emergy theory: A case study of Anhui Province, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, G.; Asnaghi, V.; Chiantore, M.; Thrush, S.; Povero, P.; Vassallo, P.; Petrillo, M.; Paoli, C. The effect of Cystoseira canopy on the value of mid-littoral habitats in NW Mediterranean, an emergy assessment. Ecol. Model. 2019, 404, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.Y.; Feng, X.; Yang, M.B. Solution of issues in emergy theory caused by pathway tracking: Taking China’s power generation system as an example. Energy 2022, 262, 125596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cai, W.; Jia, S.; Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; Hu, L.; Jiang, Z. Emergy-based evaluation and improvement for sustainable manufacturing systems considering resource efficiency and environmental performance. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 177, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zhang, J.H. Progress and its enlightenments in application research on emergy theory. In Proceedings of the 2011 19th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.L.; Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.X. Evaluation of sustainability of cement manufactory based on emergy theory. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2013, 53, 766–771. [Google Scholar]
- Odum, H.T. Environmental Accounting. In Emergy and Environmental Decision Making; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, S.F.; Qin, P.; Lu, H.F. Emergy Analysis of Ecological Economic Systems; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, S.F.; Qin, P. Emergy Analysis of Ecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 12, 129–131. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).