Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Autonomous Docking with Multi-Sensor Perception in Sim-to-Real Transfer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. PPO-Based Reinforcement Learning
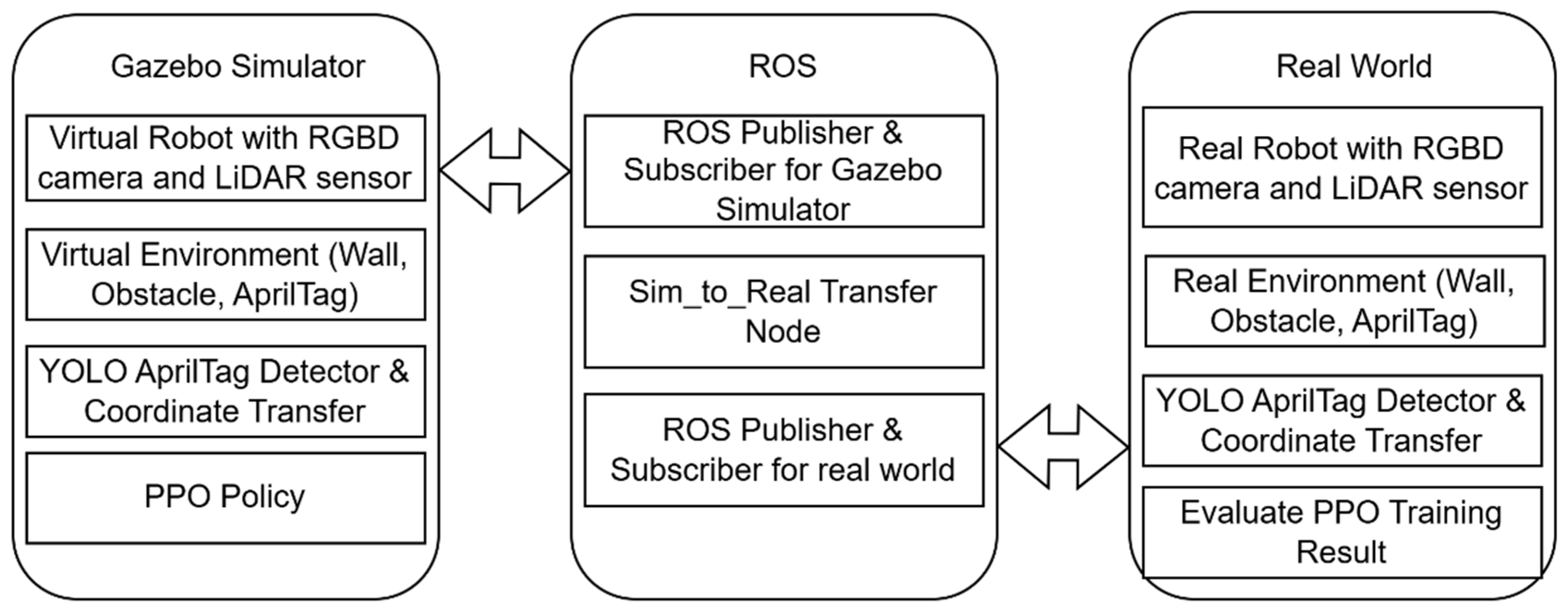
2.2. Sim-to-Real Transfer System
3. Simulation and Experiment Results
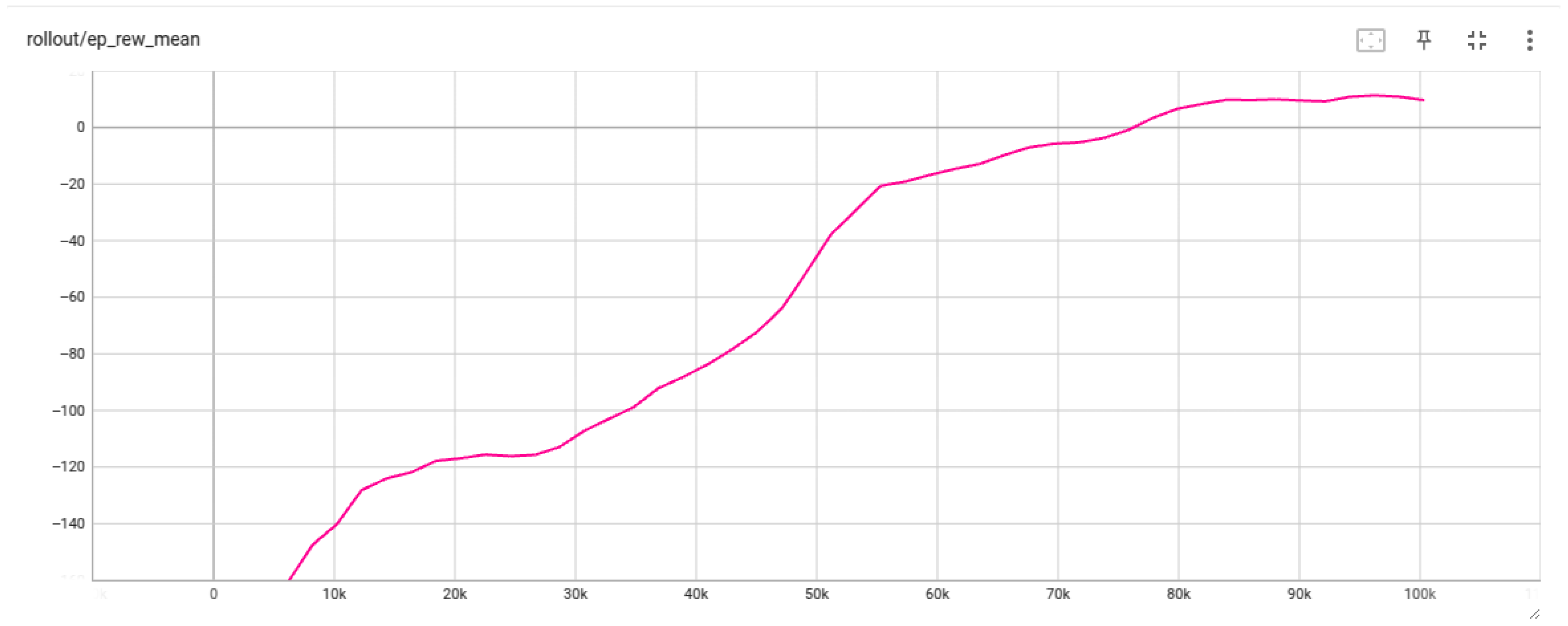
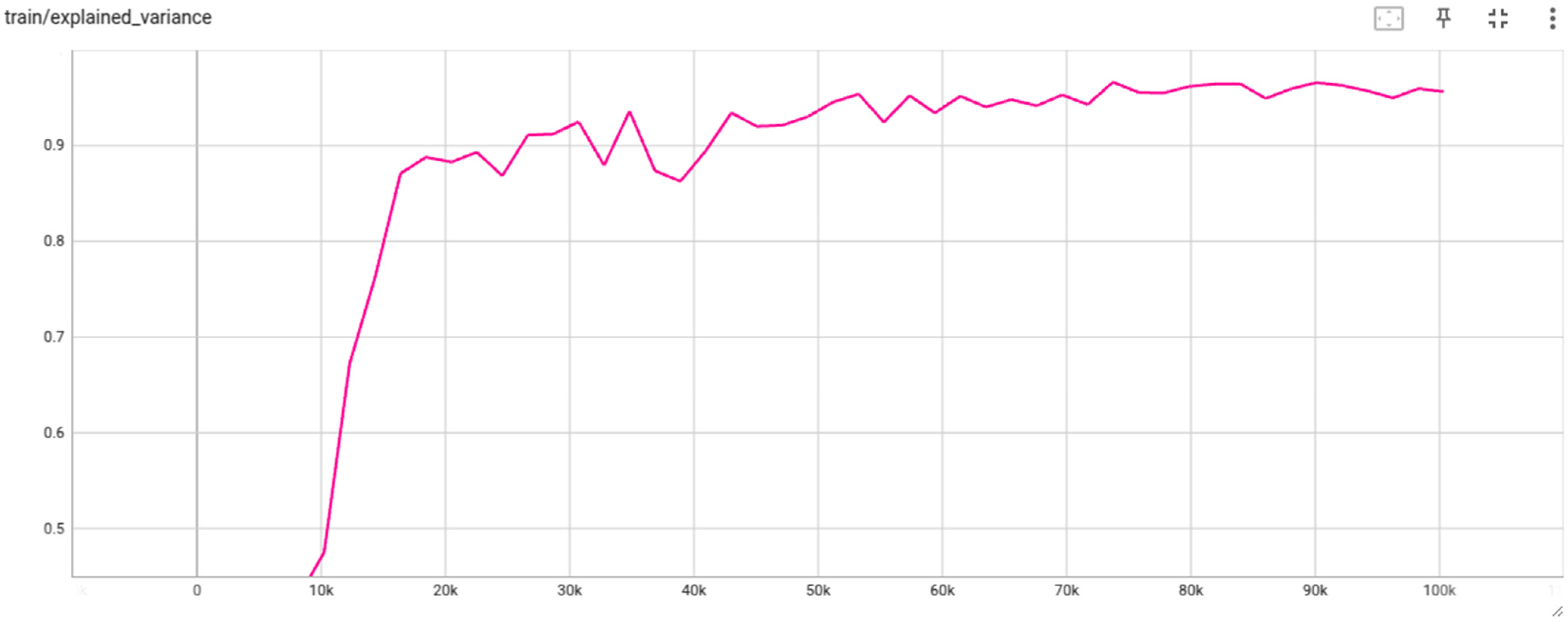
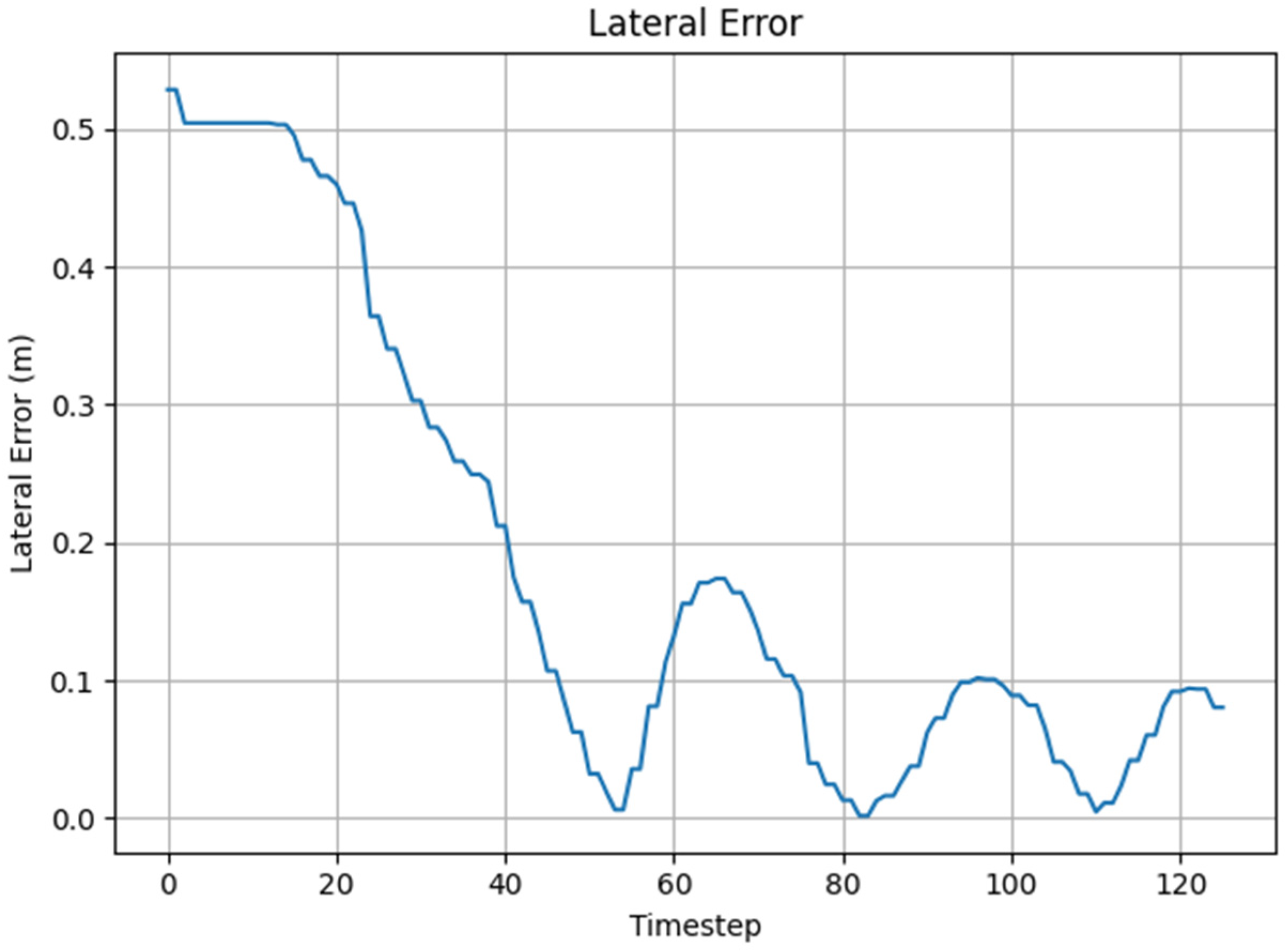
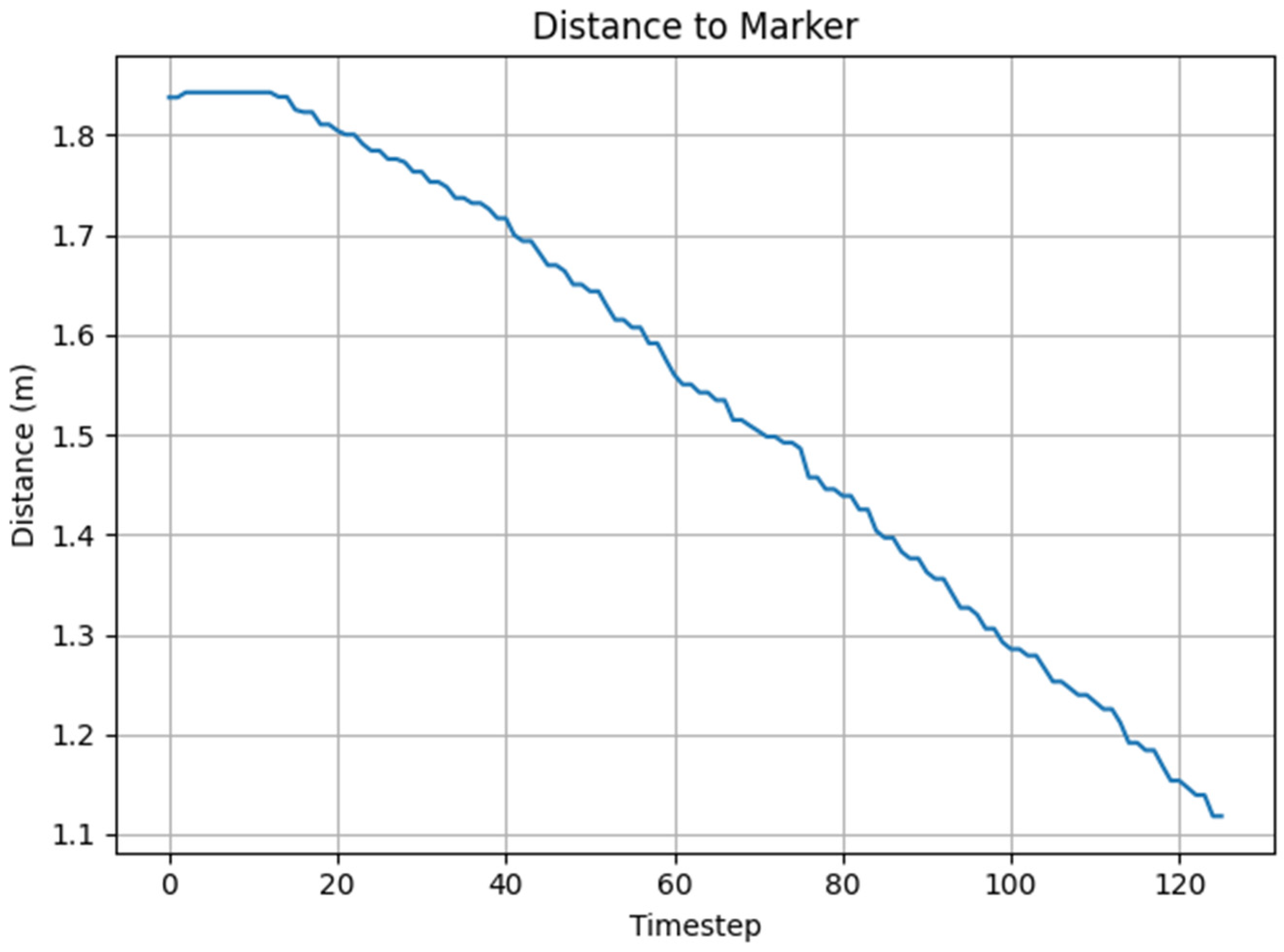
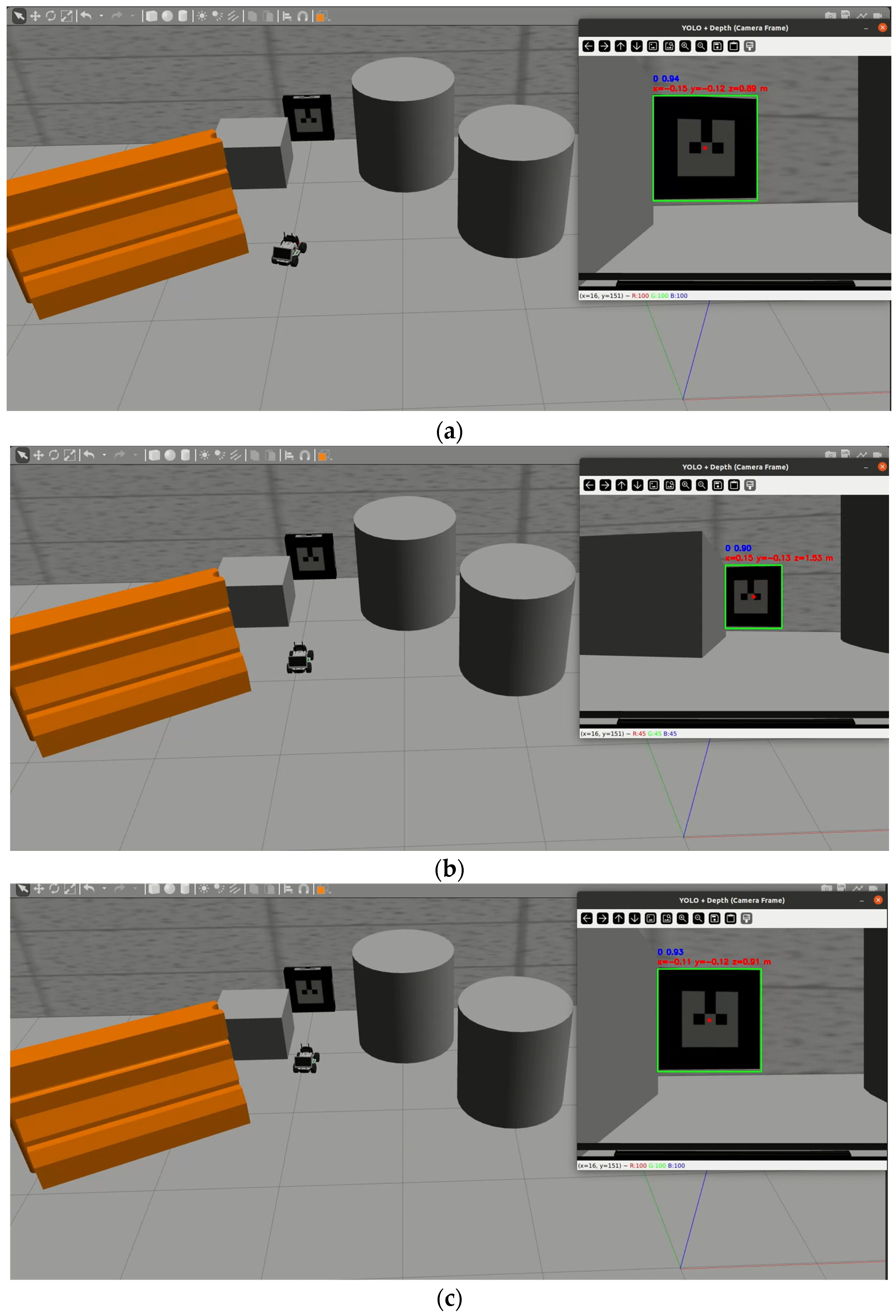
3.1. PPO Based Docking Simulation
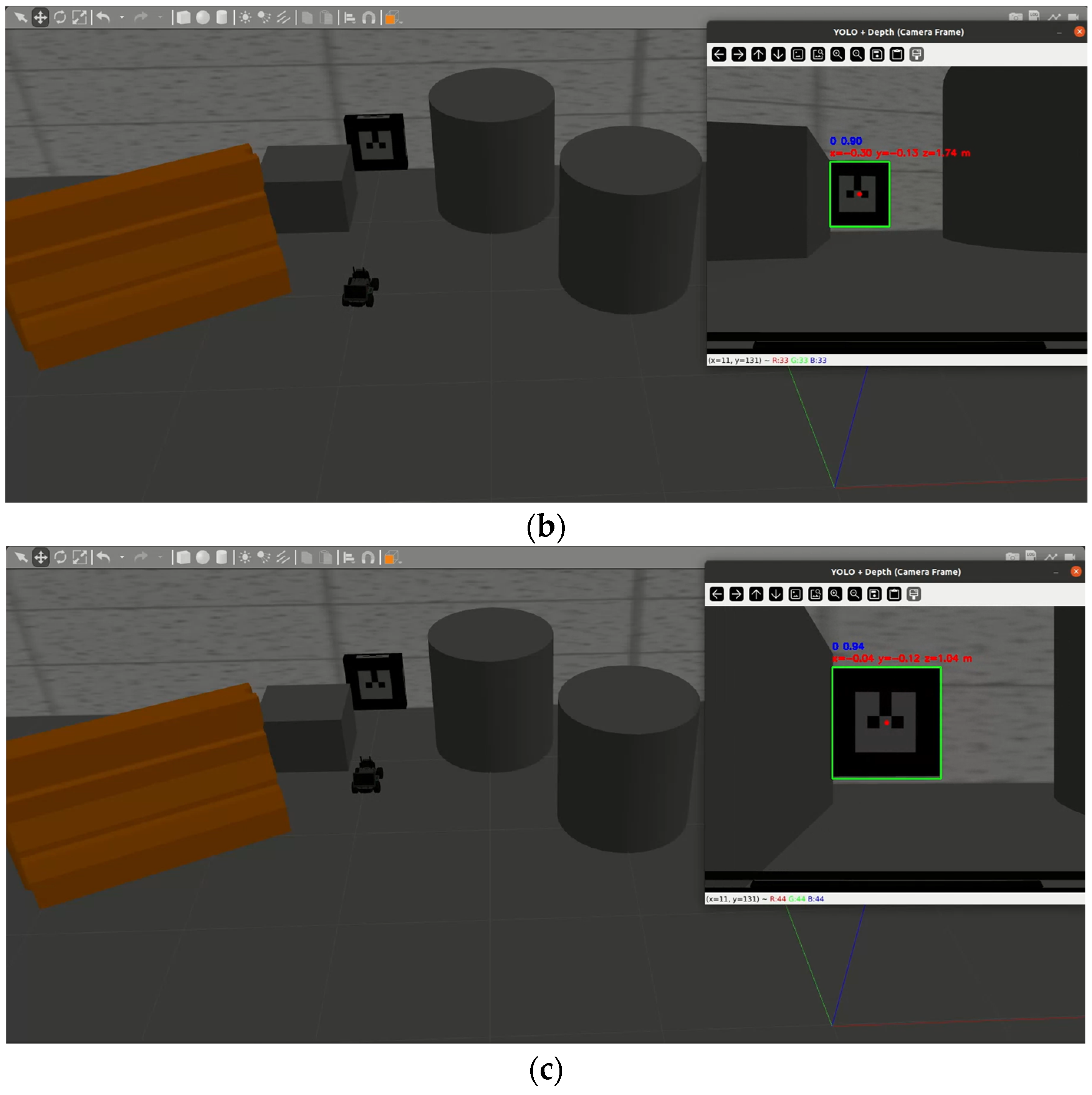
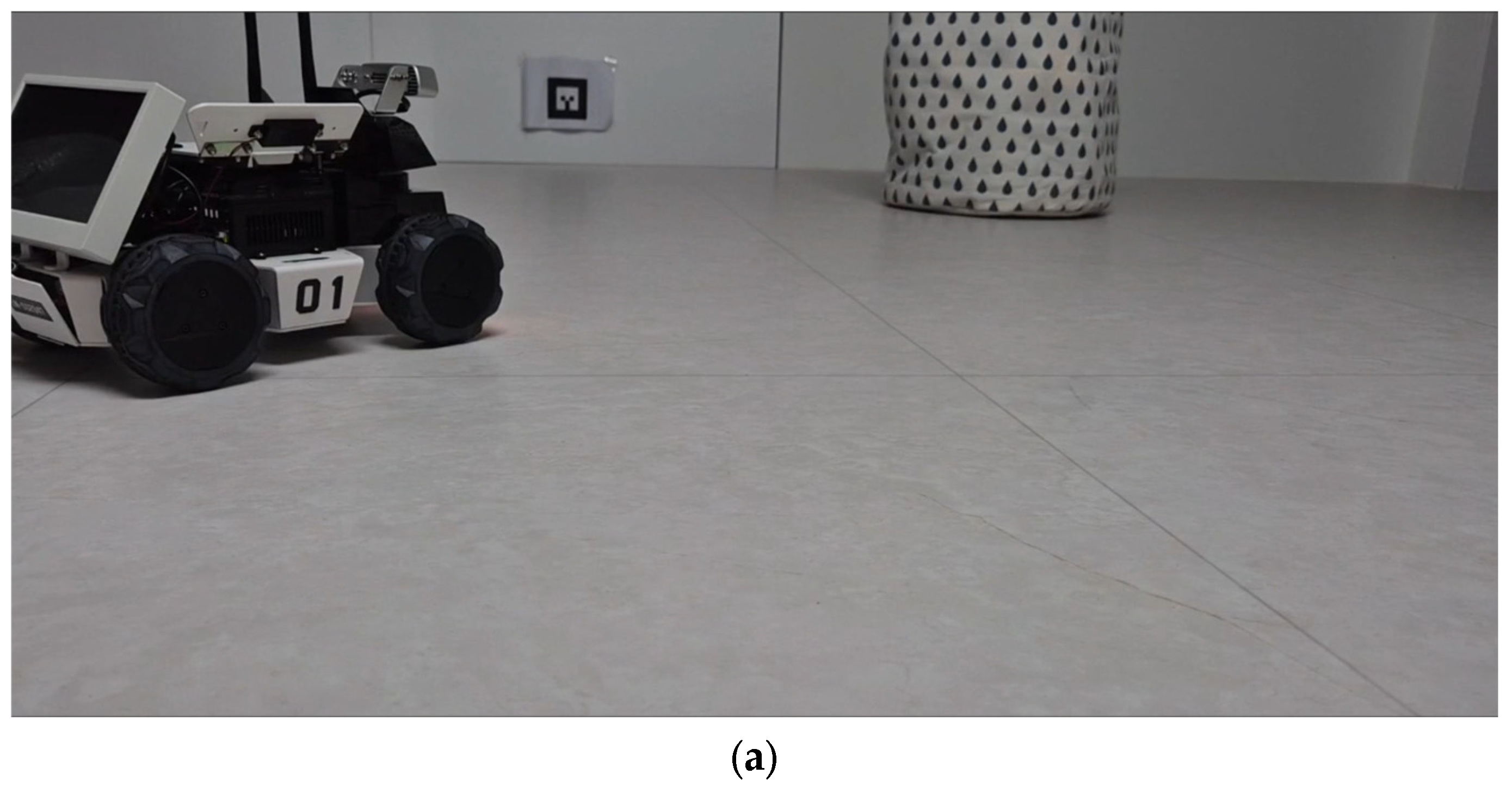
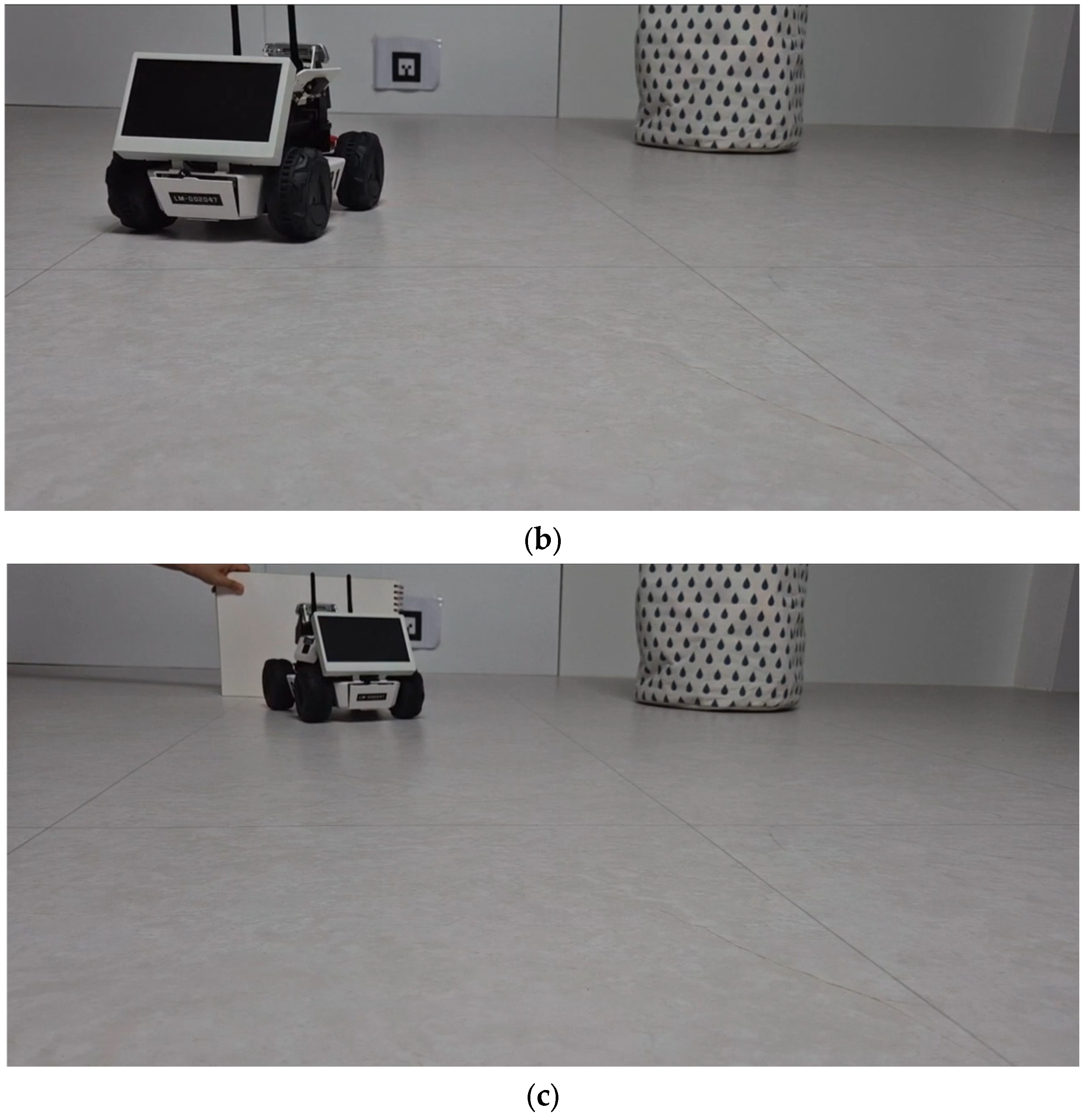
3.2. Sim-to-Real-Based Docking Deployment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMRs | Autonomous mobile robots |
| PPO | Proximal policy optimization |
| RL | Reinforcement learning |
| ROS | Robot operating system |
References
- Vongbunyong, S.; Thamrongaphichartkul, K.; Worrasittichai, N.; Takutruea, A. Automatic precision docking for autonomous mobile robot in hospital logistics-case-study: Battery charging. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Afaq, M.; Ripka, B.; Huda, Q.; Ahmad, R. Vision- and Lidar-Based Autonomous Docking and Recharging of a Mobile Robot for Machine Tending in Autonomous Manufacturing Environments. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hercik, R.; Byrtus, R.; Jaros, R.; Koziorek, J. Implementation of Autonomous Mobile Robot in SmartFactory. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Temeltas, H. A multi-stage localization framework for accurate and precise docking of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). Robotica 2024, 42, 1885–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragapane, G.; de Koster, R.; Sgarbossa, F.; Strandhagen, J.O. Planning and control of autonomous mobile robots for intralogistics: Literature review and research agenda. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 294, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Huang, Y.; Huber, S.; Coros, S. Budget-optimal multi-robot layout design for box sorting. arXiv 2025, arXiv:22412.11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Mo, H. Deep Learning-Based Multi-Modal Fusion for Robust Robot Perception and Navigation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.19002. https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.19002. [Google Scholar]
- Lbiyemi, M.O.; Olutimehin, D.O. Revolutionizing logistics: The impact of autonomous vehicles on supply chain efficiency. Int. J. Sci. Res. Updates 2024, 8, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosari, A.; Jahanshahi, H.; Razavi, S.A. An optimal fuzzy PID control approach for docking maneuver of two spacecraft: Orientational motion. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.N.; Lexau, A.; Lekkas, M.; Breivik, M. Nonlinear PID Control for Automatic Docking of a Large Container Ship in Confined Waters Under the Influence of Wind and Currents. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, H.; Dong, F.; Liu, X.; Lin, C. A Lightweight Model for Shine Muscat Grape Detection in Complex Environments Based on the YOLOv8 Architecture. Agronomy 2025, 15, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, S.; Xiong, A.; Yang, Y. Enhanced YOLOv8 With VTR Integration: A Robust Solution for Automated Recognition of OCS Mast Number Plates. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 179648–179663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telepov, A.; Tsypin, A.; Khrabrov, K.; Yakukhnov, S.; Strashnov, P.; Zhilyaev, P.; Rumiantsev, E.; Ezhov, D.; Avetisian, M.; Popova, O.; et al. FREED++: Improving RL Agents for Fragment-Based Molecule Generation by Thorough Reproduction. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.09840. https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.09840. [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk, S.; Lanza, L.; Worthmann, K.; Lux-Gottschalk, K. Reinforcement Learning for Docking Maneuvers with Prescribed Performance. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Luo, X. Autonomous Docking of the USV using Deep Reinforcement Learning Combine with Observation Enhanced. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering and Computer Applications (AEECA), Dalian, China, 27–28 August 2021; pp. 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-C.; Yang, B.-J.; Lin, C.-J. Applying Reinforcement Learning for AMR’s Docking and Obstacle Avoidance Behavior Control. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderlini, E.; Parker, G.G.; Thomas, G. Docking Control of an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle Using Reinforcement Learning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. An Evaluation of DDPG, TD3, SAC, and PPO: Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Controlling Continuous System. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Data Science, Advanced Algorithm and Intelligent Computing (DAI 2023), Shanghai, China, 24–26 November 2024; pp. 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, J.; Muknahallipatna, S. A Comparison of PPO, TD3 and SAC Reinforcement Algorithms for Quadruped Walking Gait Generation. J. Intell. Learn. Syst. Appl. 2023, 15, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stączek, P.; Pizoń, J.; Danilczuk, W.; Gola, A. A Digital Twin Approach for the Improvement of an Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR’s) Operating Environment—A Case Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, J. A Review on Digital Twin for Robotics in Smart Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 17th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Chengdu, China, 16–19 December 2022; pp. 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szybicki, D.; Pietruś, P.; Burghardt, A.; Kurc, K.; Muszyńska, M. Application of Digital Twins in Designing Safety Systems for Robotic Stations. Electronics 2024, 13, 4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Y.; Lee, K. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Autonomous Docking with Multi-Sensor Perception in Sim-to-Real Transfer. Processes 2025, 13, 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092842
Dai Y, Lee K. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Autonomous Docking with Multi-Sensor Perception in Sim-to-Real Transfer. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092842
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Yanyan, and Kidong Lee. 2025. "Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Autonomous Docking with Multi-Sensor Perception in Sim-to-Real Transfer" Processes 13, no. 9: 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092842
APA StyleDai, Y., & Lee, K. (2025). Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Autonomous Docking with Multi-Sensor Perception in Sim-to-Real Transfer. Processes, 13(9), 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092842





