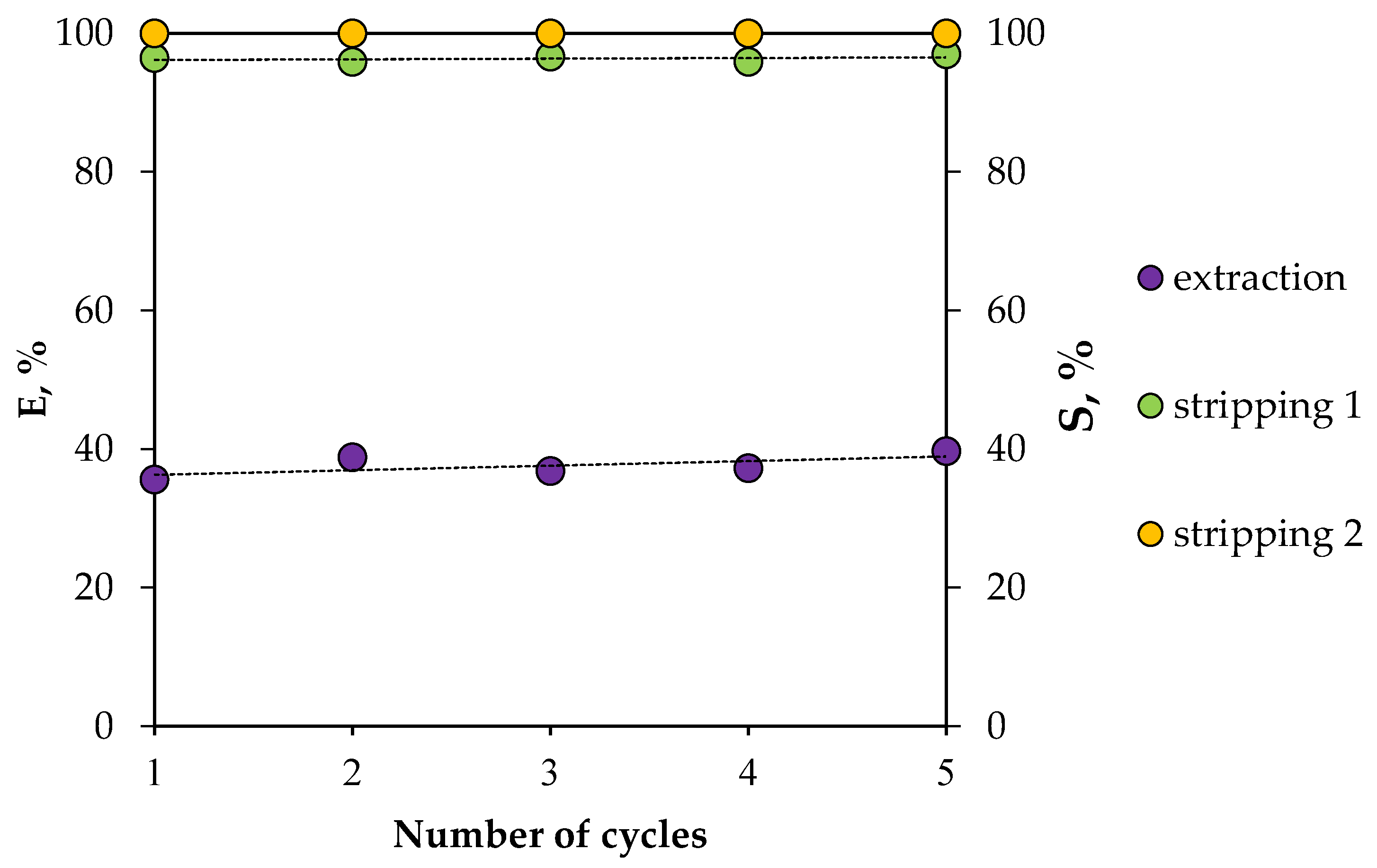Abstract
A pressing scientific task is the development of modern extractants that meet the increased requirements for efficiency and safety. In this work, a new three-component eutectic solvent based on bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid (BTMPPA), tributyl phosphate (TBP) and phenol was proposed. The formation of the eutectic solvent was confirmed by IR and 31P NMR spectroscopy. The temperature dependences of the main physical properties of the proposed eutectic solvent—the refractive index, density and viscosity—were determined. For the first time, the extraction properties of the eutectic solvent BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) were studied using the example of the extraction of metal ions from aqueous nitrate solutions. The extraction efficiencies of Pr, Nd and Dy in a single stage were 34, 38 and 81%, respectively. The extraction behaviour of Pr, Nd and Dy with the eutectic solvent BTMPPA/TBP/phenol was studied as a function of pH, salting-out agent concentration, component ratio in the eutectic mixture, phase volume ratio, etc. Nitric acid with a concentration of 0.5 mol/L was chosen as a stripping agent, and the chemical stability of the eutectic solvent BTMPPA/TBP/phenol during extraction–stripping cycles was evaluated. In summary, the proposed hydrophobic eutectic solvent has good physical characteristics and enables a more efficient recovery of rare-earth elements from nitrate solutions.
1. Introduction
Currently, the majority of hydrometallurgical processes include a liquid–liquid extraction stage, and promising new-generation extraction systems are continually being developed [1,2,3,4]. Modern extractants are subject to numerous requirements, such as stability, low cost and availability. There is growing interest in environmentally safer syst-ems that are less volatile and flammable, are non-toxic and do not require complex or hazardous production methods [5,6]. Therefore, new extractants that can solve technological challenges more effectively are actively being developed.
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs), proposed by Abbott in 2003 [7], represent a modern class of extractants. DESs are two- or multi-component mixtures of hydrogen bond donors and acceptors [8]. They are eutectic solvents whose components demonstrate enthalpy-driven negative deviations from thermodynamic ideality, and they are characterised by tuneable physicochemical properties, ease of preparation and low flammability [9]. Since the discovery of eutectic solvents, the prospects for their practical application have been actively studied; this has included their use as novel extractants for the extraction of metals [10,11,12,13], organic compounds [14,15], etc.
Numerous works have dealt with the synthesis, study of the physicochemical properties and application of two-component deep eutectic solvents [16,17,18,19]. Interest in three-component hydrophobic eutectic solvents (HESs) has recently increased, as the introduction of an additional component into the composition enables broad modulation of the physical properties of the resulting solvent and enhances its selectivity or other characteristics [20,21].
Three-component hydrophobic eutectic solvents have been described in the literature [22,23,24] as promising extractants for the extraction of rare-earth elements (REEs) from aqueous solutions. For example, an HES based on lauryl alcohol, myristyl alcohol and trioctylphosphine oxide was studied as an extractant for Co, Fe, Pr, Nd and Dy from nitrate solutions [22]. The three-component HES with a lauryl alcohol/myristyl alcohol/trioctylphosphine oxide (5:5:4) composition showed greater efficiency in the extraction of REEs than a two-component HES comprising the same components, and it enabled their separation from Fe.
Previously, the authors proposed [25] an HES with a bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)dithiophosphinic acid/trioctylphosphine oxide/menthol (1:1:2) composition that was used as an extractant for Pr, Nd and Eu from nitrate solutions. This HES was shown to be a more efficient extractant than a two-component HES with bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)dithiophosphinic acid/menthol and trioctylphosphine oxide/menthol, and it demonstrated a synergistic effect.
A series of HESs based on bis(2-ethylhexyl)amine, 1-decanol and a number of carboxylic acids were used as promising extractants for the separation of Y from heavy REEs. An HES with a composition of 1-decanol/oleic acid/bis(2-ethylhexyl)amine (9:1:5) showed a high separation factors for heavy REEs (Dy-Lu) and Y in an industrial Y-enriched solution: Dy/Y ≥ 3.05, Ho/Y ≥ 3.37, Er/Y ≥ 4.29, Tm/Y ≥ 6.00, Yb/Y ≥ 10.8 and Lu/Y ≥ 11.2 [23].
Previously [26,27], the authors proposed a deep eutectic solvent with a bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid/phenol (1:3) composition, and they studied its extraction ability with respect to a wide range of REEs. The solvent was found to have a high extraction efficiency for heavy rare-earth elements and was able to separate subgroups of light and heavy REEs. The current paper proposes a new hydrophobic eutectic solvent with a BTMPPA/TBP/phenol composition, where TBP is introduced into the composition to improve its physical properties, reduce the concentration of BTMPPA and phenol, and study the effect of TBP on the extraction ability of the HES with respect to a series of REEs. Praseodymium, neodymium and dysprosium nitrate solutions were chosen as model objects, since they are the main, and widespread, impurity components in neodymium magnets and there is a promising technological process for their refinement [28,29].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
Pr(NO3)3∙6H2O (99.9%), Nd(NO3)3∙6H2O (99.9%) and Dy(NO3)3∙6H2O (99.9%) were purchased from LANHIT, Moscow, Russia. Solutions of nitrates of rare-earth metals were prepared by dissolving precisely weighed portions of these salts in distilled water. HNO3 (65%, Aldosa, Moscow, Russia), HCl (37%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), H2SO4 (98%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and NaNO3 (99%, Chimmed, Moscow, Russia) were used as a stripping agent, as a salting-out agent and to create acidity in the aqueous phase, respectively. Bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid (90%, Macklin, Shanghai, China), phenol (99%, Chimmed, Moscow, Russia) and tributyl phosphate (97%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) were used to prepare eutectic solvents. Hydranal Coulomat AG, AK and Hydranal Titrant 2 and Solvent for volumetric Karl Fischer titration were purchased from Honeywell Inc. (Morristown, NJ, USA).
2.2. Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent Synthesis
To synthesise eutectic mixtures, the initial reagents used were mixed in the required molar ratio. For this purpose, the reagents were weighed on AND HR-100AZ (A&D, Tokyo, Japan) analytical scales and placed into 50 mL plastic tubes. The tubes were then placed in a thermostatically controlled Enviro-Genie SI-1202 shaker (Scientific Industries, Inc., Bohemia, NY, USA, accuracy ± 0.2 °C) and stirred for 15 min at a rate of 35 rpm at 65 °C until a homogeneous liquid mixture formed. The resulting mixture was cooled to room temperature. The following mixture was used: BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2), where CBTMPPA = CTBP = 1.309 mol/L.
2.3. Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent Characterisation
FTIR spectra in the range of 4000 to 600 cm−1 were recorded on an IRTracer-100 spectrometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with a diamond crystal ATR accessory. The density of the HES was determined within the temperature range of 15 to 60 °C using an Anton Paar DMA 1001 (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) with an accuracy of ±0.0001 g·cm−3. The refractive indices of the HES were measured using an Anton Paar Abbemat 3200 refractometer (Anton Paar, Graz, Austria) with an accuracy of ±0.0001. HES viscosity was studied by rotational viscometry on a ROTAVISC lo-vi instrument with an ELVAS-1 adapter spindle set (IKA, Staufen im Bresgau, Germany); the rotational speed of the spindle was 5 rpm. 1H and 31P NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Fourier 300 HD (300 MHz Billerica, MA, USA. The Karl Fischer coulometric and volumetric titration method was performed using a T-40VC Karl Fischer titrator (NANBEI, Zhengzhou, China).
2.4. Extraction Experiments
All experiments for the study of metal extraction were performed at 298 K, under an atmospheric pressure of ~100 kPa and in 15 mL graduated centrifuge tubes, using an Enviro-Genie SI-1202 shaker thermostat (Scientific Industries Inc., Bohemia, NY, USA). The volume ratio of the aqueous and organic phases was 1:1. The concentration of metal ions in the stock solution was 0.01 mol/L; the initial pH value of the aqueous phase was 4 to 5. After mixing, the samples were placed in a SIA ELMI CM-6MT centrifuge (Elmi, Riga, Latvia) for 5 min at 2500 rpm for the complete separation of phases. The aqueous and organic phases were then separated. The concentration of metal ions in the stock solution and in the aqueous phase after extraction was determined spectrophotometrically at 568 to 574 nm [30]. The concentration of the metal in the organic phase was determined by the difference between its concentration in the stock solution and that in the aqueous phase after extraction. The concentration of nitrate ions in the initial solution and in the aqueous phase after extraction was determined spectrophotometrically at 301 nm. The concentration of phenol in the aqueous phase after extraction was measured on a Cary-60 spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The relative error of the spectrophotometric measurements was less than 5%.
The pH values of the aqueous phase before and after extraction were determined using an OHAUS Starter 5000 pH meter (Parsippany, NJ, USA) with an STMICRO5 (Parsippany, NJ, USA) combined glass electrode.
The metal extraction efficiency (E%) was determined using the following equation:
where CMe(in) and CMe(aq) are the concentrations of the metal ions in the aqueous phase before and after extraction (mol/L), respectively, and Vin and Vaq are the volumes of the aqueous phase before and after extraction (L), respectively.
The distribution ratio (D) was determined using the following equation:
where CMe(aq) and CMe(org) are the concentrations of metal ions in the aqueous and organic phases after extraction, respectively.
The metal stripping efficiency (S%) was determined using the following equation:
The separation factor (SF) was determined using the following equation:
where DMe1 and DMe2 are the distribution ratios.
The experimental data presented here are the results of three experiments, processed using methods of mathematical statistics. Standard deviation (SD) calculations are shown in Tables S1 and S2.
3. Results
BTMPPA, TBP and phenol were chosen for the preparation of eutectic solvents. Their structural formulas are presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Structural formulas of the initial components of the HES.
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of the Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent BTMPPA/TBP/Phenol
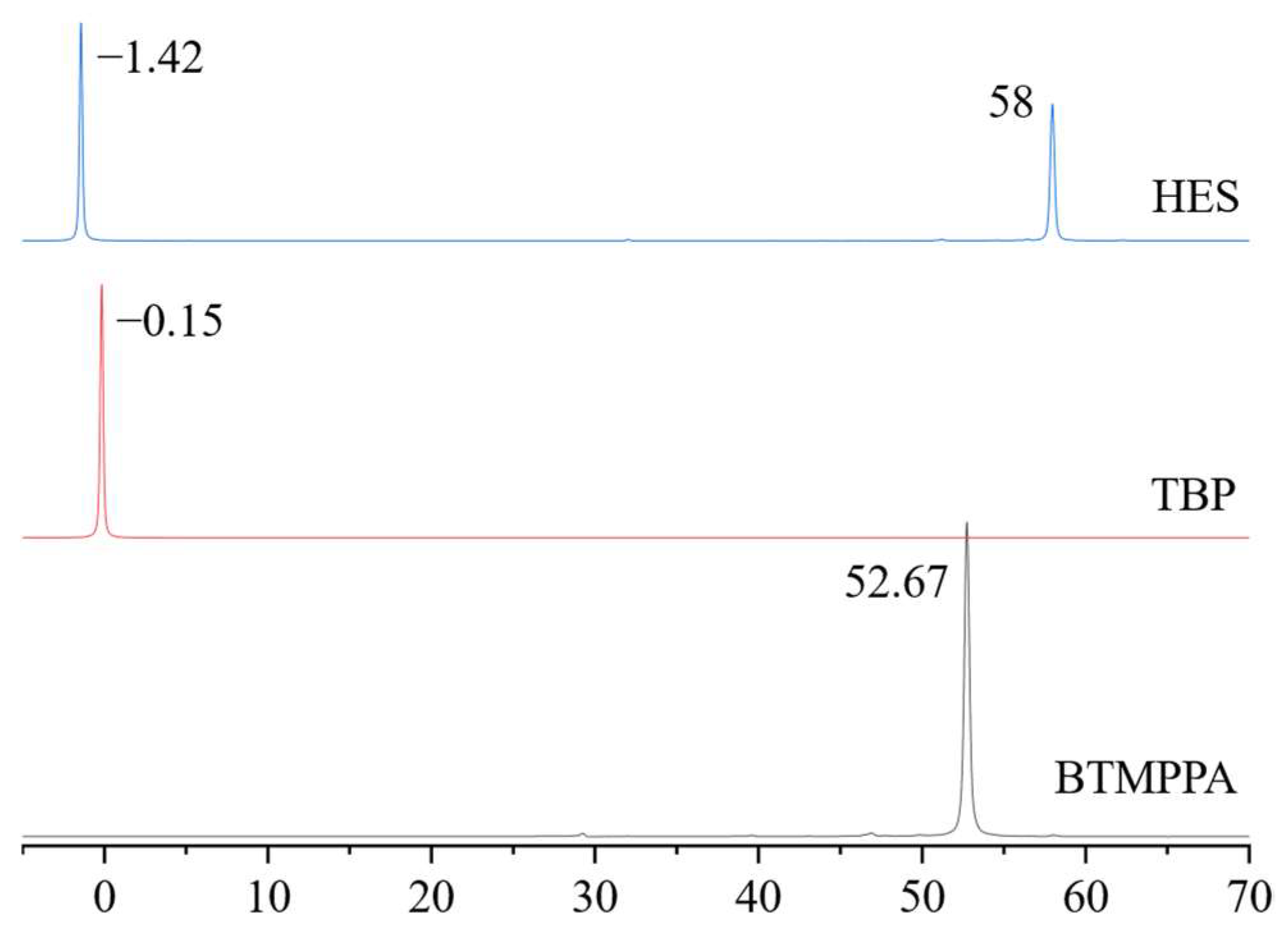
To establish the intermolecular interactions between the components in the mixture, a comparative analysis of the 31P NMR spectra of tributyl phosphate and BTMPPA, both as individual compounds and in the composition of the HES with phenol in a 1:1:2 BTMPPA/TBP/phenol molar ratio, was carried out. Figure 2 shows a characteristic shift in the signal of the BTMPPA phosphorus atom at the P-OH bond from 52.7 to 58 ppm and a shift in the TBP phosphorus signal from −0.15 to −1.42 ppm, indicating the existence of intermolecular interactions between BTMPPA, TBP and phenol. A similar effect has been described previously in the HES spectra of BTMPPA/menthol [31], TOPO/thymol [32] and other HESs.
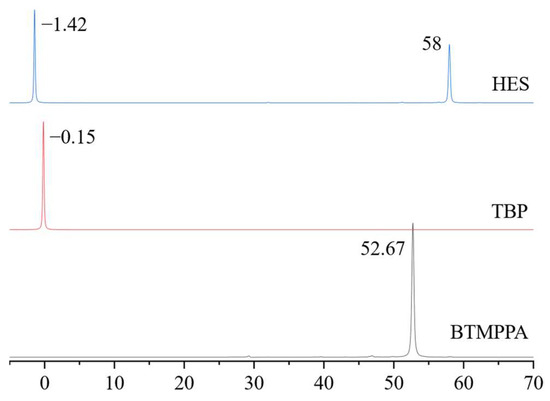
Figure 2.
31P NMR spectra of the HES and its components.
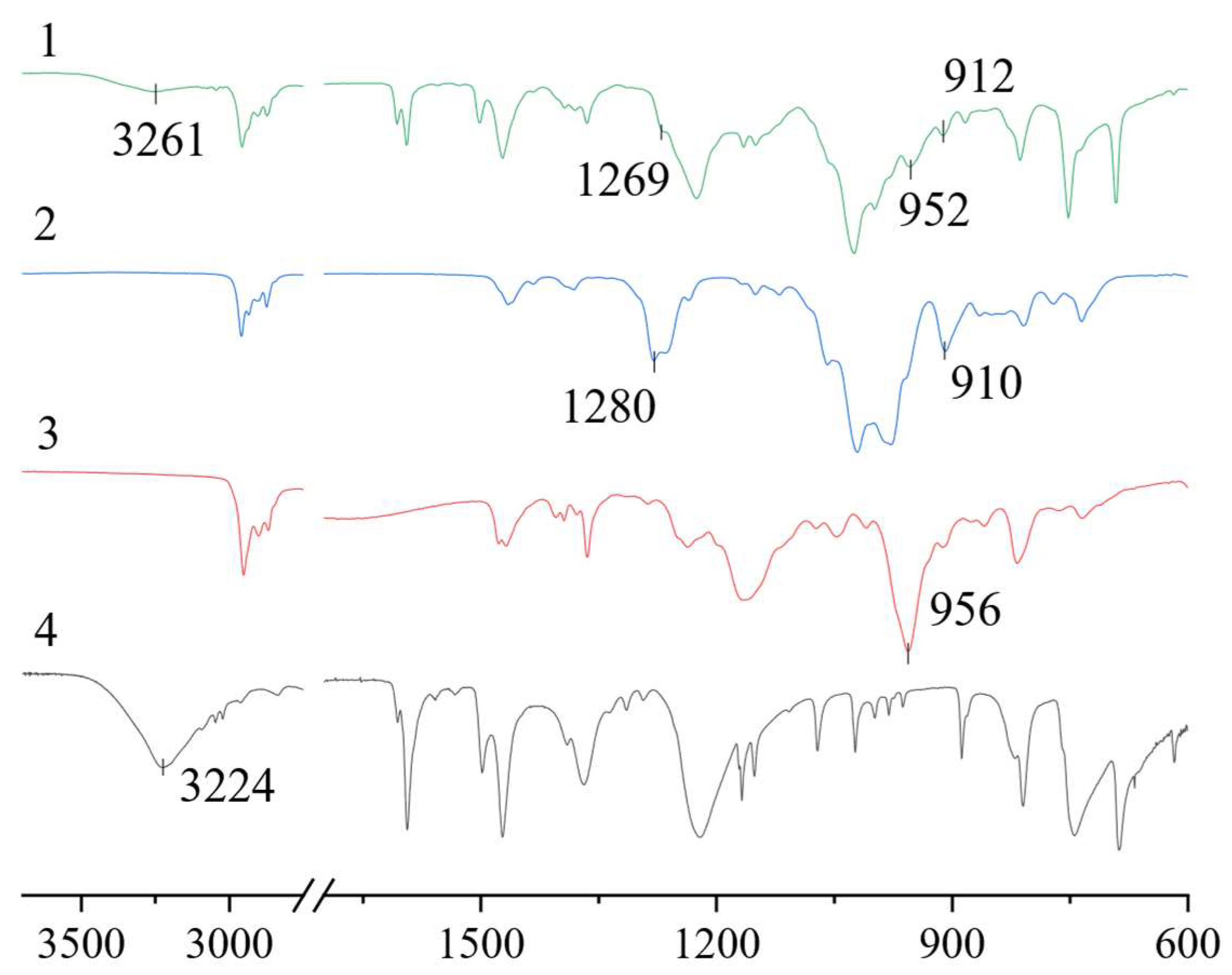
The features of hydrogen bond formation in a eutectic solvent were studied using IR spectroscopy. A comparison of the spectra of individual components and the HES obtained was made. It can be seen that, in the BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) spectrum, there is a shift in the position of the peaks of some characteristic groups relative to the position of the peaks in the pure components (Figure 3). The spectra show a shift in the stretching vibrations of the -OH group of phenol towards higher frequencies, from 3224 cm−1 in pure phenol to 3261 cm−1 in the HES. The peak of the P-O-H stretching vibrations in BTMPPA also shifts, from 956 to 952 cm−1. A shift in the P=O vibrations in TBP, from 1280 to 1269 cm−1, can also be observed. The presence of such shifts can be associated with interactions between all three components of the HES. Neither a shift in peaks nor the disappearance or formation of new vibration peaks can be observed in other parts of the spectrum, indicating the absence of other interactions between the mixture components and the lack of formation of new compounds.
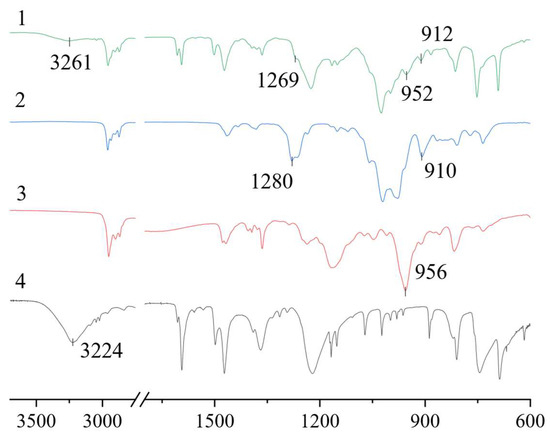
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1), TBP (2), BTMPPA (3) and phenol (4).
3.2. Stability of the BTMPPA/TBP/Phenol (1:1:2) HES upon Interaction with Water and Mineral Acid Solutions
Experiments were carried out to study the stability of the proposed HES BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) upon interaction with water and HCl, HNO3 and H2SO4 solutions. The water content in the hydrophobic eutectic solvent after preparation and after the extraction experiments was measured using coulometric and volumetric Karl Fischer titration. The water content before the extraction experiments was 0.97% (wt.), and after the extraction and recovery of the extractant, it increased to 1.267% (wt.).
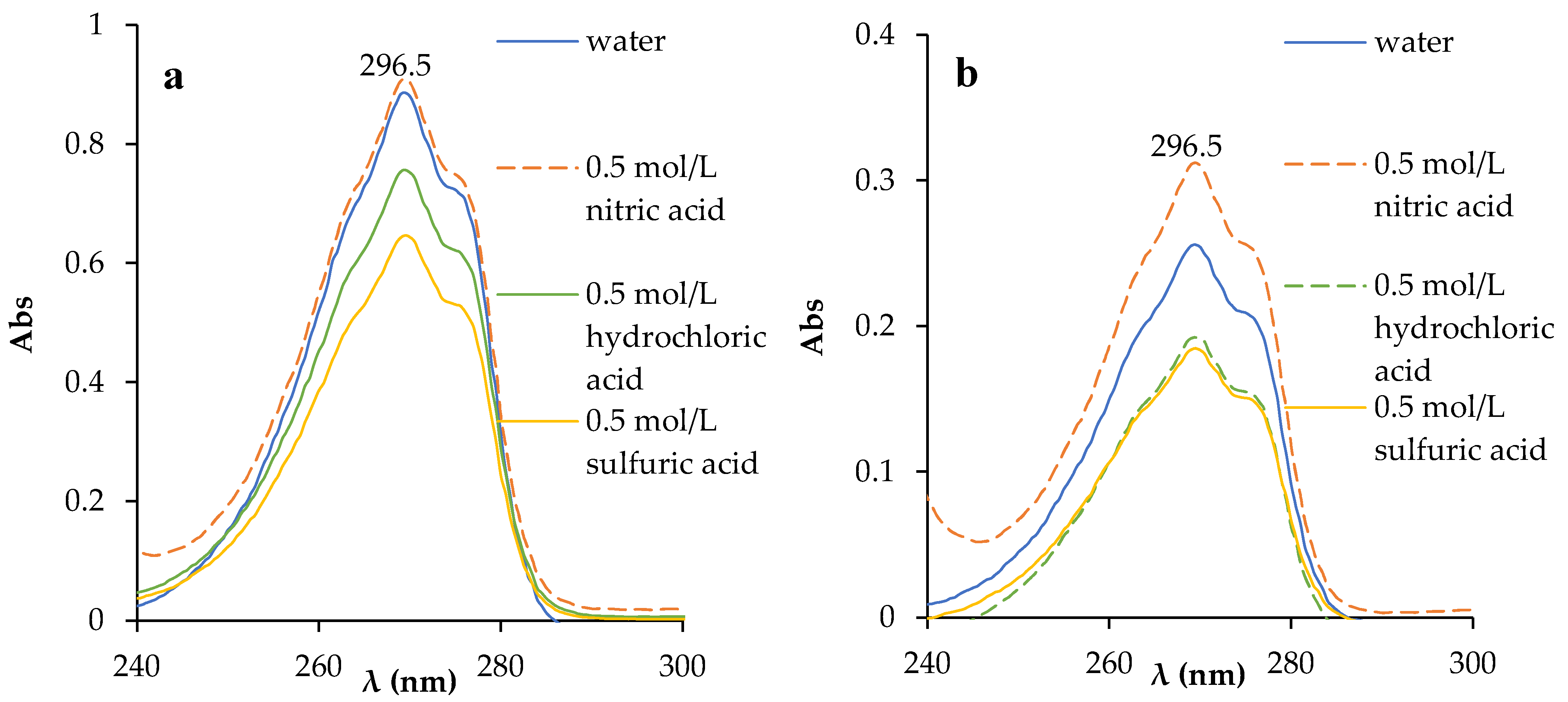
The interfacial transition of phenol from the organic phase to the aqueous phase upon interaction with water and 0.5 mol/L nitric acid, hydrochloric and sulfuric acid solutions was evaluated by UV absorption spectroscopy. Absorption spectra were obtained after interaction with the aqueous phase in a 1:1 volume ratio for 24 h (Figure 4). In both cases, an increase in the amount of phenol in the aqueous phase was observed. Using the linear equation from the calibration plot (Equation (S1)), the concentration of phenol in the aqueous phase after phase contact was determined (Table 1). The calculated values of phenol transfer from the organic phase to aqueous solutions were less than 0.02%. A comparative analysis of the two HESs showed that the addition of TBP to the two-component HES improved its physicochemical properties by reducing the solubility of its components in the aqueous phase, thereby preventing their significant loss during repeated use in a chemical process.
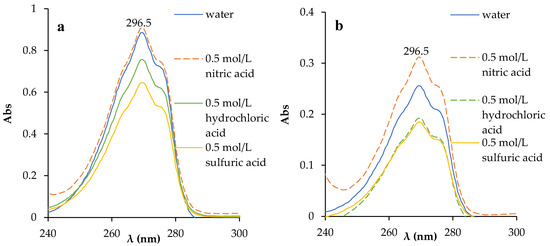
Figure 4.
Absorption spectra of the aqueous phase after the interaction of BTMPPA/phenol (1:3) (a) and BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) (b) with water and mineral acid solutions.

Table 1.
Concentration of phenol in the aqueous phase after the interaction of the HES with water and mineral acids (A/O = 1).
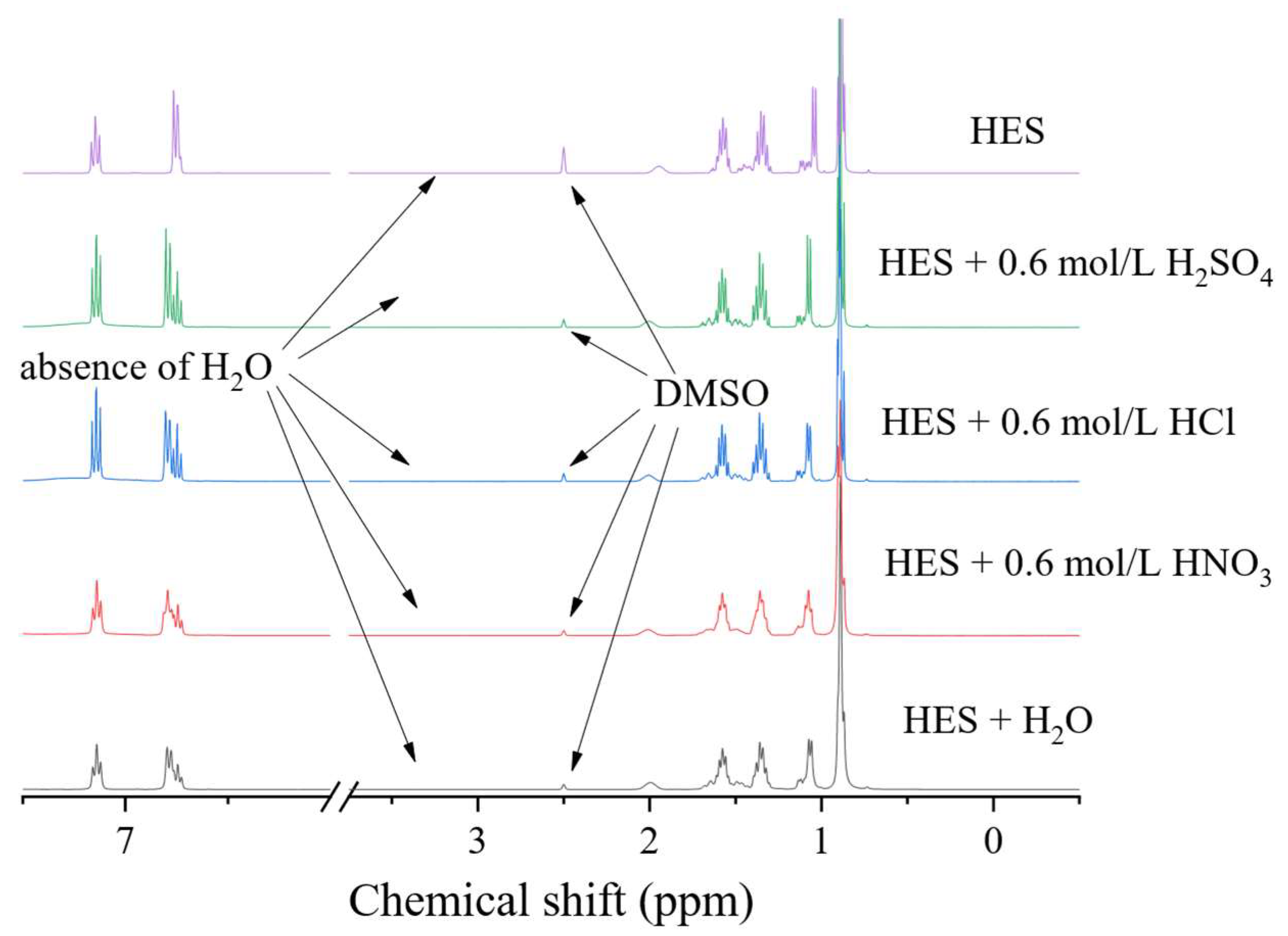
An important aspect is the stability of the eutectic solvent when interacting with mineral acids, since this determines the range of working pH values and establishes the possibility of their use as stripping agents. For this purpose, the eutectic solvent was shaken with the aqueous phase, in a 1:1 volume ratio, for 24 h at 25 °C. The organic phase was then separated and analysed using 1H NMR spectroscopy. As can be seen in Figure 5, after the interaction of the BTMPPA/TBP/phenol with water and solutions of HCl, H2SO4 and HNO3, no changes in, or degradation of, the solvent occurred. Evidence of this is the absence of any significant changes in the 1H NMR spectra. This indicates that water and these mineral acids can be used as stripping agents in concentrations not exceeding 0.6 mol/L.
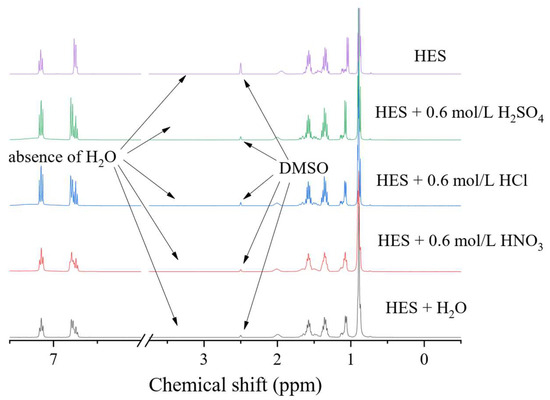
Figure 5.
1H NMR spectra of BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) before and after interaction with water and the HNO3 solution.
Thermal stability was also investigated during several heating and cooling cycles in the range from 25 to 80 °C, and no changes occurred in the IR spectra of the HES studied, which indicates its stability in this temperature range (Figure S1).
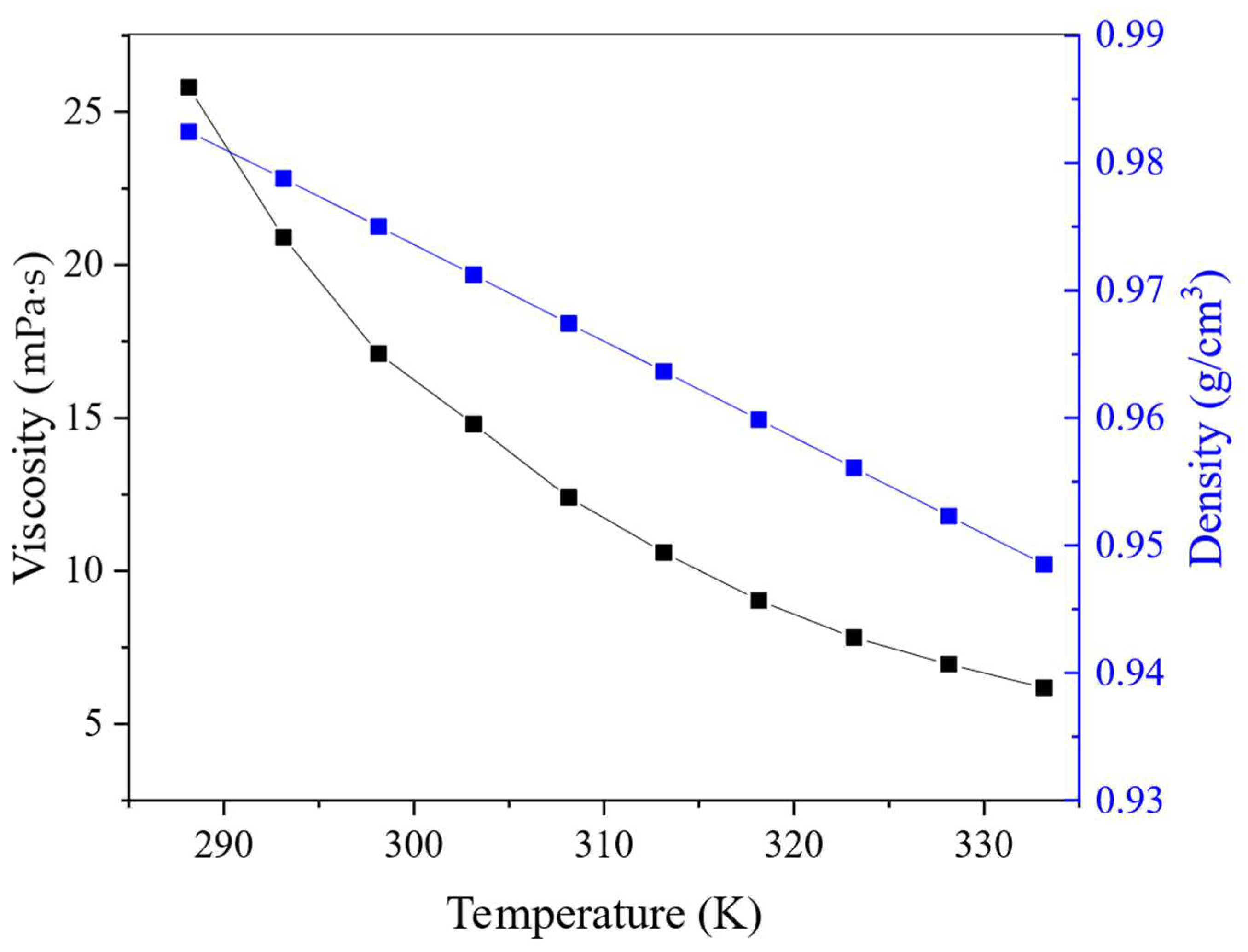
The effect of temperature on the viscosity, refractive index and density of the HES was also studied. These physical properties are important because of their influence on the rate of system delamination and the probability of emulsion formation during the extraction process, which are critical parameters when moving from laboratory research to the technological level. The dependence of the density and viscosity of BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) on temperature is presented in Figure 6, in which the viscosity values of the HES decrease exponentially with increasing temperature. Similar dependencies are demonstrated by many eutectic solvents, as presented in the literature [9]. Both the density (Figure 6) and refractive index (Figure S2) decreased linearly with increasing temperature, which is in good agreement with known literature data [33,34]. The HES had low density and viscosity throughout the studied range, which will improve the efficiency of mass transfer [35]. Moreover, the addition of TBP into the HES composition has a positive effect on its physical characteristics and reduces its viscosity. For example, a DES with a composition of BTMPPA/phenol (1:3) has a viscosity of 27.3 mPa·s at 25 °C [26], whereas the viscosity of an HES with a composition of BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) is as low as 17.1 mPa·s at the same temperature.
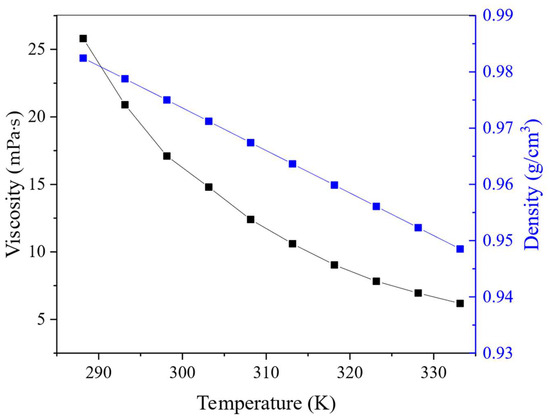
Figure 6.
Temperature effect on viscosity and density of HES.
3.3. REE Extraction from Nitrate Solutions with HES BTMPPA/TBP/Phenol
The dependences of the parameters of REE extraction using the proposed hydrophobic eutectic solvent BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) were studied, using praseodymium, neodymium and dysprosium ions as examples. Previously, the equilibrium values of the distribution coefficient and extraction degree of the trivalent metal ions under study, from nitrate solutions with the BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) HES, were determined (Table 2). The table shows that there was an increase in the recovery rate from 32.9% for Pr3+ to 81% for Dy3+, with a decrease in the ionic radius of the metal, in the REE series.

Table 2.
Quantitative characteristics of metal ion extraction from 0.01 mol/L solution using BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2).
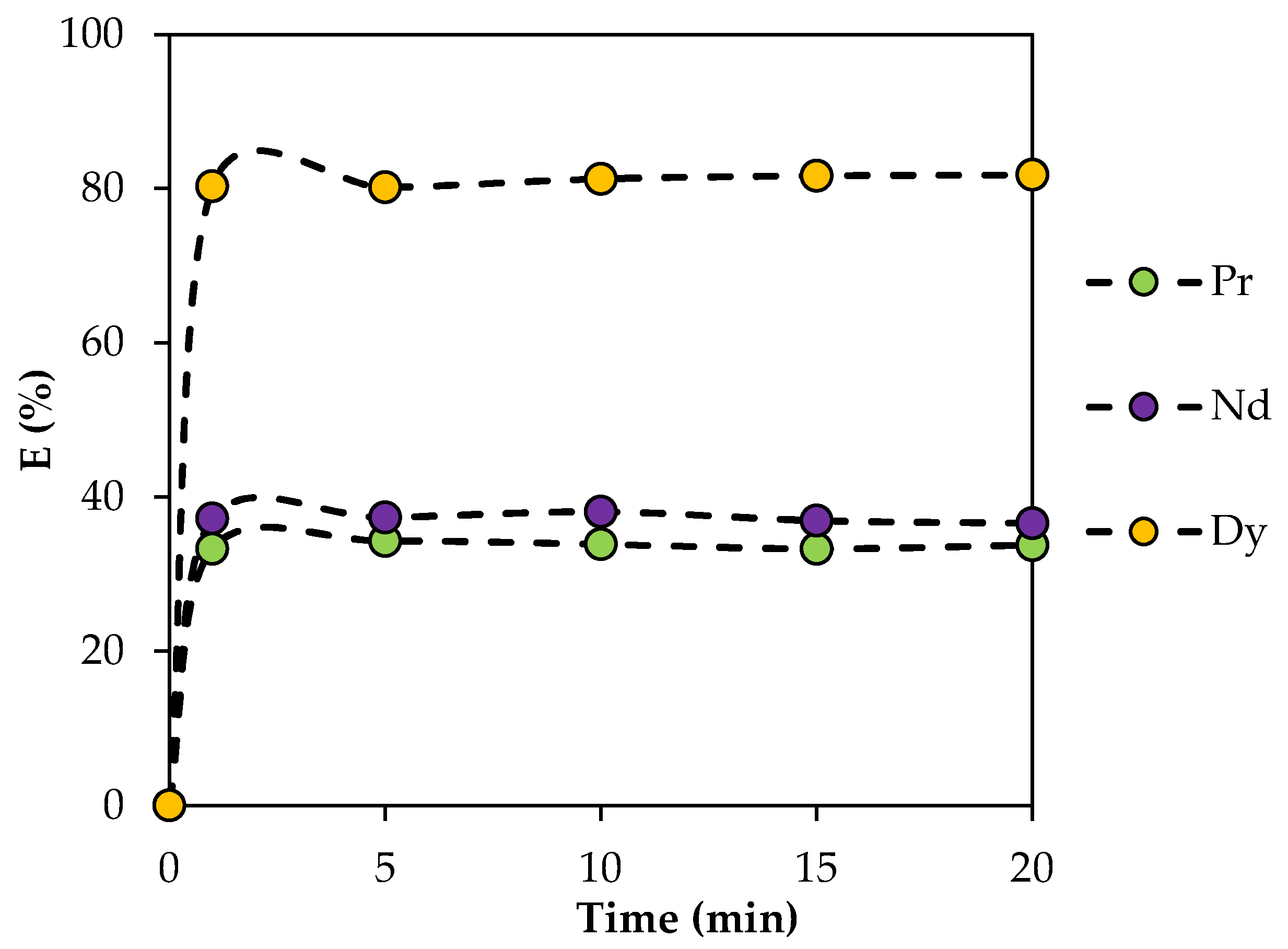
The dependence of the extraction efficiency on the phase contact time was studied in the range from 1 to 20 min. It was found that, from 0 to 1 min, there was a sharp increase in the extraction efficiency, which then stopped, with the dependence reaching a plateau after 5 min (Figure 7). This indicates the onset of thermodynamic equilibrium. All further experiments were carried out under thermodynamic equilibrium conditions, and a phase contact time of 15 min was chosen.
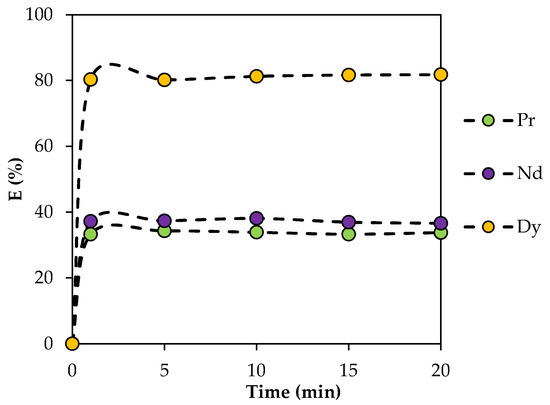
Figure 7.
Dependence of the rate of REE extraction with BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) on phase contact time. CMe(in) = 0.01 mol/L, A/O = 1, T = 25 °C.
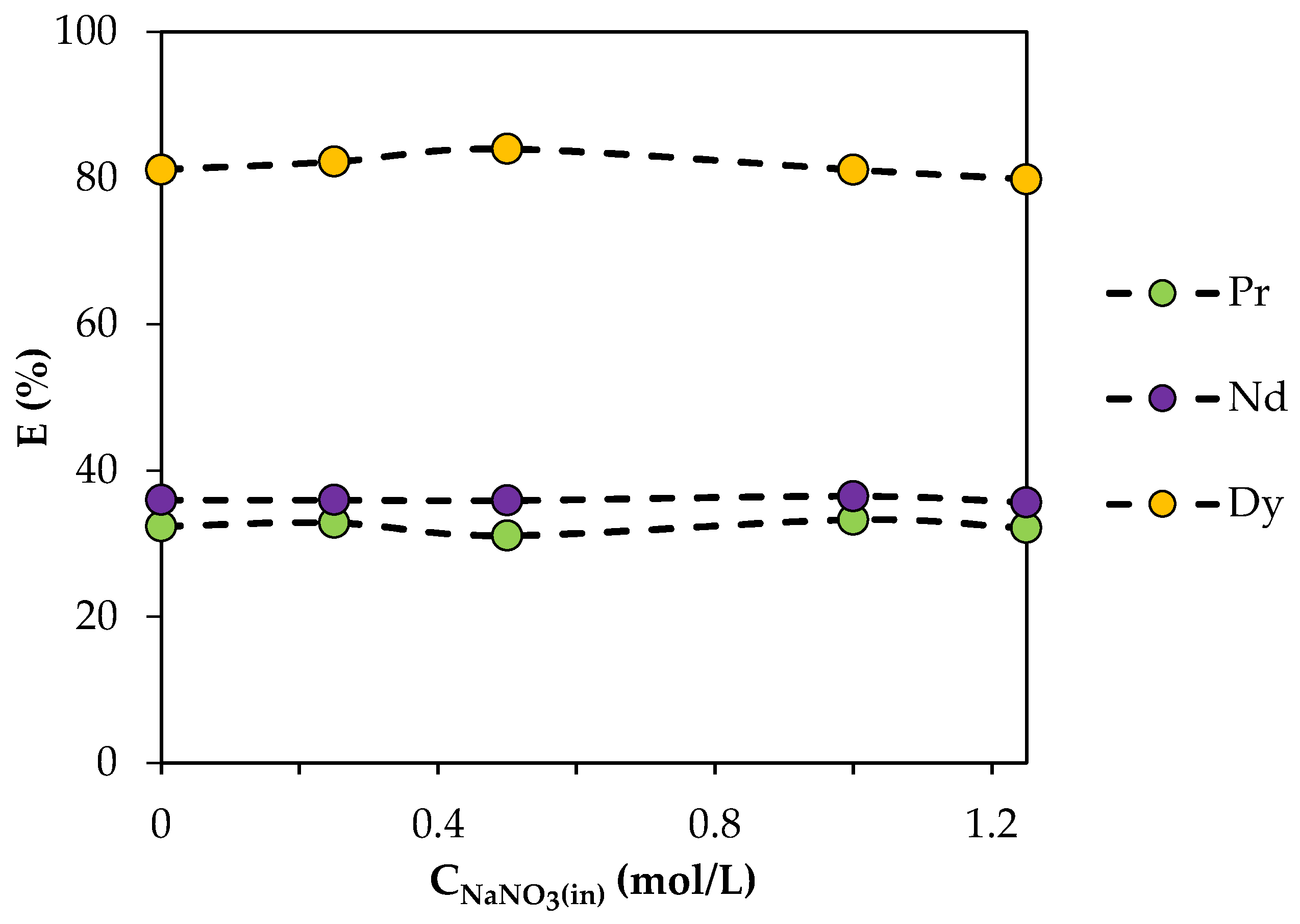
To determine the effect of the NO3− concentration, extraction characteristics were studied in a range of NaNO3 concentrations from 0.25 to 1.25 mol/L (Figure 8). The extraction efficiency remained almost unchanged with an increase in the NO3− concentration in the aqueous phase. This may indicate that NO3− ions were not involved in the extraction mechanism and were not part of the extracted compound.
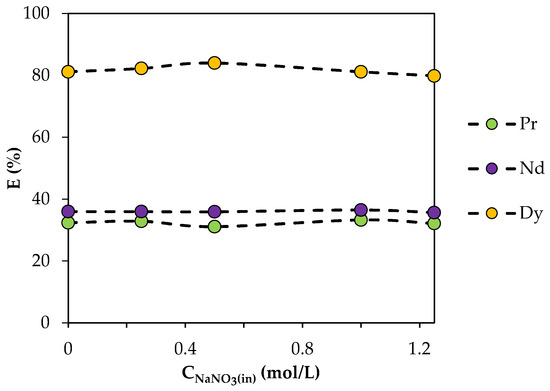
Figure 8.
Dependence of the degree of REE extraction by BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) on the initial NaNO3 concentration. CMe(in) = 0.01 mol/L, A/O = 1, T = 25 °C.
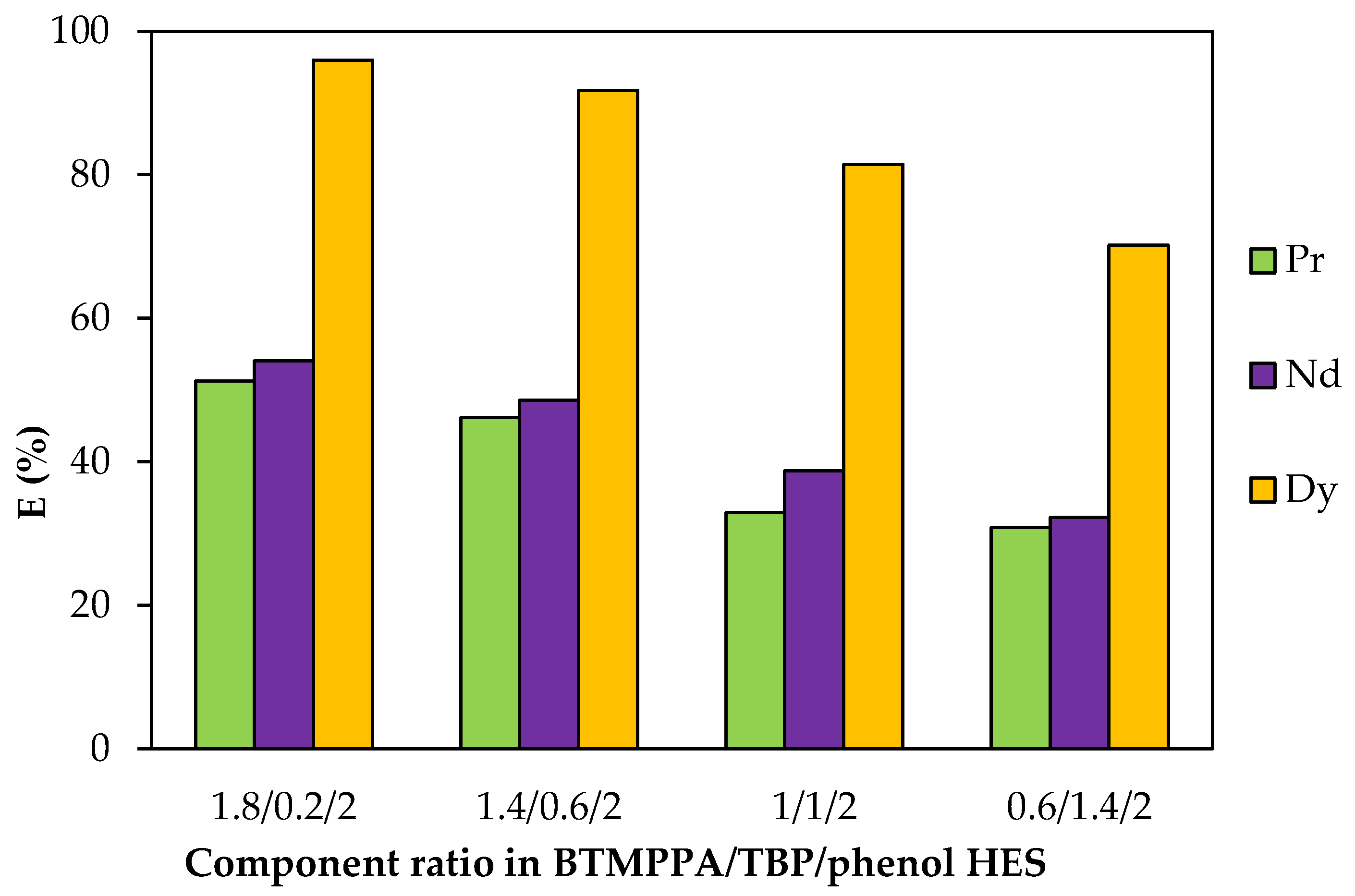
The dependence of the REE extraction efficiency on the component ratio in the HES was obtained and analysed. To vary the BTMPPA/TBP ratio, the concentration of dialkylphosphinic acid was varied within the range of 0.27 to 2.26 mol/L, while the concentration of TBP was varied within the range of 0.25 to 2.45 mol/L. The concentrations of the components of each of the compositions are summarised in Table S3. As the TBP content increased and the fraction of BTMPPA decreased, a reduction in the recovery of Pr3+ from 50 to 30%, of Nd3+ from 54 to 32% and of Dy3+ from 95.9 to 70% was observed (Figure 9). For the BTMPPA/TBP/phenol HES with a 0.2:1.8:2 molar ratio of the components, precipitation occurred during the extraction.
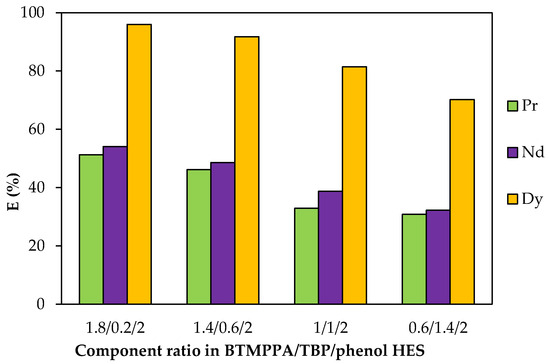
Figure 9.
Effect of the BTMPPA/TBP ratio on the REE recovery rate. CMe(in) = 0.01 mol/L, A/O = 1, T = 25 °C.
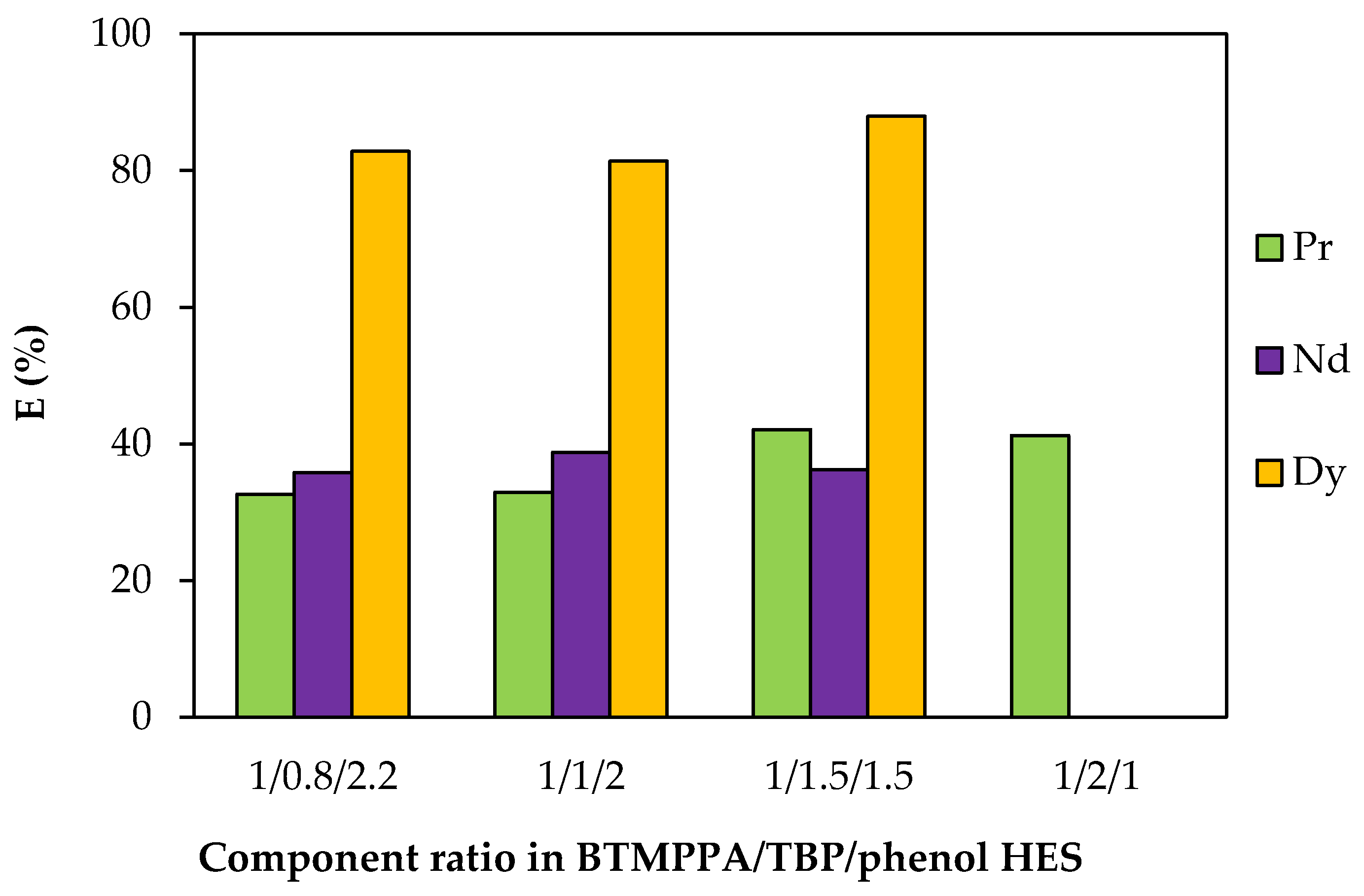
To vary the TBP/phenol ratio, the TBP concentration was varied from 1.11 to 2.64 mol/L (Table S3). An insignificant change in the extraction efficiency of REE ions with an increase in the fraction of TBP and a corresponding decrease in the fraction of phenol was observed (Figure 10). With an increase in the proportion of TBP in the HES composition, the formation of a third phase at the interface was observed during extraction. For the BTMPPA/TBP/phenol HES with a molar ratio of 1:2:1, this occurred only during the extraction of Nd and Dy; with a further increase in the proportion of TBP, the formation of a third phase was observed during the extraction of all the REEs studied. In this regard, the extraction efficiency under these conditions was not determined. Increasing the TBP concentration does not result in a decrease in the REE extraction efficiency and may positively affect HES viscosity, but precipitation during the metal extraction process limits the possible fraction of TBP in the composition of the ternary HES.
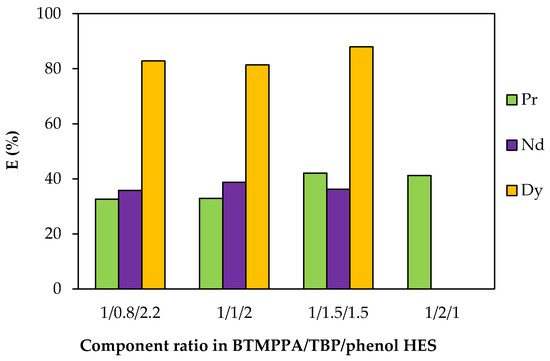
Figure 10.
Effect of the TBP/phenol ratio on the REE recovery rate. CMe(in) = 0.01 mol/L, A/O = 1, T = 25 °C.
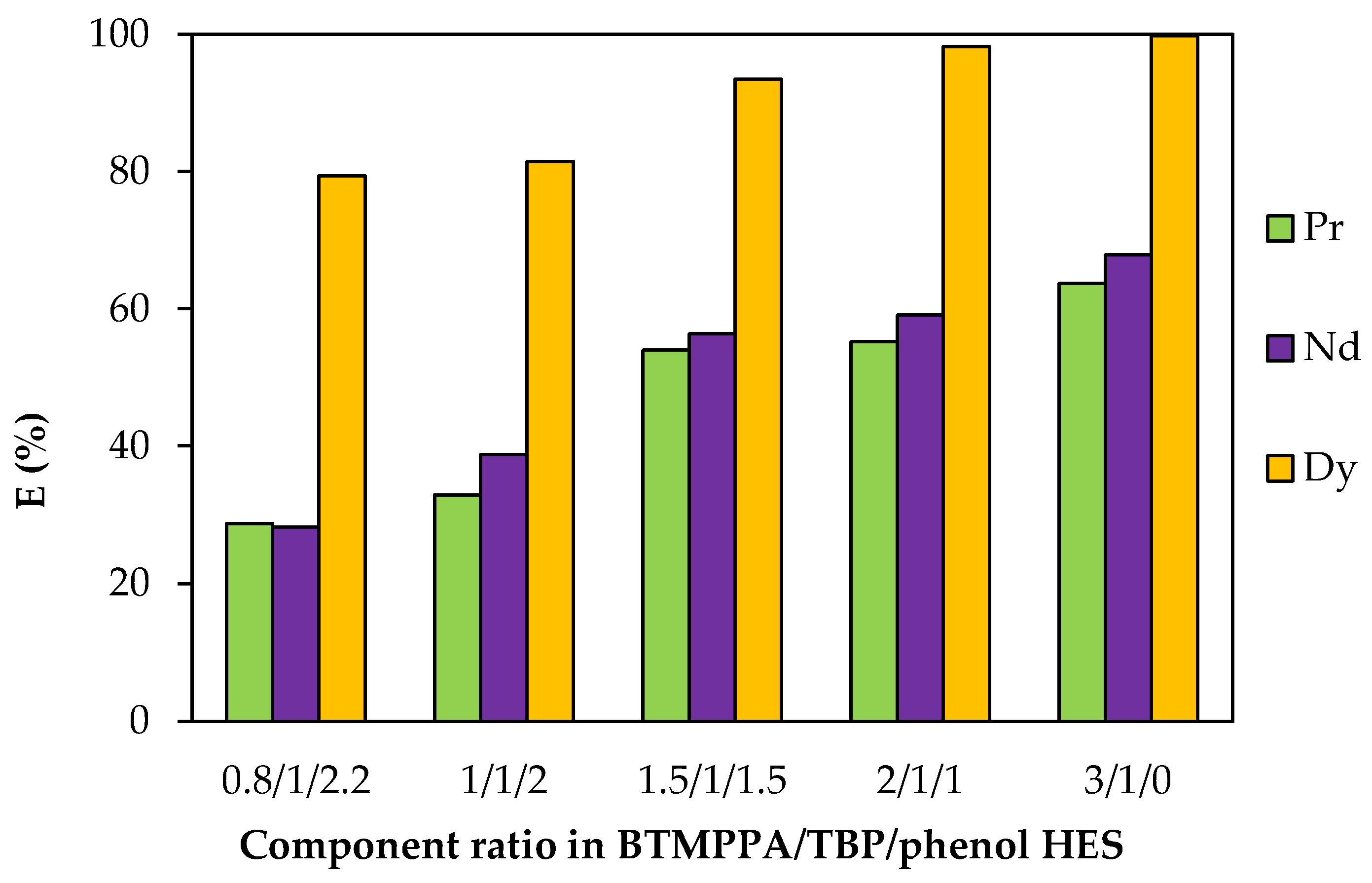
When the BTMPPA/phenol ratio was varied, the BTMPPA concentration ranged from 1.11 to 2.45 mol/L (Table S3). An increase in the fraction of BTMPPA and the corresponding decrease in the fraction of phenol led to an increase in the extraction efficiency of REE ions: from 28.8% to 63.6% for Pr3+, from 28.3% to 67.8% for Nd3+ and from 79.4% to 99.7% for Dy3+ (Figure 11). No precipitation was observed during the extraction process for the BTMPPA/TBP/phenol HES within this range of the BTMPPA/phenol ratio.
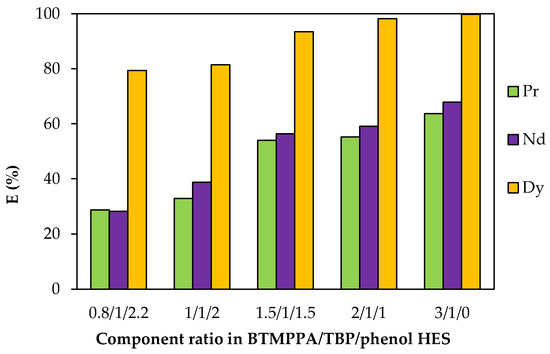
Figure 11.
Effect of the BTMPPA/phenol ratio on REE recovery rate. CMe(in) = 0.01 mol/L, A/O = 1, T = 25 °C.
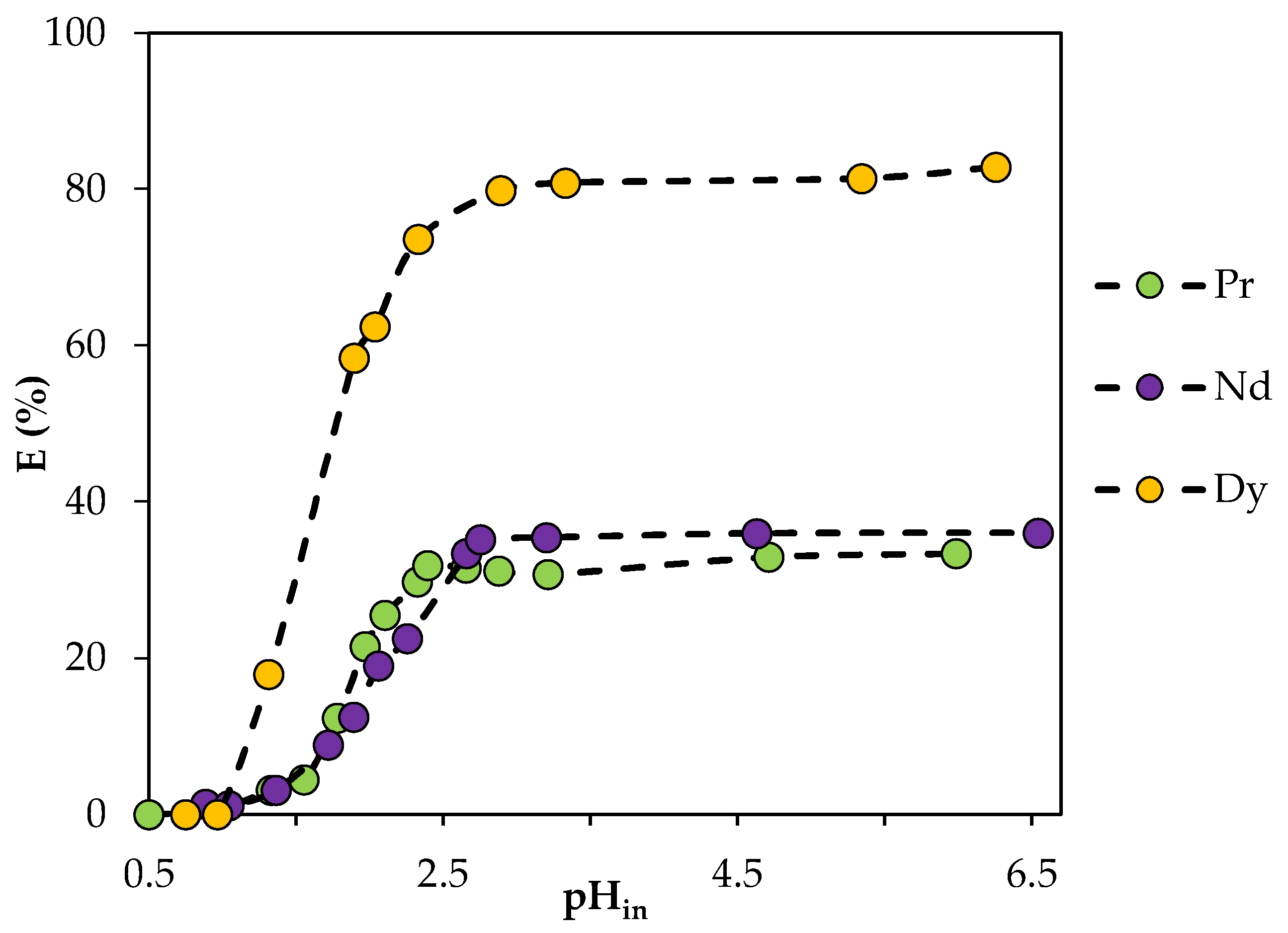
In addition, the extraction capabilities of the HES were studied in the initial pH range from 0.5 to 6.5 (Figure 12). The results show that the extraction efficiency increased to 31% for Pr(III), to 35.5% for Nd(III) and to 81% for Dy(III) when pH was increased from 1 to 2.5; thereafter, it remained practically unchanged. The shape of the curves is similar to that in the literature data for cation exchange extraction using classical solvents [36,37]. This suggests a cation exchange mechanism for REE extraction that is consistent with the typical BTMPPA-based extraction mechanism.
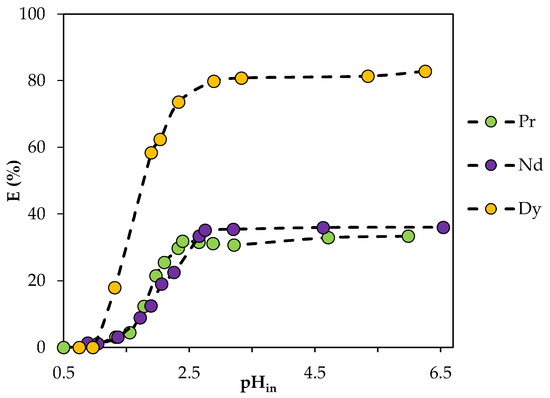
Figure 12.
Dependence of the degree of REE extraction by BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1:1:2) on the initial pH of the aqueous phase. CMe(in) = 0.01 mol/L, A/O = 1, T = 25 °C.
It can also be noted that the separation of Pr and Nd from Dy at a pH greater than 2.5 will be difficult, with the values of the separation factors being SFDy/Pr = 8.95 and SFDy/Nd = 7.65. At the initial pH of 1.8, there was a difference in the efficiency of extraction of light REE and dysprosium; the values of the separation factors under these conditions were SFDy/Pr = 10 and SFDy/Nd = 9.86, respectively.
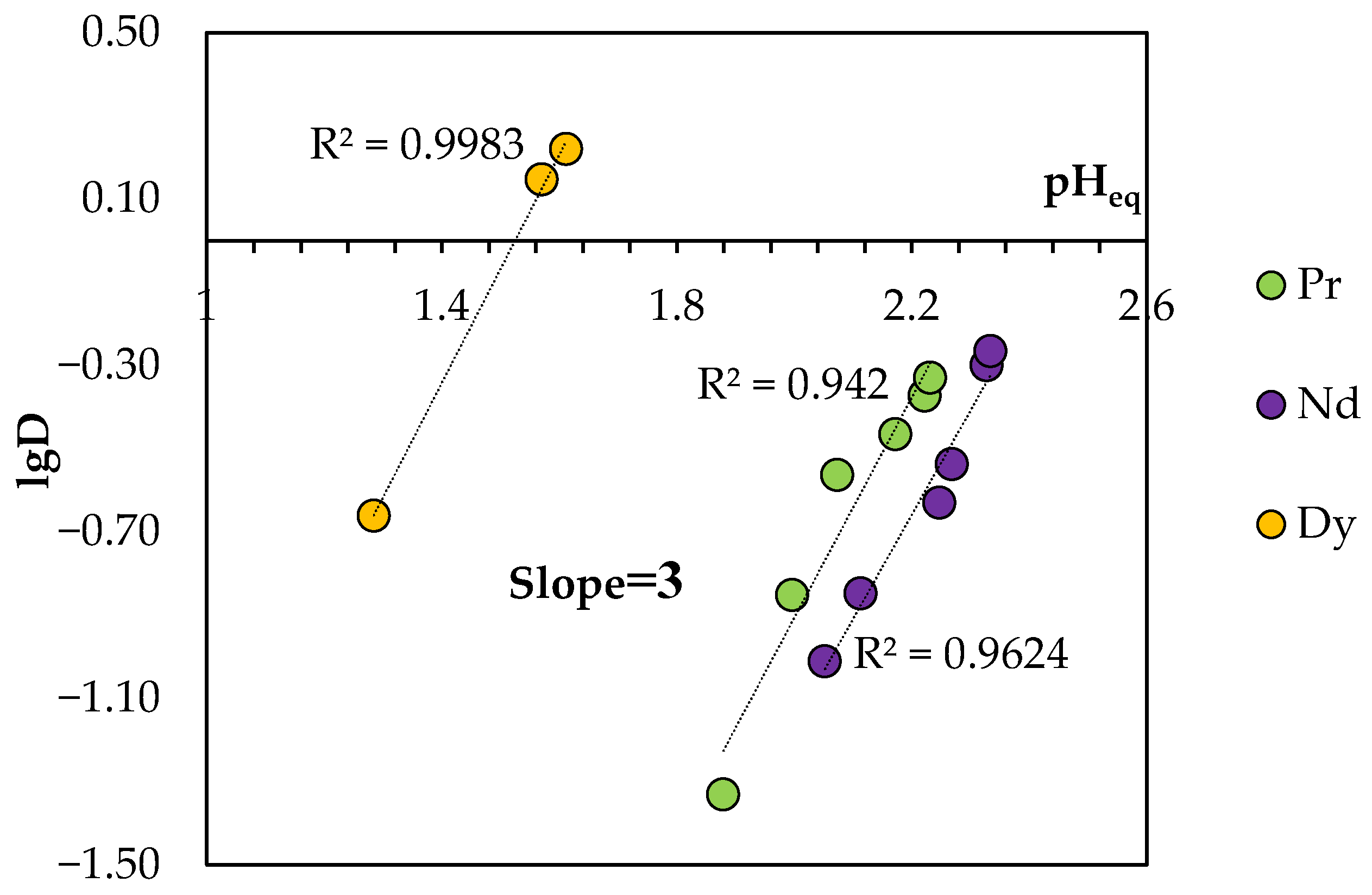
The equilibrium pH (pHeq) values were substantially lower than the initial values, which indicates the transition of H+ ions into the aqueous phase during extraction. As shown in Figure 13, the plot of lgD vs. pHeq presents straight lines with a slope of 3 for the REEs studied, suggesting that the totally released protons included three hydrogen ions for BTMPPA/TBP/phenol.
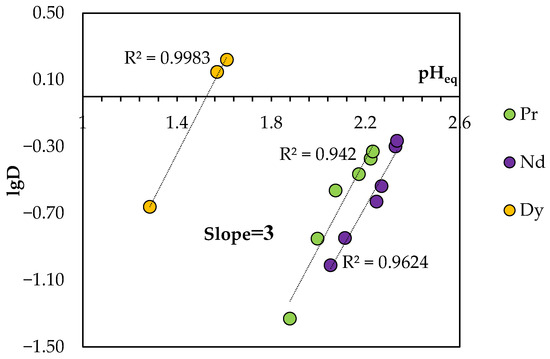
Figure 13.
Logarithmic plot of the REE distribution coefficient in the BTMPPA/TBP/phenol system (1:1:2) vs. the equilibrium pH of the aqueous phase. CMe(in) = 0.01 mol/L, A/O = 1, T = 25 °C.
Based on these data, it can be assumed that the extraction of the REE ions studied in this work can be described by the following equation of a heterogeneous cation exchange reaction in a general form, without taking additional interactions into account:
where HA(org) is the monomeric form of BTMPPA in the eutectic solvent. The subscripts (aq) and (org) denote the aqueous and organic phases, respectively.
3.4. The Stripping of Rare-Earth Metals in the BTMPPA/TBP/Phenol System (1:1:2)
The stripping of REE ions from the HES was studied. Nitric acid was used because the HES is stable in its solutions. The authors previously showed [26] that efficient metal stripping from BTMPPA/phenol (1:3) DES using 0.5 M nitric acid is possible. Stripping was carried out for 15 min, with A/O = 1 and T = 25 °C. The degree of stripping of Pr3+, Nd3+ and Dy3+ ions exceeded 95% in a single step (Table 3).

Table 3.
Degrees of metal ion recovery during stripping with 0.5 mol/L HNO3 solution.
The stability of the HES was also studied during several extraction–stripping cycles, using Nd(III) as an example (Figure 14). Two consecutive stripping steps were carried out in order to quantitatively transfer REE ions from the organic phase to the aqueous phase. It was found that the REE extraction efficiency did not change during this experiment, indicating that the proposed HES can be used repeatedly.
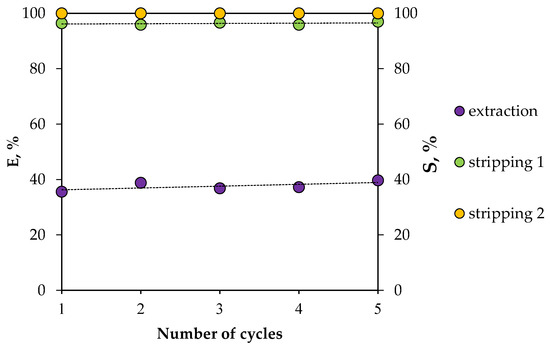
Figure 14.
Dependence of extraction and re-extraction efficiencies on the number of HES BTMPPA/TBP/phenol use cycles (A/O = 1, T = 25 °C).
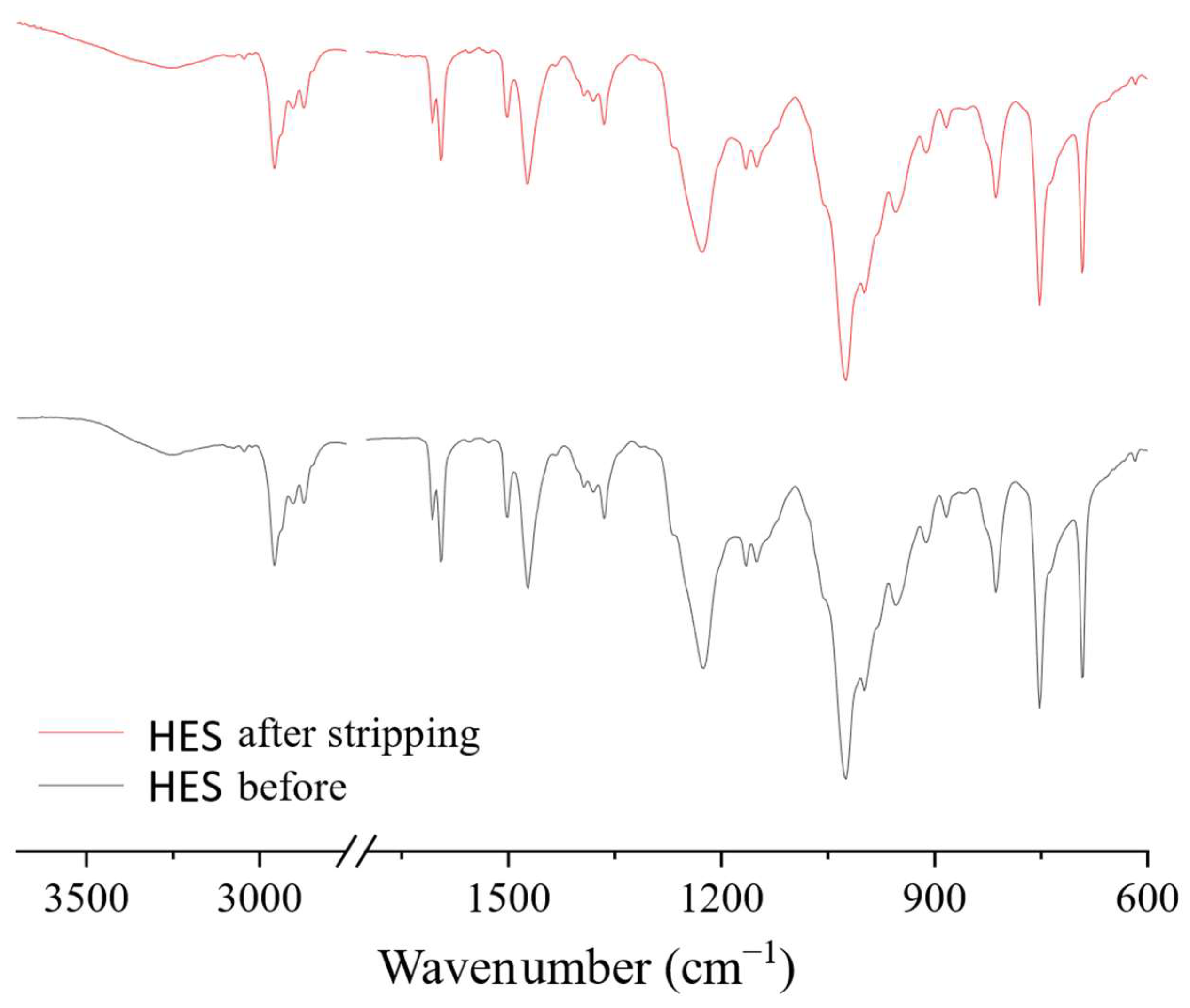
FTIR spectra of the HES before and after the extraction–stripping cycles were also obtained. No significant changes in the spectra were observed after the regeneration of the extractant, which indicates the stability of the HES (Figure 15).
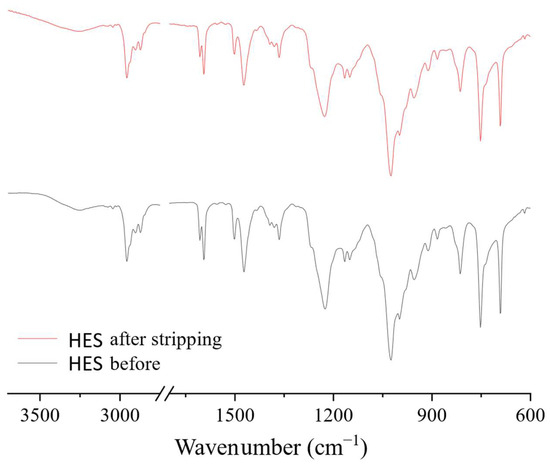
Figure 15.
FTIR spectra of BTMPPA/TBP/phenol HES before extraction and after regeneration.
At present, there are not many hydrophobic eutectic solvents based on bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid (Table 4). It can be noted that the Nd extraction rates presented in the HES literature do not reach 100% despite the fact that, during extraction with dialkylphosphinic acid in traditional solvents, the extraction rates of all REEs under similar conditions usually reach 100%. This suggests that the transition to hydrophobic eutectic solvents may allow for a more efficient separation of REEs from one another due to the significant difference in distribution coefficients.

Table 4.
HES based on bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid in Nd3+ extraction.
4. Conclusions
The hydrophobic eutectic solvent BTMPPA/TBP/phenol was prepared and characterised using modern instrumental analytical techniques. The temperature dependence of the main physical properties of the HES, such as its viscosity, density and refractive index, were determined. The viscosity of the HES at 25 °C was 17.1 mPa·s, indicating its suitability for technological applications.
The characteristics of extraction systems based on the proposed HES were studied, and it was shown that thermodynamic equilibrium in the system was reached within 5 min. The extraction efficiency of Pr(III), Nd(III) and Dy(III) ions reached a plateau at pH values above 2.5. An increase in the molar fraction of BTMPPA in the HES composition led to an increase in the extraction efficiency, while a significant increase in the molar fraction of TBP resulted in the precipitation of the compounds being extracted during the extraction process. A cation exchange mechanism of REE extraction was confirmed, and the composition of the compounds being extracted was proposed.
A 0.5 mol/L HNO3 solution was proposed as a stripping agent, enabling the recovery of metals from the organic phase, with an extraction efficiency exceeding 95% in a single step. The stability of the HES during the interaction with the selected stripping agent, and during multiple extraction–stripping cycles, was demonstrated.
The results obtained may be used for the development and application of new hydrophobic eutectic solvent compositions for liquid extraction.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13092830/s1. Equation (S1): Calibration equation of phenol concentrations; Figure S1: IR spectra of the studied HES after several heating and cooling cycles; Figure S2: Dependence of the refractive index on temperature for BTMPPA/TBP/phenol (1/1/2); Table S1: Standard deviation of extraction efficiency; Table S2: Standard deviation of extraction efficiency for pH-varying experiments; Table S3: Table of compositions of hydrophobic eutectic solvents.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, I.V.Z.; methodology, I.V.Z.; software, T.Y.C.; validation, A.A.V.; formal analysis, Y.A.Z.; investigation, T.Y.C. and S.A.Y.; resources, A.A.V.; data curation, Y.A.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, T.Y.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.A.Z.; visualisation, T.Y.C. and S.A.Y.; supervision, I.V.Z. and Y.A.Z.; project administration, A.A.V.; funding acquisition, A.A.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (project No. 24-29-00667), https://rscf.ru/en/project/24-29-00667/ (accessed on 9 February 2025).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| HES | Hydrophobic eutectic solvent |
| REEs | Rare-earth elements |
| BTMPPA | Bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid |
| TBP | Tributyl phosphate |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, W.; Xie, H.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Deep Eutectic Solvents Inspired Synthesis of Novel Bi-Component Rare Earths Extractants for Neodymium Separation. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 418, 126730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, L.; Fang, D.; Zhang, A.; Xiao, C. Progress in Phenanthroline-Derived Extractants for Trivalent Actinides and Lanthanides Separation: Where to Next? Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 11415–11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Vovers, J.; Thuan Lu, H.; Stevens, G.W.; Mumford, K.A. Investigation of Green Solvents for the Extraction of Phenol and Natural Alkaloids: Solvent and Extractant Selection. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodyńska, D.; Burdzy, K.; Hunger, S.; Aurich, A.; Ju, Y. Green Extractants in Assisting Recovery of REEs: A Case Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Rutkowska, M.; Owczarek, K.; Tobiszewski, M.; Namieśnik, J. Extraction with Environmentally Friendly Solvents. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Bailey, P.J.; Tasker, P.A.; Turkington, J.R.; Grant, R.A.; Love, J.B. Solvent Extraction: The Coordination Chemistry behind Extractive Metallurgy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 43, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea Mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xue, Z.; Mu, T. Eutectics: Formation, Properties, and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8596–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Vaz, I.C.M.; Pinheiro, M.S.; Olea, F.; Hanada, T.; Dourdain, S.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Examining the Potential of Type V DESs for the Solvent Extraction of Metal Ions. Green Chem. 2025, 27, 4438–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaño, S.; Petranikova, M.; Onghena, B.; Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Banerjee, D.; Foreman, M.R.S.; Ekberg, C.; Binnemans, K. Separation of Rare Earths and Other Valuable Metals from Deep-Eutectic Solvents: A New Alternative for the Recycling of Used NdFeB Magnets. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32100–32113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrachart, G.; Couturier, J.; Dourdain, S.; Levard, C.; Pellet-Rostaing, S. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements (REEs) Using Ionic Solvents. Processes 2021, 9, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zante, G.; Boltoeva, M. Review on Hydrometallurgical Recovery of Metals with Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 1, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Kumar, S. Potential of Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green and Sustainable Solvents for the Recovery of Carboxylic Acids from Aqueous Solution: A Review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2025, 100, 1541–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstiss, L.; Weber, C.C.; Baroutian, S.; Shahbaz, K. Menthol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Extractants for the Isolation of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids from Perna canaliculus. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 98, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Physicochemical Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and Properties of Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Yong, W.F.; She, Q.; Esteban, J. Status and Advances of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Metal Separation and Recovery. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1895–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Torres-Cornejo, M.V.; Álvarez-Rivera, G.; Mendiola, J.A. Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Natural Sources and Agricultural By-Products. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Lobovich, D.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zinov’eva, I.V.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. The Use of Organophosphorus Extractants as a Component of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents (HDES) for the Processing of Spent Lithium-iron Phosphate Batteries. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 228, 106369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, L.; Xi, X.; Nie, Z. Design Insights into Eutectic Solvents: Selective Recovery of Transition Metal Elements from Laterite Nickel Ore Leachate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Ni, S.; Gao, Y.; Mo, D.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, X. Recovery of Rare Earth Metal Oxides from NdFeB Magnet Leachate by Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent Extraction, Oxalate Stripping and Calcination. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 223, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Gao, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Sun, X. Tailored Ternary Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents for Synergistic Separation of Yttrium from Heavy Rare Earth Elements. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 7148–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, G.; Saneie, R.; Abdollahi, H.; Ebrahimi, E.; Rezaei, A.; Mohammadkhani, M. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) as a Green Lixiviant for Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Caustic-Treated Monazite Concentrate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Chikineva, T.Y.; Salomatin, A.M.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extraction of Rare Earth Elements from Nitrate Solutions by Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Phosphorus-Containing Compounds. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 21587–21602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Chikineva, T.Y.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Bis(2,4,4-Trimethylpentyl)Phosphinic Acid/Phenol Deep Eutectic Solvent: Physicochemical Properties and Application Prospects for the Extraction of Trivalent Rare Earth Elements. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 423, 126984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Chikineva, T.Y.; Yakovleva, S.A.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extraction of Rare-Earth Elements with Deep Eutectic Solvent Di(2,4,4-Trimethylpentyl)Phosphinic Acid/Phenol. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2024, 58, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önal, M.A.R.; Aktan, E.; Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Guo, M. Recycling of NdFeB Magnets Using Nitration, Calcination and Water Leaching for REE Recovery. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Sheridan, R.; Güth, K.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Buchert, M.; Steenari, B.M.; Van Gerven, T.; Jones, P.T.; et al. REE Recovery from End-of-Life NdFeB Permanent Magnet Scrap: A Critical Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdlička, A.; Havel, J.; Moreno, C.; Valiente, M. Micellar-Enhanced Highly Sensitive Reaction of Rare Earths with Xylenol Orange and Surfactants. Study of Reaction Conditions and Optimization of Spectrophotometric Method. Anal. Sci. 1991, 7, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Kozhevnikova, A.V.; Milevskii, N.A.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. New Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent Based on Bis(2,4,4-Trimethylpentyl)Phosphinic Acid and Menthol: Properties and Application. Eng. Proc. 2023, 37, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Conceição, J.H.; Martins, M.A.; Neves, M.C.; Pérez-Sánchez, G.; Gomes, J.R.; Papaiconomou, N.; Coutinho, J.A. Non-Ionic Hydrophobic Eutectics—Versatile Solvents for Tailored Metal Separation and Valorisation. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2810–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; Alnashef, I.M. Prediction of Deep Eutectic Solvents Densities at Different Temperatures. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 515, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.Z.; Yin, J.M.; Liu, Q.S.; Li, C.P. Properties of Four Deep Eutectic Solvents: Density, Electrical Conductivity, Dynamic Viscosity and Refractive Index. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2015, 31, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, G. Mass Transfer in Liquid-Liquid Taylor Flow in a Microchannel: Local Concentration Distribution, Mass Transfer Regime and the Effect of Fluid Viscosity. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 223, 115734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.N.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, M.S. Review on the Comparison of the Chemical Reactivity of Cyanex 272, Cyanex 301 and Cyanex 302 for Their Application to Metal Separation from Acid Media. Metals 2020, 10, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; Bond, A.H. Influence of Aggregation on the Extraction of Trivalent Lanthanide and Actinide Cations by Purified Cyanex 272, Cyanex 301, and Cyanex 302. Radiochim. Acta 2002, 90, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).