Improving Performance of a Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cell by Hydrophobic Treatment for Cathode Current Collector
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Fabrication of MEA
2.2. PTFE Hydrophobic Treatment
2.3. TiO2/PDMS Hydrophobic Treatment
2.4. Gradient Hydrophobic Treatment
2.5. Physical Characterization
2.6. Electrochemical Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM Characterization
3.2. Contact Angle Test
3.3. Comparison of Electrochemical Properties Under Different Hydrophobic Treatments
3.4. Electrochemical Properties Under Graded Hydrophobic Treatment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, G.; Cui, M.; Yu, H.; Fan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.; Sun, J.; Yang, B.; Du, D. Global Environmental Change Shifts Ecological Stoichiometry Coupling Between Plant and Soil in Early-Stage Invasions. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 2402–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.J.; Li, G.; Nazir, M.M.; Zulfiqar, F.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Iqbal, B.; Du, D. Harnessing soil carbon sequestration to address climate change challenges in agriculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 237, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhai, N.; Miao, J.; Sun, H. Can Green Finance Effectively Promote the Carbon Emission Reduction in “Local-Neighborhood” Areas?—Empirical Evidence from China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Ni, C.; Wu, J.; Hao, C. High performance hybrid supercapacitors assembled with multi-cavity nickel cobalt sulfide hollow microspheres as cathode and porous typha-derived carbon as anode. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 189, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algburi, S.; Munther, H.; Al-Dulaimi, O.; Fakhruldeen, H.F.; Sapaev, I.B.; Seedi, K.F.K.A.; Khalaf, D.H.; Jabbar, F.I.; Hassan, Q.; Khudhair, A.; et al. Green Hydrogen Role in Sustainable Energy Transformations: A Review. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Tu, Z.; Chan, S.H. Recent development of hydrogen and fuel cell technologies: A review. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 8421–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, B.C.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Basri, S. Direct liquid fuel cells: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 10142–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phogat, P.; Chand, B.; Shreya; Jha, R.; Singh, S. Hydrogen and methanol fuel cells: A comprehensive analysis of challenges, advances, and future prospects in clean energy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 109, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Zabed, H.M.; Wei, Y.; Qi, X. Technoeconomic and environmental perspectives of biofuel production from sugarcane bagasse: Current status, challenges and future outlook. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 188, 115684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.S.; Chen, R.; Yang, W.W.; Xu, C. Small direct methanol fuel cells with passive supply of reactants. J. Power Sources 2009, 191, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.P.T.; Ferreira, N.S.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Pinto, A.M.F.R.; Mendes, A.; Sales, M.G.F. A passive direct methanol fuel cell as transducer of an electrochemical sensor, applied to the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 175, 112877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá, M.H.; Pinto, A.M.F.R.; Oliveira, V.B. Passive direct methanol fuel cells as a sustainable alternative to batteries in hearing aid devices—An overview. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 16552–16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.S.; Carneiro, L.P.T.; Viezzer, C.; Almeida, M.J.T.; Marques, A.C.; Pinto, A.M.F.R.; Fortunato, E.; Sales, M.G.F. Passive direct methanol fuel cells acting as fully autonomous electrochemical biosensors: Application to sarcosine detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 922, 116710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjewar, S.S.; Thombre, S.B.; Mallick, R.K. Approaches to overcome the barrier issues of passive direct methanol fuel cell–Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 1087–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, X. Overcoming undesired fuel crossover: Goals of methanol-resistant modification of polymer electrolyte membranes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Nie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Elimination of water flooding of cathode current collector of micro passive direct methanol fuel cell by superhydrophilic surface treatment. Appl. Energy 2014, 126, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. An improved strategy of passive micro direct methanol fuel cell: Mass transport mechanism optimization dominated by a single hydrophilic layer. Energy 2023, 274, 127276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F.; Chen, Q.; Xu, J. Flexible, versatility and superhydrophobic biomass carbon aerogels derived from corn bracts for efficient oil/water separation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 115, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, E.E.; Taymaz, I. Experimental study on performance evaluation of PEM fuel cell by coating bipolar plate with materials having different contact angle. Fuel 2019, 253, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadi, F.; Rezaeian, A.; Edris, H. Influence of surface roughness and hydrophobicity of bipolar plates on PEM performance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 389, 125676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Lee, J.R.; Teng, P.J.; Tsai, S.Y. A Hydrophobic Surface Based on a Ni-P-PTFE Coating on a Metallic Bipolar Plate. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 3147–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, X.; Jin, J. Comprehensive performance study of multilayer Ni-P/Cr/CrMoAlN-coated aluminum alloy bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2024, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Faghri, A.; Li, X. Improving the water management and cell performance for the passive vapor-feed DMFC fed with neat methanol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 8468–8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. A CNT (carbon nanotube) paper as cathode gas diffusion electrode for water management of passive μ-DMFC (micro-direct methanol fuel cell) with highly concentrated methanol. Energy 2015, 82, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Liu, X. A hydrophobic layer-based water feedback structure for passive μ-DMFC. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 190, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Yu, W.; Rehman Asghar, M.; Zhang, W.; Su, H.; Li, C.; Xing, L.; Xu, Q. Effect of graphene aerogel as a catalyst layer additive on performance of direct methanol fuel cell. Fuel 2024, 360, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, G. Analysis of PTFE-modified superhydrophobic PDMS decorative coating and surface properties. Shanxi Chem. Ind. 2024, 44, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Yin, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yang, K. Preparation and properties of superhydrophobic TiO2/PDMS coatings on carbon steel surface for corrosion protection. China Surf. Eng. 2021, 34, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, F.; Woodruff, E.; Fordon, A.G.; Xu, Y.; Putnam, S.A. Multiscale modeling of microdroplet evaporation and single pulse spray cooling. Fluid. Dyn. Res. 2025, 57, 025504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
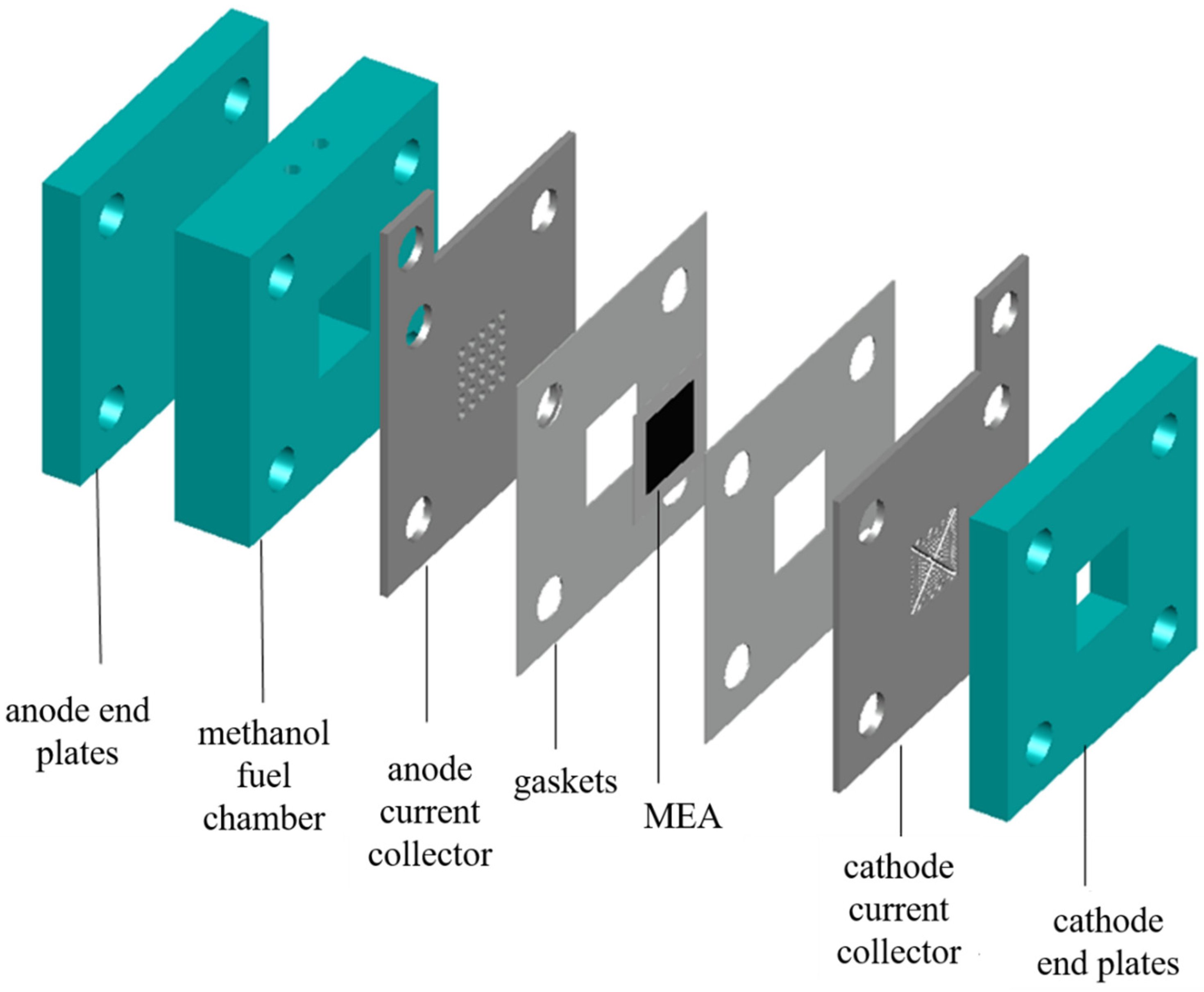
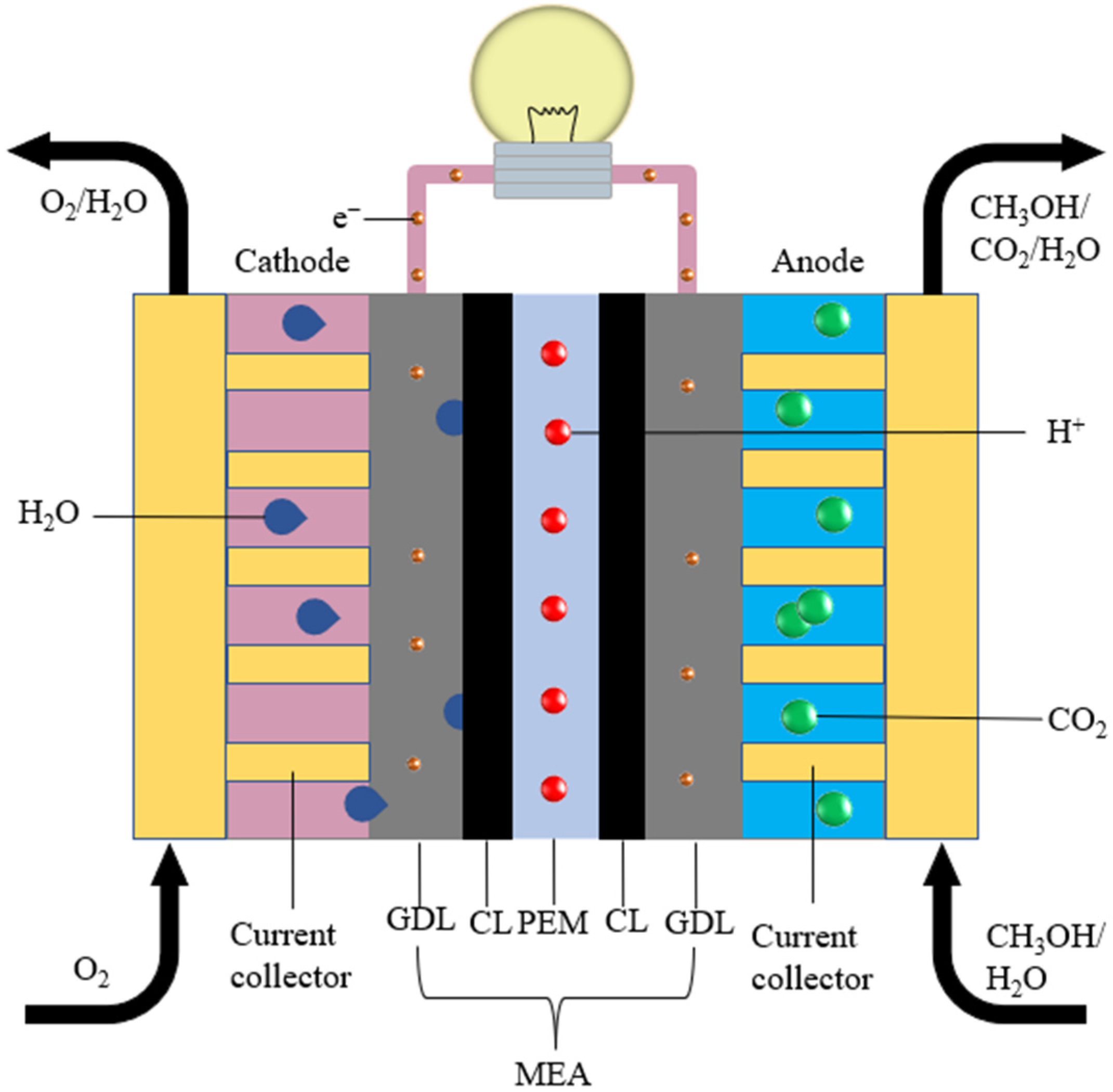
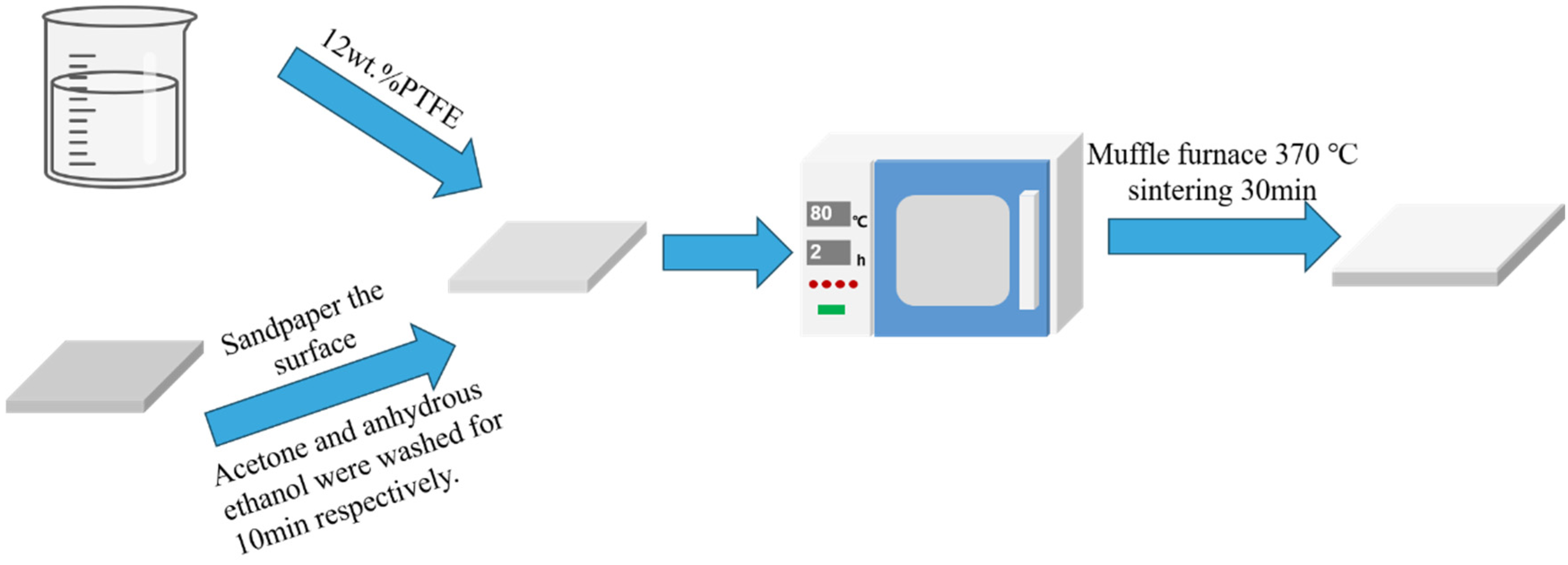

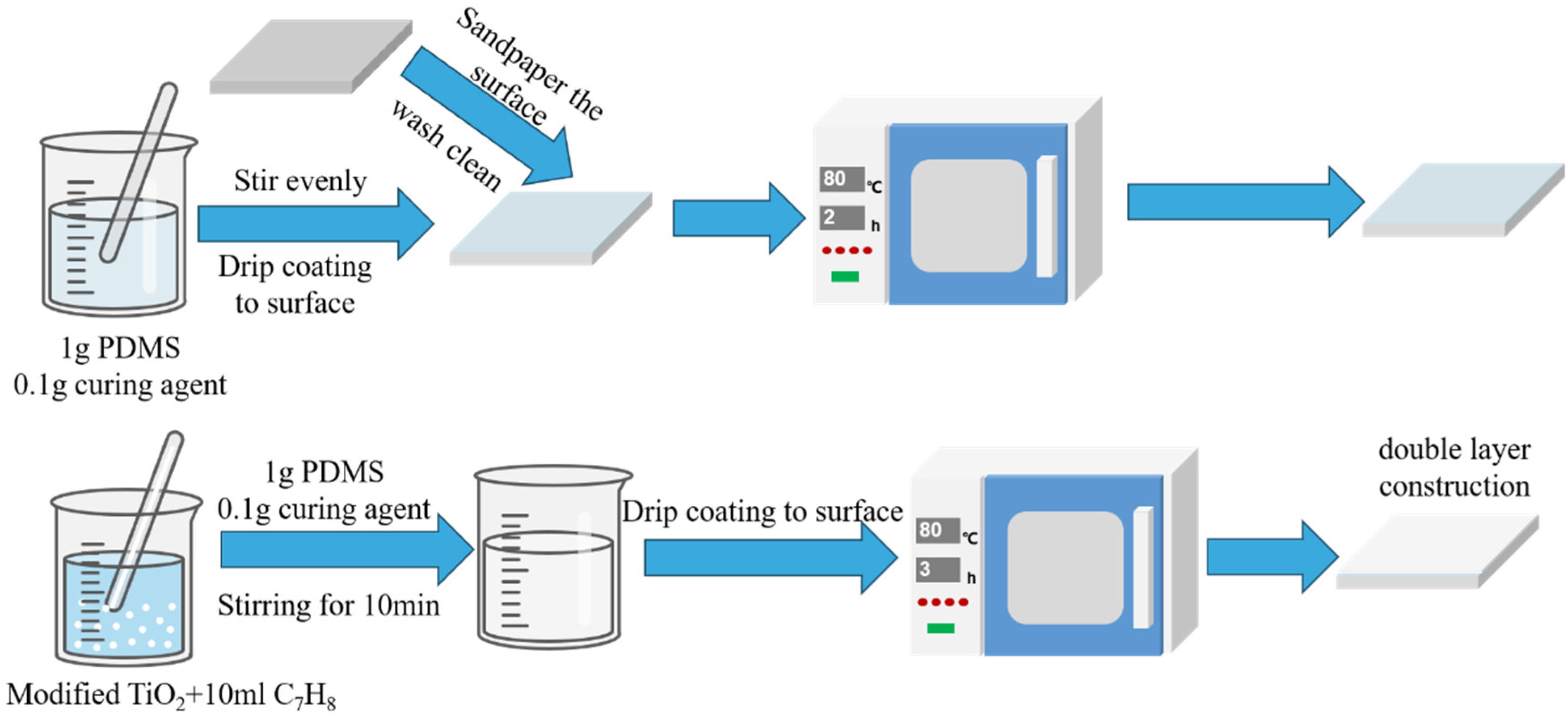

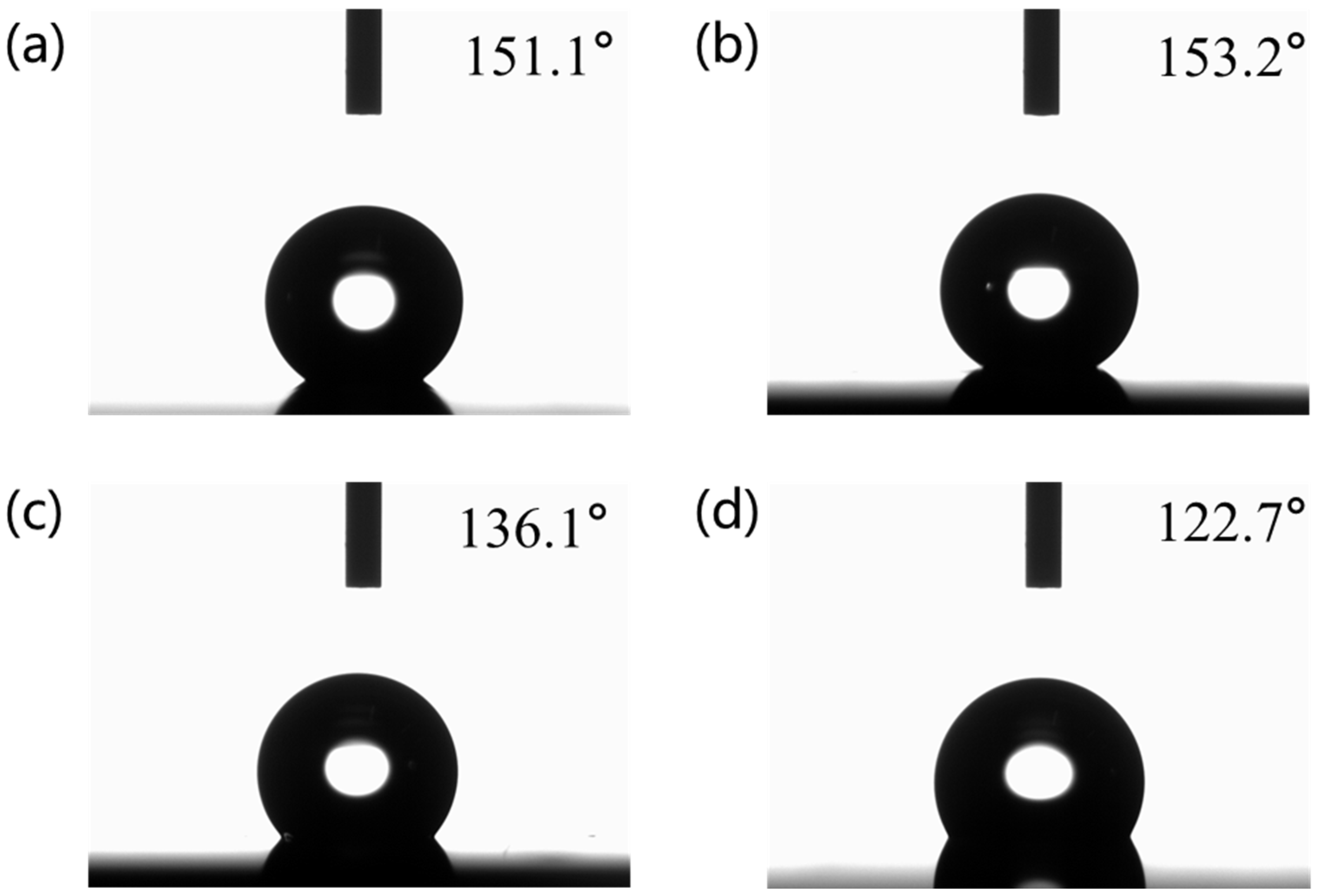

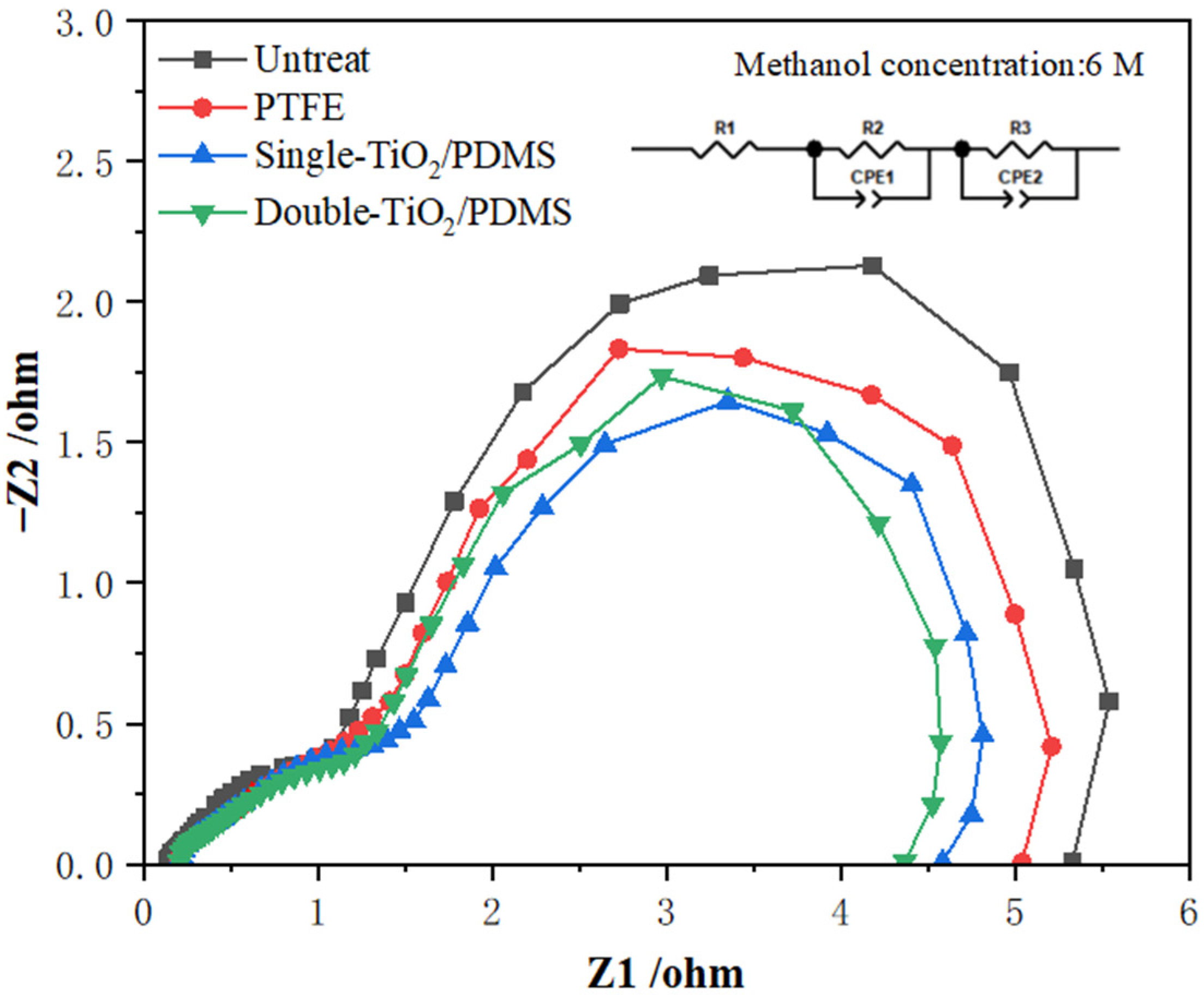

| Parameters | Untreated | PTFE-Treated | Single-Layer TiO2/PDMS | Double-Layer TiO2/PDMS | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs | 0.1325 | 0.17259 | 0.17784 | 0.17970 | Ω |
| Rct | 2.865 | 2.635 | 2.335 | 2.153 | Ω |
| Rmt | 3.843 | 3.386 | 2.725 | 2.074 | Ω |
| Treatment | Max. Current Density (mA/cm2) | Peak Power Density (mW/cm2) | Power Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 12.5 | 3.55 | 0 |
| PTFE coating | 20.0 | 4.24 | +19.4 |
| Single-layer TiO2/PDMS | 22.5 | 4.39 | +23.7 |
| Bilayer TiO2/PDMS | 22.5 | 4.53 | +27.6 |
| Gradient TD-1 | 25.1 | 4.80 | +35.2 |
| Gradient TD-2 | 25.8 | 4.92 | +38.6 |
| Gradient TD-3 | 24.3 | 4.82 | +35.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, X.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Su, H.; Xing, L.; Xu, Q. Improving Performance of a Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cell by Hydrophobic Treatment for Cathode Current Collector. Processes 2025, 13, 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092757
Shen X, Yu W, Zhang Z, Lu L, Zhang W, Liu H, Su H, Xing L, Xu Q. Improving Performance of a Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cell by Hydrophobic Treatment for Cathode Current Collector. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092757
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Xiaozhong, Weibin Yu, Zihao Zhang, Lu Lu, Weiqi Zhang, Huiyuan Liu, Huaneng Su, Lei Xing, and Qian Xu. 2025. "Improving Performance of a Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cell by Hydrophobic Treatment for Cathode Current Collector" Processes 13, no. 9: 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092757
APA StyleShen, X., Yu, W., Zhang, Z., Lu, L., Zhang, W., Liu, H., Su, H., Xing, L., & Xu, Q. (2025). Improving Performance of a Passive Direct Methanol Fuel Cell by Hydrophobic Treatment for Cathode Current Collector. Processes, 13(9), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092757











