Dual-Path Attention Network for Multi-State Safety Helmet Identification in Complex Power Scenarios
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- Complex background interference: The background elements of the power scenarios are diverse and similar, which is easy to cause misjudgment of the model. Strong noise in the background also interferes with feature extraction.
- 2.
- Inadequate accuracy of status identification: Most of the existing studies focus on the two categories (wearing/not wearing), and there are relatively few studies on the identification of the key dangerous state of “wrongly wearing”, and the accuracy is not high.
- 3.
- Inadequate scenario generalization capability: The performance of the model trained for specific scenarios may be significantly reduced in the face of different lighting conditions, weather, or different substation and line environments.
- 1.
- To address the challenge of complex background interference, we introduce the convolutional block attention module (CBAM) into the YOLOv5 network, creating the YOLO-CBAM architecture. The design employs coordinated channel-spatial attention mechanisms to dynamically focus on critical head and helmet regions while actively suppressing irrelevant and noisy background elements prevalent in power operation site.
- 2.
- To overcome the inadequate scenario generalization capability, we construct a high-quality special dataset for safety helmet status identification in diverse power operation environments. This dataset captures a wide spectrum of real-world challenges, including varied lighting condition, numerous personnel poses, and all critical helmet states (correctly wearing/not wearing/wrongly wearing).
- 3.
- To tackle the inadequate accuracy of status identification, particularly for the critical “wrongly wearing” state, we apply the proposed method to electrical power operation scenarios. Extensive experiments show YOLO-CBAM achieves an outstanding mean average precision of 98.81% for identifying all three helmet states, with particular emphasis on the high accuracy attained for the critical “wrongly wearing” state.
2. Proposed Method
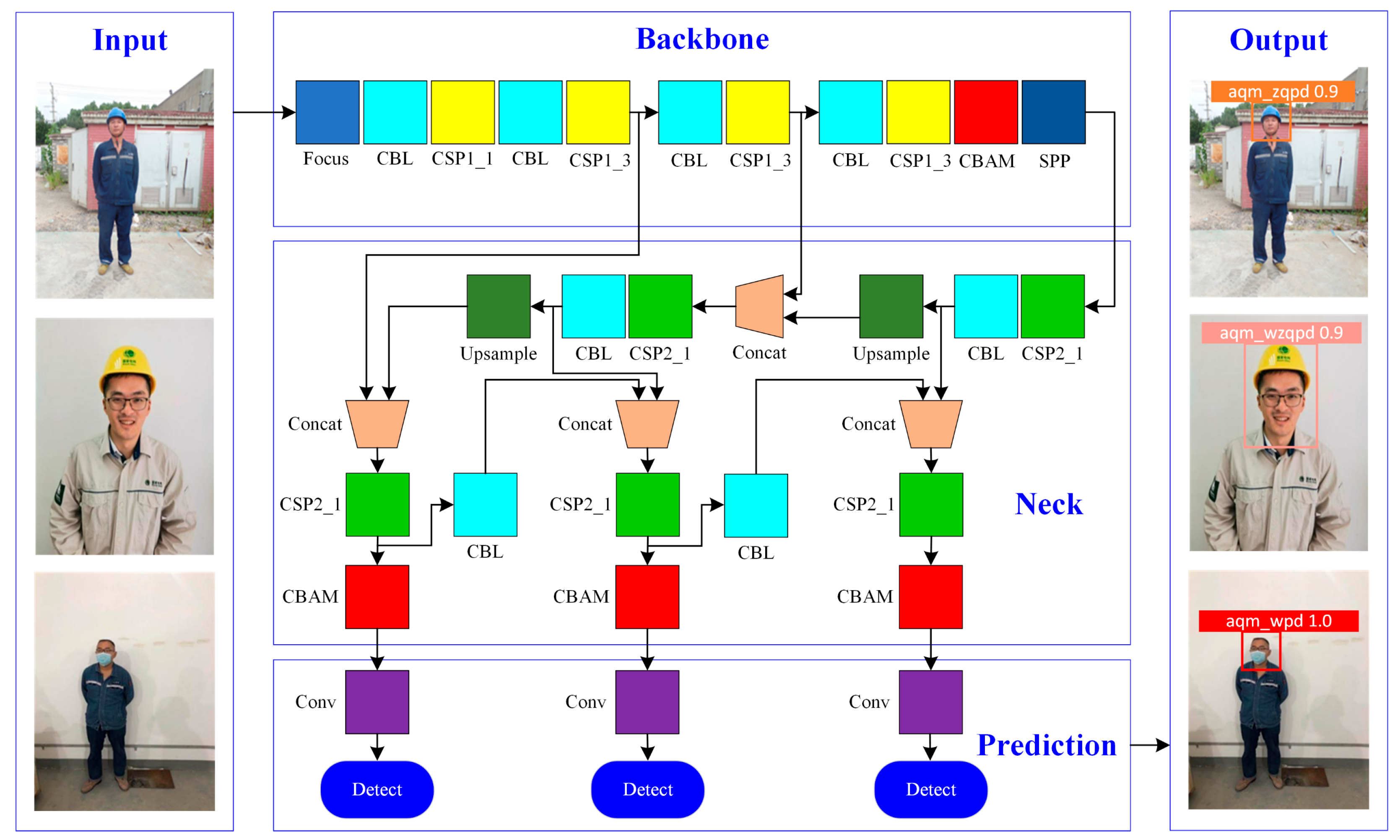
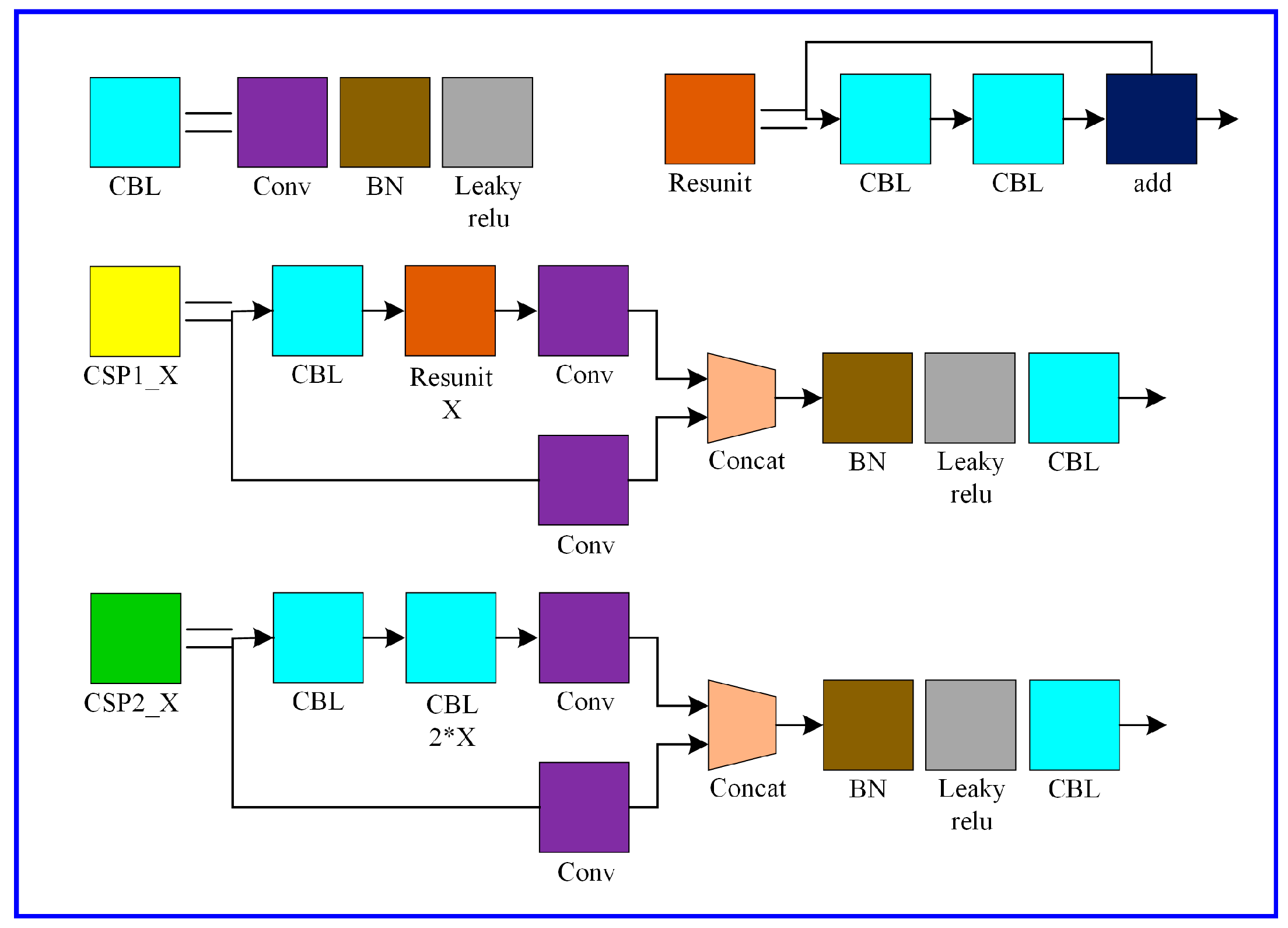
2.1. The Overall Structure of Proposed Method
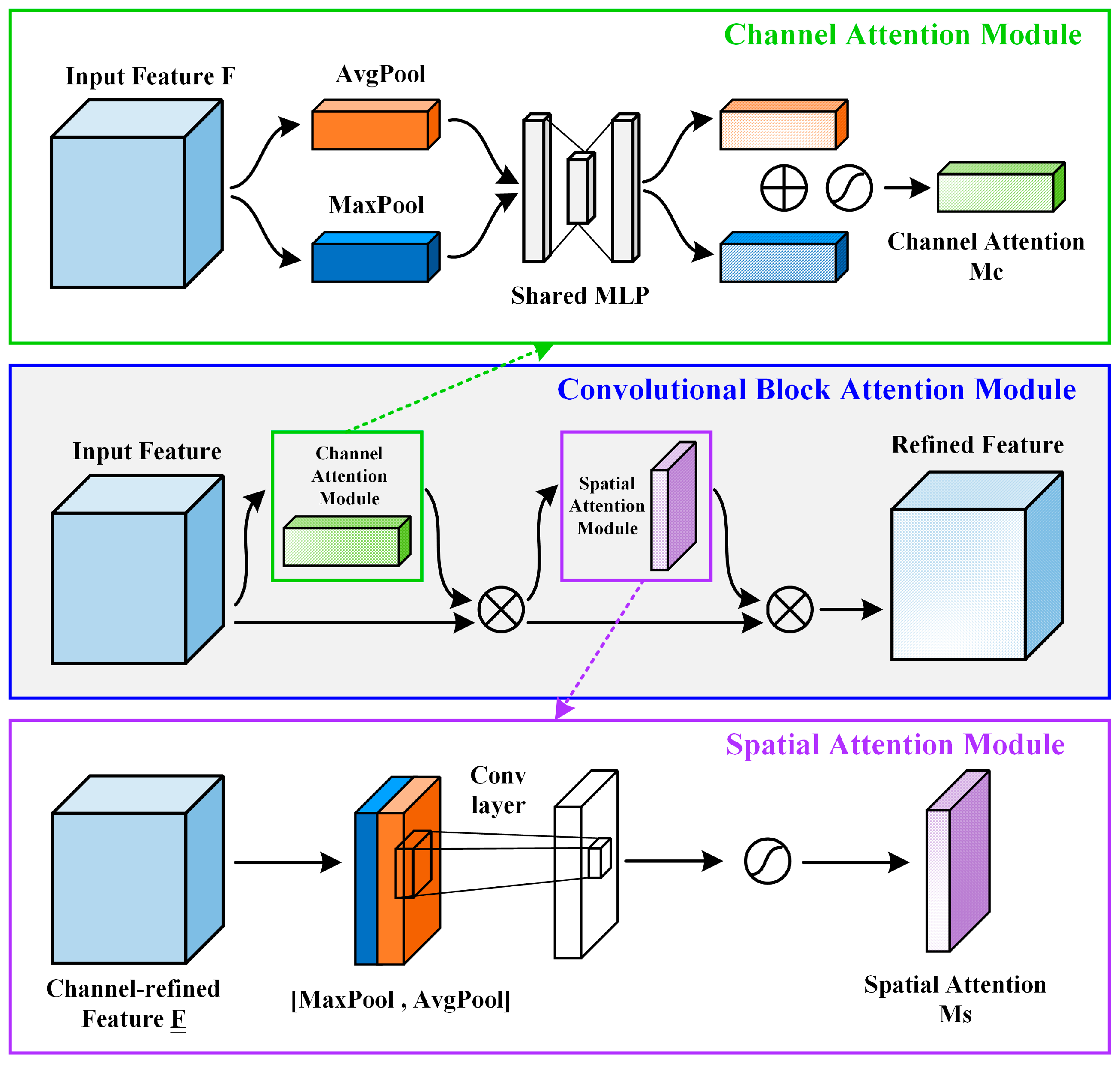
2.2. Convolutional Block Attention Module
2.3. Backbone Enhancement with CBAM
2.4. Neck Enhancement with CBAM
2.5. Prediction Module
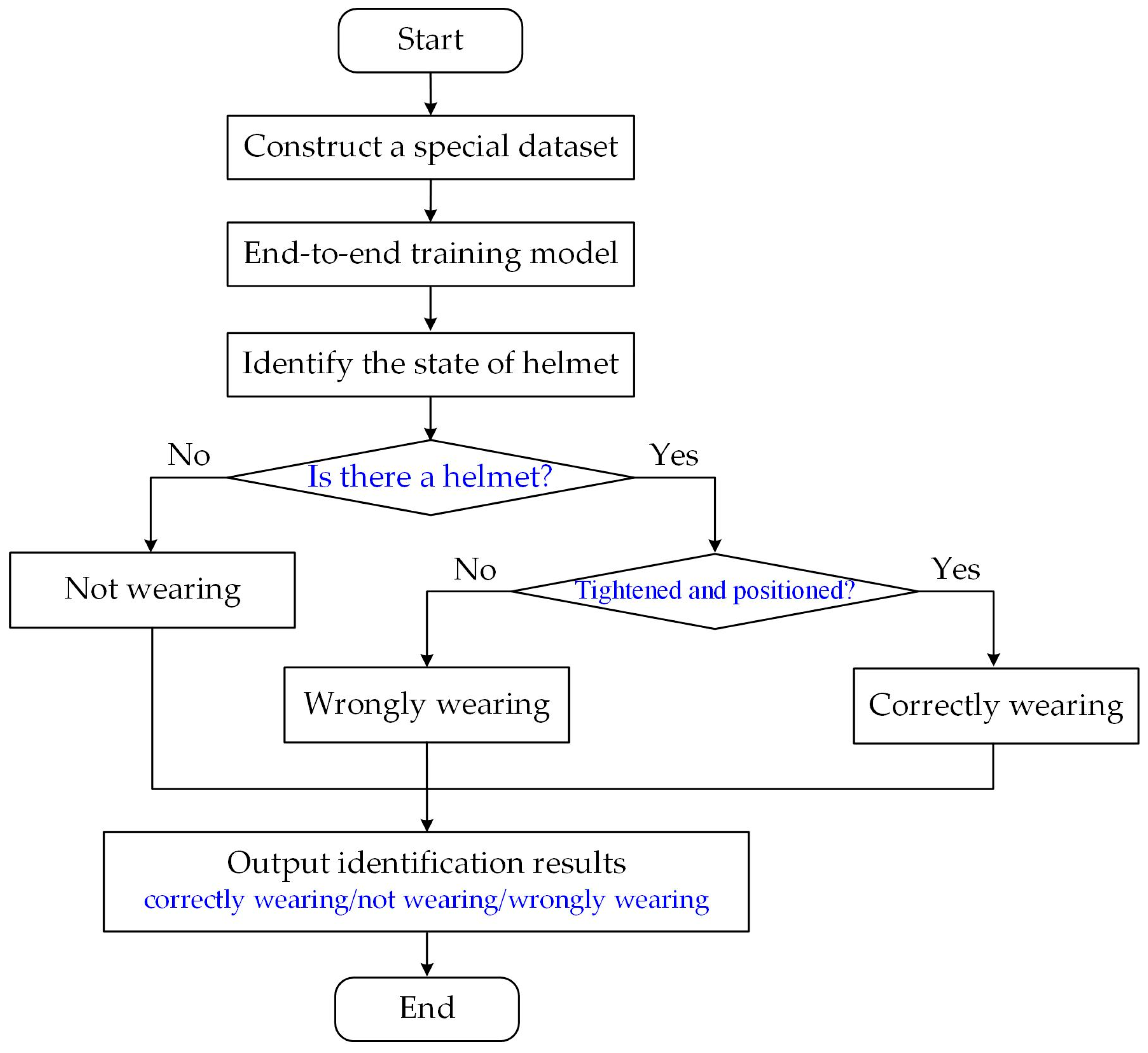
2.6. Flow of Multi-State Safety Helmet Identification
3. Experimental Setup and Result Analysis
3.1. Data Description
3.2. Experimental Environment
3.3. Evaluate Metrics
3.4. Selection of YOLOv5 Models
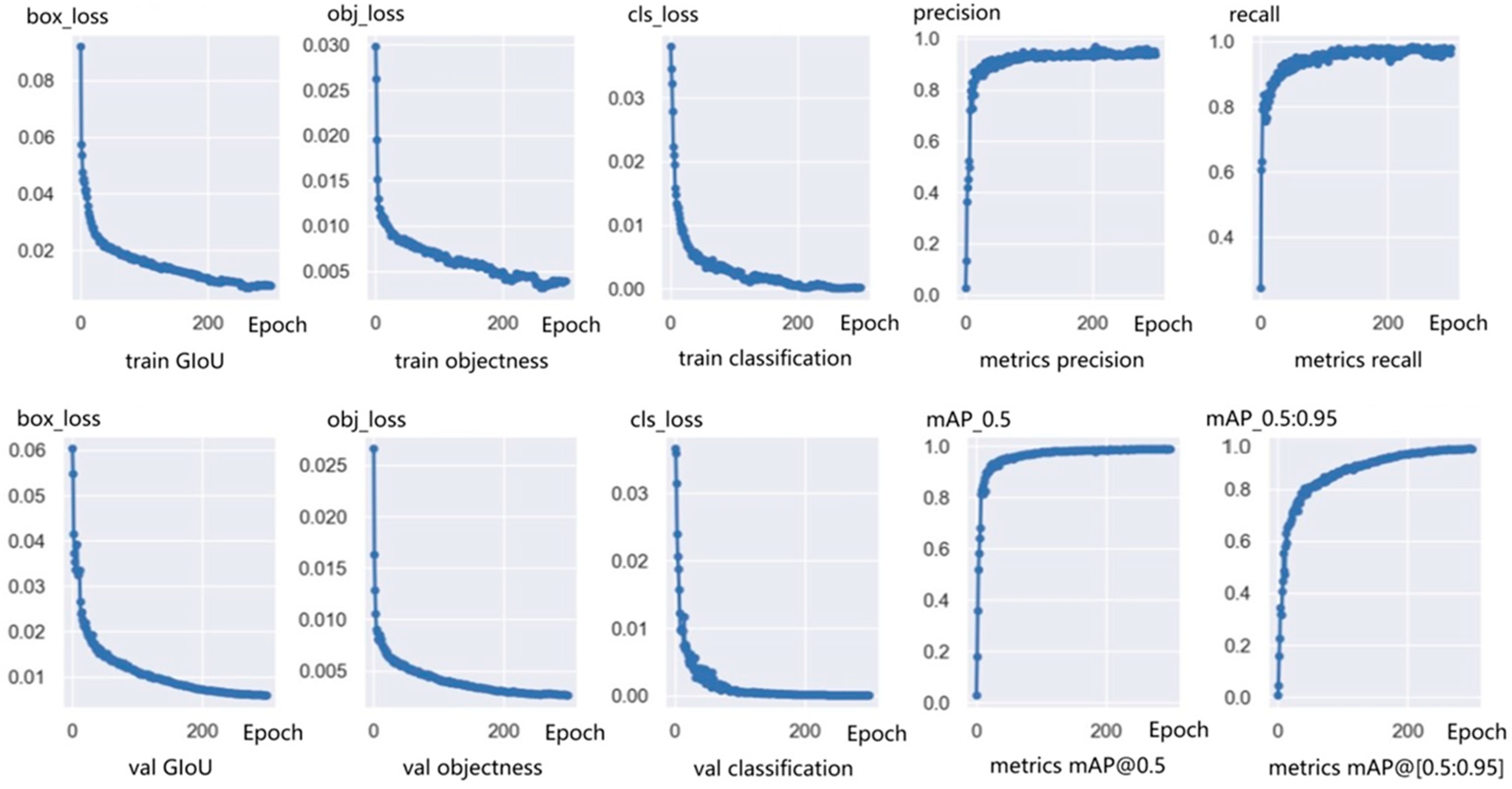
3.5. Model Parameter Setting and Training
3.6. Ablation Experiments
3.7. Comparative Experiments
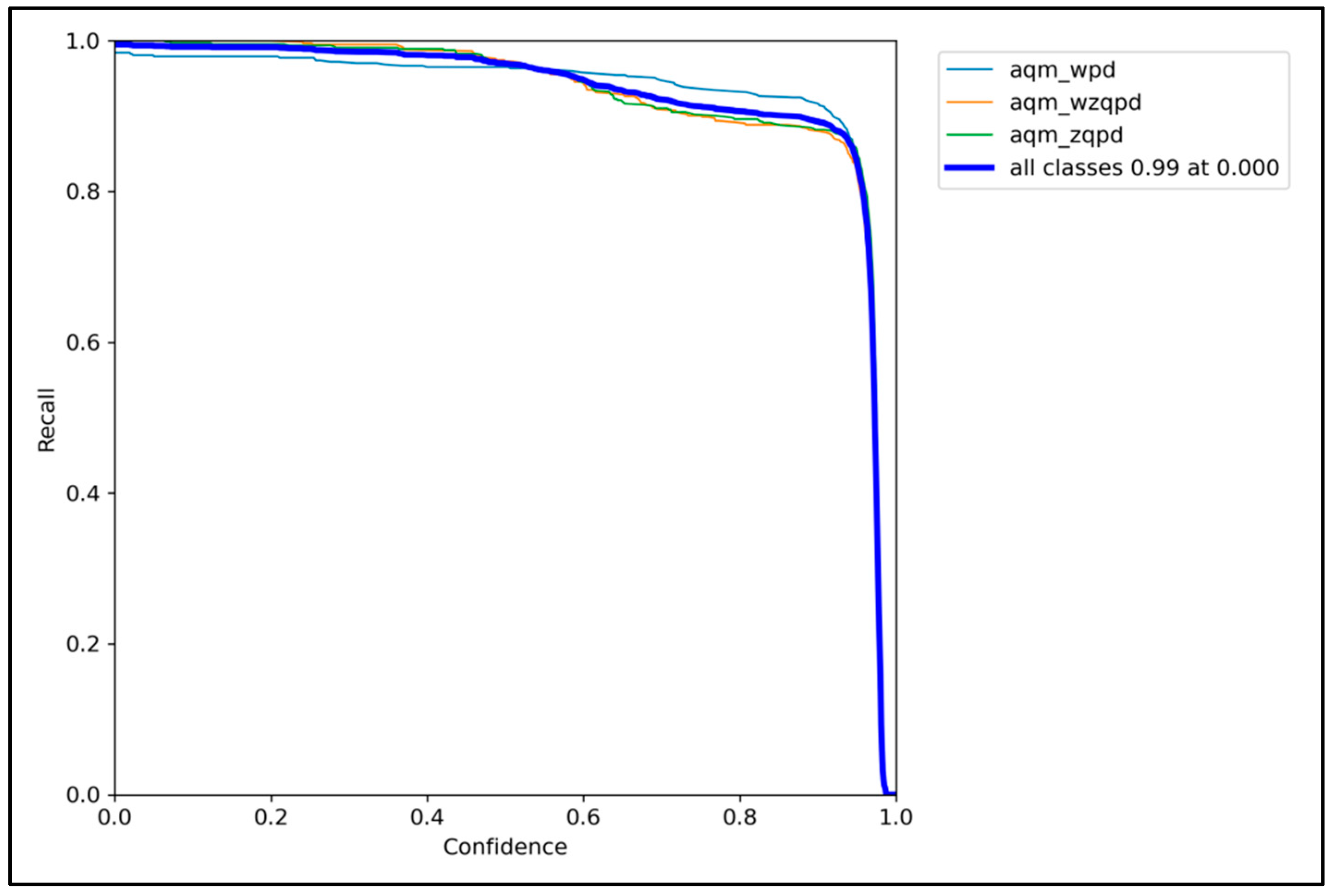
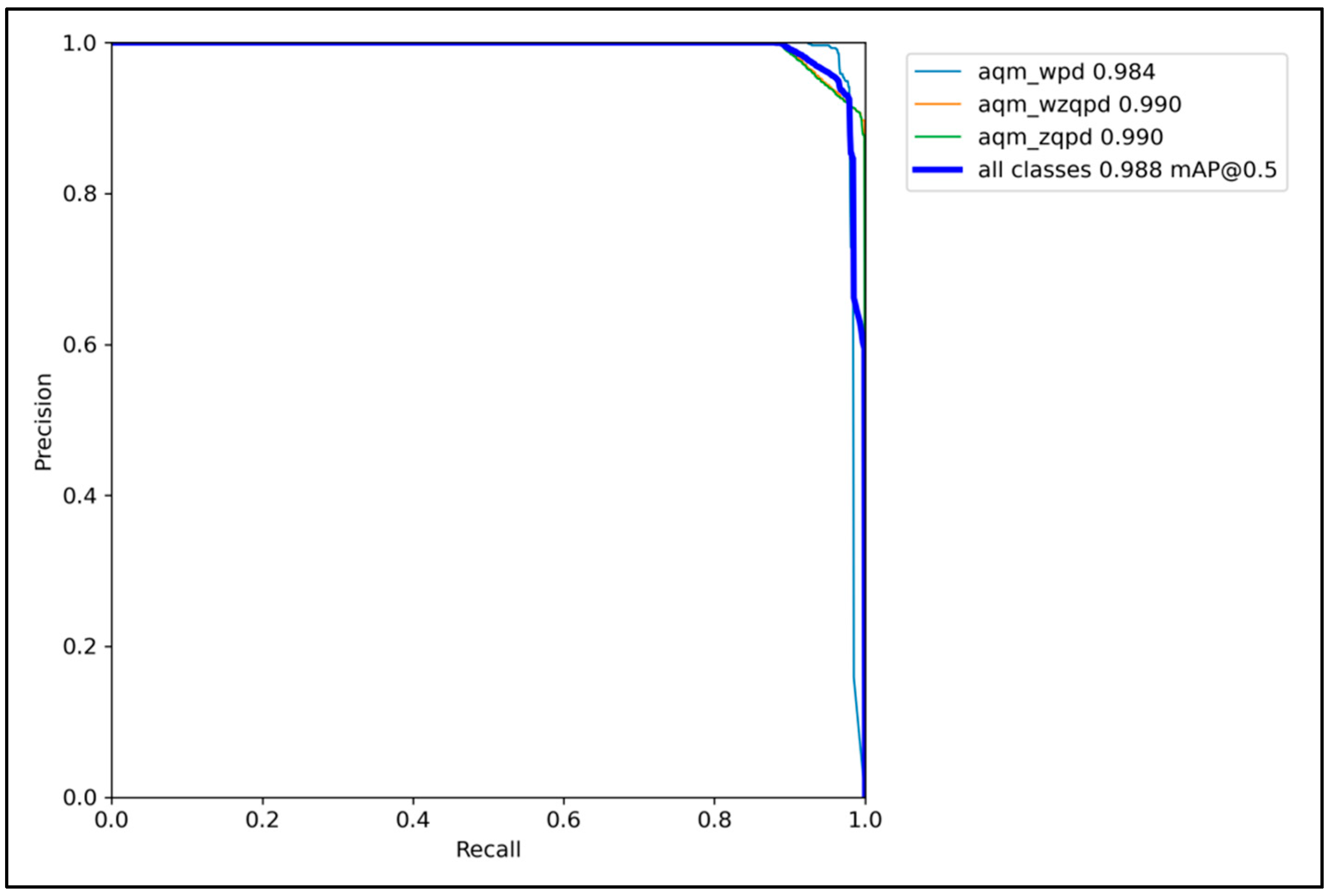
3.8. Identification Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBAM | Convolutional block attention module |
| YOLO | You only look once |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| HOG | Histogram of oriented gradient |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| SSD | Single shot multibox detector |
| RFEM | Receptive field enhancement module |
| FPN | Feature pyramid structure |
| PAN | Path aggregation network |
| CAM | Channel attention module |
| SAM | Spatial attention module |
| GAP | Global average pooling |
| GMP | Global max pooling |
| MLP | Multilayer perceptron |
| CSPNet | Cross stage partial network |
| PANet | Path aggregation network |
| AP | Average precision |
| mAP | Mean average precision |
| IoU | Intersection over union |
References
- Brenner, B.; Cawley, J.C.; Majano, D. Electrically hazardous jobs in the US. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lim, D.; Lee, J. Safety Autonomous Platform for Data-Driven Risk Management Based on an On-Site AI Engine in the Electric Power Industry. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Kanaan, D.A. An Experimental Study of a Novel System Used for Cooling the Protection Helmet. Energies 2023, 16, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Tan, S.; Zhao, J.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Ma, B.; Li, J. Efficient and Lightweight Neural Network for Hard Hat Detection. Electronics 2024, 13, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.I.; Saraireh, L.; Rahman, A.; Al-Qarawi, S.; Mhran, A.; Al-Jalaoud, J.; Al-Mudaifer, D.; Al-Haidar, F.; AlKhulaifi, D.; Youldash, M.; et al. Personal protective equipment detection: A deep-learning-based sustainable approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, A.; Gupta, R.; Zualkernan, I.; Das, S.K. Role of IoT technologies in big data management systems: A review and Smart Grid case study. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2024, 100, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhi, V.S.K.; Sankarlal, R.; Thomas, A. Detection of personal protective equipment (PPE) compliance on construction site using computer vision based deep learning techniques. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Wu, H.B. Detection and tracking of safety helmet in construction site. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2021, 218, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, W.; Fan, W.; Tian, Z. Segmentation method for personnel safety helmet based on super pixel features and SVM classification. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Xu, K.; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Zhang, W.; Wu, H. Detection and tracking of safety helmet in factory environment. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 105406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, D.; Fan, Y.; Bai, J. Safety helmet wearing status detection based on improved boosted random ferns. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 16783–16796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Seo, S. UAV low-altitude remote sensing inspection system using a small target detection network for helmet wear detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Zhao, J. Detection and tracking of safety helmet based on DeepSort and YOLOv5. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 10781–10794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J. An improved helmet detection algorithm based on YOLO V4. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 2022, 33, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthan, K.S.; Domnic, S. An attentive convolutional transformer-based network for road safety. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 16351–16377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hao, T.; Li, F.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z. Faster R-CNN-LSTM construction site unsafe behavior recognition model. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Hong, X.; Sheng, Y.; Sun, L. YOLO-Helmet: A novel algorithm for detecting dense small safety helmets in construction scenes. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 107170–107180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, X.; Gao, H. Method based on the cross-layer attention mechanism and multiscale perception for safety helmet-wearing detection. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 95, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Hou, Z.; Dai, W. A Lightweight Safety Helmet Detection Algorithm Based on Receptive Field Enhancement. Processes 2024, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, Q. Safety Helmet-Wearing Detection System for Manufacturing Workshop Based on Improved YOLOv7. J. Sens. 2023, 2023, 7230463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Tohti, T.; Hamdulla, A. BDC-YOLOv5: A helmet detection model employs improved YOLOv5. Signal Image Video Process. 2023, 17, 4435–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, M.; Qiu, Z. Lg-yolov8: A lightweight safety helmet detection algorithm combined with feature enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, Q.; Tan, Q. Detection of helmet use among construction workers via helmet-head region matching and state tracking. Autom. Constr. 2025, 171, 105987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otgonbold, M.E.; Gochoo, M.; Alnajjar, F.; Ali, L.; Tan, T.H.; Hsieh, J.W.; Chen, P.Y. SHEL5K: An extended dataset and benchmarking for safety helmet detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.; Jadhav, R.; Suryawanshi, Y.; Chumchu, P.; Khare, G.; Shinde, T. HelmetML: A dataset of helmet images for machine learning applications. Data Brief 2024, 56, 110790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Hamed, H.N.A.; Zhou, D. Relation explore convolutional block attention module for skin lesion classification. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2025, 35, e70002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Guan, C. Tensor-cspnet: A novel geometric deep learning framework for motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 10955–10969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Fan, X.; Gong, M.; Ma, W.; Miao, Q. PANet: A point-attention based multi-scale feature fusion network for point cloud registration. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2512913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warhade, K.K.; Merchant, S.N.; Desai, U.B. Performance evaluation of shot boundary detection metrics in the presence of object and camera motion. IETE J. Res. 2011, 57, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, H.A.A.; Murni, A.; Chahyati, D. Enhancing Bounding Box Regression for Object Detection: Dimensional Angle Precision IoU-Loss. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 81029–81047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Chu, H.; Tu, X. Enhancing object detection in low-light conditions with adaptive parallel networks. J. Electron. Imaging 2025, 34, 013007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Wu, Y. Rethinking PASCAL-VOC and MS-COCO dataset for small object detection. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 93, 103830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Object Types | Labels | Training Set | Validation Set | Test Set | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | Objects | Images | Objects | Images | Objects | Images | Objects | ||
| correctly wearing | aqm_zqpd | 700 | 1357 | 100 | 188 | 200 | 375 | 1000 | 1920 |
| wrongly wearing | aqm_wzqpd | 700 | 763 | 100 | 112 | 200 | 225 | 1000 | 1100 |
| not wearing | aqm_wpd | 700 | 1302 | 100 | 181 | 200 | 367 | 1000 | 1850 |
| Total | / | 2100 | 3422 | 300 | 481 | 600 | 967 | 3000 | 4870 |
| Configuration Name | Specific Information |
|---|---|
| Server type | DELL Precision T5820 GPU |
| CPU | i9-10980XE, 18 cores, 3.0 GHz |
| GPU | RTX3090, 24 GB |
| Memory | 128 GB |
| Hard disk | 10 T, solid-state drive (SSD) |
| Model | Parameters (M) | Computation (GFLOPs) | mAP@0.5 | mAP@[0.5:0.95] | Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 7.2 | 16.5 | 56.8% | 37.4% | 156 |
| YOLOv5m | 21.2 | 49.0 | 64.1% | 45.4% | 98 |
| YOLOv5l | 46.5 | 109.1 | 67.3% | 49.0% | 67 |
| YOLOv5x | 86.7 | 205.7 | 68.9% | 50.7% | 34 |
| Model | Location of CBAM | AP/% (↑Improvement) | Speed (FPS) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correctly Wearing | Wrongly Wearing | Not Wearing | |||
| YOLOv5s | None | 96.20 | 89.40 | 94.30 | 142.00 |
| YOLOv5s-m1 | Backbone only | 97.63 (↑1.43) | 93.85 (↑4.45) | 96.82 (↑2.52) | 131.50 (↓7.39%) |
| YOLOv5s-m2 | Neck only | 97.05 (↑0.85) | 95.47 (↑6.07) | 95.12 (↑0.82) | 126.80 (↓10.70%) |
| YOLO-CBAM | Dual path | 99.08 (↑2.88) | 98.76 (↑9.36) | 98.31 (↑4.01) | 115.30 (↓18.80%) |
| Model | AP/% | mAP@0.5/% | mAP@[0.5:0.95]/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correctly Wearing | Wrongly Wearing | Not Wearing | |||
| SSD | 86.30 | 75.87 | 82.74 | 81.58 | 58.23 |
| Faster R-CNN | 92.13 | 84.72 | 90.49 | 89.12 | 67.78 |
| Mask R-CNN | 93.77 | 86.54 | 91.87 | 90.69 | 70.34 |
| YOLOv5s | 96.20 | 89.40 | 94.30 | 93.30 | 76.10 |
| YOLO-CBAM | 99.08 | 98.76 | 98.31 | 98.81 | 84.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Jia, R.; Chen, X.; Cao, G.; Zhao, Z. Dual-Path Attention Network for Multi-State Safety Helmet Identification in Complex Power Scenarios. Processes 2025, 13, 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092750
Li W, Jia R, Chen X, Cao G, Zhao Z. Dual-Path Attention Network for Multi-State Safety Helmet Identification in Complex Power Scenarios. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092750
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Rong Jia, Xiangwu Chen, Ge Cao, and Ziyan Zhao. 2025. "Dual-Path Attention Network for Multi-State Safety Helmet Identification in Complex Power Scenarios" Processes 13, no. 9: 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092750
APA StyleLi, W., Jia, R., Chen, X., Cao, G., & Zhao, Z. (2025). Dual-Path Attention Network for Multi-State Safety Helmet Identification in Complex Power Scenarios. Processes, 13(9), 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092750






