Shear-Induced Degradation and Rheological Behavior of Polymer-Flooding Waste Liquids: Experimental and Numerical Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Setup
- Initial Stage (0–3 min): Open-loop shear mode, where the solution passed through the shear zone multiple times for effective treatment.
- Stable Stage (3–20 min): Closed-loop shear mode to establish a stable flow field, maintained for 20 min to ensure shear equilibrium.
2.3. Numerical Simulation Model Establishment
3. Results and Discussions
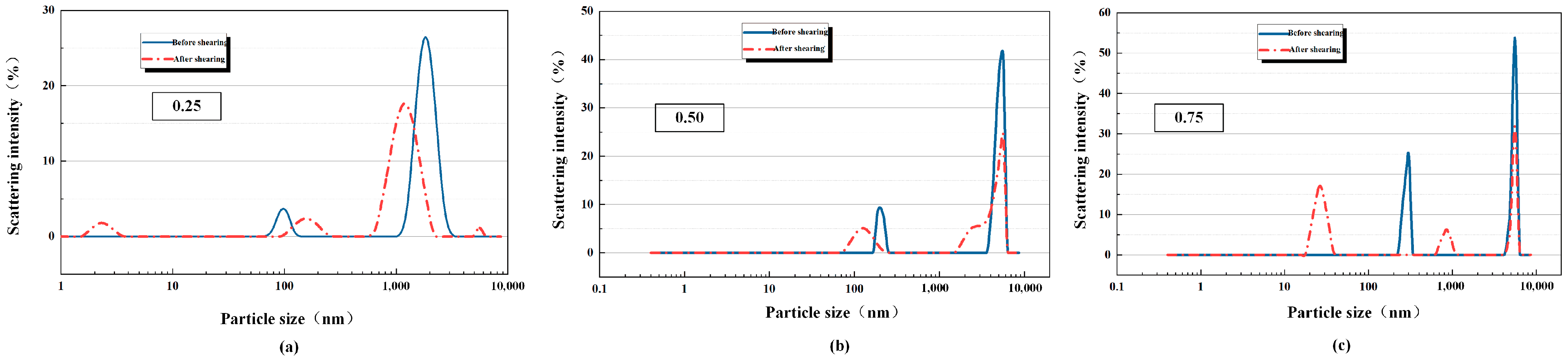
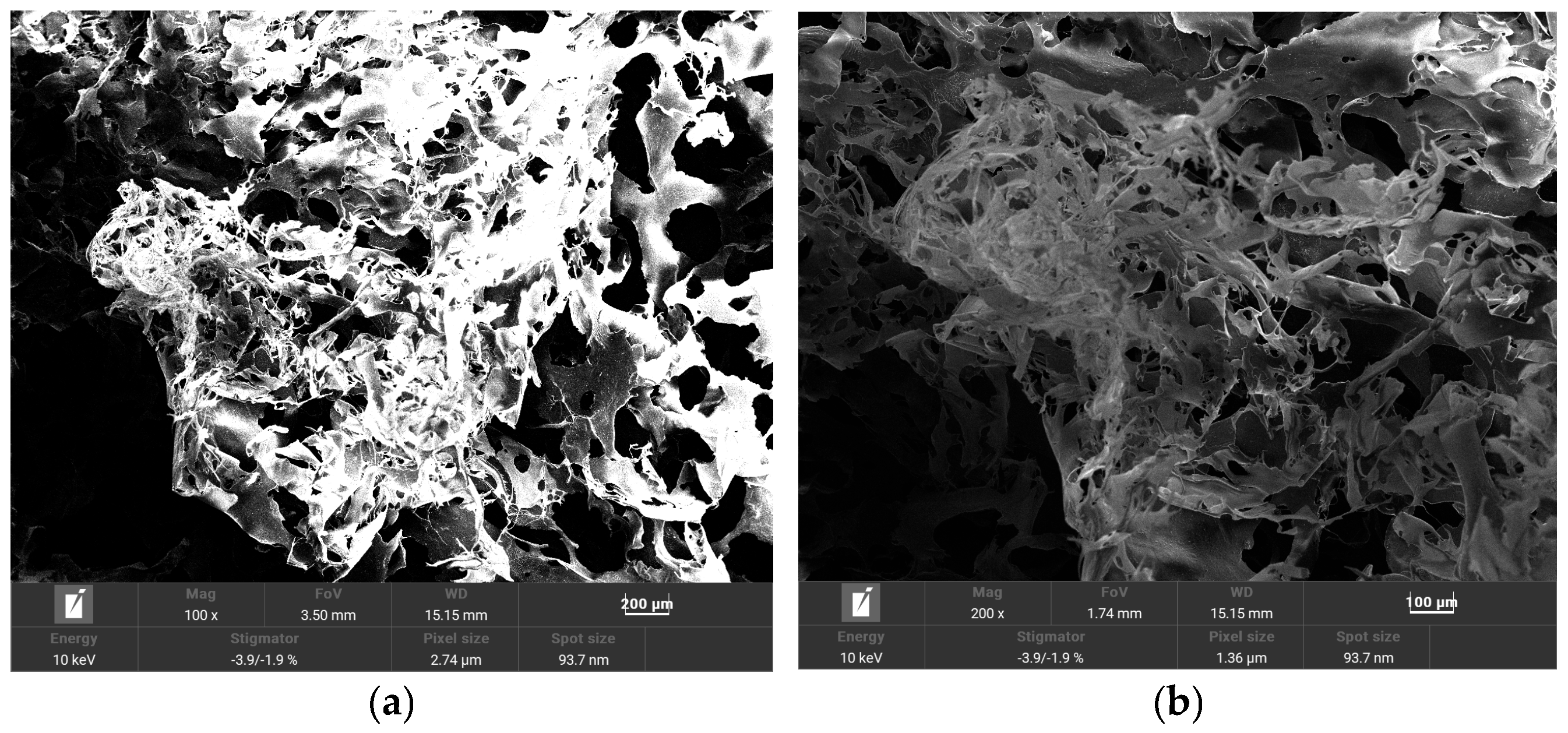
3.1. Shearing Mechanism and Microstructural Evolution of Polymer Flooding Solutions
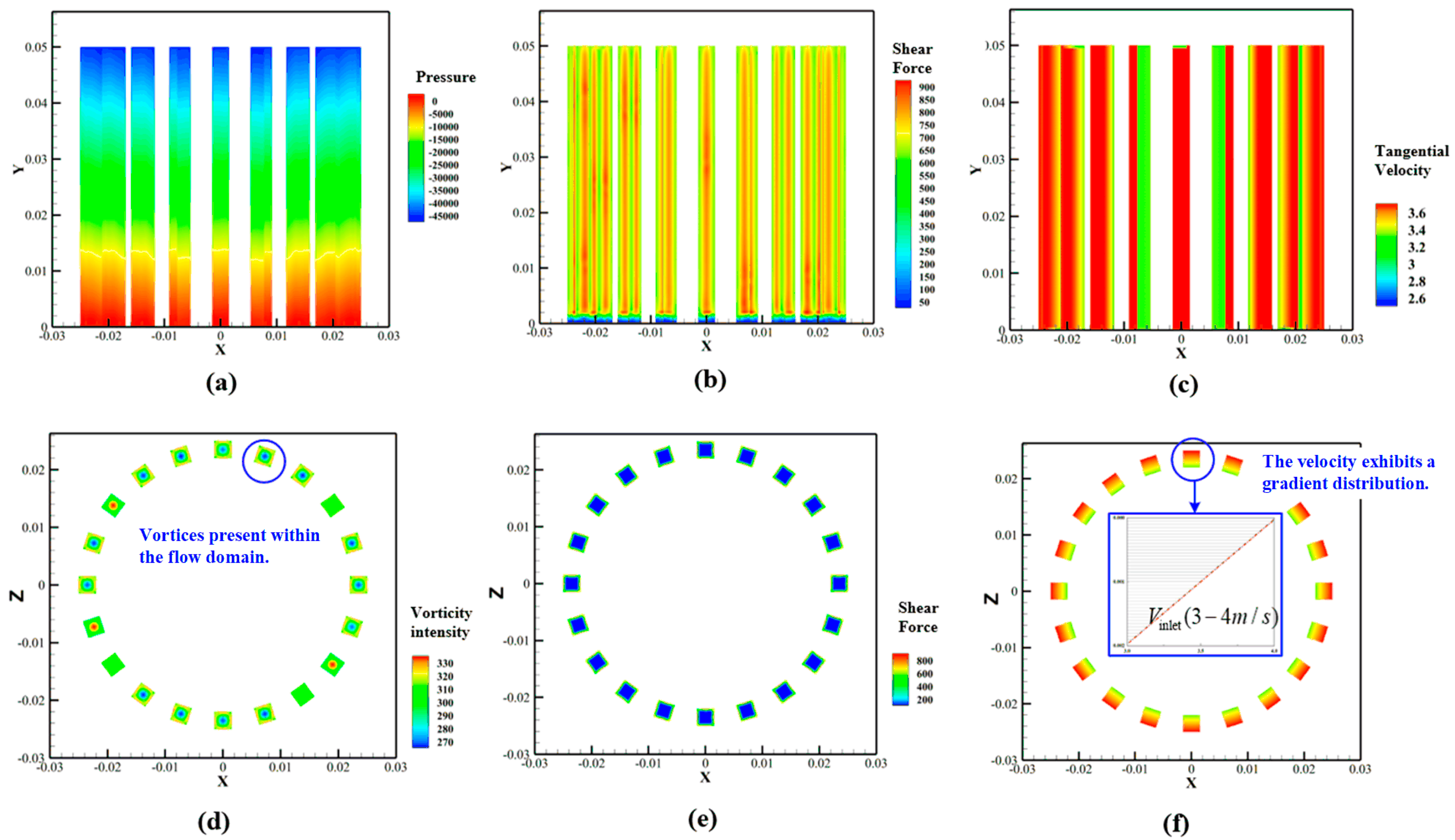
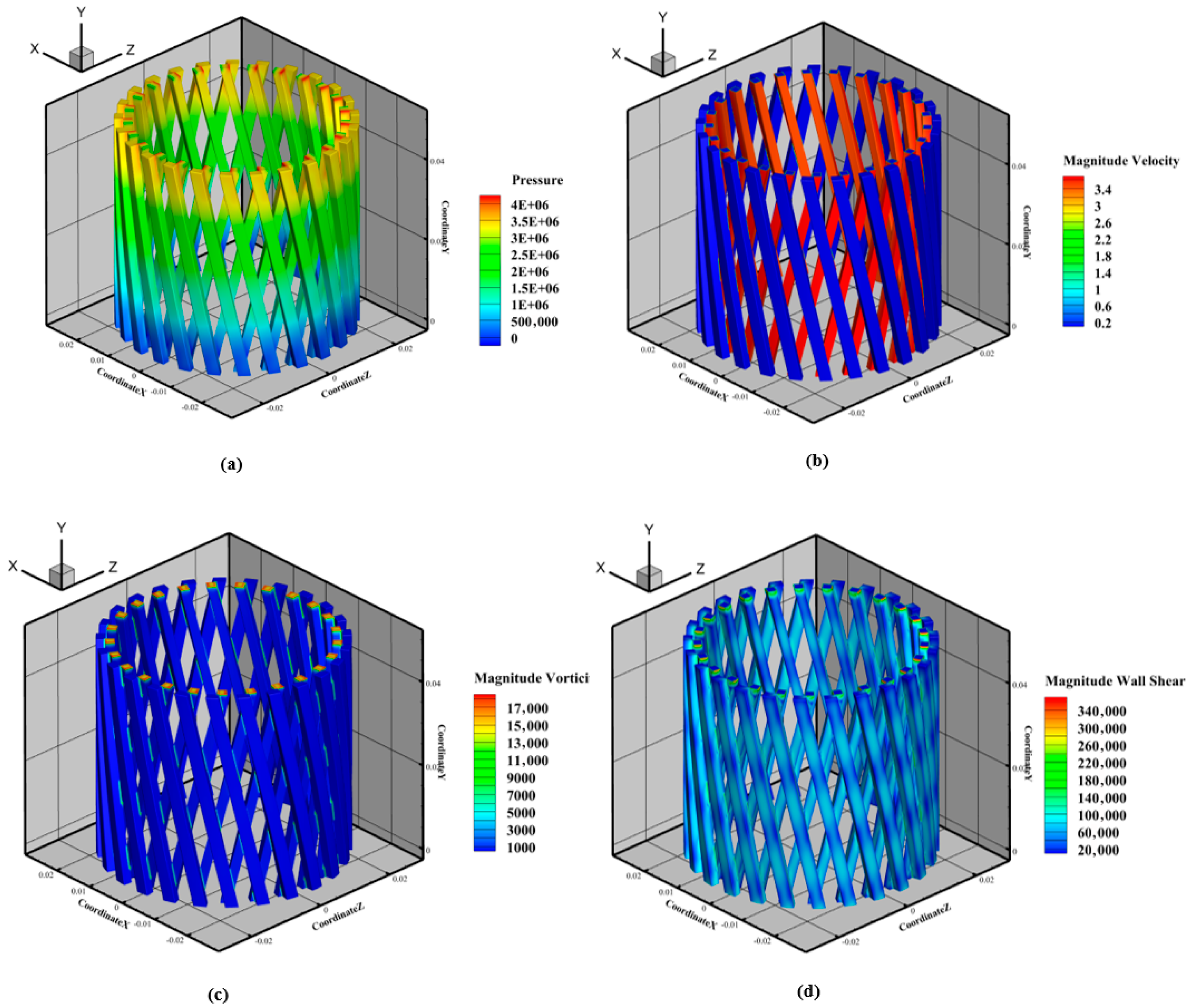
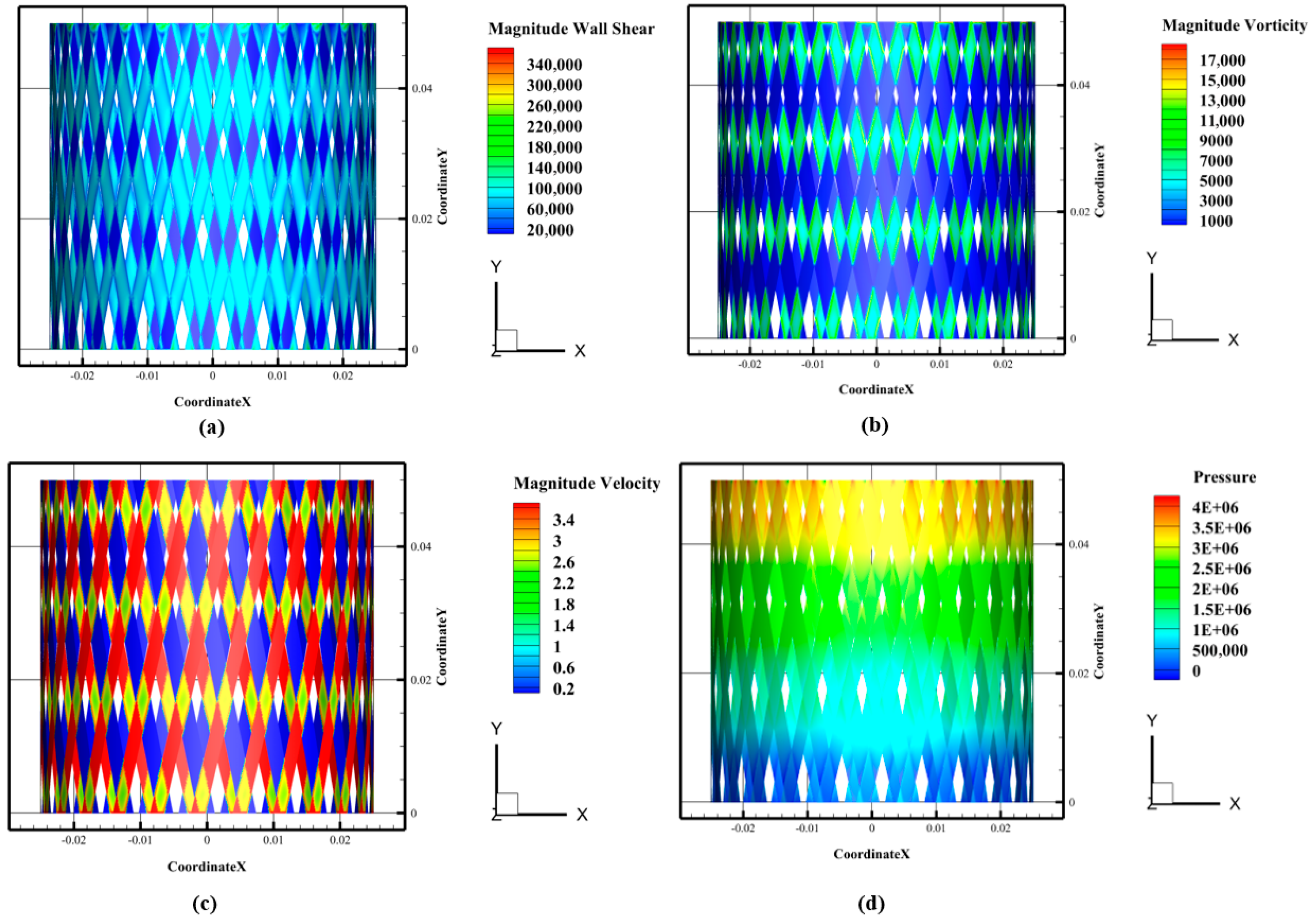
3.2. Shear Characteristics of Flow Field in Rotor–Stator Domains: A Comparative Analysis
3.3. Study on the Influence of Rotor–Stator Flow Domain Structure on Shear Flow Characteristics
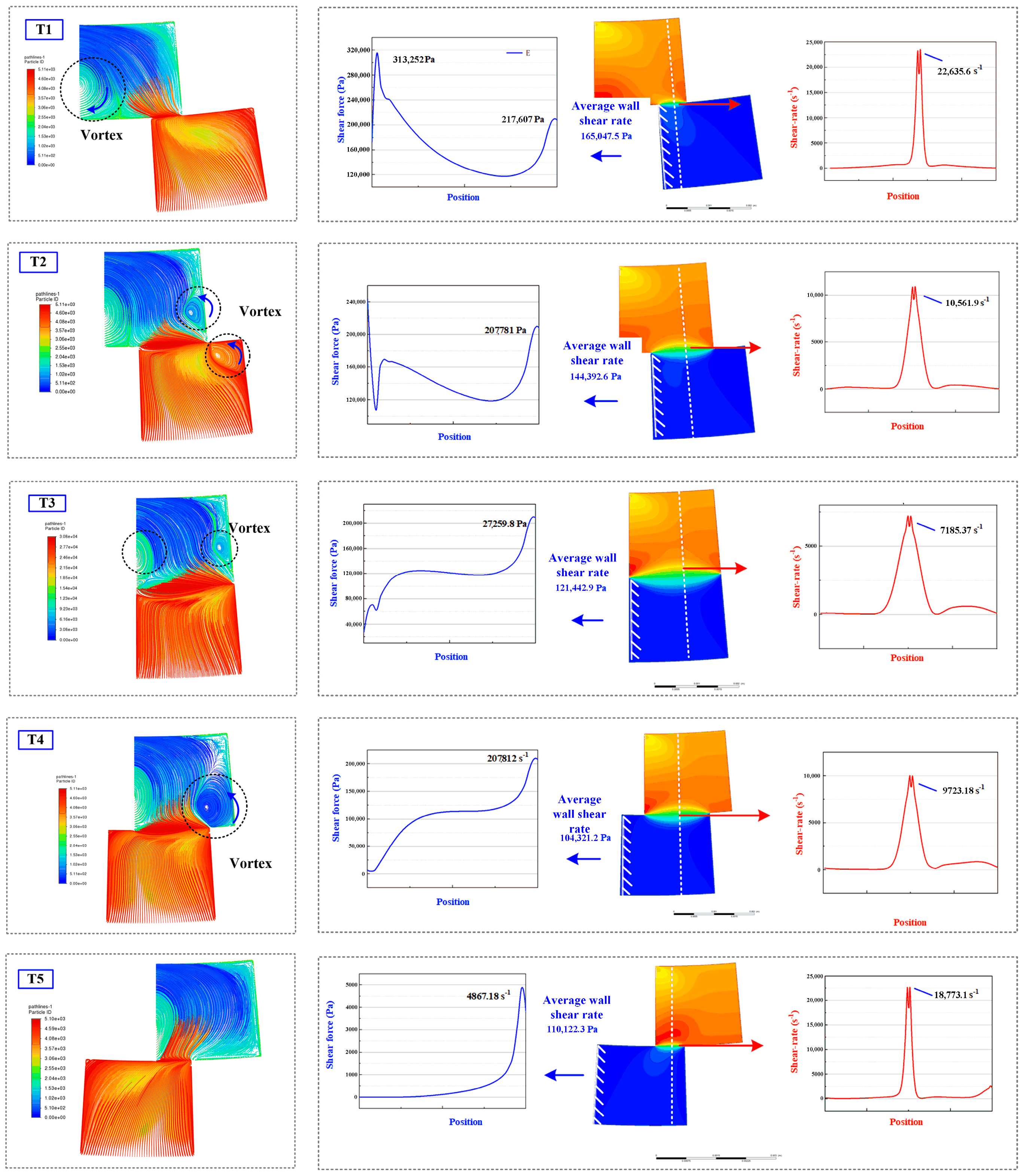
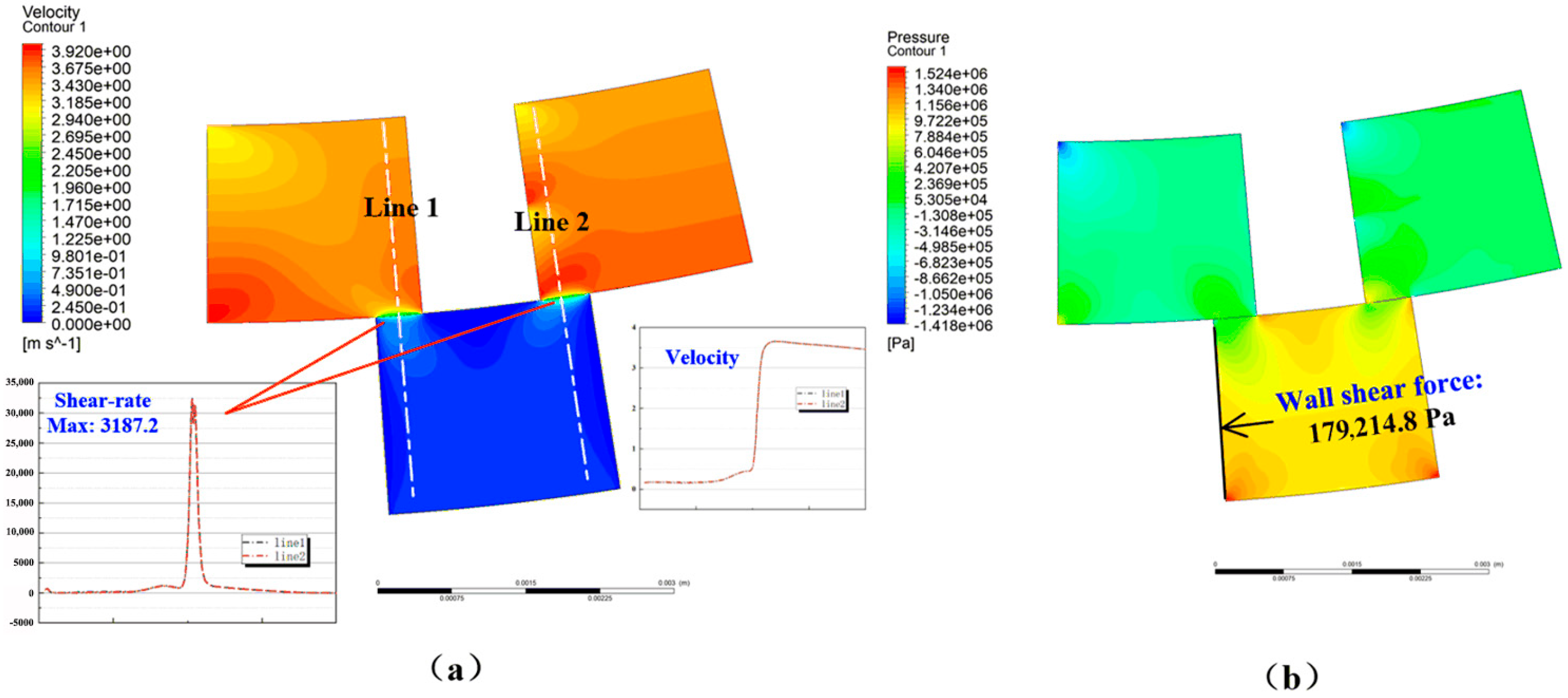
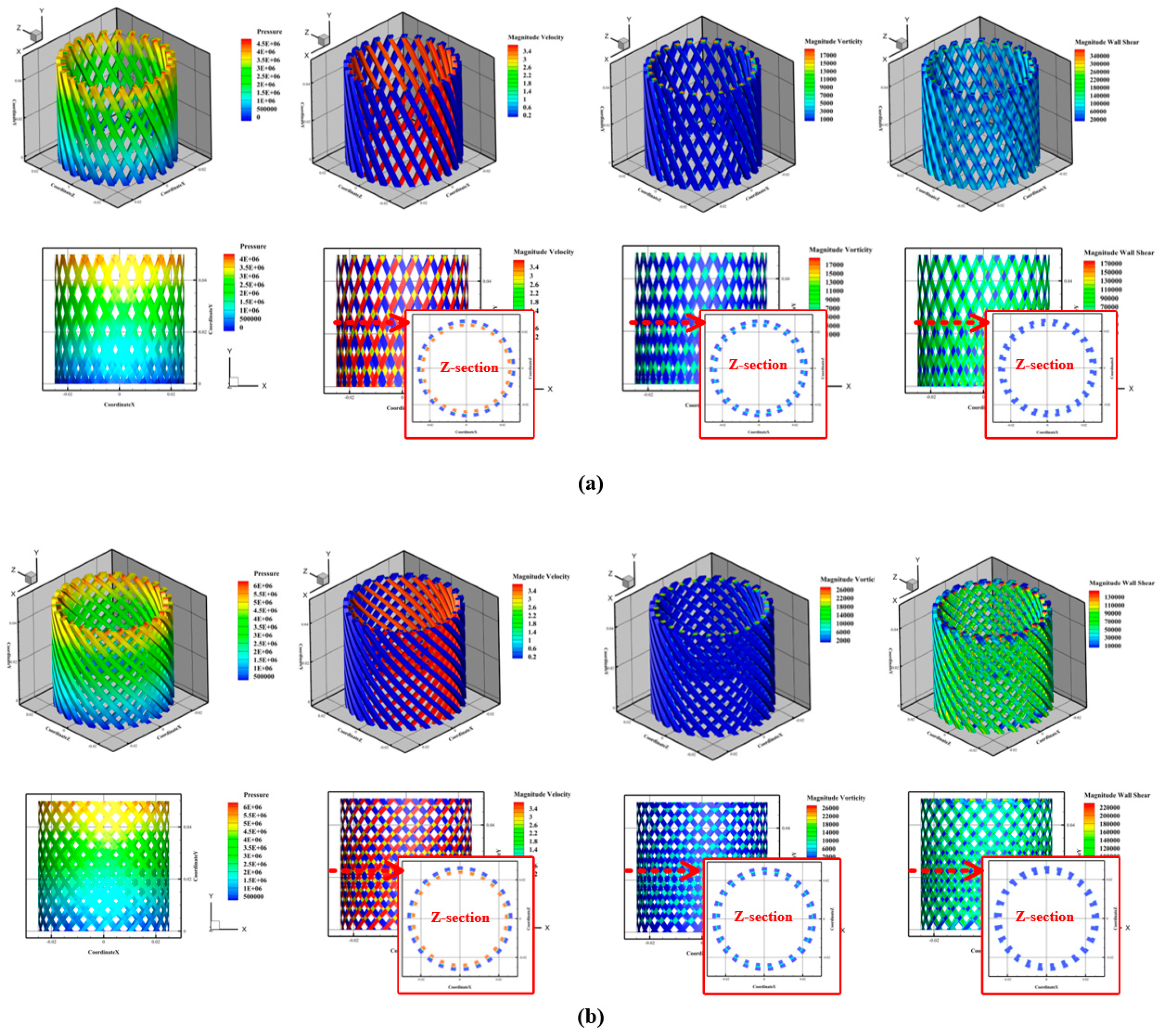
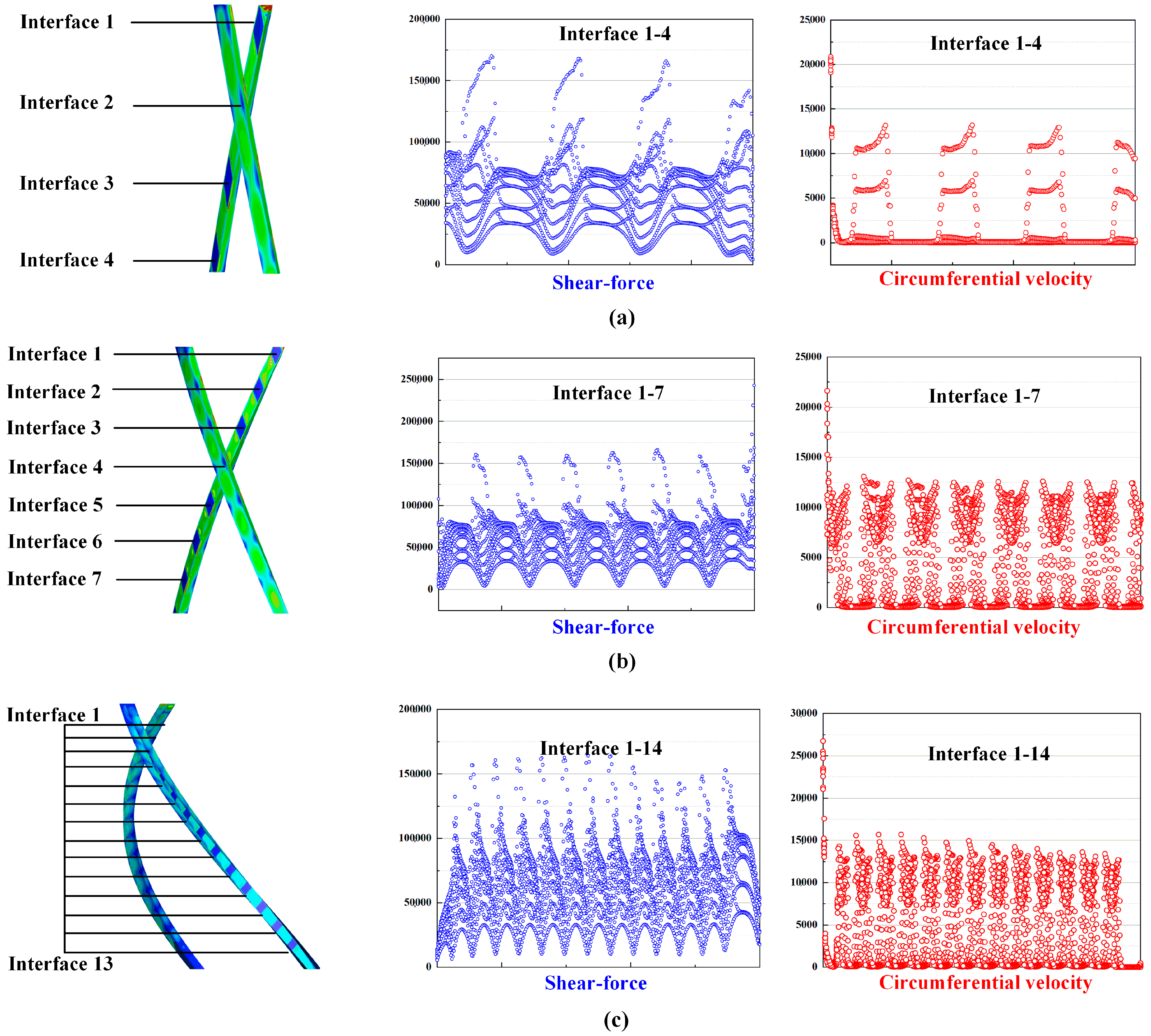
3.3.1. Rotating Flow Domain with 30° Torsion
3.3.2. Rotating Flow Domain with 60° and 90° Torsion
3.4. Methodological Limitations and Scope of Interpretation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PFWL | Polymer flooding waste liquids |
| EOR | Polymer flooding is an enhanced oil recovery |
References
- Andrews, W.; Bradley, S.; Reed, P.; Salehi, M.; Chappell, D. Enhanced Polymer Flooding—Reservoir Triggering Improves Injectivity and Eliminates Shear Degradation. In Proceedings of the IOR 2017–19th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, Strasbourg, France, 24–27 April 2017; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands, 24–27 April 2017; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Wang, J. Pretreatment of alkali/surfactant/polymer (ASP)-flooding produced wastewater by electron beam radiation to improve oil-water separation. Chemosphere 2024, 351, 141252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husveg, T.; Stokka, M.; Husveg, R.; Jouenne, S. The Development of a Low-Shear Valve Suitable for Polymer Flooding. SPE J. 2020, 25, 2632–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.Y. Shear-induced transitions in colloidal and polymeric liquids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 290, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, J.J.; Prada, L.C.; Maya, G.A.; Gomez-Vergel, J.L.; Castro, R.H.; Quintero, H.I.; Jimenez, R.; Perez, E.E. CFD simulation of HPAM EOR solutions mechanical degradation by restrictions in turbulent Flow. CT&F-Cienc. Tecnol. Futuro 2020, 10, 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.; Yu, G.; Ma, R.; Wu, K.; Chen, Z. Effect of Polymer Degradation on Polymer Flooding in Homogeneous Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering, Manufacturing Technology and Control (ICMEMTC 2018), MATEC Web of Conferences. Bangkok, Thailand, 6 August 2018; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2018; Volume 187, p. 01006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupas, A.; Hénaut, I.; Rousseau, D.; Poulain, P.; Tabary, R.; Argillier, J.; Aubry, T. Impact of Polymer Mechanical Degradation on Shear and Extensional Viscosities: Toward Better Injectivity Forecasts in Polymer Flooding Operations. In Proceedings of the SPE International Conference on Oilfield Chemistry, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 8–9 April 2013. Paper SPE-164083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, S.; Wang, W.; She, Y.; Patmonoaji, A.; Suekane, T. Enhanced oil recovery by using polymer flooding with shear-thinning property and in-situ chemical reaction. In Proceedings of the THERMOFLUID XII: The 12th International Conference on Thermofluids, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 10–11 November 2021; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2023; p. 020001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavland, A.; Åsen, S.; Mebratu, A.; Gathier, F. Scaling of Mechanical Degradation of EOR Polymers: From Field-Scale Chokes to Capillary Tubes. SPE Prod. Oper. 2020, 36, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Mohanty, K. Laboratory treatment of HPAM polymers for injection in low permeability carbonate reservoirs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 185, 106574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Romero-Zerón, L.; Penlidis, A. Evaluation of Polymeric Materials for Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery. Processes 2020, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Yu, G.; Chen, Z.; Wu, K.; Dong, X.; Zhu, Z. Effect of Polymer Degradation on Polymer Flooding in Heterogeneous Reservoirs. Polymers 2018, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Yu, G.; Wu, K.; Dong, X.; Chen, Z. Polymer Flooding in Heterogeneous Heavy Oil Reservoirs: Experimental and Simulation Studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shu, Z.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liang, S. An Improved Study of Near-well Zone Flooding for Polymer Solution through the Mechanical Shearing and Forchheimer Flow Simulation. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shakry, B.; Skauge, T.; Shiran, S.; Skauge, A. Impact of Mechanical Degradation on Polymer Injectivity in Porous Media. Polymers 2018, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shakry, B.; Skauge, T.; Shaker Shiran, B.; Skauge, A. Polymer injectivity: Investigation of mechanical degradation of enhanced oil recovery polymers using in-situ rheology. Energies 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, G.; Zhu, S.; Ye, Z.; Shu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, D. The Effect of Shear on the Properties of an Associated Polymer Solution for Oil Displacement. Polymers 2023, 15, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambeau, O.; Alves, M.; Andreu, N.; Loriau, M.; Passade-Boupat, N. Management of Viscosity of the Back Produced Viscosified Water. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 21–23 March 2016. Paper SPE-179776-MS. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qi, M.; Zhang, G.; Yi, C. Comparative experiments on polymer degradation technique of produced water of polymer flooding oilfield. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th International Conference on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (ICEESD 2017), Shenzhen, China, 30–31 December 2017; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing: Bristol, England, 2018; Volume 113, p. 012208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, L.; Duan, M.; Yao, M.; Fang, S.; Wang, C.; Chen, S. The chemical degradation of the oil sludge produced from polymer flooding in offshore oilfield. Energy Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Han, M.; Leng, Z.; Wang, J. Study on polymer mechanical degradation in core plugs versus in capillary tubes. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2022, 13, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Ge, H.; Jin, H.; Guo, L. Experimental investigation on the degradation of polymer-containing oily sludge in sub-/supercritical water. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Shen, F.; Ren, J.; Yi, Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of Solid Particles in Polymer Waste Liquid on Grinding Tool Wall Erosion. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2834, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, F.; Torne, J.; Prada, A.; Perez, G. Shear degradation model of HPAM solutions for the design of regulator valves in polymer flooding EOR. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 2587–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Wilton, R.; Bowers, A.; O’brien, T.; Cao, Y.; Wilson, C.; Metidji, O.; Dupuis, G.; Ravikiran, R. Reinjection of Produced (Sheared) Polymer in a Canadian Viscous Oil Reservoir: Considerations to Improve Economics and Reduce Carbon Footprint. SPE J. 2022, 28, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tiwari, R.; Husein, M.; Yadav, U. Enhancing the Performance of HPAM Polymer Flooding Using Nano CuO/Nanoclay Blend. Processes 2020, 8, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, J.; Cao, X.; Wei, B.; Ji, Y.; Wang, H. Laboratory studies of the feasibility for microencapsulated polymer flooding. Fuel 2023, 354, 129378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfazazi, U.; Mushtaq, M.; Thomas, N.; Al-Shalabi, E.; Alameri, W.; Masalmeh, S.; AlSumaiti, A. Polymer Injectivity in Low Permeability Carbonate Cores: Impacts of Polymer Filtration, Mechanical Shearing, and Oil Presence. In Proceedings of the SPE Improved Oil Recovery Conference, Tulsa, OK, USA, 21–23 April 2024; Paper SPE-218233-MS. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Steeman, P.; Bulters, M.; Yu, W. Shear-induced breakdown and agglomeration in nanoparticles filled polymer: The shift of phase boundary and kinetics. J. Rheol. 2021, 65, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, S.; Ye, Z.; Xue, X.; Liu, C.; Lan, X. Effect of microscopic aggregation behavior on polymer shear resistance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.; Hénaut, I.; Dupas, A.; Poulain, P.; Tabary, R.; Argillier, J.; Aubry, T. Impact of Polymer Mechanical Degradation on Shear and Extensional Viscosities. In Proceedings of the IOR 2013-17th European Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, St. Petersburg, Russia, 16–18 April 2013; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; p. cp-342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, V.; Sharma, G. Decoding the Impact of Injection-Induced Fractures on the Sweep Efficiency of a Mature Polymer Flood through Pressure Falloff Analysis. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2022, 26, 348–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouenne, S.; Klimenko, A.; Levitt, D. Polymer Flooding: Establishing Specifications for Dissolved Oxygen and Iron in Injection Water. SPE J. 2016, 22, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Johns, M.L.; Barentin, C.; Gaillard, N. Rheological properties of partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (HPAM) solutions in the presence of surfactants and salts. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 184, 106464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Kovács, N.; Xu, H.; Pletcher, D.; Russell, A.E. Limitations of identical location SEM as a method of degradation studies on surfactant capped nanoparticle electrocatalysts. J. Catal. 2021, 395, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoult, C.; Di Martino, J.; Ruch, D. Prediction and limitation of polymer degradation in Environmental SEM. Ultramicroscopy 2012, 123, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, T.-T.; Luo, Z.-H.; Zhou, Y.-N. Simulation of irreversible and reversible degradation kinetics of linear polymers using sectional moment method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 275, 118704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
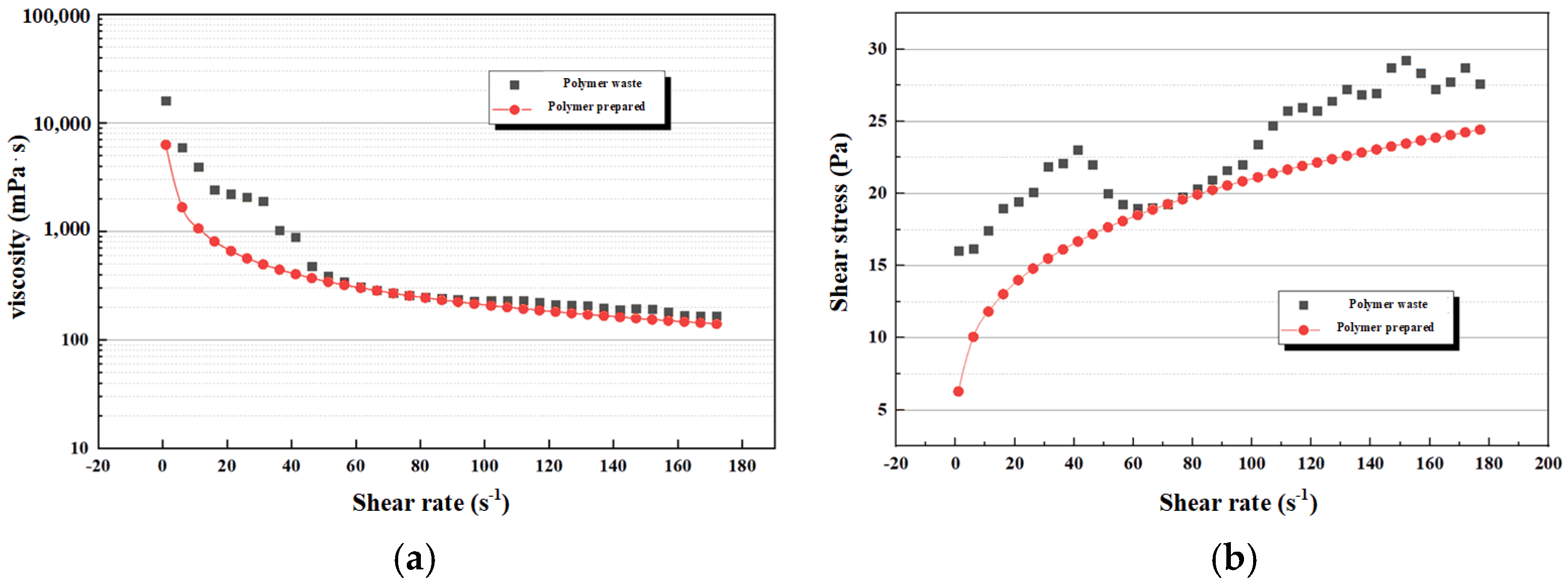
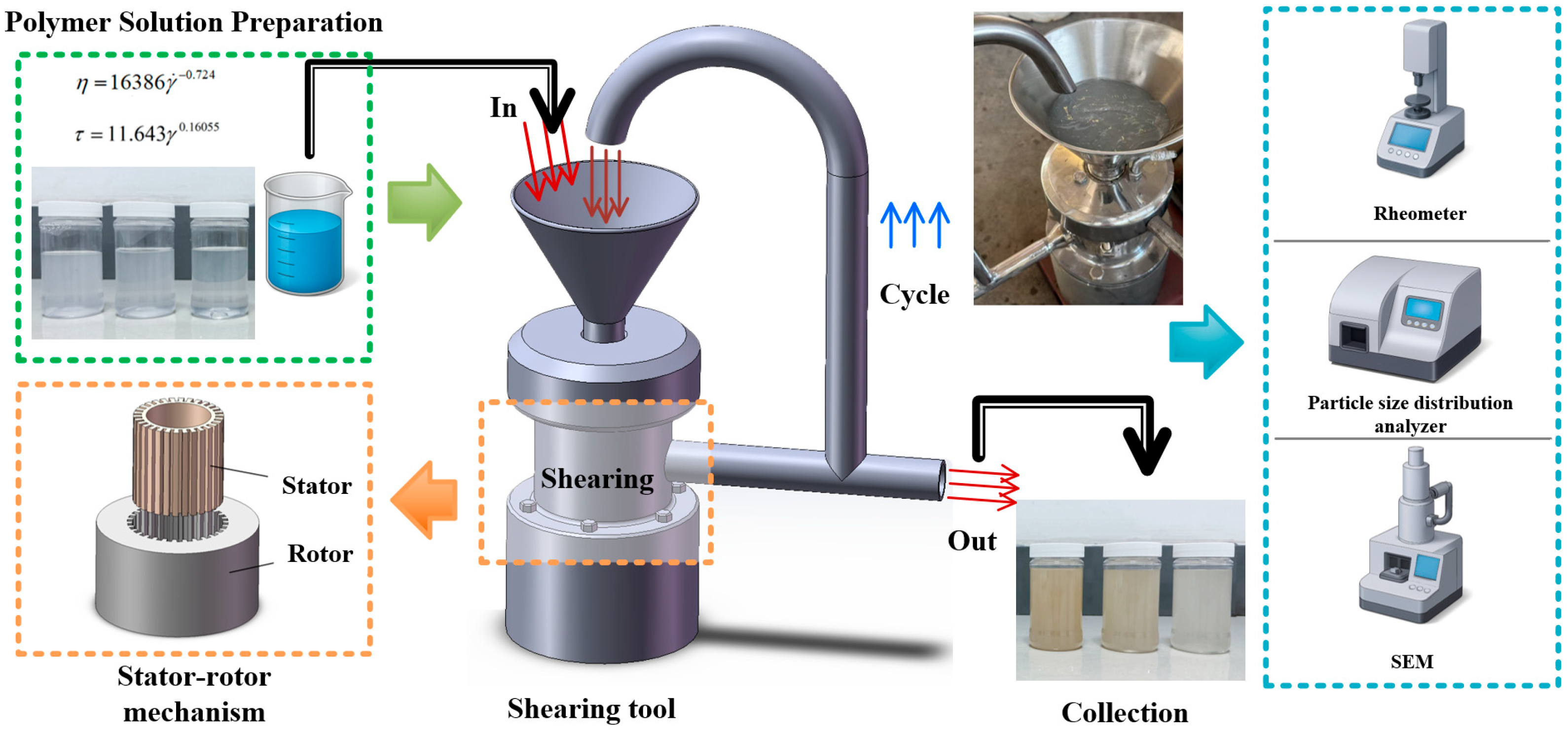

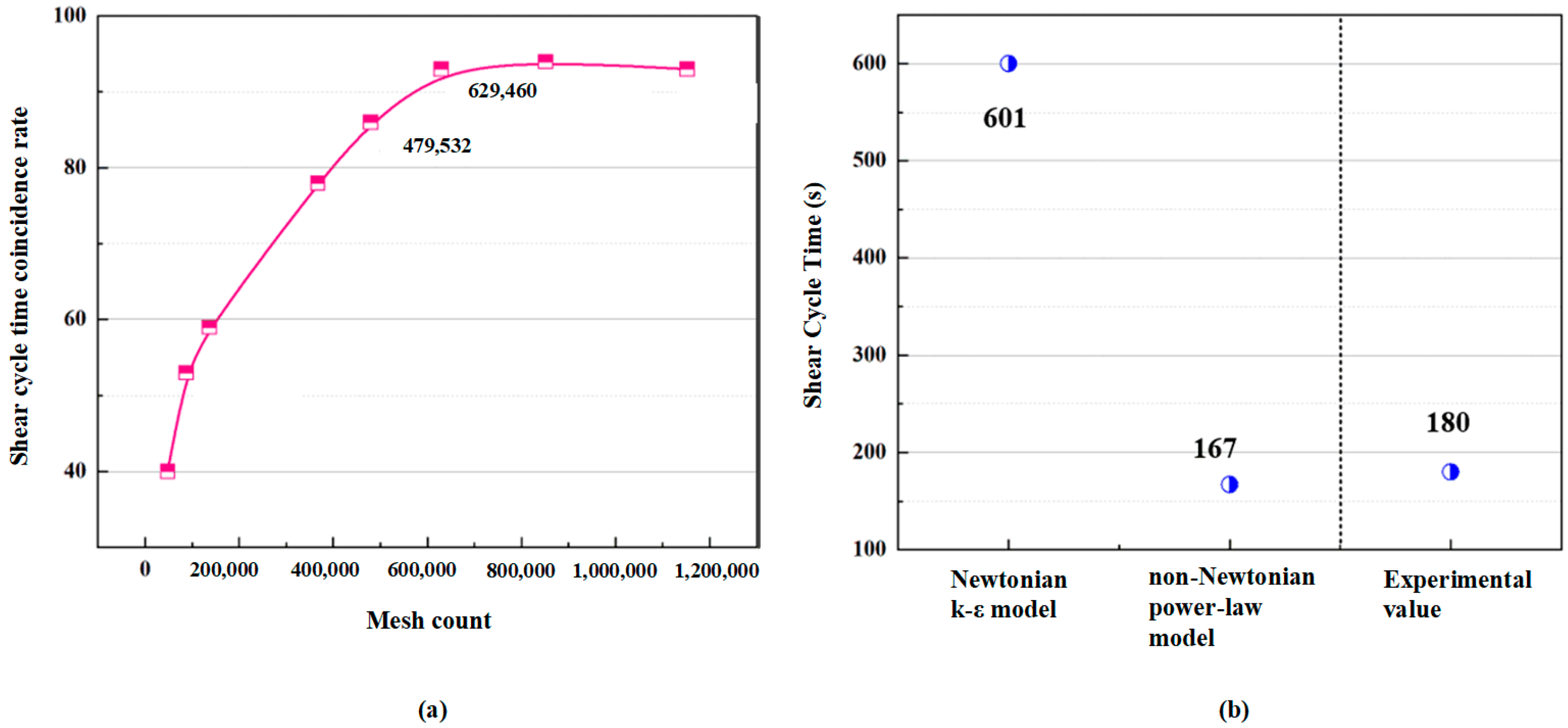













| Parameters | PFWL | 0.5% Simulated Solution | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| μ (Pa·s) | 12.7 | 12.1 | 4.7% |
| Power-law index (n) | 0.28 | 0.26 | 7.1% |
| (s−1) | 8.5 | 9.2 | 8.2% |
| Parameters | Dimension, mm |
|---|---|
| Single-shear solution volume | 1 L |
| Shearing time, Ts | 10 min |
| Motor speed, | 1450 rpm |
| Flow rate inlet, | 1.667 × 10−4 kg/s |
| Rotate domain, | 151.8 rad/s |
| Density, | 1031 kg/m3 |
| Consistency coefficient, K | 16,386 Pa s |
| Flow behavior index, n | 0.276 |
| Concentration of Polymer Flooding Simulation Fluid/% | Viscosity Before Shearing/mPa·s | Viscosity After Shearing/mPa·s | Viscosity Reduction Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 993 | 257 | 74.1 |
| 0.5 | 1647 | 597 | 63.8 |
| 0.75 | 2844 | 1223 | 57 |
| Shear Rate (s−1) | (mPa·s) | Viscosity After Shearing (mPa·s) | Viscosity Reduction Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 48.0 | 40.5 | 15.6 |
| 300 | 46.2 | 34.8 | 24.6 |
| 600 | 44.8 | 28.0 | 37.5 |
| 900 | 43.5 | 22.0 | 49.4 |
| 1200 | 42.0 | 18.8 | 55.2 |
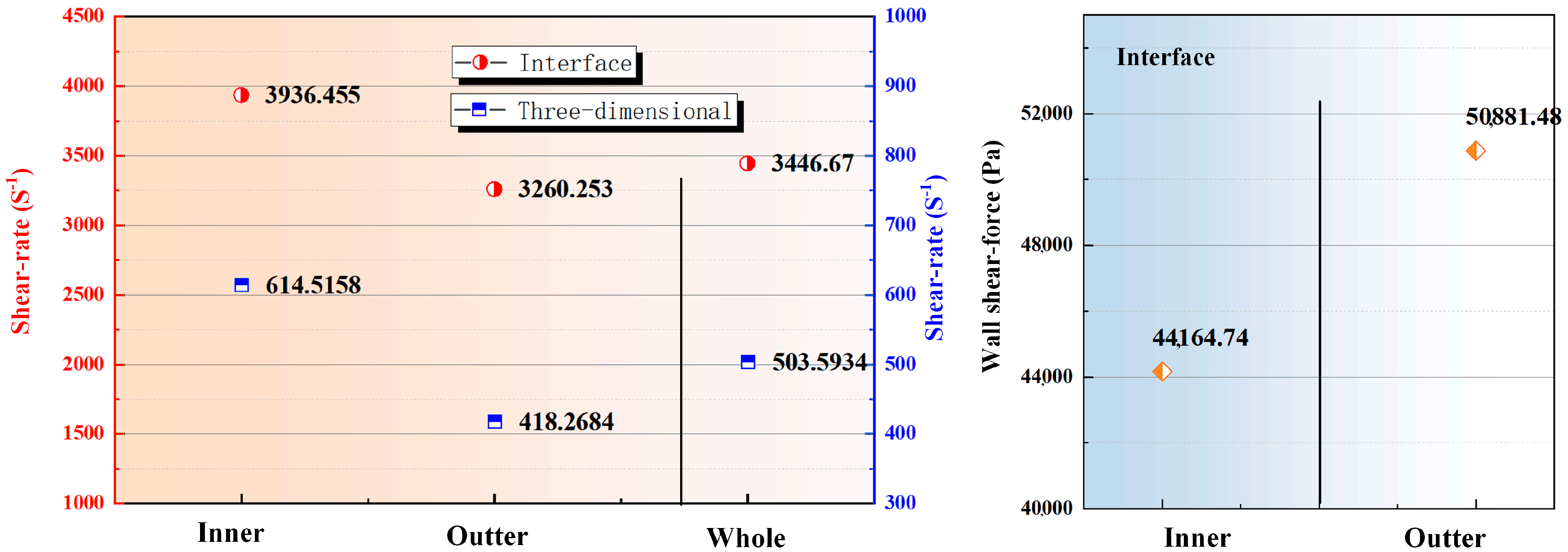
| 30° | 60° | 90° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shear-rate (s−1) | Rotating flow domain (rotor) | 659.1554 | 614.5158 | 596.7599 |
| Fixed flow domain (stator) | 443.6194 | 418.2684 | 396.5019 | |
| Whole domain | 537.3301 | 503.5934 | 483.5736 | |
| Flow field interface of rotating domain | 4285.358 | 3936.455 | 3526.047 | |
| Flow field interface of fixed domain | 3505.214 | 3260.253 | 3483.451 | |
| Wall shear force (Pa) | Inner wall shear force | 37,880.35 | 44,164.74 | 54,947.58 |
| Outter wall shear force | 44,332.21 | 50,881.48 | 55,285.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Lv, W.; Li, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Cao, H. Shear-Induced Degradation and Rheological Behavior of Polymer-Flooding Waste Liquids: Experimental and Numerical Analysis. Processes 2025, 13, 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092677
Sun B, Wang H, Liu Y, Lv W, Li Y, Ma S, Wang X, Cao H. Shear-Induced Degradation and Rheological Behavior of Polymer-Flooding Waste Liquids: Experimental and Numerical Analysis. Processes. 2025; 13(9):2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092677
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Bingyu, Hanxiang Wang, Yanxin Liu, Wei Lv, Yubao Li, Shaohua Ma, Xiaoyu Wang, and Han Cao. 2025. "Shear-Induced Degradation and Rheological Behavior of Polymer-Flooding Waste Liquids: Experimental and Numerical Analysis" Processes 13, no. 9: 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092677
APA StyleSun, B., Wang, H., Liu, Y., Lv, W., Li, Y., Ma, S., Wang, X., & Cao, H. (2025). Shear-Induced Degradation and Rheological Behavior of Polymer-Flooding Waste Liquids: Experimental and Numerical Analysis. Processes, 13(9), 2677. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13092677






