Analysis of the Characteristics of a Multi-Generation System Based on Geothermal, Solar Energy, and LNG Cold Energy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. System Model and Validation
2.1. Thermodynamic Model
2.2. Performance Evaluation
2.3. Model Validation
- (1)
- The system is in stable operation state;
- (2)
- The ambient temperature is 298.15 K and the pressure is 101.3 kPa.
3. Performance Analysis
3.1. Impact of Solar Radiation
3.2. Impact of Collector Tube Bundles
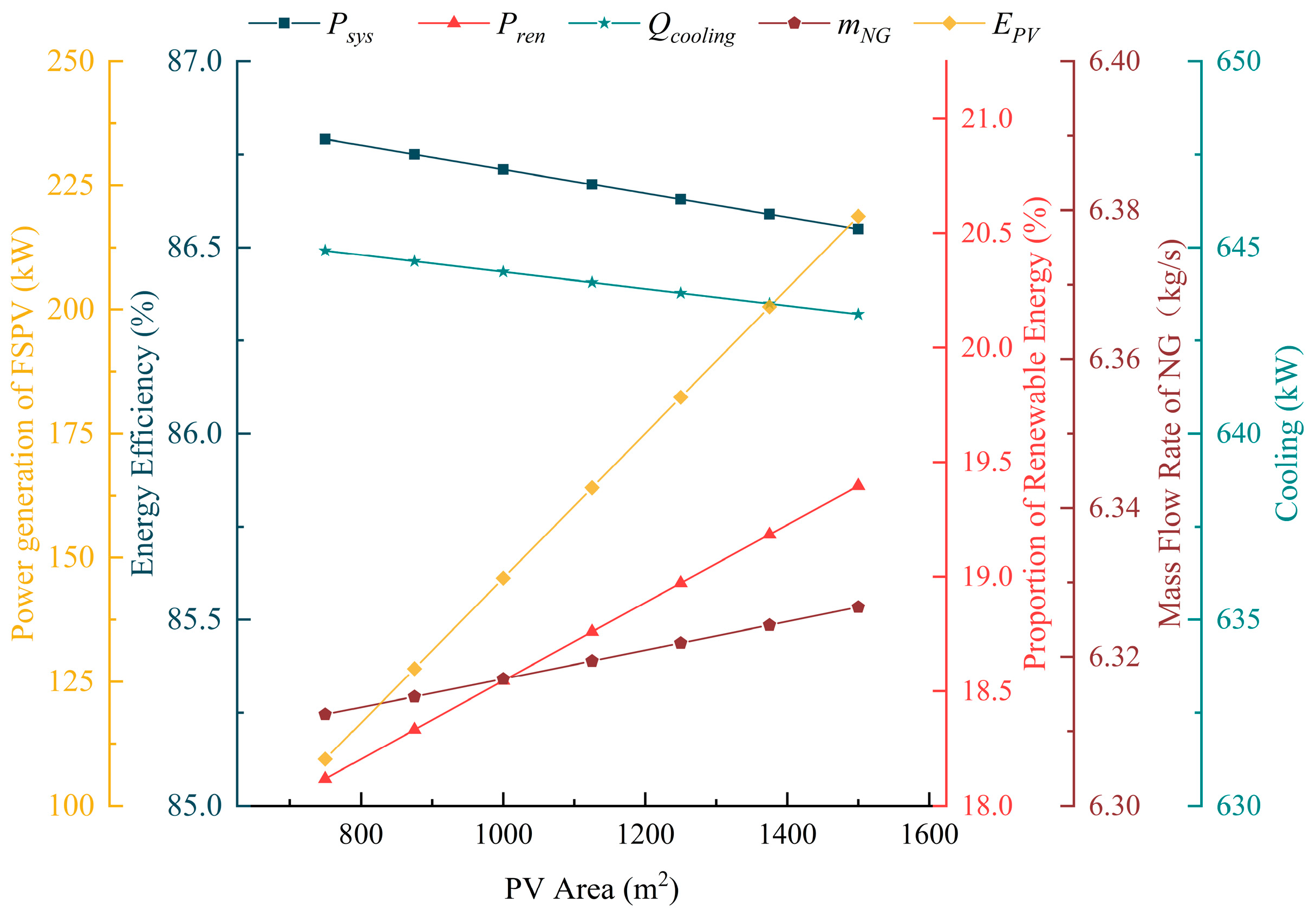
3.3. Impact of Photovoltaic Area
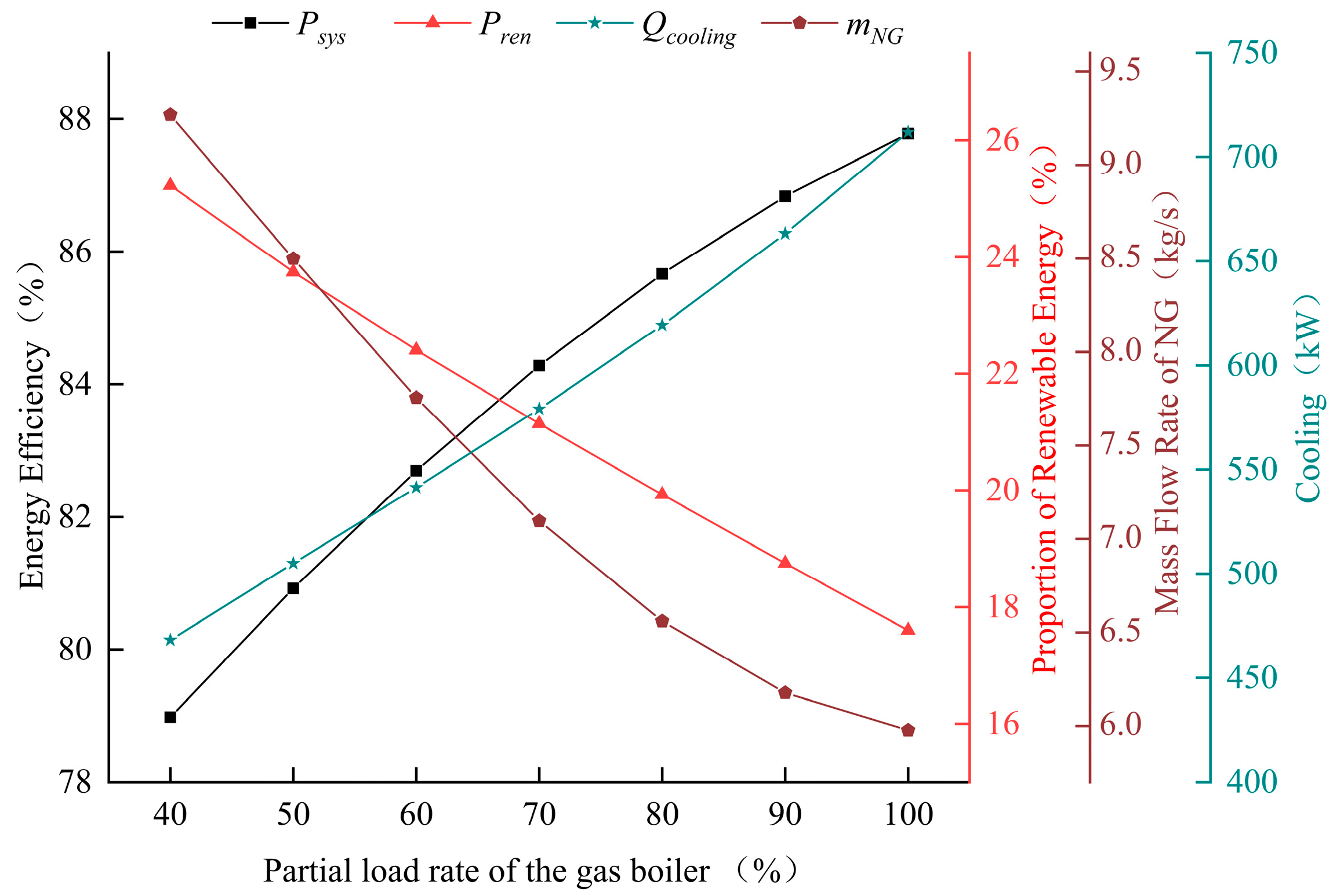
3.4. Impact of Partial Load Rate of the Gas Boiler
4. Multi-Objective Optimization of the Coupled Steam Generation System
4.1. NSGA-II Algorithm
4.2. System Optimization Model
4.2.1. Objective Functions
4.2.2. Decision Variables
4.2.3. Constraints
4.3. Optimization Results Analysis
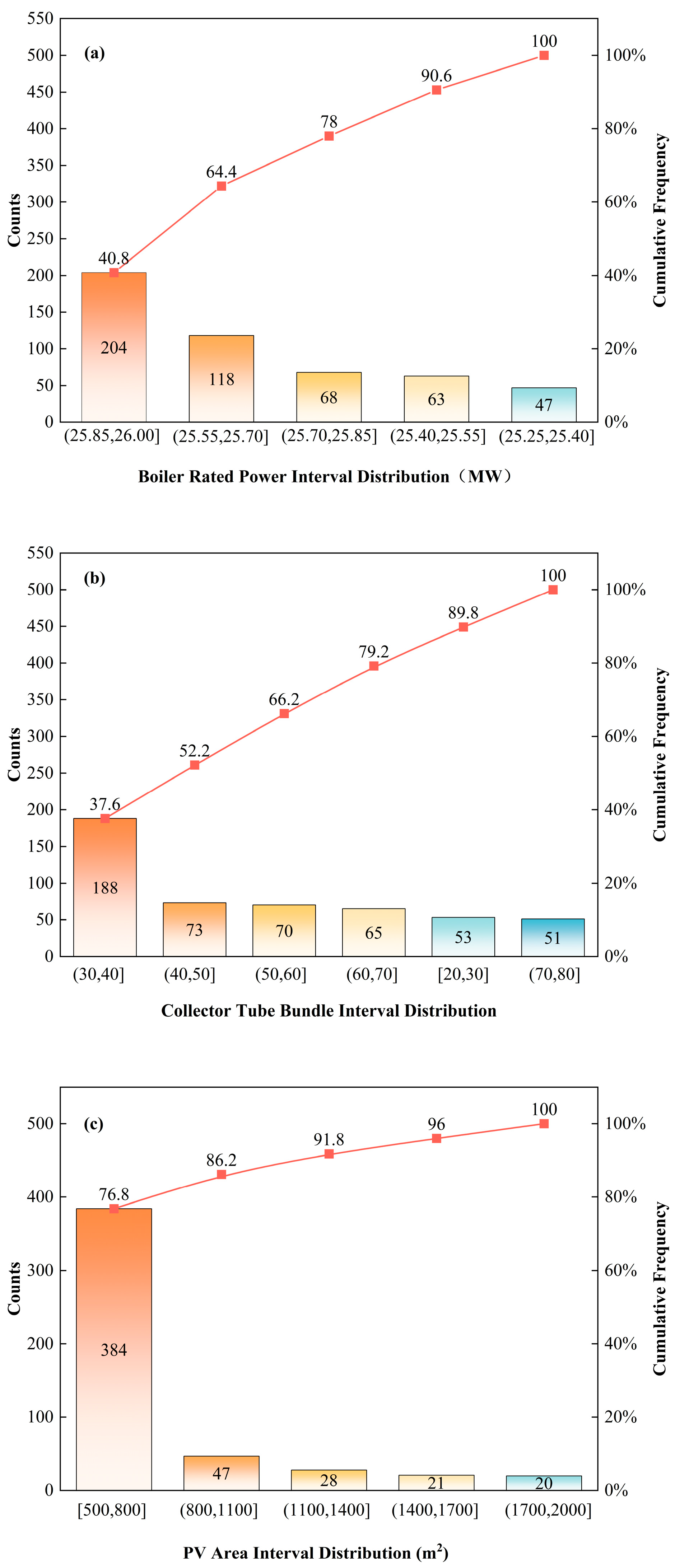
4.3.1. Distribution of Decision Variable Intervals
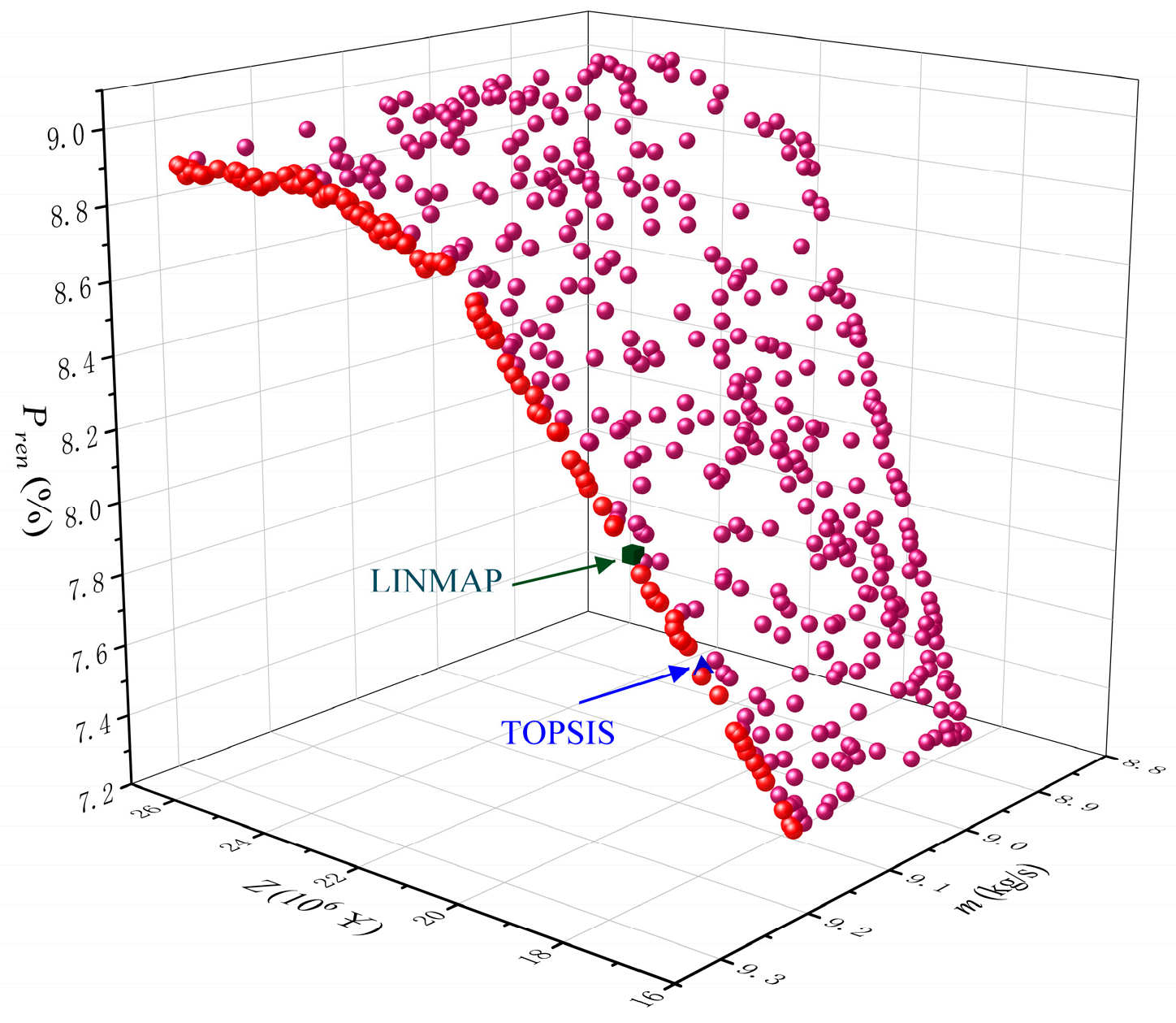
4.3.2. Optimal State Points
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| CHP | Combined heat and power |
| CS | Cold storage |
| FSPT | Full-spectrum photo-thermal |
| FSPV | Full-spectrum photovoltaic |
| GB | Gas boiler |
| HE | Heat exchanger |
| LINMAP | The linear programming technique for multidimensional analysis of preference |
| LNG | Liquefied natural gas |
| NG | Natural gas |
| NSGA-II | Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm |
| PTC | Parabolic trough collector |
| PV/T | Photovoltaic/thermal |
| PW | Production well |
| RW | Reinjection well |
| Sep | Separator |
| TOPSIS | The technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution |
| WFP | Working fluid pump |
| Symbols | |
| A | Area (m2) |
| C | Cost (CNY) |
| DNI | Direct normal irradiance (W/m2) |
| E | Power generation (kW) |
| ED | Euclidean distance |
| EQE | Spectral external quantum efficiency |
| f | Partial load rate |
| FF | Fill factor |
| h | Specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) |
| H | Convective heat transfer coefficient |
| I | Solar irradiance of the AM1.5 spectrum |
| J | Current (A) |
| k | Constant |
| n | Ideal factor |
| n | Number |
| ObjF | Objective function |
| P | System efficiency |
| Q | Heat energy (kW) |
| q | Elementary charge |
| R | Spectral reflectivity |
| RC | Relative closeness |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| V | Voltage (V) |
| α | Absorption rate |
| β | Ideal factor |
| γ | Incidence factor |
| Γ | Exchange rate |
| ε | Emissivity |
| η | Efficiency |
| λ | Wave length |
| σ | Stefan–Boltzmann constant |
| τ | Transmittance |
| ω | Construction coefficient |
| Subscripts | |
| 0 | Ambient state |
| 1,2,… | State point |
| a | Aperture |
| abs | Absorber |
| B | Boltzmann |
| c | Collector |
| cf | Cold fluid |
| ci | Inner surface of glass cover |
| co | Outer surface area of glass cover |
| Cref | Reflector’s full-spectrum reflectivity |
| f | Working fluid |
| g | Bandgap |
| GC | Glass cover |
| gt | Geothermal |
| hf | Hot fluid |
| inc | Incident energy |
| OC | Open-circuit |
| opt | Optical |
| OT | Overall transmittance |
| PT | Photothermal |
| rec | Received |
| ren | Renewable energy |
| ri | Inner surface of absorber |
| ro | Outer surface of the absorber |
| s | Isentropic state |
| SC | Short-circuit |
| sur | Surface |
| sys | Total system |
| TC | Temperature coefficient |
References
- Dogan, B.; Nketiah, E.; Ghosh, S.; Nassani, A.A. The impact of the green technology on the renewable energy innovation: Fresh pieces of evidence under the role of research & development and digital economy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 210, 115193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, A.M.; Alhuyi, M.; Hossein, M. Power generation by utilization of different renewable energy sources in five Middle Eastern countries: Present status, opportunities and challenges. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2025, 73, 104101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, S.; Astaraei, F.R.; Jahangir, M.H. Sustainability assessment of a petrochemical plant electricity supply based on 4E optimization of various hybrid renewable energy systems scenarios. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 325, 119357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouni, W.; Beucher, Y.; Zoughaib, A. Thermodynamic architecture for steam generation using heat pumps system valorizing industrial waste heat. Int. J. Refrig. 2025, 172, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaş, A.; Şener, R.; Uslu, S.; Der, O. Experimental study on performance and emission optimization of MgO nanoparticle-enriched 2nd generation biodiesel: A method for employing nanoparticles to improve cleaner diesel combustion. J. Energy Inst. 2025, 120, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhamshetty, V.; Arudchelvam, Y.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Johnson, D.C. Modeling dark fermentation for biohydrogen production: ADM1-based model vs. Gompertz model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Ellegaard, L.; Ahring, B.K. A mathematical model for dynamic simulation of anaerobic digestion of complex substrates: Focusing on ammonia inhibition. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1993, 42, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, F.; Karimi, I.A.; Farooq, S. Low-emissions hydrogen from MCH dehydrogenation: Integration with LNG regasification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 321, 119012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, K.; Das, D. Improvement of fermentative hydrogen production: Various approaches. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 65, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Sun, S.; Wu, C.; Gao, N.; Liu, H.; Liu, R. Migration characteristics of geothermal fluids in karst geothermal reservoirs in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Plain. Geosci. Front. 2025, 102104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumlao, S.M.G.; Ogata, S. Japan’s local consumption of solar energy: The role of energy demand in residential and small-scale solar projects. Sol. Energy 2025, 287, 113175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agberegha, L.O.; Aigba, P.A.; Nwigbo, S.C.; Onoroh, F.; Samuel, O.D.; Bako, T.; Der, O.; Ercetin, A.; Sener, R. Investigation of a Hybridized Cascade Trigeneration Cycle Combined with a District Heating and Air Conditioning System Using Vapour Absorption Refrigeration Cooling: Energy and Exergy Assessments. Energies 2024, 17, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, H.; Le Pierrès, N.; Chèze, D.; Wurtz, E. Assessing the energy performance of solar photovoltaic, thermal and hybrid PVT panels in a building context: A systematic study of the criteria’ definitions and studies parameters. Sol. Energy 2025, 286, 113126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Lior, N. Exergo-economic analysis method and optimization of a novel photovoltaic/thermal solar-assisted hybrid combined cooling, heating and power system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, P.A.; Ryu, B.R.; Song, M.K.; Nam, D.; Kang, H. Thermodynamics analysis of a novel designation of LNG solid oxide fuel cells combined system with CO2 capture using LNG cold energy. J. Eng. Res. 2024, 12, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, C.; Arslan, M.; Tokgoz, N.; Ozdemir, S.N. Thermoeconomic optimization of a geothermal-assisted hybrid LNG and power generation system: Simulation, performance assessment, and sustainability insights. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 73, 106426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toker, S.C. A comprehensive thermodynamic assessment of an innovative solar-geothermal driven multigeneration system for sustainable production of energy, hydrogen, freshwater, heating and cooling. Renew. Energy 2025, 252, 123571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, F.R.; Hussy, I.; Kyazze, G.; Dinsdale, R.; Hawkes, D.L. Continuous dark fermentative hydrogen production by mesophilic microflora: Principles and progress. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Hidalgo, A.M.; Smoliński, A.; Sanchez, A. A meta-analysis of research trends on hydrogen production via dark fermentation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 13300–13339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabadi, Z.K.; Boyaghchi, F.A. Thermodynamic, economic and environmental impact studies on various distillation units integrated with gasification-based multi-generation system: Comparative study and optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, F.; Shen, H.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, X.M.; Heydarian, D. Design and analysis of an innovative biomass-powered cogeneration system based on organic flash and supercritical carbon dioxide cycles. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 80, 623–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xie, H.; Sun, L.; Gao, T.; Xia, E.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Long, X. Advanced exergy analysis and multi-objective optimization of dual-loop ORC utilizing LNG cold energy and geothermal energy. Renew. Energy 2025, 239, 122164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yang, M.; Fan, Y.; Luo, T.; Li, H.; Liu, T.; Tang, S.; Zhao, K. Thermodynamic evaluation of a combined cooling, heating, hydrogen, and power multi-generation system for full-spectrum solar energy utilization. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 300, 118019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, S.; Yue, W.; Tian, Z.; Yang, C.; Gao, W. Energy, exergy, economic and environmental (4E) evaluation of a solar-integrated energy system at medium–high temperature using CO2 as the parabolic trough collector (PTC) working medium. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 296, 117683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Chen, H.; Zhong, F.; Jia, J.; Song, Y. Multi-objective optimization of a novel CCHP system with organic flash cycle based on different operating strategies. Energy 2023, 276, 127577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Chen, H.; Jia, J.; Song, Y.; Zhong, F.; Yang, S.; Xue, G. Thermodynamic analysis of a CCHP system integrated with a regenerative organic flash cycle. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 202, 117833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Fu, C.; Wang, J.; Yao, W.; Wu, T.; Ding, S.; Xu, P. Exergy-cost-carbon nexus of power-to-X system from carbon dioxide/water co-electrolysis driven by solar full-spectrum energy. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 308, 118382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.B.; Pitt, L.; Love, M. Biohydrogen production: Prospects and limitations to practical application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2004, 29, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosaffa, A.H.; Farshi, L.G. Thermodynamic and economic assessments of a novel CCHP cycle utilizing low-temperature heat sources for domestic applications. Renew. Energy 2018, 120, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Chen, H.; Wu, D.; Zhong, F.; Song, Y. Thermodynamic and exergo-economic evaluation of biomass-to-X system combined the chemical looping gasification and proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 322, 119132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamnejad Takleh, H.; Zare, V.; Mohammadkhani, F.; Sadeghiazad, M.M. Proposal and thermoeconomic assessment of an efficient booster-assisted CCHP system based on solar-geothermal energy. Energy 2022, 246, 123360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Hao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; He, Y. Thermodynamic and exergoeconomic evaluation of coal and biomass co-gasification as solid oxide fuel cell feed coupled with supercritical carbon dioxide and organic Rankine cycle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 300, 117951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
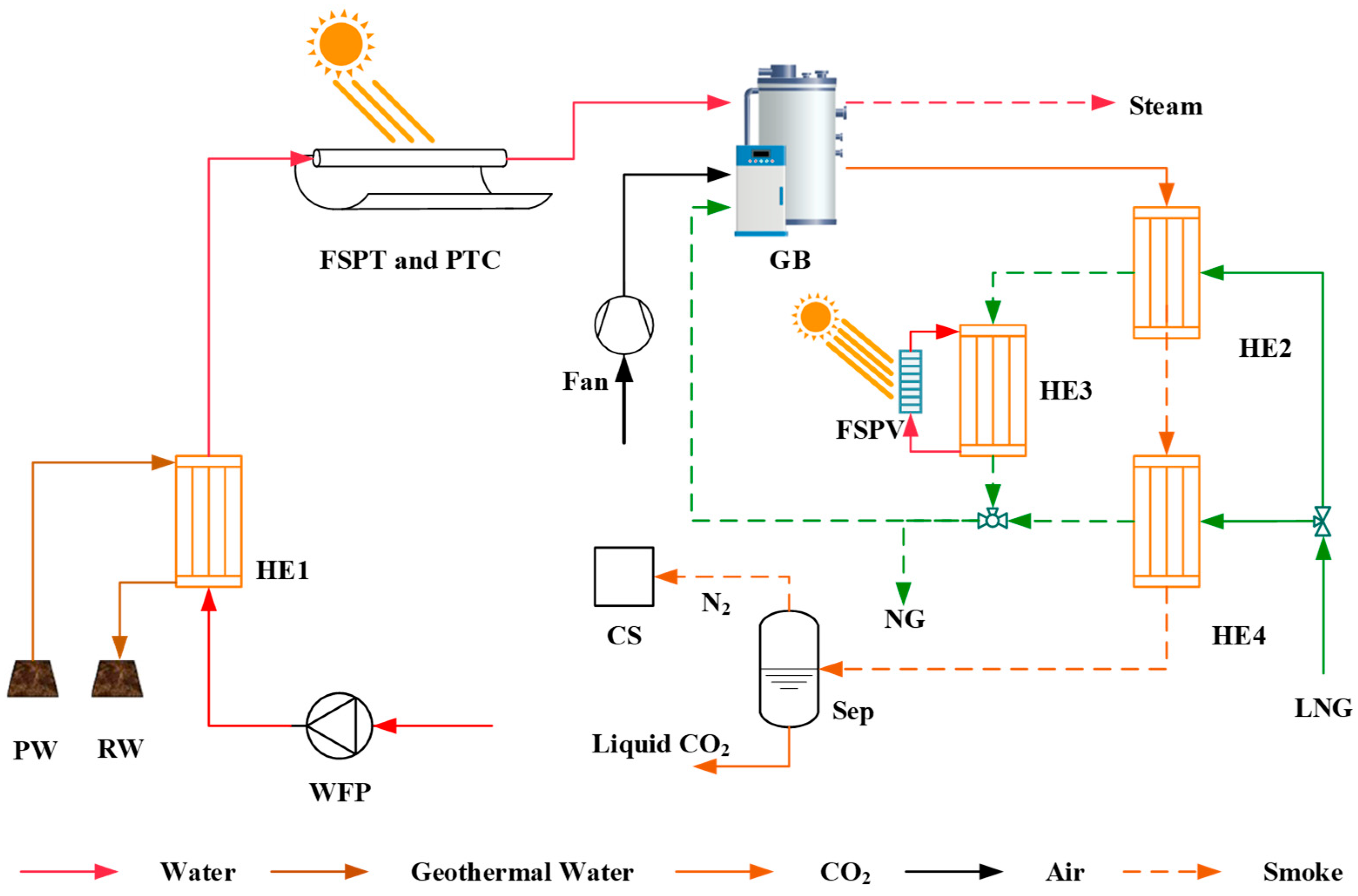
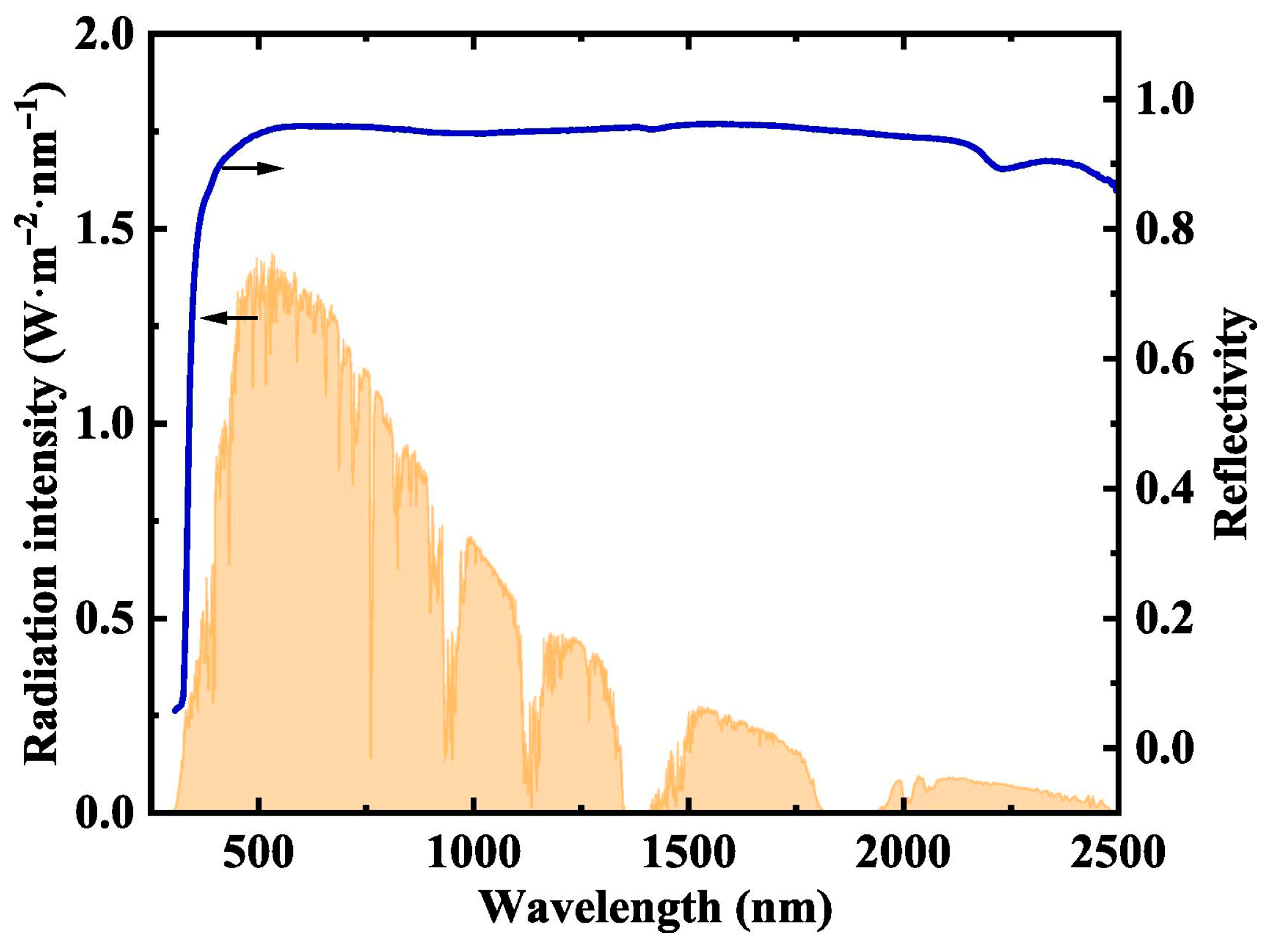
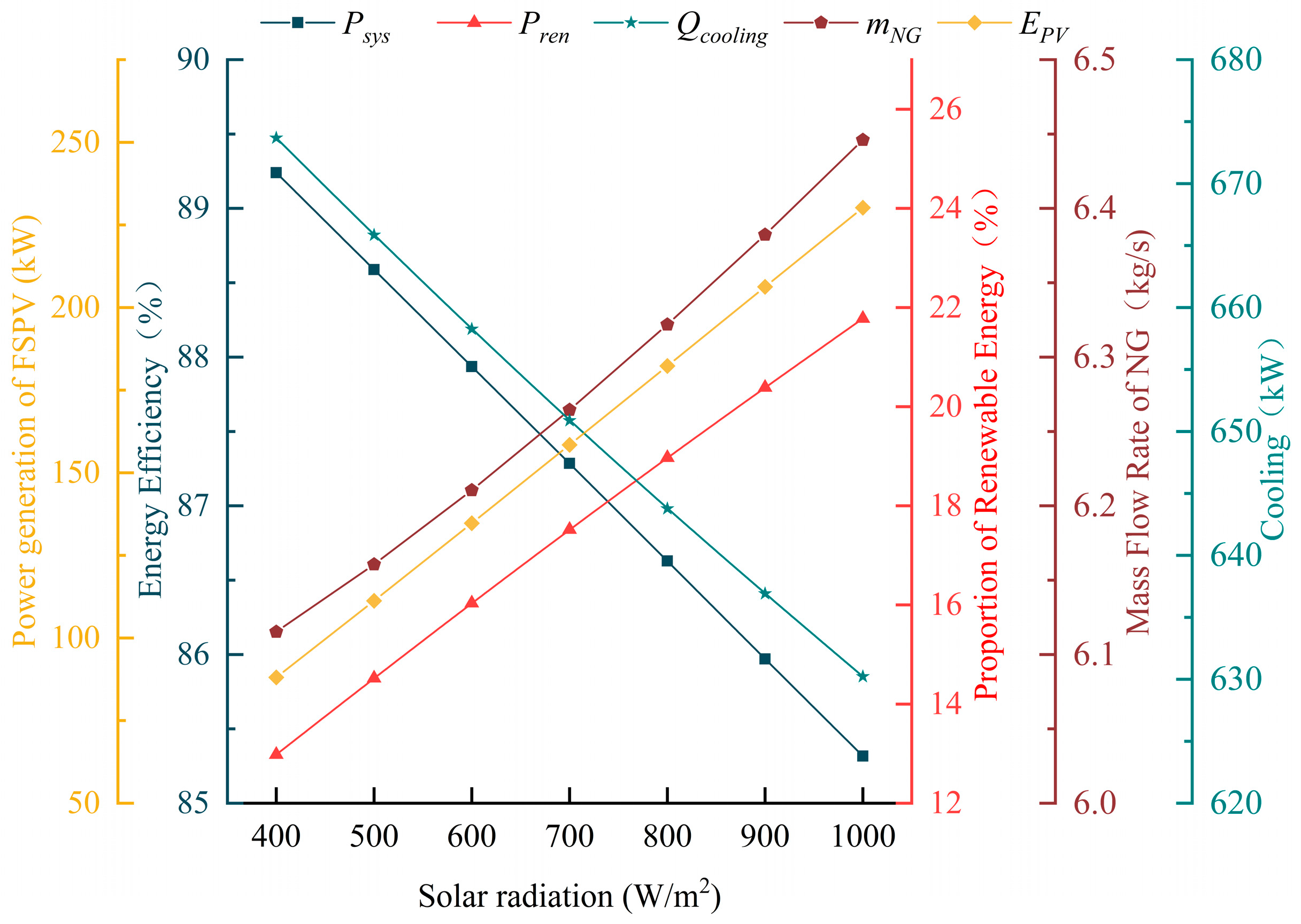
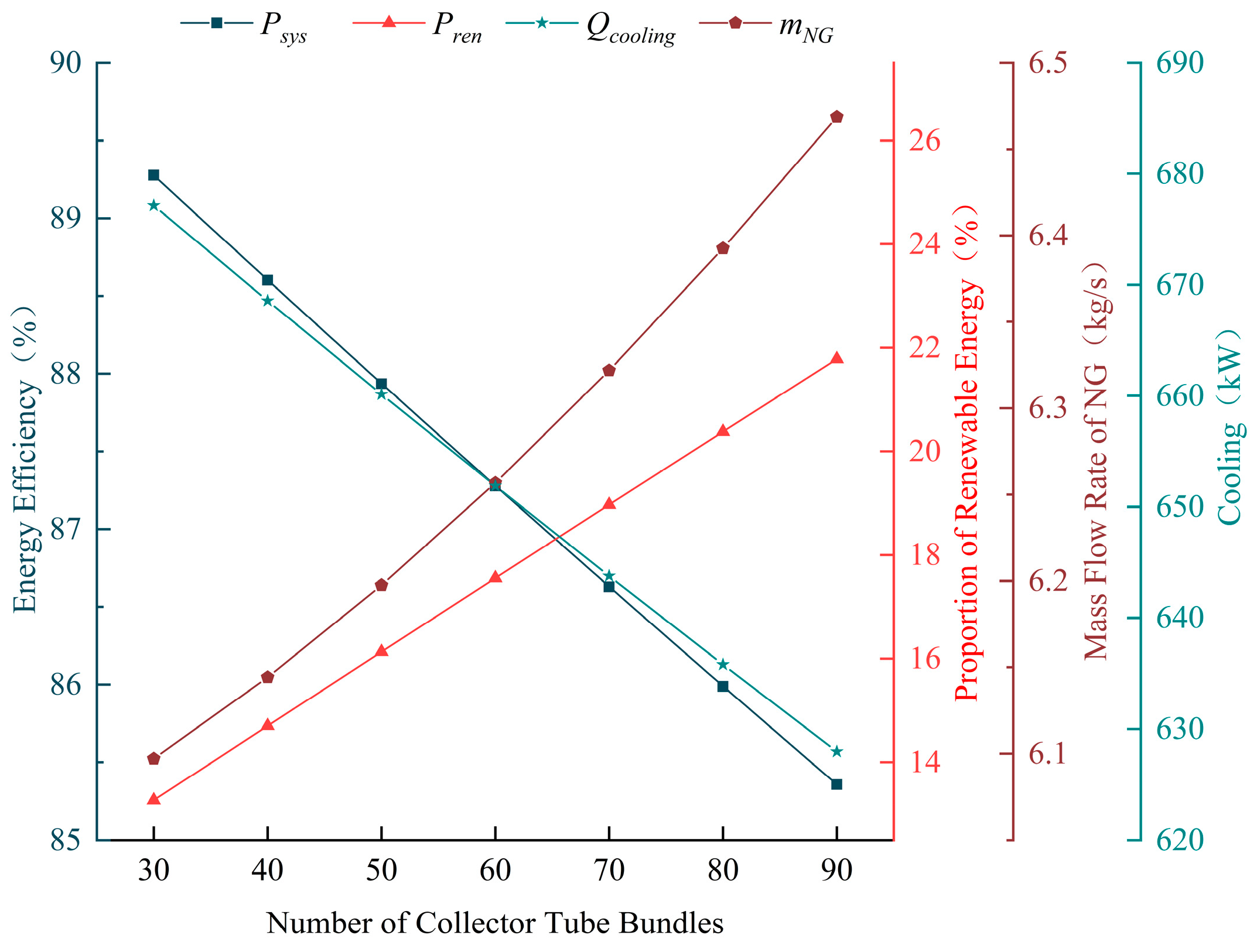
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| PV absorption rate | 0.98 |
| PV incidence factor | 0.98 |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient of the PV (W·m−2·K−1) | 0.105 |
| Photovoltaic cell temperature (K) | 333.15 |
| Ambient temperature (K) | 298.15 |
| Elementary charge (C) | 1.62 × 10−19 |
| Aperture area of the receiver of PTC (m2) | 69.6 |
| Inner diameter of the absorber of PTC (m) | 0.066 |
| Outer diameter of the absorber of PTC (m) | 0.07 |
| Inner diameter of the cover of PTC (m) | 0.12 |
| Outer diameter of the cover of PTC (m) | 0.125 |
| Emissivity of the absorber surface | 0.88 |
| Emissivity of the glass cover surface | 0.095 |
| Convective heat transfer coefficient of PTC (W·m−2·K−1) | 10 |
| Isentropic efficiency of the fan and pump | 0.75 |
| Temperature of steam (K) | 473.15 |
| Area of the PV (m2) | 1250 |
| Number of collector tubes | 70 |
| Rated capacity of gas boiler (MW) | 25 |
| Geothermal water temperature (K) | 343.15 |
| Geothermal water reinjection temperature (K) | 308.15 |
| Mass flow rate of geothermal water (kg/s) | 10 |
| Parameter | Reference [23] | Simulation Result | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photothermal Proportion (%) | 18.87 | 18.55 | 1.677 |
| PV Component Light Loss Proportion (%) | 5.79 | 5.73 | 1.004 |
| Thermal Loss Proportion (%) | 0.38 | 0.39 | 3.049 |
| Photoelectric Proportion (%) | 23.4 | 22.79 | 2.612 |
| Fluid Absorption Proportion (%) | 44.58 | 44.52 | 0.134 |
| Radiation Intensity (W/m2) | Inlet Water Temperature (K) | Thermal Efficiency | Reference [24] | Simulation Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | 450 | 0.7005 | 0.7280 | 3.93 |
| 800 | 500 | 0.7034 | 0.7246 | 3.01 |
| 800 | 550 | 0.7005 | 0.7206 | 2.86 |
| 800 | 600 | 0.6820 | 0.7154 | 4.90 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Population Size | 500 |
| Number of Generations | 20 |
| PV Area (m2) | [500, 2000] |
| Number of Collector Tubes | [20, 80] |
| Boiler Rated Power (MW) | [24, 26] |
| Decision Method | PV Area (m2) | Collector Tube Bundles | Boiler Capacity (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINMAP | 1963 | 67 | 25,990 |
| TOPSIS | 503 | 24 | 258,715 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z.; Ai, T.; Qi, Z.; Hou, H.; Chen, H.; Song, Y. Analysis of the Characteristics of a Multi-Generation System Based on Geothermal, Solar Energy, and LNG Cold Energy. Processes 2025, 13, 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082377
Guo X, Li H, Wang T, Wang Z, Ai T, Qi Z, Hou H, Chen H, Song Y. Analysis of the Characteristics of a Multi-Generation System Based on Geothermal, Solar Energy, and LNG Cold Energy. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082377
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xinfeng, Hao Li, Tianren Wang, Zizhang Wang, Tianchao Ai, Zireng Qi, Huarong Hou, Hongwei Chen, and Yangfan Song. 2025. "Analysis of the Characteristics of a Multi-Generation System Based on Geothermal, Solar Energy, and LNG Cold Energy" Processes 13, no. 8: 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082377
APA StyleGuo, X., Li, H., Wang, T., Wang, Z., Ai, T., Qi, Z., Hou, H., Chen, H., & Song, Y. (2025). Analysis of the Characteristics of a Multi-Generation System Based on Geothermal, Solar Energy, and LNG Cold Energy. Processes, 13(8), 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082377







