Flying Steel Detection in Wire Rod Production Based on Improved You Only Look Once v8
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- In order to improve the accuracy of flying steel, the ODConv is added to the YOLOv8 model to enhance the feature extraction ability of the model to the input data and efficiently capture the feature representations of the wire rod.
- (2)
- Improve the network lightweight module C2f-PCCA_RVB to lighten the neck network and improve the detection speed of the model.
- (3)
- The EMA module is added to the neck network, so that the model integrates global context information in the feature extraction process, thereby improving the feature extraction ability and detection accuracy of the model.
2. Theoretical Foundations
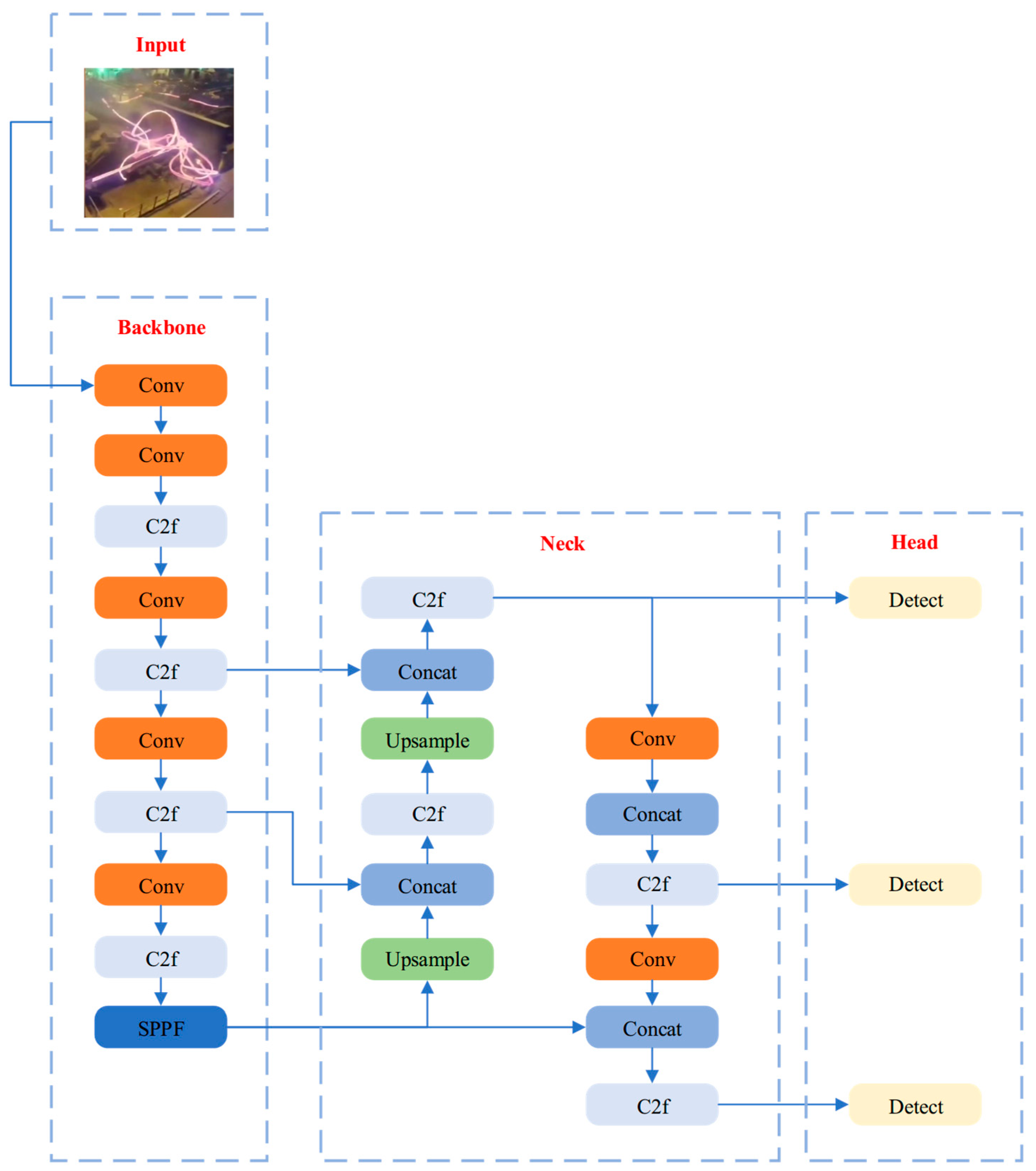
2.1. YOLOv8
- (1)
- Adaptive NMS: An adaptive threshold to reduce missed detection and false detection.
- (2)
- Automatic mixing accuracy training: Speeds up the training speed and reduces memory usage.
2.2. RepViTBlock
2.3. PConv
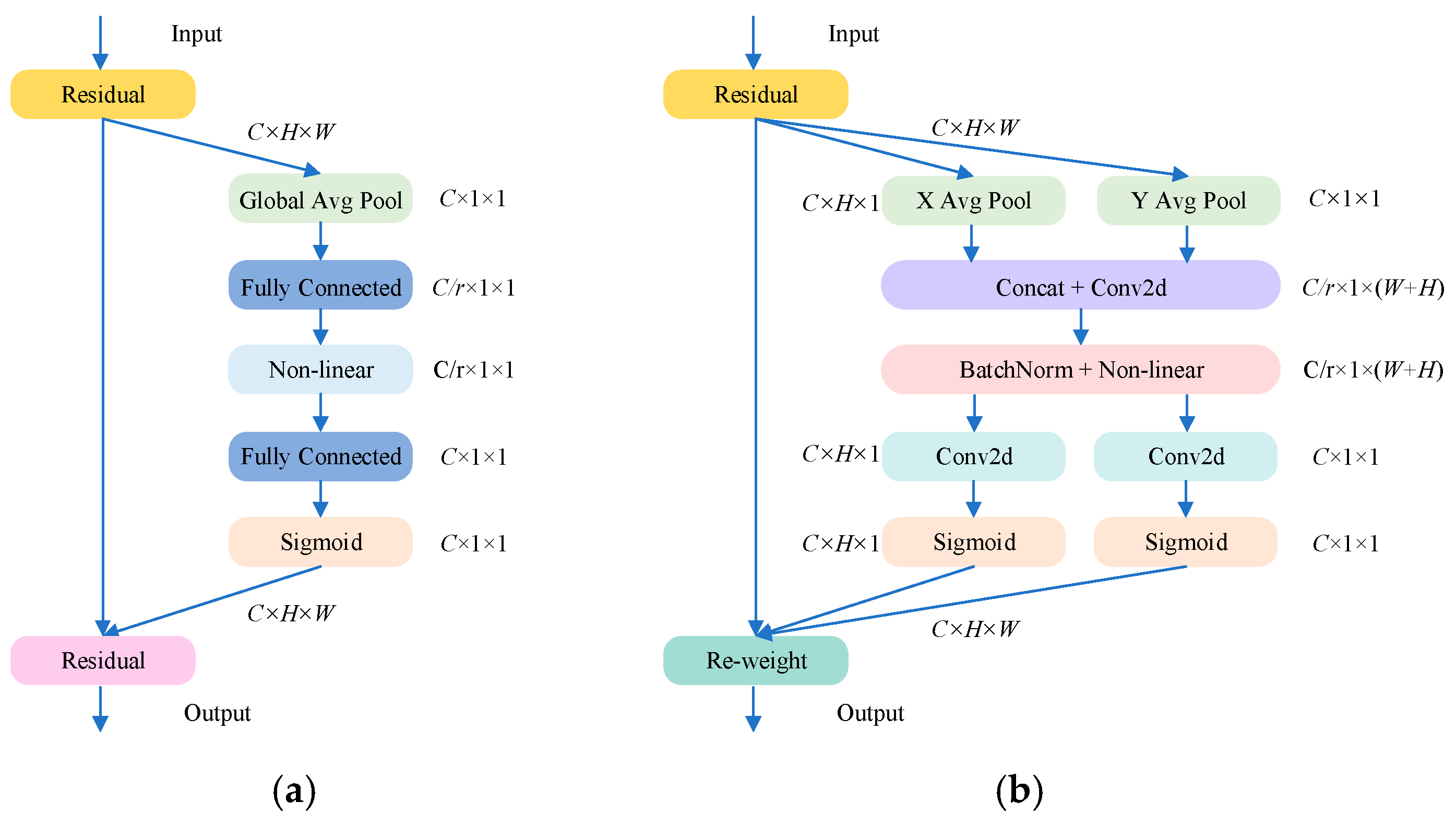
2.4. CA
3. Flying Steel Detection Model
3.1. ODConv
3.2. C2f-PCCA_RVB
3.3. EMA
4. Experiments
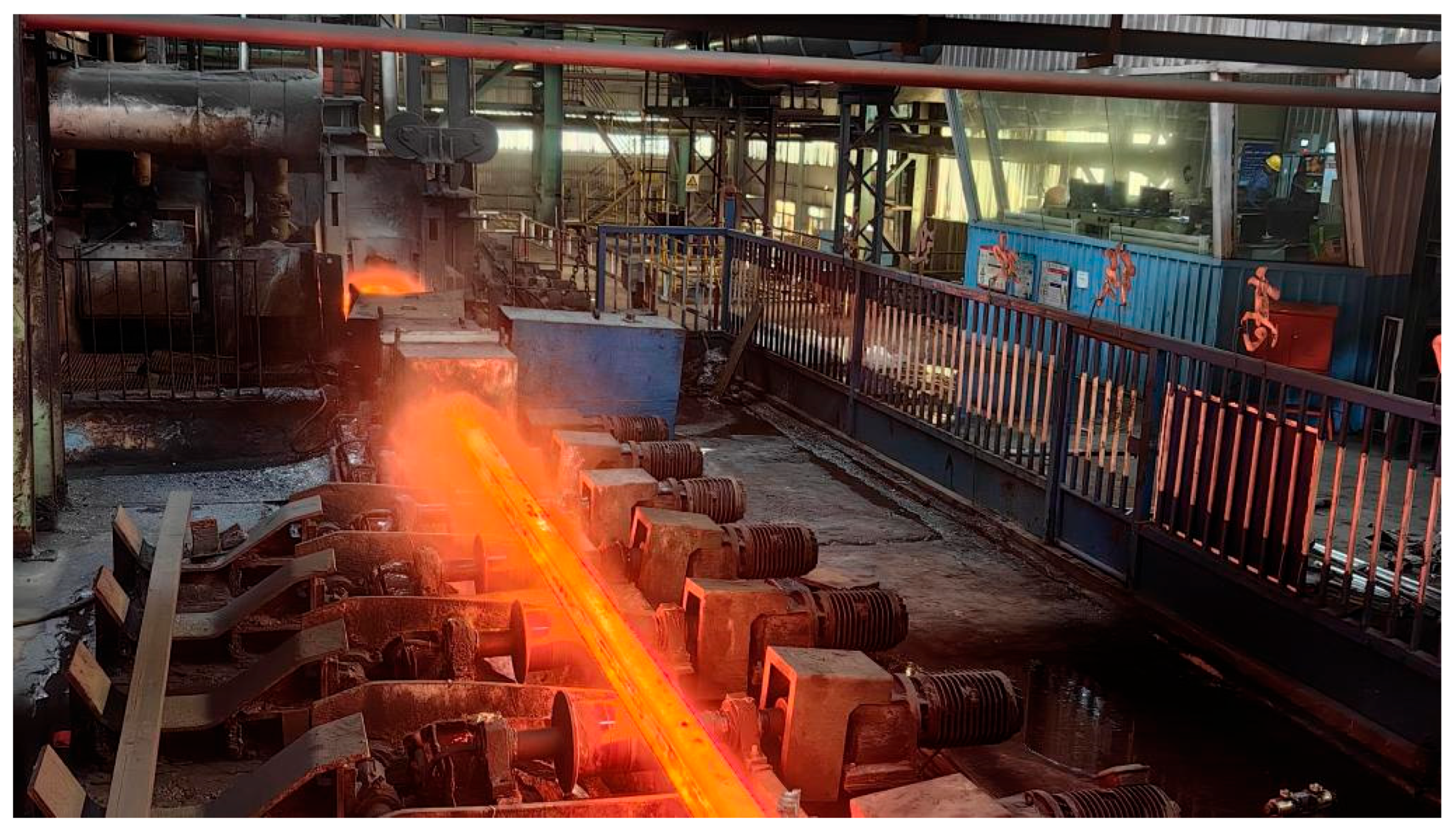
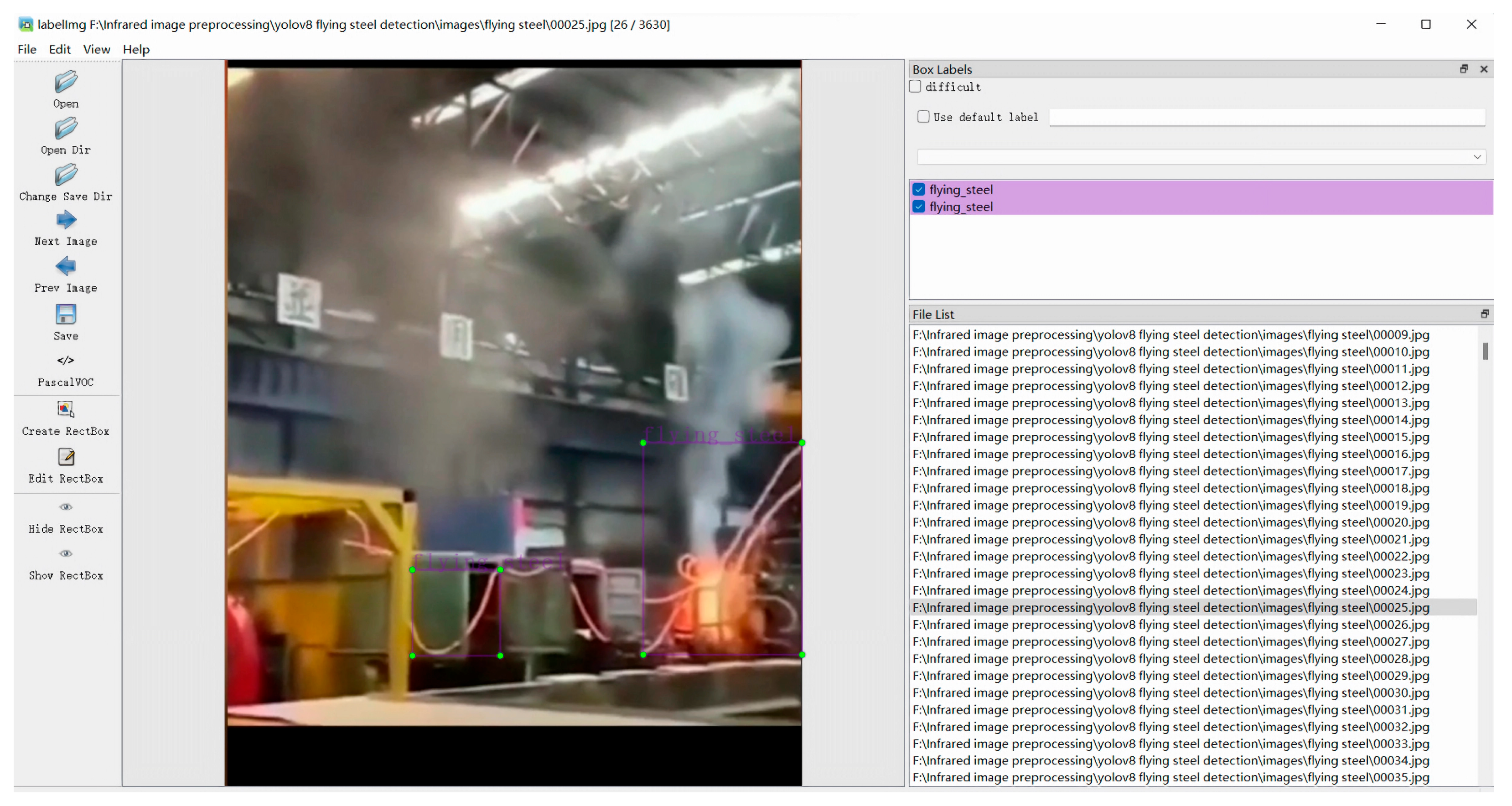
4.1. Datasets and Preprocessing
- Sampling from production site monitoring videos: Image data is extracted by systematically sampling frames from monitoring videos recorded at the production site.
- Internet-based data collection: Flying steel data is gathered from online resources to expand the diversity of the dataset.
4.2. Experimental Parameter Setting and Model Training
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
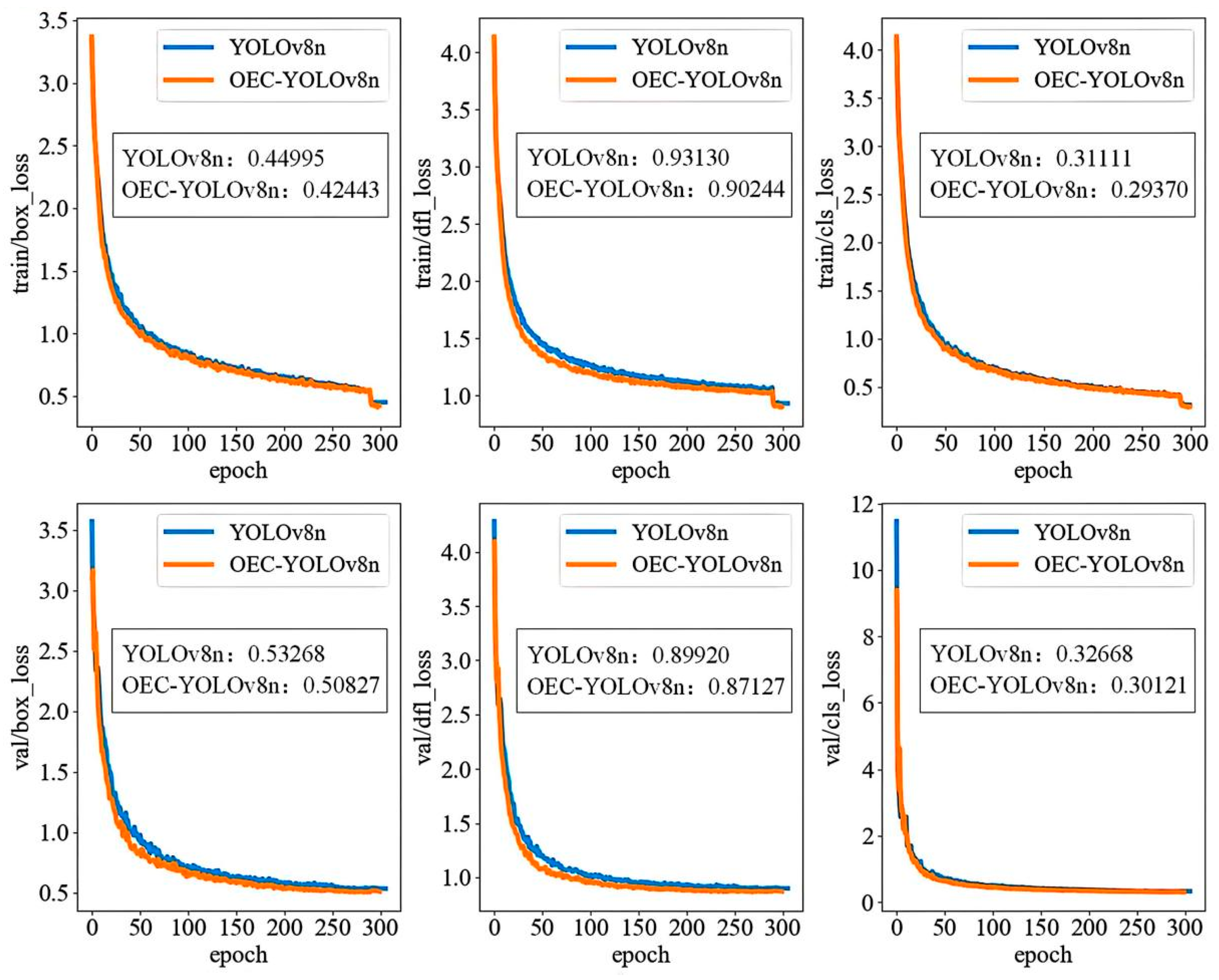
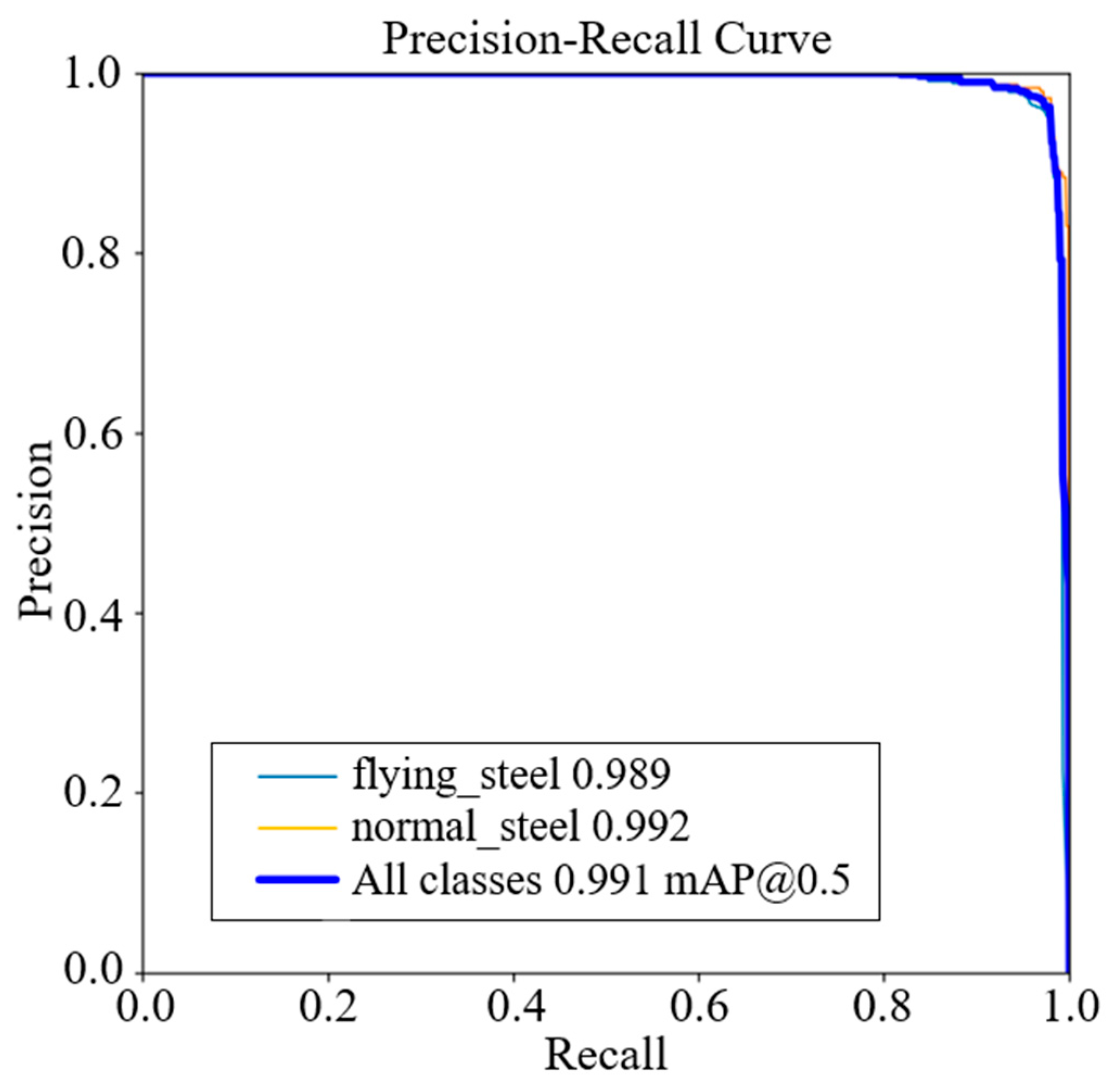
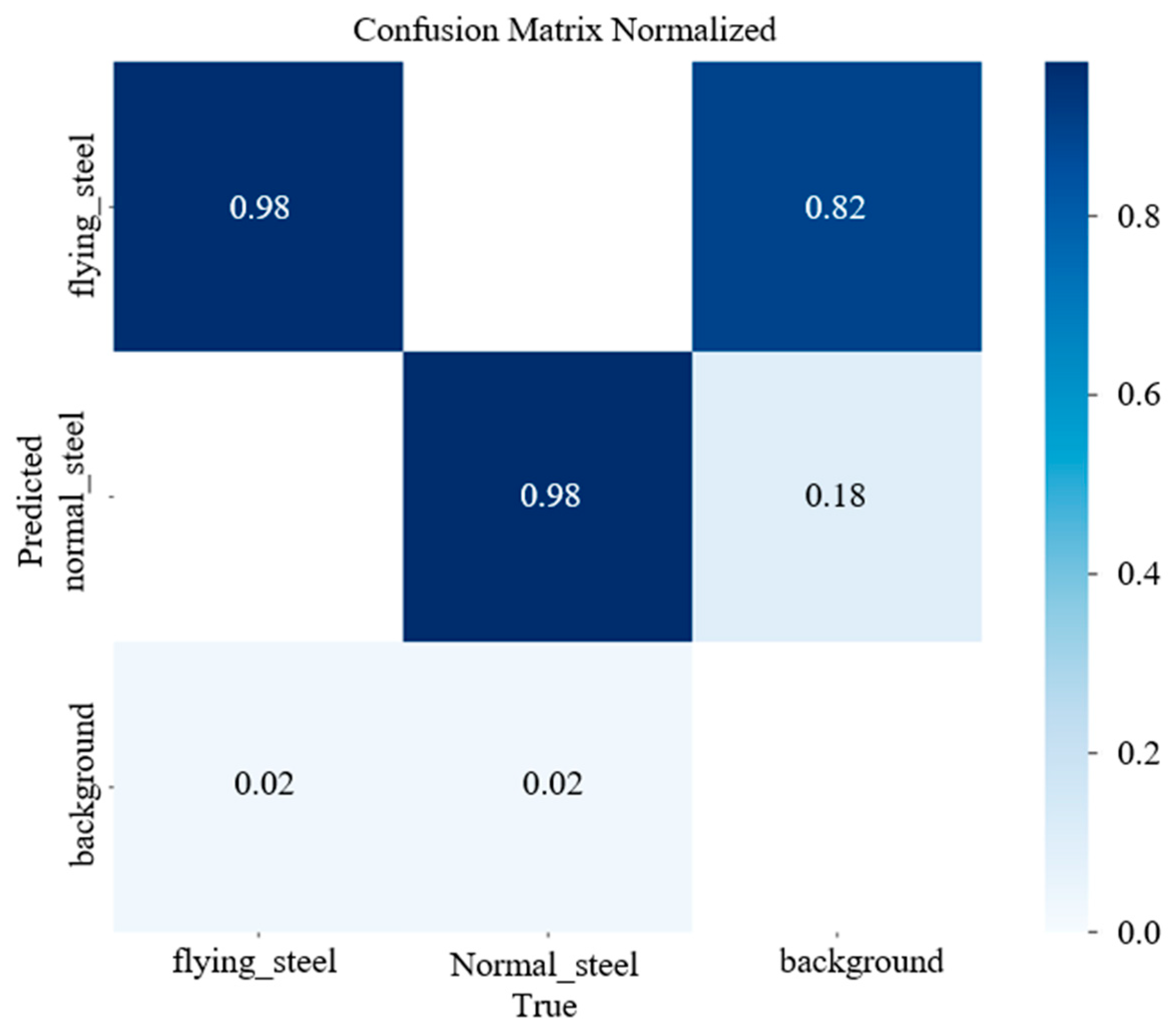
5.1. Training Results and Analysis
5.2. Ablation Experiments
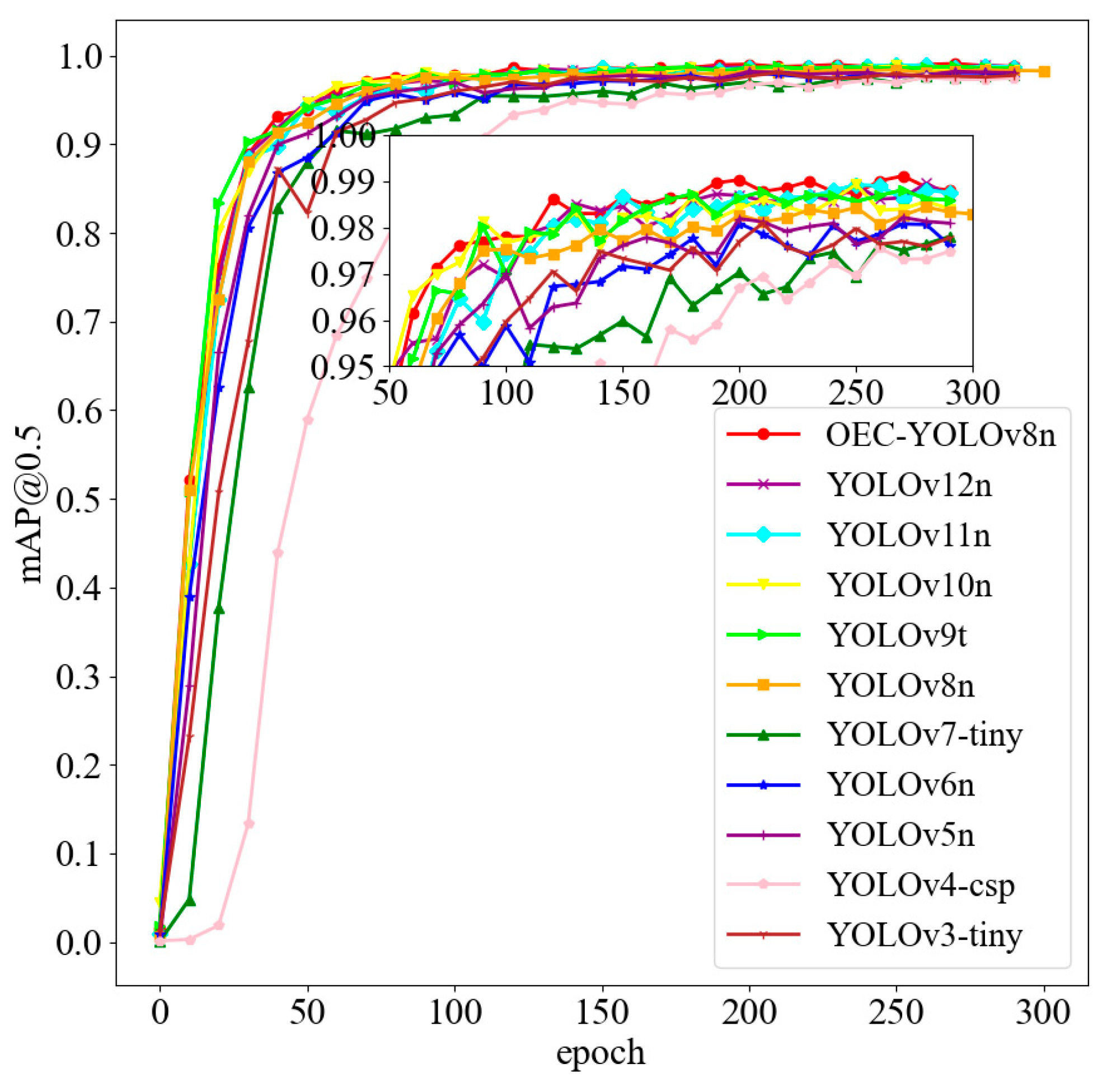
5.3. Comparative Experiment
6. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, D.; Xiao, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Liao, B. Investigation on grain refinement and precipitation strengthening applied in high speed wire rod containing vanadium. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 592, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causes and Treatment of Piled Steel in the Rolling Process of High-Speed Wire Rod. Available online: https://lmmrolls.com/causes-and-treatment-of-piled-steel-in-the-rolling-process-of-high-speed-wire-rod/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Z. Cause analysis and countermeasures of steel piling accident in hot rolling coiler. Metall. Power 2018, 21, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High-Speed Wire Rod Roughing Mill Unit Steel Accumulation. Available online: https://lmm-rollingmill.com/blog/analysis-and-treatment-of-pile-up-accidents-in-high-speed-wire-rod-roughing-mill/ (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Safety and Health in the Steel Industry: Data Report 2024. Available online: https://worldsteel.org/safety-and-health/safety-and-health-in-the-steel-industry-data-reports/safety-and-health-in-the-steel-industry-data-report-2024/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- de Sena, A.P.C.; de Freitas, I.S.; Filho, A.C.; Sobrinho, C.A.N. Fuzzy diagnostics for gearbox failures based on induction motor current and wavelet entropy. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2021, 43, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Gao, L. Hybrid Fault Diagnosis for High Speed Wire Rod Finishing Mill. In Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Symposium on Autonomous Systems (ISAS), Nanjing, China, 23–25 June 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Yue, Y.; Hao, G.; Hua, C. A novel multi-source sensing data fusion driven method for detecting rolling mill health states under imbalanced and limited datasets. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 171, 108903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Shi, P.; Tian, J.; Xu, X.; Hua, C. Rolling mill health states diagnosing method based on multi-sensor information fusion and improved DBNs under limited datasets. ISA Trans. 2022, 134, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. CoRR. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Sun, X.; Ma, W. A lightweight multi-scale feature fusion steel surface defect detection model based on YOLOv8. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Luo, H. YOLOv5-CD: Strip steel surface defect detection method based on coordinate attention and a decoupled head. Meas. Sens. 2023, 30, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, C.; Wan, G.; Cui, S. A surface defect detection method for steel pipe based on improved YOLO. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2024, 21, 3016–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, R.; Sambath, M. YOLOv8: A Novel Object Detection Algorithm with Enhanced Performance and Robustness. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Tamil Nadu, India, 18–19 April 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.0312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S. A Lightweight Real-Time Infrared Object Detection Model Based on YOLOv8 for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Drones 2024, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Rauf, Z.; Sohail, A.; Rehman, A.; Asif, H.; Asif, A.; Farooq, U. A survey of the vision transformers and their CNN-transformer based variants. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.09880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. RepViT: Revisiting Mobile CNN From ViT Perspective. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.09283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Liu, S.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. CondenseNet: An Efficient DenseNet Using Learned Group Convolutions. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.09224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Chen, B.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Le, Q.V. MnasNet: Platform-Aware Neural Architecture Search for Mobile. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.11626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kao, S.; He, H.; Wen, S.; Lee, C. Run, Don’t Walk: Chasing Higher FLOPS for Faster Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 12021–12031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; p. 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Zark, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Liu, M.; Chen, D.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Dynamic Convolution: Attention Over Convolution Kernels. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11027–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, A.; Yao, A. Omni-Dimensional Dynamic Convolution. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.07947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, D.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Guo, H.; Zhan, J.; Huang, Z. Efficient Multi-Scale Attention Module with Cross-Spatial Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.13563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1809.02983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Zhu, S. A wind turbine damage detection algorithm designed based on YOLOv8. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 154, 111364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Label Class | Number of Labels |
|---|---|
| Flying_steel | 1692 |
| Normal_steel | 842 |
| Parameter | Settings |
|---|---|
| Image size | 640 × 640 |
| Initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| Final learning rate | 0.01 |
| Batch size | 4 |
| Epoch | 300 |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Weight_decay | 0.0005 |
| Warmup_epochs | 3.0 |
| Warmup_momentum | 0.8 |
| Warmup_bias_lr | 0.1 |
| Name | Configuration Information |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows 11 |
| Development Language | Python 3.8.5 |
| Framework | Pytorch 2.0.0 + CUDA11.8 |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 (12 GB) |
| CPU | Intel 12th Gen Core i7-1360P |
| Memory Size | 16 GB |
| ODConv | C2f- PCCA_RVB | EMA | mAP@0.5 | Detection Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.983 | 2.7 | |||
| √ | 0.985 | 2.8 | ||
| √ | √ | 0.988 | 2.4 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | mAP@ 0.5 | mAP@ 0.5~0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3-tiny | 0.972 | 0.961 | 0.978 | 0.766 |
| YOLOv4-csp | 0.949 | 0.947 | 0.974 | 0.799 |
| YOLOv5n | 0.978 | 0.962 | 0.981 | 0.804 |
| YOLOv6n | 0.966 | 0.967 | 0.979 | 0.811 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 0.953 | 0.959 | 0.978 | 0.822 |
| YOLOv8n | 0.982 | 0.968 | 0.983 | 0.830 |
| YOLOv9t | 0.982 | 0.970 | 0.985 | 0.837 |
| YOLOv10n | 0.984 | 0.973 | 0.987 | 0.845 |
| YOLOv11n | 0.983 | 0.974 | 0.989 | 0.849 |
| YOLOv12n | 0.986 | 0.976 | 0.990 | 0.856 |
| OEC-YOLOv8n | 0.985 | 0.977 | 0.991 | 0.864 |
| Method | Parameters (M) | FLOPs (G) | Detection Speed (FPS) | Detection Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv3-tiny | 103.8 | 283.3 | 61.35 | 16.3 |
| YOLOv4-csp | 52.5 | 52.5 | 68.97 | 14.5 |
| YOLOv5n | 2.6 | 7.8 | 384.62 | 2.6 |
| YOLOv6n | 4.7 | 11.4 | 263.16 | 3.8 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 6.2 | 13.8 | 192.30 | 5.2 |
| YOLOv8n | 3.2 | 8.7 | 370.37 | 2.7 |
| YOLOv9t | 2.0 | 7.7 | 384.62 | 2.6 |
| YOLOv10n | 2.3 | 6.7 | 357.14 | 2.8 |
| YOLOv11n | 2.6 | 6.5 | 416.67 | 2.4 |
| YOLOv12n | 2.6 | 6.5 | 400.00 | 2.5 |
| OEC-YOLOv8n | 2.8 | 7.8 | 400.00 | 2.5 |
| Method | Precision | Recall | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5~0.95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.966 | 0.957 | 0.975 | 0.786 |
| SSD | 0.958 | 0.964 | 0.980 | 0.788 |
| MobileNetv3-small | 0.971 | 0.973 | 0.985 | 0.813 |
| ShuffleNetv2-0.5x | 0.963 | 0.962 | 0.982 | 0.806 |
| OEC-YOLOv8n | 0.985 | 0.977 | 0.991 | 0.864 |
| Method | Parameters (M) | FLOPs (G) | Detection Speed (FPS) | Detection Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 45.1 | 148.9 | 64.94 | 15.4 |
| SSD | 23.0 | 28.5 | 178.57 | 5.6 |
| MobileNetv3-small | 3.2 | 68.6 | 232.56 | 4.3 |
| ShuffleNetv2-0.5x | 1.2 | 149.6 | 312.50 | 3.2 |
| OEC-YOLOv8n | 2.8 | 7.8 | 400 | 2.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, L.; Xiang, X. Flying Steel Detection in Wire Rod Production Based on Improved You Only Look Once v8. Processes 2025, 13, 2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072297
Lu Y, Zhang F, Li X, Zhang J, Xiao X, Wang L, Xiang X. Flying Steel Detection in Wire Rod Production Based on Improved You Only Look Once v8. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072297
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yifan, Fei Zhang, Xiaozhan Li, Jian Zhang, Xiong Xiao, Lijun Wang, and Xiaofei Xiang. 2025. "Flying Steel Detection in Wire Rod Production Based on Improved You Only Look Once v8" Processes 13, no. 7: 2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072297
APA StyleLu, Y., Zhang, F., Li, X., Zhang, J., Xiao, X., Wang, L., & Xiang, X. (2025). Flying Steel Detection in Wire Rod Production Based on Improved You Only Look Once v8. Processes, 13(7), 2297. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072297







