Effect of Port-Injecting Isopropanol on Diesel Engine Performance and Emissions by Changing EGR Ratio and Charge Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Arrangement
3. Methodology Descriptions
4. Results and Discussion
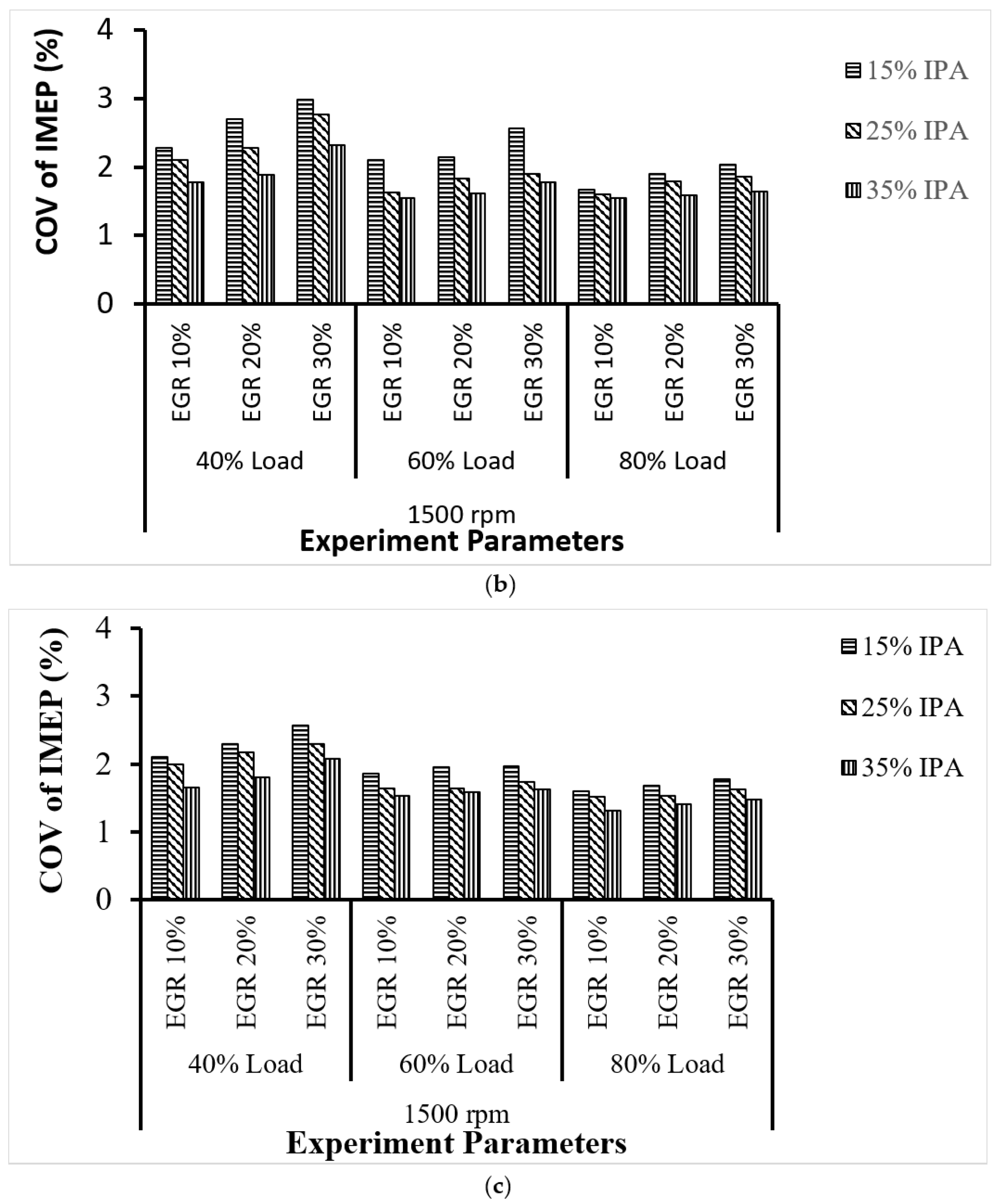
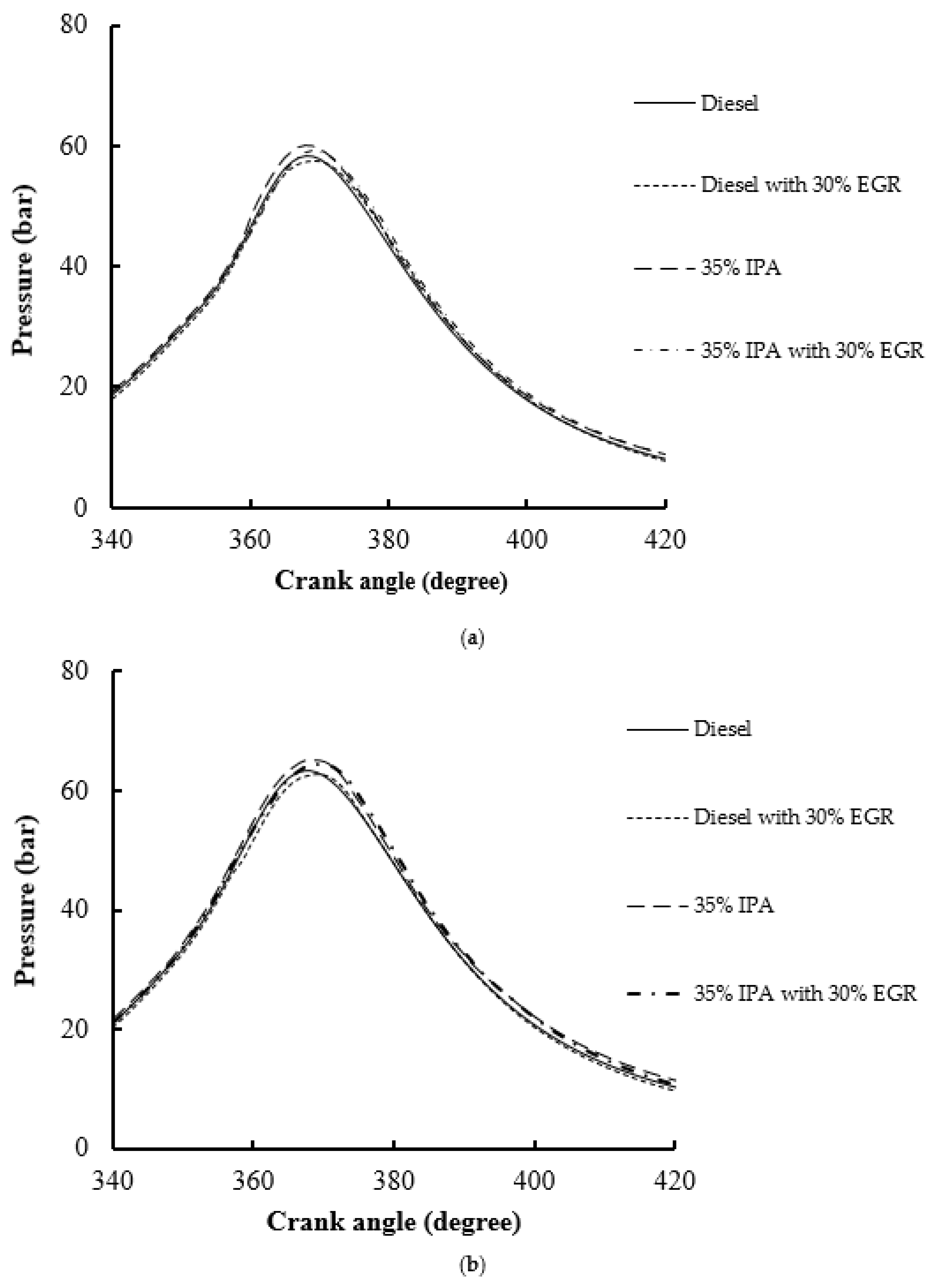
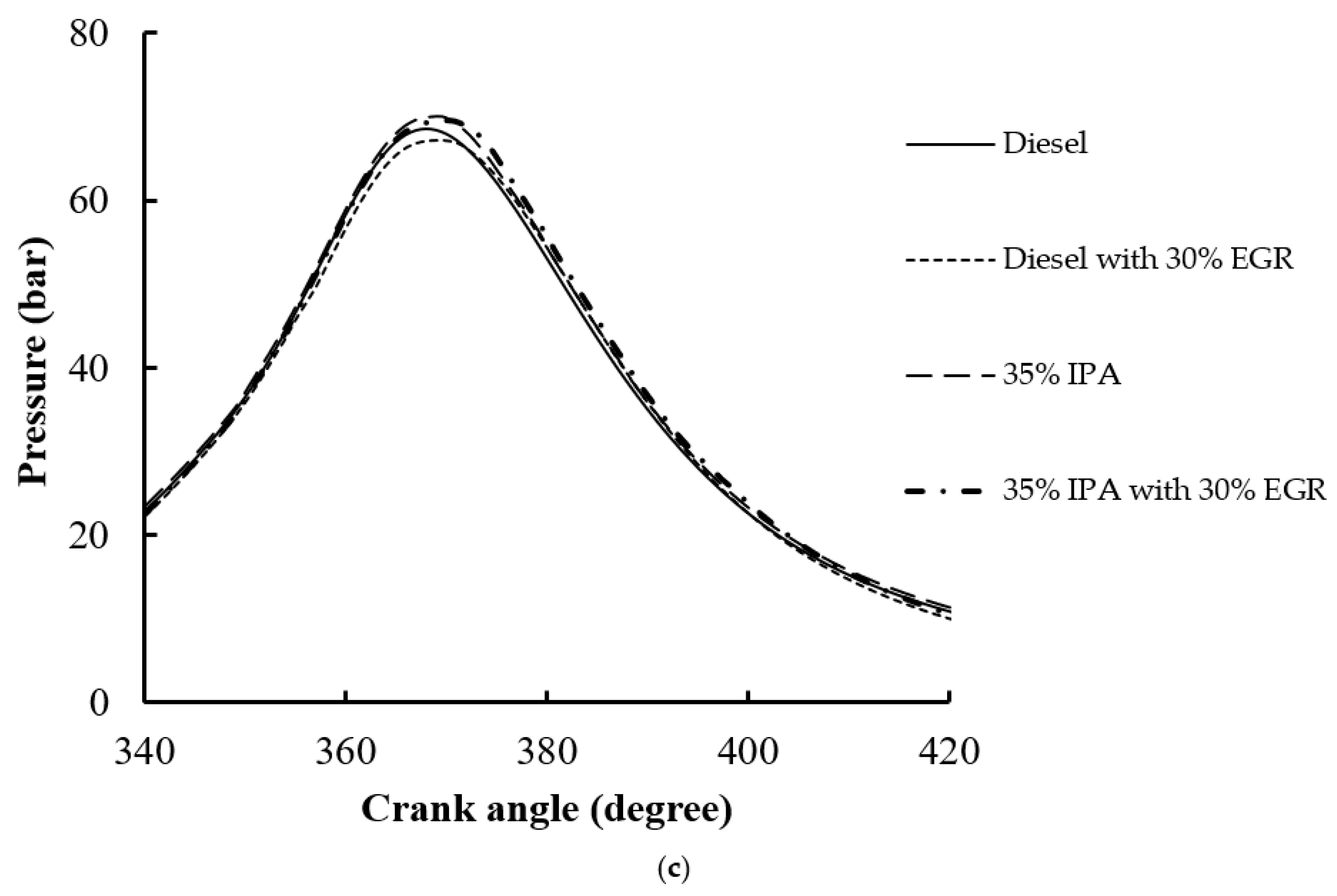
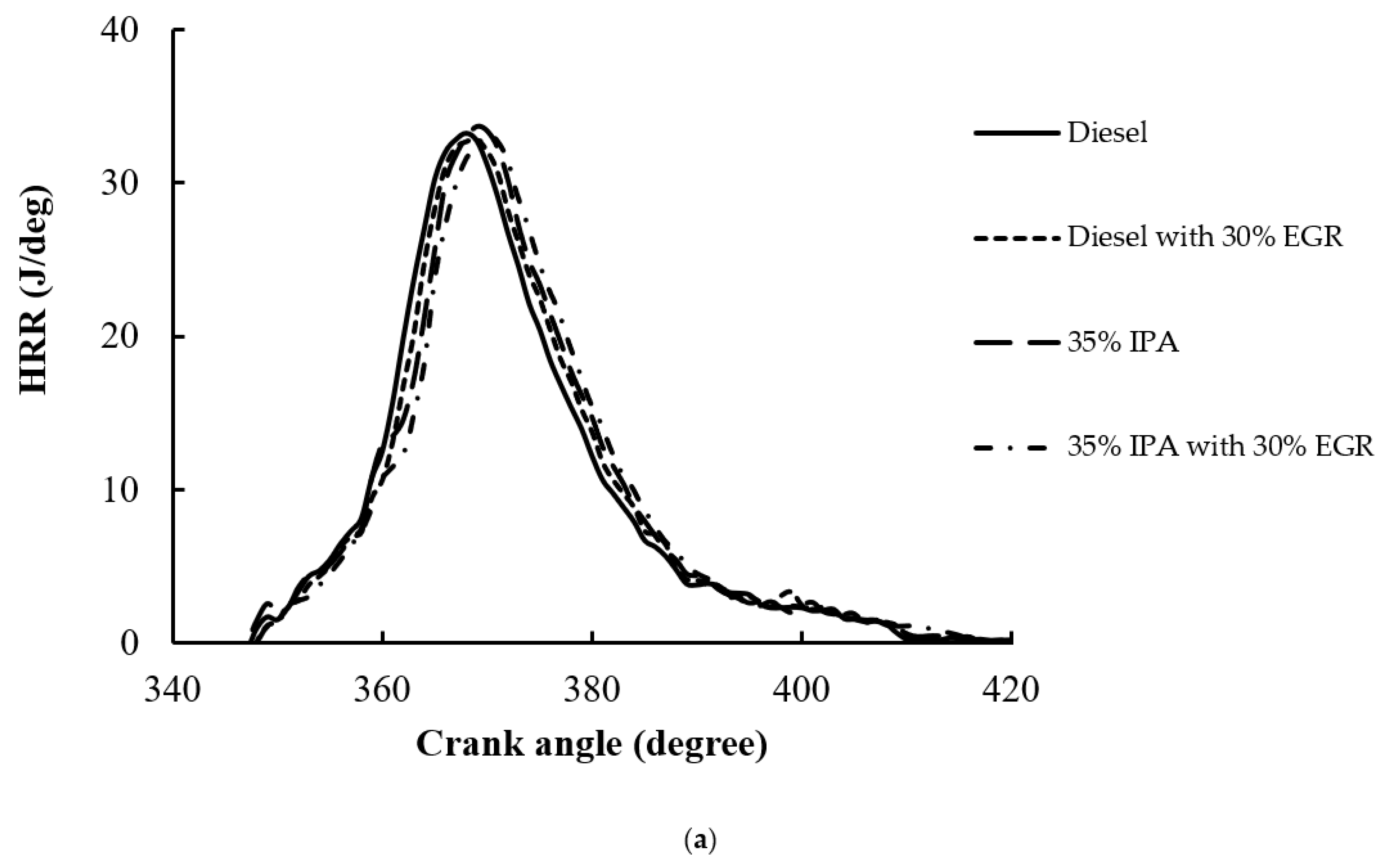
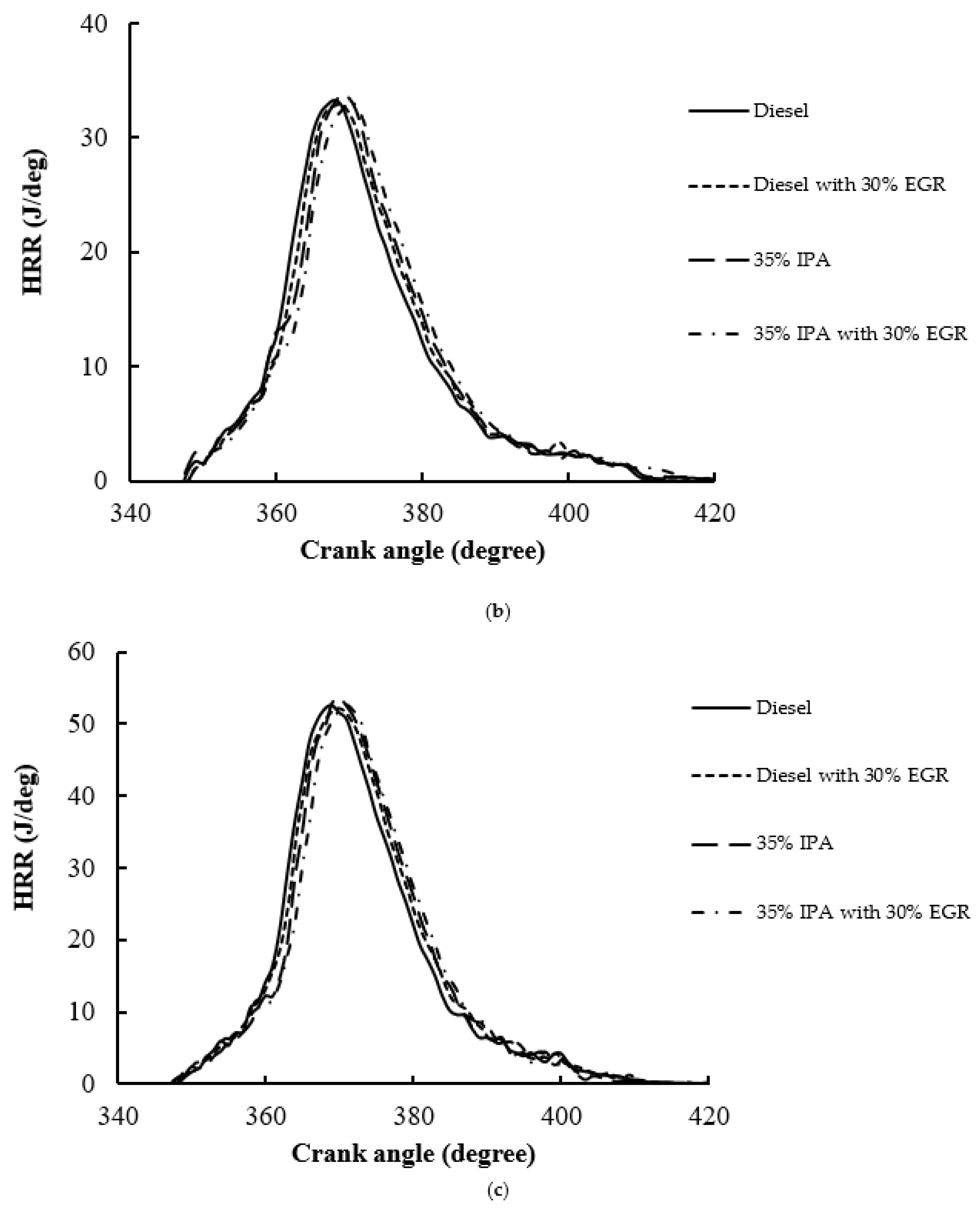
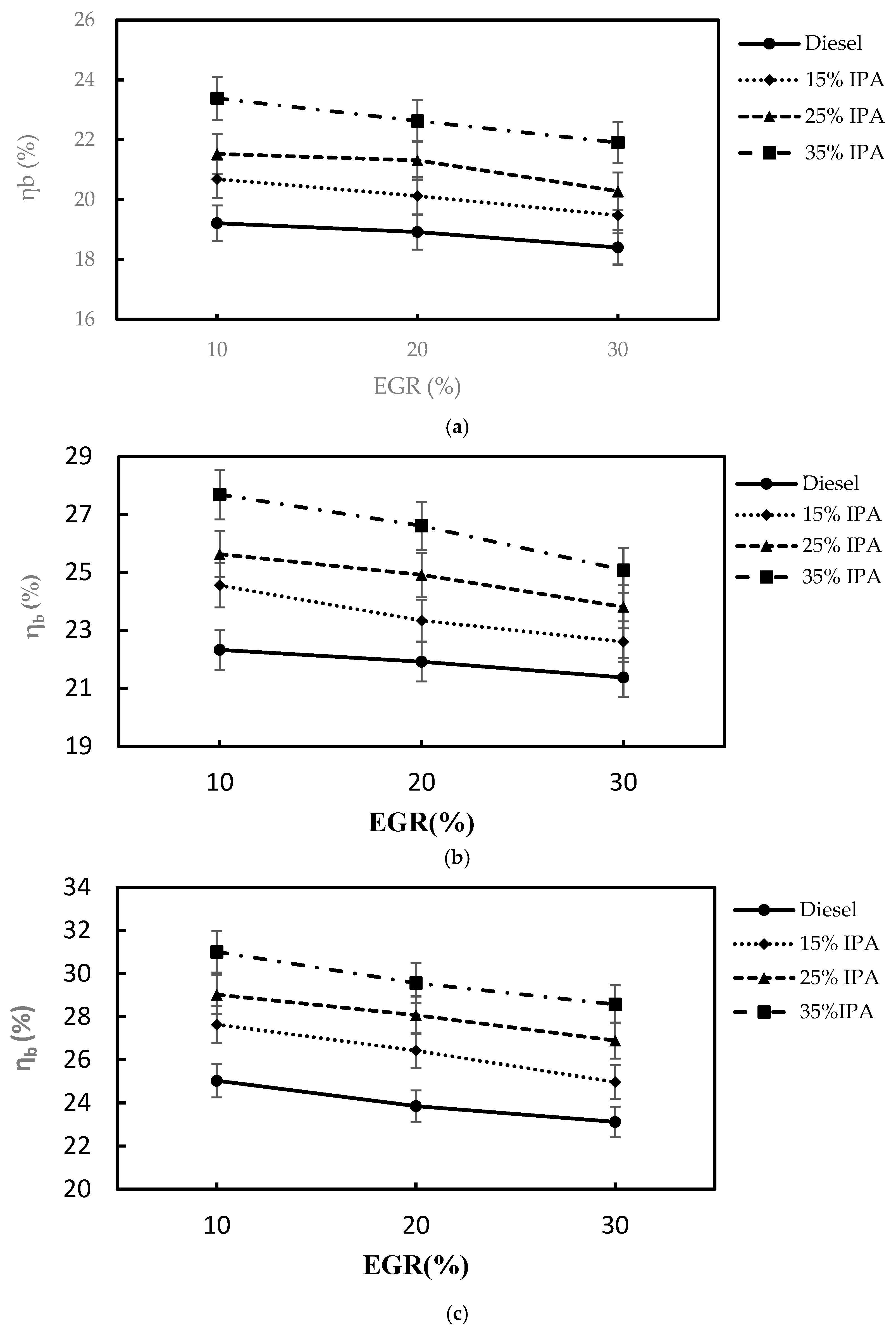
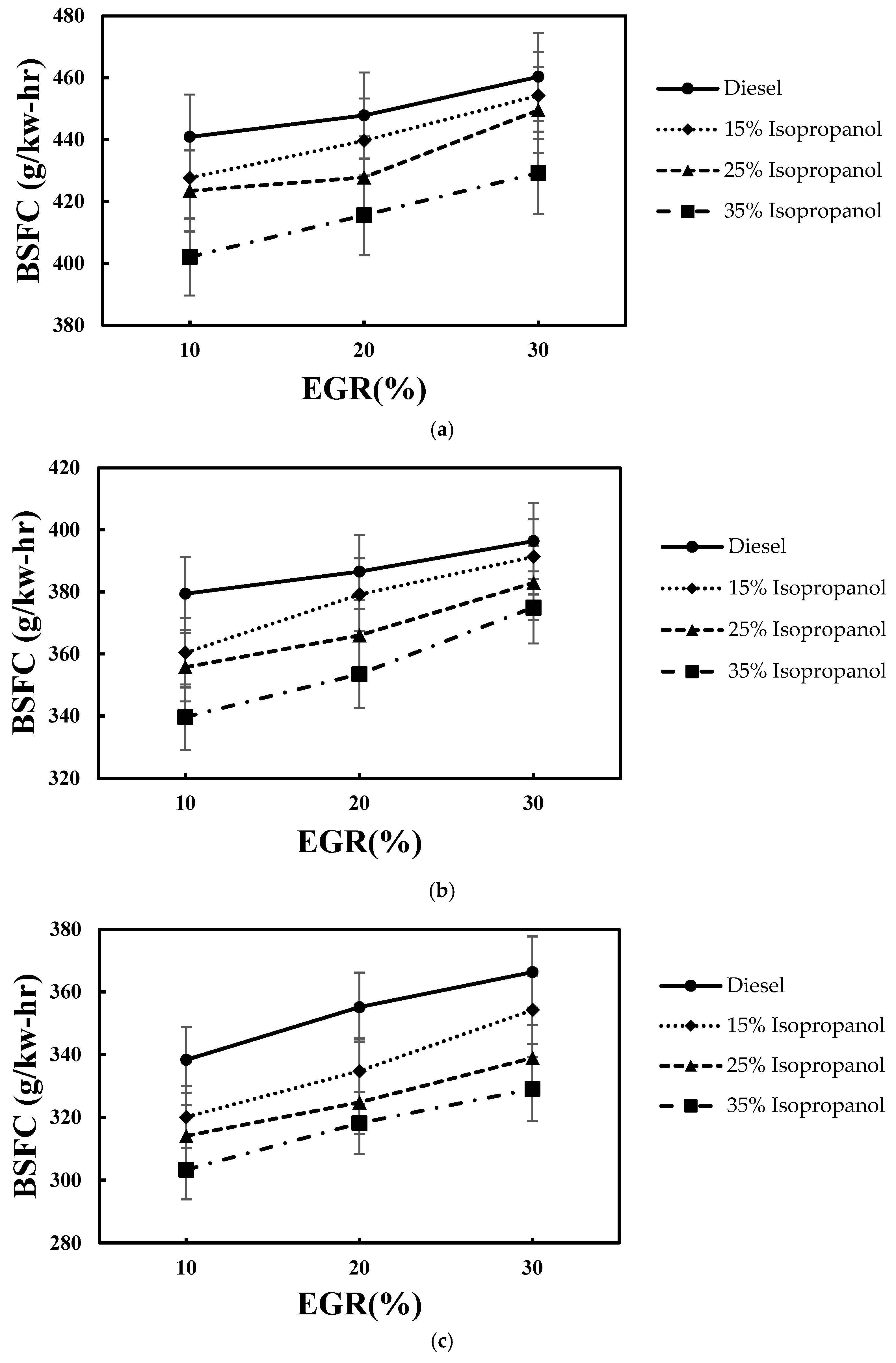
4.1. Combustion Performance
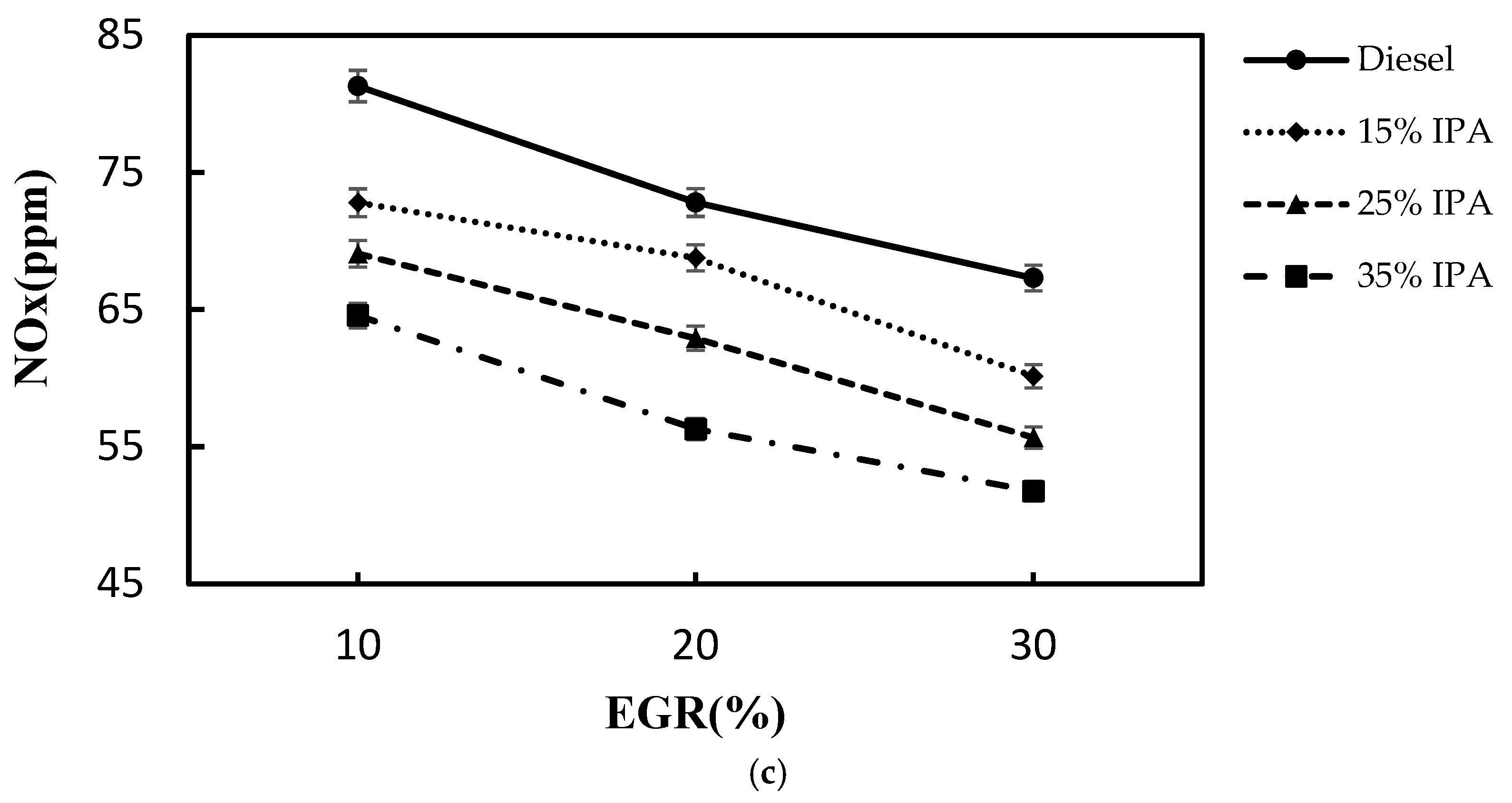
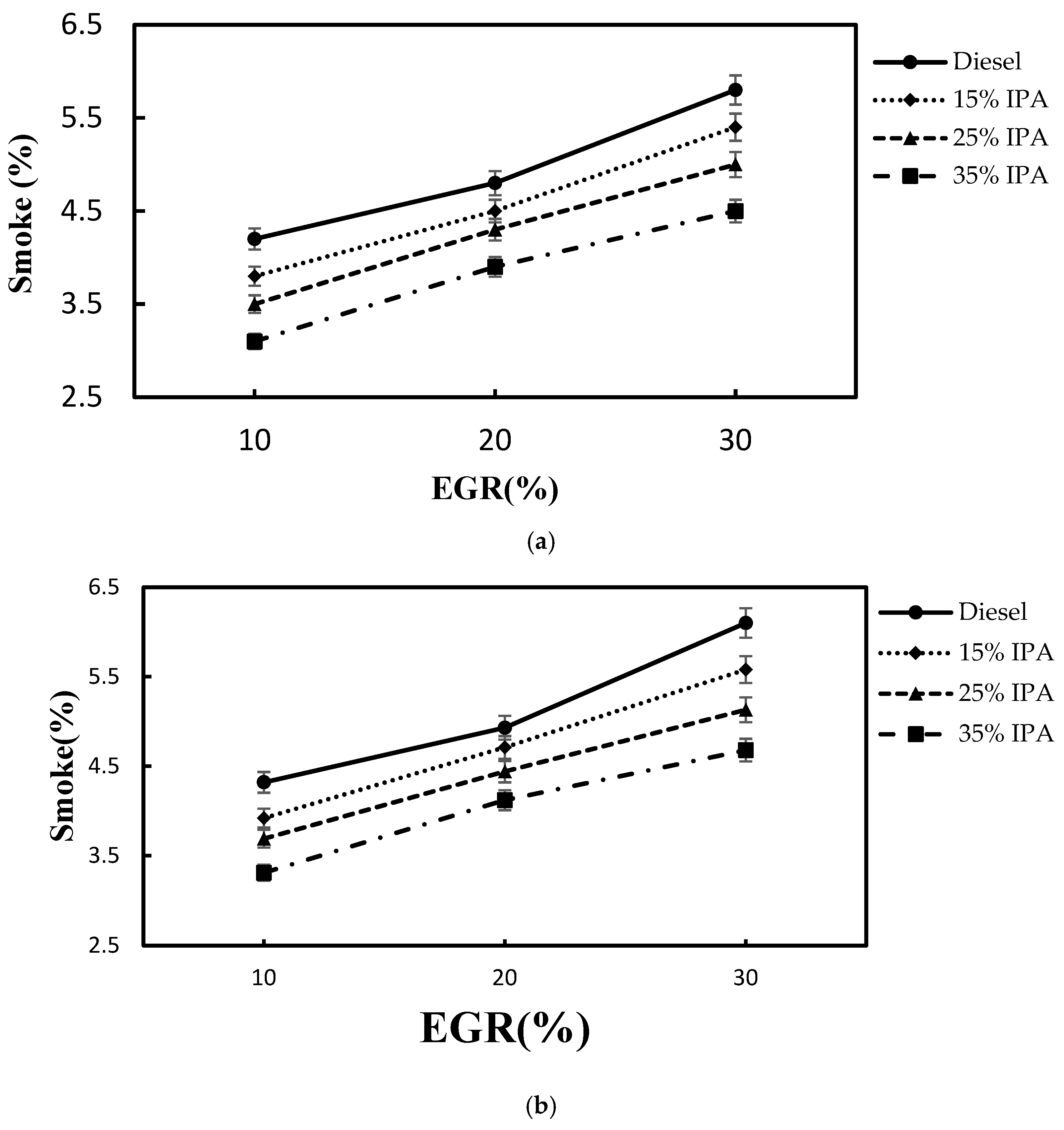
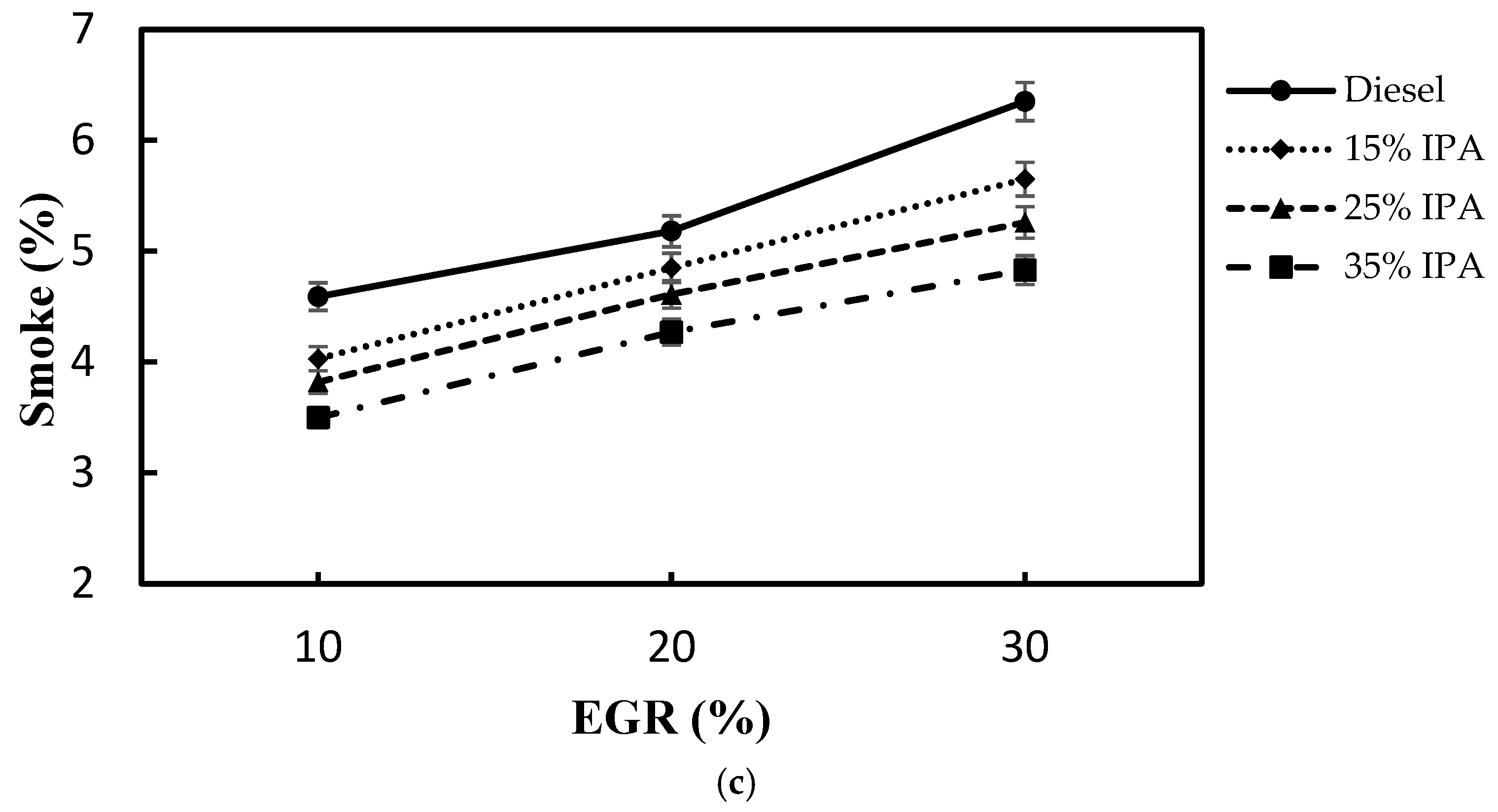
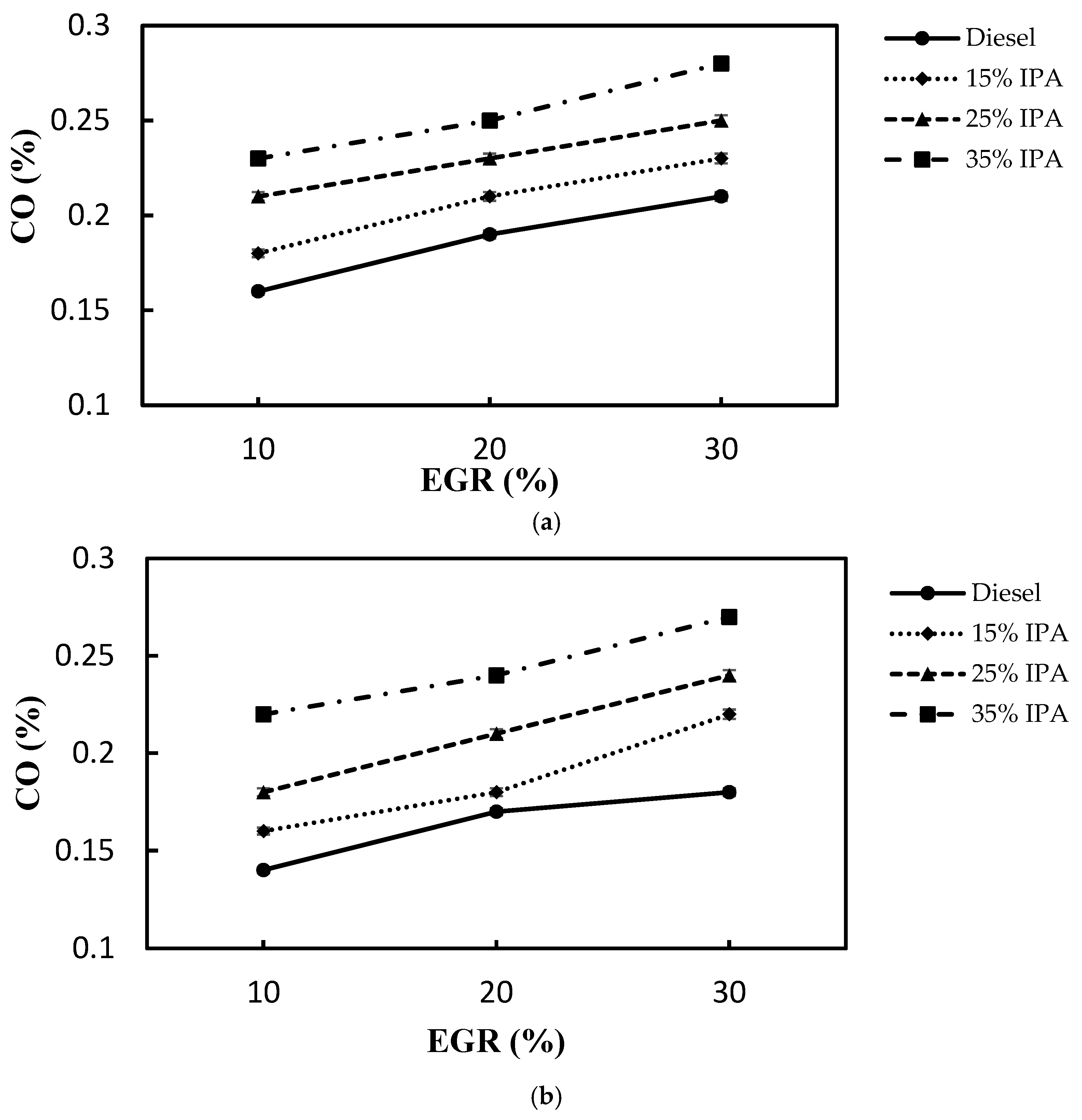
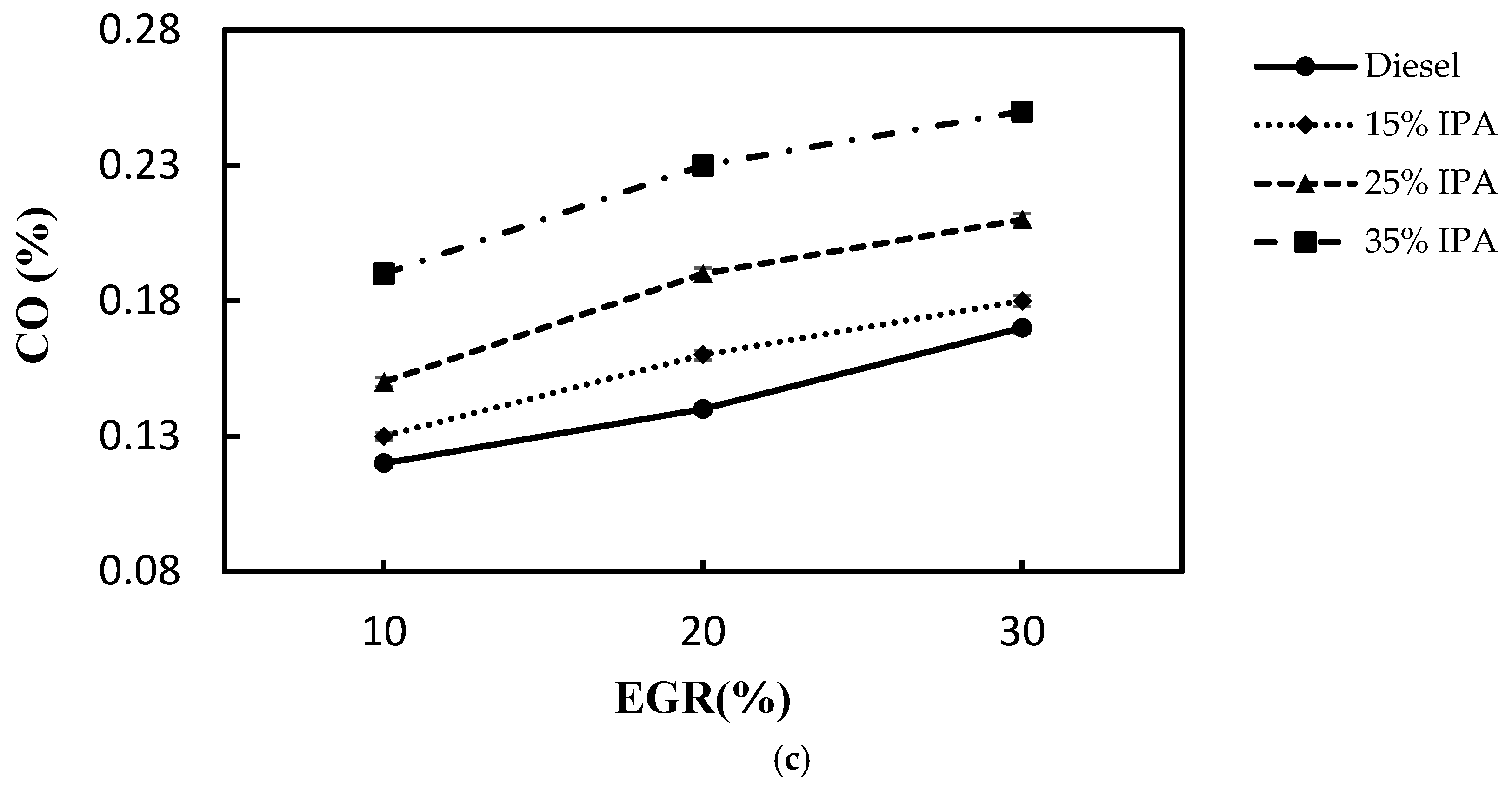
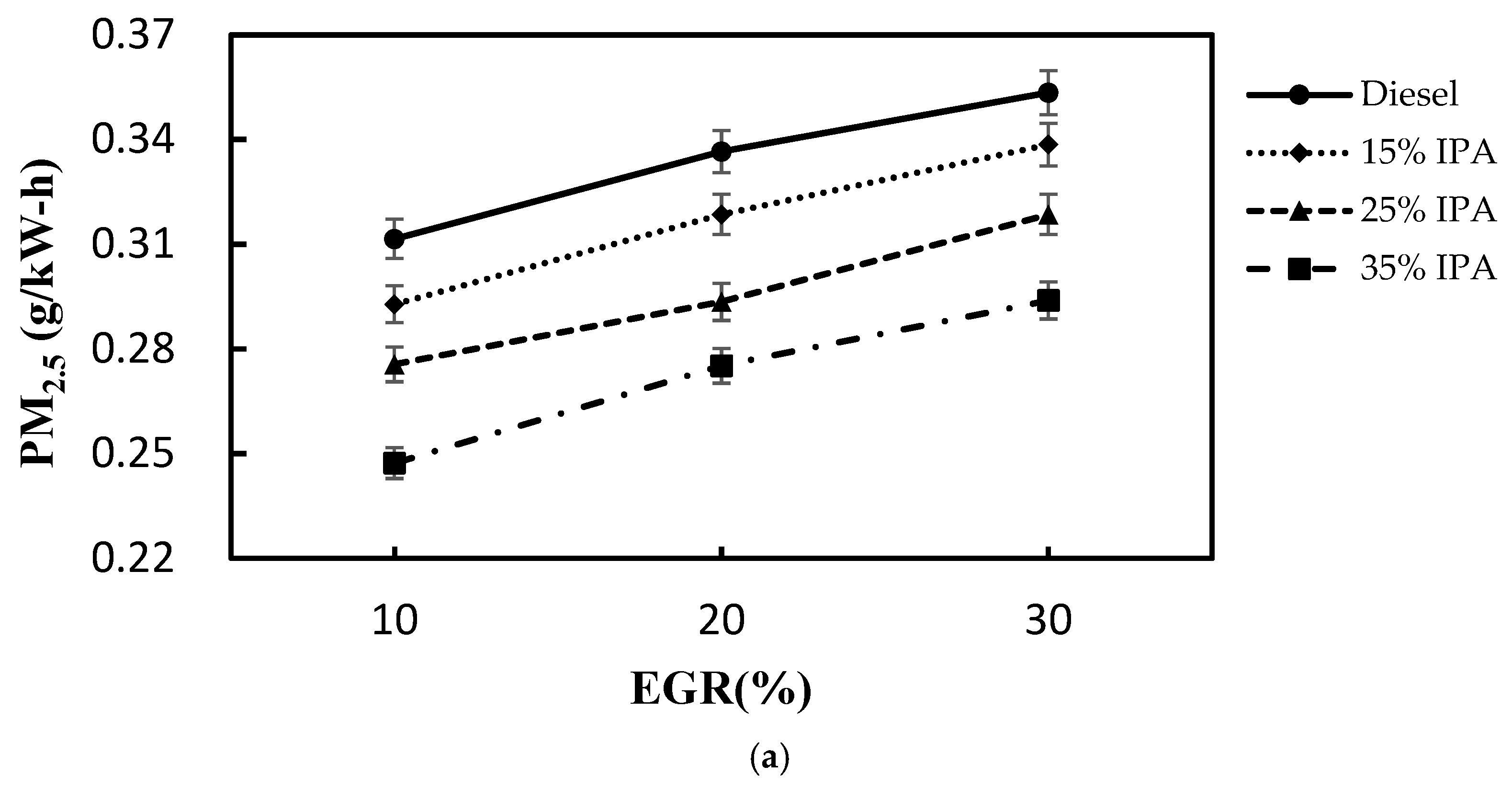
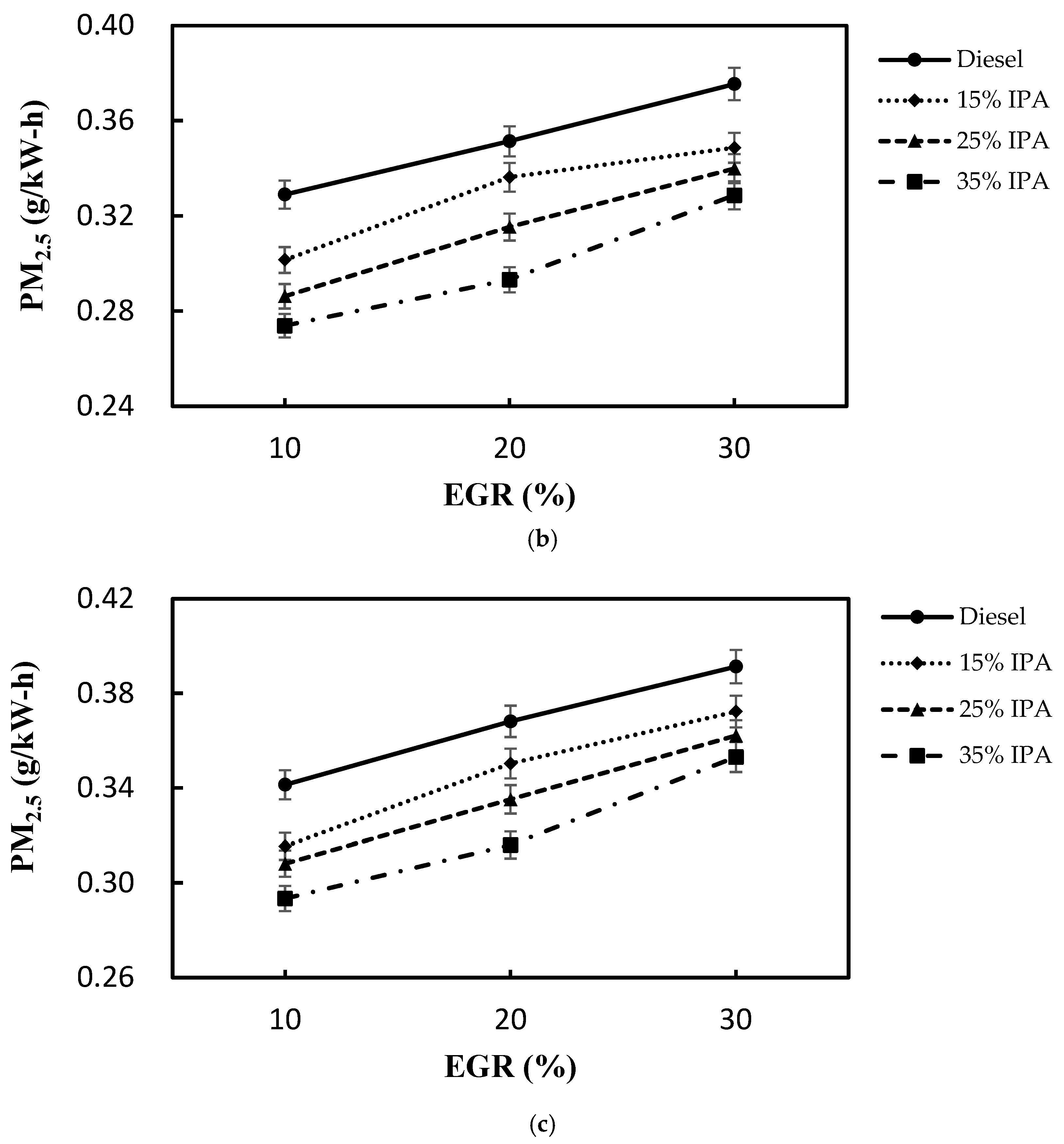
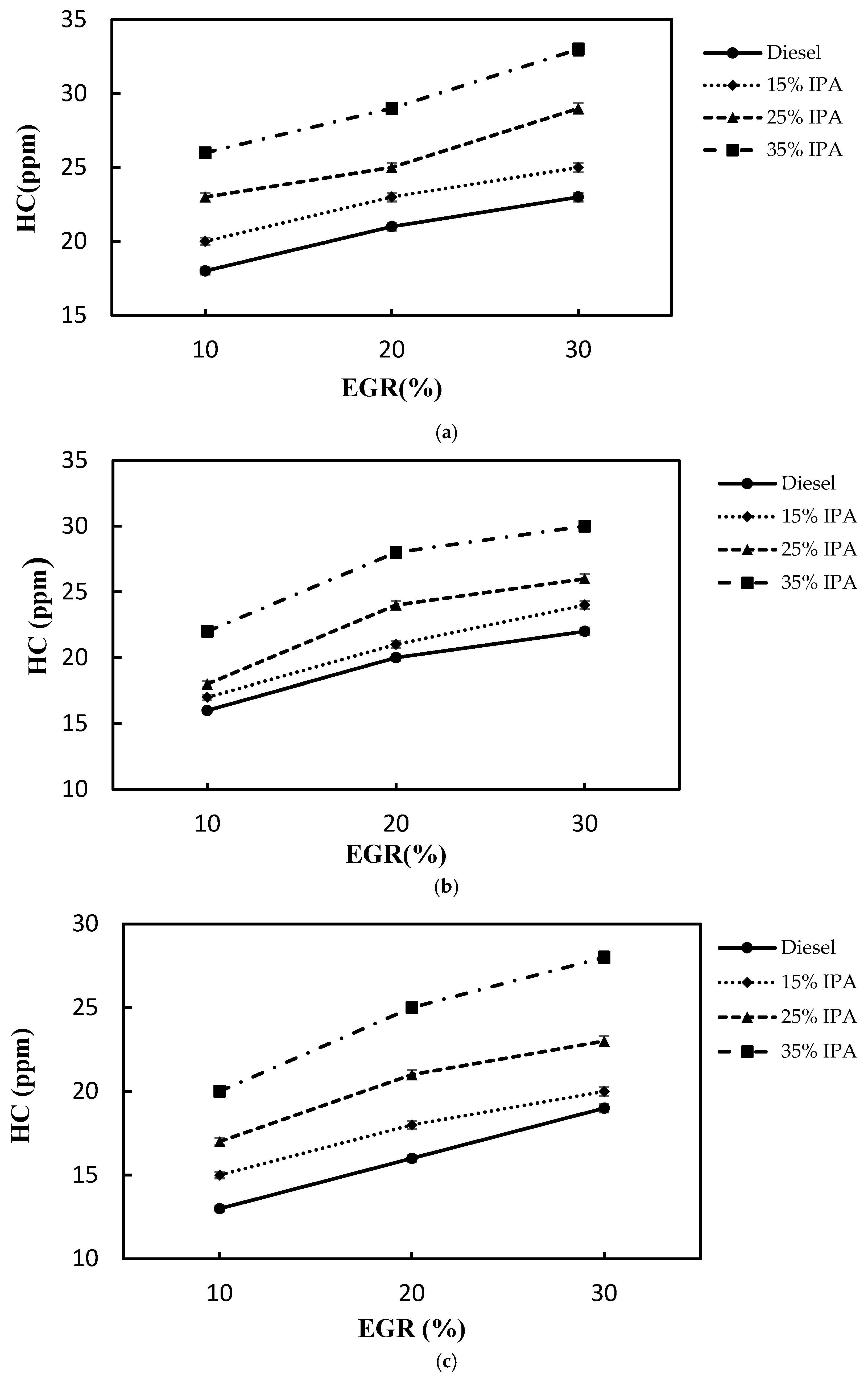
4.2. Effect on Emissions (NOx, Smoke, CO, PM2.5, and HC)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BP | Brake power (kW) |
| BSFC | Brake-specific fuel consumption (g/kW-h) |
| COV(IMEP) | Coefficient of variance for IMEP (%) |
| EGR ratio | Exhaust gas recirculation ratio (%) |
| IMEP | Indicated mean effective pressure (bar) |
| Averaged mean effective pressure (bar) | |
| LHV | Lower heating value (kJ/g) |
| Mass rate (g/h) | |
| N | Sampling cycle number |
| NOx | Nitric oxide concentrations (ppm) |
| p | In-cylinder pressure (bar) |
| ppm | Parts per million |
| Q | Heat release (J) |
| rpm | Revolutions per minute |
| T | Gas temperature (K) |
| V | Volume (m3) |
| Specific heat ratio | |
| Brake thermal efficiency (%) | |
| θ | Crank angle (degrees) |
| Standard deviation | |
| Subscripts | |
| a | Actual |
| air | Air |
| D | Diesel oil |
| i | The ith cycle |
| IPA | Isopropanol |
| s | Stoichiometric |
References
- Kirkpatrick, A.T. Internal Combustion Engines: Applied Thermosciences, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.K.; Sahu, S.K.; Panda, A.K. Current status and prospects of alternate liquid transportation fuels in compression ignition engines: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Zhong, Y.H.; Lu, S.S.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Tan, D.L. A Comprehensive Review of the Properties, Performance, Combustion, and Emissions of the Diesel Engine Fueled with Different Generations of Biodiesel. Processes 2022, 10, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.T.; Nguyen, X.P.; Pham, V.V.; Le, V.V.; Le, A.T.; Bui, V.T. Effect of alcohol additives on diesel engine performance: A review. Source Energy Sources Part A—Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2025, 47, 2011490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.F.; Wei, J.W.; Wu, X.; Ukaew, A. Performance and exhaust emissions from diesel engines with different blending ratios of biofuels. Processes 2024, 12, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.W.; Wang, R.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Ou, D.J.; Chen, T.Y. Influence of port-inducted ethanol or gasoline on combustion and emission of a closed cycle diesel engine. Energy 2014, 64, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redel-Macías, M.D.; Pinzi, S.; Babaie, M.; Cubero-Atienza, A.Z.A.; Dorado, M.P. Bibliometric Studies on emissions from diesel engines running on alcohol/diesel fuel blends. a case study about noise emissions. Processes 2021, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanenko, D.; Rudnicki, J.; Kneba, Z. Impacts of using exhaust gas recirculation and various amount of dimethyl ether premixed ratios on combustion and emissions on a dual-fuel compression ignition engine. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2024, 18, 196–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Wu, H.W.; Hung, H.H. Applying Taguchi method to combustion characteristics and optimal factors determination in diesel/biodiesel engines with port-injecting LPG. Fuel 2014, 117, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, W.; Sahoo, N.; Prasad, V.V.D.N. Investigation of engine performance and combustion. and use of oxidation catalysts in an LPG-diesel dual-fuel engine. J. Energy Eng. 2021, 147, 04021055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Pham, T.Y.; Le, H.C.; Nguyen, V.; Nguyen, L.H. Exploring the feasibility of dimethyl ether (DME) and LPG fuel blend for small diesel engine: A simulation perspective. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2024, 13, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.T.; Chen, D.D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, T.; Li, G.X.; Chen, H.W. Effect of pilot injection strategy on performance of diesel engine under ethanol/F-T diesel dual-fuel combustion mode. Processes 2023, 11, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.W.; Fan, C.M.; He, J.Y.; Hsu, T.T. Optimal factors estimation for diesel/metha nol engines changing methanol injection timing and inlet air temperature. Energy 2017, 141, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.B.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Qin, B.Y.; Cui, S.W. Effects of different injection strategies on combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine fueled with dual fuel. Processes 2021, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luna, F.E.T.; Jaguaribe, E.F.; Rumao, A.S.; Henríquez, J.R. A turbocharged diesel engine adapted to operate in dual diesel/natural gas Mode. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, S.; Volza, A.; Scrignoli, F.; Savioli, T.; Mattarelli, E.; Rinaldini, C.A. Combustion chamber optimization for dual-fuel biogas-diesel co-combustion in compression jgnition engines. Processes 2023, 11, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdiwansyah; Mamat, R.; Sani, M.S.M.; Sudhakar, K.; Kadarohman, A.; Sardjono, R.E. An over view of Higher alcohol and biodiesel as alternative fuels in engines. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Su, X.; Chen, H.; Geng, L.M.; Zhao, X. Experimental investigation on NOx and PM pollutions of a common-rail diesel engine fueled with diesel/gasoline/isopropanol blends. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 2260–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilçin, K.; Altun, S. Effect of biodiesel addition in a blend of isopropanol-butanol-ethanol and diesel on combustion and emissions of a CRDI engine. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 4727–4739. [Google Scholar]
- Rayapureddy, S.M.; Matijosius, J.; Rimkus, A. Comparison of research data of diesel-biodiesel-isopropanol and diesel-rapeseed oil-isopropanol fuel blends mixed at different proportions on a CI Engine. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilçin, K.; First, M.; Altun, S.; Okcu, M. Effect of blending ratio and injection timing on combustion and emissions of a common-rail diesel engine fueled by isopropanol-butanol-ethanol (IBE) and conventional diesel. J. Polytech. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, Z.G.; He, J.J.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, X. Effect of isopropanol and n-pentanol addition in diesel on the combustion and emission of a common rail diesel engine under pilot plus main injection strategy. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, D.C.; Devarajan, Y.; Raja, T. Characterization of isopropanol-enhanced Caesalpinia bonduc biodiesel blends: A sustainable strategy for decarbonization. Result Eng. 2025, 103849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Xu, B.; Jia, J.H.; Wu, J.A.; Shang, W.W.; Ma, Z.H. Effect of injection timing on performance and emissions of DI-diesel engine fueled with isopropanol. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Mechatronics, ICEEM, Phuket Island, Thailand, 20–21 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Okcu, M.; Varol, Y.; Altun, S.; Firat, M. Effects of isopropanol-butanol-ethanol (IBE) on combustion characteristics of a RCCI engine fueled by biodiesel fuel. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talamala, V.; Kancherla, P.R.; Basava, V.A.R.; Kolakoti, A. Experimental investigation on combustion, emissions, performance and cylinder vibration analysis of an IDI engine with RBME along with isopropanol as an additive. Biofuels 2017, 8, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halis, S. An experimental study of operating range, combustion and emission characteristics in an RCCI engine fueled with isopropanol/n-heptane. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, T.V.; AppaRao, B.V.; Kolakoti, A. Engine combustion analysis of an IDI-diesel engine with Rice Bran Methyl Ester and Isopropanol Injection at suction end. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Tang, C.L.; Huang, Z.H. Emission characteristics of isopropanol/gasoline blends in a spark-ignition engine combined with exhaust gas re-circulation. Therm. Sci. 2014, 18, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Dai, J.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Lee, T.H. Optical investigation on combustion and soot formation characteristics of isopropanol-butanol-ethanol (IBE)/diesel blends. Energy Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 2311–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Vu, M.T.; Le, V.V.; Pham, V. Impacts of charge air parameters on combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel Marine Engine. Termo 2023, 3, 494–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyumaz, A. An experimental investigation into combustion and performance characteristics of an HCCI gasoline engine fueled with n-heptane, isopropanol and n-butanol fuel blends at different inlet air temperatures. Energy Conver. Manag. 2015, 98, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, S.; Lafrance, S.; Liko, B.; Guo, H.S. A study on effect of engine operating parameters on NOx emissions and exhaust temperatures of a heavy-duty diesel engine during idling. Int. J. Enhine Res. 2022, 24, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jo, S.; Lee, J.T.; Park, S. Biodiesel fueled combustion performance and emission characteristics under various intake air temperature and injection timing conditions. Energy 2020, 206, 118154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannakis, R.G. Study of air inlet preheating and EGR impacts for improving the operation of compression ignition engine running under dual fuel mode. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 68, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, Y.H.; Huspi, H.A.; How, H.G.; Sher, F.; Din, Z.U.; Le, T.D.; Nguyen, H.T. Effect of intake air temperature and premixed ratio on combustion and exhaust emissions in a partial HCCI-DI diesel engine. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Saha, U.K. Experimental probe into a biogas run dual fuel diesel engine using oxygenated ternary blends at optimum Equivalence Ratio and under the effect of intake charge preheating. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2022, 144, 061010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, C.S. Reduction of nitric oxides and soot by premixed fuel in partial HCCI engine. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2005, 128, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroskhan, M.; Ismail, S.; Reddy, M.G.; Teja, A.S. Effects of charge preheating on the performance of a biogas-diesel dual fuel CI engine. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency, U.S. EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pm/ (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Wu, H.W.; Hsu, T.T.; Fan, C.M.; He, P.H. Reduction of smoke, PM2.5, and NOx of a diesel engine integrated with methanol steam reformer recovering waste heat and cooled EGR. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 172, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.B. Experimental Methods for Engineers; McGraw Hill Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Obert, F.E. Internal Combustion Engines and Air Pollution; Index Education Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Peragón, F.; Jiménez-Espadafor, F.J.; Palomar, J.A.; Dorado, M.P. Influence of a combustion parametric model on the cyclic angular speed of internal combustion engines. Part I: Setup for sensitivity analysis. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J.B. Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]





| Item | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Engine type | Water cooling |
| Displacement | 624 cc |
| Maximum output | 9.2/2400 kW/rpm |
| Continuous output | 7.7/2200 kW/rpm |
| Maximum torque | 39.6/1800 N-m/rpm |
| Combustion chamber type | Direct injection |
| Compression ratio | 18 |
| Injection pressure | 21.57 to 22.56 MPa |
| Start of injection | 21.5 °CA to 23.5 °CA BTC |
| Measuring Instruments | Measurement Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| CO/HC Gas detector | CO: 0–10% (Vol.) | ±0.01% |
| HC: 0–15,000 (ppm) | ±0.022% | |
| NOx analyzer | 0–5000 (ppm) | ±0.02% |
| Smoke analyzer | 0–100% | ±0.1% |
| Item | Uncertainty |
|---|---|
| Pressure | ±1.3% |
| Smoke | ±2.7% |
| NOx | ±1.4% |
| HC | ±1.3% |
| PM2.5 | ±1.8% |
| CO | ±1.1% |
| Brake power | ±2.5% |
| ±3.1% | |
| Heat release rate | ±3.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.-W.; He, P.-H.; Yeh, T.-W. Effect of Port-Injecting Isopropanol on Diesel Engine Performance and Emissions by Changing EGR Ratio and Charge Temperature. Processes 2025, 13, 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072224
Wu H-W, He P-H, Yeh T-W. Effect of Port-Injecting Isopropanol on Diesel Engine Performance and Emissions by Changing EGR Ratio and Charge Temperature. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072224
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Horng-Wen, Po-Hsien He, and Ting-Wei Yeh. 2025. "Effect of Port-Injecting Isopropanol on Diesel Engine Performance and Emissions by Changing EGR Ratio and Charge Temperature" Processes 13, no. 7: 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072224
APA StyleWu, H.-W., He, P.-H., & Yeh, T.-W. (2025). Effect of Port-Injecting Isopropanol on Diesel Engine Performance and Emissions by Changing EGR Ratio and Charge Temperature. Processes, 13(7), 2224. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072224







