Abstract
Nitrogen is a vital nutrient and plays a pivotal role in maintaining ecosystem equilibrium. Owing to human activities, particularly industrial production, vehicle emissions, fossil fuel combustion, and the improper use of chemical fertilizers, nitrogen pollution has emerged as a pressing global environmental issue. It exacerbates air pollution, water eutrophication, and soil acidification, all of which pose profound risks to both ecosystems and human health. This review conducts a holistic analysis of nitrogen sources and the current status of nitrogen pollution, with a particular focus on the treatment of nitrogen-laden wastewater. It assesses various nitrogen pollution remediation technologies, including biological and physicochemical methods. In recent years, the application of novel metal–phenolic networks (MPNs) has garnered considerable scholarly attention. As innovative materials, it has been demonstrated that MPNs have great potential in nitrogen removal. For example, studies have demonstrated that iron–tanninate has the capacity to remove over 95% of ammonium nitrogen. Despite the progress made with current remediation methods, each approach has inherent limitations, such as long treatment durations, high energy demands, and poor selectivity for diverse nitrogen pollutants. Therefore, sustained research endeavors and technological innovation are indispensable for advancing nitrogen pollution control technologies. It is against this backdrop that we conducted this review. This study summarizes and analyzes the current status of nitrogen pollution and nitrogen removal technologies, and provides an overview of novel nitrogen removal MPNs. MPNs are promising and innovative materials with great potential, although current research is still at the laboratory stage and is ongoing.
1. Introduction of Nitrogen
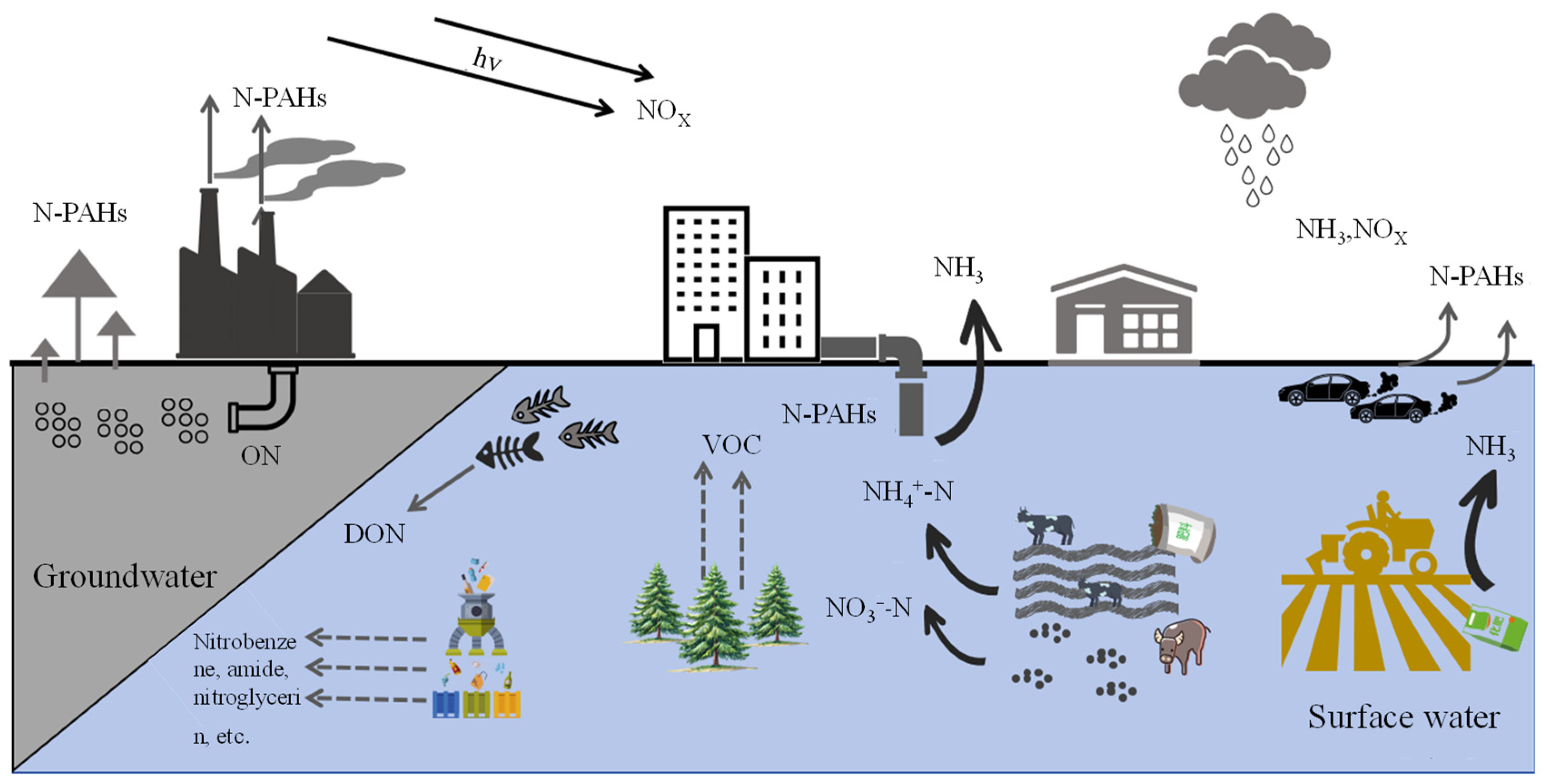
Nitrogen plays a crucial and multifaceted role in nature [1,2]. As one of the primary components of the atmosphere, nitrogen gas (N2) makes up approximately 78% of it. Nitrogen is a fundamental component of proteins, nucleic acids, and other vital biological molecules, directly influencing the growth, development, and function of organisms. It is also a key element for plant growth and industrial production, being essential for crop yields and the quality of synthetic materials [3,4]. The rapid growth of industrial production has led to human activities tripling the nitrogen (N) input rate into global terrestrial ecosystems compared to the pre-industrial era [5]. Nitrogen pollution primarily arises from human activities, including industrial production, automobile exhaust emissions, fossil fuel combustion, improper fertilizer use, large-scale deforestation, and vegetation burning [6], as illustrated in Figure 1. For instance, excessive emissions of harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and free ammonia (NH3) contribute to air pollution, soil erosion, acidification, and the contamination of surface and groundwater [7]. According to data from China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment, between 2016 and 2019, ammonia nitrogen NH3-N discharges in wastewater ranged from 46.3 to 56.8 million tons, while NOx emissions in waste gas ranged from 12.34 to 15.03 million tons [8]. According to the 2020 China Ecological and Environmental Statistics Yearbook, nationwide emissions of NOx in waste gas reached 10.197 million tons, and NH3-N discharges in wastewater surged to as high as 9.84 million tons [9]. In addition, according to data from the National Agricultural Sustainable Development Plan (2015–2030) [10], the fertilizer and pesticide utilization rate in the country is below one-third, the mulch film recycling rate is under two-thirds, the effective treatment rate of livestock and poultry waste is less than 50%, and straw burning and water bodies are severely eutrophied. Notably, nitrogen fertilizer use in the country accounts for 35% of the world’s total consumption, with the usage per unit area being 2.74 times higher than the global average [11].
Figure 1.
A schematic diagram showing nitrogen sources and their distribution.
Although critical thresholds for total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP), exceeding 0.2 mg/L and 0.02 mg/L, respectively, can lead to water body eutrophication [12], global standards for TN and TP remain relatively low. For instance, in 2002, the TN and TP values in the first-level A standards [13] for urban sewage treatment plants, as issued by China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment, were 15 mg/L and 0.5 mg/L, respectively [13], which were significantly higher than the nitrogen and phosphorus requirements in the Class IV water standards for surface water [12]. The 2009 Nutrient published in the United States summarizes typical design targets for advanced wastewater treatment processes, specifying effluent total nitrogen concentrations of ≤10 mg/L and total phosphorus concentrations in the range of 0.1–1 mg/L [14]. The 1991 EU Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive requires effluent discharged into sensitive areas from urban wastewater treatment plants to meet only total nitrogen ≤10 mg/L and total phosphorus ≤1 mg/L [15], while the 2000 Water Framework Directive only requires Member States to determine TN and TP control standards themselves, based on river basin management objectives, to achieve good water status. [16]. Furthermore, NO2 and its secondary reaction derivatives (such as HNO3 and particulate NO3−) in the atmosphere have seen a continuous surge [17]. For example, nitrogen precipitation in China has increased by approximately 60% over the past 30 years, making it one of the three global hotspots for nitrogen deposition, alongside Western Europe and North America [18]. In 2019, the United Nations Environment Assembly called for enhanced action through its resolution on sustainable nitrogen management [19]. In October 2019, UN member states approved the proposed Colombo Declaration on sustainable nitrogen management in Colombo, aiming to reduce TN pollutants by 50% by 2030 [20]. Therefore, mitigating and curbing nitrogen pollution is crucial for protecting both the environment and human health.
2. Nitrogen Pollution Issue
Nitrogen is a crucial element in maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems and plays a significant role in stabilizing water quality [21]. Currently, nitrogen pollution in water has emerged as one of the most pressing environmental issues globally. Nitrogen in water exists in two primary forms: organic nitrogen and inorganic nitrogen. Inorganic nitrogen encompasses nitrogen compounds such as NH3-N, NO3−-N, and NO2−-N. These nitrogen compounds primarily originate from agricultural, industrial, and domestic wastewater, which is discharged into natural water bodies, including rivers, lakes, and oceans, leading to significant water quality degradation and adverse effects on both aquatic ecosystems and human health [22,23].
NH3-N in water is a key factor influencing the environmental quality of aquatic ecosystems. The primary forms of NH3-N are ionic ammonia and free ammonia [24]. NH3-N disrupts the respiration and ionic balance of fish, thereby impacting the survival of aquatic organisms. It often leads to water body eutrophication, causing issues such as “water blooms” and “red tides” [25]. Elevated NH3-N levels in drinking water promote bacterial growth in water supply pipelines, causing the corrosion of the inner walls and further deterioration of the effluent water quality [26]. Additionally, NH3-N is a major precursor of disinfection by-products. NH3-N forms chloramine during chlorination and disinfection, thereby reducing disinfection efficiency [27]. It can also be converted into NO3−-N while depleting dissolved oxygen (DO) in the water. Furthermore, nitrogen compounds can form ammonia in water, which emits an irritating odor and adversely affects the respiratory system and mucosa [28]. Prolonged exposure to high concentrations of ammonia may cause symptoms such as burning eyes, shortness of breath, and sore throat. In severe cases, prolonged exposure may lead to diseases such as tracheitis and pneumonia [29].
NO3−-N is a nitrogen compound with high solubility in aqueous solutions. The nitrogen element exists in the +5 oxidation state, and it is the most stable nitrogen-containing compound in aerobic environments [30]. It typically arises from the improper use of agricultural nitrogen fertilizers, the discharge of untreated industrial wastewater, the unregulated release of livestock and poultry manure waste, domestic sewage, atmospheric deposition, and soil erosion [31]. Due to the long self-purification cycles of ecosystems and their limited degradation capacity, NO3−-N concentrations in the water environment gradually accumulate and increase, eventually exceeding standard limits and causing a range of ecological and environmental issues. For instance, excessive NO3−-N concentrations in water can lead to frequent planktonic and algal blooms, red tides, and other issues [32]. Aquatic organisms may fail to obtain sufficient oxygen, impairing their reproduction and leading to mortality [33]. Additionally, consuming drinking water with excessive NO3−-N concentrations may lead to health issues in humans, such as thyroid dysfunction, cardiovascular disease, blue baby syndrome, and growth defects in infants [7,34]. When NO3−-N levels in drinking water significantly exceed the standard, nitrate reductase in the human body converts NO3−-N into NO2−-N. Nitrite is one of the most toxic substances responsible for causing acute poisoning in humans. The poisoning dose for normal adults ranges from 300 to 500 mg, and the lethal dose is as low as 3 g [35]. The combination of nitrite and hemoglobin in the human body forms methemoglobin, which impairs oxygen transport, leading to vision and cognitive disorders, blood vessel dilation, blood pressure changes, and even death [36]. Therefore, the harm of nitrogen-containing wastewater extends beyond ecosystem damage and biodiversity loss, posing a deeper threat to human health and quality of life. Research on efficient and cost-effective wastewater treatment technologies is essential for reducing nitrogen concentrations and eliminating nitrogen pollution in water.
3. Research Statistic and Analysis
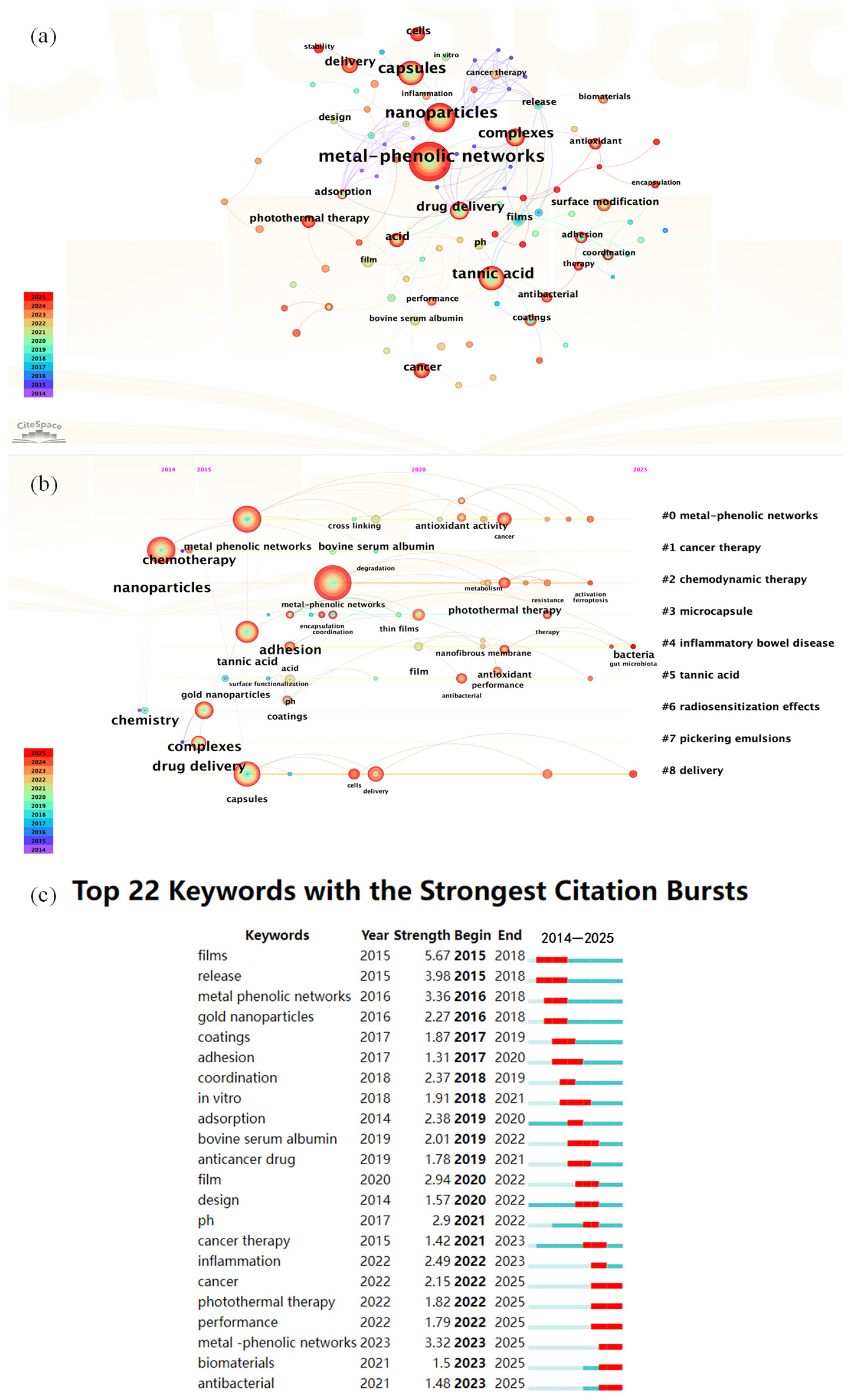
The preceding section introduced the background and impacts of nitrogen pollution. Herein, we present a statistical analysis of research articles pertaining to nitrogen pollution and metal–phenolic networks (MPNs), with a focus on the application of MPNs in nitrogen removal processes. The analysis was conducted using data retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection. After conducting a keyword search for ‘nitrogen pollution’ and ‘metal-phenolic networks’ in the Web of Science database, we selected authoritative articles and exported their data. The data were analyzed using the software CiteSpace V6.3R1 (Philadelphia, PA, USA). The results are presented in Figure 2.
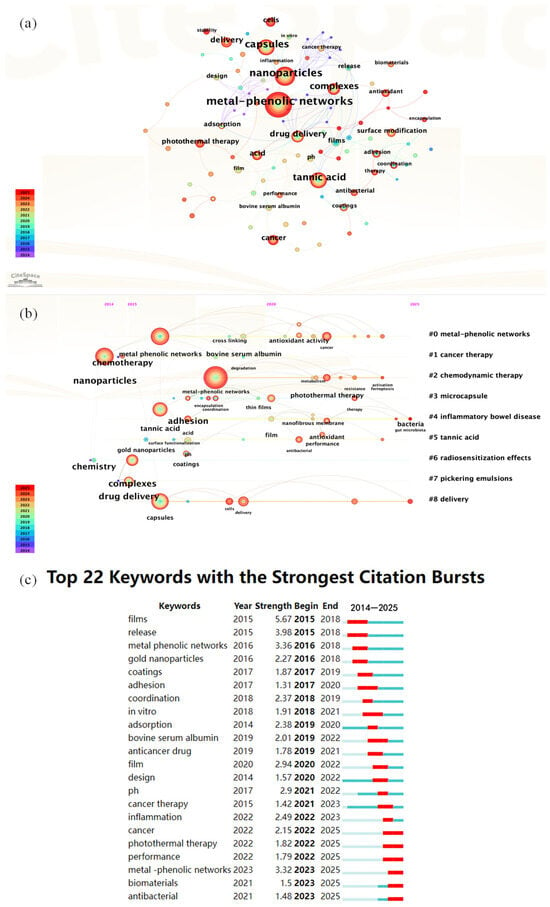
Figure 2.
(a) Keyword Co-occurrence Network Map; (b) Keyword Time-Zone View; (c) Top 22 Keywords with the Strongest Citation Bursts.
Figure 2a shows a keyword co-occurrence network map generated by CiteSpace, V6.3R1 (Philadelphia, PA, USA) based on the literature published from 2014 to 2025. The core nodes are clustered around three primary themes: ‘metal-phenolic networks,’ ‘tannic acid,’ and ‘nanoparticles’. Emerging research hotspots extend outward, encompassing ‘drug delivery’, ‘photothermal therapy’, ‘surface modification’, ‘capsules’, and ‘complexes’. The node colors shift from light to dark (blue to red), indicating the temporal progression from 2014 to 2025. Significantly, there has been rapid growth in emerging research directions, such as ‘drug delivery’, ‘photothermal therapy’ and ‘surface modification’ in recent years. When applied to nitrogen removal research, metal–phenolic network materials, which are characterized by multivalent metal centers strongly coordinated with phenolic hydroxyl groups and abundant surface functional groups, can be tailored through surface modification or nanocomposite strategies to create highly efficient adsorbents or catalysts. These materials facilitate highly selective adsorption and transformation of nitrogen pollutants, such as ammonia and nitrate, in water, thereby opening up new application prospects for MPNs in environmental nitrogen remediation.
Figure 2b shows a CiteSpace keyword timeline view based on the literature from 2014 to 2025, highlighting nine major thematic clusters (#0 to #8). Cluster #0, “metal-phenolic networks,” serves as the core theme. Other emerging subfields include #1 “cancer therapy,” #2 “chemodynamic therapy,” #3 “microcapsules,” #4 “inflammatory bowel disease,” #5 “tannic acid,” #6 “radiosensitization effects,” #7 “Pickering emulsions,” and #8 “delivery.” These clusters have gradually emerged along the timeline, with node colors shifting from blue to red, reflecting research hotspots evolving from early to recent focus. In the context of nitrogen removal, the multipoint coordination and crosslinking features of MPNs, combined with their interfacial enrichment advantages in Pickering emulsions and microcapsule construction, offer promising avenues. Through surface functionalization or enzyme-catalyzed embedding, these networks can achieve efficient adsorption, selective transformation, and controlled release of ammonia and nitrate in water, paving the way for innovative applications of MPNs in environmental nitrogen removal and remediation of complex pollution.
Figure 2b shows a keyword timeline view generated by CiteSpace, based on the literature spanning from 2014 to 2025, and highlights nine major thematic clusters labeled #0 to #8. Cluster #0, ‘metal-phenolic networks’ is identified as the core theme. Other emerging subfields encompass #1 ‘cancer therapy’, #2 ‘chemodynamic therapy’, #3 ‘microcapsules’, #4 ‘inflammatory bowel disease’, #5 ‘tannic acid’, #6 ‘radiosensitization effects’, #7 ‘Pickering emulsions’, and #8 ‘delivery’. These clusters have gradually emerged over the timeline, with node colors changing from blue to red, indicating the evolution of research hotspots from early to recent focus. In the context of nitrogen removal, the multipoint coordination and cross-linking characteristics of MPNs, along with their interfacial enrichment advantages in the construction of Pickering emulsions and microcapsules, provide promising prospects. By means of surface functionalization or enzyme-catalyzed embedding, these networks can achieve efficient adsorption, selective transformation, and controlled release of ammonia and nitrate in water, thus paving the way for innovative applications of MPNs in environmental nitrogen removal and the remediation of complex pollution.
Figure 2c shows the Top 22 Keywords with the Strongest Citation Bursts from 2014 to 2025, including their burst periods and strengths. Recent keywords like “metal-phenolic networks” (2023–2025), “photothermal therapy” (2022–2025), “cancer”, “inflammation”, “biomaterials”, and “adsorption” reflect growing interest in multifunctional materials for biomedical and environmental use. Earlier bursts such as “films” and “gold nanoparticles” peaked around 2015–2018. For nitrogen removal, these trends highlight the potential of material science in environmental applications. MPNs, with their tunable structure and strong metal coordination, are promising for nitrogen adsorption and catalytic transformation. Continued focus on adsorption and biomaterials suggests that bio-based materials (e.g., polyphenols) could be tailored for selective ammonia/nitrate capture and controlled release. The emergence of photothermal therapy also hints at using photothermal effects to enhance catalytic or microbial nitrogen conversion. Overall, MPNs offer a promising path for advanced water treatment and nitrogen pollution control.
4. Technologies for Remediation of Nitrogen Pollution
4.1. Biological Methods
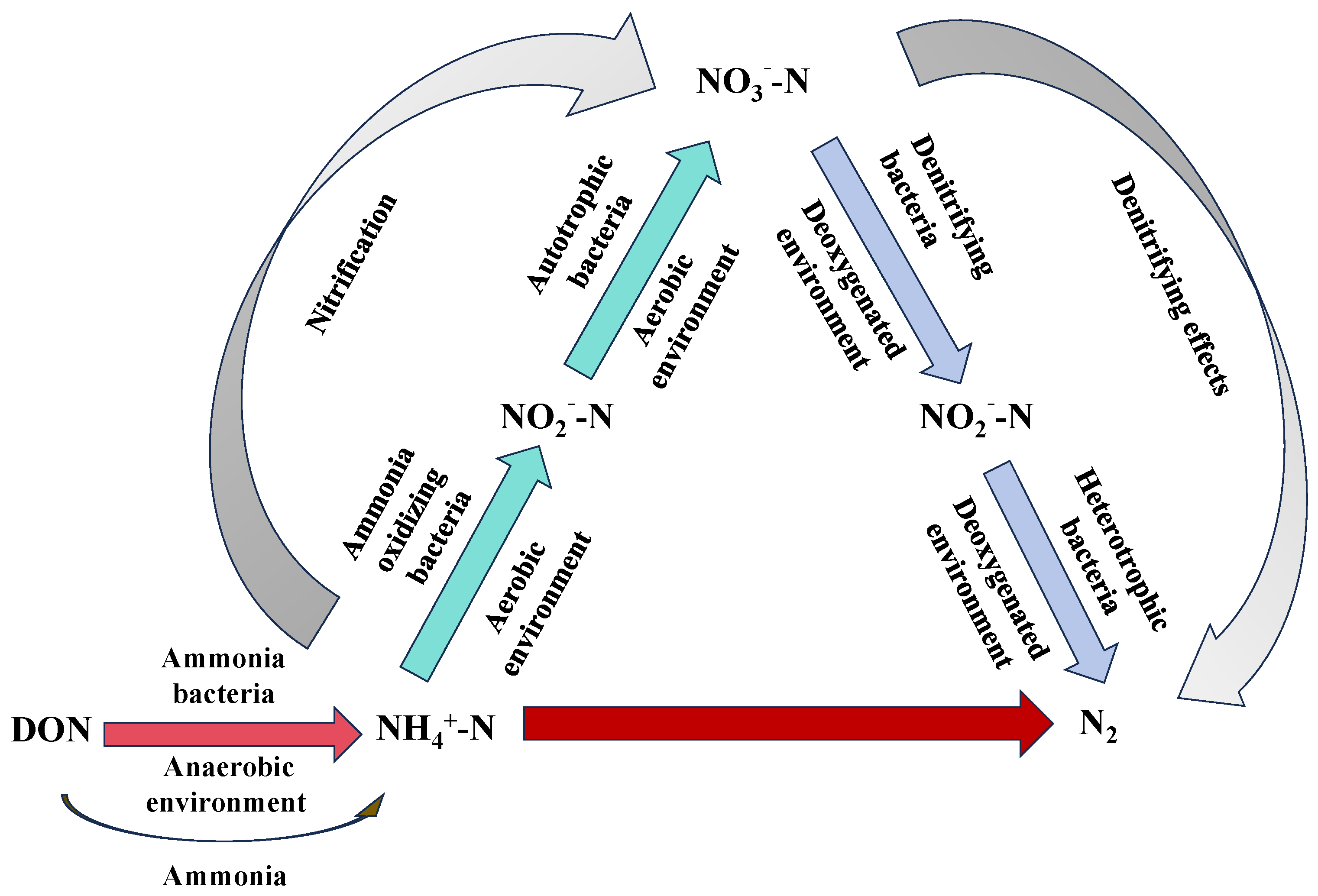
Bio-nitrogen removal refers to the process in which microorganisms catalyze biochemical reactions to convert nitrogen in wastewater into N2, thus removing nitrogen from the water. The conversion process is illustrated in Figure 3. Currently, existing biotechnologies can be classified into traditional and advanced biological nitrogen removal technologies [37]. Advanced biological nitrogen removal processes, which are developed from traditional methods, mainly include biofilm technology, anaerobic ammonia oxidation (ANAMMOX), simultaneous nitrification, and shortcut nitrification–denitrification [38,39].
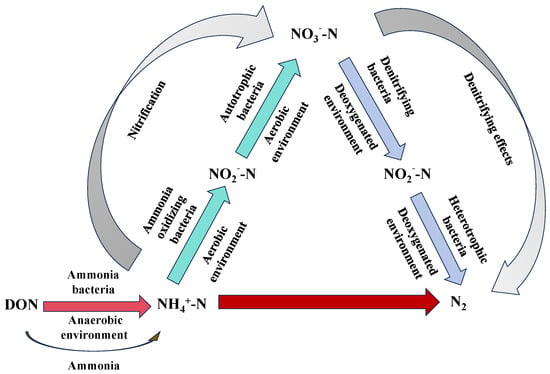
Figure 3.
A schematic diagram showing the process of nitrogen removal using biological technology.
Traditional biological nitrogen removal is based on the principle of nitrification–denitrification. In this process, NH4+-N and nitrogen-containing organic matter in wastewater are initially oxidized by ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB), respectively, converting them into NO2−-N and subsequently into NO3−-N. The nitrification process comprises two key enzymatic reactions: ammonia is oxidized to NO2−-N by AOB via the enzyme ammonia monooxygenase, and NO2−-N is further oxidized to NO3−-N by NOB through the enzyme nitrite oxidoreductase. The overall reactions are shown in Equations (8) and (9). During the denitrification phase, denitrifying bacteria utilize nitrate as an electron acceptor under anoxic conditions, reducing it stepwise to N2 via NO2−-N, nitric oxide, and nitrous oxide (N2O), which is then released into the atmosphere. This integrated process effectively removes nitrogen from wastewater [40,41,42]. Currently, processes such as hypoxia/aerobic, anaerobic/hypoxia/aerobic, oxidation ditches, and the SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor-Activated Sludge Process) are widely applied in urban sewage treatment in China [43]. Bai et al. [44] used powdered activated carbon to enhance the activated sludge method for treating nitrogen and phosphorus in petrochemical wastewater. The removal rates of NH3-N and TN were two and three times higher than those of the traditional method, respectively. Wang et al. [45] studied the SBR process performance of aerobic granular sludge and found that, although the SBR process performs well in removing organic matter and phosphate, its TN removal efficiency is moderate, with an average removal rate of approximately 52%. Duan et al. [46] investigated the properties of nitrogen and phosphorus removal as well as microbial characteristics using an iron–carbon microelectrolytic coupling and anaerobic–oxidative–aerobic process. The results indicated that the Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), TN, NH4+-N, and TP concentrations in the effluent were 75.80, 0.65, 0.62, and 0.74 mg/L, respectively, meeting the emission standards of GB21900-2008 [47]. However, the process had the drawback of requiring a long treatment time [48]. Therefore, although traditional biological nitrogen removal processes are stable and effective for removing nitrogen from wastewater containing organic matter, they have drawbacks such as long process flows and treatment times, large area requirements, low efficiency at low temperatures, and often the need for additional carbon sources.
The biofilm method involves allowing sewage to flow over the surface of a filler and promoting the adhesion and growth of microorganisms, which eventually form membrane-like microbial flocs [49]. This method is primarily used to remove soluble and colloidal organic pollutants from wastewater. The main applications of this method include biological filters, biological rotating disks, and biological fluidized beds [50]. Biofilm reactors generally occupy a small area, produce minimal sludge, support abundant microbial populations, and demonstrate better performance in treating NH3-N wastewater. For instance, Mao et al. [51] used a sequencing batch biofilm reactor to treat high-concentration NH3-N wastewater, achieving an NH3-N removal rate of 91.6%. Li et al. [52] used membrane bioreactors to treat nitrogen-containing wastewater under low-temperature conditions, achieving a TN removal rate of 85%, with a residual NO3−-N concentration of approximately 2 mg/L, and a removal rate of up to 94.0%. However, the biofilm method also has drawbacks, including high energy consumption, long start-up times, extended hydraulic retention times, and sensitivity to ambient temperature, which hinder the rapid treatment and purification of nitrogen-containing wastewater. ANAMMOX is a biochemical process in which NH4+-N and NO2−-N are converted into N2 under anaerobic conditions, facilitated by H+ and HCO3− [53,54]. ANAMMOX is widely employed in treating high-concentration NH3-N wastewater, including coking wastewater, garbage leachate, and digested sludge dewatering liquid. Sui et al. [55] employed advanced nitrogen removal in a fixed-bed ANAMMOX reactor following a hypoxia/oxygenation reactor, resulting in an increase in TN and NH4+-N removal efficiency by 12.7–23.4% and 17.2–20.0%, respectively. Chen et al. [56] adopted the ANAMMOX process and constructed a rapid permeability system to study the influence of organic matter on both the ANAMMOX properties and the microbial community structure. The results indicated that after 83 days of domestication, the removal efficiencies for NH4+-N, NO2−-N, and TN were 99.7 ± 0.3%, 99.8 ± 0.2%, and 91.3 ± 0.2%, respectively. Li et al. [57] employed partial denitrification and ANAMMOX to reduce the TN concentration in NH4+-N wastewater, initially at 30–50 mg/L, to 8.9 ± 1.0 mg/L. In comparison to the traditional biological denitrification process, the ANAMMOX process does not require aeration, thereby reducing the demand for O2 and COD. CO2 serves as the carbon source and energy, while the small reaction structure and minimal residual sludge contribute to reduced energy consumption and costs. However, the slow proliferation rate of anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, their low resistance to dissolved oxygen (DO), long equipment start-up times, and low initial nitrogen removal rates limit their industrial application [58,59].
Synchronous nitrification–denitrification is a mechanism in which both nitrification and denitrification processes occur simultaneously within the same biological treatment reactor [60]. Currently, three primary theories explain this process: the microenvironment theory, the macroenvironment theory, and the microbiological theory [61]. Its process flow is simple, reaction time is short, alkalinity addition is minimized, and there is no need for pH adjustment or carbon source addition, making it widely applied in practical research. For instance, Chen et al. [62] employed a synchronous nitrification–denitrification process to treat domestic wastewater. After two months of operation, the TN removal rate of the bioreactor stabilized at approximately 50%, with a hydraulic retention time of 12 h. Cao et al. [63] applied the synchronous nitrification–denitrification process to remove nitrogen from micro-contaminants, achieving a removal efficiency of NO3−-N exceeding 90%. Although the synchronous nitrification–denitrification process is effective, challenges remain, such as the need for a strict inlet carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, DO control, HRT (hydraulic retention time), and temperature regulation. Short-range nitrification–denitrification [64], also known as incomplete nitrification–denitrification, occurs when NO2−-N/(NO2−-N + NO3−-N) > 50%, which directly leads to the hypoxia denitrification stage, ultimately achieving nitrogen removal. The transformation process for short-range nitrification–denitrification is NH4+ → NO2− → N2. During the stage of oxidizing NH4+-N to NO2−-N, aeration volume is reduced by 25% compared to traditional processes [65]. Under hypoxic conditions, denitrifying bacteria use organic compounds to reduce NO2−-N to N2, resulting in a 40% reduction in carbon source use compared to traditional nitrogen removal processes. Furthermore, compared to traditional nitrogen removal processes, short-range nitrification–denitrification offers advantages such as a 50% reduction in sludge production, improved TN removal rates, decreased alkaline injection requirements, and reduced reaction time [66]. However, short-range nitrification–denitrification processes also have drawbacks, such as high energy consumption due to temperature requirements and the necessity to combine with ANAMMOX processes [67]. For instance, Ban et al. [68] combined short-range nitrification with an ANAMMOX-coupled denitrification system to treat toilet sewage containing NH3-N concentrations of 400–500 mg/L. After approximately 75 days of operation, the NH4+-N and TN concentrations in the effluent were 40.20 mg/L and 67.40 mg/L, respectively, with removal rates of 90.84% and 86.90%. Biotechnology offers advantages such as stability, efficiency, environmental protection, cost-effectiveness, and widespread application. However, it also has drawbacks, including long processing times, complex and incomplete reactions, large equipment footprints, and susceptibility to environmental impacts.
Biological nitrogen removal technologies, encompassing traditional processes, biofilm methods, anammox, synchronous nitrification–denitrification, denitrification processes, and short-range nitrification–denitrification processes, offer notable advantages, including high nitrogen removal efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. These technologies are energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, making them valuable tools in wastewater treatment. However, they also face several limitations. Their effectiveness is typically limited to specific nitrogen species, such as NH4+-N and NO3−-N, and their performance is diminished for other nitrogenous compounds. Moreover, their operation is highly sensitive to environmental factors such as pH, temperature, and dissolved oxygen, which can affect microbial activity and system stability. Challenges also encompass long start-up times, complex reactor designs, high operational and maintenance costs, as well as the need for meticulous microbial management. In addition, the production of sludge and greenhouse gases, such as N2O, imposes further environmental and treatment burdens. As a result, while biological nitrogen removal shows strong potential, its capacity to handle high pollutant loads or sudden water quality fluctuations remains limited.
4.2. Physical–Chemical Method
The primary physical and chemical technologies include the blowing-off and stripping method, break-point chlorination, the chemical precipitation method, the membrane separation method, the adsorption method, and the active metal reduction method [69,70]. The blowing-off and stripping method is a water treatment technique that utilizes the oxidation reaction of dissolved gases in wastewater when air is passed through. This causes volatile substances to transfer from the liquid phase to the gas phase, thereby separating and removing them [71]. The blowing-off and stripping method increases the concentration of hydroxide ions in wastewater, enabling the continuous production of NH3 in an alkaline environment. NH3 then evaporates into the air, thereby reducing the NH4+-N concentration in the water. This method is easy to operate and provides stable removal efficiency. However, it requires a continuous stream flow during the treatment process, has a long blowing-off and stripping time, high costs, and equipment that is prone to scaling and clogging [72]. Additionally, there are difficulties in NH3 collection.
The primary principle of the break-point chlorination method [73] involves introducing Cl2, NaClO, or Ca(ClO)2 into nitrogen-containing wastewater. In this process, NH4+-N is oxidized to N2 by the strong oxidizing action of the generated HClO. As NH4+-N is gradually removed and its concentration approaches 0, the residual chlorine content reaches its lowest point. This point is referred to as the “break-point” of the reaction. The chemical reaction equation for the break-point chlorine addition method is as follows [74]:
NH4+ + 1.5 HClO → 0.5 N2 + 1.5 H2O + 2.5 H+ + 1.5 Cl−
While the break-point chlorination method is effective for treating high-concentration NH3-N wastewater, the by-products in the treated water pose health risks and may even cause cancer.
The chemical precipitation method involves adding specific chemical precipitants (e.g., Mg2+ or PO43−) to water while controlling the reaction pH and molar ratio [75]. It ensures that the solubility of the precipitants (Mg2+ or PO43−) exceeds that of the insoluble salts, thus forming insoluble magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation to remove NH3-N [76]. The chemical reaction equation is as follows [77]:
Mg2+ + NH4+ + PO43− + H2O → MgNH4PO4·6H2
Additionally, magnesium ammonium phosphate recycling is convenient and, as a sustained-release fertilizer, facilitates the recycling and utilization of resources [78]. Although this method is technologically simple, operationally flexible, highly efficient, and stable [79], making it suitable for treating high-concentration wastewater that cannot be processed by biological treatment [80], it also presents challenges. These include the large addition of phosphate and magnesium salts, high treatment costs, the need for mechanical stirring during the reaction, and significant energy consumption [81].
Membrane separation technology [82] involves the selective separation of molecular mixtures with different particle sizes as they pass through semipermeable membranes at the molecular level. Based on the varying pore sizes of semipermeable membranes, membrane separation technologies can be categorized into microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, electrodialysis, and reverse osmosis. The membrane separation method offers advantages such as low energy consumption, high automation, simplicity of operation, no involvement of chemical agents, and environmental friendliness. It can intercept NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and NO2−-N in wastewater on the surface of the membrane, thereby achieving their removal. However, the membrane separation method lacks ion selectivity and removes all impurities (including non-target substances) from wastewater, which increases treatment costs. Additionally, while it collects, concentrates, and even migrates NH4+-N and NO3−-N, it does not achieve complete purification and requires further processing. Furthermore, the membrane is prone to contamination, and it is expensive. Also, it requires regular maintenance and replacement due to clogging and damage. Consequently, this technology is not commonly used in practical nitrogen removal applications.
The adsorption method involves capturing target pollutants (one or more) from water onto the surface of a material through static or dynamic adsorption, followed by desorption using a specific method, ultimately achieving separation and enrichment [83]. Adsorption technology is widely employed in sewage nitrogen removal due to its advantages, including operational simplicity, cost-effectiveness, environmental friendliness, and efficient removal capabilities. The adsorption mechanisms [84] include ion exchange (primarily relying on electrostatic attraction), physical adsorption (mainly relying on intermolecular forces), and chemical adsorption (predominantly relying on chemical bond forces), among others. Common adsorbent materials, such as activated carbon, bentonite, and zeolite, are widely used in experimental research and practical engineering for NH4+-N treatment due to their abundant availability, low cost, and non-toxicity [85]. However, these adsorbents have a low recycling rate and are only suitable for treating low-concentration NH3-N wastewater. Additionally, there is limited research on the removal of NO3−-N and NO2−-N in wastewater, and the removal efficiency is generally poor. For instance, Bhatnagar et al. [86] used activated carbon to adsorb NO3−-N, and the activated carbon modified with ZnCl2 exhibited an adsorption capacity of only 1.7 mg/g. Mizuta et al. [87] heated bamboo powder at 900 °C for 1 h to prepare bamboo powder carbon (BPC), but its NO3−-N adsorption capacity was only 1.25 mg/g. However, the nitrate adsorption capacity can reach 50 mg/g using the polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan prepared by Rajeswari et al. [88]. Wang et al. [89] used corn stalks as the raw material to produce biochar, which was subsequently modified using KOH and FeCl3. The modifications significantly improved the biochar’s NH3-N adsorption capacity, achieving values of 15.71 mg/L and 22.61 mg/L, respectively. Li et al. [90] co-modified attapulgite and zeolite using La and Al, and integrated the modified materials with aquatic plants for the treatment of eutrophic water bodies. The study found that the modified materials effectively reduced nitrogen levels in the sediments. However, the high preparation cost of numerous modified materials currently restricts their practical application in engineering projects. Identifying an adsorbent material that is cost-effective, environmentally friendly, efficient, and has strong recycling and regeneration capabilities is of utmost importance. Currently, numerous adsorption systems encounter limitations due to high operational costs and performance degradation over multiple cycles, primarily resulting from fouling and the structural deterioration of the adsorbents. Therefore, the development of effective strategies, such as chemical regeneration, surface modification, and the utilization of low-energy materials, presents both a substantial challenge and a promising opportunity to improve the reusability and economic feasibility of adsorption-based technologies.
The reactive metal reduction method involves gradually reducing NO3−-N to N2 or NH4+-N through the reduction properties of elemental materials such as copper, aluminum, and iron [31]. Active metals commonly used for NO3−-N reduction include zero-valent magnesium (Mg0) [91], zero-valent iron (Fe0) [92], zero-valent zinc (Zn0), zero-valent copper (Cu0), and zero-valent aluminum (Al0) [93], among others. Guo et al. [94] employed synergistic systems combining zero-valent iron with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), potassium permanganate (KMnO4), or chromate (CrO42−) to enhance the removal of NO3−-N. At pH 5, the NO3−–N removal efficiency increased from 94% to 97%, while at pH 7, it markedly rose from 74% to 98%. Yang et al. [95] reported that, in the absence of external reducing agents, nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) primarily reduces nitrate to NH4+-N. In addition to nZVI and other nanometals, the high cost and limited availability of aluminum and zinc further constrain their practical applications and hinder research and development in this area. It is imperative to identify novel materials that can facilitate the concurrent reduction of NO3−-N by zero-valent metals. However, little research is focused on the removal of residual NH4+-N.
Physicochemical nitrogen removal methods provide the benefits of rapid processing and high efficiency in water treatment. However, they also present several notable drawbacks. First, the operational costs are relatively high, primarily owing to the substantial consumption and elevated prices of chemical reagents, which substantially elevate overall expenses. Second, these methods may result in secondary pollution, such as the formation of chemical precipitates or hazardous by-products, necessitating additional treatment and raising environmental concerns. Furthermore, physicochemical methods exhibit lower adaptability to fluctuations in water quality, potentially leading to reductions in treatment efficiency. The systems are generally complex and necessitate frequent maintenance. In large-scale applications, regular inspections and component replacements further augment operational difficulty and cost. Overall, physicochemical nitrogen removal is more appropriate for short-term or emergency pollution control, yet less suitable for long-term, stable water treatment operations.
4.3. Emerging Technologies
The electrobiochemical system is an innovative water treatment technology that integrates electrochemical and biological processes. In recent years, it has attracted significant attention for nitrogen pollution control. Its primary mechanisms encompass the electro-oxidation of ammonia, electro-reduction of nitrate/nitrite, electro-assisted microbial denitrification, and electro-Fenton reactions. Notably, by adjusting the electrode potential, microbial activity can be selectively enhanced. This, in turn, promotes processes such as simultaneous nitrification–denitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation. For example, Yang et al. [96] reported a total nitrogen removal rate of 96.4% using algae biofilm microbial fuel cells. Compared with traditional methods, electrochemical systems offer several advantages. They exhibit rapid reactions, high efficiency even at low nitrogen concentrations, strong controllability, and can be effectively integrated with other treatment technologies, including membrane filtration, adsorption, and biological processes. However, several challenges hinder their large-scale application. These include high energy consumption, the high cost of electrode materials, electrode fouling, and uncertain long-term stability. To advance the practical applications of electrobiochemical systems in treating urban sewage, agricultural runoff, and high-strength industrial wastewater, future research should focus on the following aspects: developing energy-efficient and durable electrodes, optimizing system design, integrating multifunctional technologies, and evaluating operational stability and economics.
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) have garnered growing interest as effective water treatment technologies for nitrogen pollution control. These processes generate highly reactive species, such as hydroxyl radicals (·OH) and sulfate radicals (SO4−·), which oxidize pollutants. AOPs are widely employed for the removal of refractory organic compounds. In the realm of nitrogen removal, AOPs demonstrate significant potential. They can convert NH4+/NH3, NO2−, and organic nitrogen compounds. By doing so, they enhance the biodegradability of nitrogen pollutants, facilitating subsequent biological treatment. Additionally, AOPs can directly remove nitrogen compounds or act as a post-treatment step [97]. Common AOP methods include ozone oxidation, photocatalysis (e.g., UV/H2O2, UV/TiO2), Electro-Fenton, and Photo-Fenton processes. For instance, Alejandro et al. [98] reported an 18.32-fold increase in NO3−-N recovery from livestock wastewater using the UV/H2O2 process. AOPs effectively break down complex organic nitrogen in wastewater, such as textile and livestock effluents, into biodegradable or inorganic forms, enabling further treatment. Despite their effectiveness, AOPs face several challenges. They often require harsh operating conditions, such as the use of UV light and high-pH environments. Moreover, they suffer from high energy consumption, the need for costly oxidants, and the potential to produce by-products like nitrite, which may cause secondary pollution. To address these challenges and improve the scalability, efficiency, and sustainability of nitrogen pollution control, future research should focus on the following aspects: developing low-energy, selective catalysts; optimizing processes; and integrating AOPs with biological and electrochemical methods.
Nanomaterials, characterized by their high surface area, abundant active sites, and excellent catalytic properties, hold great promise for nitrogen pollution control in water treatment [99,100]. Recent research has centered on utilizing nanomaterials to eliminate pollutants like ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite, investigating their efficient nitrogen removal capabilities in urban wastewater, agricultural runoff, and industrial effluents. One prevalent type of nanomaterial is metal oxides, such as TiO2, Fe3O4, and ZnO. These metal oxides can oxidize ammonia to nitrogen gas or reduce nitrate to harmless substances through photocatalysis or electrocatalysis. For instance, TiO2 generates hydroxyl radicals under UV light, effectively decomposing ammonia. As a result, it is widely employed in photocatalytic nitrogen removal studies [101,102]. Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles not only possess good adsorption properties but also facilitate rapid recovery and reuse [103]. Another important category of nanomaterials is carbon-based materials, including graphene, carbon nanotubes, and activated carbon. These materials are often used as supports for functionalized nanocatalysts or combined with other adsorbents to enhance nitrogen adsorption and transformation. For example, graphene oxide can be combined with metals or metal oxides to improve its catalytic performance for ammonia or nitrate conversion while maintaining excellent chemical stability and regeneration capability [104]. In addition, novel porous nanomaterials, such as metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) and covalent organic frameworks (COFs), are also being explored for efficient nitrogen removal. These materials are highly tunable and have rich functional sites, enabling the selective recognition and capture of nitrogen pollutants while offering good regeneration capacity. Despite their significant potential, several challenges persist. These include high production costs, unclear environmental safety, and the need to enhance their stability and resistance to interference in real-world water systems. To achieve efficient and sustainable nitrogen pollution control, future research should focus on the following aspects: conducting systematic studies on the environmental behavior and toxicity of nanomaterials, developing green synthesis methods, and integrating nanomaterials with traditional treatment technologies.
Integrating multiple technologies to achieve synergistic effects is an effective strategy for enhancing overall nitrogen removal efficiency. Single technologies often face challenges such as low efficiency, long treatment times, and high costs. However, combining technologies can leverage their strengths and address individual limitations [105]. A common approach is integrating biological denitrification with physical–chemical methods. For example, coupling electrochemical denitrification with traditional biological processes allows electrochemical techniques to rapidly remove nitrogen sources like ammonia and nitrate, while adjusting electrode potentials can enhance microbial denitrification efficiency. Electrochemical systems provide ideal conditions for microorganisms, enabling simultaneous nitrification–denitrification to improve nitrogen removal rates. Another effective integration involves combining AOPs with adsorption techniques. AOPs generate strong oxidants (e.g., ·OH radicals) to degrade organic nitrogen pollutants, while adsorbents (such as activated carbon or nanomaterials) can further capture nitrogen compounds or intermediate products, reducing secondary pollution. This combination enables both rapid removal and long-term adsorption, improving nitrogen removal efficiency. Additionally, incorporating nanomaterials can enhance the catalytic activity and reaction rate of the denitrification process. By combining multiple advanced technologies, a complementary effect is achieved, significantly improving nitrogen removal while optimizing costs and treatment efficiency, thereby advancing the development of water treatment technologies.
4.4. Application in Treatment of Typical Wastewater
In recent years, black and odorous water bodies have emerged as a significant environmental pollution issue. These water bodies typically exhibit low transparency, often appearing black, and emit a strong, unpleasant odor. Additionally, they suffer from poor circulation, resulting in low DO levels and elevated NH3-N concentrations. According to the 2015 guidelines issued by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, the “Classification Standard for the Pollution Degree of Urban Black and Odorous Water Bodies” categorizes these water bodies into mild and severe pollution levels based on parameters such as transparency, DO levels, redox potential, and NH3-N concentration (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Degree of Urban Black and Odorous Water Bodies [106].
The formation of black and odorous water bodies is influenced by a variety of environmental factors. According to the existing literature, these factors can be summarized into the following key aspects: One significant factor is the early construction of urban infrastructure, which lacked comprehensive coverage or maintenance. As a result, untreated exogenous pollutants enter water bodies, leading to excessive oxygen consumption and creating an imbalance between reoxygenation and oxygen depletion [107]. Muezzinoglu’s research [108] demonstrates that the decomposition of large amounts of organic matter in water results in an oxygen consumption rate that exceeds the reoxygenation rate. Additionally, the decomposition by anaerobic microorganisms produces foul-smelling compounds such as hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and NH3, contributing to the unpleasant odor of the water [109]. Hishida et al. [110] identified insufficient hydrodynamics as a key factor contributing to the blackening and odor of rivers. Low flow velocity promotes excessive algal reproduction, leading to algal blooms. Temperature plays a significant role in the severity of water blackening and odor, with the effects being most pronounced during hot weather and less noticeable in colder conditions. Ambient temperature influences the growth and activity of microorganisms in aquatic environments. Under optimal temperature conditions, the rate of microbial decomposition accelerates, leading to increased DO consumption and a greater release of toxins into the water [111]. Conversely, temperature also influences the saturation of DO in water bodies. As temperature increases, the DO content in the water decreases, leading to a reduction in the reoxygenation rate of the water body [112]. The bottom sludge is an integral component of the aquatic ecosystem, and the pollutants it contains create favorable conditions for microorganisms. Wu [113] investigated the release patterns of pollutants in riverbed sediment, concluding that high concentrations of organic matter facilitate the release of TP from the sediment. Liu [114] observed that humic acid absorbs significant amounts of pollutants upon entering water bodies; however, once decomposed, it leads to the accumulation of NH3, TN, and total TP in the sediment, thereby increasing the organic matter content of the riverbed [115]. The formation of black and odorous water bodies results from the combined effects of physical, chemical [116], and biological processes, with current research identifying Fe, Mn, and S as the primary contributing elements [117]. The degradation of organic matter creates an oxygen-deprived environment in the water, where anaerobic microorganisms decompose organic material, producing pungent gases such as hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and thiols [118].
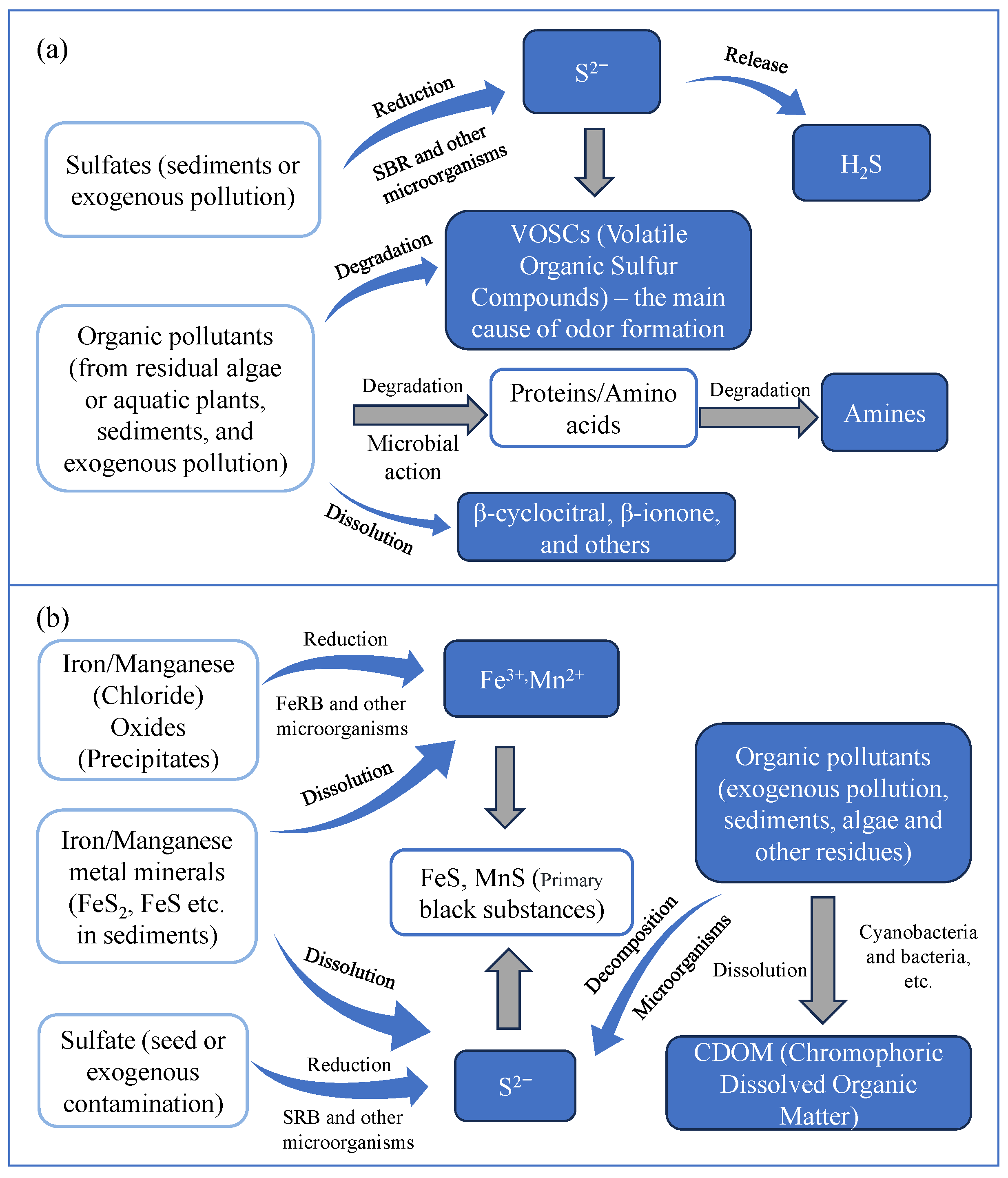
Nitrogen compounds, particularly ammonium and nitrate, play a pivotal role in the formation of black and odorous water bodies, as they facilitate the development of anaerobic conditions and stimulate the generation of malodorous compounds, including ammonia and amines. Additionally, black compounds like FeS and MnS contribute to the water’s discoloration [119]. The primary chemical reactions responsible for the blackening are outlined below [120]. The primary process is illustrated in Figure 4a.
sour protein → cysteine + H2 → H2S + NH3 + CH3CH2COOH
SO42 + organic substances → H2S + H2O + CO2
Fe(OH)3 → Fe2+, Fe2+ + H2S → FeS
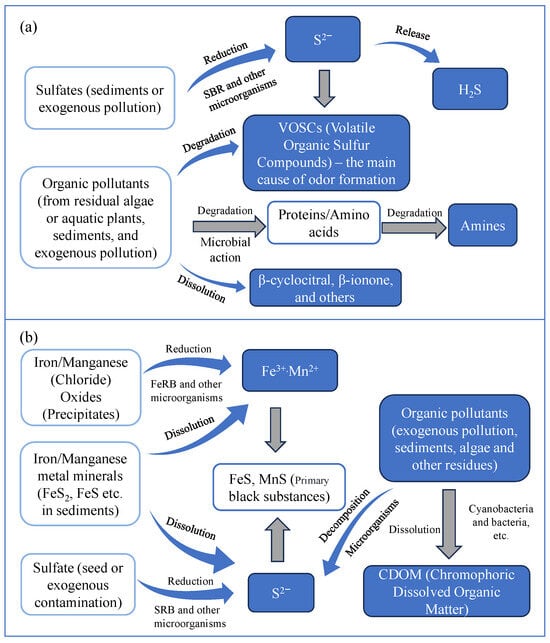
Figure 4.
A schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism behind the formation of water blackening and odor [116]. (a) The process of water darkening; (b) The process of odor formation in water bodies.
The main chemical reactions responsible for the odor are outlined below [121]. The primary process is illustrated in Figure 4b.
SO42− + 2(CH2O) + 2H+ → H2S + 2CO2 + 2H2O
HO2C-CH(NH2)-SH + H2O → 3CH3-CO-CO2H + H2S + NH3
The detrimental effects of black and odorous water bodies manifest in multiple ways: the offensive odor they emit disrupts the lives of nearby residents, potentially causing symptoms such as dizziness and chest tightness in extreme cases and impairing concentration; notably, hydrogen sulfide gas, which is present in these waters, emits a distinct rotten-egg smell at low concentrations but becomes odorless at higher levels [122]; these water bodies also degrade the water quality of rivers in the affected area, exacerbating the existing water resource crisis; moreover, they serve as breeding grounds for harmful microorganisms, bacteria, and mosquitoes, thereby posing a significant threat to public health by potentially leading to large-scale epidemics [123].
Black and odorous water emits a strong, unpleasant odor and deposits black sediments along the channel’s banks, significantly affecting a city’s ecological landscape and detracting from its visual appeal. In service-oriented cities, the degradation of the ecological landscape negatively impacts local tourism, consumption, and overall urban economic development. According to data from China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment, during the 13th Five-Year Plan period, direct investment in black and odorous water treatment exceeded 1.5 trillion RMB over three years [124]. However, some regions only addressed the symptoms rather than the underlying causes. After treatment, the water bodies became less prone to blackening and odor formation, but the issue was not fully resolved. Treating black and odorous water is a long-term and challenging process, and the associated costs are substantial. Managing black and odorous water bodies involves controlling both water sources and sediment. The treatment of black and odorous water should adhere to the technical approach of “external emission reduction, endogenous control, water quality purification, clean water supply, and ecological restoration” [125]. Once exogenous pollutants are eliminated, the release of organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus nutrients from endogenous sediments poses a significant obstacle to the treatment of black and odorous water. Effective control of black and odorous water bodies also requires the restoration of sediments [126].
Physical methods for treating black and odorous water bodies include aeration, hydraulic circulation, and covering/isolation. Aeration, which involves adding oxygen to the water [127,128], enhances the DO content, improves the water body’s self-purification capacity, and promotes ecosystem recovery. Common aeration methods include blower aeration, brush aeration, and jet aeration. Wang [129] conducted experimental studies on river wastewater using laboratory simulations of artificial aeration. The study indicated that intermittent aeration promotes nitrogen removal and inhibits the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from the bottom sludge. Aeration and oxygenation can alter the properties of bottom sludge and affect the nitrogen content in various forms. However, aeration is energy-intensive and may lead to the re-diffusion of pollutants from the bottom sludge. Hydraulic circulation involves using water conservancy infrastructure to direct clean water into the system or recycle water within it to supplement the water body. This method promotes the migration and diffusion of pollutants by increasing the water volume in contaminated areas, thereby diluting pollutant concentrations [130,131]. However, this approach does not address the root cause of the problem; it only mitigates blackening and odor to a certain extent and does not provide long-term sustainability for the water body. Covering and isolation involve using materials to cover the bottom sludge, separating the sediment from the water, and preventing pollutants from spreading into the water body. Zhou et al. [132] used natural materials, such as soil and diatomaceous earth, to cover anaerobic sludge and conducted ecological restoration of dead grass. The results indicated that covering the material slowed the release of TN and TP in the water and increased DO levels.
Chemical methods for water treatment are categorized into oxidation, flocculation, and precipitation based on their reaction principles. These methods effectively reduce the pollution load and enhance water transparency. Commonly used chemical agents include inorganic and organic polymer flocculants [133] (such as polymeric aluminum chloride and polyacrylamide), oxidants [134,135] (such as calcium peroxide and hydrogen peroxide), precipitants [136] (such as iron hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide), and algae removal agents [137] (such as copper sulfate and ozone). Chemical methods offer advantages such as lower costs and shorter treatment times. However, the addition of chemical agents can lead to secondary pollution of water bodies [138] and negatively affect biological growth, thereby limiting their long-term applicability.
Biological–ecological technology harnesses the purification capabilities of animals, plants, and microorganisms, along with the food chain output and transfer functions of various organisms, to purify and restore contaminated water bodies [139]. This technology offers advantages such as stability, effectiveness, low energy consumption, and ease of management. Common ecological technologies include artificial wetlands, bioreactors, and artificial floating islands [140]. Artificial wetlands consist of complexes made up of artificial media, plants, and microorganisms. These components collectively utilize adsorption, fixation, filtration, interception, redox reactions, microbial degradation, transformation, and metabolism to purify water [141,142]. Based on the water distribution method, artificial wetlands can be classified into surface flow and submerged types. Submerged wetlands are further divided into vertical flow, horizontal flow, and tidal flow systems [143]. Research on artificial wetlands in China began relatively late, with the first artificial wetland sewage treatment project established in Shenzhen from China in 1990. Since 2000, the number of artificial wetland systems in operation has increased, accompanied by a rise in research on these systems. Biogrid is a novel pollution purification technology that integrates biofilm technology with aquatic plants. It offers advantages such as cost-effectiveness, practicality, esthetic appeal, and ecological sustainability [144]. Yu et al. [145] employed biogrid technology to manage the tributaries of the Zhongtang River in Ningbo. After more than six months of operation, the water’s color returned to normal, the blackness and odor were eliminated, and the water quality indicators met the required standards. However, biogrid technology is still under development and has not yet been widely applied; further research is needed. An artificial floating island also referred to as an ecological floating island or artificial floating bed, is primarily composed of three components: filler, plants, and carriers. This is an ecological technology that integrates agronomic and ecological engineering measures to restore and rehabilitate damaged aquatic ecosystems [146]. The mechanisms by which artificial floating islands purify water bodies include absorbing and utilizing organic matter from polluted water to synthesize their own tissues, adsorbing and enriching suspended matter in the water to thereby enhance treatment efficiency, releasing oxygen from plant roots to accelerate the decomposition of organic pollutants, and using floating island carriers to block light, thereby inhibiting the large-scale reproduction of algae and preventing “water blooms.”.
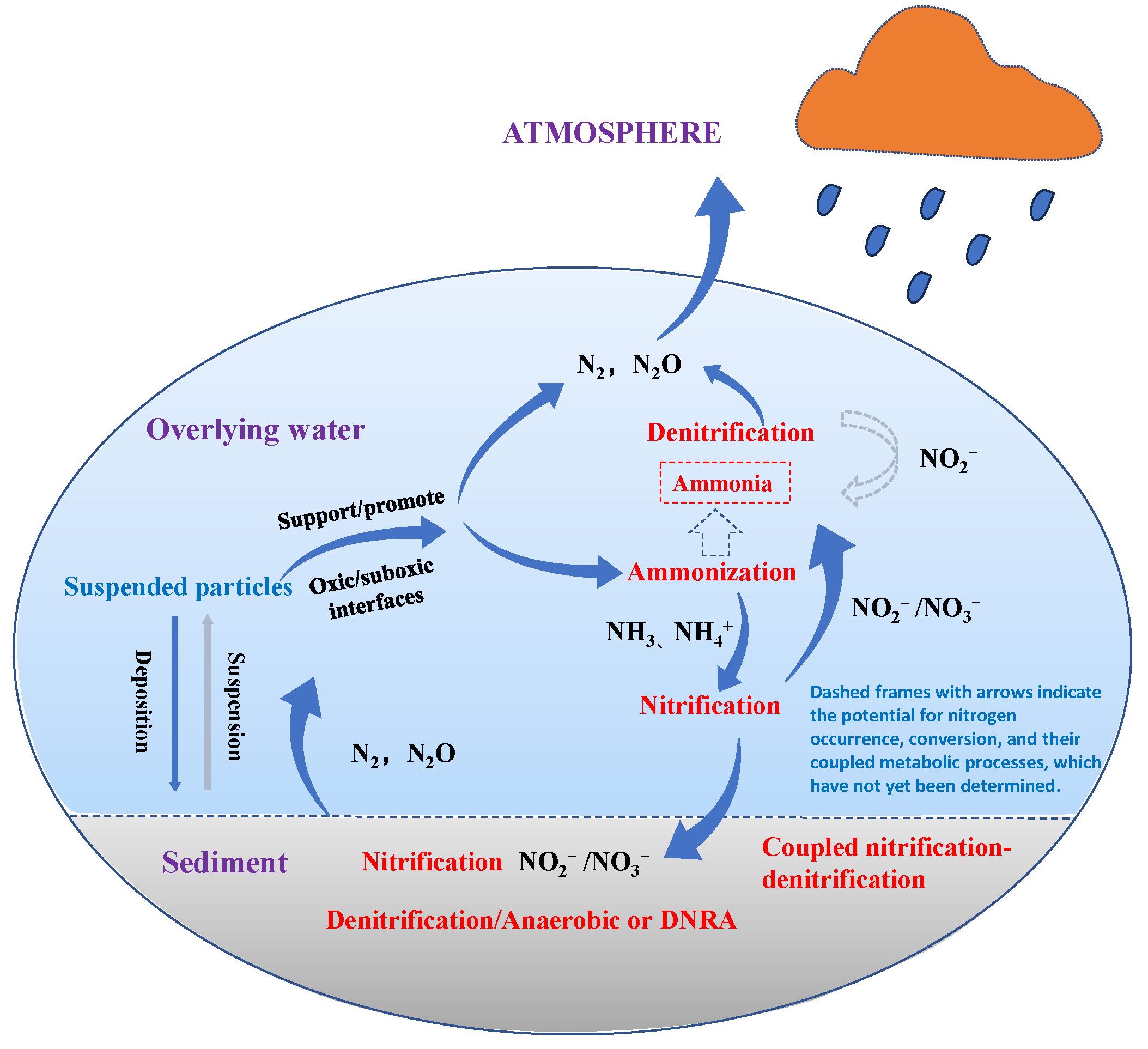
According to the classification in the “Grading Standards for Pollution Levels of Urban Black and Odorous Water Bodies” [106], NH3-N concentration is a critical indicator of black and odorous water bodies. NH3-N in black and odorous water arises from various sources, including domestic sewage, industrial wastewater, and residual fertilizers from agricultural activities. NH3-N primarily exists in two forms in water: NH4+ and NH3. Under acidic conditions, NH3-N predominantly exists as NH4+, whereas under neutral or alkaline conditions, it primarily exists as NH3. At high water temperatures, NH3-N is more likely to be present as ammonium salts, whereas at lower temperatures, free NH3 is the dominant form [147]. NH3-N is a primary contributor to the eutrophication of water bodies and the formation of harmful algal blooms, such as red tides. Elevated concentrations of NH3-N significantly impact the survival of aquatic organisms. The microbial activity associated with NH3-N consumption depletes DO, further reducing oxygen levels in black and odorous water and thereby severely disrupting the ecological environment. Additionally, NH3-N is a major precursor of disinfection by-products. It forms chloramine during the chlorination and disinfection processes, thereby reducing disinfection efficiency [148]. NH3-N in black and odorous water reacts under microbial influence, and a schematic diagram illustrating the conversion of NH3-N, NO3−-N, and NO2−-N is shown in Figure 5.
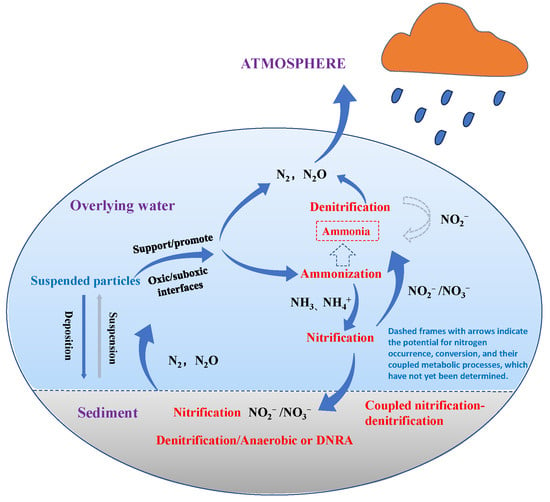
Figure 5.
A schematic diagram showing nitrogen conversion processes within an aquatic system [149].
The primary methods for removing NH3-N from water include chemical methods (such as breakpoint chlorination and chemical precipitation), biological methods (such as nitrification-denitrification and ANAMMOX) [150], and physical methods (such as adsorption, membrane separation, aeration, and stripping). These methods facilitate the effective elimination of NH4+ from black and odorous water bodies through its conversion into N2 or insoluble precipitates, thus contributing to the effective alleviation of black and odorous water problems. The core principle of the breakpoint chlorination method in chemical treatments is an oxidation reaction. In this process, chlorine or sodium hypochlorite is introduced into the water, oxidizing NH3-N to nitrogen gas [73]. The chemical precipitation method involves adding a precipitant to wastewater, where NH3-N reacts with anions in the precipitant to form solid particles. However, this method faces challenges such as high costs for the precipitant and difficulties in handling the large volumes of generated precipitates.
The biological removal of NH3-N [151] occurs through the activity of both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. NH4+ is first oxidized to NO2− by NOB. The nitrite is then converted to NO3− under the influence of NOB and is ultimately reduced to N2 through denitrification, thus removing NH3-N. The overall reaction equations for these processes are as follows [152]:
2NH4+ + 3O2 → 2NO2− + 2H2O + H+ + ∆E
2NO2− + O2 → 2NO3− + ∆E
5C(Organic Carbon) + 2H2O + 4NO3− → 2N2↑ + 4OH− + 5CO2
This method is commonly employed in large- and medium-sized sewage treatment plants. It is effective in nitrogen removal; however, the biological method requires a significant amount of time due to the sequential nature of the microbial processes involved.
The stripping method in physical treatments involves expelling NH3 gas molecules under alkaline conditions [153]. This method offers advantages such as simple equipment operation and stable efficiency. However, it necessitates continuous aeration, leading to high energy consumption. Additionally, the ammonia released can contribute to atmospheric pollution [71]. The adsorption method relies on using an adsorbent with selective adsorption capabilities for NH4+, removing them through ion exchange or the combination of anions and cations [154]. This method is easy to operate; however, the treatment of saturated adsorbents presents a significant challenge. Each method has its unique characteristics and limitations, with adsorption being one of the key technologies for NH3-N removal. It has been extensively studied and applied. Identifying an adsorbent material with broad availability, low cost, high efficiency, and non-toxicity holds significant practical value. Water resources are among the most valuable natural assets essential to human survival. Human survival and development are intrinsically linked to water availability. Moreover, water constitutes a vital component of the ecological environment system. With the rapid growth of China’s economy, water consumption for industrial, agricultural, and domestic purposes has continued to rise, resulting in the discharge of large volumes of industrial wastewater and domestic sewage into surrounding water bodies. This has overwhelmed their self-purification capacity, leading to increasingly severe water pollution [155]. Furthermore, due to damaged urban infrastructure and the challenges of renovation, a significant amount of pollutants is discharged directly into rivers without treatment. Additionally, the entry of garbage into rivers and the accumulation of bottom sediment contribute to some surface waters becoming seasonally or persistently black and odorous throughout the year [156]. According to the 2021 “China Environmental Status Bulletin” [157], among the 3632 national surface water monitoring sections, 3.4% are classified as Class V (indicating severely polluted water). As of 2022, according to the “National Notice on the Inspection of Black and Odorous Water Bodies in County-level Cities” issued by the Ministry of Ecology and Environment [158], 220 black and odorous water bodies were identified in 91 county-level cities across the country. According to relevant guidelines, by 2025, 90% of black and odorous water bodies in the built-up areas of county-level cities are expected to be eliminated. Therefore, significant efforts remain to be made in managing black and odorous water bodies in urban areas.
5. Principles of MPNs and Adsorption of Nitrogen
5.1. Principle of Metal–Phenolics Network
MPNs are primarily a series of supramolecular materials formed through diverse metal–organic interactions [159]. They possess versatile bonding properties and are characterized by simple operational methods. Research on the metal ions associated with MPNs mainly focuses on silver, iron, copper, zinc, calcium, titanium, cobalt, manganese, and zirconium [160,161]. Polyphenols are secondary metabolites predominantly found in plants, with phenol groups as their core structure. They are characterized by the presence of at least one phenol ring and the absence of nitrogen-containing functional groups. Common polyphenols studied include tannin, epicatechin, gallic acid, anthocyanins, and polydopamine [162]. In MPN applications, inorganic components serve various functions, such as promoting tissue regeneration, enhancing photothermal effects, exhibiting antibacterial properties, contributing to sensor functionality, and providing specific magnetic or electrochemical properties [163,164]. Organic components play crucial roles by altering the shape or properties of the material’s substrate, modifying hydrophobicity, providing an active reaction interface, and contributing to specific physicochemical properties (e.g., electrical or optical properties) [160,165,166].
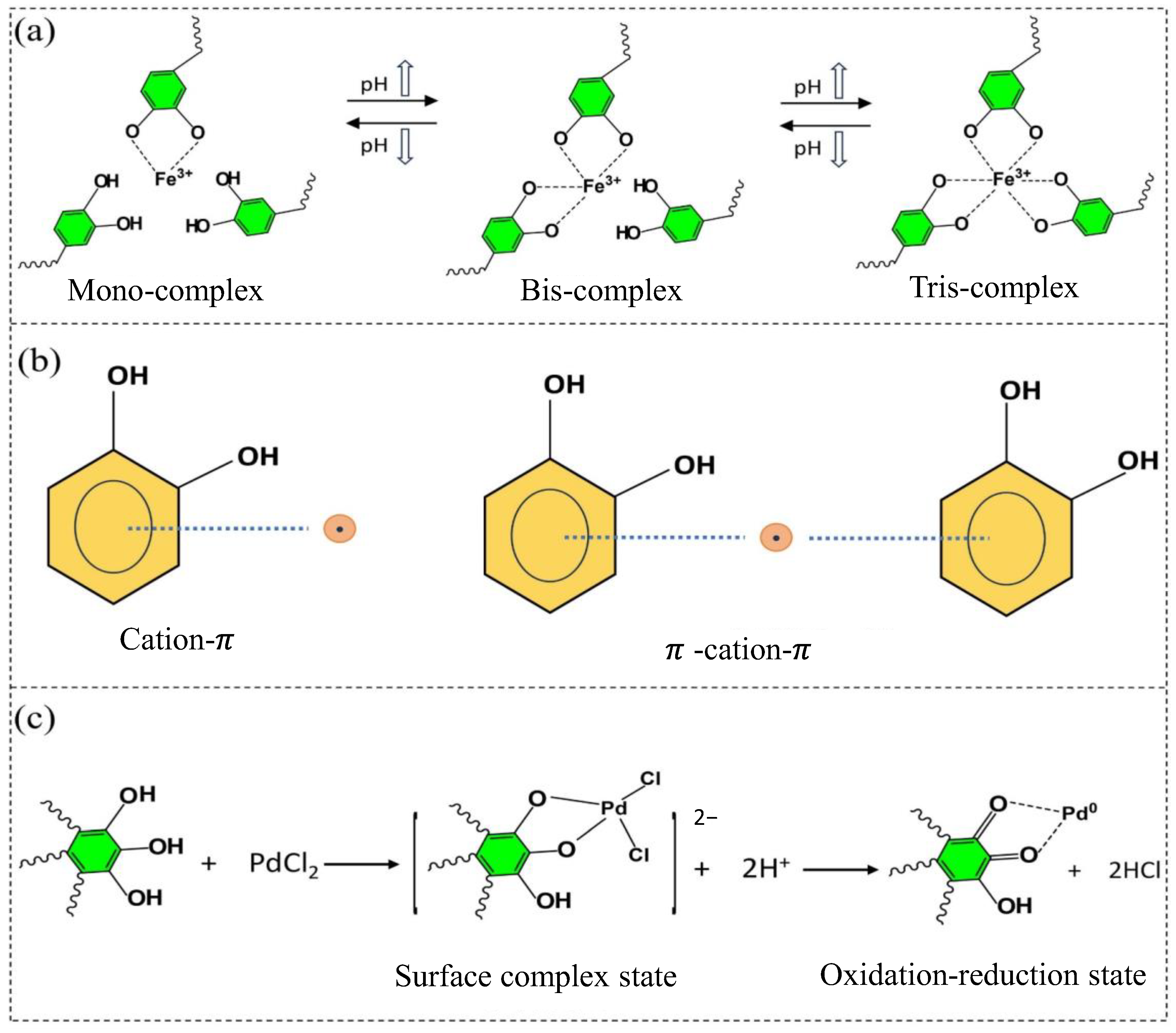
The formation mechanism between precursor metal ions and phenolic substances in MPNs involves the primary metal ions, which possess empty orbitals in their electronic configurations, allowing them to act as electron acceptors. Phenolic compounds, containing high π electron density and aromatic properties, function as electron donors [160]. MPNs primarily achieve stability through cation–π bonding, coordination, and redox reactions, as shown in Figure 6. Specifically, as illustrated in Figure 6a, metal–phenolic coordination occurs when two or more phenolic ligands donate non-bonding electron pairs to the empty orbitals of metal ions. However, this coordination in MPNs is highly pH-dependent: at low pH, monocomplexes form as most catechol groups are protonated, while at higher pH, bis- and tris-complexes are generated [167]. As illustrated in Figure 6b, cation–π interactions, which include binary cation–π units and ternary π–cation–π units. Cation–π interactions are essentially electrostatic forces, where aromatic side groups with varying electron densities in polyphenolic substances, such as hydroxyl and catechol groups, affect the strength of these interactions. Additionally, cation–π bonds are influenced by the type of metal ions, with alkaline earth metal ions (e.g., Mg2+ and Ca2+) typically exhibiting stronger interactions with phenols than transition metal ions (e.g., Ag+ and Cu2+). As illustrated in Figure 6c, the redox principle is evident as noble metal ions, with higher redox potentials, easily oxidize polyphenolic substances with lower redox potentials. When noble metal ions are reduced to their elemental form, the oxidized polyphenols help protect and stabilize the noble metals.
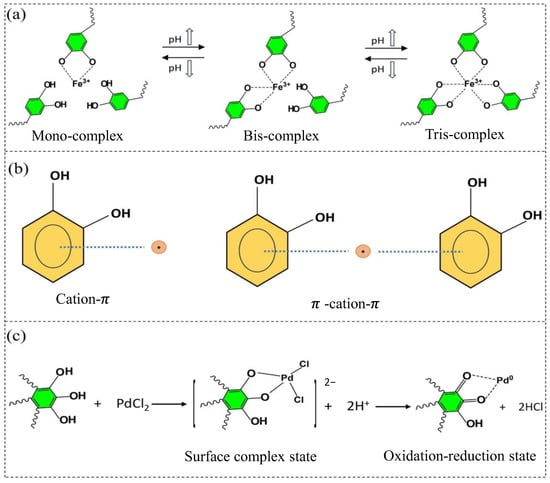
Figure 6.
Metal–polyphenol interaction mechanisms as illustrated in [160]: (a) coordination, (b) cation–π Bond, (c) redox reactions.
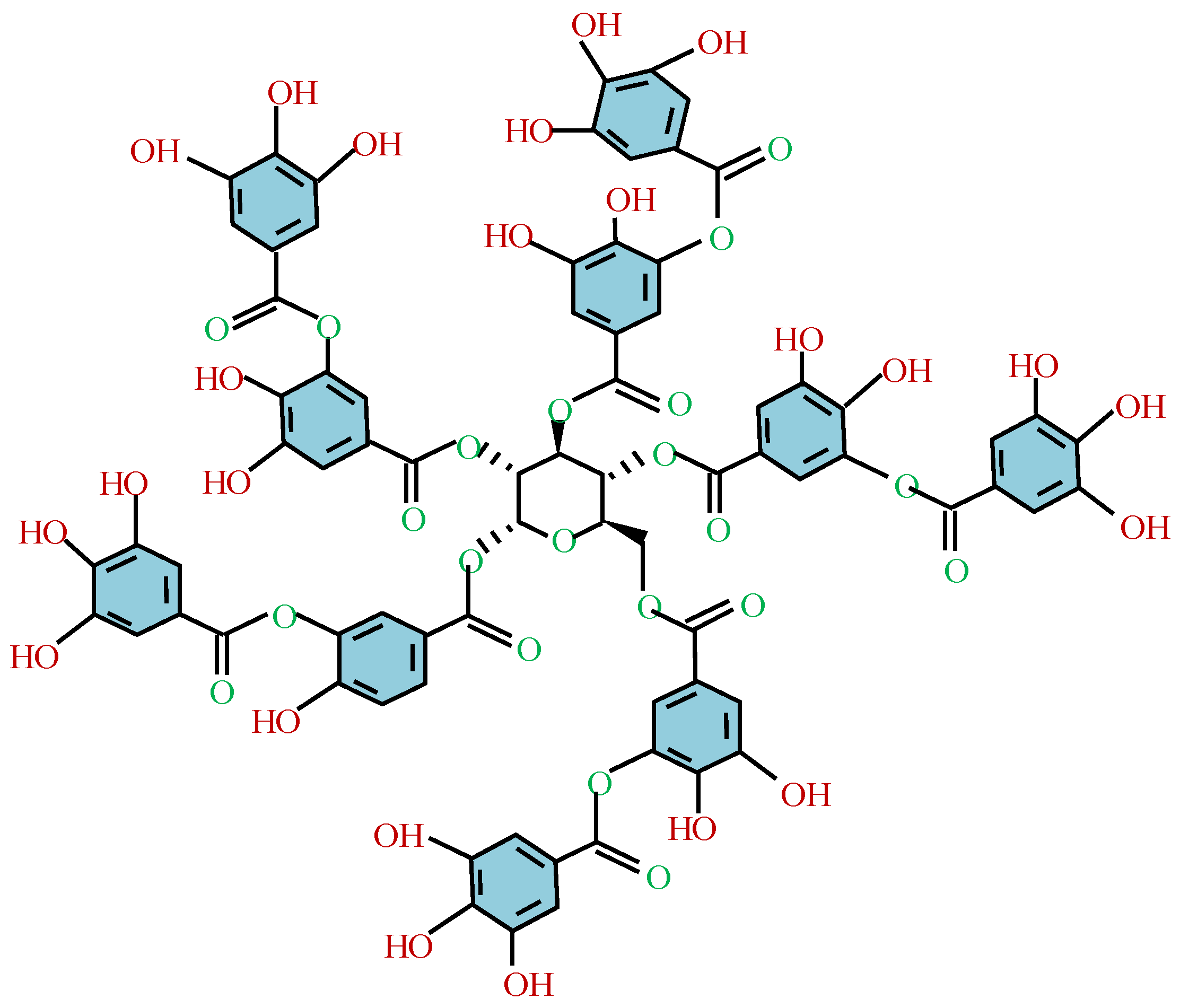
Among the fundamental polyphenols in MPNs, tannic acid (TA) is the most extensively studied and widely utilized (see Figure 7). Due to its unique properties, tannic acid has long been employed in various applications, including as food additives [168], antioxidants [169], biosorbents [170,171], and binders [172]. So far, three primary types of metal ions have been found to coordinate with TA to form functional MPNs: main-group elements (e.g., Al, Ga, In, and Bi), transition metals (e.g., Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Zr, Ru, and Mo), and rare earth elements (e.g., La, Ce, Eu, Sm, and Gd) [173,174]. The conditions for this complexation reaction are mild, efficient, and straightforward to implement. The formation of MPNs is significantly affected by pH. For example, Caruso et al. [167,175] investigated the MPN formed by TA and Fe3+. At pH 2 to 3, most of the phenolic groups are protonated, resulting in unstable coordination bonds and network decomposition. However, at pH > 7, stable octahedral TA-Fe complexes can be formed.
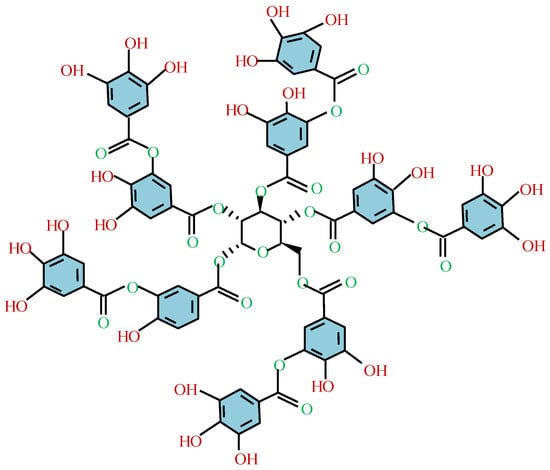
Figure 7.
A molecular structure of tannic acid.
The MPNs have broad applications in environmental protection, energy materials, biomedicine, and various other fields. In environmental protection, TA can effectively remove various heavy metals and organic pollutants [176,177], making it widely used in water treatment projects. Zhang et al. [178] employed the tannic acid precipitation–separation cerium sulfate titration method to determine niobium content in titanium–aluminum–niobium alloys. They found that this method reduces the complex steps and potential errors in removing the impurity element titanium, achieving high measurement accuracy. Lu et al. [179] utilized a tannic acid–sulfuric acid system to leach manganese from manganese oxide ore. They discovered that tannic acid can effectively leach manganese from manganese oxide ore in a sulfuric acid medium with a low initial concentration, achieving a manganese leaching rate of 90.86%. Wang et al. [180] used tannic acid as a flocculant to enhance solid–liquid separation, significantly reducing NH3, N2O, CO2, and CH4 levels in the soil and mitigating the impact of liquid manure on soil greenhouse gas emissions. Chang et al. [181] employed Ti4+ and TA to chelate a titanium–tanninate (Ti-TA) composite adsorbent and systematically studied its adsorption properties and mechanisms for fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Qiu et al. [182] prepared a novel TA-Fe adsorbent through simple self-assembly. Fixed-bed experiments demonstrated excellent Pb(II) adsorption capacity and recycling performance, with an adsorption capacity for Pb(II) ions exceeding 350 mg/g. After 10 adsorption–regeneration cycles, the adsorption performance remained stable. Feng et al. [183] prepared a highly effective phosphorus-removing iron–tanninate (Fe-TA) adsorbent, capable of removing excess phosphorus from wastewater. Furthermore, the phosphorus-saturated Fe-TA adsorbent can be utilized as a sustained-release fertilizer, enabling the recycling of phosphorus resources. Sun et al. [184] used Fe-TA and ferrous tanninate to remove phosphorus. Their research demonstrates that Fe-TA and ferrous tanninate exhibit good adsorption properties for phosphorus, with the primary adsorption mechanisms being ligand exchange and electrostatic interactions. Zhi et al. [185] revealed that a novel composite flocculant, prepared by tannic acid and zinc chloride, can adsorb methylene blue from wastewater and reduce COD concentration in water. Wu et al. [186] prepared a Ti-TA dual-network membrane on the surface of polysulfone using a biomimetic one-pot assembly method. The dye retention rates of this membrane for methyl blue and Congo red were as high as 96.8% and 97.2%, respectively. These research findings offer valuable insights for the practical application of metal–polyphenols in the treatment of contaminated water.
In the field of materials science, Hu et al. [187] immersed a metal electrode (Zn) in a TA solution, forming a stable metal–chelate interface on the surface. Liu et al. [188] utilized tannic acid and copper sulfate as raw materials and synthesized the product via the hydrothermal method. This material exhibits excellent antibacterial properties, minimal color change, and high visible-light transmittance, making it suitable for cultural relic preservation. Zmozinski et al. [189] employed tannin–zinc and tannin–magnesium as anticorrosion pigments in epoxy coating formulations. Zhong et al. [190] studied the spray assembly of MPNs, sequentially depositing tannic acid and ferric chloride solutions onto a substrate to form a coating. By spraying and assembling the MPN layer, effective oil–water separation and ultraviolet shielding can be achieved. Zhao et al. [191] employed coordination-driven crosslinking and assembly within the polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane matrix to successfully incorporate and evenly distribute Ti-TA in the prepared PVDF/TA-Ti membrane. The membrane exhibits excellent hydrophobicity and antifouling properties, with a flux recovery rate of up to 100%.
In the field of biomedicine, Xu et al. [192] utilized TA and Ag+ to form a TA-Ag nanoenzyme. The uniform distribution of TA-Ag nanoenzymes in the interpenetrating network of sodium alginate (SA) and polyacrylamide (PAAm) simulated the dermal structure in a flexible conductor, resulting in the preparation of a TA-Ag-SA/PAAm hydrogel with excellent mechanical properties, conductivity, and adhesion. In terms of food preservation, Zhang et al. [193] utilized chitosan–tannic acid coatings to investigate their effects on beggar chickens. The study found that chitosan–tannic acid coatings exhibit anti-corrosion and preservation properties, effectively delaying lipid and protein oxidation.
5.2. MPNs Effects on Adsorption of NH3-N
MPNs are rich in organic ligands and metal ions. Among these, the organic ligands can include TA, dopamine (DA), polydopamine, and ferulic acid. Metal ions such as Fe3+, Al3+, Cu2+, Ti4+, etc., can also be incorporated into these networks. Given that TA and DA possess polyhydroxy interface modification capabilities and superior adhesion properties, respectively [194], tannin-based metal phenolic networks (TA-MPNs) and dopamine-based metal phenolic networks (DA-MPNs) have emerged as key topics in current research. NH4+-N in water predominantly exists as polar molecules. Based on the principle of attracting like charges and repelling opposite charges, adsorbents often require surface modification. Polar oxygen-containing functional groups such as -OH, -C=O, and -C-O are the primary modification groups used for this purpose [195,196]. Tannic acid molecules possess a unique molecular structure and high chemical reactivity. The phenolic functional groups within the molecule can act as hydrogen donors and acceptors in various chemical reactions. The polar phenolic hydroxyl groups on the phenol ring are easily deprotonated to form phenolate anions (PhO−), which exhibit strong nucleophilicity. Consequently, tannin can participate in various ionic reactions as oxygen- or carbon-based nucleophiles, significantly enhancing its ability to adsorb NH4+-N in water. Tannin-based metal phenolic networks possess unique properties imparted by the metal ions they incorporate and feature polyphenol structures with a high affinity for various surfaces. Through interactions such as hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interactions, and π-π stacking, these networks exhibit strong adhesion and can be easily coated onto various matrix/carrier surfaces [197,198,199], facilitating their engineering applications. Currently, there is relatively limited research on the nitrogen removal performance of tannin-based MPNs, both domestically and internationally. Nevertheless, some studies on nitrogen removal mechanisms have been conducted, primarily focusing on Fe-TA, Ti-TA, and zirconium–tanninate.
Fe-TA is synthesized by reacting tannic acid with a salt solution containing iron ions, resulting in a type of tannic acid–metal chelate. Studies have indicated [167,200,201] that Fe3+ and tannic acid form a complex and undergo a redox reaction. Under neutral pH conditions, one Fe3+ ion can form a stable complex with three tannic acid molecules. Tannic acid complexes with one oxygen anion and one phenolic hydroxyl group, or with two oxygen anions and an iron ion, form a positively charged divalent or monovalent complex. During the reaction between tannic acid and Fe3+, the phenolic hydroxyl groups engage in a complex reaction with Fe3+. Additionally, the phenolic hydroxyl groups reduce part of the Fe3+ to Fe2+, resulting in the formation of ferrous tannic acid. However, due to the instability of ferrous tannic acid, it is easily oxidized back to iron tannic acid upon exposure to air. Research has demonstrated that Fe-TA can adsorb NH4+-N in water [202], making it a promising adsorbent material for practical applications. In studies examining the properties and mechanisms of Fe-TA adsorption and the removal of inorganic nitrogen from water, Zhang [202] et al. found that Fe-TA can achieve an NH4+-N removal rate exceeding 95%. Liu [203] combined Fe-TA with sodium alginate to develop a nitrogen deoxygenation material for catalytic ammonia oxidation. Lin et al. [204] employed bentonite to prepare microspheres for NH4+-N removal from black and odorous water, thereby reducing the cost of the adsorbent while enhancing removal efficiency. However, although Fe-TA can be separated using magnetic separation technology during application, Fe-TA collected by magnetic media is difficult to thoroughly rinse and partially dissolves after prolonged immersion in water. This leads to material loss and reduced reuse efficiency. Therefore, it is highly valuable to explore new metals to enhance the adsorption capacity and rate of such materials, as well as to improve the separation performance of tannic acid-metal chelates. Moreover, increasing the frequency of material recycling will significantly reduce the cost of nitrogen removal. Nevertheless, current research on NH3-N removal using Fe-TA in actual black and odorous water is insufficient, and the development of related products remains limited. Furthermore, after drying, Fe-TA becomes powdery, presenting challenges in solid–liquid separation and a tendency to be easily lost during practical application. It is essential to identify a suitable carrier to recombine with Fe-TA, enhancing its separation performance and facilitating subsequent use and recycling.
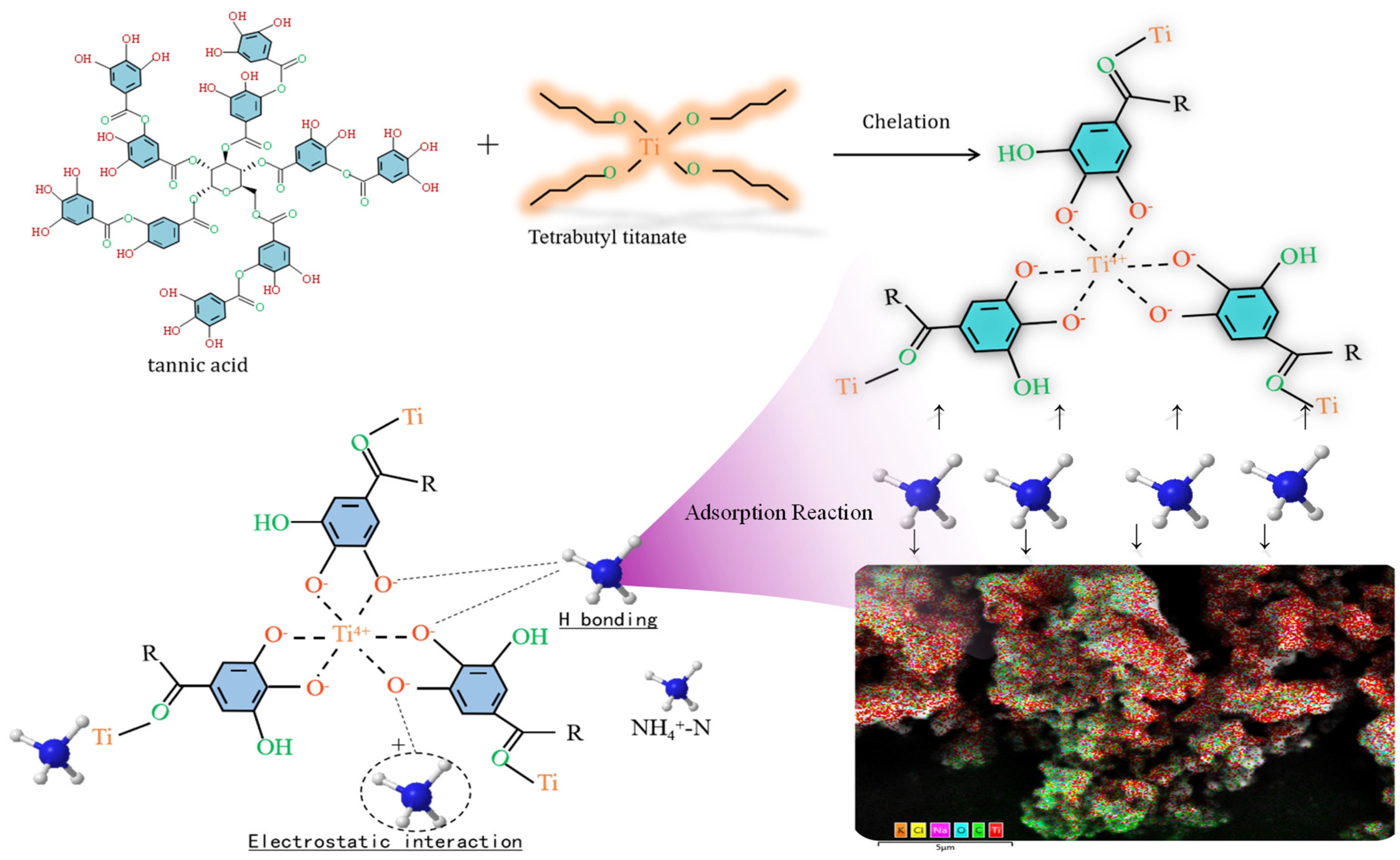
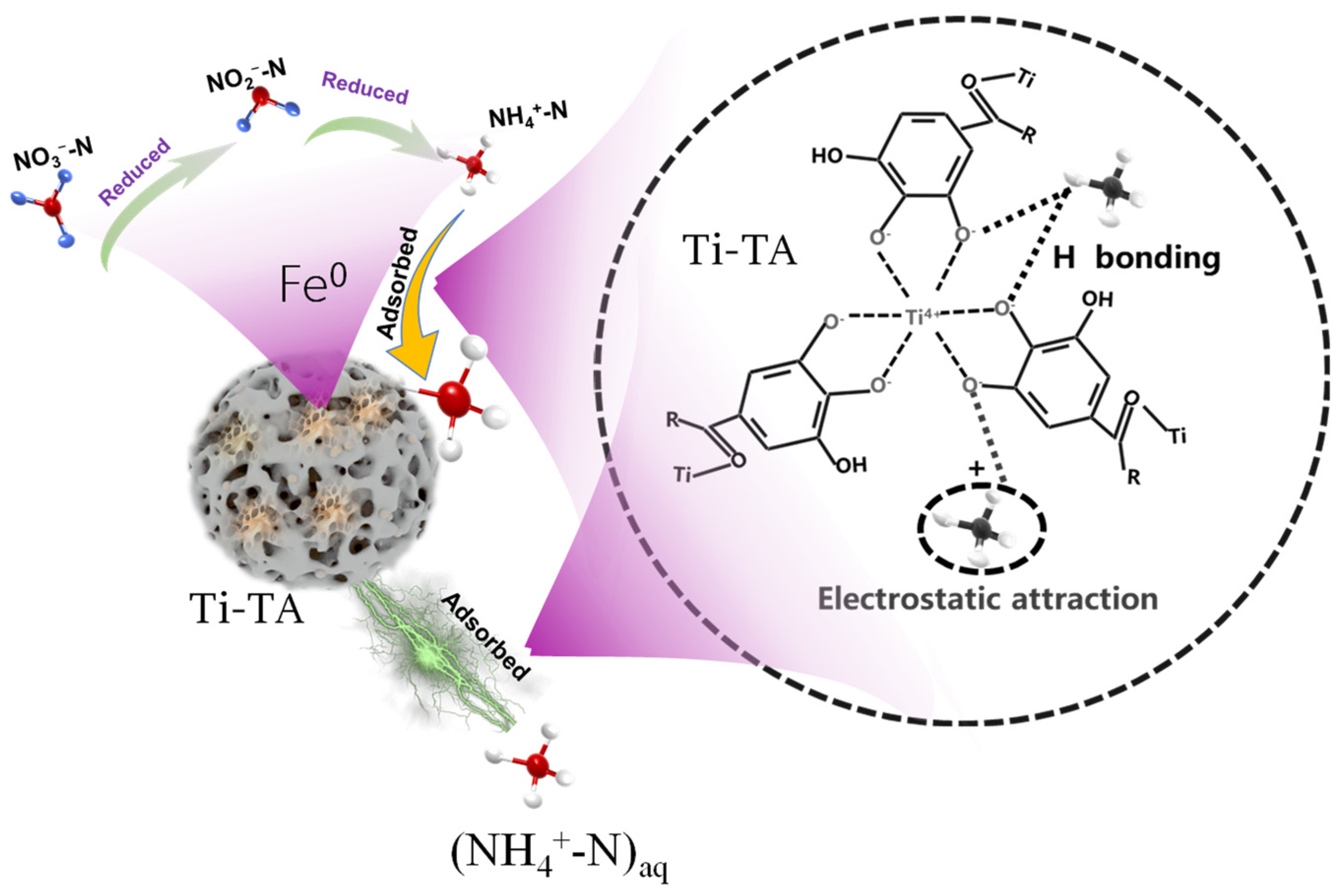
Research on MPNs has revealed several shortcomings, including a limited variety of available networks, pH dependence (with better adsorption rates observed in neutral environments), poor or ineffective adsorption of NO3−-N, and an increase in undesirable effects. This is attributed to the redox electrode potential of NO3−/NH4+, which is E°(A) = 0.881 V. Under acidic conditions, NO3− exhibits strong oxidative properties, while NH4+ displays weak reduction properties. Strongly oxidative Fe3+ can react with NH4+ as follows: Fe3+ + NH4+ + H2O → Fe2+ + NO2− + 2H+. The oxidation of NH4+-N by Fe3+ is a key factor contributing to the indirect increase in NO3−-N, which is highly detrimental to environmental protection. According to redox principles, utilizing metals with a negative redox electrode potential may prevent the oxidation of NH3-N. For instance, some metals have redox electrode potentials (E°) below zero, such as titanium (Ti4+/Ti3+, E° = −0.04 V), magnesium (Mg2+/Mg, E° = −2.364 V), and aluminum (Al3+/Al, E° = −1.662 V). Research by Lv and Qian et al. [205,206] indicates that titanium–tannin, formed by Ti4+, does not significantly increase NO3−-N, demonstrating the effectiveness of metals with a negative redox electrode potential (E° < 0) in inhibiting such an increase. A simple scheme showing the process of treating nitrogen as well as key data is shown in Figure 8.
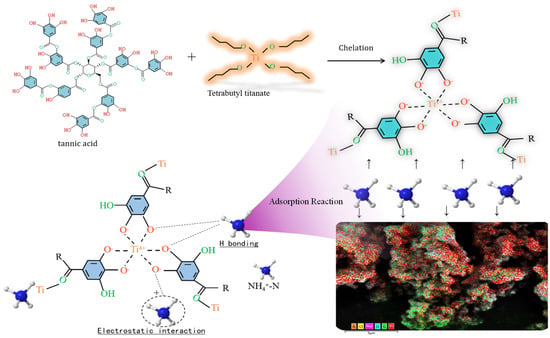
Figure 8.
A schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism of NH4+-N adsorption onto Ti-TA, along with key data points [205,206].
However, the redox electrode potential is influenced by various environmental conditions, and the extent of their impact on this inhibitory characteristic remains unclear. Additionally, the role of metals with varying potential magnitudes requires further investigation. The pH responsiveness of metal–phenolics significantly affects the denitrification ability of these functional materials [207,208]. For example, under neutral conditions, triligand Fe-TA exhibits effective adsorption. In contrast, under acidic conditions, it exists as a soluble diligand and monoligand, resulting in poor adsorption of NH4+-N. Some MPNs, such as iron–tannin, lack solid stability. However, others, like Ti-TA, exhibit relatively stronger acid resistance than Fe-TA and demonstrate a certain adsorption effect. In any case, these MPNs generally exhibit superior adsorption performance under neutral conditions.
5.3. Synergistic Effect on Complete Removal of Nitrogen
MPNs can effectively adsorb inorganic nitrogen in water, such as NH4+-N and NO2−-N, and catalyze their reduction to N2, making it a novel method for water body remediation [202,209]. However, this method has some limitations, such as an increase in NO3−-N after adsorption and a narrow pH range of applicability, which limits its effectiveness in wastewater treatment. This is because the redox electrode potential of NO3−/NH4+-N is EΘ(A) = 0.881 V. Under acidic conditions, NO3− exhibits strong oxidation properties, while NH4+-N shows weak reduction properties. The strongly oxidative Fe3+ and NH4+-N can react as follows: Fe3+ + NH4+-N + H2O → Fe2+ + NO2−-N + H+. Experimental results confirm that the oxidation of NH4+-N by Fe3+ is the primary cause of the indirect increase in NO3−-N, which is highly detrimental to environmental protection. According to the redox principle, using metals with a negative redox electrode potential may prevent the oxidation of NH3-N. The redox electrode potential (EΘ) of some metals is below zero, for example, Ti (Ti4+/Ti3+, EΘ = −0.04), magnesium (Mg2+/Mg, EΘ = −2.364), and aluminum (Al3+/Al, EΘ = −1.662 V). Zero-valent metals are simple to prepare, environmentally friendly, and exhibit strong NO3−-N reduction capabilities [210,211]. The main product of the zero-valent metal reduction of NO3−-N is NH4+-N [211,212]. MPNs leverage their excellent NH3-N adsorption capacity to adsorb and recover NH4+-N released during the reduction process, addressing the limitations of zero-valent metals. Qian et al. [206] demonstrated that the combination of metal–phenol networks and zero-valent metals can achieve the dual effects of adsorption and reduction (see Figure 9). Finally, other zero-valent metals may also become significant subjects of research. The redox electrode potential of zero-valent aluminum is EΘ = −1.662 V, lower than that of zero-valent iron (EΘ = −0.4402 V) and zero-valent zinc (EΘ = −0.7628 V). It is a more potent NO3−-N reducing agent and is expected to be widely utilized.
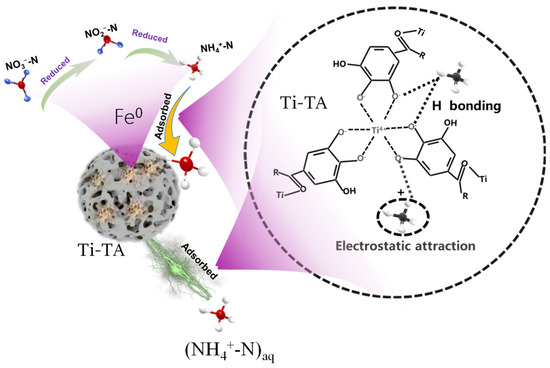
Figure 9.
A schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism for the removal of aquatic nitrogen by the nZVI/Ti-TA composite [206].
It is of great significance to delve into the unique advantages of MPNs compared with other materials. This is because many materials are capable of removing nitrogen from water treatment plants, which makes it difficult to highlight the differences between MPNs and these materials. In fact, MPNs have a notable advantage: they can easily be coated to the surface of carriers and combine with various carriers effortlessly, thus achieving synergistic applications. For instance, in the process of combining some engineering materials with other substances to form composite functional bodies, chemical agents such as silane coupling agents or surfactants are typically required. This not only frequently significantly increases the cost but also results in a composite structure that is not robust enough and is prone to detachment. However, MPNs do not have these issues. They can be firmly loaded onto the carrier surface without the need for additional chemical agents. In the latest report, researchers combined MPNs with magnetic ferric oxide (Fe3O4) [103]. As a result, MPNs were endowed with magnetization properties, which facilitate their subsequent recovery. This innovative approach has added new functions to MPNs, enabling them to perform more effectively in the flocculation–denitrification process.
5.4. Challenges and Potential
MPNs have received extremely limited research attention compared with other materials for the removal of nitrogen. Despite their good nitrogen removal performance, they also have several significant limitations. The core drawbacks include the following two aspects. The first drawback is pH dependence. The pH value can influence the formation of different MPN structures. Current research indicates that the three-dimensional structured MPNs, formed under neutral conditions with a pH of 7, exhibit good adsorption performance. In contrast, other MPN structures have poorer adsorption effects. In particular, the two-dimensional structures of MPNs are prone to dissolution. This makes the regulation of the pH value an indispensable step in practical applications. The second drawback is the issue of low adsorption capacity. As mentioned earlier, MPNs have good nitrogen removal effects. However, their adsorption capacity is relatively low compared with the demands of practical applications. This results in the need to use a large quantity of the material. As a result, the economic cost of MNP applications is higher than that of traditional methods. Therefore, enhancing the adsorption capacity of MPNs remains an urgent challenge.
MPNs exhibit strong NH3-N adsorption under neutral pH conditions (pH 7), but their performance diminishes in acidic or alkaline environments [207,213]. In contrast, MNP-modified composite materials show excellent NH3-N removal efficiency under mildly acidic, neutral, and mildly alkaline conditions, demonstrating good chemical stability [206,208]. MPNs and their modified composite materials also exhibit the following adsorption characteristics [206207,208,213]: (1) They show good adsorption performance across a wide range of environmental temperatures (15 °C to 45 °C), with adsorption efficiency increasing as the temperature rises. (2) The presence of various cations and anions, such as Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl−, CO32−, PO43−, and SO42−, influences their adsorption efficiency, with the degree of impact depending on the type of ions and increasing with higher ion concentrations. (3) They demonstrate excellent nitrogen removal efficiency in various types of wastewater, including black and odorous water bodies with varying levels of pollution, agricultural runoff, poultry farming wastewater, domestic wastewater from construction sites, slaughterhouse effluents, and dyeing and printing wastewater. (4) MPNs are highly reusable, and although their adsorption capacity slightly decreases after repeated regeneration cycles, they still retain relatively strong performance. However, the long-term stability of MPNs remains unclear. Although MPNs have seen applications in the medical field, they have yet to be industrially applied in the ecological and environmental sectors, and their potential environmental impacts in such contexts remain to be fully explored.
Although MPNs have been widely applied in the medical field, their use in the water treatment industry remains largely confined to laboratory research. Industrial applications still face several challenges, including addressing limitations in application conditions (e.g., expanding the applicable pH range), reducing costs (e.g., increasing adsorption capacity and decreasing reagent dosage), and optimizing the reagent preparation process. Additionally, integrating MPNs with existing processes to achieve efficient reagent recovery and regeneration remains a significant challenge.
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6), launched in 2024, aims to ensure access to clean water and sanitation, with nitrogen pollution control playing a critical role. Excessive nitrogen discharge causes eutrophication and water quality deterioration, posing significant threats to drinking water safety and ecosystem health. In response, countries have implemented stringent discharge standards and regulatory policies to address nitrogen pollution, promote the adoption of nitrogen removal technologies, and encourage optimized fertilization practices in agriculture to reduce nitrogen loss. To tackle nitrogen pollution and control, extensive research has been devoted to various nitrogen removal materials, each exhibiting distinct properties and limitations. Table 2 summarizes some typical materials and their nitrogen adsorption capacities in wastewater. Under these stricter environmental standards and policy support, MPNs have demonstrated immense potential for research and practical application.

Table 2.
Typical materials’ adsorption capacity of nitrogen from wastewater.
6. Conclusions
This paper investigates and analyzes the sources, hazards, and remediation strategies of nitrogen pollution in water, with a specific emphasis on advanced nitrogen removal technologies. Currently, biological methods dominate as the primary nitrogen removal technologies, particularly due to their cost-effectiveness and suitability for large-scale applications. However, numerous challenges persist in nitrogen pollution management. For instance, conventional flocculation methods prove ineffective in treating black and odorous water. In dye wastewater, the excessively high NH3-N content impedes the application of biological treatment methods, resulting in elevated treatment costs. Moreover, even after treatment, the nitrogen content in the effluent of industrial wastewater may still fail to meet the stringent standards. To comply with increasingly strict environmental regulations, enterprises are compelled to increase operational costs and invest more human, material, and financial resources. Given this context, research on new technologies is of paramount importance. In recent years, new technologies have shown significant potential compared to traditional ones. MPNs (MPNs) represent a novel class of nitrogen removal materials. They exhibit stable nitrogen removal capabilities and favorable preparation properties. When combined with zero-valent metals, MPNs can simultaneously achieve adsorption and reduction functions, offering an innovative approach to nitrogen pollution management. Nevertheless, several challenges remain. Firstly, synthesizing MPNs with high adsorption capacities remains a major hurdle. Secondly, the engineering application of MPNs is constrained by pH conditions, and this issue requires urgent attention. Only by overcoming these challenges can we better achieve the goal of sustainable nitrogen pollution management. In the future, research on MPNs will focus on reducing production costs, facilitating large-scale industrial applications, and developing integrated technological solutions.
Author Contributions
H.L., J.L., S.L., Y.Q. and S.X.: writing—original draft; Y.L. and Z.W.: editing; G.Z.: conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, and reviewing and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 21A0324) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (Nos. 2018JJ2128 and 2021JJ30272).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Du, X.; Fang, M.; Ye, X. Research progress on the sources of inorganic nitrogen pollution in groundwater and identification methods. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 5266–5275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Follett, R.F.; Hatfield, J.L. Nitrogen in the Environment: Sources, Problems, and Management. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.; Zhao, X.Q.; Shen, R.F. Bacillus pumilus promotes the growth and nitrogen uptake of tomato plants under nitrogen fertilization. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, S.; Yu, S. Effect of nitrogen nutrition on protein and nucleic acid metabolism during senescence of flag leaf. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2003, 9, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, D.; Coyle, M.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Cape, J.N.; Reis, S.; Sheppard, L.J.; Jenkins, A.; Grizzetti, B.; Galloway, J.N.; et al. The global nitrogen cycle in the twenty-first century. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130164. [Google Scholar]
- Kanter, D.R.; Chodos, O.; Nordland, O.; Rutigliano, M.; Winiwarter, W. Gaps and opportunities in nitrogen pollution policies around the world. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolenko, O.; Jurado, A.; Borges, A.V.; Knöller, K.; Brouyère, S. Isotopic composition of nitrogen species in groundwater under agricultural areas: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1415–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. 2016–2019 China Ecological Environment Statistics Annual Report; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2020. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/sthjtjnb/202012/P020201214580320276493.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. 2020 China Ecological Environment Statistics Annual Report; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2022. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/sthjtjnb/202202/t20220218_969391.shtml (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- Ministry of Agriculture. National Sustainable Agricultural Development Plan (2015–2030). China Agric. Inf. 2016, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y. China Consumes Nearly a Third of the World’s Fertilizers, Underscoring the Challenges of Overreliance on Chemical Inputs. XINHUANET. 2015. Available online: https://news.hebccw.cn/system/2015/03/18/015130673.shtml (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- GB 18918-2002; Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Nutrient Control Design Manual: State of Technology Review [R/OL]. 2019. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-02/documents/nutrient-control-design-manual-state-tech.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2025).
- European Union. Council Directive 91/271/EEC Concerning Urban Wastewater Treatment; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; EUR-Lex: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Jia, Y.; He, N.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Piao, S.; Liu, X.; He, H.; Guo, X.; et al. Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Aber, J.A.; Erisman, J.W.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Howarth, R.W.; Cowling, E.B.; Cosby, B.J. The nitrogen cascade. Bioscience 2003, 53, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Environment Assembly. Sustainable Nitrogen Management Resolution; UN Environment Assembly: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Colombo Declaration on Sustainable Nitrogen Management; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, J.N.; Winiwarter, W.; Leip, A.; Leach, A.M.; Bleeker, A.; Erisman, J.W. Nitrogen footprints: Past, present and future. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 115003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Cao, Y.; Shi, S.; Sun, G.; Du, L.; Zhu, J. Sources of Nitrogen Pollution and Denitrification in the Taihu Lake Region. Sci. China (Ser. B) 2001, 31, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Ding, J.; Xuan, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, R. Composition and Source Identification of Nitrogen in Groundwater in an Urbanized Basin. Trop. Geogr. 2023, 43, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Nitrogen. Water Quality: An Introduction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 269–290. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, J.A.; Alonso, Á. Ecological and toxicological effects of inorganic nitrogen pollution in aquatic ecosystems: A global assessment. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 831–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Tian, J.; Li, G. Factors influencing ammonia removal of biological activated filter in drinking water treatment. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2008, 59, 2316–2321. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Xu, B. Impact Factors of Monochloramine Formation Efficiency during Chloramination Disinfection. China Water Wastewater 2021, 37, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Piccardo, M.T.; Geretto, M.; Pulliero, A.; Izzotti, A. Odor emissions: A public health concern for health risk perception. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Meng, L.; Pang, M. Ammonia Production, Hazards and Mitigation Measures in a Pig House. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 27, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L. Current Status, Hazards, and Removal Technologies of Nitrate Pollution in Water. City Town Water Supply 2013, 27, 70–72. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J. Study on Effective Reduction of Nitrate to Nitrogen by Electrochemical Corrosion Cooperated with Photo Catalytic of Iron. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W. Coastal eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: Importance of atmospheric deposition and groundwater as “new” nitrogen and other nutrient sources. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42 Pt 2, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, G.N.; Wang, Z.; Brooks, B.W. Revisiting inland hypoxia: Diverse exceedances of dissolved oxygen thresholds for freshwater aquatic life. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3139–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L. Nitrate Contamination of Groundwater and its Control and Evaluation Forecast Methods. Ground Water 2006, 28, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H. The Harm of Nitrite to Human Health and Its Prevention. Stud. T Race Elem. Health 2003, 20, 57–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Hu, J.; Tang, Z. Research Progress on Methemoglobin. J. SNAKE (Sci. Nat.) 2016, 28, 65–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Y. Sustainable nitrogen elimination biotechnologies: A review. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Ai, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Qu, H.; Bian, D. Research progress on novel biological denitrification and dephosphorization technology for urban wastewater treatment. Water Purif. Technol. 2021, 40, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Novel Biological Nitrogen Removal Processes and Their Technical Principles. China Water Wastewater 2000, 16, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, E.M.; Müller, E.; Horn, H.; Lackner, S. Microbial activity of suspended biomass from a nitritation–anammox SBR in dependence of operational condition and size fraction. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 8795–8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, J. Water Quality Engineering Volume II; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Yang, E.; Chen, J.; Gu, Y.; Wu, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Li, H. A critical review on microbial ecology in the novel biological nitrogen removal process: Dynamic balance of complex functional microbes for nitrogen removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W. Water Quality Engineering; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhao, L. Process Study of Enhancement of Activated Sludge Progress by Powdered Activated Carbon for The Treatment of Petrochemical Wastewater. Water Supply Technol. 2023, 17, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Lu, S.; Wei, Y.; Ji, M. Characteristics of aerobic granule and nitrogen and phosphorus removal in a SBR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Huang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhu, J. Iron-carbon (Fe-C) micro-electrolysis coupling with anaerobic-anoxic-oxic (A2/O) process: Nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance and microbial characteristics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Emission Standard of Pollutants for Electroplating; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, H.; Jia, L.; Wu, W.; Wang, J. Simultaneous biological removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from secondary effluent of wastewater treatment plants by advanced treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, A.; Rocha, V.; Barros, B.; Sliva, B.; Tavares, T. Bacterial biofilm attachment to sustainable carriers as a clean-up strategy for wastewater treatment: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Heijnen, J.J.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Model-based evaluation of temperature and inflow variations on a partial nitrification–ANAMMOX biofilm process. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4839–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; He, X.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J. Effect of Temperature on Performance of Single-stage Autotrophic Nitrogen Removal System for Treating High NH3-N Wastewater. China Water Wastewater 2019, 35, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Hao, R.; Meng, C. Start-up of Three-dimensional Electrode Biofilm Reactor at Low Temperature. China Water Wastewater 2013, 29, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Li, J.; Duan, C.; Peng, Y. Recent Progress of Anammox Bacteria Enrichment Strategies in Wastewater Treatment. J. Beijing Univ. Technol. 2024, 50, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wang, D.; Peng, L.; Ni, B.-J.; Wei, W.; Liu, Y. New perspectives on microbial communities and biological nitrogen removal processes in wastewater treatment systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Di, F.; Zhang, J.; Gong, H.; Jiang, L.; Wei, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, J. Advanced nitrogen removal in a fixed-bed anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor following an anoxic/oxic reactor: Nitrogen removal contributions and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, J. Effect of organic matter on the anammox performance of constructed rapid infiltration systems. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Gao, R.; Yang, L.; Deng, L.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Highly enriched anammox within anoxic biofilms by reducing suspended sludge biomass in a real-sewage process. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, G.; Li, Y. A review on upgrading of the anammox-based nitrogen removal processes: Performance, stability, and control strategies. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 127992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Sun, T.; Wang, Z. Effect of Organic substrate on nitrogen removal of Anammox. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 3, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lv, X.; Inose, Y. Study on Nitrogen Removal by Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrificatio. Water Wastewater Eng. 2001, 27, 22–24+1. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, W. Treatment of High Ammonia Wastewater by Partial Nitrification and Anaerobic Ammonia Oxidation. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Jianzhu University, Hefei, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Ouyang, W.; Huang, S.; Peng, X. Microbial community composition in a simultaneous nitrification and denitrification bioreactor for domestic wastewater treatment. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publ. 2018, 112, 012007. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; He, Q. Study on the efficiency and mechanism of solid phase autotrophic-heterotrophic denitrification and removalof trace pollutants. China Environ. Sci. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Cao, J.; Qian, Y. New denitrification process: SHARON process. Environ. Pollut. Control 2003, 25, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, X. Achieving nitrogen removal via nitrite in a pilot-scale continuous pre-denitrification plant. Water Res. 2009, 43, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Study on Nitrogen Removal in Partial Nitrification Denitrification Biological Filters. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, L. What is the Best Biological Process for Nitrogen Removal: When and Why? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3835–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, W.; Tian, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Qi, L.; Yu, M. Treatment of toilet sewage by coupled denitrification system of short-cut nitrification and anammox. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Capodaglio, A.G.; Hlavínek, P.; Raboni, M. Physico-chemical technologies for nitrogen removal from wastewaters: A review. Rev. Ambiente Agua 2015, 10, 481–498. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, A.; Almomani, F.; Qiblawey, H.; Rasool, K. Advances in nitrogen-rich wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review of modern technologies. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Hu, Z. Experimental Study on Combined Stripping Treatment Process for Wastewater with High NH3-N Content. Technol. Water Treat. 2022, 48, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- O’Farrell, T.P.; Frauson, F.P.; Cassel, A.F.; Bishop, D.F. Nitrogen removal by ammonia stripping. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1972, 44, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Stefan, D.; Erdelyi, N.; Izsak, B.; Zaray, G.; Vargha, M. Formation of chlorination by-products in drinking water treatment plants using breakpoint chlorination. Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driss, K.; Bouhelassa, M. Modeling drinking water chlorination at the breakpoint: I. Derivation of breakpoint reactions. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 5757–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Zhan, Z.; Luo, J.; Lei, Y. Fate of micropollutants in struvite production from swine wastewater with sacrificial magnesium anode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, L.; Ren, H.; Xiong, X. Ammonium nitrogen removal from coking wastewater by chemical precipitation recycle technology. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5209–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myllymäki, P.; Pesonen, J.; Romar, H.; Hu, T.; Tynjälä, P.; Lassi, U. The use of Ca-and Mg-rich fly ash as a chemical precipitant in the simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus—Recycling and reuse. Recycling 2019, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, S.; Kwag, J.H.; Ra, C. Magnesium ammonium phosphate formation, recovery and its application as valuable resources: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhao, Q.L.; Hao, X.D. Ammonium removal from landfill leachate by chemical precipitation. Waste Manag. 1999, 19, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tünay, O.; Kabdasli, I.; Orhon, D.; Kolçak, S. Ammonia removal by magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation in industrial wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Luo, Z.; Qiu, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Cai, Q.; et al. Nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from livestock wastewater via magnesium ammonium phosphate precipitation: A critical review of methods, progress, and insights. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Jin, L. Efficient Removal Technology of NH3-N by Membrane Separation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2022, 45, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X. Experimental Study on Adsorption of NH3-N in Water by Natural and Modified Zeolite. Master’s Thesis, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. A critical review of various adsorbents for selective removal of nitrate from water: Structure, performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 1, 132728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Qiu, T.; Yan, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, S. Removal of NH3-N from aqueous media with low-cost adsorbents: A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozokwelu, D.; Zhang, S.; Okafor, O.; Cheng, W.; Litombe, N. Chapter 5—Separation Science and Technology. In Novel Catalytic and Separation Processes Based on Ionic Liquids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Mizuta, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Hatate, Y.; Nishihara, K.; Nakanishi, T. Removal of nitrate-nitrogen from drinking water using bamboo powder charcoal. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeswari, A.; Amalraj, A.; Pius, A. Adsorption studies for the removal of nitrate using chitosan/PEG and chitosan/PVA polymer composites. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 9, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shi, E.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z. A study on and adsorption mechanism of ammonium nitrogen by modified corn straw biochar. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2023, 10, 221535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Yang, P.; Yin, H.; Zhang, E. Enhanced nutrient control efficiency in sediments using modified clay inactivation coupled with aquatic vegetation in the confluence area of a eutrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Chakraborty, S. Chemical denitrification of water by zero-valent magnesium powder. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X. Effect of common ions on nitrate removal by zero-valent iron from alkaline soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 231–232, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, G.M.; Limonti, C.; Siciliano, A.; Kabdaşlı, I. Nitrate Removal by Zero-Valent Metals: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H.; Lv, X.; Tu, Q.; Ren, Q.; Xia, X.; Jing, C. Common oxidants activate the reactivity of zero-valent iron (ZVI) and hence remarkably enhance nitrate reduction from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 146, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.C.C.; Lee, H. Chemical reduction of nitrate by nanosized iron: Kinetics and pathways. Water Res. 2005, 39, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Pei, H.; Hou, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, L.; Nie, C. Algal biofilm-assisted microbial fuel cell to enhance domestic wastewater treatment: Nutrient, organics removal and bioenergy production. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for reduction of organic pollutants in landfill leachate: A review. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2009, 4, 366–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Marin, A.D.; Roé-Sosa, A.; Solis-Marcial, O.J.; Chavarría, J.; Mendivil-Garcia, K.; Amabilis-Sosa, L.E. Nutrient-efficient recovery process from real livestock wastewater using UV/H2O2 and UV/PMS: Kinetic study and statistical optimization. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 74, 107811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Jeevanantham, S.; Jawahar, M.J.; Neshaanthini, J.P.; Saravanan, R. A review on synthesis methods and recent applications of nanomaterial in wastewater treatment: Challenges and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Green-synthesized nanocatalysts and nanomaterials for water treatment: Current challenges and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Song, W.; Xu, Z. Improved photocatalytic conversion of high−concentration ammonia in water by low−cost Cu/TiO2 and its mechanism study. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, M.; Moradi, N.; Faryadi, M.; Safari, S. Removal of ammonia by high-frequency ultrasound wave (1.7 MHz) combined with TiO2 photocatalyst under UV radiation. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 15999–16007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, G.; Yan, S.; Hursthouse, A.S. Magnetic seed technology for the efficient removal of nitrogen from wastewater. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 2619–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, M. Graphene-supported metal/metal oxide nanohybrids: Synthesis and applications in heterogeneous catalysis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 3903–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabuba, J.; Lephallo, J.; Rutto, H. Comparison of various technologies used to eliminate nitrogen from wastewater: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin., P. Interpretation of the “Guidelines for the Remediation of Urban Black and Odorous Water Bodies”. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2015, 14–15+21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B. Purification Performance of Odorous-Black Water and It’s Microbial Mechanisms in Integrated Constructed Wetland. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Muezzinoglu, A. A study of volatile organic sulfur emissions causing urban odors. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, G.; Zhu, X. Analysis of Control and Remediation Technology for Black and Odorous Rivers in Shanghai. Water Purif. Technol. 2010, 29, 1–3+45. [Google Scholar]
- Hishida, Y.; Ashitani, K.; Fujiwara, K. Occurrence of Musty Odor in the Yodo River. Water Sci. Technol. 1988, 20, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.H.; Jia, J.; Kettner, A.J.; Xing, F.; Wang, Y.P.; Xu, X.N.; Yang, Y.; Zou, X.Q.; Gao, S.; Qi, S.; et al. Changes in water and sediment exchange between the Changjiang River and Poyang Lake under natural and anthropogenic conditions, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Fan, C. Identification of black suspended particles in the algae-induced black bloom water column. J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 591–598. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B. Study on Remediation of Contaminatied River by Sediment Stabilization and Biofiltration. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. Study on the Effect of Humic Acid on Nitrogen and Phosphor Conversion Process in Black-Odor Water. Master’s Thesis, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Cao, C. Pollution Control, Water Quality Improvement, and Ecological Restoration of Urban Rivers. Constr. Sci. Technol. 2011, 43–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Cao, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, D.; Xu, M.; Shen, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Ding, S. A critical review of the appearance of black-odorous waterbodies in China and treatment methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Feng, Z.; Shang, J.; Fan, C.; Deng, J. Black Water Bloom Induced by Different Types of Organic Matters and Forming Mechanisms of Major Odorous Compounds. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 3152–3159. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Wu, Y. Factors Affecting the Production of Volatile Organic Sulfur Compounds (VOSCs) from Algal-Induced Black Water Blooms in Eutrophic Freshwater Lakes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, X.; Fang, Y.; Huang, R. Analysis on the formation condition of the algae-induced odorous black water agglomerate. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, M.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. The relationship between the form transformation of iron and sulfur and the black-odor water body. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 33, 1–3+7. [Google Scholar]
- Na, B. Microbiological Process Involved in Formation Black Malodorous Water in Typical Areas. Master’s Thesis, Capital University of Economics and Business, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Detection Method of Hydrogen Sulfide Gas and Safety Precautions. Metrol. Meas. Tech. 2021, 48, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S. Study on the Effect of Gravity Compression Fiber Ball on Nitrogen/Phosphorus Treatment in Black and Odorous Water. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. The Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE) Held a Press Conference to Answer Questions on the Protection of Water Ecosystems; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Lin, C.; Wu, X.; Qu, F.; Chen, Q. Outlook on the Governance of Black and Smelly Water in China. Chem. Ind. 2017, 35, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Deng, S.; Chen, J.; Xia, Z. River sediment pollution and its control and restoration. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 1708–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Wu, D.; Chen, W.; Feng, C.; Wei, C. Biocathode denitrification of coke wastewater effluent from an industrial aeration tank: Effect of long-term adaptation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 125, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liang, P.; Yan, X.; Zuo, K.; Xiao, K.; Xia, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wu, S.; Huang, X.; et al. Reducing aeration energy consumption in a large-scale membrane bioreactor: Process simulation and engineering application. Water Res. 2016, 93, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Study on Effect of Aeration on Water Body Remediation of Black-Odor River. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Water Environment Improvement of Zhongdong River by Water Diversion and Distribution in Hangzhou. Meteorol. Environ. Res. 2017, 8, 61–66+71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, C.; Qin, H. Water diversion project for the improvement of water quality in Shenzhen River-Bay system. Water Resour. Prot. 2008, 24, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Pan, G.; Chen, H. Effect of in-situ capping on contaminated sediment remediation using local soil. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 5, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.J.; Jiang, B.; Huang, G.Q.; Li, X.G. Laboratory column study for remediation of MTBE-contaminated groundwater using a biological two-layer permeable barrier. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z. Calcium Peroxide Complex Agent in-Situ Remediation for River Sediment Pollution. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Sun, S.; Gu, X.; Chen, K. Preliminary study about application of calcium peroxide in the heavily contaminated sediments remediation. J. Lake Sci. 2015, 27, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, G.; Tong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yin, H.; Xia, S.; Su, S. Ammonia-Nitrogen Removal from Black and Odorous Water by Chemical Precipitation. Hunan Nonferrous Met. 2017, 33, 54–57+70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Lv, H.; Han, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, J. Deodorant, Bactericidal, and Algaecide Agent for Emergency Treatment of Urban Black and Odorous Water Bodies, Its Preparation Method, and Application. China Patent CN201910309005.5, 17 April 2019. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Hua, T. Research advances in environmental effect and ecological toxicity of commonly used chemical flocculants. Chin. J. Ecol. 2007, 26, 943–947. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Deng, C. A New Green Phytoremediation Technology of Aquatic Plants. Water Sav. Irrig. 2007, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Juwarkar, A.A.; Singh, S.K.; Mudhoo, A. A comprehensive overview of elements in bioremediation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2010, 9, 215–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.H. Chemical, Physical and Biological Cycles in Treatment Wetlands. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. The migration of pollutants in artificial wetlands. China Water Wastewater 1994, 10, 40–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. Role and Mechanism Study on Microbe in Treatment of Science Water by Biological Grid. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.; Huang, M.; Wu, L.; Dai, X.; Ruan, Y. The control test-study of biological purification tank on malodorous river water purification. China Environ. Sci. 2008, 28, 433–437. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, Z.; Sha, H. Improvement and Ecological Remediation of Malodorous River, Zhongtang River Tributary in Ningbo City. China Water Wastewater 2013, 29, 64–67+70. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zou, G.; Song, X.; Fu, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Effect of ryegress floating-bed on the nitrogen cycling bacteria and nitrogen removal in the synthetic unicipal wastewater. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J. Nitrogen-Containing Wastewater Treatment Technology and Its Application; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, S. Ultrasonically Modified Zeolite for Removing NH3-N from Micro-polluted Raw Water. China Water Wastewater 2014, 30, 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. The cycle of nitrogen in river systems: Sources, transformation, and flux. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2018, 20, 863–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, N. Removal of NH3-N from Wastewater: A Review. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xia, C.; Wang, W.; Zhou, R.; Wang, C.; Jetteen, M.S.M.; et al. Ubiquitous anaerobic ammonium oxidation in inland waters of China: An overlooked nitrous oxide mitigation process. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhu, G. Biological nitrogen removal with nitrification and denitrification via nitrite pathway. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinidi, L.; Tan, I.A.W.; Abdul Wahab, N.B.; Tamrin, K.F.B.; Hipolito, C.N.; Salleh, S.F. Recent development in ammonia stripping process for industrial wastewater treatment. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3181087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Z. Ammonia-nitrogen removal from low concentration wastewater by ion exchange. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 6, 2715–2719. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, H. Current situation, problems and future direction for governance of black and odorous water bodies in Chinese cities. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2019, 13, 507–510. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, H. Classification and systematic treatment practices of black and odorous water bodies in urban rivers in China. Water Wastewater Eng. 2018, 54, 1–5+39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Department of Ecological Environment. China Ecological Environment Status Bulletin 2021 (Excerpt). Environ. Prot. 2022, 50, 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. National Notice on the Inspection of Black and Odorous Water Bodies in County-Level Cities; Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Wen, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, L. Progress reports of metal-phenolic network engineered membranes for water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhong, Q.Z.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F.; Hao, J. Metal Ion-Directed Functional Metal-Phenolic Materials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 11432–11473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miao, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, K.; Lu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Guo, J. Recent advances in the development and antimicrobial applications of MPNs. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2202684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wu, F.G.; Dai, Y.; Chen, X. Polyphenol-containing nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and therapeutic delivery. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Cai, M.H.; Tao, X.H.; Fan, Y.B.; Mou, X.Z. Surface Engineered Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) Based Novel Hybrid Systems for Effective Wound Healing: A Review of Recent Developments. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 576348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tao, C. Recent advances in metal-organic framework-based materials for anti-staphylococcus aureus infection. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6220–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, Z. Polydopamine antibacterial materials. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 1618–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Kitagawa, S.; Wang, B.; Uemura, T. Hybridization of MOFs and polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3108–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, H.; Richardson, J.J.; Liang, K.; Best, J.P.; van Koeverden, M.P.; Such, G.K.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F. One-Step Assembly of Coordination Complexes for Versatile Film and Particle Engineering. Science 2013, 341, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Guo, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. A review on astringency and bitterness perception of tannins in wine. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 40, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, İ.; Huyut, Z.; Elmastaş, M.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of tannic acid. Arab. J. Chem. 2010, 3, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Verma, N. Surface ion imprinting-mediated carbon nanofiber-grafted highly porous polymeric beads: Synthesis and application towards selective removal of aqueous Pb(II). Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Dhiware, P.; Sharma, P.; Janu, V.C.; Gupta, R. Simultaneous Adsorption of Th(IV) and U(VI) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by a Tannic-Acid-Modified Nanomagnetite Adsorbent. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2023, 1, 2649–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Sun, W.; Kim, J.P.; Lu, X.; Li, Q.; Lin, M.; Mrowcrzynski, O.; Rizk, E.B.; Cheng, J.; Qian, G.; et al. Development of tannin-inspired antimicrobial bioadhesives. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, T.; Yang, S.; Qi, C.; Qiu, P.; Yang, J.; et al. A Universal Single-Atom Coating Strategy Based on Tannic Acid Chemistry for Multifunctional Heterogeneous Catalysis. Angew. Chem. 2022, 61, e202200465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, M.; Huang, C. A versatile approach to antimicrobial coatings via metal-phenolic networks. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 187, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, Y.; Guo, J.; Ejima, H.; Chen, X.; Richardson, J.J.; Sun, H.; Caruso, F. pH-responsive capsules engineered from metal-phenolic networks for anticancer drug delivery. Small 2015, 11, 2032–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Shi, Q.; Shao, G.; Hu, D. Research progress on preparation of tannic acid functional adsorption materials and its application. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2023, 52, 2468–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Lim, M.Y.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, J.J.; Kang, H.; Lee, J.C. Reverse osmosis nanocomposite membranes containing graphene oxides coated by tannic acid with chlorine-tolerant and antimicrobial properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, J. determination of niobium in titanium-aluminum-niobium alloy by tannic acid precipitation separation-ceric sulfate titration method. Metall. Anal. 2024, 44, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Su, L.; Zhao, Y. Study on leaching of manganese from manganese dioxide ore with tannic acid-sulfuric acid system. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2022, 54, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Cui, Y.; Wang, W.; Bai, Y.; Han, Y.; Gao, Z. Ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from soil applied with liquid fractions by enhanced solid-liquid separation technology with tannic acid. Environ. Chem. 2024, 43, 3194–3203. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Q.; Gao, B.; Liu, B.; Long, C.; Yang, H. Preparation of tannic acid—Titanium composite adsorbent and its adsorption performance and mechanisms in removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Environ. Chem. 2022, 41, 2180–2192. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Ni, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q. Remarkable ability of Pb(II) capture from water by self-assembled metal-phenolic networks prepared with tannic acid and ferric ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Xing, X.; Bi, X.; Liang, P. Preparation Method and Application of Iron-Tannic Acid Adsorbent for High-Efficiency Phosphorus Removal. China Patent CN200810117949.4, 18 August 2008. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Gao, T.; You, Y. Adsorption Characteristics of Ferric Tannate and Ferrous Tannate to Phosphorus. Leather Sci. Eng. 2020, 30, 9–15+32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Study on Treatment of the Combination of Tannic Acid and Zinc Chloride on Methylene Blue Solution. Environ. Sci. Surv. 2018, 37, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Mao, L. One-pot assembly tannic acid-titanium dual network coating for low-pressure nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 233, 116051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Qin, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; He, H. Tannic acid assisted metal-chelate interphase toward highly stable Zn metal anodes in rechargeable aqueous zinc-ion batteries. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 981623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Zhang, K.; Shen, J.; Liu, H. Study on preparation and properties of tannic acid-copper modified polyacrylate materials for preservation of cultural heritage. J. Shaanxi Univ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 42, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zmozinski, A.V.; Peres, R.S.; Freiberger, K.; Ferreira, C.A.; Tamborim, S.M.M.; Azambuja, D.S. Zinc tannate and magnesium tannate as anticorrosion pigments in epoxy paint formulations. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 121, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.Z.; Pan, S.; Rahim, M.A.; Yun, G.; Li, J.; Ju, Y.; Lin, Z.; Han, Y.; Ma, Y.; Richardson, J.J.; et al. Spray Assembly of Metal-Phenolic Networks: Formation, Growth, and Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33721–33729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jia, N.; Cheng, L.; Liu, L.; Gao, C. Metal-polyphenol coordination networks: Towards engineering of antifouling hybrid membranes via in situ assembly. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Wang, L.; Shan, W.; Gao, K.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhou, W. Highly Stretchable and Self-Adhesive Wearable Biosensor Based on Nanozyme-Catalyzed Conductive Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 2188–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, W.; Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Zhou, J.; Fan, L. Effect of Chitosan-tannic Acid Coating on the Microbial Diversity of Jiaohuaji Chicken. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, J.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H. Construction and Functional Characterization of Metal-Polyphenol Network and Its Application in Food Field: A Review of Recent Literature. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 43, 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Tian, H.; Qiu, B.; Sun, D. Synthesis of ammonia molecularly imprinted adsorbents and ammonia adsorption separation during sludge aerobic composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, H.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Wan, P.; Fan, G. High removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from black-odorous water using a novel aeration-adsorption system. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, P.; Tan, J.; Xiong, K.; Maitz, M.F.; Pan, C.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Huang, N. Assembly of metal–phenolic/catecholamine networks for synergistically anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticoagulant coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 40844–40853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejima, H.; Richardson, J.J.; Caruso, F. Metal-phenolic networks as a versatile platform to engineer nanomaterials and biointerfaces. Nano Today 2017, 12, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhong, Q.Z.; Li, J. Metal-phenolic network coatings for engineering bioactive interfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaén, J.A.; De Obaldía, J.; Rodríguez, M.V. Application of Mössbauer spectroscopy to the study of tannins inhibition of iron and steel corrosion. Hyperfine Interact. 2011, 202, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gust, J.; Suwalski, J. Use of Mssbauer Spectroscopy to Study Reaction Products of Polyphenols and Iron Compounds. Corrosion 2012, 50, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Performance and Mechanism of Ferric Tannate in the Removal of Inorganic Nitrogen from Wastewater. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 4141–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Study on the Synthesis, Performance and Mechanism of Embedded Ferric Tannate in the Removal of Nitrogen from Wastewater. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Science and Technology, Shijiazhuang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Luo, B.; Wan, P.; Wang, J.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Li, S.; Zhu, G. A metallic phenolic network-enhanced bentonite for ammonical nitrogen removal from black-odorous water. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 182, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Luo, H.; Zhu, G. Characterization and application of titanium tannate (Ti-TA) metallic phenolic network for removal of NH3-N. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 73, 107703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wan, P.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Zhu, G. A novel zero-valent iron/titanium tannate composite for deep removal of nitrogen from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H. Mechanism of Inorganic Nitrogen Removal by Titanium Tannate Coupled with Iron Powder. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S. Preparation and Study on NH3-N Removal of Magnetic Zirconium Tannate. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Synthesis and characterization of ferric tannate as a novel porous adsorptive-catalyst for nitrogen removal from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40785–40791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, L.; Peng, M.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, G. Nitrate reduction by nanoscale zero valent iron (nFe0)-based Systems: Mechanism, reaction pathway and strategy for enhanced N2 formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Reduction of nitrate by zero valent iron (ZVI)-based materials: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, B. Recent advances in non-noble metal electrocatalysts for nitrate reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J. Research on Removal of NH3-N from Black Smelly Water by Bentonite Supported Ferric Tannate. Master’s Thesis, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Raji, M.; Mirbagheri, S.A.; Ye, F.; Dutta, J. Nano zero-valent iron on activated carbon cloth support as Fenton-like catalyst for efficient color and COD removal from melanoidin wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.R.; Othman, M.H.D.; Hubadillah, S.K.; Abd Aziz, M.H.; Jamalludin, M.R. Application of natural zeolite clinoptilolite for the removal of ammonia in wastewater. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloomi, F.; Jalali, M. Ammonium removal from aqueous solutions by natural Iranian zeolite in the presence of organic acids, cations and anions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Qu, X.; Wang, G.; Zheng, S.; Frost, R.L. Removal characteristics of ammonium nitrogen from wastewater by modified Ca-bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 107, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Woo, S.H. The removal of nitrate from aqueous solutions by chitosan hydrogel beads. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaouar Yadi, M.; Benguella, B.; Gaouar-Benyelles, N.; Tizaoui, K. Adsorption of ammonia from wastewater using low-cost bentonite/chitosan beads. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 21444–21454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Application of struvite precipitation in treating ammonium nitrogen from semiconductor wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desireddy, S.; Pothanamkandathil Chacko, S. A review on metal oxide (FeOx/MnOx) mediated nitrogen removal processes and its application in wastewater treatment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2021, 20, 697–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).