Preparation of Graft-Functionalized SBS/SBS Composite Latex Modifier and Its Effect on Emulsified Asphalt Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
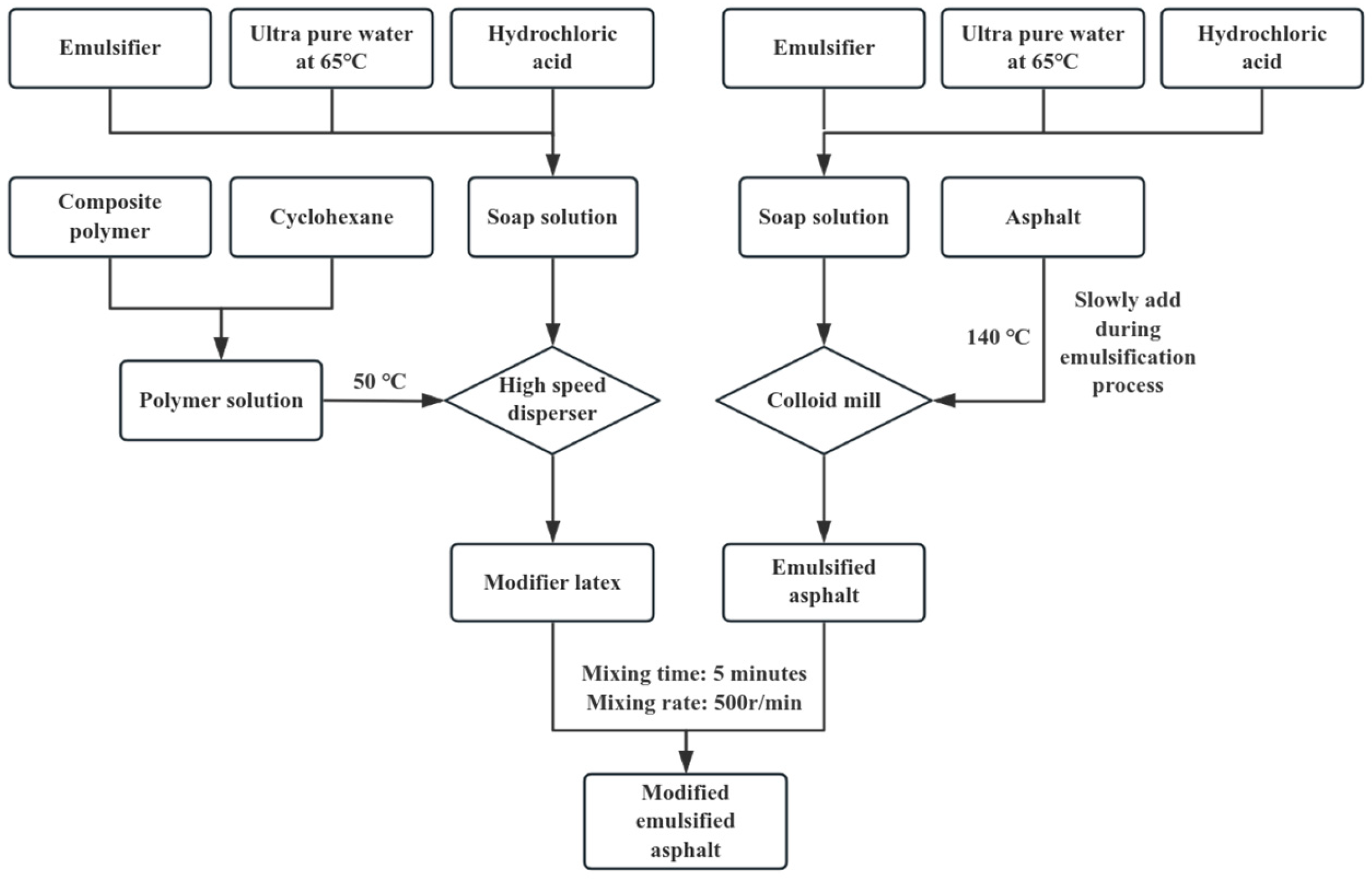
2.2. Preparation of Modified Emulsified Asphalt
2.3. Testing Methods
2.3.1. Routine Performance Testing
2.3.2. Fluorescence Microscopy Testing
2.3.3. DSR Testing
2.3.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Testing
2.3.5. Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR) Test
3. Results and Discussion
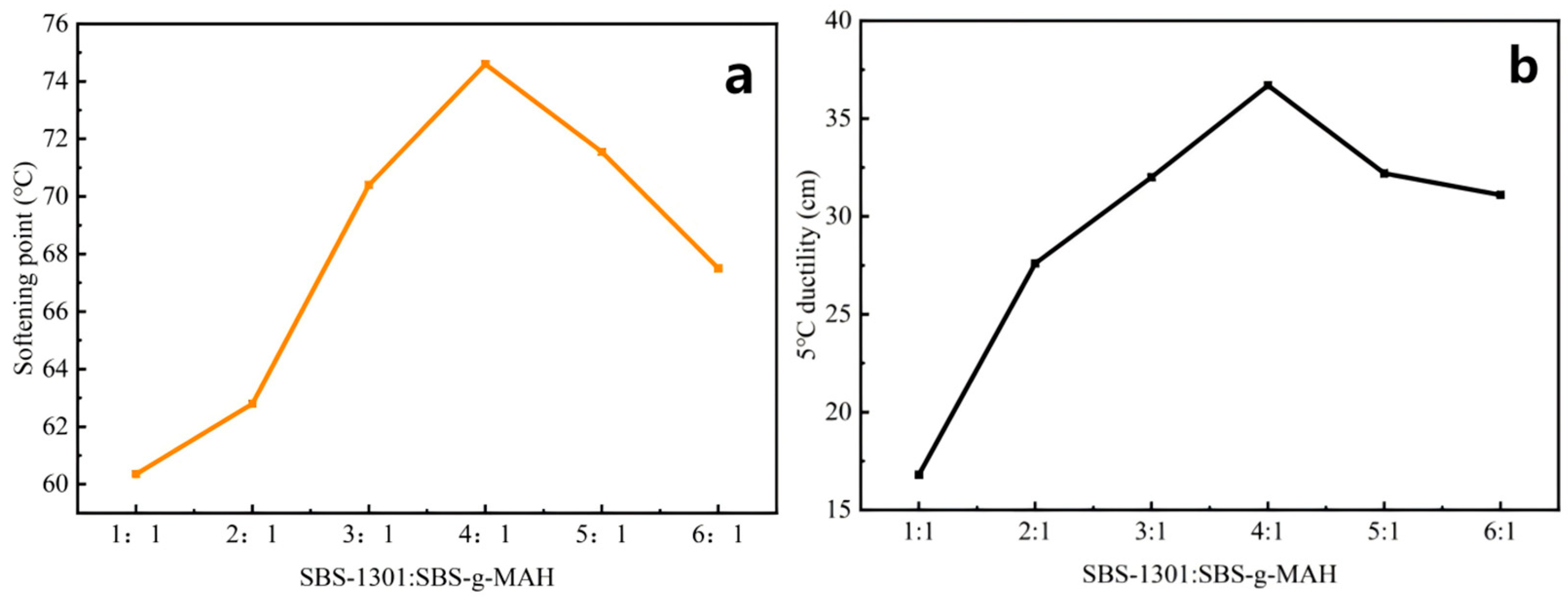
3.1. Effect of the Ratio of MA-g-SBS to SBS on the Conventional Properties of Modified Emulsified Asphalt
3.2. Conventional Performance Testing of MSMEA with Optimal Proportion
3.3. Analysis of Fluorescence Microscope Test Results
3.4. Analysis of DSR Test Results
3.5. Analysis of Infrared Spectrum Test Results
3.6. Analysis of Creep Test Results of Bending Beam
3.7. Economic Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
References
- Xin, X.; Yao, Z.; Shi, J.; Liang, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yao, K. Rheological properties, microstructure and aging resistance of asphalt modified with CNTs/PE composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghnejad, M.; Shafabakhsh, G. Use of Nano SiO2 and Nano TiO2 to improve the mechanical behaviour of stone mastic asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitao, S.D.; Picado-Santos, L.G.; Martinho, F. Pavement engineering materials: Review on the use of warm-mix asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, N.; Barreneche, C.; Cabeza, L. Asphalt emulsion formulation: State of the art of formulation, properties and results of HIPR emulsions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronald, M.; Luis, F. Asphalt emulsions formulation: State-of-the-art and dependency of formulation on emulsions properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Qian, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, S.; Nan, G.; Kong, X.; Fan, W. The influencing factors of evaporation residue of emulsified modified asphalt to optimize the environmental adaptability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356, 129169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Comparison of SBS latex replacement SBR latex used in modified emulsified asphalt. Pet. Asphalt. 2017, 31, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, H.; Wen, G.; Yang, Y. Determine of optimum SBR latex content in SBR modified asphalt emulsion based on macro and micro characters. Mater. Sci. Eng. J. 2018, 36, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadivar, A.; Kavussi, A. Rheological characteristics of SBR and NR polymer modified bitumen emulsions at average pavement temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Song, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, D.; Chen, X. Mechanical and rheological properties of polyurethane-polyurea (PU-PUa) modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K. Preparation of High Performance SBS Modifed Emulsifed Asphalt. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Dongying, China, 2019. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27644/d.cnki.gsydu.2019.000125 (accessed on 1 May 2019).
- Zhang, K. Synthesis and Performance Characterization of SBS Modifed Asphalt Emulsifer. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.G.; Liao, K.; Hong, C. Study on the properties of environmentally friendly SBS modifed fame retardant asphalt. Pet. Ref. Chem. 2016, 47, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Li, X.; Zong, Q. Chemical, morphological and rheological investigations of SBR/SBS modifed asphalt emulsions with waterborne acrylate and polyurethane. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fan, W.; Wang, T.; Nan, G.; Sunarso, J. Influence of emulsification on the properties of styrene–butadiene–styrene chemically modified bitumens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, W. Rheological characteristics and phase discrimination of linear SBS modified asphalt under different time aging. J. Southeast Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 49, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, P. Rejuvenation performance and mechanism of aged SBS modified asphalt rejuvenated by bio-oil based rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shi, X.; Xue, J. Laboratory evaluation of composed modified asphalt binder and mixture containing nano-silica/rock asphalt/SBS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xie, L.; Dou, D.; Li, L.; Yu, M.; Yao, S. Storage stability and compatibility of asphalt binder modified by SBS graft copolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, G.; Shi, C. Aging rheological characteristics of SBR modified asphalt with multi-dimensional nanomaterials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Jiang, H.; Liang, M.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, W.; Zhang, X. Chemical, rheological properties and microstructure of road asphalt prepared from deoiled asphalt, slurry oil and polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Research on the Performance of SBR Modified Emulsified Asphalt Cold Laying Mixture. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, S.; Kassem, H.; ElKordi, A.; Joumblat, R. Incorporating Artificial Intelligence Applications in Flexible Pavements: A Comprehensive Overview. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Test Items | Results | Requirements | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C)/0.1 mm | 88 | 80~100 | |
| Penetration index | −1.33 | −1.5~+1.0 | |
| Softening point/°C | 45.0 | ≥44 | |
| Ductility (10 °C)/cm | 50 | ≥20 | |
| Ductility (15 °C)/cm | greater than 100 | ≥100 | |
| Dynamic viscosity (60 °C)/Pa·s | 152 | ≥140 | |
| Density (15 °C)/(g·cm−3) | 1.029 | / | |
| Thin-film oven test (163 °C, 5 h) | Mass loss/% | −0.09 | ±0.8 |
| Penetration ratio/% | 63 | ≥57 | |
| Ductility (10 °C)/cm | 12.5 | ≥4 |
| pH | Ionic Charge | Solid Content/% | Particle Size/µm | Viscosity/mPa·s | Stability/Month |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2–3 | + | 40.2 | 4.57 | 340.2 | ≥6 |
| 1 d Stability/% | 5 d Stability/% | Screen the Remaining Amount/% | Solid Content/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsified asphalt | 0.47 | 3.40 | 0.00 | 62.10 |
| MSMEA | 0.93 | 4.88 | 0.00 | 60.30 |
| SEA | 0.68 | 3.78 | 0.00 | 60.63 |
| Dosage | 0% | 1% | 3% | 5% | 7% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engla viscosity | 3.1 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 4.7 | 5.2 |
| Function Expression | R2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Delta | y = 75.60032 − 4.33831x + 0.58508x2 − 0.06296x3 | 0.99987 |
| G* | y = 39,959.96825 + 21,859.64021x − 5002.11508x2 + 605.87963x3 | 0.99774 |
| G*/sin δ | y = 41,194.25397 + 24,080.47354x − 5371.90079x2 + 698.5463x3 | 0.99789 |
| Failure temperature | y = 67.05714 + 4.57857x − 1.20357x2 + 0.175x3 | 0.99933 |
| SBS Latex | MA-g-SBS/SBS Latex | |
|---|---|---|
| Modifier price (USD/ton) | 3486.8 | 3609.5 |
| Dosage/% | 5 | 5 |
| Cost of modified emulsified asphalt (USD/ton) | 741.6 | 756.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Preparation of Graft-Functionalized SBS/SBS Composite Latex Modifier and Its Effect on Emulsified Asphalt Properties. Processes 2025, 13, 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072125
Wang K, Liu Y, Cao Z, Zhang Y, Wang J, Li X. Preparation of Graft-Functionalized SBS/SBS Composite Latex Modifier and Its Effect on Emulsified Asphalt Properties. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kunyu, Yifan Liu, Zhenhao Cao, Yanyan Zhang, Jia Wang, and Xue Li. 2025. "Preparation of Graft-Functionalized SBS/SBS Composite Latex Modifier and Its Effect on Emulsified Asphalt Properties" Processes 13, no. 7: 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072125
APA StyleWang, K., Liu, Y., Cao, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., & Li, X. (2025). Preparation of Graft-Functionalized SBS/SBS Composite Latex Modifier and Its Effect on Emulsified Asphalt Properties. Processes, 13(7), 2125. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072125





