Experimental Study on Thermal Performance of PCM in an Inclined Shell-and-Tube Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Unit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental System
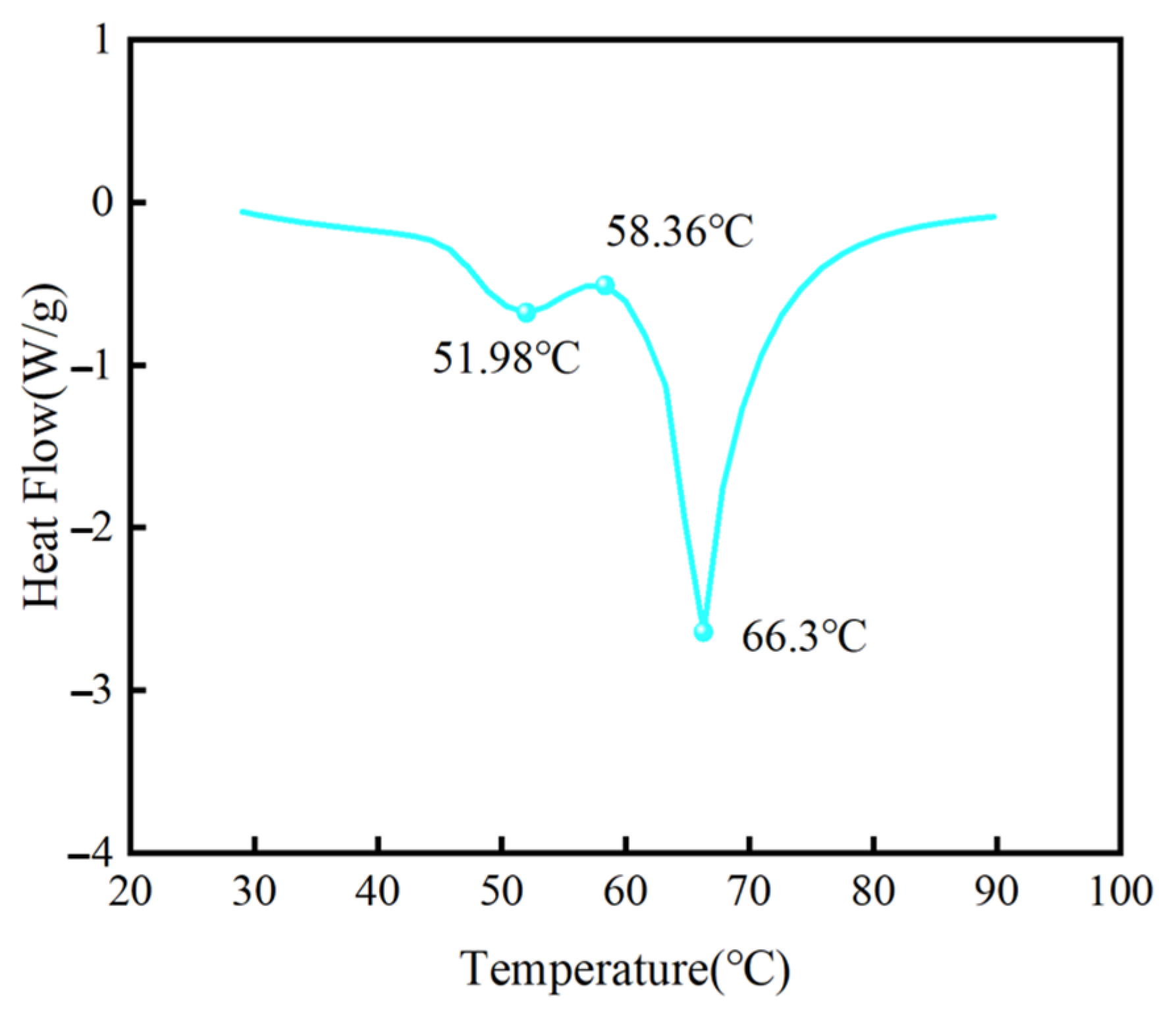
2.1. Heat Storage Material
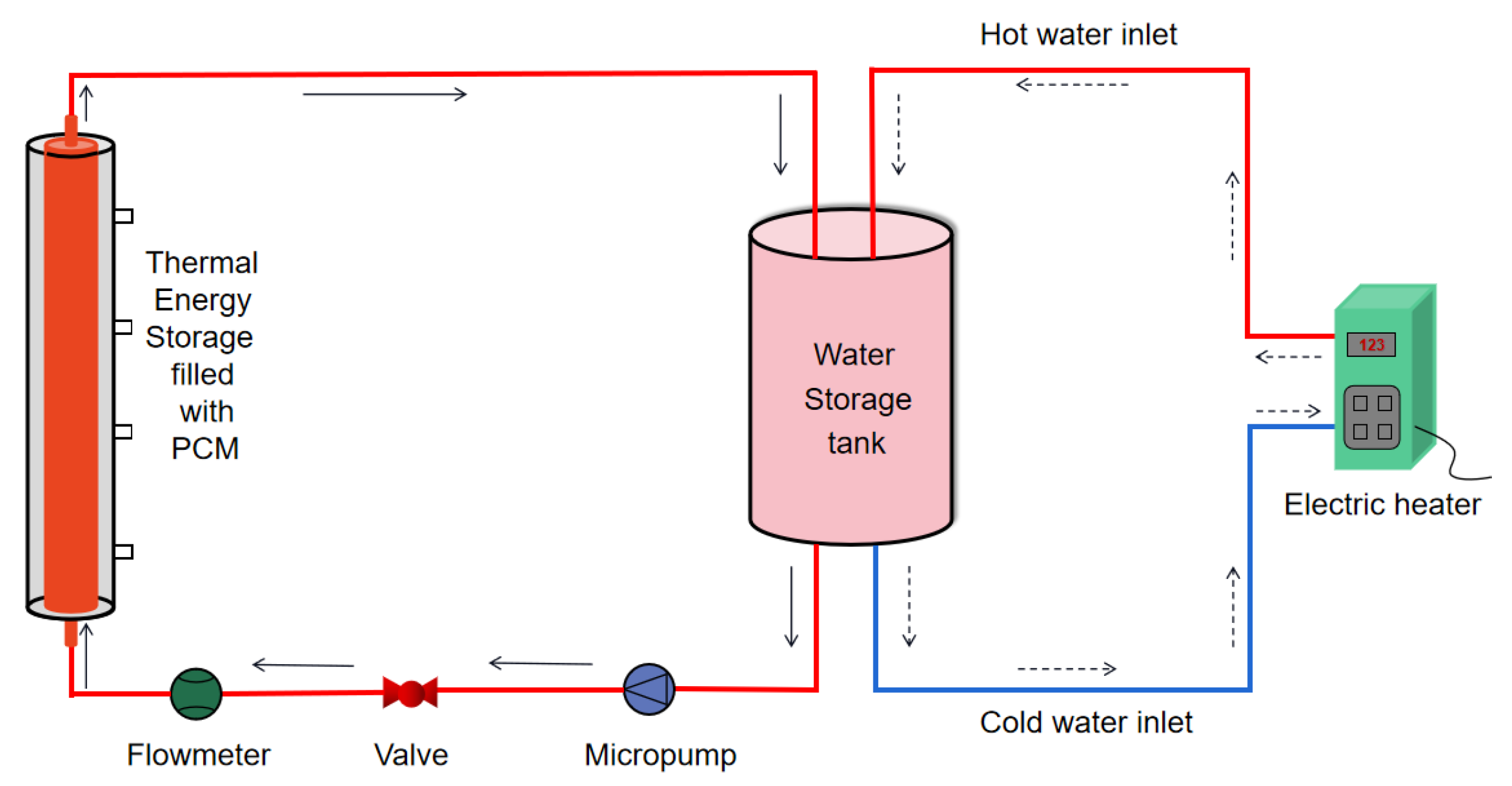
2.2. Experimental Apparatus
2.3. Uncertainty Analysis
3. Experimental Results
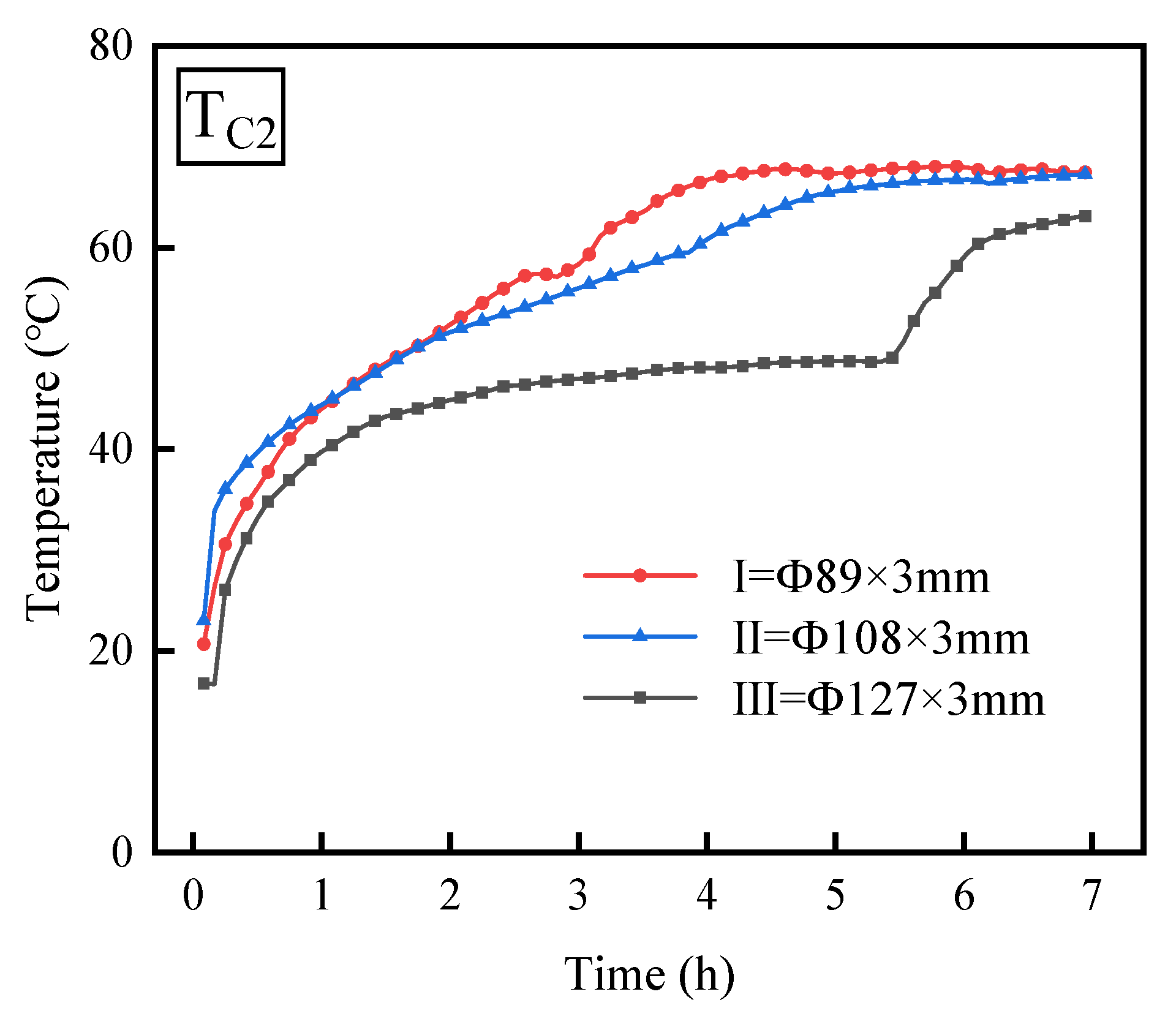
3.1. Effect of Outer Tube Diameter
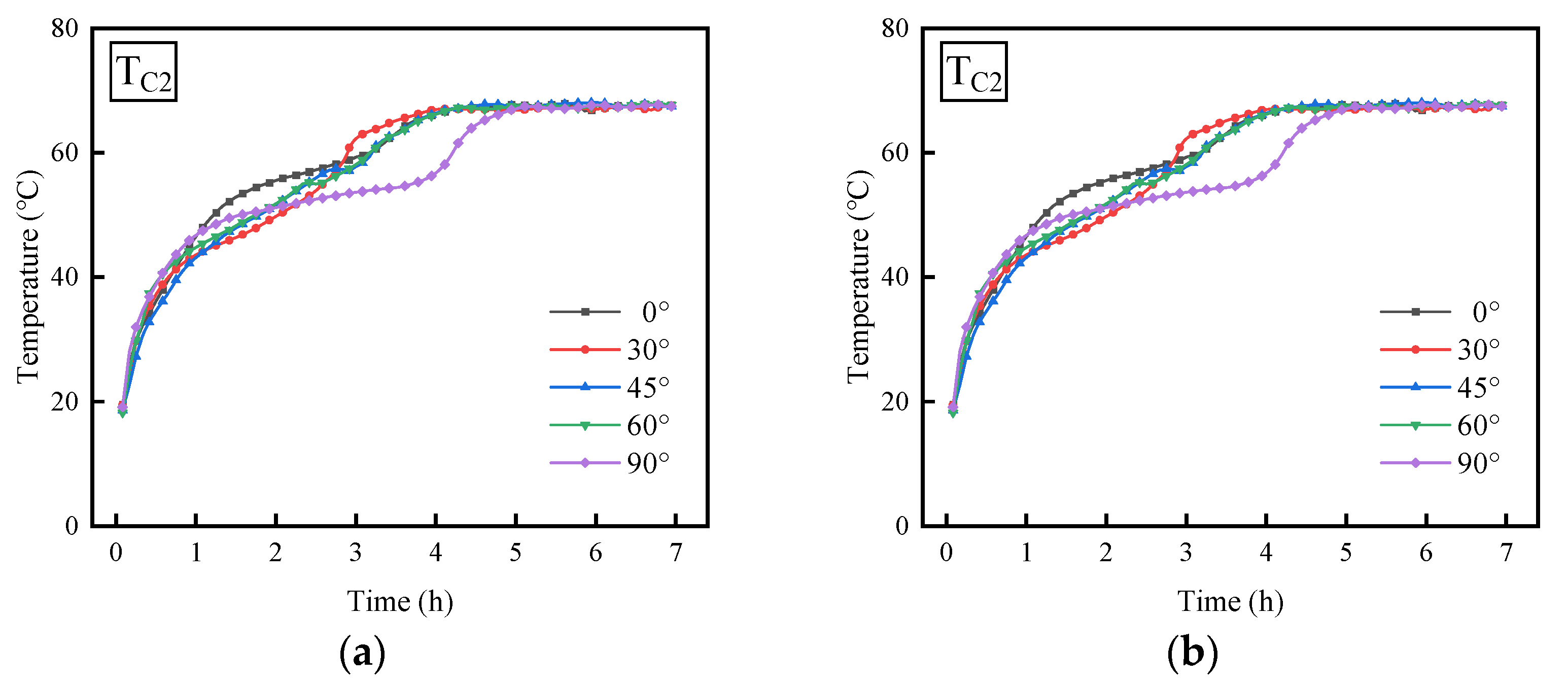
3.2. Effect of Inclination Angle
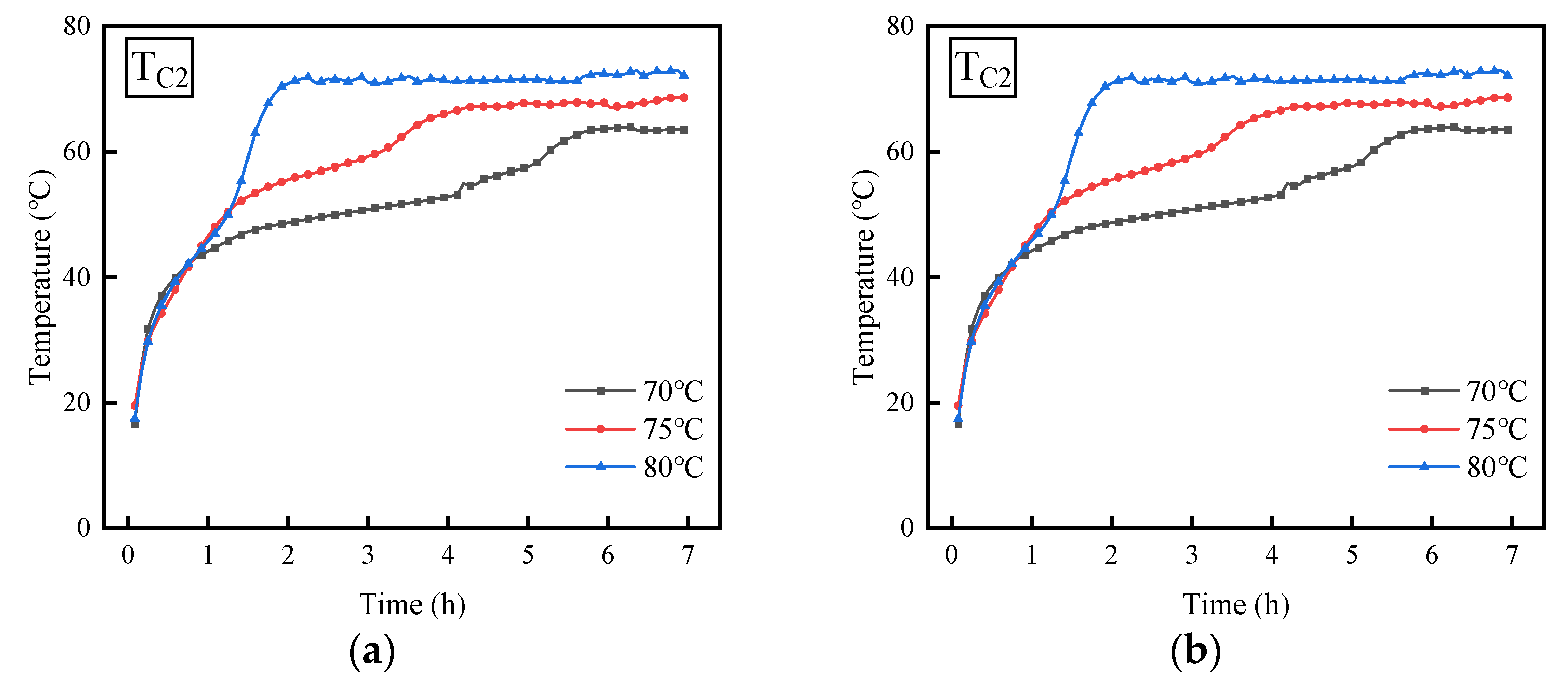
3.3. Effect of Inlet Temperature
3.4. Effect of Water Flow Direction
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- When the outer diameters of the thermal energy storage device are 89 mm and 108 mm, the temperature variation trends of the PCM are basically consistent. However, when the outer diameter is 127 mm, the temperature fluctuation pattern of the PCM differs during the middle phase compared to the other two diameters. Furthermore, as the diameter of the outer tube increases, the time required for the PCM temperature to reach stability also lengthens, while the PCM’s melting rate steadily declines.
- (2)
- The temperature variation trends of the PCM are fundamentally consistent under different inclination angles, characterized by a sharp increase in the initial phase, followed by a relatively gentle growth phase, and finally accelerating again until thermal equilibrium is achieved. As the angle of inclination for the thermal energy storage device rises from 0° to 90°, the duration necessary for the PCM to achieve equilibrium is extended, while simultaneously, the melting rate of the PCM experiences a reduction.
- (3)
- When the temperature of the water rises from 70 °C to 80 °C, the time needed for the PCM to stabilize diminishes, suggesting an increase in the melting rate of the PCM. Moreover, when the inclination angle of the shell-and-tube thermal energy storage device is 0°, for every 5 °C increase in water temperature, the time required to reach thermal equilibrium is shortened by 2 h.
- (4)
- Under the same water temperature and inclination conditions, the PCM temperatures are basically consistent whether the inlet is at the top or bottom, and the melting rates of the PCM are largely the same.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hedau, A.; Singal, S.K. Heat transfer and fluid flow analysis of PCM-based thermal energy storage concept for double pass solar air heater. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 157, 107813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Norouziasas, A.; Hamdy, M. PCM as an energy flexibility asset: How design and operation can be optimized for heating in residential buildings. Energy Build. 2024, 322, 114721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshamuthu, S.; Jegan, S.; Benyameen, J.J.; Selvakumar, V.; Anandeeswaran, K.; Iyahraja, S. Experimental analysis of small size solar dryer with phase change materials for food preservation. J. Energy Storage 2020, 33, 102095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, H.B.; Wang, H.L.; Bao, X.; Cui, H. Enhancing energy efficiency of air conditioning system through optimization of PCM-based cold energy storage tank: A data center case study. Energy 2024, 286, 129641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.F.; Yan, T.; Kuai, Z.H.; Pan, W.G. Thermal conductivity enhancement on phase change materials for thermal energy storage: A review. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 25, 251–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.X.; Jia, Y.T.; Alva, G.; Fang, G.Y. Review on thermal conductivity enhancement, thermal properties and applications of phase change materials in thermal energy storage. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2730–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.W.; Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, Y.-Q.; Yu, Z.-T.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y.-C.; Cen, K.-F. Effects of various carbon nanofillers on the thermal conductivity and energy storage properties of paraffin-based nanocomposite phase change materials. Appl. Energy 2013, 110, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Liu, T.; Alshamrani, A.; Jan, A. Thermal analysis of Reiner–Philippoff fluid flow with nanoparticles and bioconvection over a radially magnetized curved stretching surface. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Farooq, U.; Sheremet, M. Convective nanofluid flow subjected to variable porosity, inclined magnetic field, and thermal radiations. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2025, 86, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Ali, H.M.; Khushnood, S. Recent advances on thermal conductivity enhancement of phase change materials for energy storage system: A review. In. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 127, 838–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esapour, M.; Hamzehnezhad, A.; Darzi, A.R.; Jourabian, M. Melting and solidification of PCM embedded in porous metal foam in horizontal multi-tube heat storage system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 171, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ren, Q.L.; Zheng, Z.J.; He, Y.L. Evaluation and optimization of melting performance for a latent heat thermal energy storage unit partially filled with porous media. Appl. Energy 2017, 193, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Huang, X.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, X.; Li, M.-J. Design and study of metal foam parameters on whole melting-solidification cycle in phase change heat storage system. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2024, 106, 109299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyenim, F.; Hewitt, N.; Eames, P.; Smyth, M. A review of materials, heat transfer and phase change problem formulation for latent heat thermal energy storage systems (LHTESS). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Liang, Y.H.; Gao, H.C.; Li, R.; Guo, Y.; Yang, L. Development and experimental analysis of a novel type of phase change material based shell-and-tube latent heat storage for heat pump system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 321, 119095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Keshteli, A.N.; Babazadeh, H. Nanoparticles favorable effects on performance of thermal storage units. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 300, 112329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Arivazhagan, S.; Muninathan, K. Experimental and computational study of melting phase-change material for energy storage in shell and tube heat exchanger. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104614. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; He, M.; Lin, W.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Ma, Z. Performance investigation and sensitivity analysis of shell-and-tube phase change material thermal energy storage. J. Energy Storage 2020, 33, 102040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Abdellatif, H.E.; Belaadi, A.; Arshad, A.; Liu, H. Numerical study of shell and tube thermal energy storage system: Enhancing solidification performance with single-walled carbon nanotubes in phase change material. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 160, 108338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trp, A. An experimental and numerical investigation of heat transfer during technical grade paraffin melting and solidification in a shell-and-tube latent thermal energy storage unit. Sol. Energy 2005, 79, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesumathy, S.P.; Udayakumar, M.; Suresh, S. Heat transfer characteristics in latent heat storage system using paraffin wax. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgun, M.; Aydin, O.; Kaygusuz, K. Thermal energy storage performance of paraffin in a novel tube-in-shell system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2008, 28, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longeon, M.; Soupart, A.; Fourmigue, J.F.; Bruch, A.; Marty, P. Experimental and numerical study of annular PCM storage in the presence of natural convection. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Wang, L.; Xie, N.N.; Lin, X.; Chen, H. Experimental study on the melting and solidification behavior of erythritol in a vertical shell-and-tube latent heat thermal storage unit. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 99, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesumathy, S.P.; Udayakumar, M.; Suresh, S.; Jegadheeswaran, S. An experimental study on heat transfer characteristics of paraffin wax in horizontal double pipe heat latent heat storage unit. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahamli, Y.; Hosseini, M.J.; Ranjbar, A.A.; Bahrampoury, R. Inner pipe downward movement effect on melting of PCM in a double pipe heat exchange. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 316, 30–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, M.S.; Mahood, H.B.; Hasan, A.F.; Khadom, A.A.; Campbell, A.N. Numerical Study on the Effect of the Location of the Phase Change Material in a Concentric Double Pipe Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Unit. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2019, 11, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Yao, F.J.; Yi, H.L.; Tan, H.P. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of convection melting in complex heat storage systems filled with phase change materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 86, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousha, N.; Rahimi, M.; Pakrouh, R.; Bahrampoury, R. Experimental investigation of phase change in a multitube heat exchanger. J. Energy Storage 2019, 23, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darzi, A.A.R.; Farhadi, M.; Sedighi, K. Numerical study of melting inside concentric and eccentric horizontal annulus. Appl. Math. Model. 2012, 36, 4080–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khillarkar, D.B.; Gong, Z.X.; Mujumdar, A.S. Melting of a phase change material in concentric horizontal annuli of arbitrary cross-section. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2000, 20, 893–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A. Thermal energy storage system with stearic acid as phase change material. Energ. Convers. Manag. 1994, 35, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A. Phase change material energy storage system employing palmitic acid. Sol. Energy 1994, 52, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddegh, S.; Wang, X.L.; Henderson, A.D. A comparative study of thermal behaviour of a horizontal and vertical shell-and-tube energy storage using phase change materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 93, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousha, N.; Hosseini, M.J.; Aligoodarz, M.R.; Pakrouh, R.; Bahrampoury, R. Effect of inclination angle on the performance of a shell and tube heat storage unit–An experimental study. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 112, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyabi, I.A.; Khanna, S.; Mallick, T.; Sundaram, S. An experimental and numerical study on the effect of inclination angle of phase change materials thermal energy storage system. J. Energy Storage 2019, 23, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khobragade, S.; Devanuri, J.K. Impact of inclination on the thermal performance of shell and tube latent heat storage system under simultaneous charging and discharging: Numerical investigation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 214, 118811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SH/T0589-94; Sinopec Corporation. Method for Determination of Transition Temperature of Petroleum Waxes. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1994.
- Moffat, R.J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1988, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, K.; Zong, S.; Gao, H.; Duan, Z. Experimental Study on Thermal Performance of PCM in an Inclined Shell-and-Tube Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Unit. Processes 2025, 13, 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051557
Fan K, Zong S, Gao H, Duan Z. Experimental Study on Thermal Performance of PCM in an Inclined Shell-and-Tube Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Unit. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051557
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Kaixing, Shouchao Zong, Huaibin Gao, and Zhongxing Duan. 2025. "Experimental Study on Thermal Performance of PCM in an Inclined Shell-and-Tube Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Unit" Processes 13, no. 5: 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051557
APA StyleFan, K., Zong, S., Gao, H., & Duan, Z. (2025). Experimental Study on Thermal Performance of PCM in an Inclined Shell-and-Tube Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage Unit. Processes, 13(5), 1557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051557




