Simulation of Biofouling Caused by Bacillus halotolerans MCC1 on FeNP-Coated RO Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterium Growth Kinetics
2.2. Growth Parameters of Biofouling Bacterium
2.3. Modeling the Bacteria Growth on RO Membranes
2.4. Modeling the Desalination Performance of Membranes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
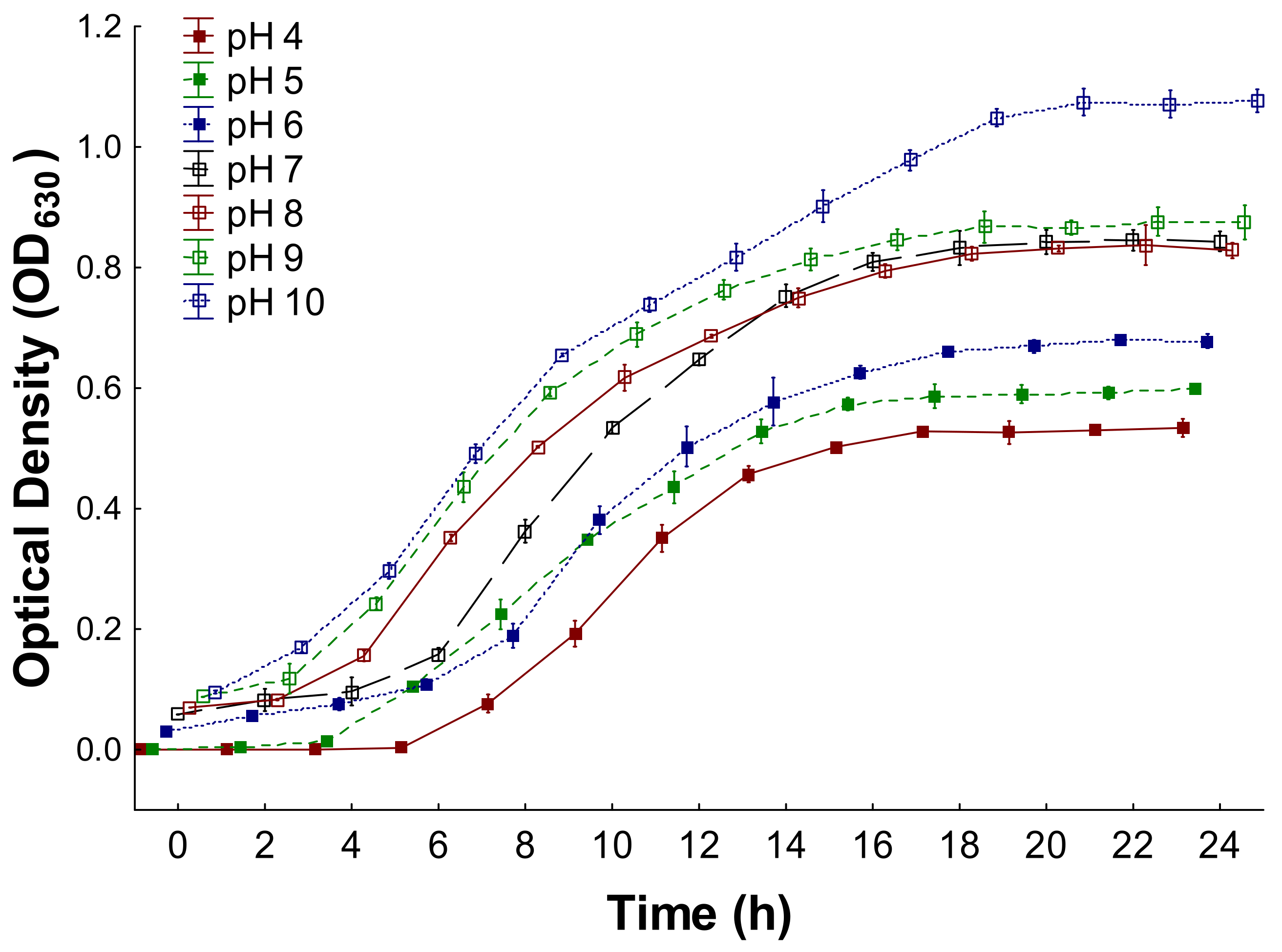
3.1. Bacterium Growth Kinetics
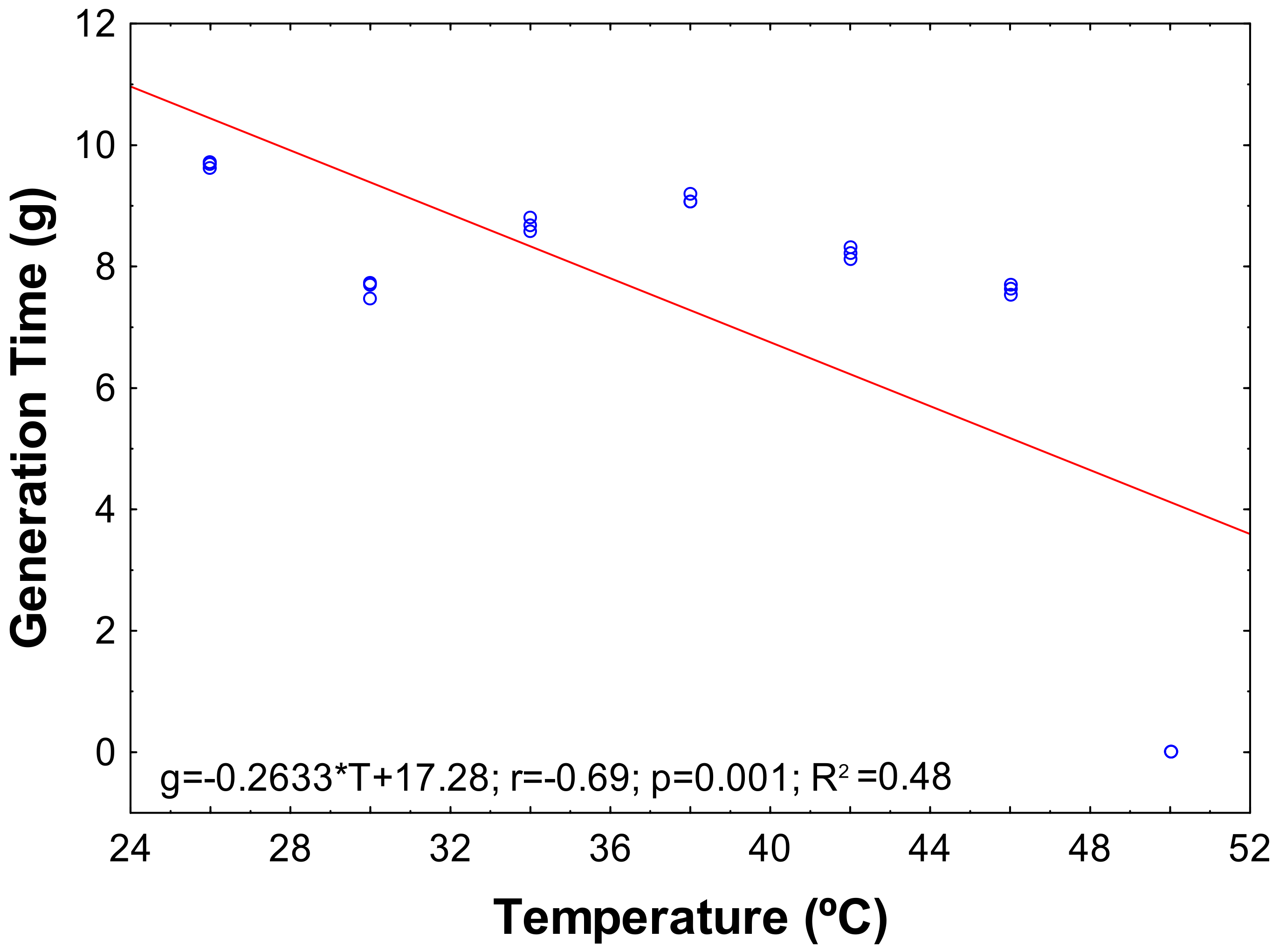
3.2. Growth Parameters of the Bacterium
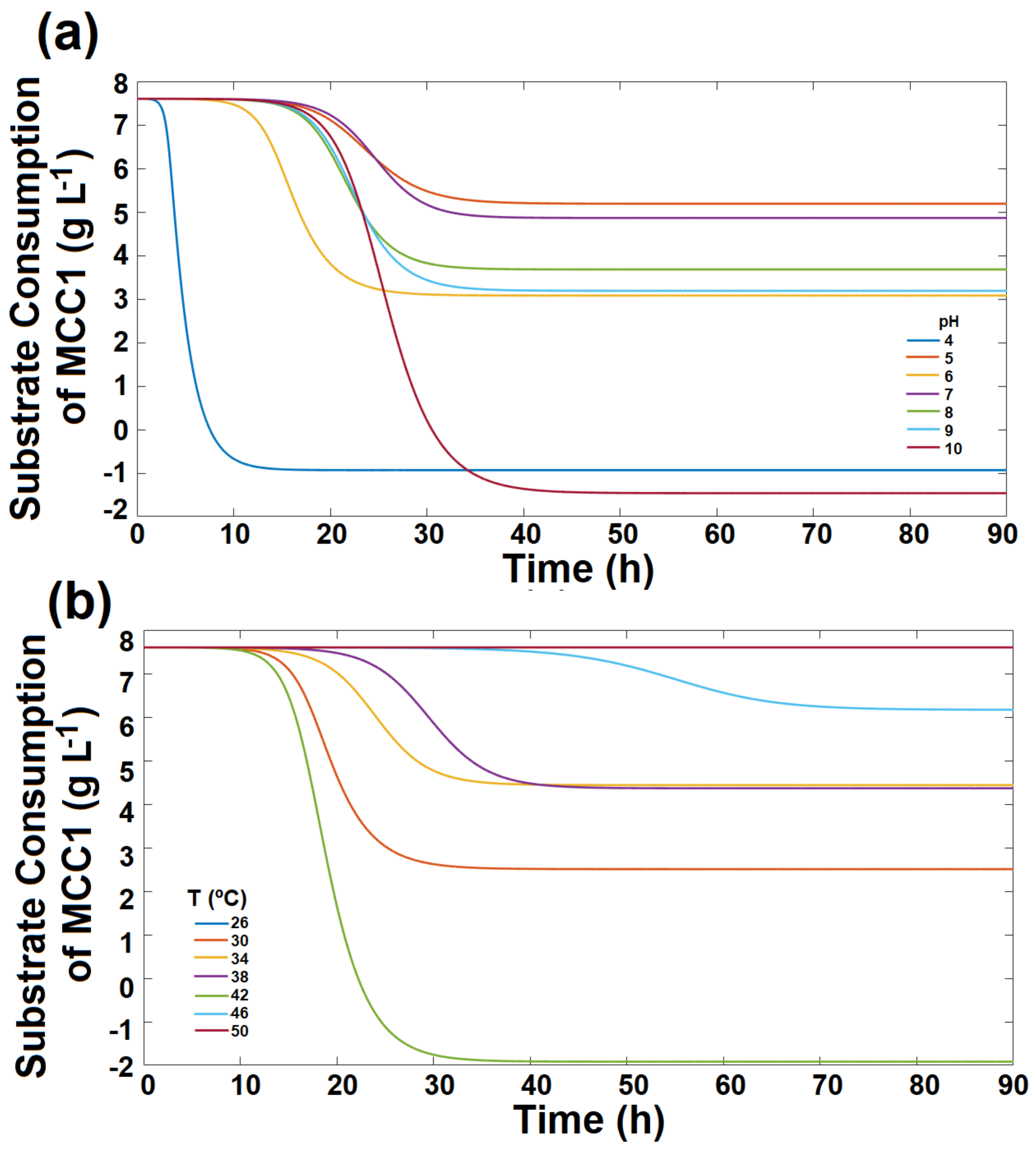
3.3. Bacterial Growth on RO Membranes
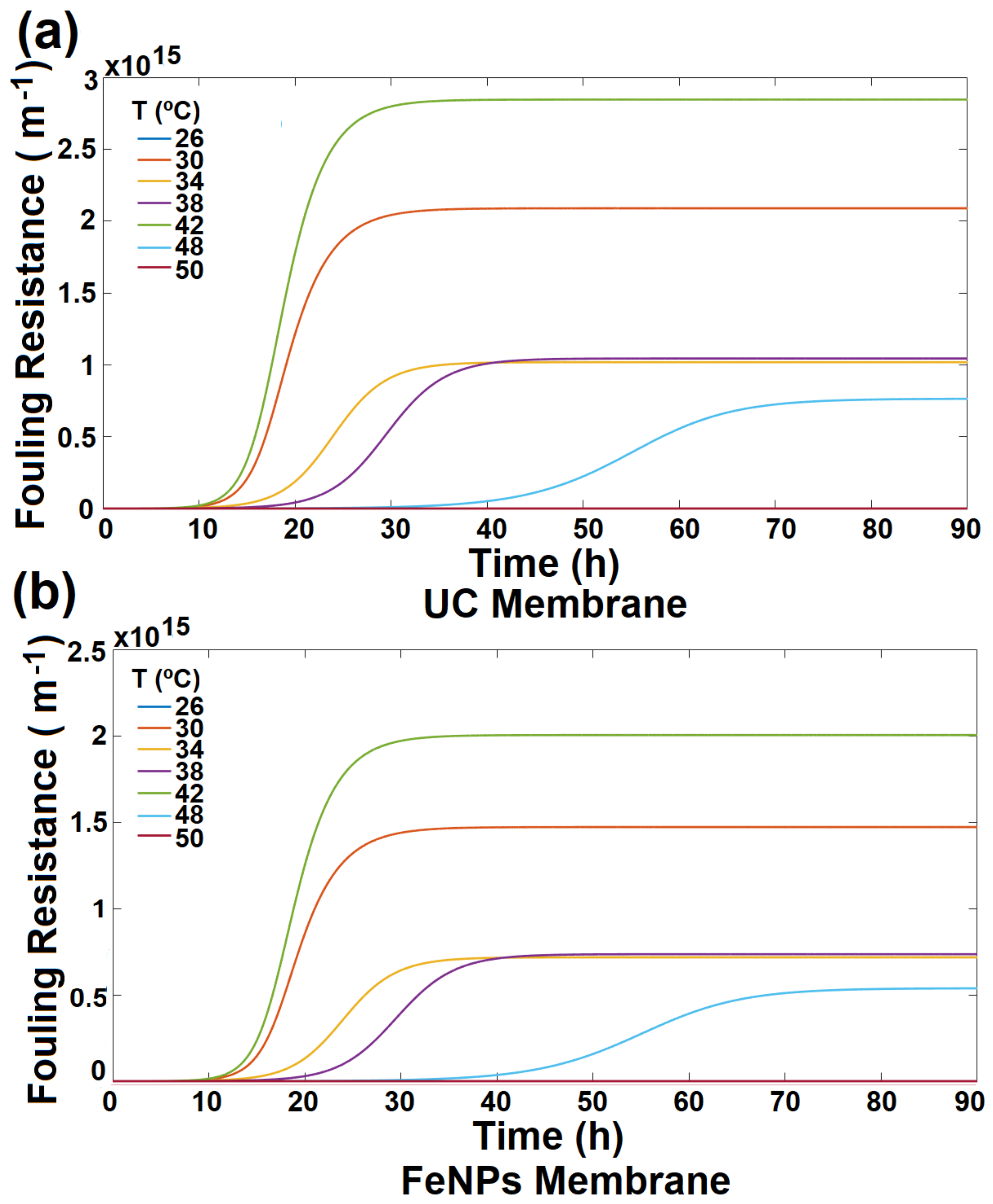
3.4. Membrane Desalination Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Variables | ||
| Symbol | Description | Units |
| C | Feed water concentration | g L−1 |
| CB | Biomass concentration at a given time | g L−1 |
| Cp | Permeate salt concentration | g L−1 |
| dCB/dt | Change in microbial biomass over time | g L−1 h−1 |
| dS/dt | Rate of substrate concentration change | g L−1 h−1 |
| EC | Electrical conductivity of seawater | µs cm−1 |
| g | Generation time | h per number of generations |
| k | Specific biomass growth rate | h−1 |
| kd | Specific death rate | h−1 |
| kmax | Maximum specific growth rate | h−1 |
| Ks | Substrate consumption rate at 50% of the maximum specific growth rate | g of substrate per g of biomass |
| Ksu | Substrate constant | g L−1 |
| Lp | Membrane permeance | m Pa−1 s−1 |
| n | Generation number | Generation of bacteria |
| N0 | Initial biomass concentration | g L−1 |
| N1 | Biomass concentration ratio at time 1 | g L−1 |
| N2 | Biomass concentration ratio at time 2 | g L−1 |
| Nn | Final biomass concentration | g L−1 |
| q | Constant obtained from the regression between Rf and CB | - |
| Rf | Fouling resistance | m−1 |
| Rm | Membrane resistance | m−1 |
| S0 | Substrate concentration at initial time | g L−1 |
| S0α | Addition of substrate | g L−1 |
| t | Time interval | h |
| T | Temperature | °C, K |
| t1 | Time 1 | h |
| t2 | Time 2 | h |
| x | Biomass concentration | g L−1 |
| Yxs | True biomass yield from substrate | g of biomass per g of substrate |
| ΔP | Transmembrane pressure | Pa |
| Greek Symbols | ||
| Symbol | Description | Units |
| α | Constant that depends on Ksu and S0. | - |
| β | Experimentally determined constant | - |
| ϕ | Water osmotic factor | Pa L K−1 g−1 |
| θ | Experimentally determined constant | - |
| µw | Water viscosity | Pa s |
| µpw | Pure water viscosity | Pa s |
| Δπ | Transmembrane osmotic pressure | Pa |
Appendix A
References
- du Plessis, A. Water Resources from a Global Perspective. In South Africa’s Water Predicament: Freshwater’s Unceasing Decline; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Park, K.; Kim, J.; Alayande, A.B.; Kim, Y. Seawater Reverse Osmosis (SWRO) Desalination: Energy Consumption in Plants, Advanced Low-Energy Technologies, and Future Developments for Improving Energy Efficiency; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, N.A.; Elcik, H.; Alpatova, A.; Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Blankert, B.; Farhat, N.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Ghaffour, N. Selected physical and chemical cleanings remove biofilm in seawater membrane distillation without causing pore wetting. NPJ Clean Water 2023, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Vanoppen, M.; van Agtmaal, J.M.C.; Cornelissen, E.R.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Verliefde, A.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Picioreanu, C. Cost of fouling in full-scale reverse osmosis and nanofiltration installations in The Netherlands. Desalination 2021, 500, 114865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.; Vrouwenvelder, J.; Van Loosdrecht, M.; Picioreanu, C. Modeling the effect of biofilm formation on reverse osmosis performance: Flux, feed channel pressure drop and solute passage. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 365, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.; Sethi, S.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.; Fimbres-Weihs, G. Applications of Iron Nanoparticles on Osmotic Membrane Processes to Reduce Energy Consumption and Biofouling. In Nanomaterials for Energy Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 308–322. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, J.; Herzberg, M. Cake/Biofilm Enhanced Concentration Polarization. In Encyclopedia of Membrane Science and Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Abushawish, A.; Bouaziz, I.; Almanassra, I.W.; AL-Rajabi, M.M.; Jaber, L.; Khalil, A.K.A.; Takriff, M.S.; Laoui, T.; Shanableh, A.; Atieh, M.A.; et al. Desalination Pretreatment Technologies: Current Status and Future Developments. Water 2023, 15, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veza, J.M.; Ortiz, M.; Sadhwani, J.J.; Gonzalez, J.E.; Santana, F.J. Measurement of biofouling in seawater: Some practical tests. Desalination 2008, 220, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A.; de los Santos Villalobos, S.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G. Biofouling of FeNP-Coated SWRO Membranes with Bacteria Isolated after Pre-Treatment in the Sea of Cortez. Coatings 2019, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashkeev, S.N.; Shomar, B. A simple reaction-diffusion model for initial stages of biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes. Environ. Res. 2020, 190, 110000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushaban, A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Philibert, M.; Le Bouille, L.; Necibi, M.C.; Chehbouni, A. Biofouling potential indicators to assess pretreatment and mitigate biofouling in SWRO membranes: A short review. Desalination 2022, 527, 115543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Álvarez-Sánchez, J.; Dévora-Isiordia, G.E.; García, A.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A. Effect of seawater variability on endemic bacterial biofouling of a reverse osmosis membrane coated with iron nanoparticles (FeNPs). Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 223, 115753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kubaish, A.; Salama, J. Impacts of Climate Change on Seawater Temperature and Total Dissolved Solids: Challenges and Sustainable Solutions for Reverse Osmosis Desalination in the Arabian Gulf Region. Comput. Water Energy Environ. Eng. 2023, 13, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Weigand, T.M.; Edalat, A. Reverse osmosis membrane biofouling: Causes, consequences and countermeasures. npj Clean Water 2022, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucs, S.S.; Radu, A.I.; Lavric, V.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Picioreanu, C. Effect of different commercial feed spacers on biofouling of reverse osmosis membrane systems: A numerical study. Desalination 2014, 343, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najid, N.; Hakizimana, J.N.; Kouzbour, S.; Gourich, B.; Ruiz-García, A.; Vial, C.; Stiriba, Y.; Semiat, R. Fouling control and modeling in reverse osmosis for seawater desalination: A review. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2022, 162, 107794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, N.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Ampah, J.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D. Measuring Biofouling Potential in SWRO Plants with a Flow-Cytometry-Based Bacterial Growth Potential Method. Membranes 2021, 11, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maceiras, A.R.; Graca, L. Identification of Foxp3+ T Follicular Regulatory (Tfr) Cells by Flow Cytometry. In T Follicular Helper Cells: Methods and Protocols; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Drioli, E.; Criscuoli, A.; Macedonio, F. Membrane-Based Desalination: An Integrated Approach (MEDINA); IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Philibert, M.; Villacorte, L.O.; Ekowati, Y.; Abushaban, A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G. Fouling and scaling in reverse osmosis desalination plants: A critical review of membrane autopsies, feedwater quality guidelines and assessment methods. Desalination 2024, 592, 118188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elma, M.; Rahma, A.; Mustalifah, F.R.; Wahid, A.R.; Lamandau, D.R.; Fatimah, S.; Huda, M.S.; Alsiren, M.A.; Nasruddin; Saraswati, N.K.D.A.; et al. Nanofiltration Technology Applied for Peat and Wetland Saline Water. In Nanofiltration Membrane for Water Purification; Ahmad, A., Alshammari, M.B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 217–245. [Google Scholar]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Fortunato, L.; Salinas-Rodríguez, S.G.; Villacorte, L.O. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) as a Tool for (Bio)-fouling Assessment in Desalination Systems. In Experimental Methods for Membrane Applications in Desalination and Water Treatment; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fortunato, L.; Bucs, S.; Linares, R.V.; Cali, C.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Leiknes, T. Spatially-resolved in-situ quantification of biofouling using optical coherence tomography (OCT) and 3D image analysis in a spacer filled channel. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, L.; Jeong, S.; Leiknes, T. Time-resolved monitoring of biofouling development on a flat sheet membrane using optical coherence tomography. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, M.; Ujihara, R.; Vogt, S.J.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Fridjonsson, E.O.; Johns, M.L. Imaging of membrane concentration polarization by NaCl using 23Na nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 600, 117868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creber, S.A.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Johns, M.L. Chemical cleaning of biofouling in reverse osmosis membranes evaluated using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridjonsson, E.O.; Vogt, S.J.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Johns, M.L. Early non-destructive biofouling detection in spiral wound RO membranes using a mobile earth’s field NMR. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 489, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manalo, C.V.; Nishijima, W. Biofouling Detection on Reverse Osmosis Membranes. In Water and Wastewater Treatment Technologies; Bui, X.-T., Chiemchaisri, C., Fujioka, T., Varjani, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 379–402. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Z.; Nghiem, L.D.; Wang, Q. Biofouling control of reverse osmosis membrane using free ammonia as a cleaning agent. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 694, 122414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali Heris, S.; Bagheri Khaniani, P.; Mousavi, S.B. Photocatalytic degradation of co-amoxiclav using hybrid TiO2/ZnO nanoparticles: Experimental and optimization. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 70, 107040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, B.E.; Armendariz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Quezada, R.; Huitrón-Segovia, E.A.; Estay, H.; García García, A.; García, A. Influence of Multidimensional Graphene Oxide (GO) Sheets on Anti-Biofouling and Desalination Performance of Thin-Film Composite Membranes: Effects of GO Lateral Sizes and Oxidation Degree. Polymers 2020, 12, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhu, T.; Tang, J.; Gan, W.; Nong, G. Doping silver nanoparticles into reverse osmosis membranes for antibacterial properties. e-Polymers 2023, 23, 20228087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Valenzuela, P.G.; Álvarez-Sánchez, J.; Dévora-Isiordia, G.E.; Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; del Rosario Martínez-Macias, M.; Pérez-Sicairos, S.; Sánchez-Duarte, R.G.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A. Modification and characterization of TFC membranes with Ag nanoparticles: Application in seawater desalination. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 6285–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; García-García, A.; Mai-Prochnow, A.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A. Optimal loading of iron nanoparticles on reverse osmosis membrane surface to reduce biofouling. Desalination 2022, 540, 115997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Water Intelligent (GWI). Desalting Plant Inventory. 2022. Available online: https://www.desaldata.com/ (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Armendariz Ontiveros, M.M.; Quintero, Y.; Llanquilef, A.; Morel, M.; Argentel Martínez, L.; García García, A.; Garcia, A. Anti-Biofouling and Desalination Properties of Thin Film Composite Reverse Osmosis Membranes Modified with Copper and Iron Nanoparticles. Materials 2019, 12, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnathan, B.J.; Stevens, D.; Shikha, S.; Slater, C.; Byford, N.; Sturdivant, R.X.; Zarzosa, K.; Braswell, W.E.; Sayes, C.M. Assessing the Effects of Surface-Stabilized Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles on Diverse Bacteria Species Using Complementary Statistical Models. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, O.T.; Motsa, M.M.; Richards, H.; Mamba, B.B.; George, M.J.; Nthunya, L.N. The impact of nanoparticle leach on sustainable performance of the membranes—A critical review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.L. The Monod Model and Its Alternatives. In Mathematical Modeling in Microbial Ecology; Koch, A.L., Robinson, J.A., Milliken, G.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 62–93. [Google Scholar]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; García García, A.; de los Santos Villalobos, S.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A. Biofouling performance of RO membranes coated with Iron NPs on graphene oxide. Desalination 2019, 451, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, P.M. Bioprocess Engineering Principles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kedem, O.; Katchalsky, A. Thermodynamic analysis of the permeability of biological membranes to non-electrolytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1958, 27, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki Valenzuela, M.F.; Sánchez Soto, F.; Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Sosa-Tinoco, I.M.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A. Improving thermal distribution in water-cooled PV modules and its effect on RO permeate recovery. Water 2021, 13, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.; Pandey, D.K.; Nongdam, P.; Shekhawat, M.S.; Dey, A.; Choudhary, K.; Sahay, S. Halophilic, Acidophilic, Alkaliphilic, Metallophilic, and Radioresistant Fungi: Habitats and Their Living Strategies. In Extremophilic Fungi: Ecology, Physiology and Applications; Sahay, S., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 171–193. [Google Scholar]
- Kevbrin, V.V. Isolation and Cultivation of Alkaliphiles. In Alkaliphiles in Biotechnology; Mamo, G., Mattiasson, B., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 53–84. [Google Scholar]
- Mangrola, A.V.; Patel, R.K.; Dudhagara, P.; Gandhi, H.; Ghelani, A.; Jain, K.R.; Shah, H.; Mevada, V.A. Thermophiles: Physiology, Metabolism, Enzymology, and Adaptation Mechanisms. In Physiology, Genomics, and Biotechnological Applications of Extremophiles; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2022; pp. 65–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Pundir, S. Bacterial cell, classification and required essential contents for growth. Asian J. Pharm. Technol. 2021, 11, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Lepcha, K.; Basak, A.; Mahanty, A.K. Chapter 16—Thermophiles and thermophilic hydrolases. In Physiological and Biotechnological Aspects of Extremophiles; Salwan, R., Sharma, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 219–236. [Google Scholar]
- DuPont, W.S. FilmTec™ SW30 Seawater Elements, Product Data Sheet. 2024. Available online: https://www.dupont.com/content/dam/water/amer/us/en/water/public/documents/en/RO-FilmTec-SW30-Seawater-PDS-45-D01519-en.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2024).
- Maddah, H.; Chogle, A. Biofouling in reverse osmosis: Phenomena, monitoring, controlling and remediation. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, L.; Esposito, R.; Nunes, S.P.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Fortunato, L. Biofilm rigidity, mechanics and composition in seawater desalination pretreatment employing ultrafiltration and microfiltration membranes. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Saha, J.; Sarkar, M.; Mandal, P. Bacterial survival strategies and responses under heavy metal stress: A comprehensive overview. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, C.; Li, K.; Su, L.; Zhang, S.; Yue, Q.; Zhao, L. Salt-tolerant mechanism and application of salt-tolerant bacteria. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Green Environmental Materials and Food Engineering, Gemfe, Tianjin, China, 26–27 March 2022; pp. 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Tawalbeh, M.; Qalyoubi, L.; Al-Othman, A.; Qasim, M.; Shirazi, M. Insights on the development of enhanced antifouling reverse osmosis membranes: Industrial applications and challenges. Desalination 2023, 553, 116460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.; Stevens, G.; Kentish, S. The effect of feed pH on the performance of a reverse osmosis membrane. Desalination 2010, 261, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, E.M.; Pranić, M.; Porada, S.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Ryzhkov, I.I.; van der Meer, W.G.J.; Biesheuvel, P.M. The influence of feedwater pH on membrane charge ionization and ion rejection by reverse osmosis: An experimental and theoretical study. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 660, 120800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Villegas-Peralta, Y.; Madueño-Moreno, J.E.; Álvarez-Sánchez, J.; Dévora-Isiordia, G.E.; Sánchez-Duarte, R.G.; Madera-Santana, T.J. Modification of Thin Film Composite Membrane by Chitosan–Silver Particles to Improve Desalination and Anti-Biofouling Performance. Membranes 2022, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Wen, D.; Bates, C.T.; Wu, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, S.; Su, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y. Nutrient supply controls the linkage between species abundance and ecological interactions in marine bacterial communities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Vione, D.; Rivoira, L.; Carena, L.; Castiglioni, M.; Bruzzoniti, M.C. A Review on the Degradation of Pollutants by Fenton-Like Systems Based on Zero-Valent Iron and Persulfate: Effects of Reduction Potentials, pH, and Anions Occurring in Waste Waters. Molecules 2021, 26, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmond, P.; Huisman, K.T.; Sanawar, H.; Farhat, N.M.; Traber, J.; Fridjonsson, E.O.; Johns, M.L.; Flemming, H.-C.; Picioreanu, C.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Controlling the hydraulic resistance of membrane biofilms by engineering biofilm physical structure. Water Res. 2022, 210, 118031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, A.; Xia, B.; Vyas, H.K.N.; Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Lin, Y.-C.; Garcia-Garcia, A.; Wang, D.K.; Cullen, P.J.; Fimbres Weihs, G.; Mai-Prochnow, A. Iron nanoparticle coating and plasma-activated water cleaning as a biofouling removal method for reverse osmosis membranes suitable for desalination. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonyadi, E.; Niknejad, A.S.; Ashtiani, F.Z.; Bazgir, S.; Kargari, A. A well-designed polystyrene/polycarbonate membrane for highly saline water desalination using DCMD process. Desalination 2022, 528, 115604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamar, A.; Kerdi, S.; Amin, N.; Zhang, X.; Vrouwenvelder, J.; Ghaffour, N. A deep neural networks framework for in-situ biofilm thickness detection and hydrodynamics tracing for filtration systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 121959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Amin, S.; Mohamed, A.A. Fouling in reverse osmosis membranes: Monitoring, characterization, mitigation strategies and future directions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, W.; Jin, J.; Meng, S.; He, Z.; Ali, M.; Saikaly, P.E. Filtration performance of biofilm membrane bioreactor: Fouling control by threshold flux operation. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, T.; Buijs, P.J.; Farinha, A.S.F.; Borges, V.R.P.; Farhat, N.M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Das, R. Seawater Reverse Osmosis Performance Decline Caused by Short-Term Elevated Feed Water Temperature. Membranes 2022, 12, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Dévora-Isiordia, G.E.; Rodríguez-López, J.; Sánchez-Duarte, R.G.; Álvarez-Sánchez, J.; Villegas-Peralta, Y.; Martínez-Macias, M.d.R. Effect of Temperature on Energy Consumption and Polarization in Reverse Osmosis Desalination Using a Spray-Cooled Photovoltaic System. Energies 2022, 15, 7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| T (°C) | k (h−1) | YXS (g g−1) | ILP (h) | FLP (h) | pH | k (h−1) | YXS (g g−1) | ILP (h) | FLP (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 12.72 ± 0.06 | 2 | 16 | 4 | 0.56 ± 0.07 | 13.35 ± 0.06 | 6 | 15 |
| 30 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 17.31 ± 0.51 | 2 | 16 | 5 | 0.37 ± 0.04 | 14.74 ± 0.01 | 3 | 13 |
| 34 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 20.91 ± 0.01 | 3 | 14 | 6 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 16.36 ± 0.07 | 4 | 17 |
| 38 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 22.45 ± 0.27 | 2 | 14 | 7 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 19.63 ± 0.06 | 5 | 16 |
| 42 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 27.37 ± 0.38 | 2 | 18 | 8 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 19.33 ± 0.09 | 3 | 17 |
| 48 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 15.49 ± 0.20 | 5 | 17 | 9 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 20.23 ± 0.09 | 3 | 16 |
| 50 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 00.00 ± 0.00 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 23.97 ± 0.08 | 1 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Romero-Cortes, T.; Pérez España, V.H.; Cuervo-Parra, J.A.; Peralta-Gil, M.; Martinez Macias, M.d.R.; Fimbres Weihs, G.A. Simulation of Biofouling Caused by Bacillus halotolerans MCC1 on FeNP-Coated RO Membranes. Processes 2025, 13, 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051422
Armendáriz-Ontiveros MM, Romero-Cortes T, Pérez España VH, Cuervo-Parra JA, Peralta-Gil M, Martinez Macias MdR, Fimbres Weihs GA. Simulation of Biofouling Caused by Bacillus halotolerans MCC1 on FeNP-Coated RO Membranes. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051422
Chicago/Turabian StyleArmendáriz-Ontiveros, Maria Magdalena, Teresa Romero-Cortes, Victor Hugo Pérez España, Jaime A. Cuervo-Parra, Martin Peralta-Gil, Maria del Rosario Martinez Macias, and Gustavo Adolfo Fimbres Weihs. 2025. "Simulation of Biofouling Caused by Bacillus halotolerans MCC1 on FeNP-Coated RO Membranes" Processes 13, no. 5: 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051422
APA StyleArmendáriz-Ontiveros, M. M., Romero-Cortes, T., Pérez España, V. H., Cuervo-Parra, J. A., Peralta-Gil, M., Martinez Macias, M. d. R., & Fimbres Weihs, G. A. (2025). Simulation of Biofouling Caused by Bacillus halotolerans MCC1 on FeNP-Coated RO Membranes. Processes, 13(5), 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051422







