Intelligent Classification Method for Tight Sandstone Reservoir Evaluation Based on Optimized Genetic Algorithm and Extreme Gradient Boosting
Abstract
1. Introduction
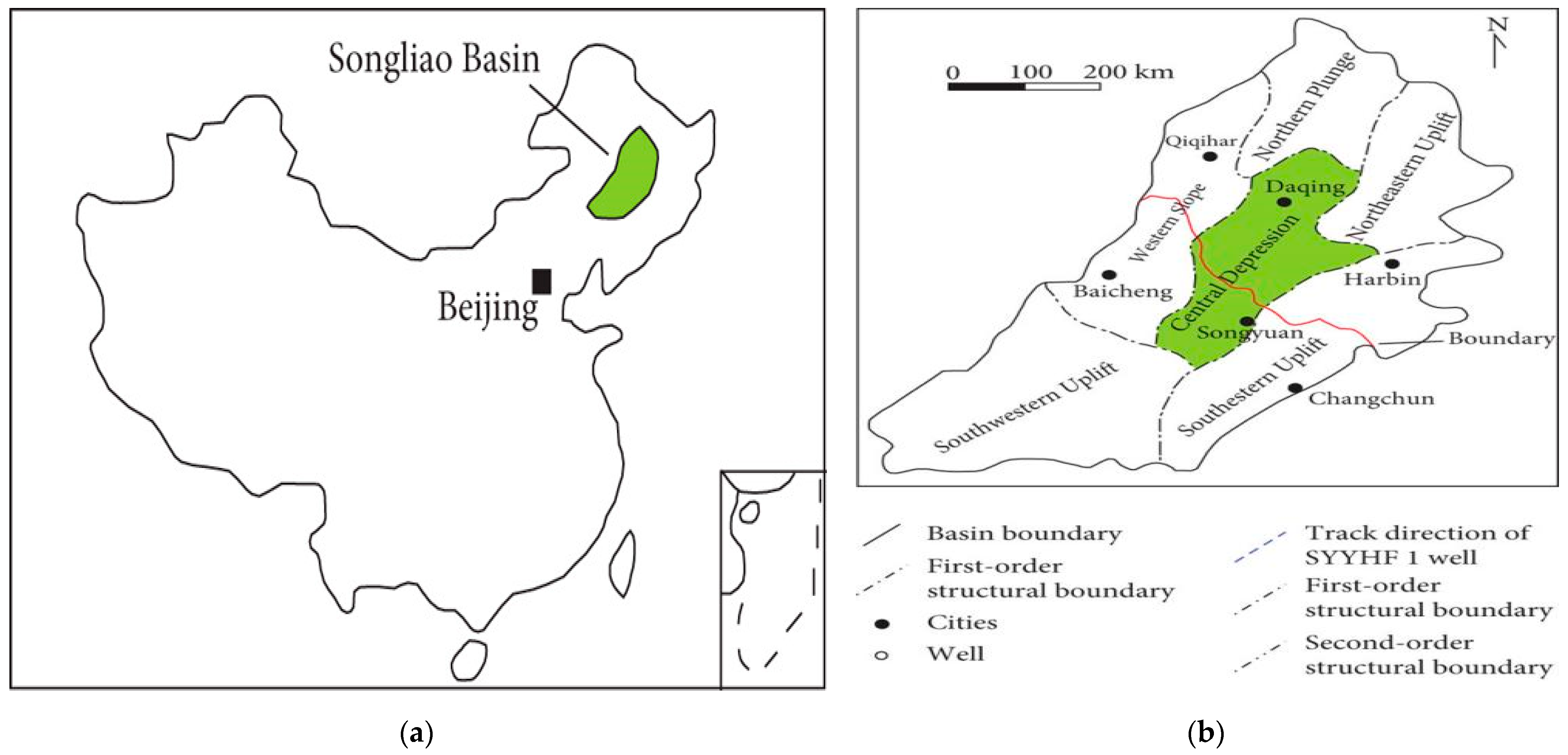
2. Overview of the Study Area
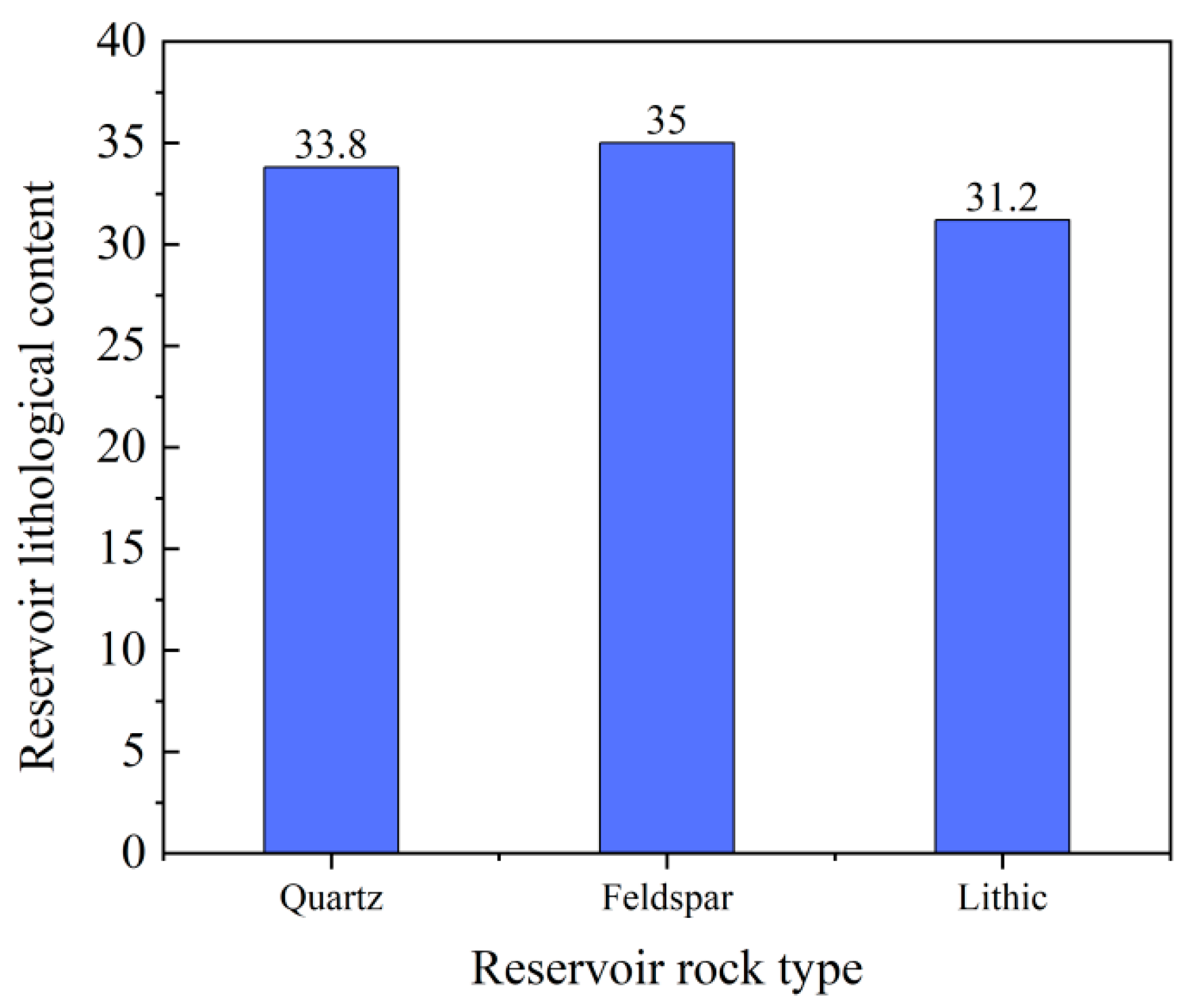
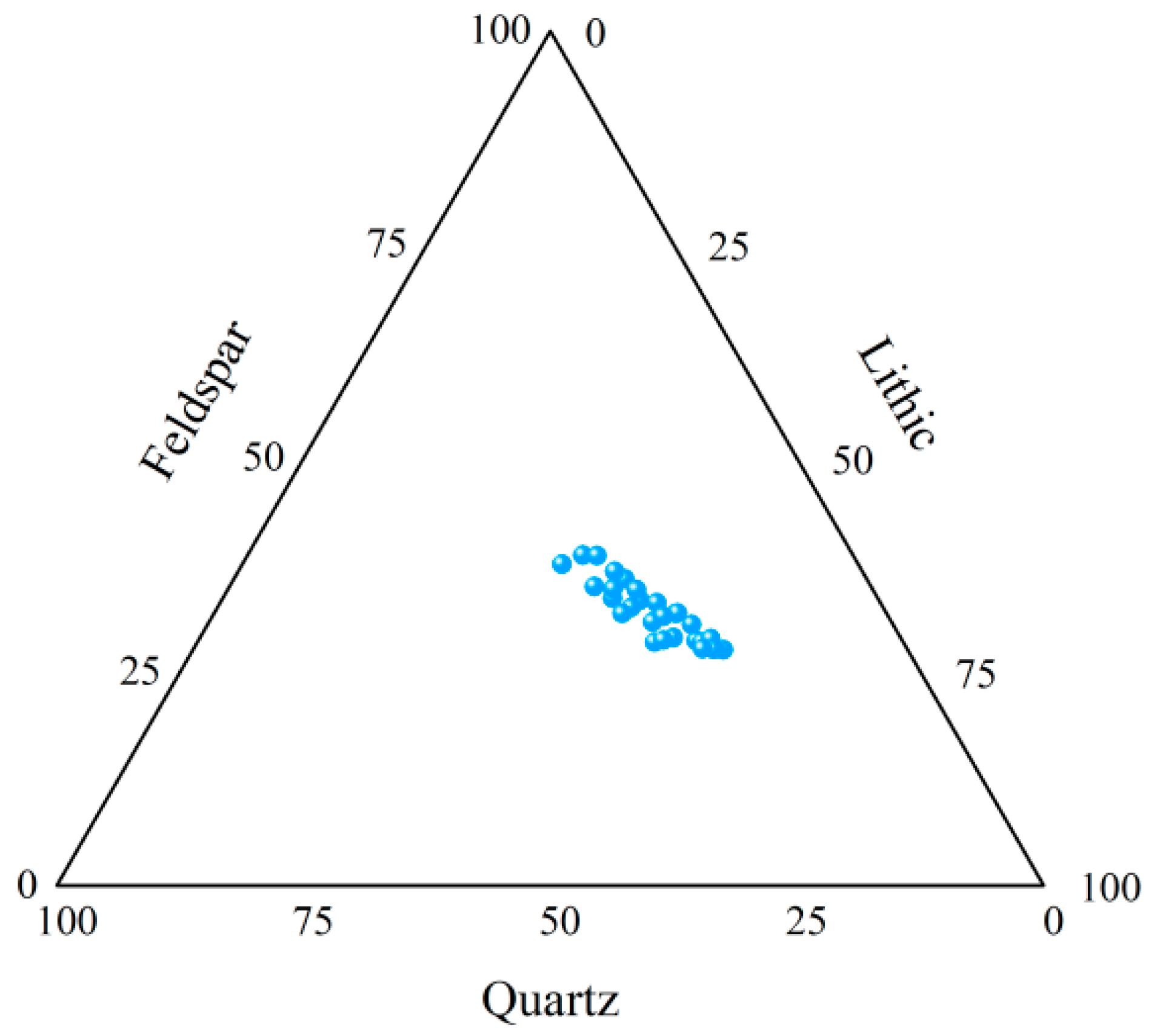
2.1. Lithological Characteristics of the Reservoir
2.2. Physical Characteristics of the Reservoir
2.3. Lithofacies Characteristics of the Reservoir
- Tabular Cross-stratified Fine Sandstone, Sa
- Troughed Cross-bedding Fine Sandstone, St
- Parallel Stratified Fine Sandstone Facies, Sp
- Undulating Stratified Fine Sandstone Facies, Sw
- Horizontal Stratified Siltstone Facies, Fh
- Undulating Bedding Argillaceous Siltstone, Fw
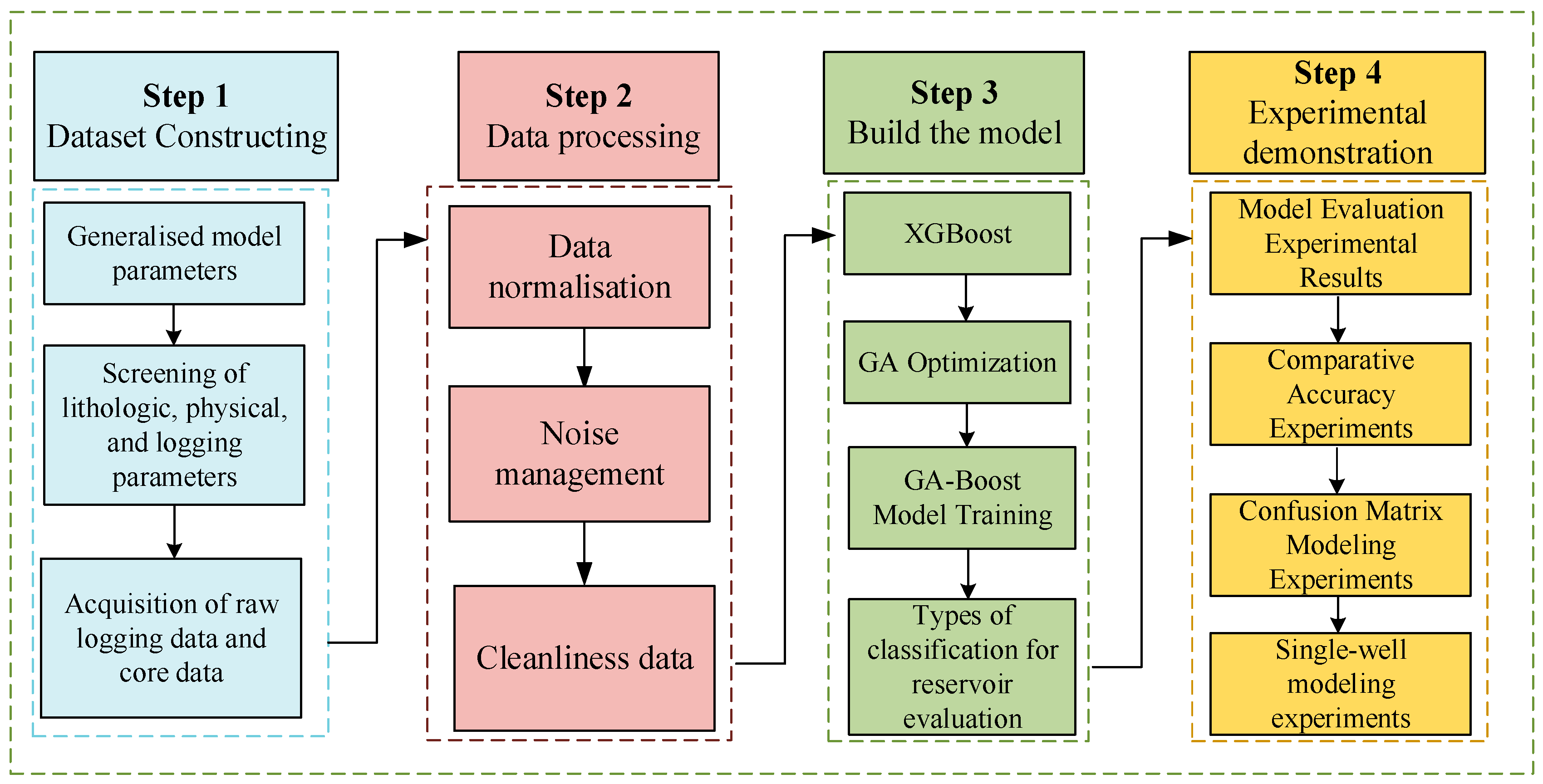
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset Analysis
3.1.1. Feature Parameter Selection
- Mineral composition (quartz, feldspar, lithic)
- Reservoir physical properties (porosity, permeability, oil saturation)
- Logging curve parameters (GR, SP, CAL, DEN, AC, LLS)
3.1.2. Data Preprocessing
3.2. GA-XGBoost Model
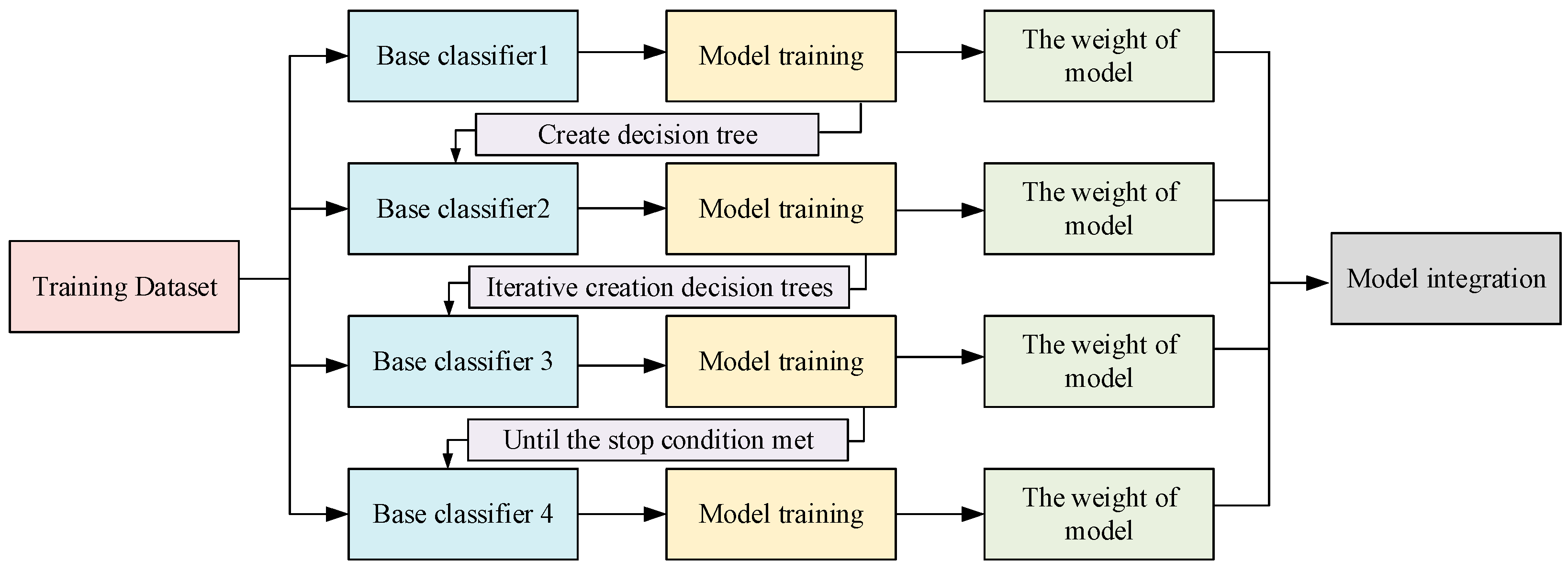
3.2.1. Extreme Gradient Boosting Algorithm
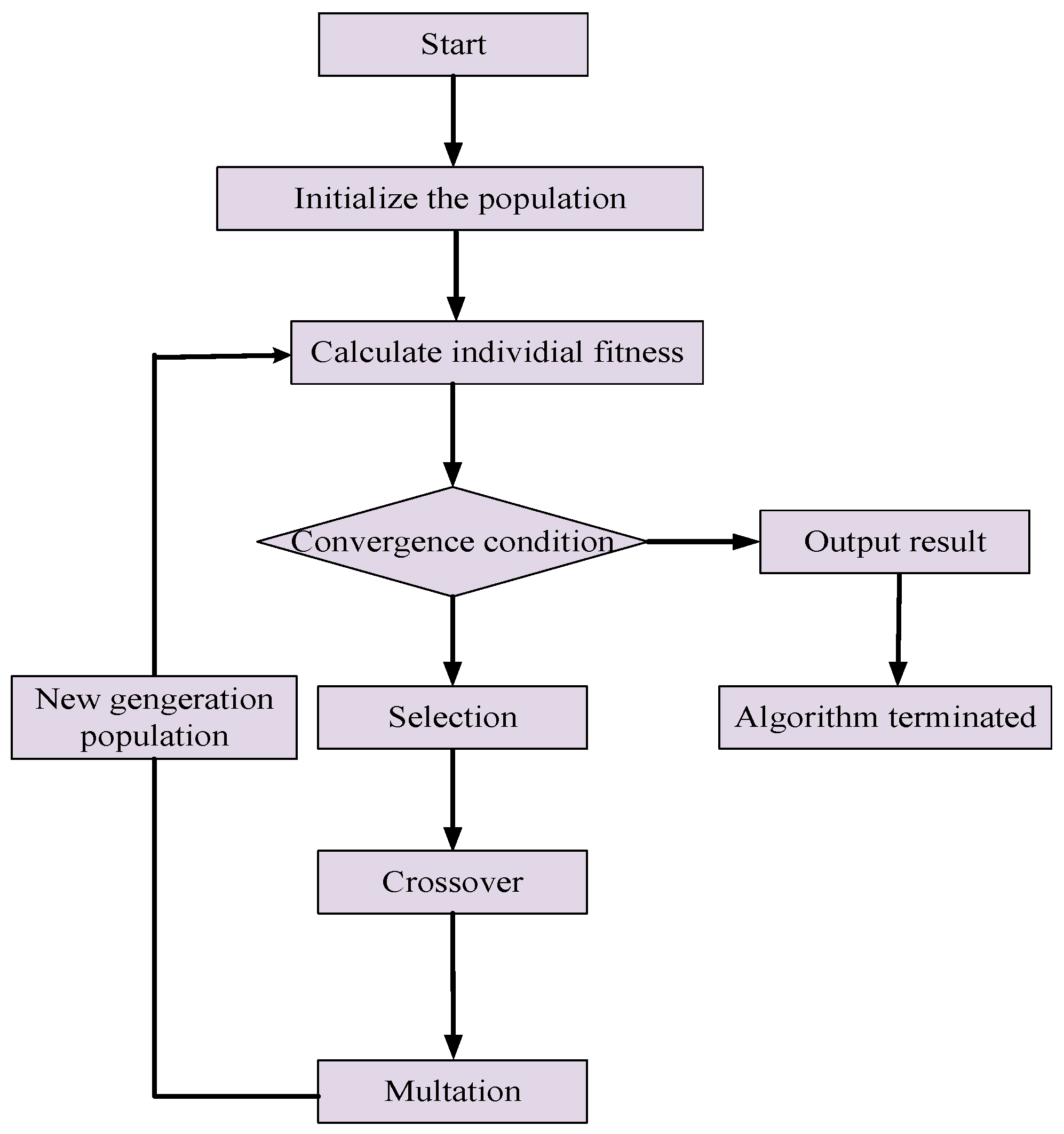
3.2.2. Genetic Algorithm
- (1)
- Selection
- (2)
- Crossover
- (3)
- Mutation
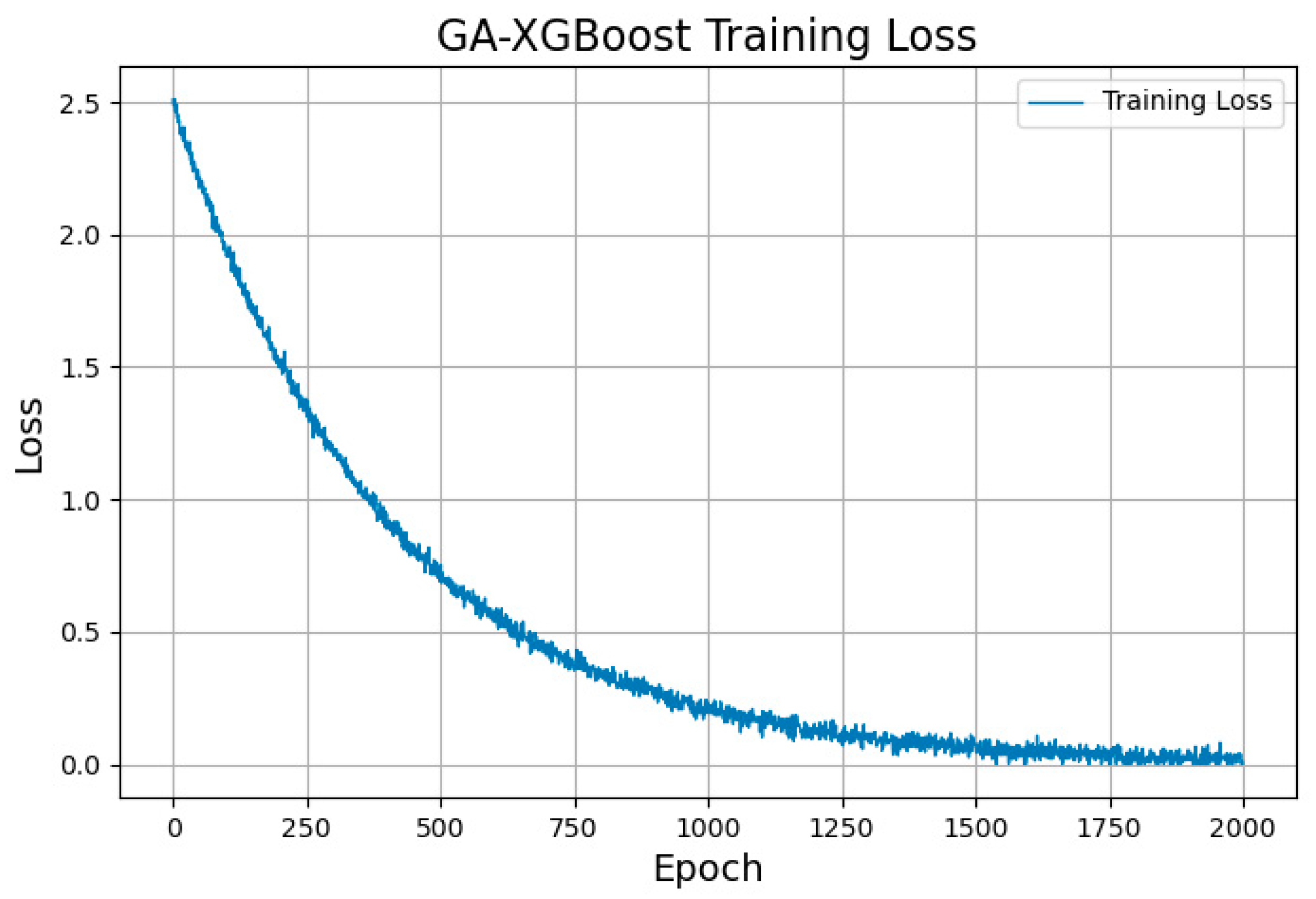
3.2.3. GA-XGBoost Model Training
3.3. Experimental Scheme
3.3.1. Model Evaluation Experiment
3.3.2. Accuracy Comparison Experiment
3.3.3. Confusion Matrix Model Experiment
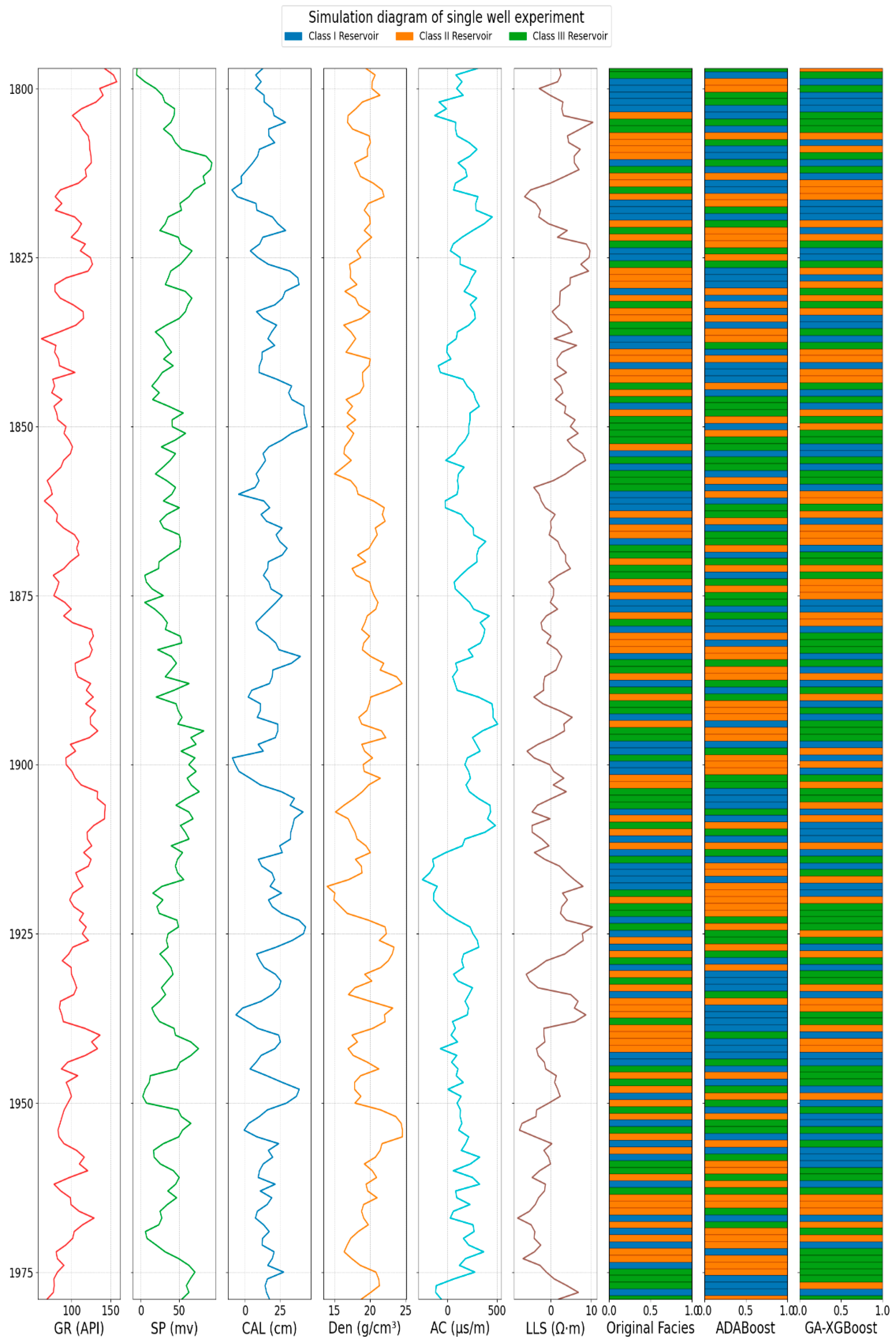
3.3.4. Single-Well Model Experiment
4. Results
4.1. Model Evaluation Results
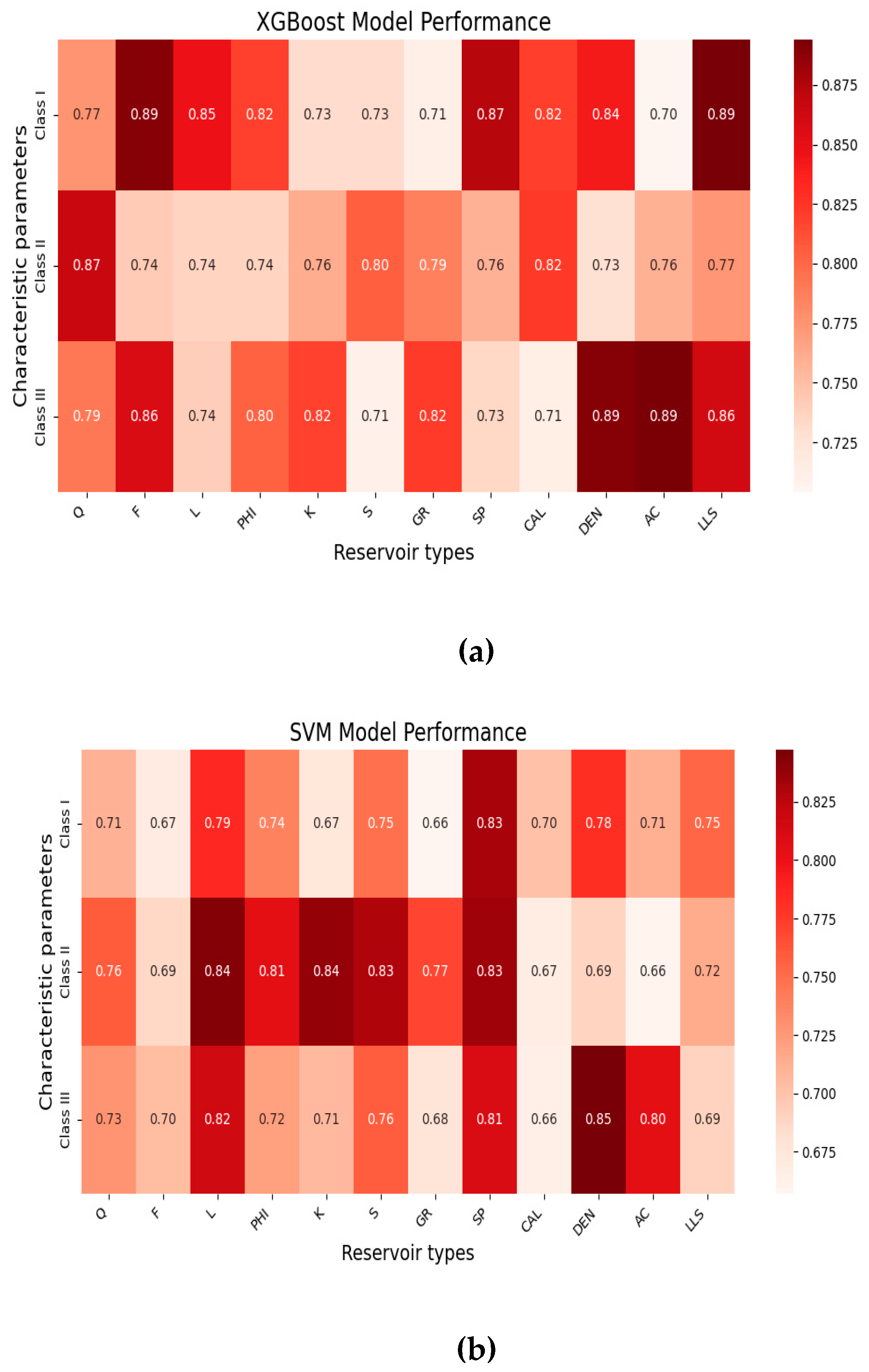
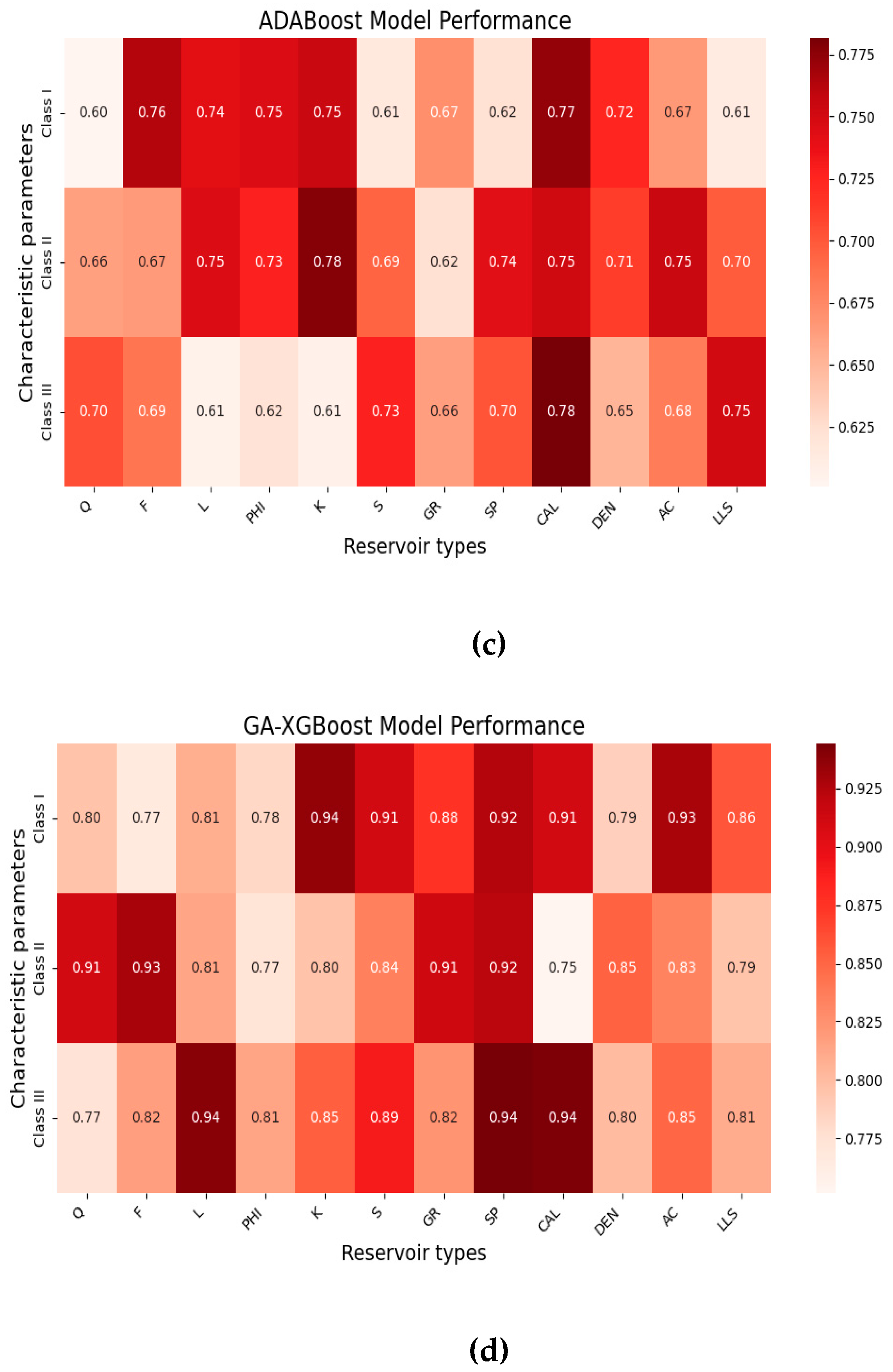
4.1.1. Precision, Recall, F1-Score Results
4.1.2. RMSE, MSE, and MAE Results
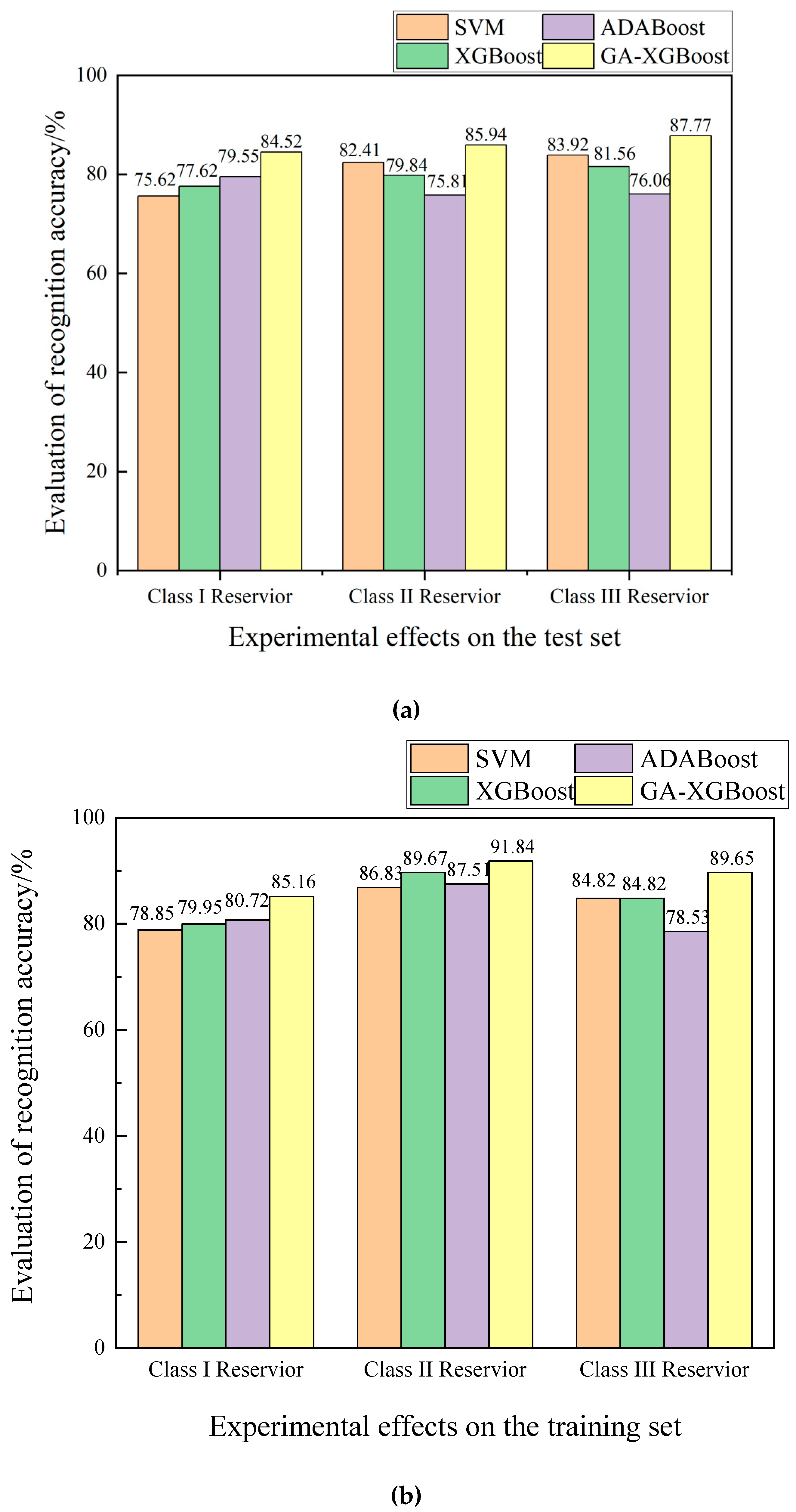
4.2. Accuary Comparison Results
4.3. Confusion Matrix Model Results
4.4. Single-Well Model Results
5. Discussion
Future Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| ADABoost | Adaptive Boosting |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| GR | Gamma Ray |
| SP | Spontaneous Potential |
| CAL | Caliper Log |
| DEN | Density |
| AC | Acoustic |
| LLS | Shallow lateral resistivity |
| SHAP | Shapley Additive Explanations |
| GA-XGBoost | Genetic Algorithm-Extreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Liu, C.; Zhou, B.; Wang, B.S.; Wang, H.; You, Q.; Zhao, G.; Dai, C.L. Synthesis of temperature and salt resistance silicon dots for effective enhanced oil recovery in tight reservoir. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 3390–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Tan, M.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, G. Fluid Identification Method of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Array Acoustic Logging for Complex Oil and Water Layers in Tight Sandstone Reservoir. Processes 2023, 11, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Qiu, F.; Liu, N.; Cai, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, B.; Qiu, Y. Pore structure characterization and its significance for gas adsorption in coals: A comprehensive review. Unconv. Resour. 2022, 2, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ding, C.; Du, Y.; Wang, J. Advances in Reservoir Evaluation Research. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2015, 34, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Q.; Xie, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Hao, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Single-Factor Comprehensive Reservoir Quality Classification Evaluation─ Taking the Hala’alat Mountains at the Northwestern Margin of the Junggar Basin as an Example. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 37065–37079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharavi, A.; Abbas, K.A.; Hassan, M.G.; Haddad, M.; Ghoochaninejad, H.; Alasmar, R.; Shigidi, I. Unconventional reservoir characterization and formation evaluation: A case study of a tight sandstone reservoir in West Africa. Energies 2023, 16, 7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, F.; Feng, N.; Li, L.; Shen, X.; Yu, H. Big data technique in the reservoir parameters’ prediction and productivity evaluation: A field case in western South China sea. Gondwana Res. 2021, 96, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Cao, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M. Research and Application of Reservoir Classification Method Based on Deep Learning. In Electronic, Proceedings of the CPS/SEG Beijing 2018 International Geophysical Conference & Exhibition, Beijing, China, 24–27 April 2018; China Petroleum Society: Beijing, China; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Beijing, China; School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum (East China): Beijing, China; Exploration and Development Research Institute, PetroChina Jidong Oilfield Company: Beijing, China, 2018; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Wei, W.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, K.Y.; Liu, Y.S. Characteristics, classification, and KNN-based evaluation of paleokarst carbonate reservoirs: A case study of Feixianguan Formation in northeastern Sichuan Basin, China. Energy Geosci. 2023, 4, 100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Liu, J.C. An intelligent approach for reservoir quality evaluation in tight sandstone reservoir using gradient boosting decision tree algorithm—A case study of the Yanchang Formation, mid-eastern Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2021, 126, 104939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.L.; Chen, H.; Xing, J.P.; Shang, L.; Wang, Q.H.; Sun, Y.C.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, J.; Lan, D.C. A novel method of quantitative evaluation and comprehensive classification of low permeability-tight oil reservoirs: A case study of Jidong Oilfield, China. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Deng, S.; Xu, F.; Niu, Y.; Hu, X. Multi-parameter logging evaluation of tight sandstone reservoir based on petrophysical experiment. Acta Geophys. 2021, 69, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.R.; Thota, S.T.; Norsahminan, D.N.P.; Kamalrulzaman, K.N.; Matter, W.S.; Al-Awah, H. Reservoir quality evaluation using petrophysical, well-log analysis, and petrographical description: A case study from the Carboniferous-Permian Kulshill group formations, southern Bonaparte Basin, Australia. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 226, 211738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Pang, X.; Xiao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, T.; Qin, Z. Prediction of reservoir quality in carbonates via porosity spectrum from image logs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 173, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.A.; Al Lawe, E.M. Clustering analysis and flow zone indicator for electro facies characterization in the Upper Shale Member in Luhais Oil Field, Southern Iraq. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition & Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 11–14 November 2019; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Feng, C.; Li, T.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, X.; Sun, M.; Ge, Y. Quantitative classification evaluation model for tight sandstone reservoirs based on machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ruhan, A.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y. Study on reservoir characteristics and evaluation methods of altered igneous reservoirs in Songliao Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.H.; Xie, R.H.; Xiao, L.Z.; Guo, J.F.; Jin, G.W.; Fu, J.W. Integrated classification method of tight sandstone reservoir based on principal component analysis—Simulated annealing genetic algorithm—Fuzzy cluster means. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 2747–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yang, J.; Rao, L.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, K.; Yan, C. Classification and evaluation of flow units in tight sandstone reservoirs based on neural network model: A case study of Chang 6 Oil Layer Group in the Northern Part of WQ Area, Ordos Basin. J. Xi’an Shiyou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 39, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ji, W.; Wang, D. Logging Evaluation Method for Tight Sandstone Reservoirs Based on Cluster Analysis. Petrochem. Ind. Appl. 2024, 43, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Xiao, H.; Tao, J.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, H. An intelligent approach for reservoir quality evaluation in tight sandstone reservoir using gradient boosting decision tree algorithm. Open Geosci. 2022, 14, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Research on Reservoir Pore Structure Evaluation and Reservoir Classification Prediction Methods Based on Deep Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xing, X.; Hu, K.; Zhou, B. Classification and evaluation of tight sandstone reservoirs based on MK-SVM. Processes 2023, 11, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.Y.; Hou, M.C.; Chen, A.Q.; Zhong, H.T.; Qi, Z.; Ren, Q.; You, J.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Ma, C. Application of machine learning in the identification of fluvial-lacustrine lithofacies from well logs: A case study from Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 215, 110610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Ge, Y.; Tong, M.; Wang, Y.; An, L.; Yu, C.; Jia, X. Lithology logging curve prediction method based on XGBoost algorithm. Well Logging Technol. 2024, 48, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xu, L. A systematic machine learning method for reservoir identification and production prediction. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Hou, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Meng, W. Quantitative evaluation of unconsolidated sandstone heavy oil reservoirs based on machine learning. Geol. J. 2023, 58, 2321–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Lauria, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Fadzil, F.; Liu, H. Fusionformer: A novel adversarial transformer utilizing fusion attention for multivariate anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Mu, M.; Zhang, S. Intelligent Identification Method for the Diagenetic Facies of Tight Oil Reservoirs Based on Hybrid Intelligence—A Case Study of Fuyu Reservoir in Sanzhao Sag of Songliao Basin. Energies 2024, 17, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.P.; Hao, S.B.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.C.; Ding, J.H.; Tang, X.; Li, C.R.; Yu, X.F. Geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon expulsion of source rocks in the first member of the Qingshankou Formation in the Qijia-Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin, Northeast China: Evaluation of shale oil resource potential. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 5, 1450–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatefi, S.; Abdel Azim, R.; Alkouh, A.; Hamada, G. Integration of multiple Bayesian optimized machine learning techniques and conventional well logs for accurate prediction of porosity in carbonate reservoirs. Processes 2023, 11, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Extracting spatial effects from machine learning models using local interpretation methods: An example of SHAP and XGBoost. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2022, 96, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Luo, Z.; Guo, Y. Reservoir evaluation method based on explainable machine learning with small samples. Unconv. Resour. 2025, 5, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Joachims, T. Making Large-Scale SVM Learning Practical; Technical Report No. 1998,28; TU Dortmund University: Dortmund, Geramny, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schapire, R.E. Explaining AdaBoost. In Empirical Inference: Festschrift in Honor of Vladimir N. Vapnik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 37–52. [Google Scholar]
- Antariksa, G.; Muammar, R.; Lee, J. Performance evaluation of machine learning-based classification with rock-physics analysis of geological lithofacies in Tarakan Basin, Indonesia. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, T.O. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE): When to use them or not. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2022, 15, 5481–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
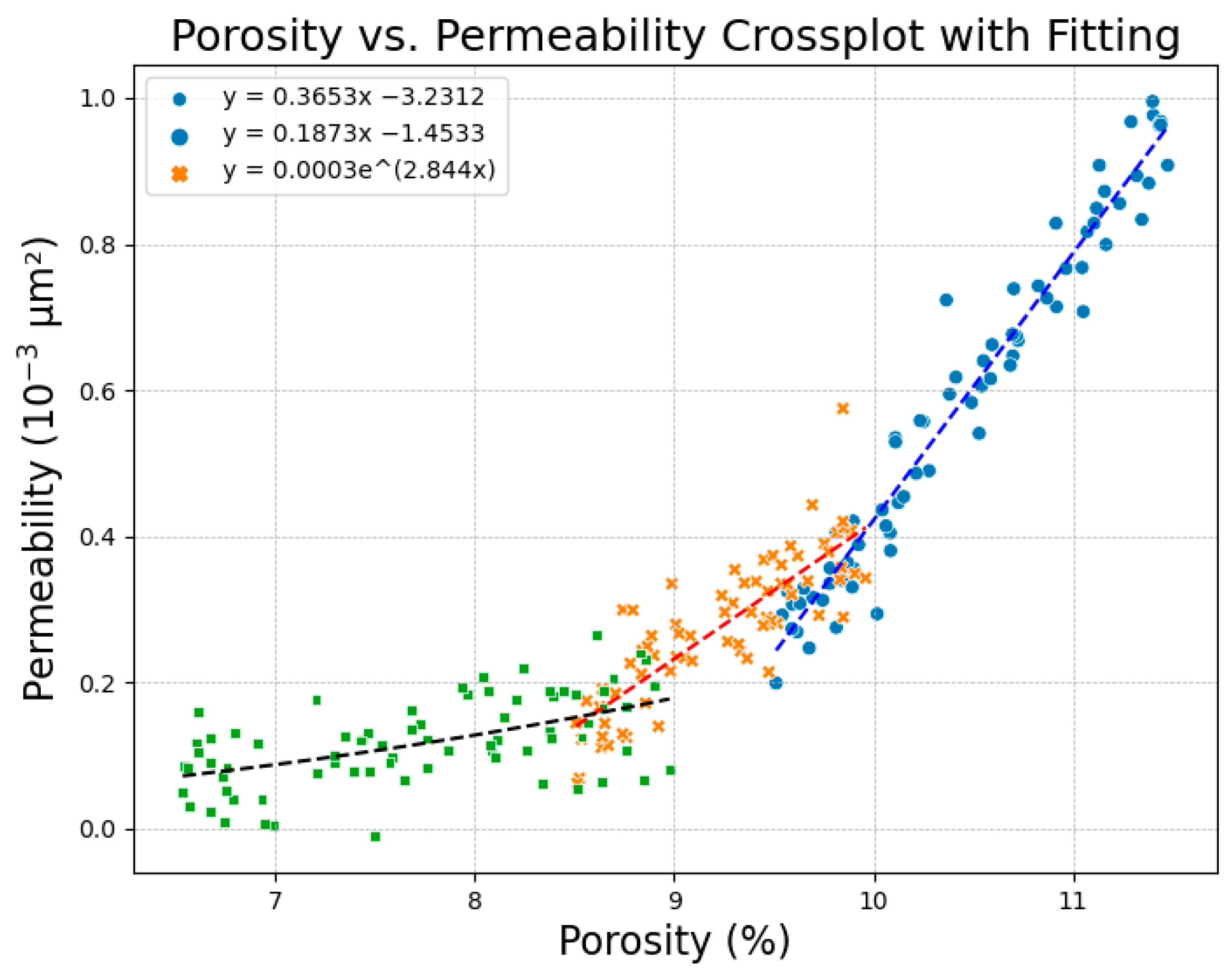
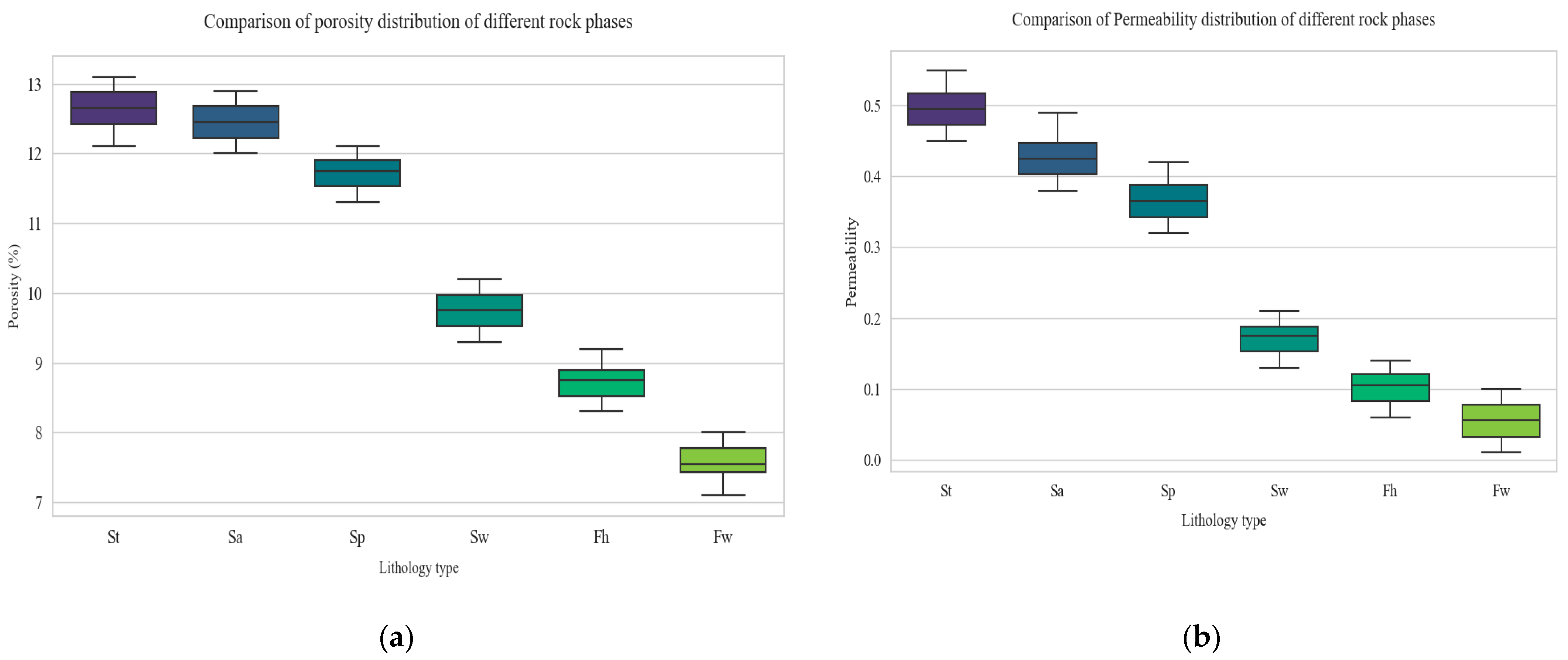
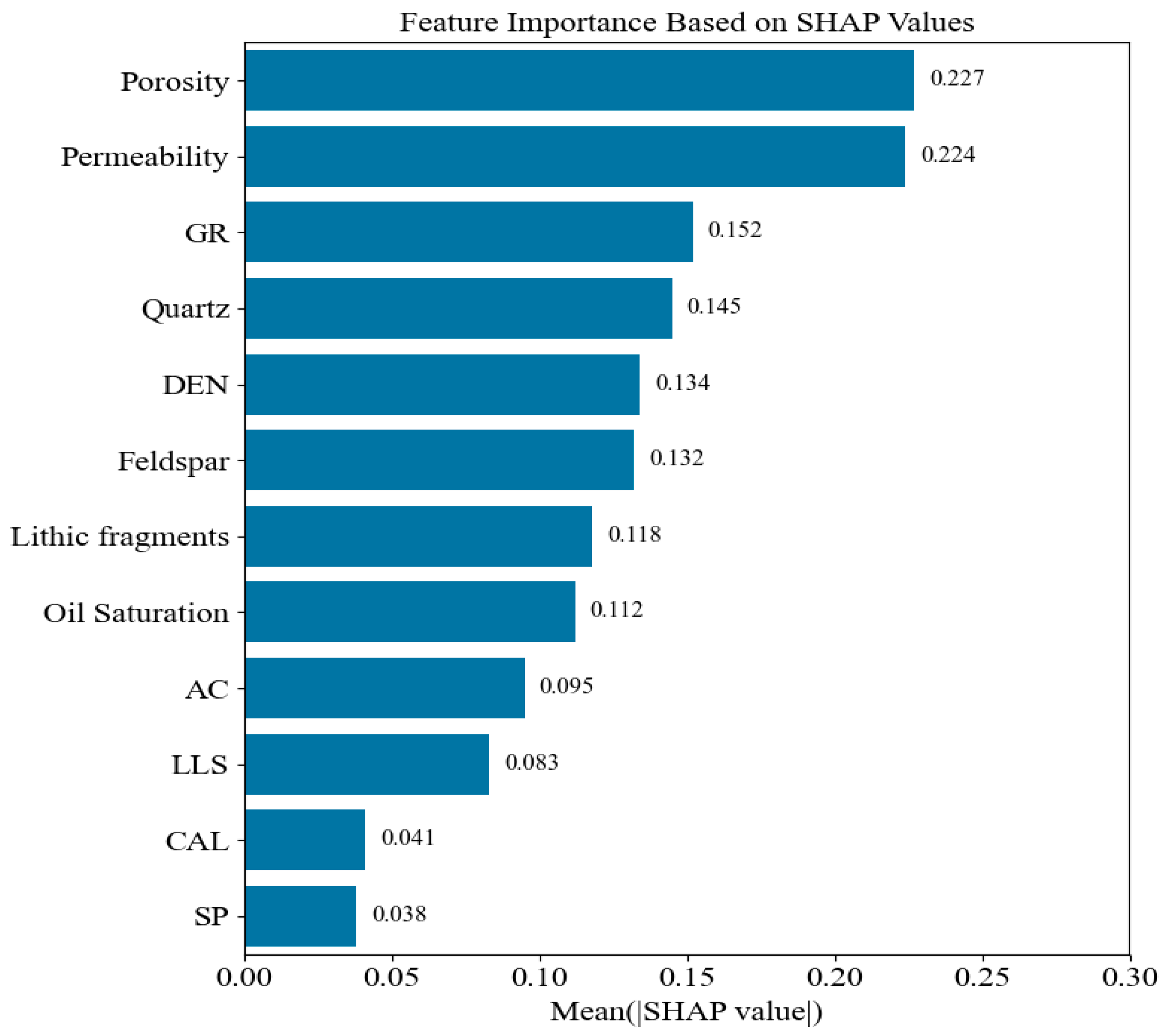
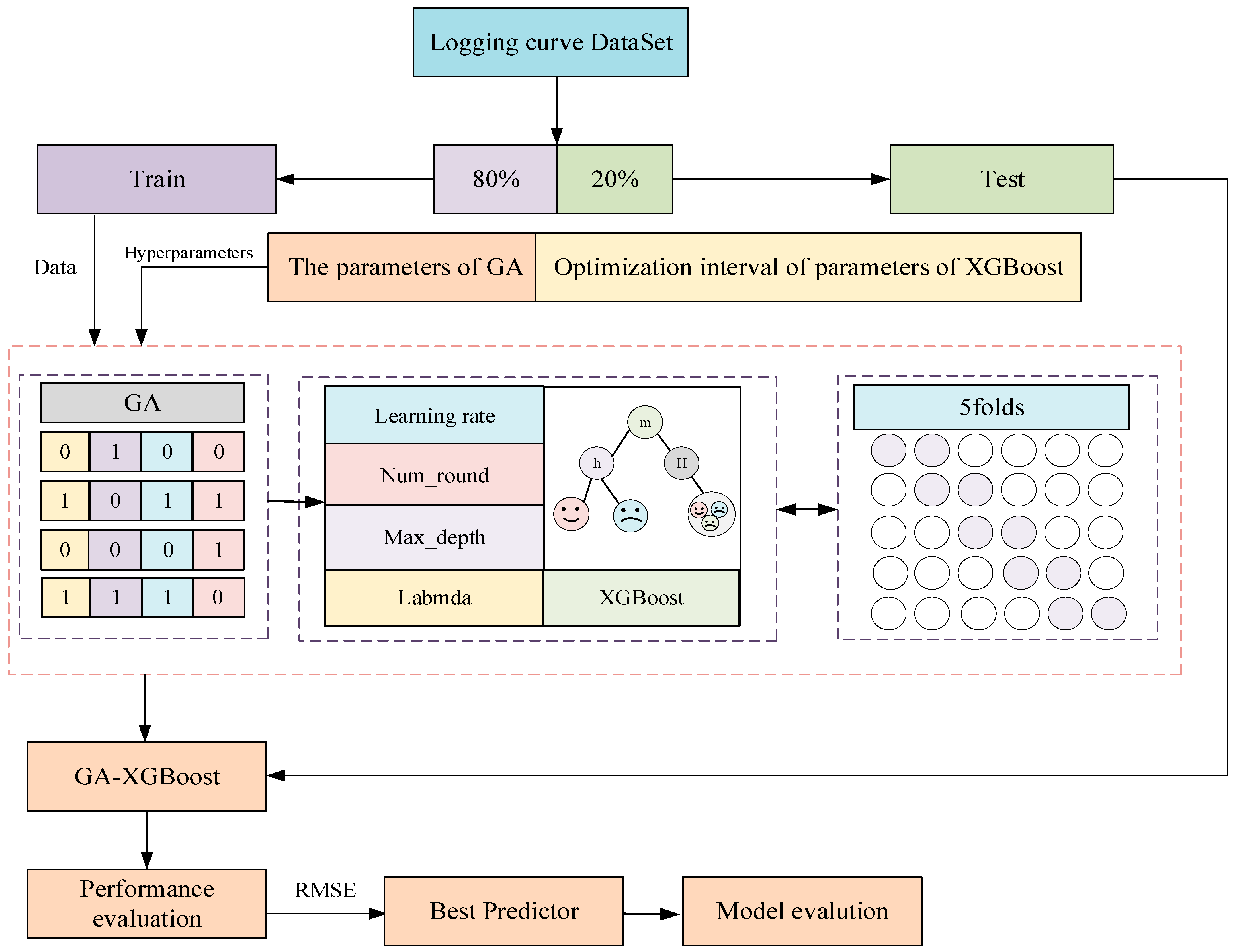
| Stratum | Lithological | Porosity | Permeability | Quartz Content | Feldspar Content | Debris Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B18 lamination | Siltstone | 10.6% | 0.75 mD | 23.5% | 30.5% | 32.5% |
| B183 lamination | Silty sandstone | 11.3% | 0.73 mD | 24.7% | 32.8% | 33.2% |
| Z11 lamination | Siltstone | 12.5% | 0.77 mD | 25.6% | 33.7% | 32.4% |
| Response Characteristics | GR | SP | CAL | DEN | AC | LLS | CNL | RT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relevance | 0.8688 | 0.6846 | 0.5693 | 0.4270 | 0.4328 | 0.4171 | 0.1241 | 0.1668 |
| Sections | 0.8688 | 1.5535 | 2.1228 | 2.4497 | 2.5688 | 2.6839 | 2.8955 | 2.9463 |
| Normalization | 0.3376 | 0.6036 | 0.8247 | 0.9518 | 0.9616 | 0.9441 | 0.9231 | 0.9171 |
| Order | Well | Coring Depth (m) | Length (m) | Order | Well | Coring Depth (m) | Length (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top | Bottom | Top | Bottom | ||||||
| 1 | B7 | 1872.700 | 2081.100 | 208.40 | 9 | F464 | 1835.95 | 1939.30 | 91.45 |
| 2 | B17 | 1858.025 | 2043.475 | 185.45 | 10 | H23-6 | 1800.020 | 1831.170 | 31.15 |
| 3 | B18 | 1836.001 | 2139.951 | 303.95 | 11 | S52 | 1719.000 | 1872.000 | 153.00 |
| 4 | B102 | 1914.500 | 1963.400 | 48.90 | 12 | S541 | 1818.025 | 1946.975 | 128.95 |
| 5 | B183 | 1895.012 | 1906.962 | 11.95 | 13 | S55 | 1754.000 | 1793.950 | 39.95 |
| 6 | B211 | 1774.99 | 1792.59 | 17.60 | 14 | X21 | 2130.37 | 2149.16 | 18.79 |
| 7 | F188 | 1835.039 | 1939.989 | 104.95 | 15 | X23 | 2070.26 | 2131.99 | 61.52 |
| 8 | F361 | 1765.325 | 1808.475 | 125.15 | 16 | Z11 | 1809.35 | 1826.46 | 15.92 |
| Reservoir Types | Reservoir Name | Mean Porosity | Mean Permeability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I | St | 12.42% | 0.48 mD |
| Class I | Sa | 12.26% | 0.42 mD |
| Class I | Sp | 11.83% | 0.38 mD |
| Class II | Sw | 9.83% | 0.19 mD |
| Class III | Fh | 8.72% | 0.13 mD |
| Class III | Fw | 7.64% | 0.09 mD |
| Evaluation Parameters | Reservoir Class I | Reservoir Class II | Reservoir Class III |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithology | Fine sandstone/Siltstone | Fine stone/Siltstone | Siltstone/Muddy siltstone |
| Porosity/% | ≥10 | 9–10 | <8 |
| Permeability/10−3 μm | ≥0.3 | 0.2–0.3 | <0.1 |
| So/% | >55 | 35–55 | <35 |
| GR/API | 58.69~92.89 | 61.18~107.64 | 72.51~108.94 |
| SP/mv | 47.93~−14.84 | 48.24~−11.23 | 61.5~−14.5 |
| CAL/cm | 8.47~9.56 | 8.47~9.17 | 8.47~9.02 |
| DEN/g/cm³ | 2.35~2.59 | 2.4~2.64 | 2.44~2.58 |
| LLS/Ω·m | 3.12~5.75 | 5.75~7.82 | 7.82~10.51 |
| AC/μs/m | 65.81~77.32 | 61.41~79.76 | 58.55~74.48 |
| Well Number | Well Type | Data Volume |
|---|---|---|
| B17 | Training well | 872 |
| B183 | Training well | 951 |
| X21 | Testing well | 1392 |
| Z11 | Testing well | 726 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.74 |
| XGBoost | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.81 |
| ADABoost | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| GA-XGBoost | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.87 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.74 |
| XGBoost | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.81 |
| ADABoost | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.81 | 0.83 |
| GA-XGBoost | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.87 |
| Model | Predicted Class I Reservoir | Predicted Class Reservoir II | ||||
| RMSE | MSE | MAE | RMSE | MSE | MAE | |
| SVM | 1.90 | 8.30 | 3.00 | 3.37 | 22.21 | 2.05 |
| XGBoost | 3.03 | 19.33 | 2.13 | 2.85 | 10.83 | 0.39 |
| ADABoost | 1.91 | 12.84 | 3.66 | 1.62 | 10.41 | 3.10 |
| GA-XGBoost | 0.86 | 11.40 | 2.30 | 2.35 | 10.69 | 2.29 |
| Model | Predicted Class Reservoir III | |||||
| RMSE | MSE | MAE | ||||
| SVM | 1.04 | 17.90 | 3.11 | |||
| XGBoost | 0.99 | 1.03 | 2.65 | |||
| ADABoost | 1.53 | 2.16 | 1.37 | |||
| GA-XGBoost | 0.94 | 10.95 | 1.61 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, Z.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhang, K.; Mu, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S. Intelligent Classification Method for Tight Sandstone Reservoir Evaluation Based on Optimized Genetic Algorithm and Extreme Gradient Boosting. Processes 2025, 13, 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051379
Mu Z, Li C, Liu Z, Liu T, Zhang K, Mu H, Yang Y, Liu L, Huang J, Zhang S. Intelligent Classification Method for Tight Sandstone Reservoir Evaluation Based on Optimized Genetic Algorithm and Extreme Gradient Boosting. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051379
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Zihao, Chunsheng Li, Zongbao Liu, Tao Liu, Kejia Zhang, Haiwei Mu, Yuchen Yang, Liyuan Liu, Jiacheng Huang, and Shiqi Zhang. 2025. "Intelligent Classification Method for Tight Sandstone Reservoir Evaluation Based on Optimized Genetic Algorithm and Extreme Gradient Boosting" Processes 13, no. 5: 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051379
APA StyleMu, Z., Li, C., Liu, Z., Liu, T., Zhang, K., Mu, H., Yang, Y., Liu, L., Huang, J., & Zhang, S. (2025). Intelligent Classification Method for Tight Sandstone Reservoir Evaluation Based on Optimized Genetic Algorithm and Extreme Gradient Boosting. Processes, 13(5), 1379. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051379







