Small-Signal Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected System for Renewable Energy Based on Network Node Impedance Modelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Background and Significance
1.2. Research Contents
2. Impedance Modelling of Grid-Connected Converters
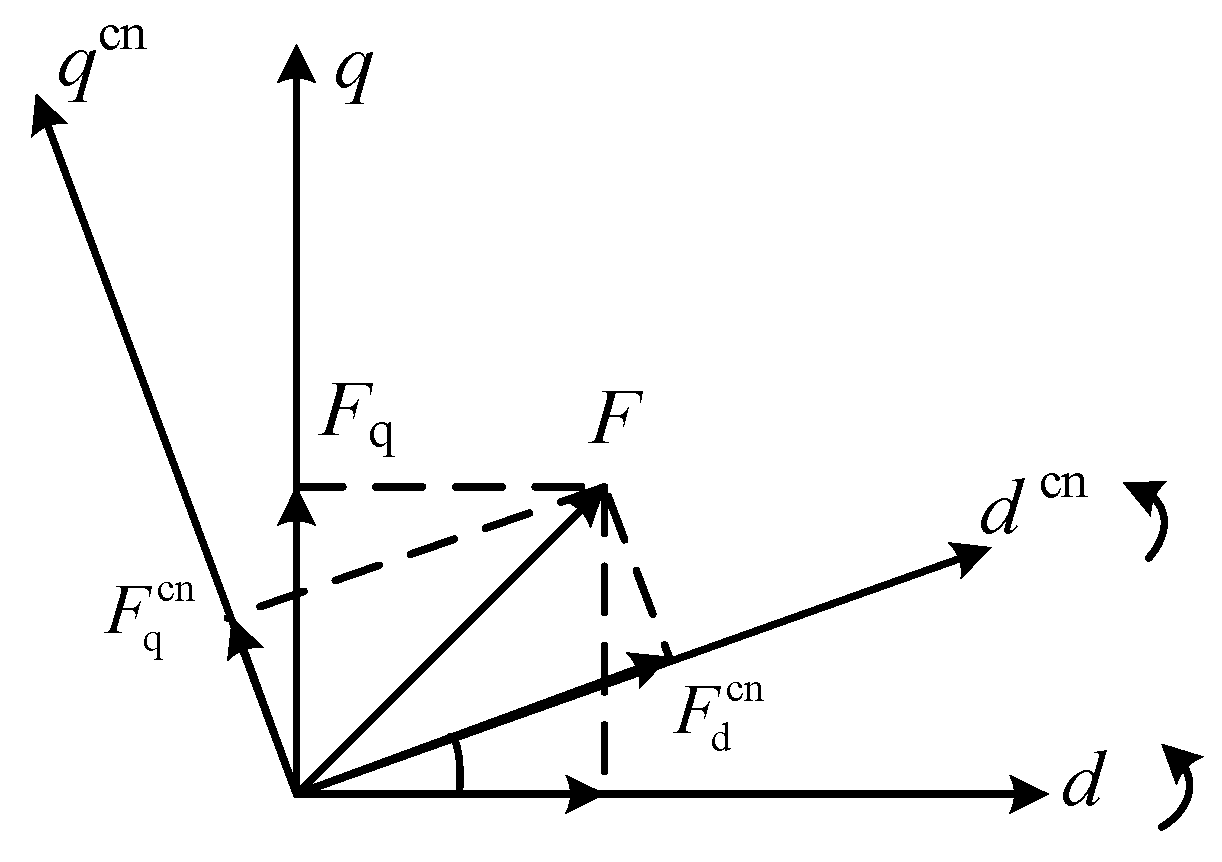
2.1. Topology of Grid-Connected Converters
2.2. Impedance Modelling for Grid-Connected Converters
2.2.1. Model of PLL
2.2.2. Model of Voltage Controllers and Current Controllers
2.3. Modelling for Integrating Multiple Grid-Connected Converters into Systems Based on Network Node Impedance
3. Stability Analysis of Control Loop for Grid-Connected Converters
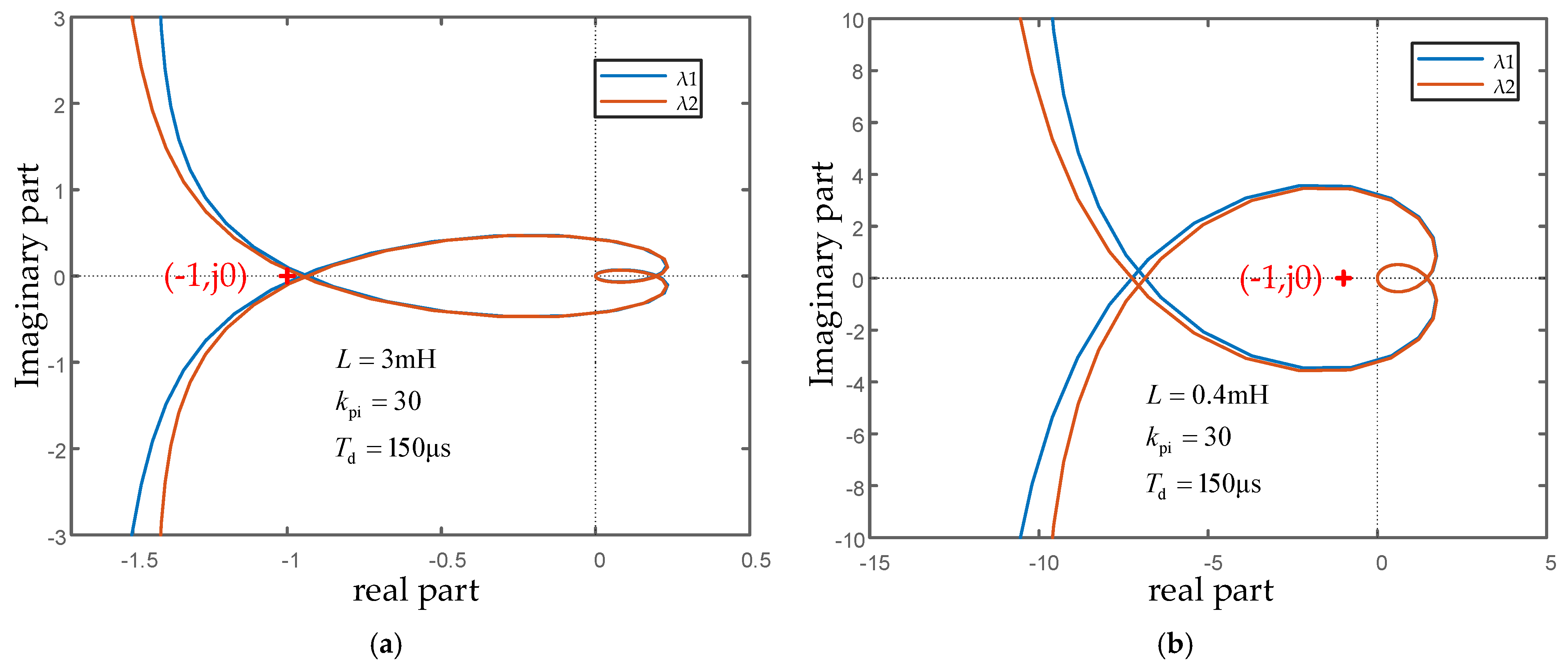
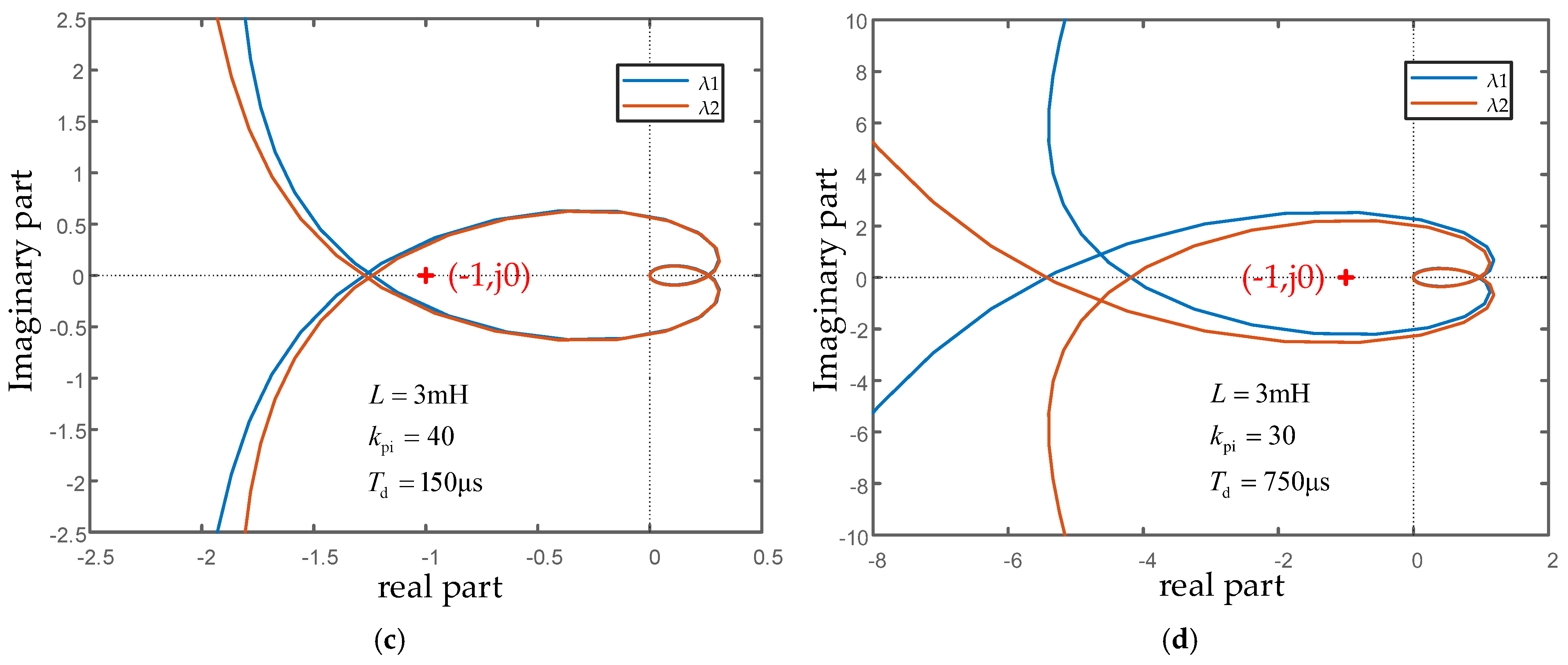
3.1. Analysis of the Impact on Current Loop of Grid-Connected Converters
3.2. Analysis of the Impact of the Phase-Locked Loop on Grid-Connected Converters
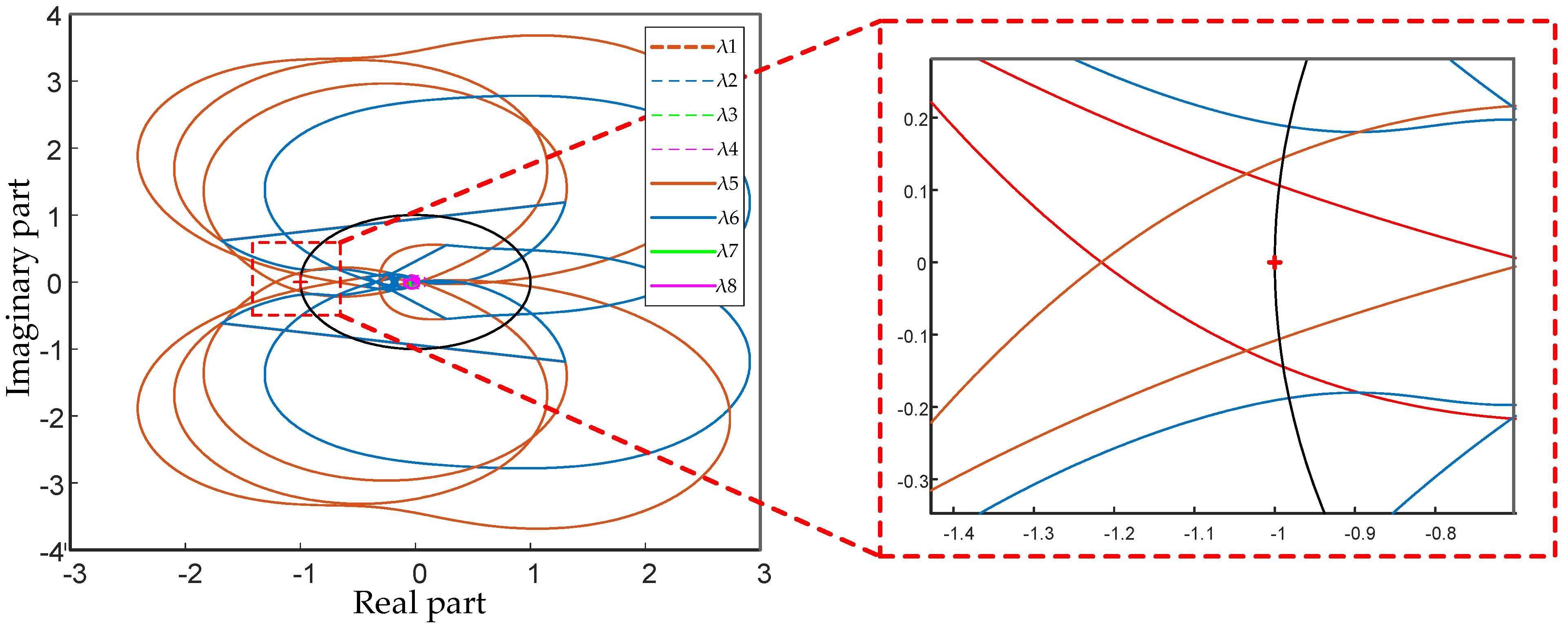
4. Stability Analysis of Renewable Energy Systems Incorporating Multiple Grid-Connected Converters
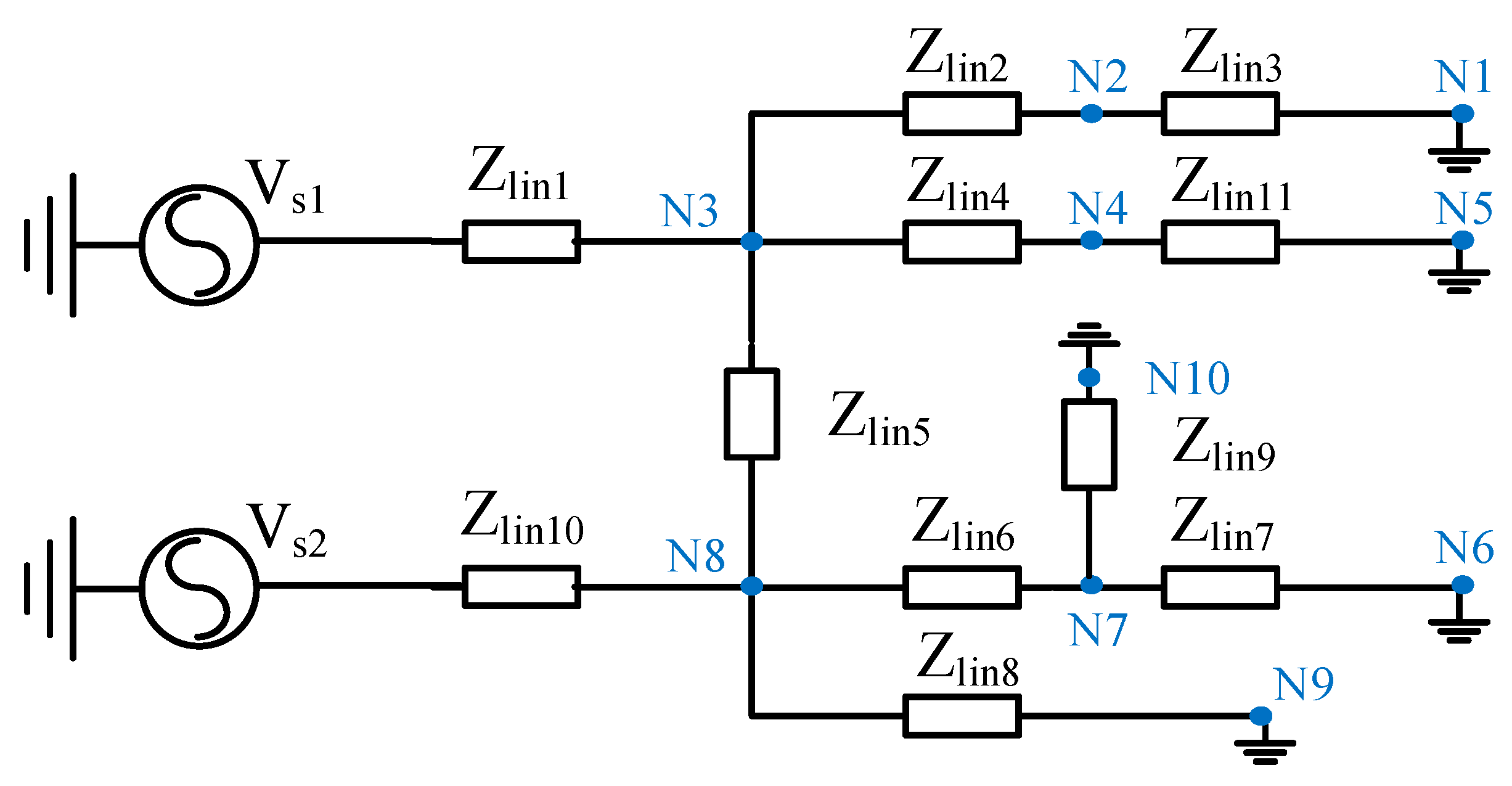
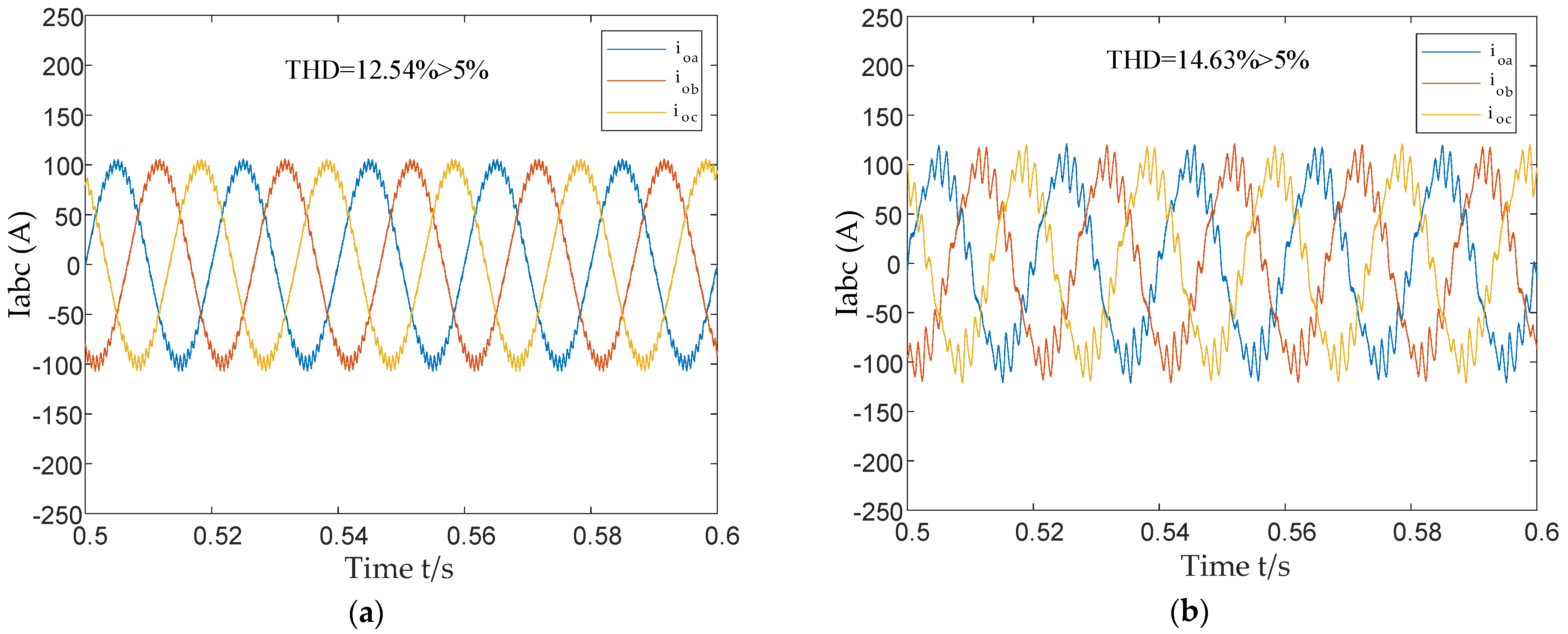
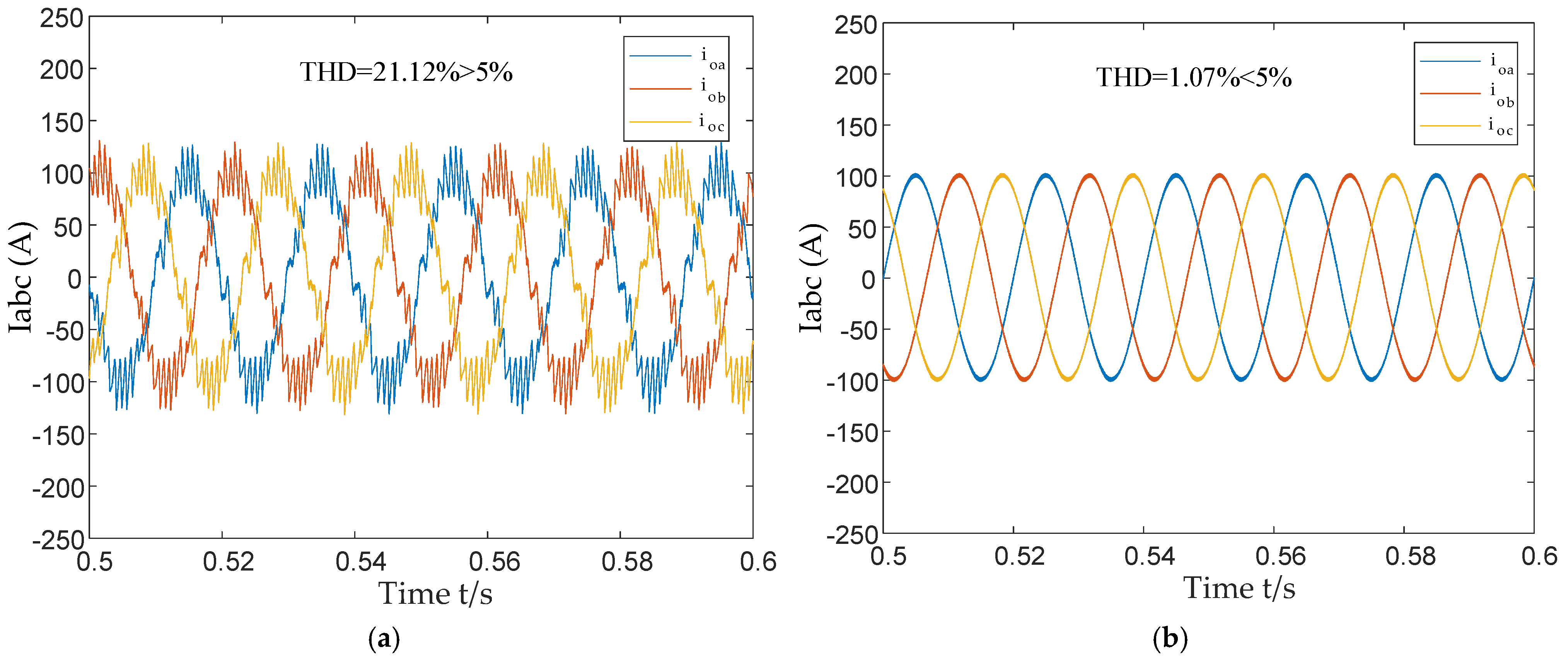
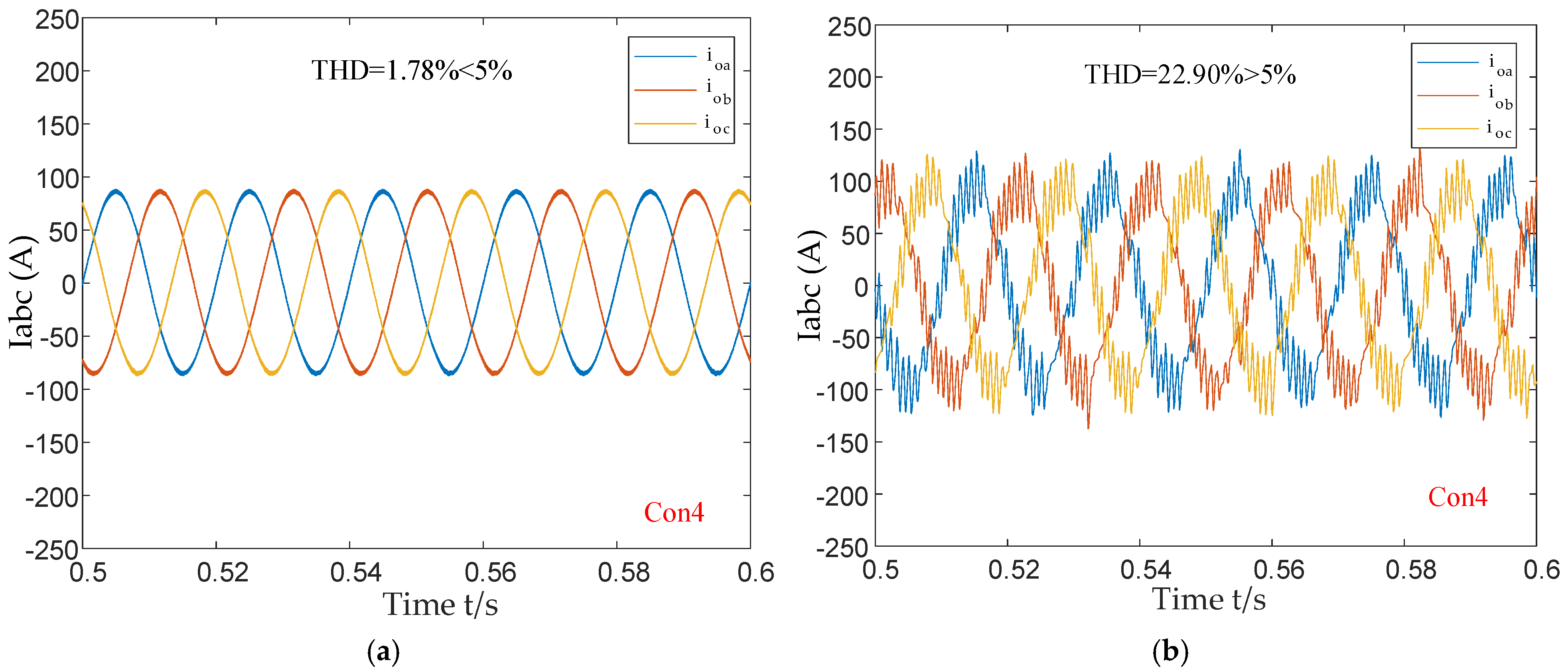
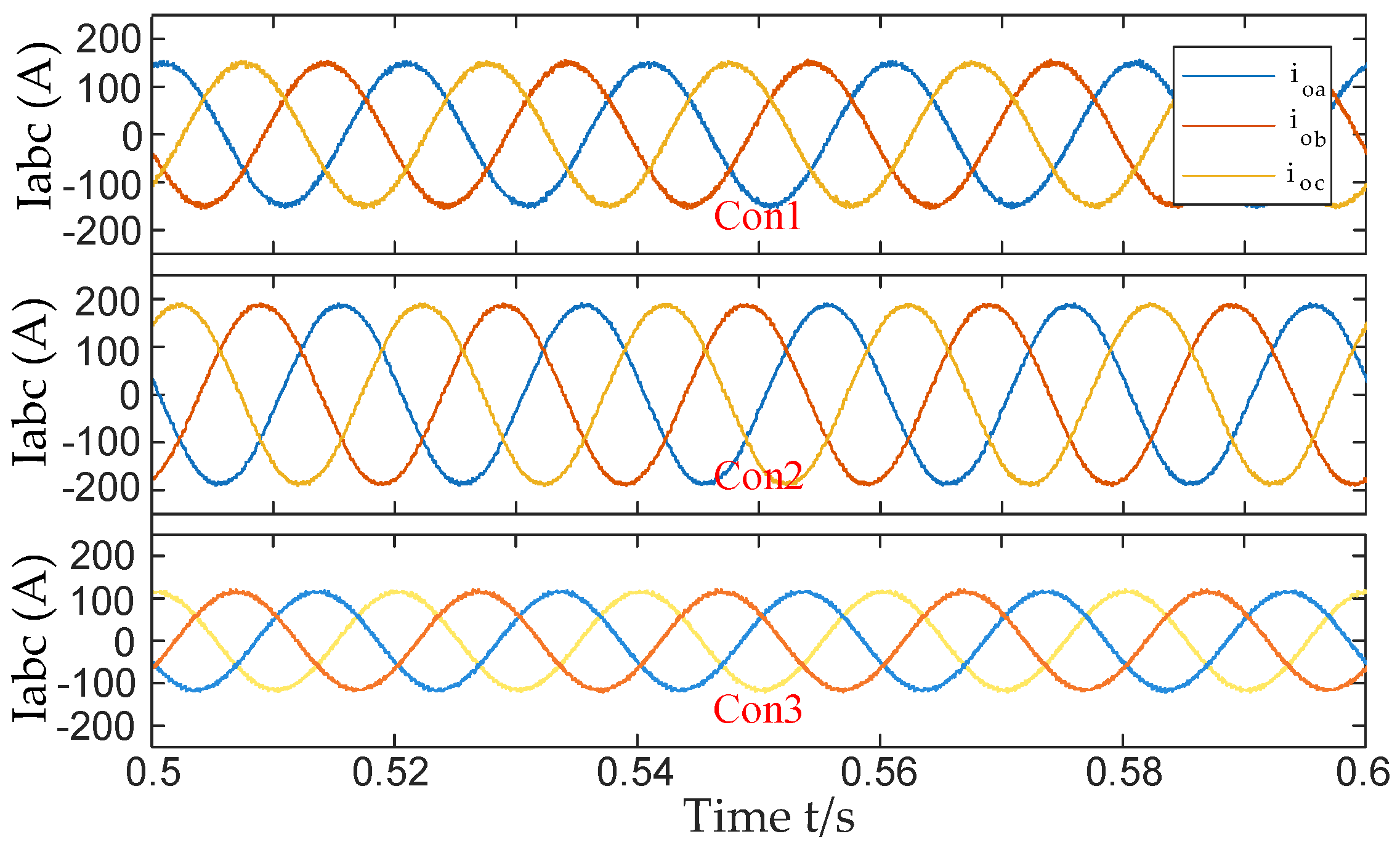
5. Case Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, Z. Suppression and stability analysis of positive feedback effect of phase-locked loop in grid connected inverters under weak power grid. Int. J. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2025, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Liu, Y.; Shao, B.; Ran, H. A path analysis method to study the sub-synchronous oscillation mechanism direct-drive wind farm with VSC-HVDC system. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 43, 6646–6660. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshizadeh, M.K.; Ghosh, S.; Yang, G.; Kocewiak, Ł. Transient Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected Converters in Wind Turbine Systems Based on Linear Lyapunov Function and Reverse-Time Trajectory. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2024, 12, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; Cao, J. Dynamic aggregation of same wind turbine generators in parallel connection for studying oscillation stability of a wind farm. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4694–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Miao, Z. Wind in weak grids: Low-frequency oscillations, sub-synchronous oscillations, and torsional interactions. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Luo, A.; Liu, X. Wideband Harmonic Voltage Feedforward Control Strategy of STATCOM for Mitigating Subsynchronous Resonance in Wind Farm Connected to Weak Grid and LCC HVDC. IEEE Trans. Emerg. 2021, 9, 4546–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Zhao, S.; Gao, B.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. Adequacy of the single-generator equivalent model for stability analysis in wind farms with VSC-HVDC systems. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fan, L.; Miao, Z. Small signal stability analysis of type-4 wind in series compensated networks. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Ren, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Comparison of methods to examine sub-synchronous oscillations caused by grid-connected wind turbine generators. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 34, 4931–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, S.; Feng, W.; Prokhorov, A.V.; Mokhlis, H.; Huat, C.K.; Tripathy, M. Damping of Subsynchronous Resonance in a Hybrid System with a Steam-Turbine Generator and an Offshore Wind Farm Using a Unified Power-Flow Controller. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, P.; Li, K.; Zou, R.; Tian, S.; Yu, H. Forced Subsynchronous Oscillations of Turbine-Generators Excited by Interharmonics from Bundled Offshore Wind Farms. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 5416–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, A.; Chen, J. Modeling of Dynamic Control Error and Emergency Frequency Control for Direct-Drive PMSG-Based Wind Turbine Under Grid Fault. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy. 2024, 15, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Shang, J. Accurate Small-Signal Terminal Characteristic Model and SISO Stability Analysis Approach for Parallel Grid-Forming Inverters in Islanded Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 6597–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Ji, X.; Liu, D.; Zheng, W.; Tian, L.; Chen, S. Small-Signal Modeling of Grid-Forming Wind Turbines in Active Power and DC Voltage Control Timescale. Electronics 2024, 13, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, Y. Effect of Coupling Impedance on Stability Assessment of Grid-Forming Converters Under Various Grid Conditions. Electronics 2024, 13, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Beik, O.; Pallapati, R.; Hoberg, S. Overview and Impedance-Based Stability Analyses of Bison Wind Farm: A practical example. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2024, 30, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, J. Stability Region Assessment with Mechanism-Data Driven Equivalent Impedance for Wind Power Plant. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 9355–9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Yang, D.; Sun, Y.; Larumbe, L.B. Dynamic Power Tracking Performance and Small Signal Stability Analysis of Integrated Wind-to-Hydrogen System. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy. 2024, 15, 2444–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shuai, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Hong, Y.; Shen, Z. Stability Analysis and Location Optimization Method for Multiconverter Power Systems Based on Nodal Admittance Matrix. IEEE Trans. Emerg. 2021, 9, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Harnefors, L.; Gong, H.; Hasler, J.P.; Nee, H.P. SISO Transfer Functions for Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected Voltage-Source Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 2931–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedra, J.; Sainz, L.; Monjo, L. Three-Port Small Signal Admittance-Based Model of VSCs for Studies of Multi-Terminal HVDC Hybrid AC/DC Transmission Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, C.; Pepiciello, A.; Debbat, A.; Tarraso, M.; Dominguez, L.J. State Space Modeling and Small-Signal Stability Analysis of a Multiport Soft Open Point Based on the Triple Active Bridge Converter. SEST—Driving the Advances for Future Electrification. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies, Torino, Italy, 10–12 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, F.; Yin, C.; Jin, G. Small Disturbance Stability Analysis of Onshore Wind Power All-DC Power Generation System Based on Impedance Method. Energies 2024, 17, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.B.; Wang, X.; Blaabjerg, F.; Bak, C.L.; Wood, A.R.; Watson, N.R. Harmonic Instability Analysis of a Single-Phase Grid-Connected Converter Using a Harmonic State-Space Modeling Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 4188–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Yin, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, X. Improved sequential impedance modeling and stability analysis of virtual synchronous generators considering frequency coupling effects. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Green, T. Impedance-Based Root-Cause Analysis: Comparative Study of Impedance Models and Calculation of Eigenvalue Sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 38, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, S.; Liu, K.; Chen, M.; Du, Y. Impedance Modeling of Wind Turbine-Variable Speed Pumped Storage Combined Operation System. Energy Reports. 2021, 7, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Mei, N.; Yue, B. Accurate Impedance Modeling and Control Strategy for Improving the Stability of DC System in Multiterminal MMC-Based DC Grid. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics. 2020, 35, 10026–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, Z. Input Impedance Modeling and Verification of Single-Phase Voltage Source Converters Based on Harmonic Linearization. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8544–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zeng, Z.; Mao, L. Small-signal stability analysis and participation factor identification for multi converter DC microgrids. J. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Gu, X.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C. Review and Prospect of Research on Frequency Safety and Stability of New Power System. Zhejiang Electr. Power. 2024, 43, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shuai, Z.; Fang, J.; Wu, X.; Shen, Z. Small-Signal Stability Analysis Method for Hybrid AC–DC Systems with Multiple DC Buses. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2021, 11, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, W.H. Radial distribution test feeders. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2002, 2, 908–912. [Google Scholar]







| Analysis Method | Feature Value Analysis Method [22,23,24]. | Impedance Analysis Method [25,26,27,28]. |
|---|---|---|
| Modeling Principle | Known system internal parameters, establish state differential equations in the time domain, obtain small-signal model through linearization | Based on system port characteristics, establish impedance model, analyze stability through equivalent impedance ratio |
| Stability Analysis Criteria | Feature Value Criteria | Nyquist criteria |
| Advantages | Fully reveals the stability characteristics of system variables | Compact form, clear physical meaning, easy calculation |
| Disadvantages | Model order may be very high, poor scalability | Frequency coupling increases analysis complexity; multi-input systems are difficult to divide into source-load subsystems |
| Applicable Scenarios | Suitable for scenarios where system structure is clear, parameters are known, and model dimensions are low | Suitable for complex topologies, where equipment parameters are not fully known or rapid assessment is needed |
| Node Number | GM/dB | PM/° |
|---|---|---|
| N1 | instability | |
| N2 | 0.6622 | 7.6340 |
| N4 | 0.6260 | 7.5370 |
| N5 | 0.6959 | 7.9410 |
| N6 | 0.6875 | 7.8440 |
| N7 | instability | |
| N8 | 0.7875 | 8.0372 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Converter DC-side voltage Vdc (kV) | 0.8 |
| Converter DC-side capacitance Cdc (uF) | 8000 |
| Distribution grid voltage Vgr (kV) | 0.38 |
| Filter inductance L (mH) | 3 |
| Filter resistance RLC (Ω) | 0.01 |
| Equivalent impedance of the grid Zgr | 0 |
| Fundamental frequency of the distribution grid f1 (Hz) | 50 |
| Sampling frequency fs (kHz) | 20 |
| Proportional coefficient of the current controller kpi | 30 |
| Integral coefficient of the current controller kii | 300 |
| Proportional coefficient of the PLL controller kpPLL | 2 |
| Integral coefficient of the PLL controller kiPLL | 200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, L.; Liu, D.; Tao, H.; Shen, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, Y. Small-Signal Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected System for Renewable Energy Based on Network Node Impedance Modelling. Processes 2025, 13, 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051292
He L, Liu D, Tao H, Shen Y, Ren J, Wang Y, Li J, Xu Y. Small-Signal Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected System for Renewable Energy Based on Network Node Impedance Modelling. Processes. 2025; 13(5):1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051292
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Lifu, Dingshan Liu, Haidong Tao, Yangwu Shen, Jiapeng Ren, Yuting Wang, Jin Li, and Yaqin Xu. 2025. "Small-Signal Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected System for Renewable Energy Based on Network Node Impedance Modelling" Processes 13, no. 5: 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051292
APA StyleHe, L., Liu, D., Tao, H., Shen, Y., Ren, J., Wang, Y., Li, J., & Xu, Y. (2025). Small-Signal Stability Analysis of Grid-Connected System for Renewable Energy Based on Network Node Impedance Modelling. Processes, 13(5), 1292. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13051292






