Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Technology Progress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bio-Based Epoxy Resins
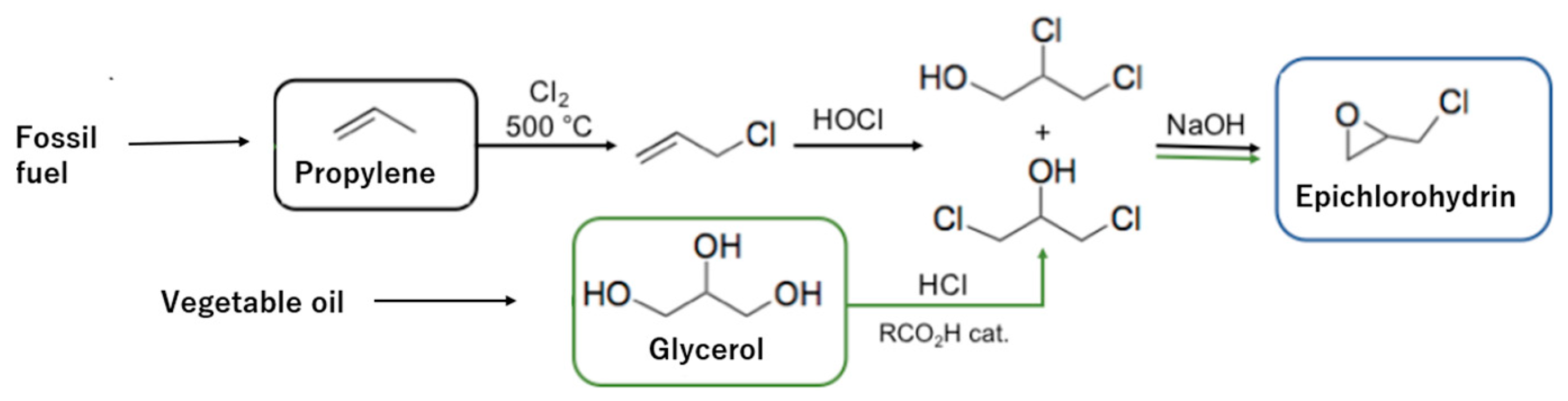
2.1. Bio-Based Epichlorohydrin
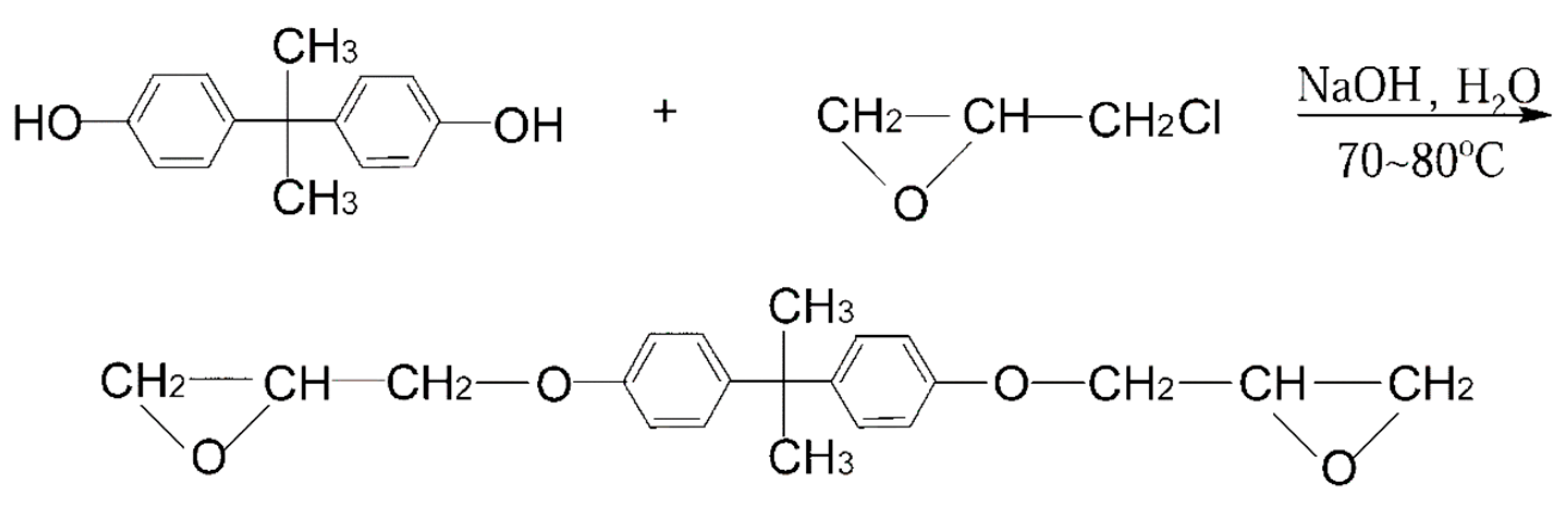
2.2. Bio-Based Conventional Epoxy Resins
2.3. Bio-Based Novel Epoxy Resins
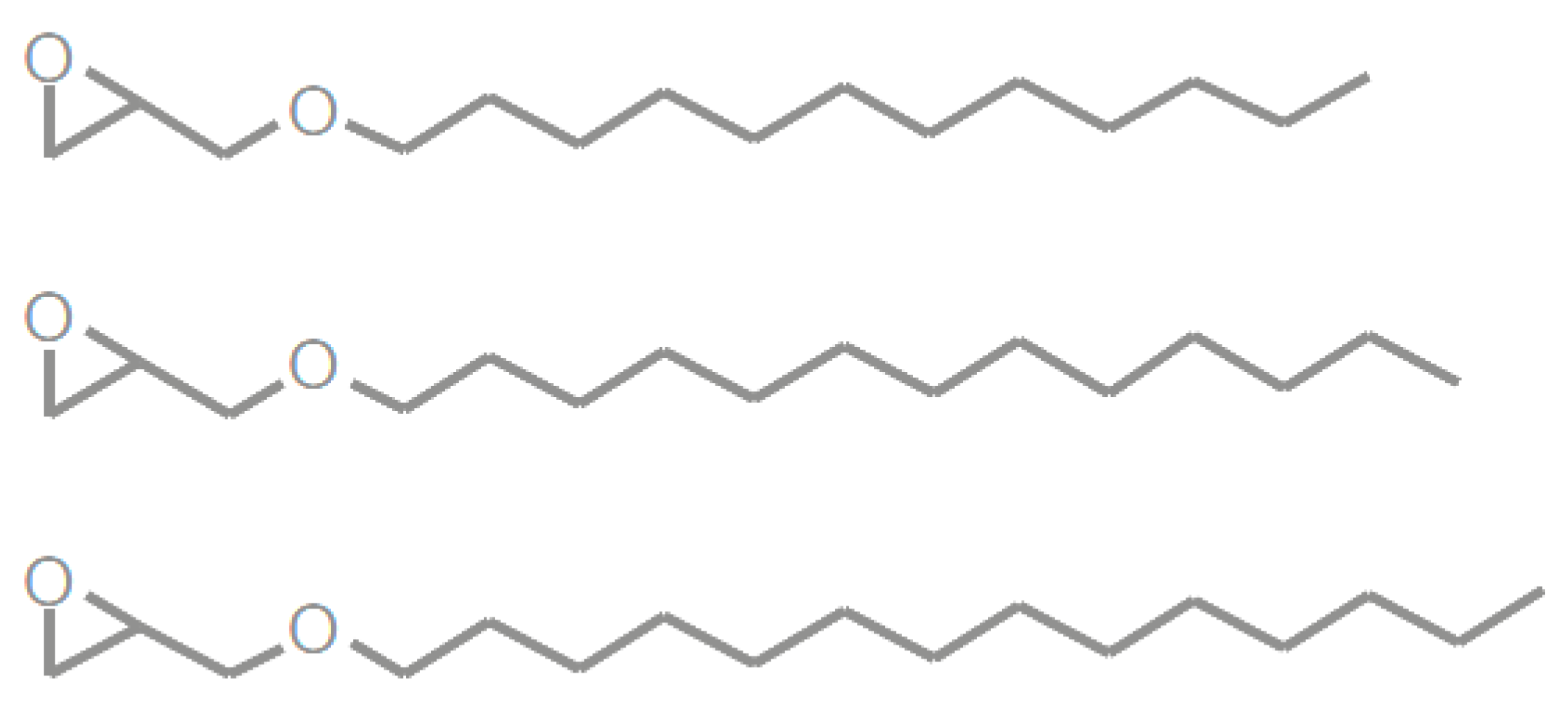
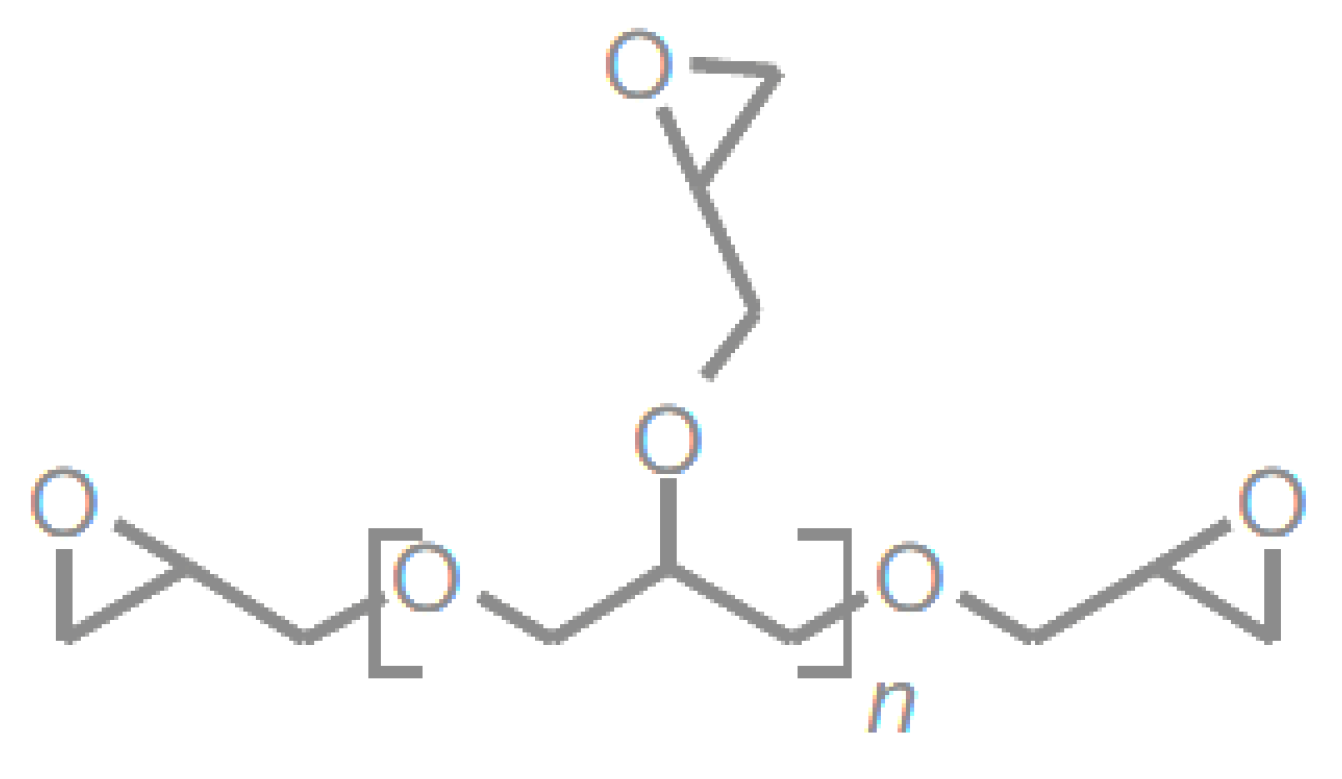
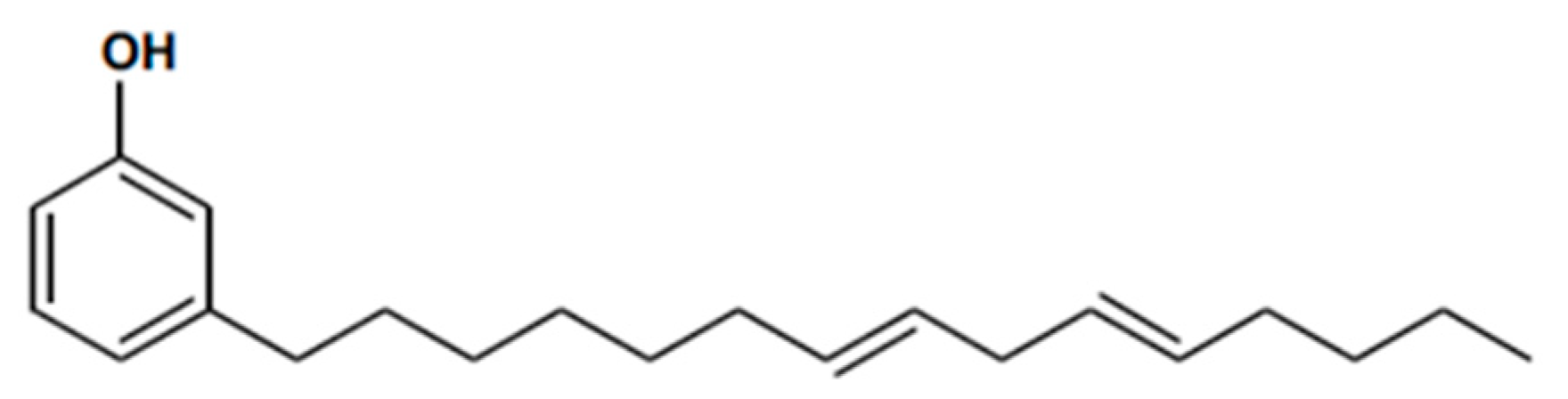
2.3.1. Vegetable-Oil-Based Epoxy Resins
2.3.2. Cardanol-Based Epoxy Resins
2.3.3. Rosin-Based Epoxy Resins
2.3.4. Sorbitol, Isosorbide-Based Epoxy Resins
2.3.5. Lignin-Based Epoxy Resins
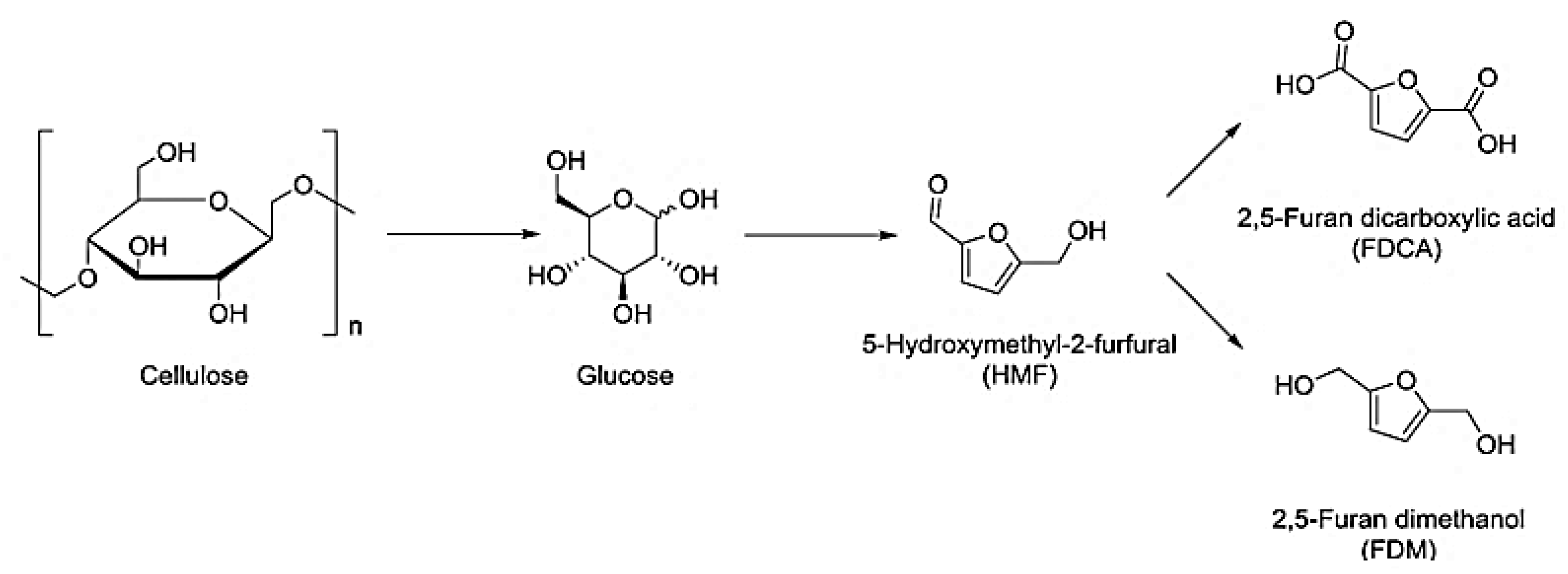
2.3.6. Furan-Based Epoxy Resins
3. Bio-Based Epoxy Curing Agents and Additives
3.1. Bio-Based Polyamine-Type Curing Agents
3.2. Bio-Based Polyamide-Type Curing Agents
3.3. Bio-Based Amidoamine-Type Curing Agents
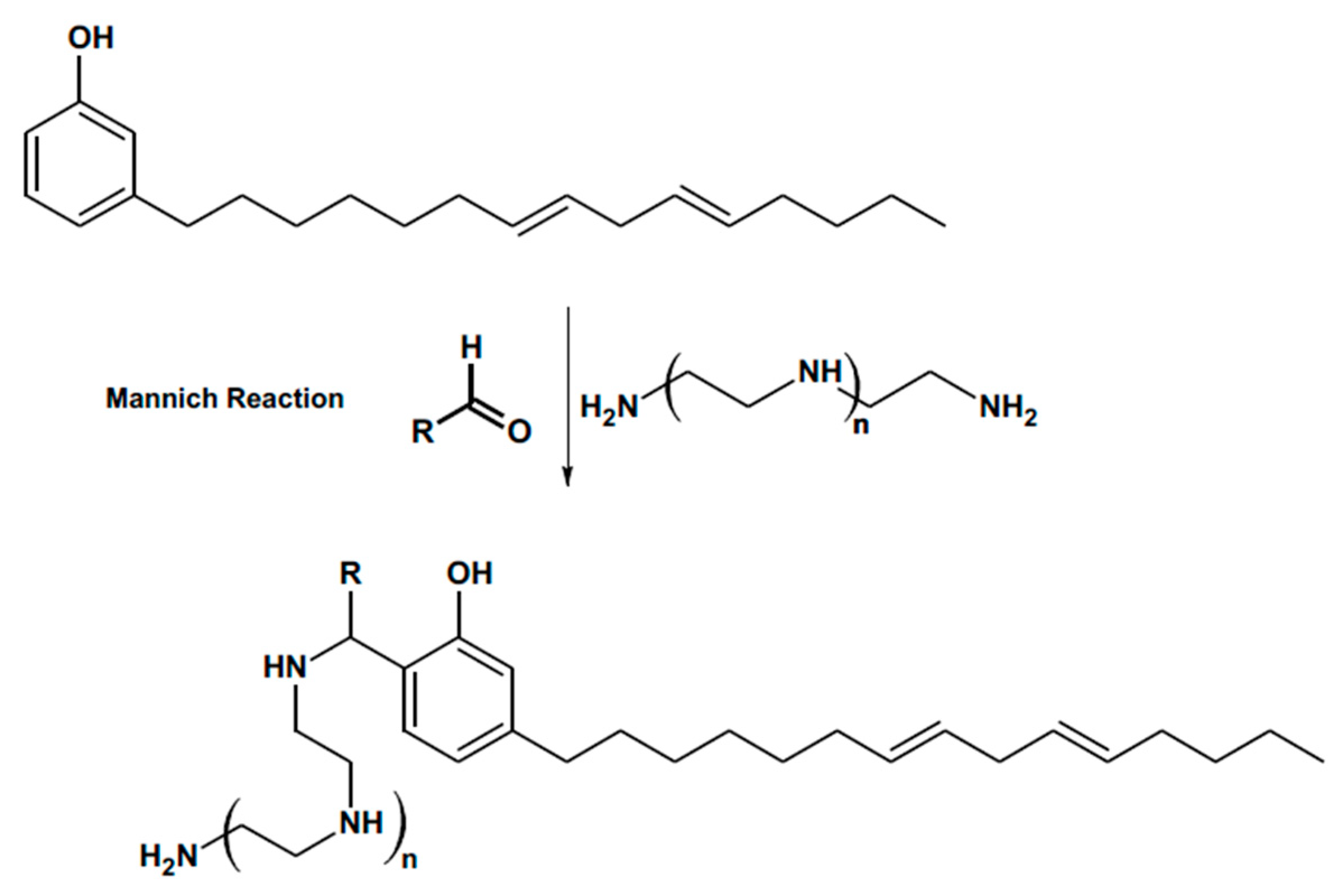
3.4. Bio-Based Phenalkamine-Type Curing Agents
3.5. Bio-Based Phenols
4. Bio-Based Formulated Epoxy Materials
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kakiuchi, H. Epoxy Resin: A Review; The Japan Society of Epoxy Resin Technology: Tokyo, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, H. Epoxy Resins Technology Handbook; Asia Pacific Business Press: New Delhi, India, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, A.F. Epoxy resin adhesives. In Epoxy Resins—Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; May, C.A., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 653–718. [Google Scholar]
- Vidil, T.; Tournilhac, F.; Musso, S.; Robisson, A.; Leibler, L. Control of reactions and network structures of epoxy thermosets. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 62, 126–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakernaak, A.; Hofstede, J.; Poulis, J.; Benedictus, R. Improvements in bonding metals for aerospace and other applications. In Welding and Joining of Aerospace Materials; Chaturvedi, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 235–319. [Google Scholar]
- Petrie, E.M. Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants; MicGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 355–373. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Epoxy adhesive technology: Latest developments and new trend. In Progress in Adhesion and Adhesives; Mittal, K., Ed.; Wiley—Scrivener: Beverly, MA, USA, 2024; Volume 8, pp. 251–284. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C. Structural epoxy adhesives. In Structural Adhesives: Properties, Characterization and Applications; Mittal, K.L., Panigraphi, S.K., Eds.; Wiley—Scrivener: Beverly, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cordes, E.H. Adhesives in the automotive industry. In Handbook of Adhesive Technology, 2nd ed.; Pizzi, A., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 983–999. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Li, B.; Kanari, M.; Lu, D. Epoxy adhesives. In Adhesives and Adhesive Joints in Industry Applications; Rudawska, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Cailoll, S.; Boutevin, B.; Pascault, J. Bio-sourced epoxy monomer and polymers. In Handbook of Adhesive Technology, 3rd ed.; Pizzi, A., Mittal, K.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 443–470. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich, L.A. Future opportunities for bio-based adhesives—Advantages beyond renewability. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1866–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudsari, G.M.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Green approaches to engineer tough biobased epoxies: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 9528–9541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijk, R.; Veraart, R. Global Legislation for Food Packaging Materials; Wiley—VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Hase, E.; Kitano, M. The role and place of risk assessment in chemical management especially in Japan, Europe and U.S.A. Jpn. J. Risk Anal. 2012, 22, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, P.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.; Chithra, P.; Thomas, S. Integration of antifouling properties into epoxy coatings: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2022, 19, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packham, D.E. The environmental impact of adhesives. In Eco-Efficient Construction and Building Materials Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), Eco-Labelling and Case Studies; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Cabeza, L.F., Labrincha, J., Magalhiies, A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 338–367. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmila, V.; Adamopoulos, S.; Karlsson, O.; Kumar, A. Development of sustainable bio-adhesives for engineered wood panels—A review. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 38604–38630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wan, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K. From renewable biomass to bio-based epoxy monomers and bio-based epoxy curing agents: Synthesis and performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 229, 110988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, B.; Pucci, A.; Wadgaonkar, P.P.; Kumar, I.; Binder, W.H.; Rana, S. Vitrimers based on bio-derived chemicals: Overview and future prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreehari, H.; Gopika, V.; Jayan, J.; Sethulekshmi, A.; Saritha, A. A comprehensive review on bio epoxy based IPN: Synthesis, properties and applications. Polymer 2022, 252, 124950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriam, F.; Irshad, A.; Umer, I.; Asghar, M.; Atif, M. Vegetable oils as bio-based precursors for epoxies. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 31, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wan, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, K. Recent development of functional bio-based epoxy resins. Molecules 2024, 29, 4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capretti, M.; Giammaria, V.; Santulli, C.; Boria, S.; Bianco, G. Use of bio-epoxies and their effect on the performance of polymer composites: A critical review. Polymers 2023, 15, 4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Dai, J.; Liu, X. Bio-based thermosetting resins: From molecular engineering to intrinsically multifunctional customization. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2311242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D6866; Standard Test Methods for Determining the Biobased Content of Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous Samples Using Radiocarbon Analysis. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- EN 16640; Determination of the Bio-Based Carbon Content Using the Radiocarbon Method. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2017.
- Santosh, E.; Yadav, K.; Palmese, G.R.; Stanzione, J.F. Recent advances in bio-based epoxy resins and bio-based epoxy curing agents. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 44103. [Google Scholar]
- Auvergne, R.; Caillol, S.; David, G.; Boutevin, B.; Pascault, J. Biobased thermosetting epoxy: Present and future. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1082–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambleton, K.; Stanzione, J. Synthesis and characterization of a low-molecular-weight novolac epoxy derived from lignin-inspired phenolics. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23855–23861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gnanasekar, P.; Nair, S.; Yi, S.; Yan, N. Curing behavior and thermomechanical performance of bio-epoxy resin synthesized from vanillyl alcohol: Effects of the curing agent. Polymers 2021, 13, 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X.; Khan, F.; Fahad, S.; Ullah, A. Adhesives properties of bio-based epoxy resin reinforced by cellulose nanocrystal additives. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 40, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, Q.; Pourchet, S.; Placet, V.; Plasseraud, L.; Boni, G. New eco-friendly synthesized thermosets from isoeugenol-based epoxy resin. Polymers 2019, 12, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, C.; Song, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, D.; Wang, Y. A bio-based epoxy resin derived from p-hydroxycinnamic acid with high mechanical properties and flame retardancy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4912–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, F.A.M.M.; Ferreira, P.; Alves, P. Synthesis and characterization of itaconic-based epoxy resin: Chemical and thermal properties of partially biobased epoxy resins. Polymer 2021, 235, 124285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.L.; Lai, J.C.; Rahman, R.A.; Adrus, N.; Al-Saffar, Z.H.; Hassan, A.; Lim, T.H.; Wahit, M.U. A review on recent approaches to sustainable bio-based epoxy vitrimer from epoxidized vegetable oils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 189, 115857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, D.J.; Tarnavchyk, I.; Kalita, H.; Chisholm, B.J.; Webster, D.C. Novel bio-based epoxy resins from eugenol derived copolymers as an alternative to DGEBA resin. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 178, 107471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaina, C.; Ursache, O.; Gaina, V.; Serban, A.; Asandulesa, M. Novel bio-based materials: From castor oil to epoxy resins for engineering applications. Materials 2023, 16, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Review of recyclable bio-based epoxy resins with dynamic chemical bonds. J. Chem. Eng. Res. Updates 2024, 11, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, P.; Wiekamp, M.; Vendamme, R.; Eevers, W. Bio-based epoxy resins from bio-refinery byproducts. BioResources 2019, 14, 3200–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czub, P.; Sienkiewicz, A. Synthesis of bio-based epoxy resins. In Bio-Based Epoxy Polymers, Blends, and Composites: Synthesis, Properties, Characterization, and Applications; Parameswaranpillai, J., Rangappa, S.M., Siengchin, S., Jose, S., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Miao, J.; Liang, G.; Gu, A. Biobased epoxy resin with ultrahigh glass transition temperature over 400 °C by post-crosslinking strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bio-Based Drop-In, Smart Drop-In and Dedicated Chemicals. Available online: https://roadtobio.eu/uploads/news/2017_October/RoadToBio_Drop-in_paper.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Liu, J.; Bai, C.; Jia, D.; Liu, D.; He, F.; Liu, Q.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. Design and fabrication of a novel superhydrophobic surface based on a copolymer of styrene and bisphenol A diglycidyl ether monoacrylate. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18025–18032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spolchemie EnviPOXY Products. Available online: https://www.spolchemie.cz/en/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Briozen Bio-Source Epoxy. Available online: https://www.tomo-e.co.jp/upload/newsJA/2C64F19-newsJA_content-033.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Leuna Harze Biobased Epoxy Resins. Available online: https://leuna-harze.de/en/move-to-green/biobased-products#c2361 (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Agbo, P.; Mali, A.; Deng, D.; Zhang, L. Bio-oil-based epoxy resins from thermochemical processing of sustainable resources: A short review. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Samal, S.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S. Recent development of biobased epoxy resins: A review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 57, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epotec RD 108G. Available online: https://www.tri-iso.com/documents/Epotec_RD-108G_TDS_pdf.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Epotec RD 124. Available online: https://www.tri-iso.com/documents/Epotec_RD-124_TDS_pdf.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Epotec RD 133. Available online: https://www.tri-iso.com/documents/Epotec_RD-133_TDS_pdf.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Epotec YD 128. Available online: https://www.tri-iso.com/documents/Epotec_YD-128_TDS_pdf.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Erysis GE-35. Available online: https://www.huntsman.com/docs/Documents/ERISYSGE-35_US_e.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Ultra Lite CNSL Technology. Available online: https://www.cardolite.com/technology/ultra-lite-technology/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Pioneering Sustainable Polymers. Available online: https://www.ingevity.com/altamer/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Brandi, F.; Al-Naji, M. Sustainable sorbitol dehydration to isosorbide using solid acid catalysts: Transition from batch reactor to continuous-flow system. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erysis GE-60. Available online: https://www.huntsman.com/docs/Documents/Erisys-GE60_eur_e.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Bio-Based Specialty Epoxies. Available online: https://nagaseamerica.com/product/green-denacol/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Epotec RD 144. Available online: https://www.tri-iso.com/documents/Epotec_RD-144_TDS_pdf.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Shibata, M.; Yoshihara, S.; Yashiro, M.; Ohno, Y. Thermal and mechanical properties of sorbitol-based Epoxy resin cured with quercetin and the biocomposites with wood flour. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2753–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszczyk, J.; Janicki, B.; Kaczmarek, M. Synthesis and properties of isosorbide based epoxy resin. Eur. Poly. J. 2011, 47, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isosorbide Diglycidyl Ether. Available online: https://specificpolymers.com/product/isosorbide-diglycidyl-ether-bio-5/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Bergamasco, S.; Zikeli, F.; Vinciguerra, V.; Sobolev, A.; Scarnati, L.; Tofani, G.; Mugnozza, G.; Romagnoli, M. Extraction and characterization of acidolysis lignin from turkey oak (Quercus cerris L.) and eucalypt (Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.) Wood from Population Stands in Italy. Polymers 2023, 15, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, C.; Colonna, M.; Tagami, A.; Medina, L.; Sevastyanova, O.; Berglund, L.A.; Lawoko, M. Lignin-based epoxy resins: Unravelling the relationship between structure and material properties. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Ferdosian, F. Lignin-based epoxy resins. In Conversion of Lignin into Bio-Based Chemicals and Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 111–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, S.; Nejad, M. Fully biobased composite made with epoxidized-lignin, reinforced with bamboo fibers. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 3926–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Ding, D.; Tian, Y. Preparation and application of lignin-based epoxy resin from pulping black liquor. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 3494–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiz, D.; Vicente, F.; Kroflic, A.; Likozar, B. Lignin-based covalent adaptable network polymers—When bio-based thermosets meet recyclable by design. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 13836–13867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Eberhardt, T.; Gu, Q.; Pan, H. Preparation of carboxylated lignin-based epoxy resin with excellent mechanical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 150, 110389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovic-Grmusa, I.; Ranci, M.; Tesi, T.; Stupar, S.; Milosevi, M.; Grzeti, J. Recent research progress on lignin-derived resins for natural fiber composite applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 2602. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Gu, X. A review on lignin-based epoxy resins: Lignin effects on their synthesis and properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 229, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yun, J.; Pan, X. Renewable furan-based epoxy resins derived from 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and furfural. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 16555–16562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggio, N.; Marotta, A.; Ambrogi, V.; Cerruti, P.; Gentile, G. Fully bio-based furan/maleic anhydride epoxy resin with enhanced adhesive properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 7195–7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.; Ambrogi, V.; Cerrutic, P.; Mija, A. Green approaches in the synthesis of furan-based diepoxy monomers. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16330–16335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolghadr, M.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Shakeri, A.; Salimi, A. Epoxy resin modification by reactive bio-based furan derivatives: Curing kinetics and mechanical properties. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 673, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, A.; Faggio, N.; Ambrogi, V.; Mija, A.; Gentile, G.; Cerruti, P. Biobased furan-based epoxy/TiO2 nanocomposites for the preparation of coatings with improved chemical resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Matharu, A. Recent developments on biobased curing agents: A review of their preparation and use. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2217–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; Li, M.; Mao, W.; Cao, S.; Xia, J. Study on the synthesis of bio-based epoxy curing agent derived from myrcene and castor oil and the properties of the cured products. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Benelli, T.; Giorgini, L. Evaluation of novel bio-based amino curing agent systems for epoxy resins: Effect of tryptophan and guanine. Processes 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benegaa, M.; Rajab, R.; Blake, J. A preliminary evaluation of bio-based epoxy resin hardeners for maritime application. Procedia Eng. 2017, 200, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Z. Kinetics of partially depolymerized lignin as co-curing agent for epoxy resin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, C.P.; Torofias, S.; Triantafyllidis, K.S. Sub-micro organosolv lignin as bio-based epoxy polymer component: A sustainable curing agent and additive. ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202300076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Fu, S.; Lou, G. Bio-based curing agent for epoxy resins: Simultaneously improved toughness, strength, and flame retardancy. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 120028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, M.D.; Harvey, B.G. Bio-based hydrophobic epoxy-amine networks derived from renewable terpenoids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Zhao, P.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Cui, X.; Hou, X.; Deng, T. A novel bio-based anhydride curing agent for the synthesis of high-performance epoxy resin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 229, 110979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silau, H.; Melas, A.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Daugaard, A.E. Bio-based amine curing agents prepared from lignin by ring-opening functionalization with cyclic aza-silanes and their curing kinetics investigated for aliphatic and aromatic epoxy species. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023, 184, 107822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savonnet, E.; Coz, C.L.; Grau, E.; Grelier, S.; Defoort, B.; Cramail, H. Divanillin-based aromatic amines: Synthesis and use as curing agents for fully vanillin-based epoxy thermosets. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenhausler, F.; Ruckdaeschel, H. L-Arginine as bio-based curing agent for epoxy resins: Temperature-dependence of mechanical properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The ECO Portfolio. Available online: https://crosslinkers.evonik.com/en/products/eco-grades (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Urban, C.; Shaffeler, N. Furan Based Amines as Curing Agents for Epoxy Resins in Low VOC Applications. European Patent 3110870, 29 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Reif, P.; Palenisek, P.; Rose, M. Toward renewable amines: Recent advances in the catalytic amination of biomass-derived oxygenates. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 10400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
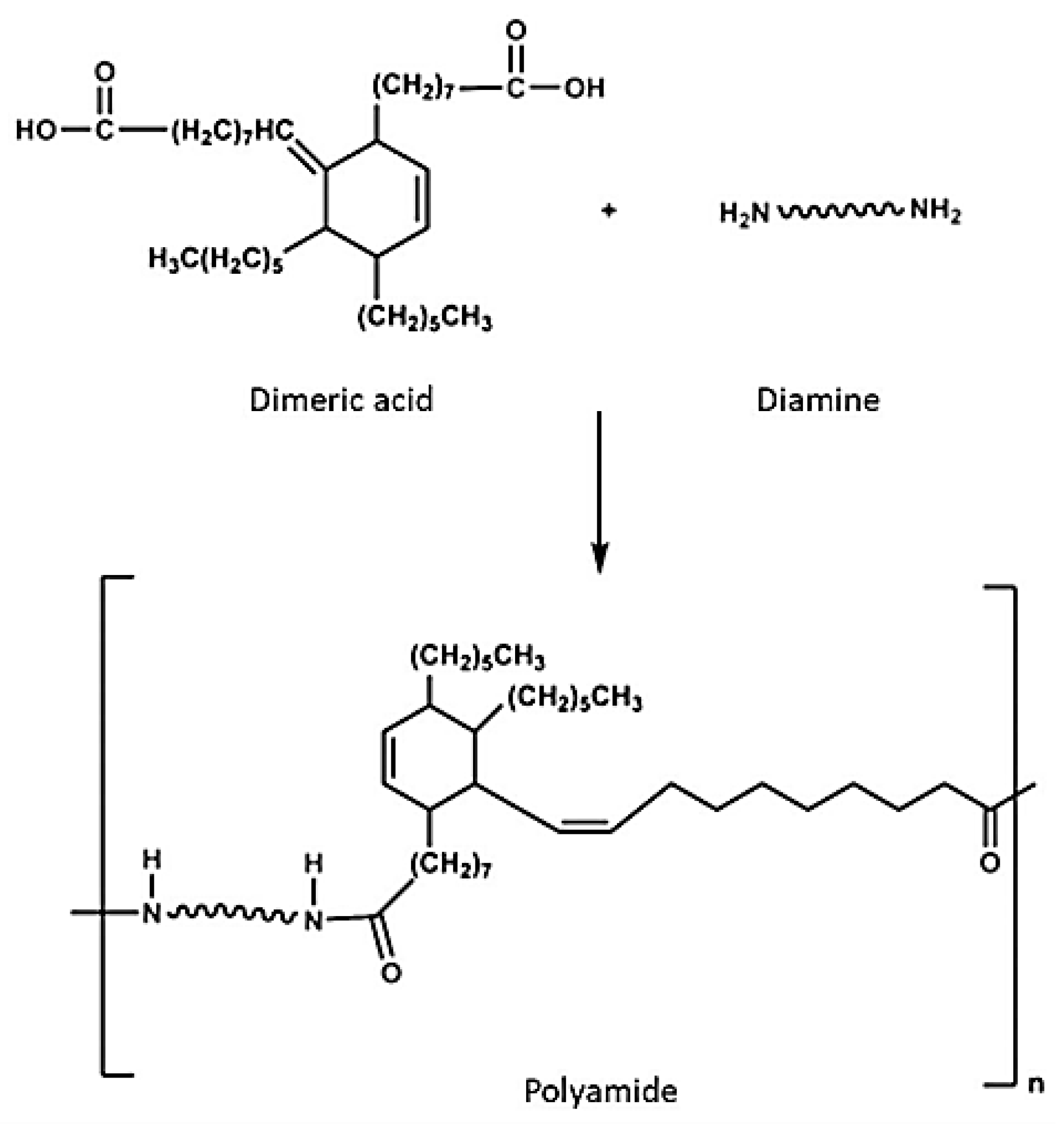
- Paraskar, P.M.; Major, I.; Ladole, M.R.; Doke, R.B.; Patil, N.R.; Kulkarni, R.D. Dimer fatty acid—A renewable building block for high-performance polymeric materials. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2023, 200, 116817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aradur 125. Huntsman Advanced Materials. Available online: http://info.lindberg-lund.no/produktblad/Norge/4-6%20TD/ARA-125.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Ancamide 350A. Available online: https://crosslinkers-web.panpage.de/en2/crosslinkers/ancamide/usa/ancamide_350a_us.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Ancamine 2719. Available online: https://products.evonik.com/assets/em/ea/Ancamine_2719_e_TDS_EN_EN_TDS_PV_52042371_en_GB_EMEA.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Phenalkamine Curing Agents. Phenalkamine Technology | Mannich Based Curing Agents | Cardolite. Available online: https://www.cardolite.com/technology/phenalkamines/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Cardanol. Cardanol—Buy Cardanol Product on GHW (Vietnam) Co., Ltd. Available online: https://en.ghw-vn.com/Cardanol-pd45964296.html (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Ma, Y.; Kou, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bei, Y.; Hu, L.; Huang, Q.; Jia, P.; Zhou, Y. Research advances in bio-based adhesives. Int. J. Adhesion. Adhes. 2023, 126, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, J.S.; Taylor, A.C. The properties and suitability of commercial bio-based epoxies for use in fiber-reinforced composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e50417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguillon, B.; Cabrera, D.; Lazo, M.; Adrian, E.; Carrasco, M.; Medina-Perilla, J.; Vera-Villalobos, J.; Rigail-Cedeno, A. Sorbitol glycidyl ether Epoxy/Brewer’s spent grain biocomposite for fiberboard applications. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 9, 100705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teijido, R.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.; Zhang, Q.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L. Sustainable bio-based epoxy resins with tunable thermal and mechanic properties and superior anti-corrosion performance. Polymers 2023, 15, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Feng, L.; Xie, H.; Wang, M.; Guo, B.; Xue, Z.; Zhu, C.; Xu, J. High-performance recyclable furan-based epoxy resin and its carbon fiber composites with dense hydrongen bonding. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 42, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Ghazawy, R.; El-Saeed, A.M.; Al-Shafey, H.I.; Abdul-Raheim, A.M.; El-Sockary, A.M. Rosin based epoxy coating: Synthesis, identification and characterization. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 69, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, E.; Sguazzo, C.; Moreira, M.G.P. A review of recent research on bio-based epoxy systems on engineering applications and potentialities in aviation sector. Aerospace 2018, 5, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosellin, C.A. Biobased coatings. Coatingstech 2022, 44–52. [Google Scholar]
- Malburet, S.; Mauro, C.; Noe, C.; Mija, A.; Sangermano, M.; Graillot, A. Sustainable access to fully biobased epoxidized vegetable oil thermoset materials prepared by thermal or UV-cationic processes. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41954–41966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, C.; Wang, G.; Wu, D.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X. Synthesis of a bio-based polyamidoamine-epichlorohydrin resin and its application for soy-based adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 44, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.B.; Rintjema, J.; Bravo, F.; Kleij, A.W.; Franco, L.; Puiggali, J.; Aleman, C.; Armeli, E. Novel biobased epoxy thermosets and coatings from poly(limonene carbonate) oxide and synthetic hardeners. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2708–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, V.B.; Aleman, C.; Rintjema, J.; Bravo, F.; Kleij, A.W.; Armelin, E. A biosourced epoxy resin for adhesive thermoset applications. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FormuLITE Amine-Cured Epoxy Systems. High Performance FormuLITE Epoxy Systems|Cardolite. Available online: https://www.cardolite.com/products/formulite/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- GreenPoxy. GreenPoxy—Delivering a Sustainable Future Without Compromising Performance. Available online: https://greenpoxy.org/ (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- CPD Sustainable Epoxy Systems. Bio Based Epoxy Resin Systems. Available online: https://polytek.com/bio-based-epoxy-resin-systems (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- SikaBiresin CR75. Available online: https://www.jacomp.fi/wp-content/uploads/sikabiresin_cr75_eng-1.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).



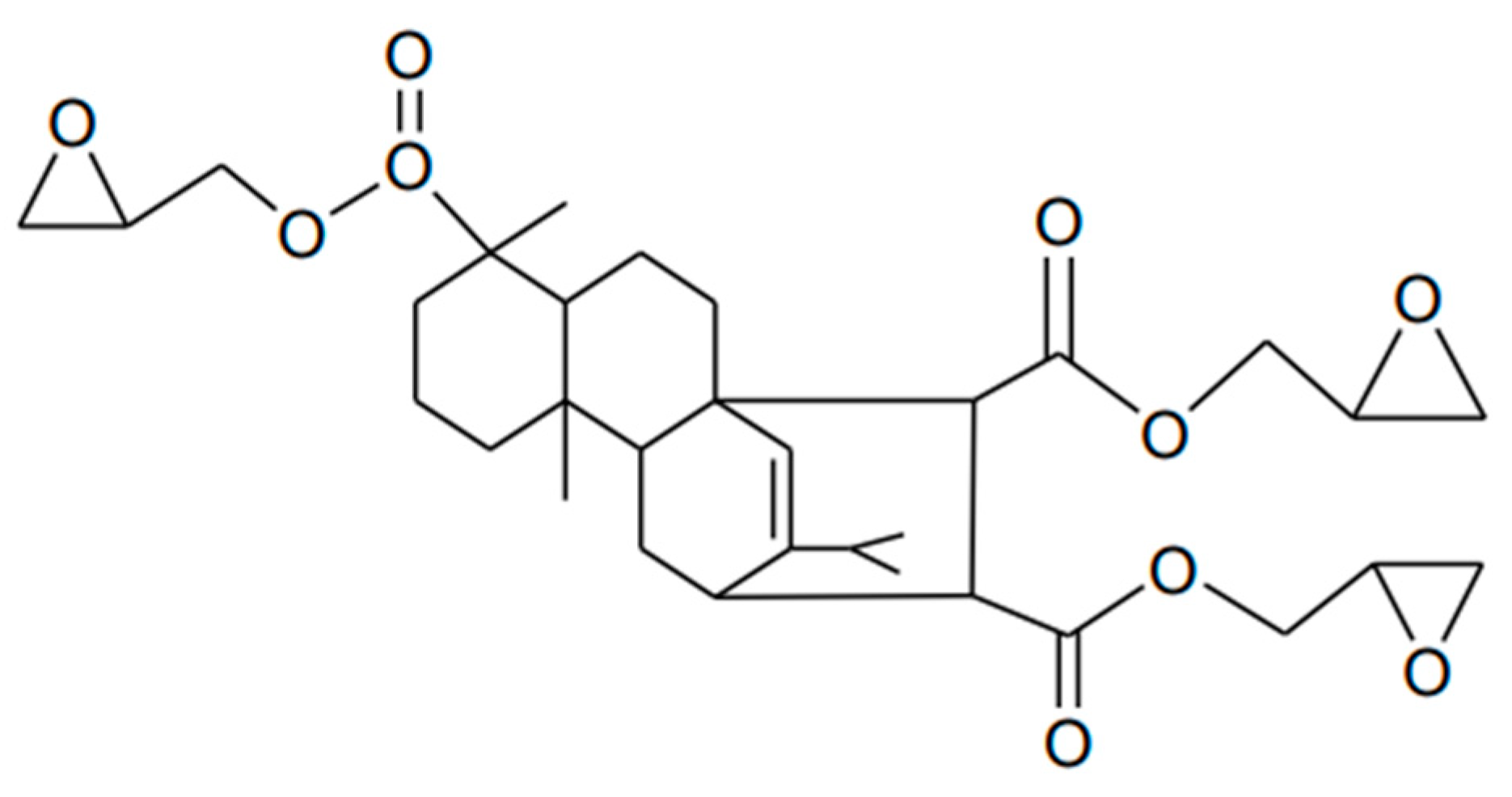

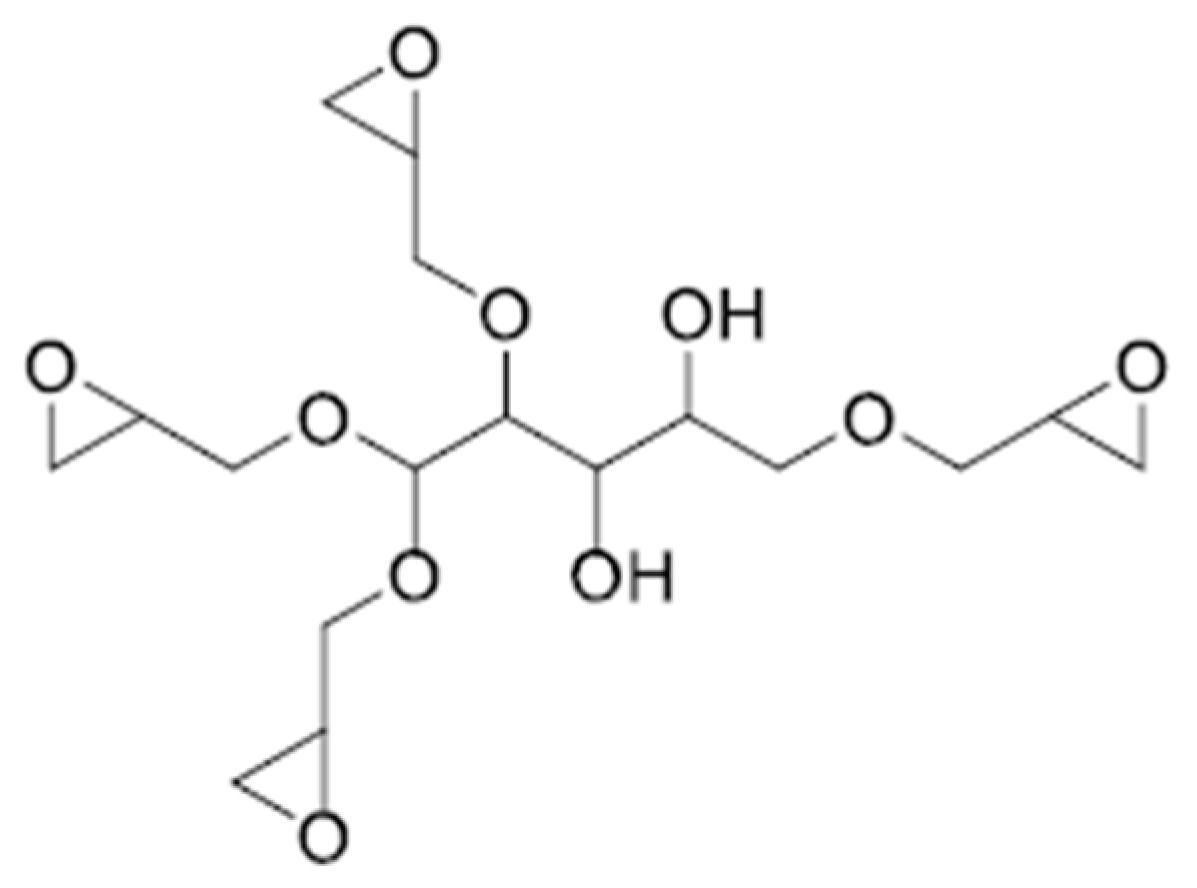
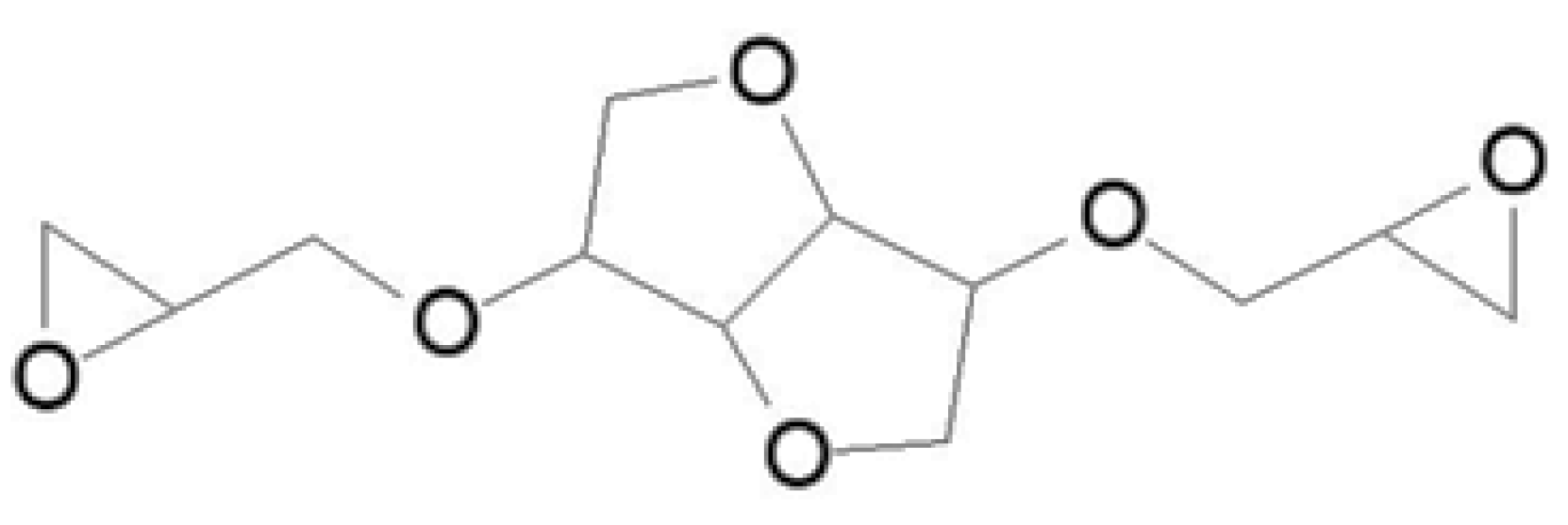



| Bio-Based Conventional Epoxy Resin | Bio-Based Carbon Content, % | EEW, g/Equ. | Viscosity, mPas@25 °C | Commercial Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquid bis-A epoxy resin | 28 | 190 | 12,000 | Epotek YD 128G * Epilox A 1903G |
| Liquid bis-F epoxy resin | 31 | 170 | 4000 | Epotek YDF 170G Epilox F 1700G |
| Liquid novolac epoxy resin | 30 | 172 | 13,000 | Epotek YDF 173G |
| Phenol novolac epoxy resin | 30 | 180 | Semi-solid | Epotek YDF 173G |
| Tetra-functional epoxy resin | 48 | 110 | 4500 | Epotek YDM 441G |
| Diglycidyl ether of 1,6-hexanediol | 50 | 150 | 20 | Epilox P 1320G |
| Diglycidyl ether of 1,4-butanediol | 60 | 135 | 17 | Epilox P 1321G |
| Bio-Based Novel Epoxy Resin | Biomass Source | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetable-oil-based epoxy resin | Vegetable oil | Aditya Birla Chemicals (Mumbai, India) Leuna-Harze GmbH (Leuna, Germany) |
| Cardanol-based epoxy resin | Cashew nut | Cardolite Corp. (Bristol, VA, USA) |
| Rosin-based epoxy resin | Pine, conifer | Ingevity Corp. (North Charleston, NC, USA) |
| Isosorbide-based epoxy resin | Starch | Huntsman Corp. (Woodlands, TX, USA) Nagase ChemteX, (Osaka, Japan) Aditya Birla Chemicals (Mumbai, India) |
| Lignin-based epoxy resin | Wood | Laboratory stage |
| Furan-based epoxy resins | Agricultural byproducts | Laboratory stage |
| Bio-Based Epoxy Resin | Biomass Source | EEW, g/Equ. | Viscosity, mPas@25 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycidyl ether of C12–C14 alcohol | Palm oil | 300 | 10 |
| Triglycidyl ether of castor oil | Castor oil | 600 | 400 |
| Triglycidyl ether of polyglycerol | Palm oil | 170 | 1200 |
| Glycidyl ether of dimeric acid | Tall oil | 430 | 700 |
| Bio-Based Polyamine | Biomass Source | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Isophoronediamine (IPDA) | Starch, glucose | Evonik Industries (Essen, Germany) |
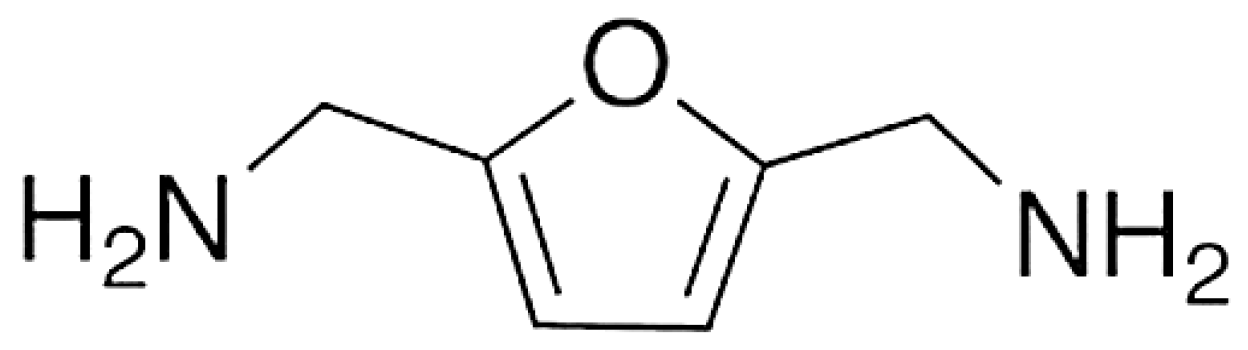
| Furan-based polyamine curing agent | Agricultural byproducts | Laboratory stage |
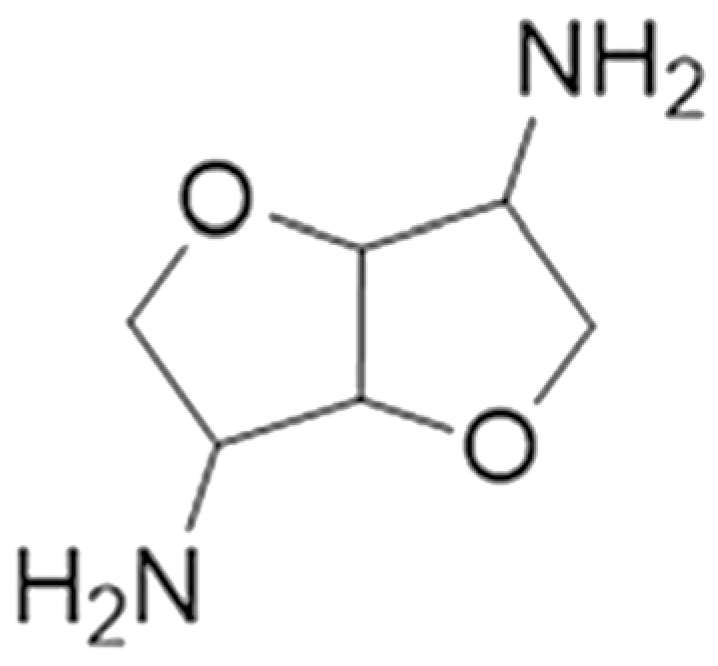
| Isosorbide-based polyamine curing agent | Starch | Laboratory stage |
| Bio-Based Formulated Epoxy Product | Product Type | Bio-Based Carbon Content | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardolite FormuLITE series | 2-component | 30–50% | Composites |
| Sicomin GreenPoxy series | 2-component | 28–56% | Laminating, bonding, coating, etc. |
| Polytek CPD series | 2-component | 20–35% | Bonding, casting, laminating |
| SikaBiresin CR75 series | 2-component | 38% | Composites |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C. Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Technology Progress. Processes 2025, 13, 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041256
Chen C. Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Technology Progress. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041256
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chunfu. 2025. "Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Technology Progress" Processes 13, no. 4: 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041256
APA StyleChen, C. (2025). Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Technology Progress. Processes, 13(4), 1256. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041256






