Abstract
Heavy metals are a common type of contaminant found in soil. However, knowledge gaps still exist in the characteristics of the heavy metals in facility farmland soils. Therefore, a differential analysis was conducted on the heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni) content in soils that were amended with different types of fertilizers (T1, organic fertilizer; T2, organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer). Regression analysis was employed to demonstrate the trends of metal content changes with cropping durations (5, 10, 15, and 20 years). The Pearson correlation analysis was applied to investigate the correlation between soil nutrients and soil metals, and to determine the key factors influencing heavy metal concentration through the random forest model. The results indicated that the average concentration of Cd (0.148 mg·kg−1) was higher than the soil background value but lower than the potential ecological risk threshold (0.3 mg·kg−1, 6.5 < pH ≤ 7.5). The Cd content in soil where only organic fertilizer was applied was 0.118 mg·kg−1, while the Cd content in soil where both organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer were applied was 0.148 mg·kg−1. There was no significant difference in Cd content between the two fertilization types. The regression analysis indicated a linear increasing trend in Cd content as the cropping duration increased. The Pearson correlation analysis showed that there were also significant correlations between pH and both As and Ni; between SOM (soil organic matter) and Cr, Cu, and Zn; as well as between Cd and EC (electrical conductivity). The random forest model exhibited high prediction accuracy when explaining the most significant factors influencing the concentrations of Cd, Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni, with overall correlation coefficients (r) of 0.009, 0.44, 0.33, 0.04, 0.32, 0.61, and 0.65, respectively. Using Hakanson’s method to conduct an ecological risk assessment on the soil in the study area, it was found that the overall potential ecological risk level was relatively low. However, the proportion of moderate to high ecological risk associated with Cd elements was close to 40%, which requires special attention.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of urbanization has exacerbated ecological risks in agriculture, with human activities such as industrial production, transportation, sewage irrigation, application of organic fertilizers, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides all contributing directly or indirectly to the accumulation of heavy metals in soil [1,2]. Compared to pollution in water bodies and air, soil heavy metal pollution is more concealed. Once heavy metals enter the soil, they are not easily degraded by microorganisms [3], and they are difficult to transport by runoff erosion, leading to their continuous accumulation in the soil [4]. When heavy metals accumulate to a certain level, they can lead to environmental deterioration, contaminate rivers and groundwater sources, and cause a decline in soil fertility, resulting in reduced crop yields. Furthermore, they may directly poison plants and indirectly impact human health [5,6,7,8,9]. This has become an urgent soil environmental issue that demands immediate attention and for relevant investigations to be conducted in some countries [10,11,12,13,14]. Among the 32 soil samples collected from India, the concentrations of six heavy metals (As, Cr, Cu, Zn, Ni, and Pb) in most urban soils were higher than the geochemical background values (Grade I) and the Canadian soil quality guideline values (Grade II) [15]. In the facility farmlands of northern Jordan, some facility farmland soils failed to meet soil quality standards, particularly for Cd, Pb, and Ni content, with average concentrations of 0.81 mg·kg−1, 53.0 mg·kg−1, and 49.3 mg·kg−1, respectively. The Cd posed the highest total hazard index (72.27–82.67%), followed by Pb (11.49–14.87%) [16]. The survey revealed that the cadmium concentration in farmland soil in Shenyang, China (0.246 ± 0.156 mg·kg−1) exceeded the standard (HJ/T 333-2006) by a proportion of 39.29% [17]. In the Wuwei region of Gansu Province in China, there was a cumulative trend of Cd, Cu, and Zn elements in facility farmland soil, with concentrations 60%, 23%, and 14% higher, respectively, than those in cultivated soil [18]. However, knowledge gaps still exist in terms of the characteristics of heavy metal in facility farmland soils.
Facility farmlands, characterized by semi-enclosed environments with high temperatures, humidity, and fertilization levels, along with continuous cultivation, have led to numerous irreversible environmental issues, including heavy metal pollution [19,20]. Among these heavy metals, Cd contamination in facility farmland soil is particularly severe. In southern, northern, and northwestern China, the exceedance rates for Cd were 41.7%, 54.5%, and 11.1%, respectively [21]. The farmland soil in Baiyin District, Gansu Province, was heavily contaminated with Cd, with 100% of samples exceeding the risk management threshold for farmland [22]. In Beijing and the Xiangfen County of China in Shanxi Province, the average Cd concentrations were higher than the soil background values and approached the limit set by the Environmental Quality Evaluation Standards for Edible Agricultural Products Production Areas (0.40 mg·kg−1), indicating a certain degree of accumulation risk [23]. Among 149 soil samples collected from four major vegetable-producing regions in Shandong Province, it was found that the cadmium contamination level was the highest, reaching 9.40% [24]. In San Luis Potosí, México, Cd concentrations ranged from 3.72 to 7.46 mg·kg−1, which were below Canadian agricultural standards [25]. In facility farmland samples from Çanakkale, Turkey, Cd concentrations ranged from 0.68 to 1.07 ug·g−1, within the acceptable range for agricultural soil [26]. In facility farmland soil in Spain, Cd concentrations (0.1–1.9 mg·kg−1) were three times higher than those in cultivated soil [27]. It is vital to understand the characteristics of Cd enriched in facility farmland soil.
Facility farmland represents a modernized approach to agricultural production that minimizes external environmental disturbances and achieves a high degree of intensification. Since the 1990s, China’s facility farmland has undergone rapid development [28], becoming a pillar industry of China’s modern agricultural development. According to the National Plan for the Construction of Modern Facility Agriculture (2023–2030) released by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, China’s facility farmland crop planting area reached approximately 26.7 million hectares in 2021, ranking first in the world [29]. Beijing, as China’s capital and political–cultural center, is also one of the largest cities in the world. By the end of 2022, its facility agricultural area reached 32,496.0 hectares, accounting for 22.11% of the total cultivated land area (Beijing Statistical Yearbook 2023) [30]. With rapid urban development, the impacts on soil environmental quality changes are accelerating, and the pressure on soil environmental pollution in facility farmland is also increasing. Consequently, soil environmental quality has attracted increasing attention from the public. To ensure the ecological environmental safety and sustainable development of facility farmland in Beijing’s suburbs, strengthening soil environmental quality monitoring is of paramount importance.
This study takes typical facility farmland in northern China as the research object, investigating the content of soil nutrients and the accumulation of heavy metals. Specifically, the objectives of this study are as follows: (1) determining the content of heavy metals in soil in northern China and evaluating the level of soil pollution; (2) clarifying the distribution of heavy metal content in soil under different fertilization types and planting years; (3) and identifying the key factors influencing the heavy metal content in facility farmland soil. We hypothesize (1) that the Cd element is a heavily enriched heavy metal in facility agriculture soils in northern China and (2) that coupling organic fertilizer and soil nutrients are significant factors influencing heavily enriched heavy metals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area and Method
This study was conducted in the northern region of the North China Plain (115.7–117.4° E, 39.4–41.6° N), which has a temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate with abundant sunshine and four distinct seasons [31]. The annual average temperature there is about 11.8 °C, and the average annual rainfall about 600 mm [32,33]. The main soil types are cinnamon soil and fluvo-aquic soil, with the soil pH being neutral or weak alkaline [33]. The production bases for facility agriculture were mainly located in the plain areas of the region. Before being renovated, the facility farmland was all used as large fields, mainly for planting wheat and corn.
From May to July 2023, a total of 69 soil samples (0–20 cm) were collected from facility farmlands in the research region. During the sampling process, special locations such as field ridges, roads, ditches, fertilizer piles, and manure heaps were avoided based on the conditions of the plots. Each facility farmland was designated as a sampling unit, and soil samples were collected using an “S”-shaped five-point sampling method within each facility farmland. After thoroughly mixing the soil samples, the quartering method was used to obtain a portion of the mixed soil sample. The mixed samples were then placed in clean self-sealing bags, properly labeled, and brought back to the laboratory for impurity removal, air-drying, crushing, and sieving through nylon sieves of 2.0, 1.0, and 0.149 mm. At the same time, information such as the planting years (5, 10, 15, and 20 years) and fertilization types (T1, organic fertilizer; T2, organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer) was also recorded. The types of organic fertilizer included sheep manure, cow manure, and chicken manure, and some of the organic fertilizers applied in this region were sourced from the surrounding area of the sampling site (self-reported by farm managers/owners based on their records).
2.2. Sample Measurement Method
In this study, seven heavy metal elements were determined. The Pb and Cd in soil were determined using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Agilent 240FS, Santa Clara, CA, USA) (GB/T17141-1997) [34], As was determined with atomic fluorescence spectrometry (Agilent 240FS) (HJ491-2019) [35], and chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), nickel (Ni) were determined by flame atomic absorption spectrometry (Agilent 240FS) (HJ491-2019). The soil organic matter (SOM) concentrations were determined using the potassium dichromate oxidation volumetric method [36]; the total nitrogen (TN) was measured with the Kjeldahl distillation method (KDY-9820, Beijing, China) [37]; available P (AP) was measured using the 0.5 mol·L−1 sodium bicarbonate extraction-spectrophotometric method (DR6000, Loveland, CO, USA) [38]; and available K (AK) was extracted with 1 mol·L−1 NH4OAc and measured by atomic absorption spectrometry [39]. The soil pH was measured with a pH meter (Mettler S220, Greifensee, Switzerland) using a 1:5 soil-to-water ratio [40]. Soil electrical conductivity (EC) was measured using the electrode method with a soil-to-water mass ratio of 1:5 [40].
2.3. Ecological Risk Assessment
The potential ecological risk index method proposed by Hakanson (1980) comprehensively considers the content, toxicity, and ecological effects of heavy metals, along with the synergistic effects of multiple heavy metals [41]. It is one of the most commonly used methods for ecological risk assessment [42]. The potential ecological risk index (Ei) of a single heavy metal element and the comprehensive potential ecological risk index (RI) were calculated as follows [43]:
where Ti is the toxic response factor for a given substance (Cd = 30, Cr = 2, Pb = 5, As = 10, Cu = 5, Zn = 1, Ni = 5) [44], Ci represents the heavy metal content in the topsoil, and Cn is the regional background heavy metal value in the topsoil [45]. The risk classification standards are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Classification of pollution grades for potential ecological risk assessment.
2.4. Variable Importance Determination
The random forest (RF) model is an ensemble machine learning algorithm based on classification and regression that can be used to analyze complex nonlinear relationships between independent and dependent variables. It utilizes the bootstrap sampling method to randomly extract smaller samples from the original data to be used as the training set and then builds decision trees based on these data. The sampling and training steps are repeated to establish a large number of decision trees, eventually forming a random forest [46]. The RF regression model can be used to model all covariates and determine their importance. The increase in mean squared error (IncMSE) was selected as the metric to quantify the variable importance. IncMSE involves randomly shuffling the values of a feature in the dataset and measuring the increase in the mean squared error (MSE) of the model’s predictions. The larger the value, the greater the importance of the variable [47]. In this study, RF was employed to identify the key factors (Cd, Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, Ni, TN, TP, AP, AK, pH, EC, and SOM) influencing the concentrations of heavy metals in the soil of facility farmland.
2.5. Data Analysis
All data were processed and analyzed using Microsoft Excel 2021 (v17.0) and IBM SPSS Statistics version 27, using difference analysis to study the impact of different fertilization types on the distribution of heavy metals in soil. The autocorrelation of the soil nutrient content (SOM, TN, TP, AP, AK) and its correlation with heavy metal content were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation analysis. RF was used to model all the covariates and determine the key factors influencing the heavy metal content in the soil of facility farmlands. Additionally, Origin 2021, Prism 9.5.1, and R 4.3.3 software were used for graphing.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Risks of Heavy Metal Content in Surface Soil (0 to 20 cm)
Table 2 lists the background values of seven heavy metals in soil. This study found that the concentrations at 66.67%, 100%, 95.65%, 95.65%, 100%, 0%, and 0% of the sampling sites exceeded the soil background values for Cd, Cr, As, Cu, Zn, Pb, and Ni, respectively. However, the average contents of the Cd, Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni elements remained below the risk screening values (GB 15618-2018) [48]. The coefficients of variation (CVs) for the seven elements were as follows: Ni (52%), Cd (37%), Cr (37%), As (21%), Cu (21%), Zn (20%), and Pb (17%). Notably, CV > 36% was classified as high variability, while 16% < CV < 36% was classified as moderate variability. Among them, Cd, Cr, and Ni have high variation, while As, Cu, Zn, and Pb had moderate variation. A higher CV indicated a greater likelihood of anthropogenic influence and less even spatial distribution. The kurtosis values for Cd, As, and Cu exceeded 1, indicating steeper normal distribution curves and extreme values. The skewness values for Cd, Cr, and As were close to 1, displaying right-skewed distributions and indicating the existence of higher abnormal values.

Table 2.
Heavy metal content characteristics of facility farmland soils.
The average EI of the seven heavy metal elements in the 0 to 20 cm soil layer were in the following order: Cd (37.4) > As (14.9) > Cu (7.9) > Cr (5.3) > Pb (4.3) > Ni (3.4) > Zn (1.7), indicating that all seven elements belonged to the category of having a slight pollution risk (Figure 1). Remarkably, the range of the Cd EI was from 14.9 to 84.2, in which slight ecological risks accounted for 60.87%, and moderate and strong ecological risks accounted for 37.68% and 1.45%, respectively. From the perspective of comprehensive risk, the average RI of the heavy metals in the 0 to 20 cm soil layer was 74.8; the overall risk level was relatively light.
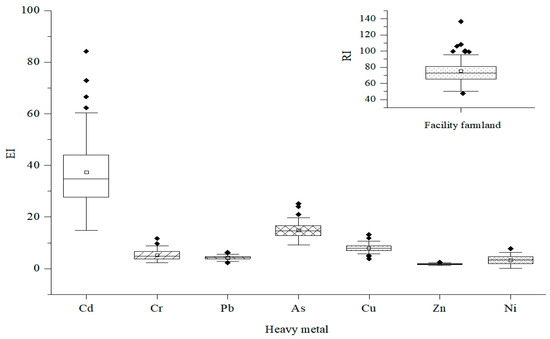
Figure 1.
Potential ecological risk index diagram of heavy metals in facility farmland soil.
3.2. Effects of Fertilizer Type and Planting Year on Soil Heavy Metal Content
The fertilization type had various effects on the heavy metal concentrations in the study (Figure 2). There were significant differences (p < 0.05) in the contents of Cr, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni between the two types of fertilized soils, T1 and T2. The average contents of Cr, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni in the T1 type of fertilized soil were 98.40 mg·kg−1, 11.03 mg·kg−1, 29.32 mg·kg−1, 97.20 mg·kg−1, and 25.88 mg·kg−1, respectively. There were no significant differences in the Cd and Pb soil contents among the two types of fertilization (p > 0.05). The Cd contents in T1 and T2 soils were 0.118 mg·kg−1 and 0.148 mg·kg−1, respectively.
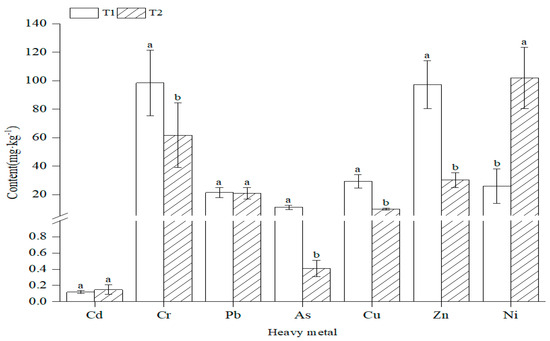
Figure 2.
Heavy metal content in facility farmland soils under different fertilization types. Note: T1, organic fertilizer; T2, organic fertilizer and chemical fertilizer. Different letters within the same heavy metals indicate significant differences (p < 0.05).
In the 0 to 20 cm soil layer, the contents of Cd and Cr increased with increasing planting years, whereas the contents of Cu, Zn, and Ni decreased with increasing planting years; there was a significant negative correlation between the copper element and planting years (p < 0.01) (Figure 3). No significant correlation was found between the concentrations of lead (Pb) and arsenic (As) in the soil of facility farmland and the planting years. It was also found that the concentration of heavy metals in the soil of facility farmland tended to decrease slightly after a certain period of cultivation. The average concentrations of Cd and Pb in the soil reached their peaks in the 11th year of cultivation, which were 0.211 mg·kg−1 and 24.25 mg·kg−1 respectively. In the fourteenth year, the average content of Cr in the soil was the highest, which was 121.25 mg·kg−1. In the fifth year of planting, the average contents of Cu and Zn in the soil were the highest, which were 49.20 mg·kg−1 and 124.60 mg·kg−1, respectively.
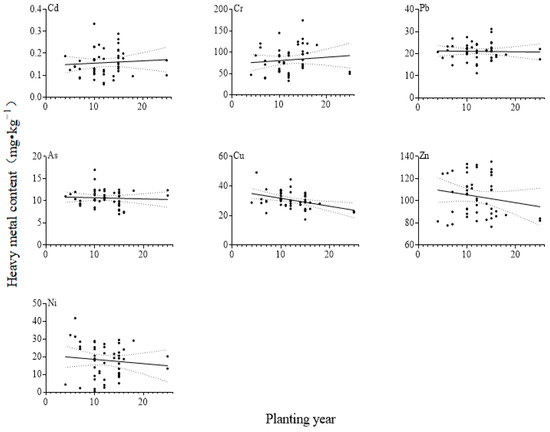
Figure 3.
The change in heavy metal content in facility farmland soils with planting year.
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Heavy Metal Concentrations and Soil Nutrients
In this study, the average value and range of pH were 7.53 and 6.67–8.09 in soil from 0 to 20 cm. The content ranges of TN, TP, AP, AK, and SOM were 0.20–1.81 g·kg−1, 0.02–0.33%, 34.61–614.20 mg·kg−1, 56.10–1449.10 mg·kg−1, and 13.67–76.26 g·kg−1, respectively. Meanwhile, the average values were 0.78 g·kg−1, 0.10%, 264.37 mg·kg−1, 508.94 mg·kg−1, and 42.05 g·kg−1, respectively (Table 3). Respectively, 39% of TP, 97% of AP, 85% of AK, and 49% of SOM sites had very abundant nutrient contents. Additionally, 55% of the surveyed sites had TN content levels that were moderate or above.

Table 3.
Soil nutrient content characteristics of facility farmlands.
In the 0–20 cm soil layer, TN, TP, AP, AK, and SOM exhibited significant positive correlations with Cu and Zn (Figure 4). The pH value showed a significant positive correlation with As and Ni (p < 0.05). The EC value had a significant positive correlation with Cd and Pb (p < 0.05). TP demonstrated a significant negative correlation with Cr and Ni (p < 0.05). AP had a significant negative correlation with As (p < 0.05). SOM exhibited a significant negative correlation with Cr (p < 0.05). Changes in soil nutrient content were related to the changes in heavy metal content. Since soil nutrient content primarily originated from fertilization, the application of organic and chemical fertilizers may have been an important reason for the increase in heavy metal content in the soil of facility farmlands.
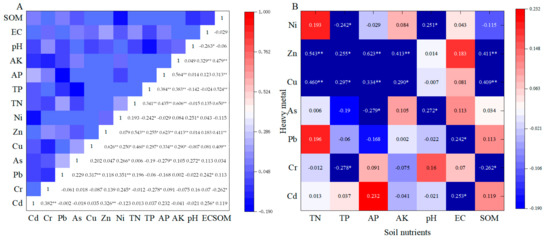
Figure 4.
Correlation plot of the soil heavy metal content with soil nutrients. Note: * correlation is significant at the 0.05 level, ** correlation is significant at the 0.01 level. TN (total nitrogen), TP (total phosphorus), AP (available phosphorus), AK (available potassium), SOM (soil organic matter), and EC value (electrical conductivity). (A) Comprehensive Correlation Analysis of Soil Parameters Including Physical-Chemical Properties, Nutrient Levels and Heavy Metal Contents; (B) Correlation Analysis of Soil Physical-Chemical Properties, Nutrient Levels and Heavy Metal Contents.
3.4. Key Factors Influencing Heavy Metal Concentrations in Farmland Soil
The overall accuracy correlation coefficients (r) of the models for Cd, Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni in the 0 to 20 cm soil were 0.009, 0.44, 0.33, 0.04, 0.32, 0.61, and 0.65, respectively, showing relatively high prediction accuracies (Figure 5). The two most important factors explaining the Cd content were Zn (40.63%) and EC (30.79%). The top three factors explaining the Cr content were TP (44.73%), AP (18.18%), and Cd (16.00%). The most important factors explaining the Pb content were Cu (42.73%), Ni (35.48%), Zn (22.34%), and AP (21.36%). Meanwhile, As was mainly influenced by Pb (40.73%), pH (21.39%), and Cu (19.89%), whereas Cu was mainly influenced by Zn (63.90%), TP (17.56%), and Cr (17.48%). The three most important factors explaining the Zn content were TP (80.37%), Zn (49.56%), and AK (33.54%). The three most important factors explaining the Ni content were Cr (27.56%), Pb (24.10%), and pH (16.77%). Overall, the variations in heavy metal content in the 0 to 20 cm soil layer were significantly influenced by fertilization (as heavy metals and nutrients commonly coexist in certain fertilizers, they are applied to the soil together, affecting the heavy metal content of the soil).
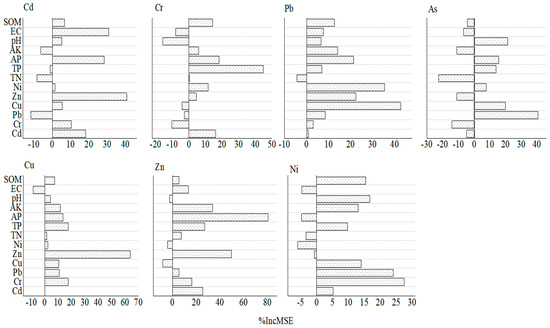
Figure 5.
Importance ranking of the factors influencing heavy metals in facility farmland soils.
4. Discussion
The findings of this study indicate that there was a significant accumulation of Cd in the surface soil of facility farmland (Table 4). This was consistent with other research findings, which showed that the cadmium content in farmland soil in Wuqing District, Tianjin, was higher than the local soil background value, indicating a clear accumulation phenomenon [49]. In two districts of Bangladesh, the Cd content in soil exceeded the local soil background value of 0.3 mg·kg−1, suggesting a significant influence from human activities [50]. Using the Hakanson potential ecological risk index, it was found that some facility farmland soils are contaminated with Cd. The accumulation of Cd in topsoil still persists within the surveyed area, and there is a trend of decreasing numbers of sites with moderate to high ecological risk levels [51,52]. However, Cd is one of the major contaminants in the soil of facility farmland in northern China. Studies have shown that its main sources include fertilizer application, pesticide use, atmospheric deposition, and irrigation water. Due to the long-term use of film-covered, semi-enclosed planting modes in facility farmland, atmospheric deposition is not the primary factor influencing the Cd content in the soil [53]. Between 2015 and 2019, compared to 2005–2009, the input of Cd from irrigation water into farmland soil in north China decreased, while the input of Cd from livestock and poultry manure increased by 18.6% [54,55]. The amount of Cd that entered into soil from livestock and poultry manure would be 3.2 to 122.4 g ha−1 yr−1; the highest concentration of Cd in the topsoil (0–20 cm) would increase 0.049 mg·kg−1 per year [56,57,58]. Pesticide application can also affect the accumulation of Cd in soil, but it is not the primary factor [59].
There are significant differences between facility farmland and open field farmland in the production process. It operates under a closed condition characterized by long-term film mulching, high temperature, high humidity, high input, and high output, representing a planting mode with intense human interference. Under different fertilization types, Cd, Cr, As, Cu, and Zn all exhibit varying degrees of accumulation, which may be related to the improper use of fertilizers [60]. In the study area, the base fertilizers for farmland mainly included sheep manure, commercial organic fertilizer, and chemical fertilizer. Research has shown that long-term fertilization can affect soil physicochemical properties, thereby influencing heavy metal content [61]. Heavy metals entering the ecosystem may lead to accumulation in the food chain, and the concentration of heavy metals in food has been proven to be closely related to the concentration of heavy metals in soil [62]. There were certain differences in the heavy metal content of livestock and poultry manure from different sources [63,64,65]. The over-limit rates of Cd, Cr, Pb, and As in chicken manure were 0%, 3.6%, 0.4%, and 6%, respectively, while the over-limit rate of As in cow manure was 1.2%. The over-limit rates of Cd, Cr, Pb, and As in sheep manure were all 0% [66]. According to the Chinese industry standard for organic fertilizers (NY 525-2012) [67], the over-limit rate of chromium in livestock and poultry manure was 2.76% [65]. It can be seen that livestock and poultry manure were a major source of heavy metals in the soil of north China [68], and they are also one of the main factors leading to the accumulation of metal elements in farmland soil.

Table 4.
Organic fertilizer raw materials and commodities, and organic fertilizer heavy metal index test samples (mg·kg−1) [66,69].
Table 4.
Organic fertilizer raw materials and commodities, and organic fertilizer heavy metal index test samples (mg·kg−1) [66,69].
| Index | Organic Fertilizer | Commercial Organic Fertilizer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep Manure (n = 63) | Cow Manure (n = 245) | Chicken Manure (n = 285) | Sheep Manure (n = 40) | Sheep/Cow Manure (n = 2) | ||
| Cd | range | 0–1.7 | 0–2.3 | 0–2.3 | 0.005–0.070 | 0.022–0.045 |
| Average | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.5 | 0.042 | 0.034 | |
| Cr | range | 0–59 | 0.6–106.9 | 0–2896 | 1.76–28.40 | 7.29–17.20 |
| Average | 20.4 ± 10.7 | 20.7 ± 16.3 | 66.3 ± 308.5 | 12.40 | 12.20 | |
| Pb | range | 2.7–46.1 | 0.3–40.9 | 0–51.7 | 0.93–38.8 | 9.33–14.70 |
| Average | 11.3 ± 8 | 8.7 ± 7.1 | 9.2 ± 8.9 | 11.80 | 12.02 | |
| As | range | 0.5–12.5 | 0.1–32.6 | 0.1–55.8 | 0.30–11.4 | 2.30–6.50 |
| Average | 5.5 ± 2.8 | 4.3 ± 3.4 | 6.0 ± 6.2 | 3.44 | 4.39 | |
| Cu | range | 0–75.4 | 11.6–36.3 | 13.4–41.2 | 4.00–123.1 | 12.2–30.3 |
| Average | 18.86 | 19.7 | 21.55 | 16.4 | 21.23 | |
| Zn | range | 0–272.6 | 38.6–319.8 | 46.0–242.0 | 14.0–154 | 55.4–82.6 |
| Average | 95.16 | 90.51 | 114.24 | 68.8 | 68.9 | |
As can be seen from Figure 4, Cd shows an overall upward trend within the planting years. Simultaneously, studies have found that the heavy metals in the soil of facility farmland exhibit a slight decreasing trend after a certain number of planting years, which may be attributed to changes in the soil’s physicochemical properties during long-term planting [61,70]. Numerous studies have also indicated that the accumulation of heavy metals in soil tends to increase with the prolongation of planting years, which is associated with the excessive application of metal-containing organic and chemical fertilizers [71], and is also related to the extensive use of pesticides containing metals, as well as the direct application of livestock and poultry manure (such as chicken manure and sheep manure) back to the farmlands [72,73].
The Pearson correlation results in this study also indicate that there were significant correlations between the total amounts of Cu, Zn, and Cr in the soil of facility farmland and SOM. There was also a significant correlation between As and Ni and pH (p < 0.05). Previous studies have also shown that soil nutrients (such as soil pH, SOM, TN, and TP) were correlated with soil heavy metal concentrations [74,75]. Further consideration of the relatively limited sources of SOM, TN, TP, and AP in facility cultivation, mainly through organic fertilizers and chemical fertilizers, is essential. The analysis of the major inputs in facility farmland soil in this study further confirms that Cd, Cr, Cu, and Zn contents in organic and chemical fertilizers are relatively high, contributing prominently to the accumulation of heavy metals in facility soil. Additionally, studies by Xu Minggang et al. [76] have shown that the long-term application of organic fertilizers made from livestock and poultry manure not only increases soil nutrient content but also leads to an increase in soil heavy metal content. Therefore, scientifically and reasonably processing livestock and poultry manure and selecting safe organic/chemical fertilizers are effective ways to slow down the degradation rate of facility farmland soil quality and ensure the safe and sustainable development of facility agriculture.
5. Conclusions
This study validated our hypothesis that Cd is a heavy metal that accumulates to a high degree in the soils of facility farmland in northern China. Compared to soil background values, the accumulation of Cd in facility farmland soils was the most severe, and the concentration of Cd in some of these farmland soils had reached levels that may pose potential risks to both the ecosystem and human health.
Heavy metal-containing chemical fertilizers and organic fertilizers were the primary sources of Cd, Cr, As, Cu, and Zn in soil. The type and quantity of the fertilizers applied were significant factors contributing to the differences in heavy metal accumulation in soil under the various fertilization practices studied.
Regression analysis also indicated that Cd content increases linearly with the number of years of cultivation. Therefore, the duration of cultivation is an important factor influencing soil nutrient and heavy metal accumulation in greenhouse farmland. Considering the close relationship between certain soil nutrient indicators and heavy metal content in soil, as revealed by Pearson correlation analysis, as well as the most significant factors influencing heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Pb, As, Cu, Zn, and Ni) content as identified through the random forest model, it is evident that long-term fertilization not only increases soil nutrient content but also leads to an increase in soil heavy metal content.
The results indicate that the long-term excessive use of chemical fertilizers and organic fertilizers containing high concentrations of heavy metals can lead to the accumulation of heavy metals in soil. Therefore, to maintain high soil quality and achieve sustainable utilization, it is necessary to control the quality of chemical fertilizers and organic fertilizers in order to manage the levels of heavy metals in facility farmland soil.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, conceptualization, data curation, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, M.Z.; investigation and data curation, G.Z., Z.Y., Y.L., N.S. and S.L. (Shangqiang Liao); conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, writing—review and editing, L.D. and S.L. (Shunjiang Li). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the study was financially supported by the grants from the National key research and development program of China (Project No.: 2023YFD1700104), and the earmarked fund for CARS (Project No.: CARS-02-23).
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, W.; Shao, Y.B.; Zhou, Y.B.; Pan, Y.C.; Dai, H.Y.; Gao, B.B.; Yan, Y.G. Multi scale analysis of spatial variability of heavy metals in farmland soils: Case study of soil Cd in Shunyi District of Beijing, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Cai, X.Y.; Ding, G.Y.; Ren, F.M.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, N.; Liu, J.X.; Li, L.X.; Shi, R.G. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils in Beijing by three improved risk assessment methods. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 57970–57982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.H.; Gao, Y.; Ning, X.L.; Li, Z.H. Research progress and hotspots on microbial remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil: A systematic review and future perspectives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 118192–118212. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xiao, P. Influence factor analysis of soil heavy metal based on categorical regression. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 7373–7386. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.B.; Liu, W.X.; Li, Z.G.; Teng, Y.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y.M. Effects of long-term fertilizer applications on peanut yield and quality and plant and soil heavy metal accumulation. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.; Ye, W.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, H.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, D.X.; Tang, Z.Y.; Ma, Y.H. Review on contamination and remediation technology of heavy metal in agricultural soil. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2013, 22, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, A.X.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.H.; Dong, W.G.; Han, P.; Zhang, G.G.; Wang, K.Y.; Pan, L.G. Annual variability and characteristics analysis of heavy metals in agricultural soil of Beijing. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2011, 44, 3778–3789. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, Q.; Chen, Q.F.; Zhao, C.S.; Liu, W.; Li, Q. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and assessment of environmental quality and safety of facility agriculture soil in Shouguang. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, R.; Lu, Y.Z.; Shen, S.Y. Assessment of heavy metal content and pollution in organic and conventional farming soils in North China. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2015, 23, 877–885. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T.; Tian, Y.Q.; Gao, L.H. Research Progress on Soil Quality in Protected Vegetable Fields. J. Chin. Veg. 2021, 10, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.G.; Yang, L.S. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Ping, L.W.; Ji, X.H.; Li, X.X.; Song, P.P.; Zhu, L.S.; Wang, J. Content analysis and pollution risk assessment of heavy metal in common fertilizers in typical north vegetable fields. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 521–529. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.L.; Li, Q.C.; Ma, L.; Jia, C.; Chen, J. Characteristics, health risks, and source analysis of heavy metals pollution in surface soil in Shan County. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 46, 442–452. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz Rizo, O.; Fonticiella Morell, D.; Arado López, J.; Borrell Muñoz, J.; D‘Alessandro Rodríguez, K.; López Pino, N. Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban topsoils from Las Tunas City, Cuba. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 91, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Adimalla, N. Heavy metals pollution assessment and its associated human health risk evaluation of urban soils from Indian cities: A review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 42, 173–190. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamad, A.A.; Al-Taani, A.A.; Ghrefat, H.; Khawajah, M.; Zoubi, A. Assessment of Heavy Metals in Greenhouse Cultivated Soils, Northern Jordan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 33, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, X.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, Y.S.; Hou, Y.X.; Zhao, X.X. Source apportionment and risk assessment of heavy metals in typical greenhouse vegetable soils in Shenyang, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 196, 72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.Y.; Zeng, X.B.; Su, S.M.; Duan, R.; Wang, Y.N.; Gao, X. Heavy metal accumulation and source analysis in greenhouse soils of Wuwei District, Gansu Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5359–5369. [Google Scholar]
- Sungur, A.; Soylak, M.; Yilmaz, E.; Yilmaz, S.; Ozcan, H. Characterization of Heavy Metal Fractions in Agricultural Soils by Sequential Extraction Procedure: The Relationship Between Soil Properties and Heavy Metal Fractions. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2014, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, K.; Yawar, W.; Akhter, P.; Rehana, I. Atomic absorption spectrometric determination of cadmium and lead in soil after total digestion. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, M.; Yang, L.S.; Wei, B.G.; Li, H.R.; Yu, J.P. Contamination assessment and spatial distribution of heavy metals in greenhouse soils in China. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2018, 34, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, T.T.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhou, J.; Cao, S.Z. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil, Baiyin suburb. Environ. Ecol. 2023, 5, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.B.; Ma, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, B.Y.; Fang, G.L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.S.; Wang, L.; Xiang, B. Assessments of levels, potential ecological risk, and human health risk of heavy metals in the soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19330–19340. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, L.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Wei, J.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Jiang, L.H.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Y.F. Analysis of heavy metal sources for vegetable soils from Shandong Province, China. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Vázquez, F.J.; Flores-Ramírez, R.; Ochoa-Martínez, A.C.; Carrizales-Yáñez, L.; Ilizaliturri-Hernández, C.A.; Moctezuma-González, J.; Pruneda-Álvarez, L.G.; Ruiz-Vera, T.; Orta-García, S.T.; González-Palomo, A.K.; et al. Human health risks associated with heavy metals in soil in different areas of San Luis Potosí, México. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2015, 22, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sungur, A.; Soylak, M.; Özcan, H. Chemical fractionation, mobility and environmental impacts of heavy metals in greenhouse soils from Çanakkale, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 334. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez Martín, J.A.; Ramos-Miras, J.J.; Boluda, R.; Gil, C. Spatial relations of heavy metals in arable and greenhouse soils of a Mediterranean environment region (Spain). Geoderma 2013, 200–201, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.X. Development and strategy of facility agriculture in China. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2019, 11, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.H.; Liang, H.Y.; Zhang, D.H.; Li, L.C.; Wei, L.L.; Wen, Y.N.; Chen, Q. Accumulation Characteristics and Control Technologies of Heavy Metal Contamination in Facility Soil of China: A review. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Beijing Statistical Yearbook 2023. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/ndsj/2023/indexeh.htm (accessed on 15 February 2025).
- Kong, C.C.; Liu, H.L.; Nie, C.J.; Ge, C.; Hu, Q.Q.; Yang, X.L.; Zhang, S.W. Spatial Distribution and Influencing Factors of Cr in Soils of Beijing Plain, China. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2018, 35, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.P.; Yu, X.X.; Jia, G.D.; Li, Y.J.; Liu, Y.J. An analysis of characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in Jiufeng Mountain areas of Beijing. Adv. Water Sci. 2013, 24, 642–650. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P. The Distribution of Heavy Metals and Assessment of Soil Quality in Capital Steel Factory in Beijing, China. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T17141-1997; Soil Quality-Determination of Lead, Cadmium-Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- HJ491-2019; Soil and Sediment—Determination of Copper, Zinc, Lead, Nickel and Chromium—Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of Nitrogen in Soil by the Kjeldahl Method. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Agronomy Monographs; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 355–356. [Google Scholar]
- Rayment, G.; Higginson, F. Australian Laboratory Handbook of Soil and Water Chemical Method; Inkata Press Pty Ltd.: Melbourne, Australia, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 4, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Sun, R.L.; Zhang, K.X.; Liu, Y.D.; Ruan, X.L.; Wang, Y.Y. Soil properties, heavy metal accumulation, and ecological risk in vegetable greenhouses of different planting years. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 995–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, P.; Yan, P.L. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution characteristics and the potentialecological risks of soil in the Zhongluotan Town. J. Gansu Sci. 2024, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ni, S.J.; Tuo, X.G.; Zhang, C.J. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.B.; Zheng, Y.M.; Chen, H.; Zheng, G.D. Background concentrations of soil heavy metals in Beijing. Environ. Sci. 2004, 25, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Stojić, A.; Stanišić Stojić, S.; Reljin, I.; Čabarkapa, M.; Šoštarić, A.; Perišić, M.; Mijić, Z. Comprehensive analysis of PM10 in Belgrade urban area on the basis of long-term measurements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 10722–10732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.-M.; Tuleau-Malot, C. Variable selection using random forests. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Soil Pollution Risk Control Standards for Agricultural Land. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Liu, Y.M.; Wang, Z.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Liu, W.Q. Impact of long-term planting on heavy metal distribution in greenhouse soil and ecological risk assessment. J. Tianjin Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2020, 40, 54–61+80. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.N.E.; Hosen, M.M.; Ullah, A.K.M.A.; Maksud, M.A.; Khan, S.R.; Lutfa, L.N.; Choudhury, T.R.; Quraishi, S.B. Pollution Characteristics, Source Identification, and Health Risk of Heavy Metals in the Soil-Vegetable System in Two Districts of Bangladesh. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 4985–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.J.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.F.; Zhang, R.; Xia, T.; Sun, Y.P.; Hu, K.; Hao, F.F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.C.; et al. Risk assessment and source identification of soil heavy metals: A case study of farmland soil along a river in the southeast of a mining area in Southwest China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yue, L.L.; Li, J.C. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and its potential ecological risk to the soil in Taiyuan, China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2011, 31, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Cheng, J.M.; Wang, X.F. Source analysis and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils around heavy metal industry in Anxin County. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10562. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Pan, Y.P.; Shi, H.D. Atmospheric deposition as a dominant source of cadmium in agricultural soils of north China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, M.Y.; Yu, X.M.; Liu, M.D. Heavy Metal Pollution and Health Risk Assessment of Vegetable–Soil Systems of Facilities Irrigated with Wastewater in Northern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.Y.; Zeng, X.B.; Li, L.F.; Pen, C.; Li, S.H. Effects of Land Use on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soils and Sources Analysis. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.F.; Zeng, X.B.; Bai, L.Y.; Mei, X.R.; Yang, J.B.; Hu, L.J. Cadmium accumulation in vegetable plantation land soils under protected cultivation: A case study. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2009, 40, 2169–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Ma, J.; Islam, M.S.; Weng, L.P.; Li, Y.T. Cd, Cu, and Zn accumulations caused by long-term fertilization in greenhouse soils and their potential risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlade, M.O.; Agbeniyi, S.O. Impact of pesticides use on heavy metals pollution in cocoa soils of Cross-River State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 3725–3728. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Qiao, Y.H.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.F.; Shao, X.M.; Ma, H.P. Characteristics and affecting factors of heavy metals content in greenhouse vegetable soils in China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 263–274. [Google Scholar]
- Muscalu, O.M.; Nedeff, V.; Chitimus, A.D.; Sandu, I.G.; Partal, E.; Mosnegutu, E.; Sandu, I.; Rusu, D.I. Influence of Fertilization Systems on Physical and Chemical Properties of the Soil. Rev. Chim. 2018, 69, 4006–4011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Yan, Z.B.; Qin, J.H.; Xiao, Z.W. Effects of long-term cattle manure application on soil properties and soil heavy metals in corn seed production in Northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7586–7595. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.X.; Chen, T.B. Concentrations of additive arsenic in Beijing pig feeds and the residues in pig manure. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2005, 45, 356–367. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.Y.; Dong, T.X.; Ru, S.H.; Su, D.C. Accumulation and migration characteristics in soil profiles and bioavailability of heavy metals from livestock manure. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 1576–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, H.Y.; Jiang, R.F.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, Y.M.; Qiao, Y.H.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, J.; Li, H.F. Heavy metal contents in animal manure in China and the related soil accumulation risks. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 986–996. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Tan, X.D.; Ji, W.; Gao, F.; Li, C.W.; He, W.M. Risk assessment of heavy metal pollution from livestock and poultry manure fertilizer in Beijing. Anhui Agron. Bull. 2021, 27, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- NY 525-2012; Agricultural Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Zhang, F.S.; Li, Y.X.; Yang, M.; Li, W. Content of Heavy Metals in Animal Feeds and Manures from Farms of Different Scales in Northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2658–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Di, C.X.; Ren, C.; Yin, X.; Li, X.P.; Li, B.H.; Dong, Q.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, T.T. Dataset of organic fertilizer raw materials and heavy metals in commercial organic fertilizer in inner mongolia in 2020. J. Agric. Big Data 2024, 6, 570–574. [Google Scholar]
- Marinari, S.; Masciandaro, G.; Ceccanti, B.; Grego, S. Organic and Inorganic Fertilizer Contaminants in Agriculture: Impact on Soil and Water Resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 72, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, Y.H.; Su, D.C.; Jiang, R.F.; Rui, Y.K.; Li, H.F. Application of ICP-MS and AFS to detecting heavy metals in phosphorus fertilizers. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2014, 34, 1403–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah Alnuwaiser, M. An Analytical Survey of Trace Heavy Elements in Insecticides. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 2019, 8150793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bawa, U.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, J.N.; Ezra, A.G. Assessment of health risks from consumption of food crops fumigated with metal based pesticides in Gwadam, Gombe State, Nigeria. Bayero J. Pure Appl. Sci. 2021, 14, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nuralykyzy, B.; Wang, P.; Deng, X.Q.; An, S.S.; Huang, Y.M. Heavy Metal Contents and Assessment of Soil Contamination in Different Land-Use Types in the Qaidam Basin. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Lv, H.F.; Qasim, W.; Xia, L.L.; Yao, Z.S.; Hu, J.; Zhao, Y.M.; Ding, X.D.; Zheng, X.H.; Li, G.Y.; et al. Heavy metal and nutrient concentrations in top- and sub-soils of greenhouses and arable fields in East China—Effects of cultivation years, management, and shelter. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119494. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.G.; Wu, H.W.; Liu, J. Evolution of heavy metal contents of three soils under long-term fertilizations. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 2319–2324. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).