Abstract
In engineering, the demand for lightweight yet strong materials has led to the widespread use of polymer matrix composites reinforced with particles. These composites offer superior mechanical properties, making them ideal for applications in areas such as the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. This paper presents a micromechanical model for particle-reinforced polymer matrix composites with interphase layers, enabling the prediction of effective bulk, shear, and Young’s moduli while accounting for damage. Model validation is achieved by comparing the calculated elastic moduli for two composite types. This study highlights that stiffer or smaller particles enhance elasticity, while a robust interphase preserves mechanical properties, despite damage. A statistical criterion describes interphase debonding probability, and the Ramberg–Osgood equation captures the polymer matrix’s elastoplastic behavior. Numerical analyses on polypropylene composites with glass beads demonstrate how particle size, interphase strength, and debonding affect performance, aligning well with experimental data.
1. Introduction
Composite materials have been widely utilized in engineering applications due to their superior mechanical properties, lightweight nature, and flexible design [1,2,3,4]. Among various types of composites, particle-reinforced composites (PRCs) have gained significant interest as they offer greater strength, stiffness, and damage resistance compared to traditional materials. Considerable attention has been paid to particle-reinforced composites (PRCs) because of their superior load-bearing performance. Numerous researchers have been inspired to study how particle reinforcement influences the overall effective properties and damage behavior of engineering composites [5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Under external loads, the stress field in PRCs is altered by the presence of reinforcing particles, which has a notable impact on both local and global mechanical properties. As a result, predicting the effective macroscopic moduli based on the volume fraction and shape of the reinforcing particles has become a fundamental issue in PRC research.
Accompanied by approximate models, various effective medium theories have been developed to determine the overall mechanical properties of PRCs with randomly distributed reinforcing particles. The generalized self-consistent method has been employed to predict the elastic moduli of both nano-particles ceramics [16] and fiber-reinforced composites [17]. To determine the effective bulk modulus of concrete, Li et al. [18] introduced a four-phase micromechanical model, where inclusions represent aggregate material, separated from the cement paste matrix by an interface layer serving as the interfacial transition zone. Shen applied the Mori–Tanaka method to evaluate the elastic moduli of PRCs under true longitudinal uniaxial strain. To enable Mori-Tanaka’s mean-field concept to effectively capture the evolution of debonding damage, matrix plasticity, and particle size effects on the deformation and damage behavior of composites, Togho [19] proposed an incremental damage model. Iwakuma and Koyama [10] developed a new averaging method by adjusting the Mori–Tanaka prediction for a two-phase composite containing two types of inhomogeneities within the matrix material.
The effects of reinforcement on the effective mechanical behavior of PRCs largely depend on the bonding quality and strength between the particles and the matrix. Substantial theoretical and numerical studies have been carried out to derive elastic solutions that address interphase issues [13,20,21]. Su [22] explored how interphase strength impacts damage modes and mechanical behavior in composites. The effect of particle size on composites was also analyzed from the perspective of the interphase. By incorporating the interphase into their micromechanical models, Boutaleb [20,23] investigated the size-dependence of the equivalent properties of PRCs.
The overall elastic modulus for a matrix material can be significantly improved by embedding rigid particles in it, but the effects of particles on the strength and toughness of the composite are more complicated [24]. A considerable number of studies have focused on damage in PRCs. Some primary failure mechanisms may occur when the composites are under stress, such as the particles debonding from the matrix material across the interface between them [8,20,25], particle cracking [26], and the plastic failure of the matrix material [27]. The bonding properties between particles and the matrix materials are critical to the overall mechanical behavior of PRCs. Imperfections at the interface usually lead to damage in PRCs, with interphase debonding considered a major failure mechanism. Additionally, interphase debonding can contribute to the formation of micro-voids in the matrix during the plastic deformation of the composites.
This paper presents a novel micromechanical model that can predict the effective elastic properties of particle-reinforced composites (PRCs), with a focus on incorporating the effects of particle debonding and the presence of micro-voids within the matrix. While existing models consider the influence of particle reinforcement and interphase properties, they often overlook the complex interactions between these factors and the resulting damage mechanisms, particularly in the context of particle debonding and matrix plasticity. The proposed model introduces a probabilistic approach for interphase debonding based on Weibull’s function coupled with the Ramberg–Osgood equation to describe the elastoplastic behavior of the matrix. This approach not only refines the prediction of overall mechanical performance but also provides deeper insights into the role of damage mechanisms, such as particle–matrix bonding degradation, in relation to the structural integrity of PRCs.
The scientific goal of this article is to offer a more comprehensive framework for understanding the mechanical behavior of PRCs under stress, specifically by integrating damage due to particle debonding and matrix micro-void formation. By considering these phenomena, this model can provide more accurate predictions of the effective elastic moduli, thereby advancing the design and application of particle-reinforced composite materials in engineering.
2. An Efficient Micromechanical Model for Three-Phase Composites
2.1. Fundamental Equations and Notation
For convenience, symbolic notation is employed where applicable. Greek letters represent second-order tensors, while ordinary capital letters denote fourth-order tensors. The inner product of two tensors is expressed as , , and , where summation is adopted for the indicial components.
Let us consider different types of isotropic spherical inhomogeneities (or pores) with volume Vr embedded in an isotropic continuous matrix with volume Vm. The elasticity tensors of the r-th phase inhomogeneities (or pores) are denoted by Lr, and by Lm for the matrix, respectively. The volume fraction of the r-th phase inhomogeneities (or pores) is , where denotes the volume of the representative volume element (RVE) of the PRCs. Based on the above definitions, the relationship between the volume fraction of the interphase and that of the particles (fp0) can be derived:
where and represent interphase thickness and particle diameter, respectively.
At a typical point x, the displacement, strain, and stress are denoted by , , and , respectively. Given that the reinforced particles, interphase, and matrix material exhibit isotropic properties, the corresponding local stress tensor and the strain tensor at any point x are related in the following way:
where the subscript m denotes the region occupied by the matrix material, and r (where r = p for particles and r = I for interphase) identifies the region with particles or the interphase, respectively.
The volume-averaged stress of the equivalent homogeneous medium is expressed using the following relations:
And the volume-averaged strain can be expressed as
2.2. The Effective Macroscopic Elastic Properties
The effective elastic stiffness tensor, , of the composite is characterized by the following relation:
Given that the reinforced particles are spherical, the volume-averaged perturbed strains can be expressed as
where , , and S represent the volume-averaged perturbed strains, eigenstrains, and Eshelby’s tensor for the particles, respectively.
On the basis of the double-inclusion model [28,29], if the eigenstrain field is uniform within the interphase, the volume-averaged perturbed strains can be expressed in the same form as in the case of spherical inclusions:
where and represent the volume-averaged perturbed strains and eigenstrains corresponding to interphase, respectively.
In the self-consistent method, the strain averaged over the volume of the r-th phase is assumed to be identical to the strain experienced by a single inhomogeneity embedded in an infinite matrix with the effective stiffness tensor . As a result, the volume-averaged strain for both the matrix and the r-th phase can be denoted as follows:
Here, and correspond to the volume-averaged strains of the matrix and the r-th phase, respectively, while represents the volume-averaged strain of the equivalent medium with an elastic stiffness tensor . The strain concentration factors for both the matrix and the r-th inhomogeneity, derived through the self-consistent method, are given by the following expressions:
Here, I denotes the fourth-order identity tensor, and S represents the Eshelby tensor. In this study, it is assumed that both the particle and interphase domains are spherical and coaxial. Consequently, the Eshelby tensor S is characterized by the constants α and β, which can be expressed as
In this context, denotes the secant bulk modulus, and represents the secant shear modulus of the matrix material under elastic–plastic deformation.
Bian [30] enhanced the self-consistent approach by treating both the matrix and inhomogeneities as inclusion phases within the composite. According to this updated model, the elastic stiffness tensor of the equivalent material, denoted as , reflects the averaged properties of the matrix and inclusions according to their respective volume fractions.
The corresponding equation for a three-phase composite can be derived as
where represents the equivalent elastic tensor for the particles.
By inserting Equations (8) and (9) into Equation (14), the resulting equation can be derived as follows:
Utilizing Equations (3) and (15), the connection between the volume-averaged strain of the particle and the total stress in the composite can be expressed as
Using Equations (8), (9) and (16), the volume-averaged strains for both the matrix and the interphase are given by
Hence, using Equations (16)–(18), the volume-averaged strains for both the matrix and the inhomogeneities can be determined from the composite’s overall stress. The equivalent elastic stiffness tensors, denoted as and , can be defined as follows:
By inserting Equations (16)–(18) into Equations (4) and (5), the composite’s effective stiffness tensor can be expressed as
where , , , and are defined by
and
2.3. Four Specific Cases
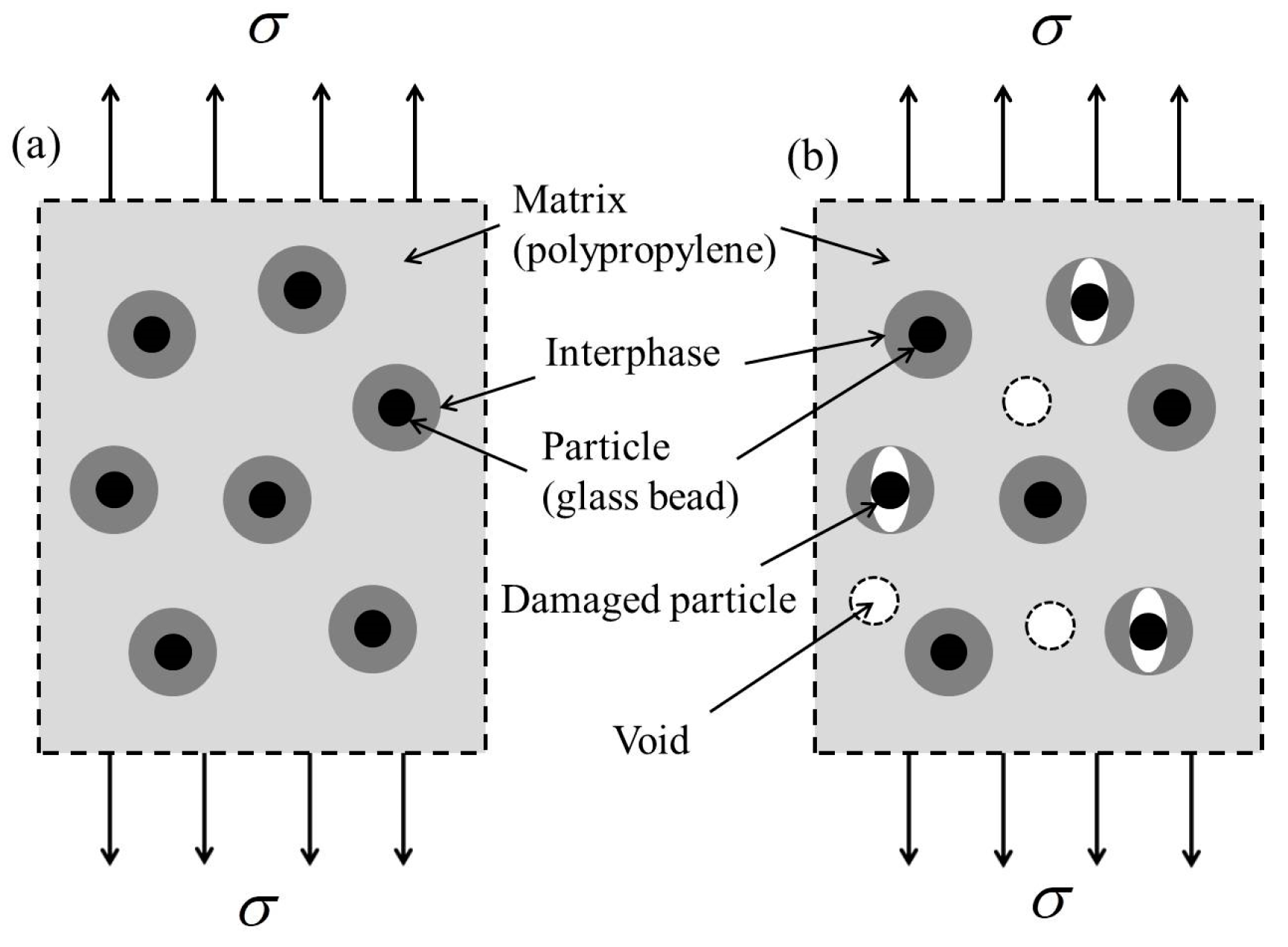
Under applied loading or deformation, the elastic properties of composites may deteriorate due to damage mechanisms such as particle–matrix debonding and the formation of voids within the matrix. If the interphase is insufficiently strong, debonding may occur between the particle and the interphase. Figure 1 illustrates the conditions of the composites before and after damage under external uniaxial stress at the boundary. Post-damage, the Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, and shear modulus of the composites differ from those in the undamaged state. The effective elastic properties of the damaged composites can be categorized into four distinct cases, which will be examined in the following discussion.
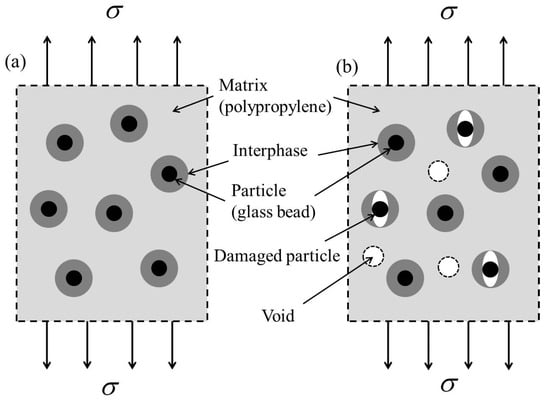
Figure 1.
Damage process of the glass-bead-filled polypropylene matrix composite: (a) the initial state (undamaged) and (b) the equivalent damaged state.
- (1)
- For a particulate composite, the analysis includes void damage but excludes debonding damage, i.e., and , denoted by and for the volume fractions of voids in the matrix and debonded particles, respectively. Given that voids are incapable of supporting any stress, the strain concentration factor of the voids can be determined as follows:
And the volume-averaged strain can be written as
Subsequently, the effective bulk modulus and shear modulus in this damaged state can be determined as follows:
where
and
- (2)
- For a particulate composite that accounts for some debonding damage while ignoring void damage, denoted by , but with , the effective bulk modulus and shear modulus are diminished:
It is assumed that upon the occurrence of debonding damage, the stress on the debonded particles is entirely relieved. This leads to a complete separation of the interface between the particle and the interphase, resulting in what is known as complete interfacial debonding. Initially perfectly bonded particles are effectively converted into voids, represented by and . Consequently, debonding damage in the composite is indicated by a reduction in the proportion of intact particles and a corresponding rise in the proportion of voids.
- (3)
- For a particle-reinforced composite experiencing both void damage and debonding damage simultaneously, denoted by and , respectively, we can obtain the following:
- (4)
- For the undamaged composite, where all particles are perfectly bonded with the interphases and no void damage has occurred, denoted by and , the effective elastic properties of the composite can be expressed as
For the particulate composites, the effective elastic properties can be determined using the following elastic relations:
3. Cumulative Probability of Damaged Reinforcements
After particles experience interfacial debonding from their surrounding interphases, they no longer contribute to load bearing and are treated as voids. Since each inhomogeneity is subjected to the same stress conditions, they do not all debond at the same time. To model this debonding phenomenon, the Weibull distribution function is utilized to represent the cumulative probability of debonding [19,31]:
where indicates the internal stress of the r-th phase particle in the 11-direction, with S0 and m representing the scale and shape parameters of the function, respectively.
The probability function, via the Gamma function, can be used to calculate the average interfacial strength between the particles and the matrix:
Using Equations (2) and (9), the stress within the domain of a particle, characterized by its elastic stiffness tensor , can be determined as follows:
4. Numerical Results and Discussion
For this section, a set of numerical analyses was conducted on a polymer-based composite, aiming to determine the composite’s effective modulus and overall stress–strain behavior. The model assumed the hard particles to be linearly elastic, while the polymer matrix and interface materials were considered to exhibit isotropic elastoplastic behavior with isotropic hardening.
To verify the finite-element cell model’s predictions, glass-bead-filled modified polypropylene (PP) was employed. Key metrics, including Young’s moduli, Poisson’s ratios, and densities for both the glass beads and PP, as listed in Table 1, were incorporated into the model. The plasticity and hardening properties of the polymer matrix and interface materials were characterized through yield stress and yield strain values obtained from the experimental tensile stress–strain curve of unfilled PP [32].

Table 1.
Material parameters of polypropylene-based composites [4].
4.1. Predictions of Young’s Modulus Equations
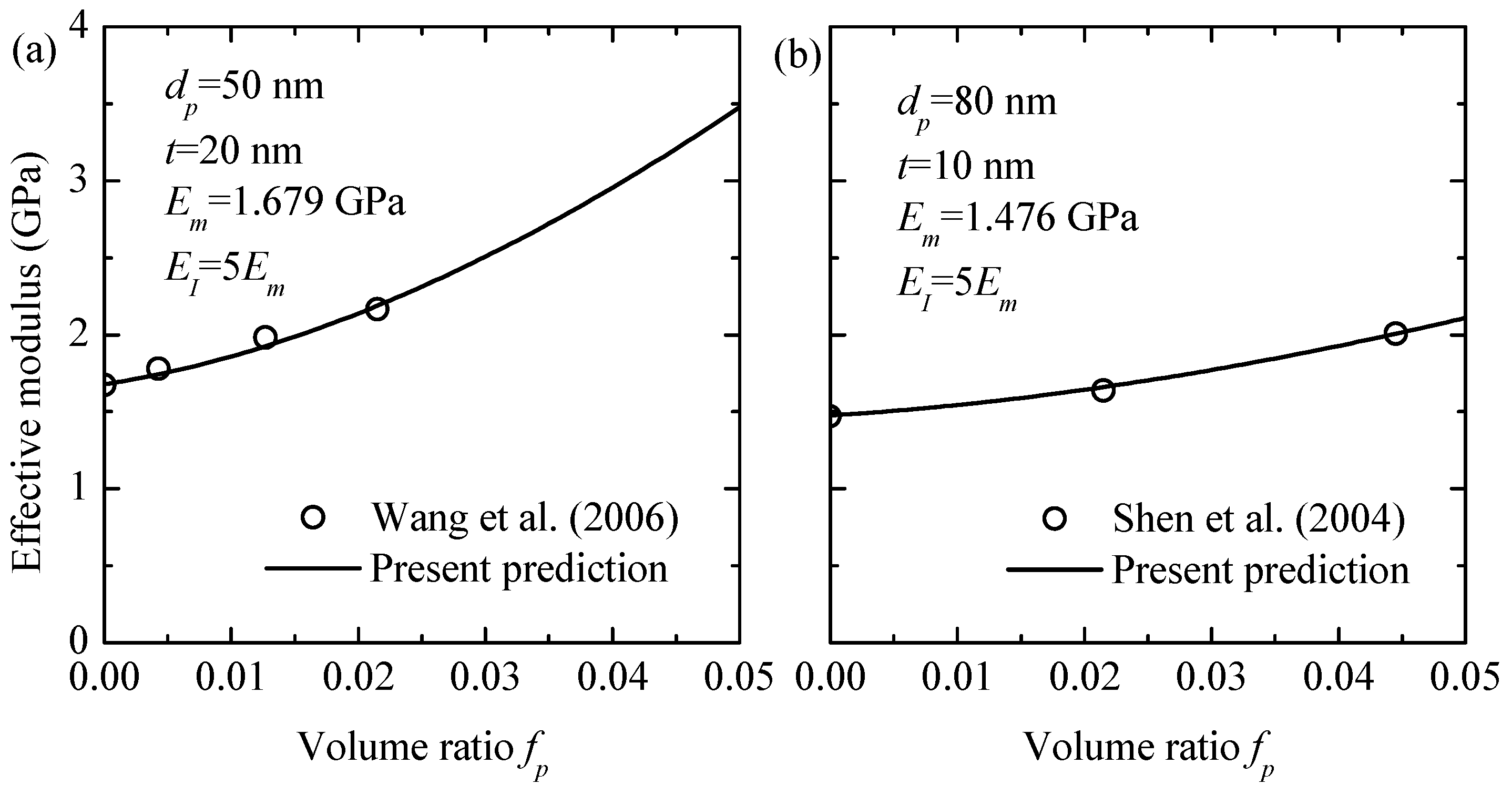
To evaluate the accuracy of the proposed model, the effective elastic modulus calculated via the current method was compared with experimental data for a silica-particle-reinforced polyamide matrix [33] and a polyimide matrix material [34], as illustrated in Figure 2. The silica particles had a Young’s modulus of = 88.7 GPa and a Poisson’s ratio of = 0.23, respectively. The Poisson’s ratio for the interphase and both polymer matrix materials was uniformly at = 0.4. The results demonstrated that increasing the volume fraction of silica particles enhances the elastic modulus. The numerical predictions showed a strong correlation with the experimental data.
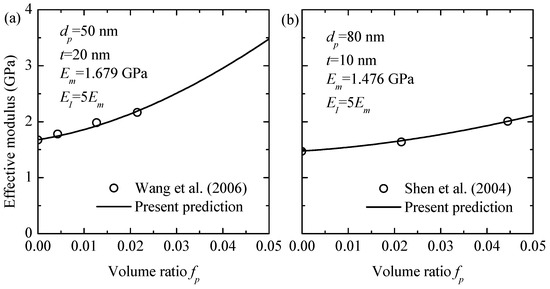
Figure 2.
Comparison between the analytical predictions and the experimental elastic modulus of various silica particle/polymer nanocomposites: (a) polyimide [34] and (b) polyamide-6 matrix [33].
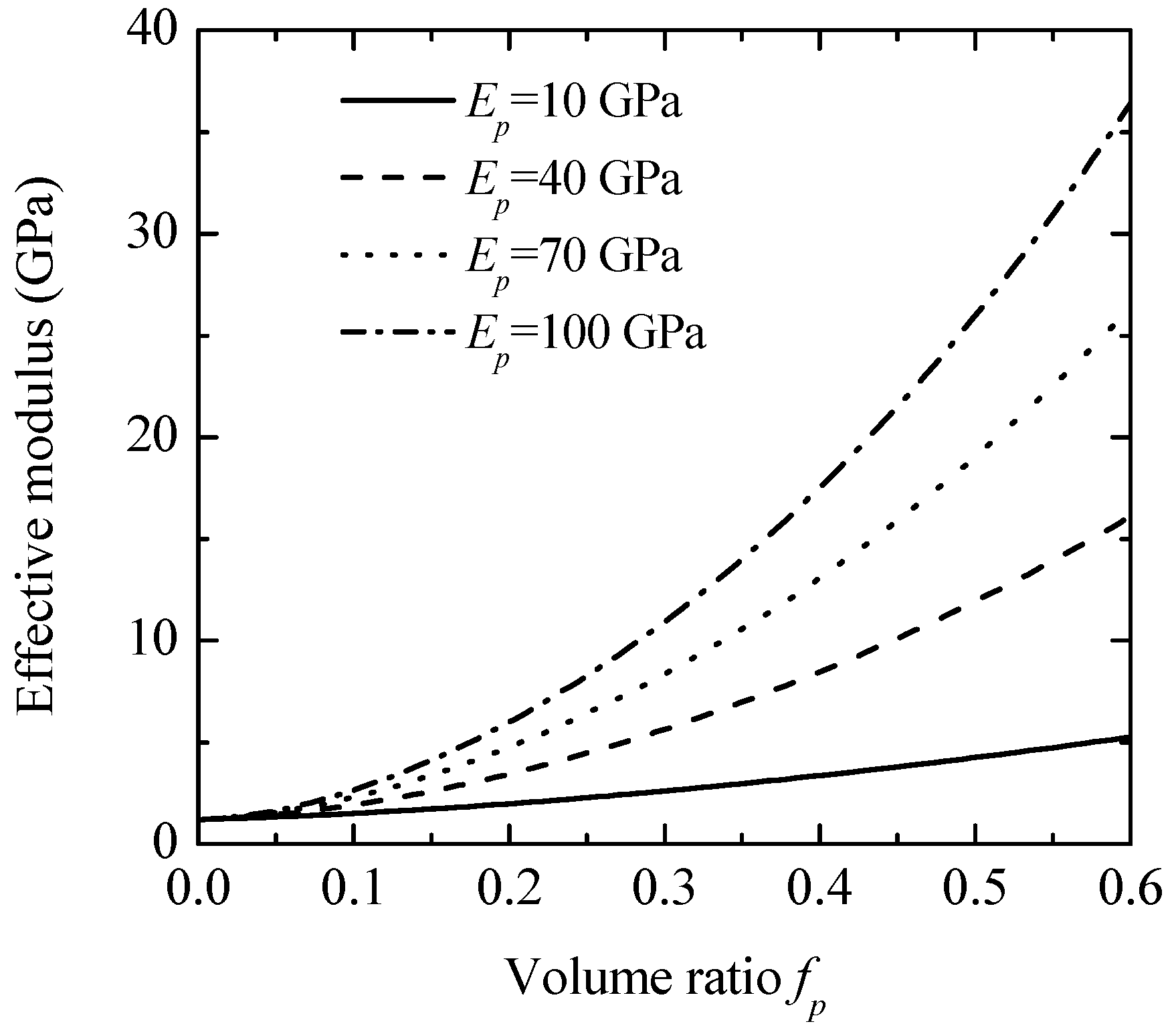
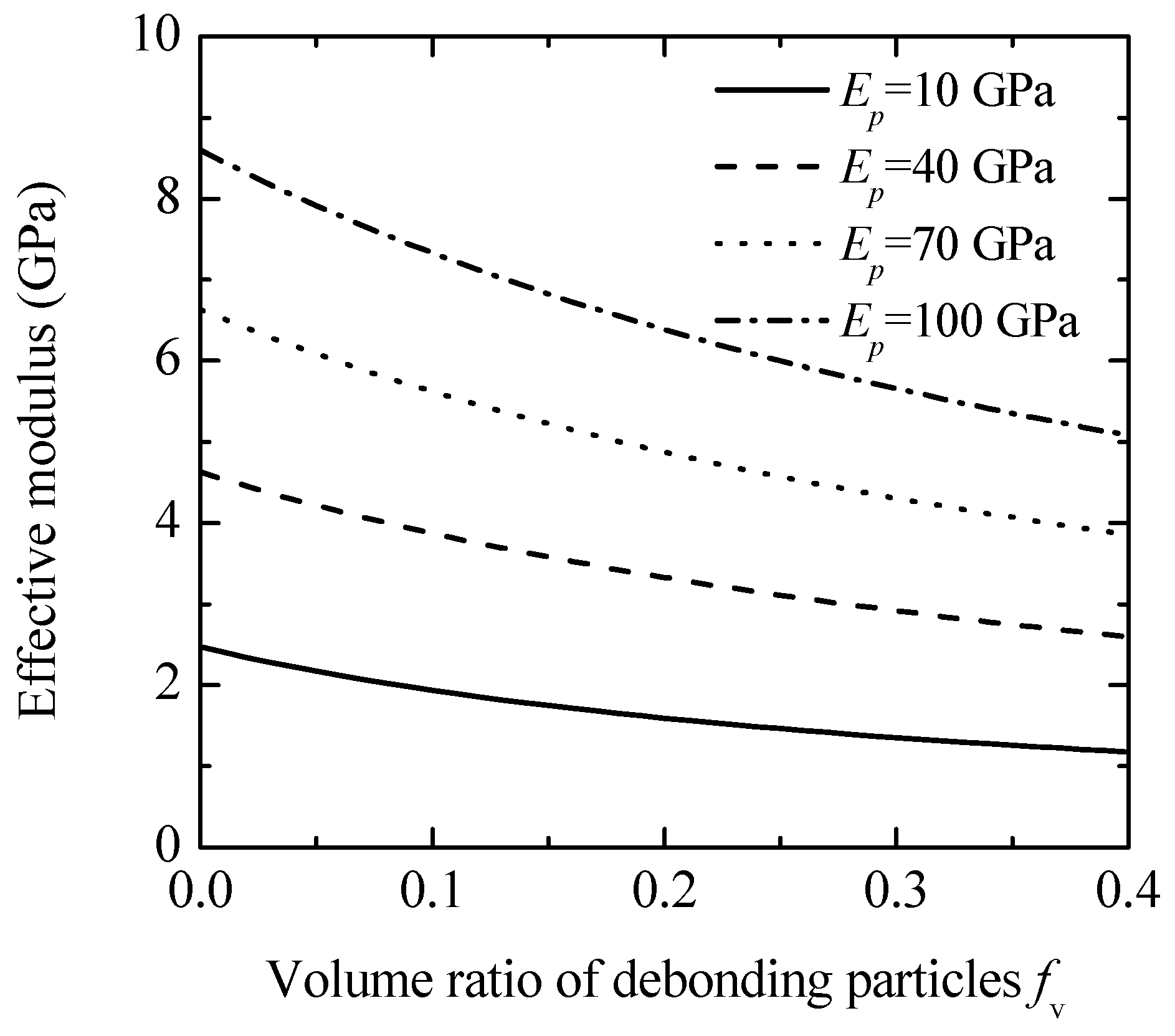
Figure 3 illustrates the effective modulus values of polypropylene (PP)-based composites reinforced with particles of higher stiffness. Calculations were performed for particles with Young’s moduli of 10, 40, 70, and 100 GPa. The material properties for the PP matrix and the interphase are detailed in Table 1. The results indicate that the effective modulus of the composites rises with the volume fraction of reinforcing particles, with a more pronounced increase observed for stiffer particles [7,10]. For instance, when the volume fraction of 70 GPa Young’s modulus particles (glass beads) is 0.4, the composite’s effective modulus reaches 13.2 GPa, which is 11 times higher than that of the matrix material.
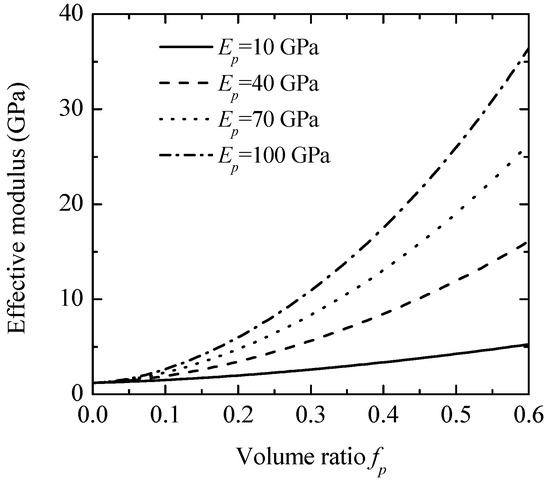
Figure 3.
The effects of the reinforced particles on the effective moduli of polypropylene-based composites.
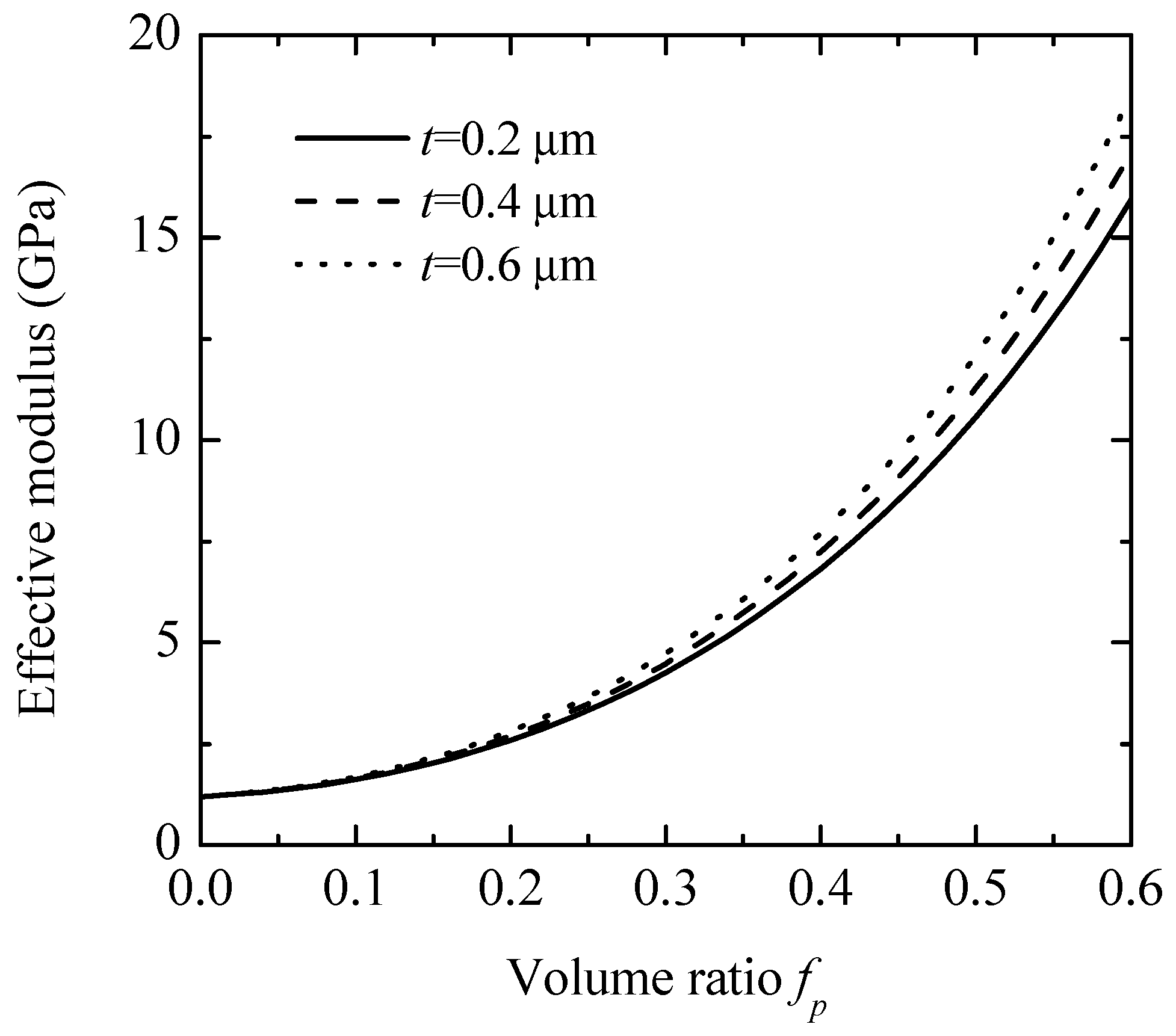
Figure 4 reveals the impact of interphase thickness on the composite’s effective modulus, using glass beads as the particle material. It shows that increasing interphase thickness has a minimal effect on enhancing the composite’s effective modulus. Figure 5 illustrates the impact of debonding damage in glass bead particles on the effective modulus of the composite, with an initial particle volume fraction of 0.4. As shown in the figure, debonding damage reduces the composite’s effective moduli. The modulus reaches its lowest value when all particles have debonded, resulting in a material that behaves similarly to a porous structure [13]. However, because debonding is assumed to occur only between the particles and the interphase, the composite’s effective modulus remains higher than that of the matrix owing to the reinforcing effect of the interphase.
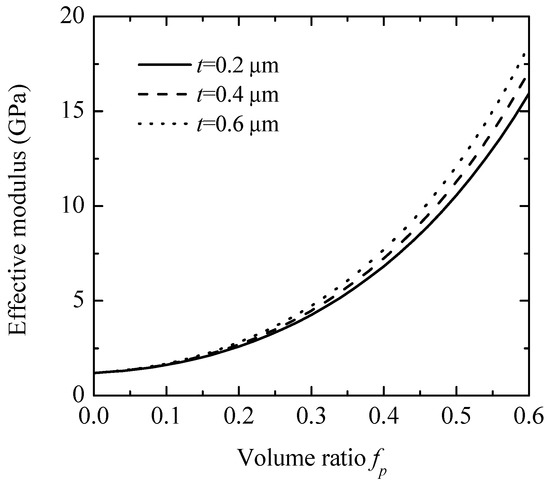
Figure 4.
Effective modulus of composites versus interface thickness.
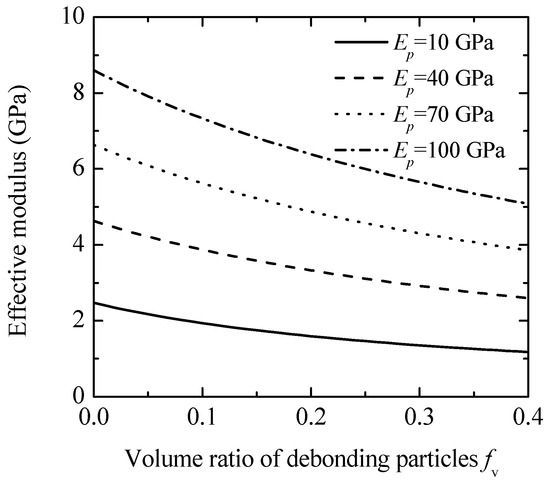
Figure 5.
Effective modulus of composites versus particle damage.
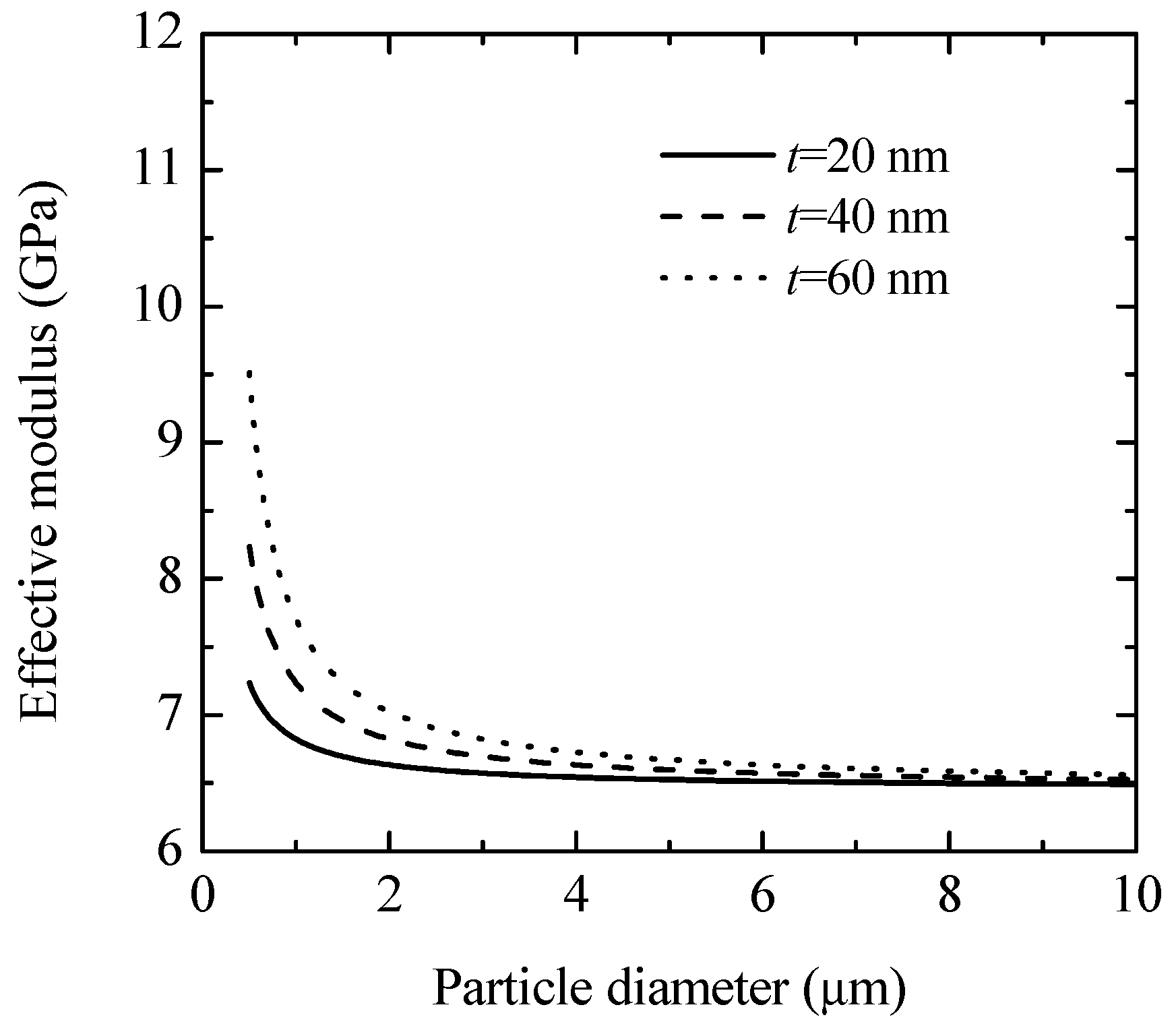
Figure 6 depicts the effect of particle diameter on the effective modulus of the composite. The diameter of the glass beads ranged from 0.5 to 10 μm, with a constant volume fraction of 0.4. The interphase thickness was set to 20, 40, or 60 nm. The results show that the PP-based composites reinforced with smaller particles exhibited higher effective moduli [3]. Specifically, with an interphase thickness of 60 nm, the effective modulus of the composites increased from 6.5 to 9.5 GPa as the particle diameter decreased from 10 to 0.5 μm.
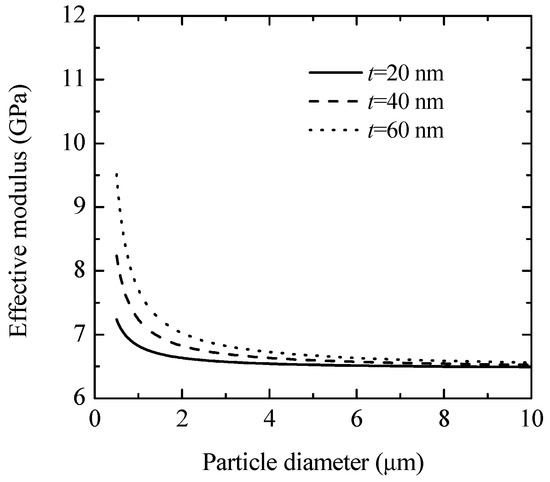
Figure 6.
Effective modulus of composite versus particle diameter.
4.2. Impact of Particle Size on the Composite’s Overall Stress–Strain Behavior
Numerical simulations were performed for glass-bead-filled PP composites under uniaxial tension. The empirical power law, exemplified by the Ramberg–Osgood equation, offers an effective means of characterizing the uniaxial stress–strain responses of different materials [35]:
In this equation, denotes the Young’s modulus of the matrix, refers to the matrix’s yield strength, n indicates the strain-hardening exponent, and is a dimensionless constant. The secant Young’s modulus of the isotropic matrix, defined as the ratio of tensile stress to tensile strain, can be expressed using the following equation:
Assuming the matrix displays plastic incompressibility, its secant bulk modulus is equal to its linear elastic bulk modulus (). As a result, the secant shear modulus and the secant Poisson’s ratio can be defined as follows:
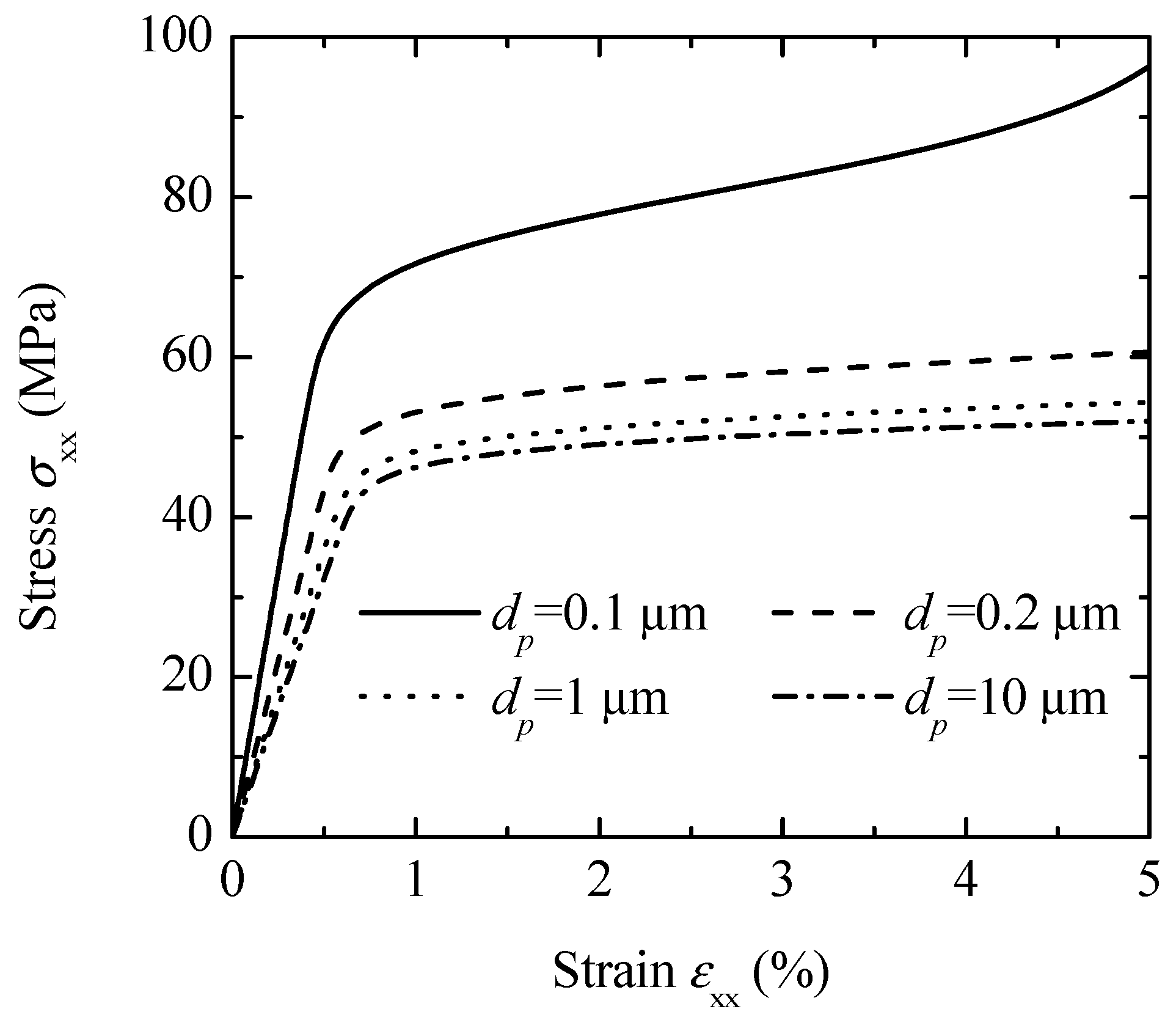
Figure 7 demonstrates how particle size affects the overall stress–strain responses of glass-bead-filled PP-based composites when no damage is present. Using an initial glass bead particle volume fraction of 0.4 and an interphase thickness of 20 nm, along with a strength coefficient of 35 MPa and a work-hardening exponent of 0.3, the Ramberg–Osgood equation outlined in Equation (58) was applied. The results reveal that smaller glass beads have a pronounced effect on the flow stress during uniaxial tension. Therefore, the current model effectively captures the effects of particle size on the behavior of PP-based composites.
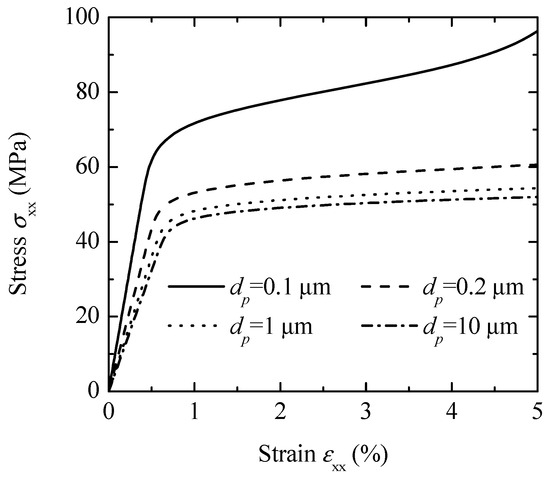
Figure 7.
Particle-size effects on the overall stress–strain behavior of the PP-based composites.
4.3. Effect of Debonding Damage on the Composite’s Overall Stress–Strain Behavior
Figure 8 demonstrates how debonding damage influences the overall stress–strain response in PP-based composites reinforced with glass bead particles. The glass bead particles had an initial volume fraction of 0.4. Figure 8 also illustrates the stress–strain behavior of both perfectly bonded composites and those that have undergone complete debonding (i.e., a porous matrix material). The results show that the stress–strain relationship for composites with varying levels of particle debonding fall within the range defined by the fully debonded composite (the lower limit) and the fully bonded composite (the upper limit).
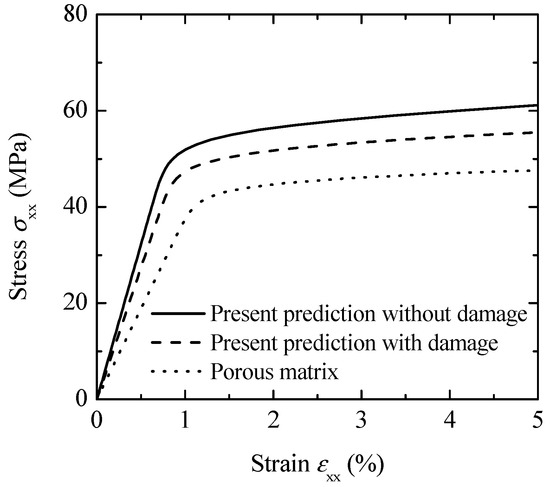
Figure 8.
Effect of debonding damage on the stress–strain behavior of PP-based composites.
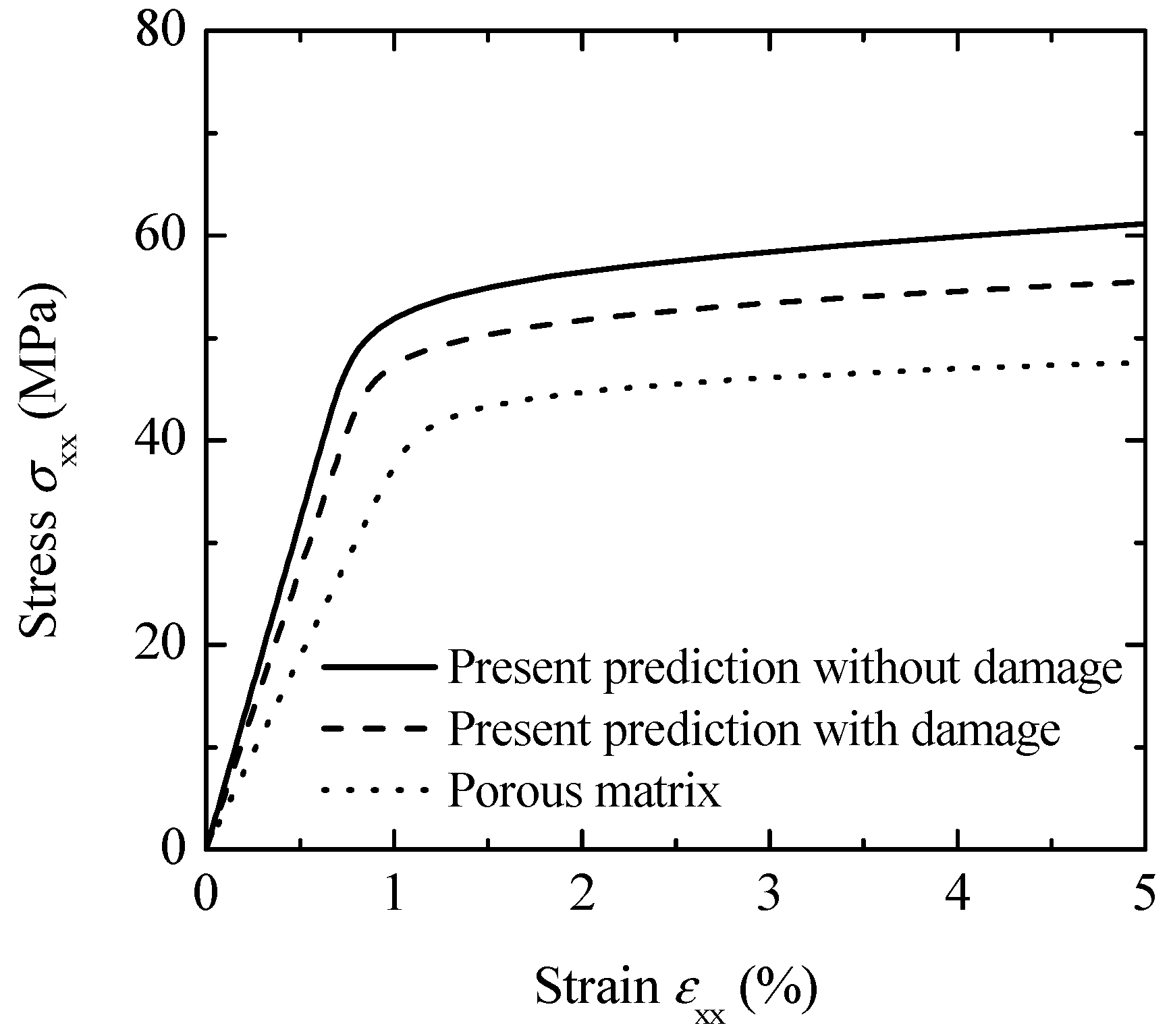
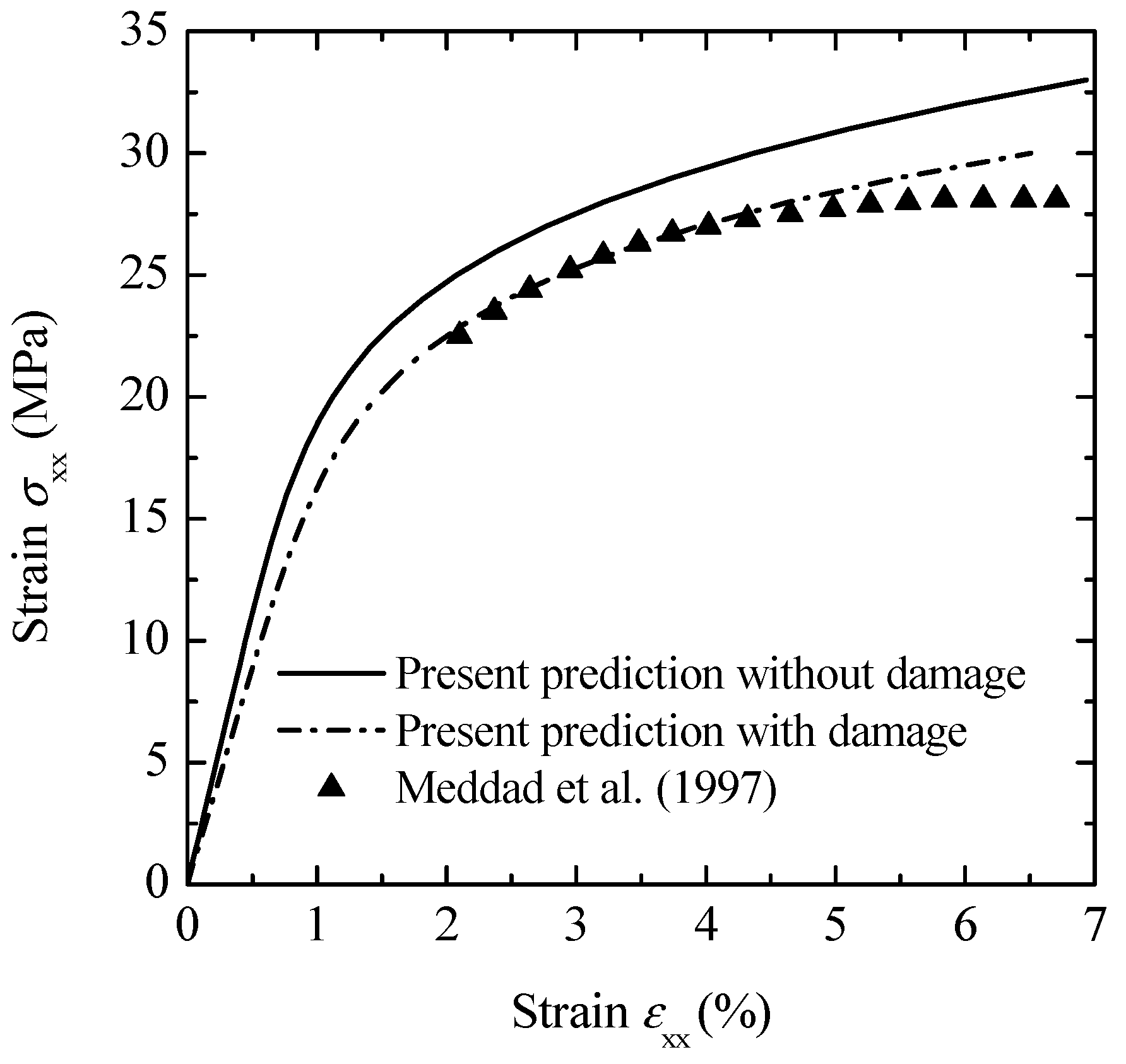
Figure 9 presents a comparison of the current predictions, both with and without damage, against the experimental data [36] for the overall stress–strain response of PP material reinforced with glass bead particles. Table 2 provides the material parameters for the composite, while Table 3 details the parameters for the interphase and the Ramberg–Osgood equation. Figure 9 illustrates that the current method can effectively model the overall stress–strain behavior of the composite, with particular accuracy in the damaged scenario.
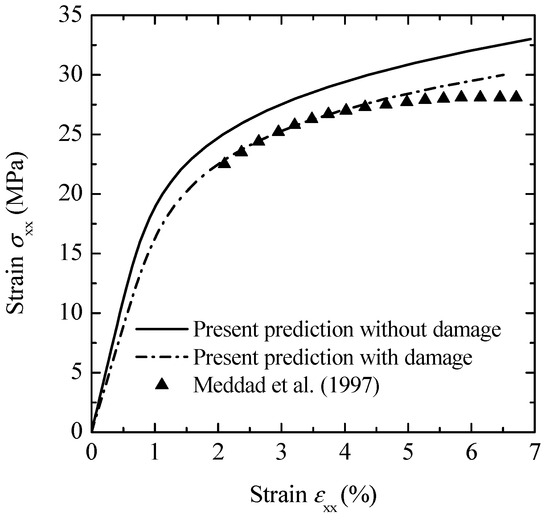
Figure 9.
Comparison between the present predictions and experimental data [36] for overall stress–strain behavior of glass-bead-filled polypropylene composites.

Table 2.
Material parameters of glass-bead filled polypropylene composites [36].

Table 3.
Parameters of interphase and Ramberg–Osgood equation for PP–glass bead composites.
5. Concluding Remarks
A micromechanical model was developed to accurately predict the effective elastic responses of polymer-based composites filled with particles. This model enables the derivation of constitutive equations that determine the overall effective properties of these composites, considering key microstructural parameters. Specifically, the model accounts for the effects of particle volume fraction, interphase characteristics, and particle size on the elastic moduli of particulate composites, offering a comprehensive framework for material property prediction. To enhance the accuracy of damage representation, Weibull’s probabilistic function was integrated into the equations to account for the varying likelihood of particle debonding. This incorporation allows for a more realistic assessment of the mechanical degradation mechanisms in particle-reinforced composites. The model’s predictions for the effective elastic properties of particle-filled polymer-based composites exhibit strong agreement with the experimental data, demonstrating its robustness and practical applicability.
Furthermore, an in-depth analysis of how particle size and damage influence the elastoplastic properties of composites was conducted using the secant modulus method. The results reveal that particle size has a particularly significant impact when smaller particles are used, as they lead to an increased interfacial area and higher stress concentrations, which affect both stiffness and damage evolution. The findings indicate that the proposed model provided reliable predictions of the composite’s mechanical behavior, aligning well with published experimental results.
This study offers valuable insights into the micromechanical behavior of particle-reinforced polymer composites and provides a solid theoretical foundation for optimizing material design. The proposed approach can be instrumental in guiding the development of advanced composite materials with tailored mechanical properties, particularly in applications where lightweight, high-strength, and damage-resistant materials are required. Future research may further extend this model to consider the effects of particle shape anisotropy, strain rate sensitivity, and multi-scale interactions, ensuring broader applicability in real-world engineering scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C.; methodology, Y.C. and H.Z.; validation, Z.W. and Y.C.; formal analysis, Y.C.; investigation, Z.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the “National Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, grant number A2021203011” and “MCC Non-steel Field Major Research and Development Program (2023-4)”.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Huichuan Zhao was employed by the company China 22MCC Group Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Yavuz, I.; Şimsir, E.; Şenol, B. Investigation of mechanical behavior of glass fiber reinforced extruded polystyrene core material composites. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 13311–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şimşir, E.; Ergün, Y.A.; Yavuz, I. Investigation of Damping Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites at Various Impact Energy Levels. Polymers 2024, 16, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Chu, P.J.; Xu, K.; Fujimori, A. Polypropylene-based nanocomposite with improved mechanical properties: Effect of cellulose nanofiber and polyrotaxane with partial miscibility. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 2977–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Joshi, M.S.; Sun, C.T. Effect of inclusion size on mechanical properties of polymeric composites with micro and nano particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, C.; Nie, S. A thermodynamics based damage mechanics model for particulate composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubnikova, I.L.; Oshmyan, V.G.; Gorenberg, A.Y. Mechanisms of particulate filled polypropylene finite plastic deformation and fracture. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-Y.; Feng, X.-Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.-W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunel, E.; Basaran, C. Influence of filler content and interphase properties on large deformation micromechanics of particle filled acrylics. Mech. Mater. 2013, 57, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashin, Z. Analysis of composite-materials—A survey. J. Appl. Mech.-Trans. ASME 1983, 50, 481–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakuma, T.; Koyama, S. An estimate of average elastic moduli of composites and polycrystals. Mech. Mater. 2005, 37, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Jing, J.K.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, B.Z. Tensile modulus of polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorca, J.; Gonzalez, C. Microstructural factors controlling the strength and ductility of particle-reinforced metal-matrix composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1998, 46, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.H.; Basaran, C. A micromechanical model for effective elastic properties of particulate composites with imperfect interfacial bonds. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 4179–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Yang, Y.W.; Yu, M.R.; Hu, G.Q.; Gan, Y.; Gao, H.J.; Shi, X.H. Diffusion of rod-like nanoparticles in non-adhesive and adhesive porous polymeric gels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2018, 112, 431–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, R.W. Elastic-moduli of a solid containing spherical inclusions. Mech. Mater. 1991, 12, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Weng, G.J. A theory of compressive yield strength of nano-grained ceramics. Int. J. Plast. 2004, 20, 2007–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.N.; Zhang, X.H.; Huang, Y.Y.; Guo, X.E. A generalized self-consistent estimate for the effective elastic moduli of fiber-reinforced composite materials with multiple transversely isotropic inclusions. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2005, 47, 922–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, S.S. Four-phase sphere modeling of effective bulk modulus of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohgo, K.; Itoh, Y.; Shimamura, Y. A constitutive model of particulate-reinforced composites taking account of particle size effects and damage evolution. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Bian, L.; Wang, Y.; Taheri, F. Influences of reinforcing particle and interface bonding strength on material properties of Mg/nano-particle composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 3168–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Wang, T.J. Interphase effect on the strengthening behavior of particle-reinforced metal matrix composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2007, 41, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.F.; Chen, H.R.; Kennedy, D.; Williams, F.W. Effects of interphase strength on the damage modes and mechanical behaviour of metal-matrix composites. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutaleb, S.; Zairi, F.; Mesbah, A.; Nait-Abdelaziz, M.; Gloaguen, J.M.; Boukharouba, T.; Lefebvre, J.M. Micromechanics-based modelling of stiffness and yield stress for silica/polymer nanocomposites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, T.; Spring, D.W.; Paulino, G.H.; Lopez-Pamies, O. Filled elastomers: A theory of filler reinforcement based on hydrodynamic and interphasial effects. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2015, 80, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, C.; Nie, S.; Hutchins, C.S.; Ergun, H. Influence of interfacial bond strength on fatigue life and thermo-mechanical behavior of a particulate composite: An experimental study. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2008, 17, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.J. Aspects of fracture in particulate reinforced metal matrix composites. Acta Metall. Et Mater. 1991, 39, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibnejad-Korayem, M.; Mahmudi, R.; Poole, W.J. Enhanced properties of Mg-based nano-composites reinforced with Al2O3 nano-particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2009, 519, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Nematnasser, S. Double-inclusion model and overall moduli of multiphase composites. Mech. Mater. 1993, 14, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Nematnasser, S. Double-inclusion model and overall moduli of multiphase composites. J. Eng. Mater. Technol.-Trans. ASME 1994, 116, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.C.; Wang, Q.; Meng, D.L.; Li, H.J. A modified micro-mechanics model for estimating effective elastic modulus of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohgo, K.; Weng, G.J. A progressive damage mechanics in particle-reinforced metal-matrix composites under high triaxial tension. J. Eng. Mater. Technol.-Trans. ASME 1994, 116, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, C.P.; Tang, C.Y.; Fan, J.P.; Xie, X.L. Prediction for initiation of debonding damage and tensile stress-strain relation of glass-bead-filled modified polyphenylene oxide. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2004, 46, 1659–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Du, Q.G.; Wang, H.T.; Zhong, W.; Yang, Y.L. In situ polymerization and characterization of polyamide-6/silica nanocomposites derived from water glass. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Lu, J.J.; Li, Y.; Fu, S.Y.; Jiang, S.Q.; Zhao, X.X. Studies on thermal and mechanical properties of PI/SiO2 nanocomposite films at low temperature. Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.W.; Clarke, D.R. The influence of particle size and particle fracture on the elastic/plastic deformation of metal matrix composites. Acta Mater. 1996, 44, 3801–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddad, A.; Fisa, B. Stress-strain behavior and tensile dilatometry of glass bead-filled polypropylene and polyamide 6. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 64, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).