Abstract
This paper presents an advanced Adaptive Sliding Mode Control (ASMC) strategy, specifically developed for a hydrogen production system based on a Proton Exchange Membrane electrolyzer (PEM electrolyzer). This work utilized a static model of the PEM electrolyzer, characterized by its V-I electrical characteristic, which was approximated by a linear equation. The ASMC was designed to estimate the coefficients of this equation, which are essential for designing an efficient controller. The primary objective of the proposed control strategy is to ensure the overall stability of the integrated system comprising both an interleaved buck converter (IBC) and PEM electrolyzer. The control framework aims to maintain the electrolyzer voltage at its reference value despite the unknown coefficients while ensuring equal current distribution among the three parallel legs of the IBC. The effectiveness of the proposed approach was demonstrated through numerical simulations in MATLAB-SIMULINK and was validated by the experimental results. The results showed that the proposed ASMC achieved a voltage tracking error of less than 2% and a current distribution imbalance of only 1.5%. Furthermore, the controller exhibited strong robustness to parameter variations, effectively handling fluctuations in the electrolyzer’s ohmic resistance (Rohm) (from ±28.75% to ±40.35%) and in the reversible voltage (Erev) (from ±28.67% to ±40.19%), highlighting its precision and reliability in real-world applications.
1. Introduction
A PEM electrolyzer cannot be connected directly to power sources; instead, a power conditioner such as an AC/DC or DC/DC converter is typically required. Since PEM electrolyzers require a low DC voltage supply, these power converters often act as step-down converters. Several types of AC/DC converters can be used with different power sources or with the AC grid [1,2]. These include uncontrolled rectifier AC/DC converters, active PWM rectifiers, semi-controlled rectifiers, and others. However, this only study focused on DC/DC converters, which was the interface between the DC bus and the PEM electrolyzer.
In a previous study, various isolated and non-isolated DC/DC step-down converter topologies were compared to identify a suitable solution for powering PEM electrolyzers [3]. The analysis indicated that the IHBC and the IBC were the most promising candidates. IBCs have garnered significant attention in research due to their simplicity, low current ripples, and fault-tolerant operation. Therefore, this study focused specifically on IBCs.
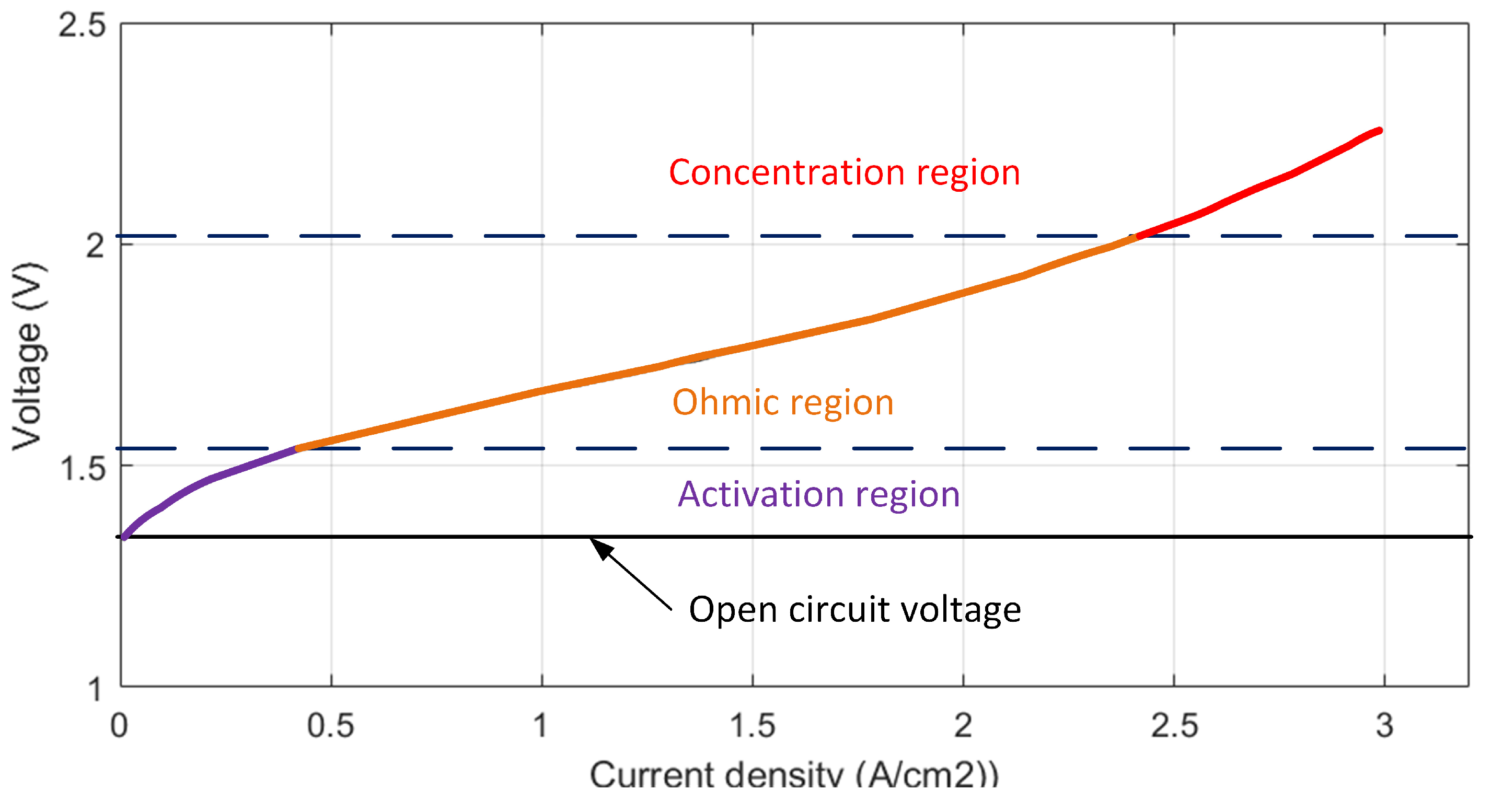
The V-I characteristic, or polarization curve, describes the relationship between voltage and current density in a PEM electrolyzer under steady-state operation. As shown in Figure 1, this curve is divided into three distinct regions: the activation region, the ohmic region, and the concentration region. At low current densities (activation region), a phenomenon known as “gas crossover” becomes significant, where hydrogen and oxygen diffuse across the membrane and mix, posing operational and safety risks. On the other hand, at high current densities (concentration region), the efficiency of the electrolyzer decreases significantly due to mass transport limitations. For optimal efficiency and safety, the PEM electrolyzer is typically operated within the ohmic region, where performance is both stable and efficient [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. In this study, the electrical characteristics of the electrolyzer were approximated using a linear equation with unknown coefficients to model and predict the behavior within the ohmic region.
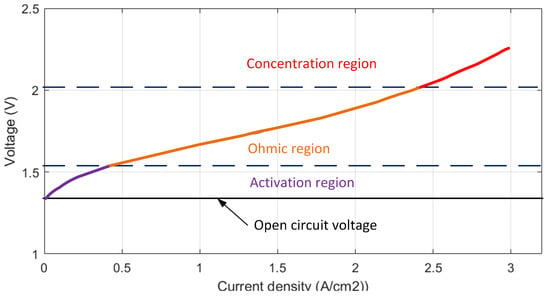
Figure 1.
Polarization curve.
Previous studies have explored various control strategies for PEM electrolyzer systems. In [4,10,11], a classical buck converter with a linear PID controller was employed to regulate the voltage and current in a PV-PEM electrolyzer configuration. Reference [9] extended this approach by implementing a stacked interleaved boost converter (IBC) with PID control, enhancing voltage and current regulation for a PEM electrolyzer.
For PEM electrolyzers connected to a DC bus, different control methods have been proposed. In [7,8,14], PI controllers with various converter topologies were used, including a synchronous buck converter, a three-stage IBC, and a stacked IBC, to regulate the electrolyzer voltage. In contrast, nonlinear Sliding Mode Control (SMC) was introduced in [3,6,15] for voltage regulation via an IBC, while Reference [16] applied SMC to current control using a quadratic buck converter. Additionally, Model Predictive Control (MPC) was explored in [5] for voltage regulation using a buck converter.
These studies indicate that most controllers rely on linear PID control and are primarily tested under fixed temperature and pressure conditions. However, the electrical behavior of PEM electrolyzers is significantly influenced by variations in these parameters. Despite some research on nonlinear controllers, the development of an adaptive control strategy that ensures robustness across a wide range of operating conditions remains an open challenge.
This study introduces an Adaptive Sliding Mode Control (ASMC) strategy for IBC-PEM electrolyzer systems, addressing key challenges in voltage regulation and current distribution. Unlike conventional PID-based methods, the proposed ASMC approach dynamically adapts to variations in temperature, pressure, and load conditions, ensuring robust and efficient performance. By estimating unknown electrolyzer parameters in real time, the strategy enables precise voltage control and balanced current distribution among the three parallel branches of the IBC.
The integration of theoretical analysis, numerical simulations, and experimental validation demonstrated the practical feasibility of the proposed control system. This research significantly advances green hydrogen production by providing a scalable and adaptable solution for real-world applications. The obtained results enhance the reliability and efficiency of hydrogen systems while establishing a solid foundation for future developments in sustainable energy technologies.
2. IBC–PEM Electrolyzer System Details, Analysis, and Modeling
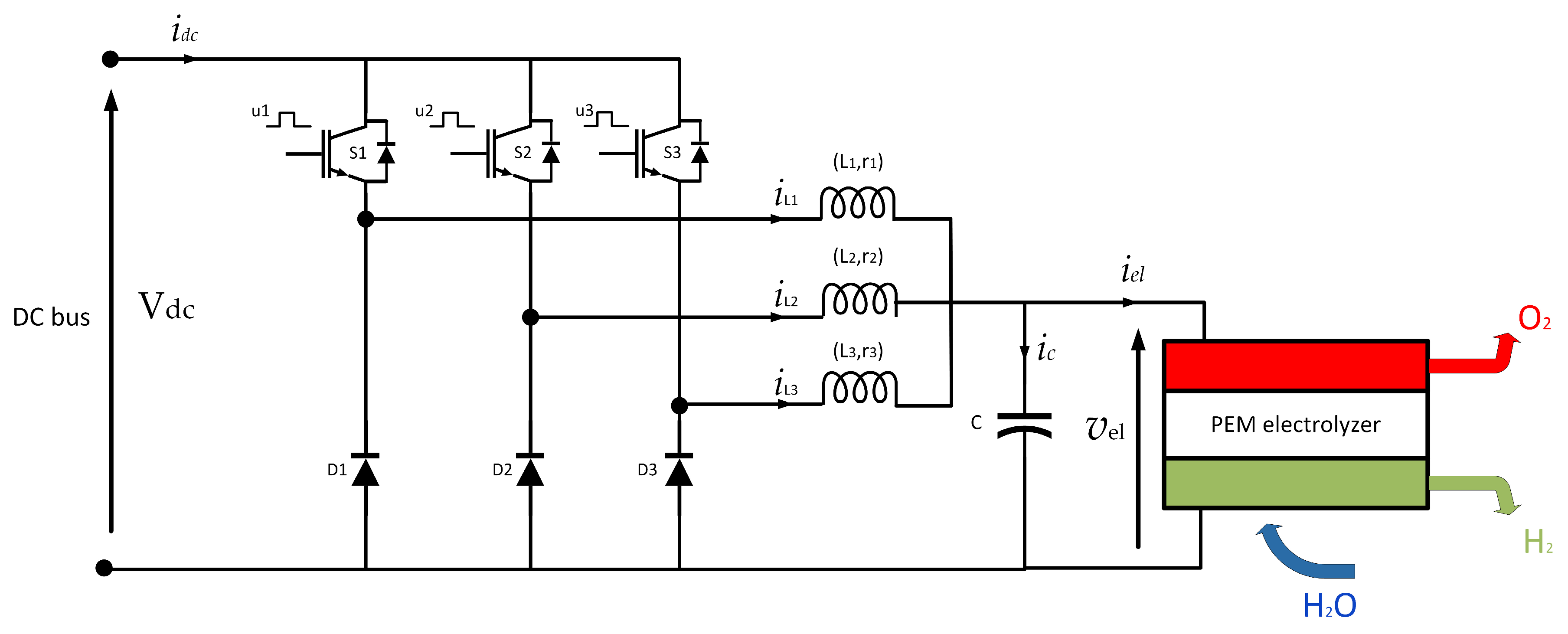
Figure 2 shows a hydrogen production system using a PEM electrolyzer. This system efficiently converts electrical energy and water into hydrogen, oxygen, and thermal energy. An IBC operates in this system as a power conditioner, creating an efficient connection between the PEM electrolyzer and the DC bus.
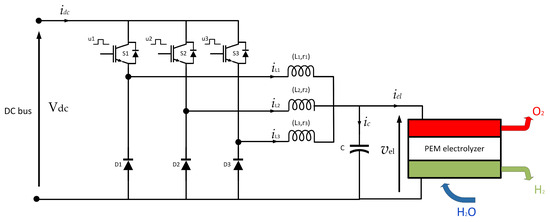
Figure 2.
Hydrogen production system based on an PEM electrolyzer.
For this study, an IBC with three branches was selected, as shown in Figure 2. The power switches are labeled S1, S2, and S3, while D1, D2, and D3 represent the power diodes. In addition, L1, L2, and L3 are ferrite core inductors that support high switching frequencies. The associated ESRs are labeled r1, r2, and r3. Finally, the capacitor (represented by C) filters the IBC output voltage.
3. PEM Electrolyzer Modeling Analysis and Approximation
As previously mentioned, at low current densities, the gas crossover phenomenon becomes more significant, while at high current densities, the efficiency of a PEM electrolyzer decreases dramatically. As a result, the PEM electrolyzer operates optimally in the ohmic region. In this region, a linear equation can approximate the electrical characteristics of the PEM electrolyzer, as shown in Equation (1).
Here, a0 and a1 represent the coefficients of the linear equation. These coefficients are highly dependent on the operating conditions; as a result, they are considered unknown parameters for the purpose of this work.
Several previous studies have used linear equations to approximate the V-I electrical characteristics of PEM electrolyzers [1,7,8,10,14,16,17,18,19]. However, these studies did not consider the effect of the operating conditions, such as temperature and gas pressure, despite their strong influence on these characteristics. In the present study, the effects of the operating conditions were considered. Therefore, we considered the coefficients in our model to be unknown parameters that require estimation for robust control.
4. Nonlinear Modeling of an IBC–PEM Electrolyzer
By applying Kirchhoff’s laws to analyze the circuit shown in Figure 2, and noting that u1, u2, and u3 are binary variables that can each take a value of 1 or 0, the following bilinear circuit model for the combined PEM electrolyzer and IBC system was derived as follows:
For the purpose of designing ASMC, it is more beneficial to consider the subsequent averaged model [20], which was derived from a bilinear model (Equations (2)–(5)) across a single switching period, Ts:
where x represents the average value of the electrical magnitude. The variables x1, x2, and x3 denote the average values of iL1(t), iL2(t), and iL3(t), respectively, while x4 represents the average value of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (Vel(t)). Additionally, μ1, μ2, and μ3 are the average values of the binary control inputs u1, u2, and u3 (duty cycle), respectively. The average model can be expressed as follows:
Here, φ and ϴ denote the vector of the average output voltage values (x4) and the vector of unknown parameters, which are detailed in Equations (11) and (12):
where and are the parameters that must be estimated.
5. Adaptive Sliding Mode Controller Design
Controlling the voltage of the PEM electrolyzer is critical to managing the hydrogen flow rate, optimizing the energy efficiency, and ensuring safety. Equation (10) illustrates the voltage dynamics of the PEM electrolyzer. However, this equation does not include a control input. Therefore, the voltage will be controlled indirectly by regulating the current through the three inductors. Using this equation, the equilibrium states can be determined, which facilitates a clearer understanding of the relationship between the PEM electrolyzer voltage and the current through the inductors in their respective equilibrium states. The equilibrium states are described by Equations (13)–(16) below.
Here, x10, x20, and x30 represent the inductor currents at the equilibrium state, while μ10, μ20, and μ30 denote the control inputs at equilibrium. Additionally, φd represents the desired voltage vector of the PEM electrolyzer xref. The secondary objective is to achieve equal current sharing among the three inductors. To begin, the desired current, Id, is introduced from Equation (17) as
As discussed in the ‘System Modeling’ section, the parameter vectors, denoted as θ, undergo significant variation. Consequently, these parameter vectors, which are considered unknown, must be estimated. As a result, the desired current, referred to as Id in Equation (17), is also unknown and needs to be estimated using these parameter vectors. Equation (18) calculates the desired current based on the estimated parameters .
5.1. Control Objectives
The control objectives of the designed ASMC can be summarized as follows:
- Ensure global stability of the control system across a wide range of operating conditions.
- Maintain precise regulation of the PEM electrolyzer voltage despite significant model uncertainties.
- Guarantee equal current sharing between the three inductors, regardless of variations in their inductance values.
5.2. Sliding Mode Controller Design
As mentioned previously, the voltage control of the PEM electrolyzer was indirect, achieved by controlling the currents through the three inductors. In addition, the currents in the inductors had to be balanced. Consequently, the tracking errors were defined as follows:
The sliding surface was defined as the sum of the tracking error and its integral (Equation (20)), in an approach known as integral sliding mode control, which is insensitive to external disturbances.
where λ21, λ22, and λ23 are positive constants used in the controller design.
Using the SMC method, the control law can be expressed as a combination of two parts (Equation (21)). The first part is a continuous term known as the equivalent control, while the second part is a discontinuous term.
When there are no disturbances or uncertainties, the equivalent control aims to maintain the system states on the sliding surface. This control law can be derived from the invariance condition, represented as () in the following equation [21]:
The discontinuous control, also known as switching control, ensures that the system state reaches and remains on the sliding surface while counteracting the effects of disturbances and uncertainties. Equation (23) provides the definitions of these discontinuous control inputs.
where α21, α22, and α23 are the positive constants used in the controller design.
The control law is obtained by substituting Equations (22) and (23) into Equation (21), resulting in the following equation:
5.3. Design of Adaptive Controller and Stability Analysis
The following theorem summarizes the main findings of this section.
Theorem 1.
Consider the closed-loop system formed by the PEM electrolyzer and IBC, as described in the averaged model (Equations (7)–(10)), with the controller defined by the control laws in Equation (24). If the dynamics of the estimated parameter vector follow Equation (30), and the desired dynamic trajectory of the PEM cell voltage, x4d, is determined by Equation (29), then it can be concluded that
- I.
- The errors (e1, e2, and e3) converge asymptotically to zero, implying equal current sharing between the three inductors.
- II.
- The PEM electrolyzer voltage x4 perfectly tracks its reference value xref.
Proof of Theorem 1.
Let us define the quadratic Lyapunov function as follows:
Here, s is the vector of the sliding surfaces (), ε is the error between x4 and its desired dynamic trajectory x4d (ε4 = x4 − x4d), and represents the parameter estimation error ). P represents a symmetric positive definite matrix.
The time derivative of quadratic Lyapunov function is given as follows:
Equation (26) is obtained by using the control law defined by Equations (24) and (10):
Rearranging Equation (27), the following is obtained:
Here, k4 is a positive designed parameter.
Equation (28) contains three terms. The first term, which is negative, can be referred to as the stabilization term. To make this equation (the time derivative of the Lyapunov function) negative definite, the second term can be set to zero by adjusting the desired dynamics of x4, as shown in Equation (29). The third term, which represents the adaptive law for parameter estimation, is defined in Equation (30).
According to the Lyapunov principle, it can be concluded that the sliding surface vector and the defined error asymptotically converge to zero. This indicates that the system error approaches zero, ensuring equal current distribution among the three parallel legs of the IBC, where x1 = x2 = x3 = Id. Using Equation (31) as a guide, the estimated steady-state reference current can be calculated.
The vector denotes the average output voltage values (x4) at the equilibrium point. Given that this corresponds to the equation defined in Equation (18), it follows intuitively that . This suggests that x4 asymptotically converges to its reference value (xref).
Remark 1.
Although the estimated parameters are bounded, they do not represent the true parameters. However, this discrepancy does not affect the effectiveness of the developed ASMC. It is possible to accurately estimate the term even without knowing the exact value of θ. This estimation is sufficient to calculate the true reference current .
For a mathematical definition regarding the estimation of the true parameter vector, the input control signal must be persistently exciting on the order of n. This is satisfied if there exists a positive constant M such that for all τ:
Here, I is the identity matrix and τ is a positive constant. □
6. Simulation Results
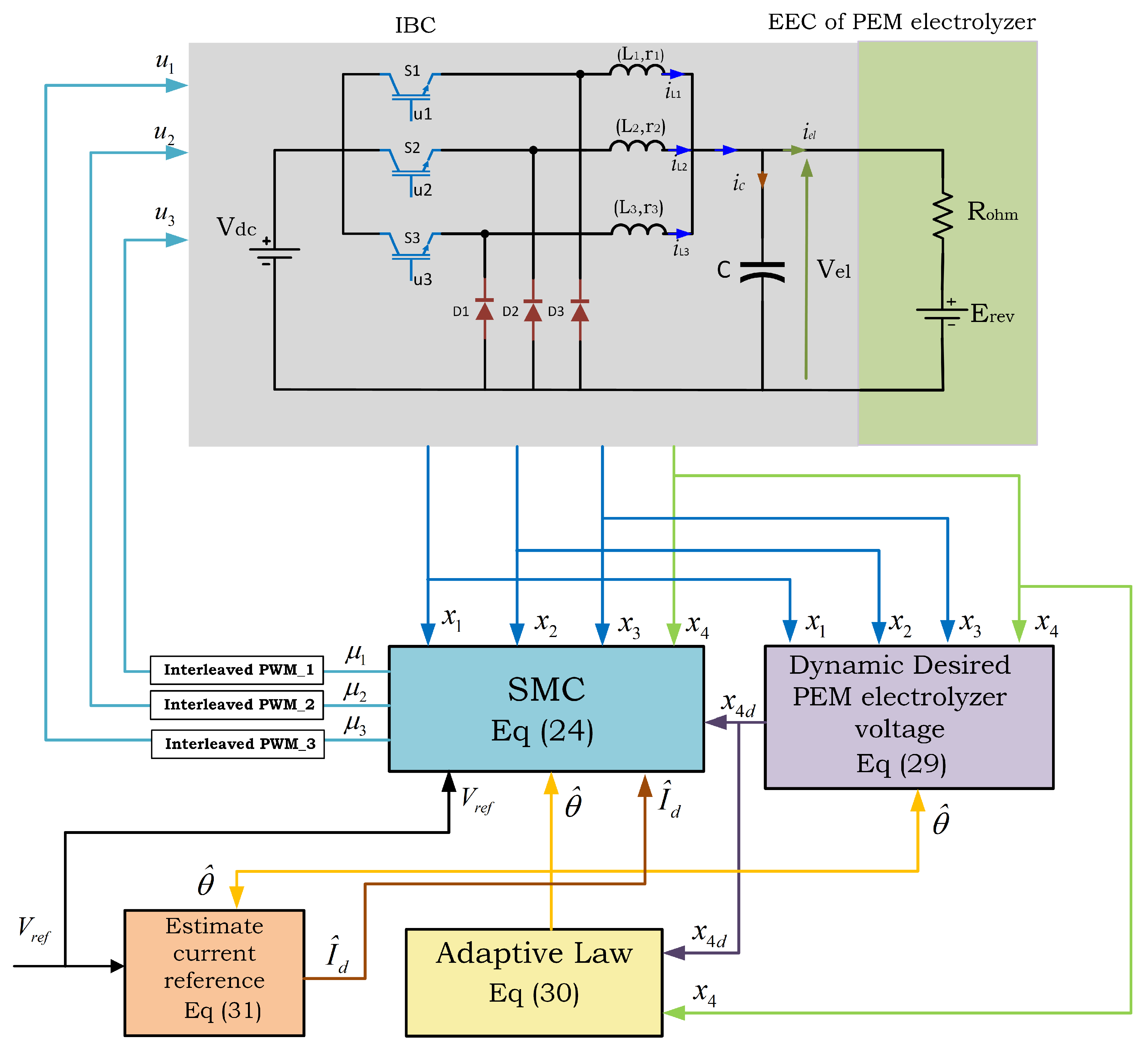
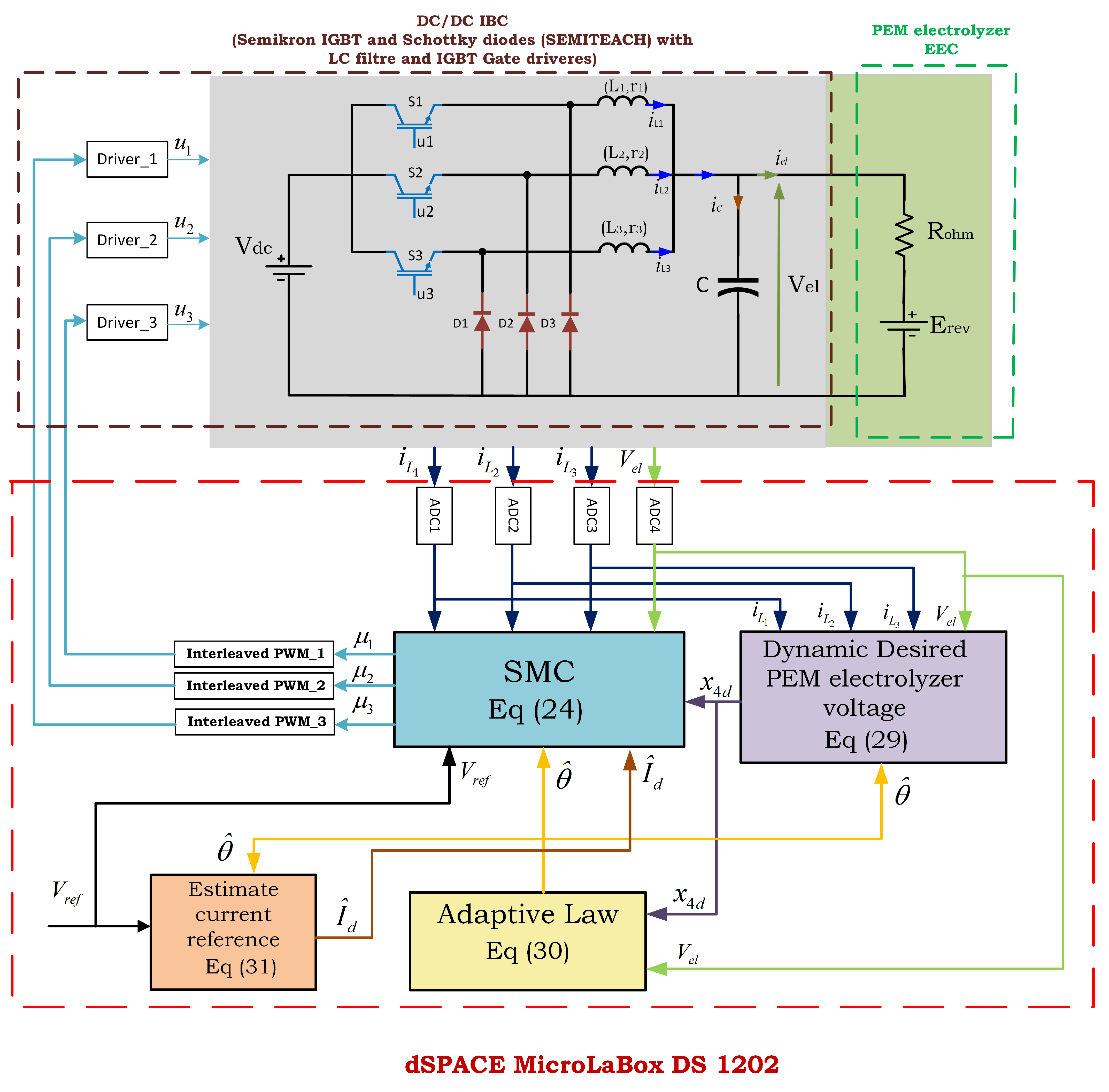
The theoretical analysis of the designed ASMC, as summarized in Theorem 1, was rigorously validated through simulation tests using MATLAB 2023b Simulink software. The test bench was employed to evaluate the performance and robustness of the designed ASMC, as illustrated in Figure 3. In this figure, the first block, represented by Equation (30), corresponds to the adaptive law utilized for estimating the vector of unknown parameters. The second block, described by Equation (29), represents the desired dynamics of the PEM electrolyzer voltage, x4d. The estimated current of reference block, , is derived using the estimated unknown parameters and the desired PEM electrolyzer voltage dynamics, as described by Equation (31). Ultimately, the SMC block described by Equation (24) generates control inputs (duty cycles) based on the estimated current reference, the desired PEM electrolyzer voltage dynamics, the reference PEM electrolyzer voltage, and the system states. Subsequently, the control inputs are transformed into PWM signals, which are phase-shifted by 120° and applied to the three power switches of the IBC.
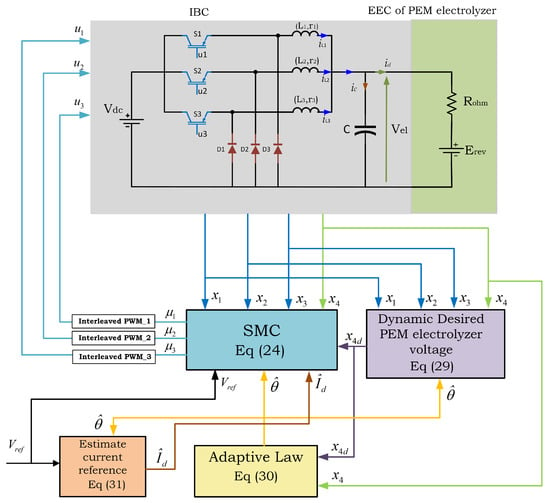
Figure 3.
Simulation test bench for ASMC.
In this simulation test, the model was not based on a real electrolyzer or any existing designs from the literature. However, by adjusting the number of cells and their area, the parameters for this work, such as the ohmic resistance and the reversible voltage, were selected to be logical and adaptable to actual PEM electrolyzer parameters. This approach was adopted to accommodate the available laboratory equipment. The main specifications of the EEC-PEM electrolyzer, IBC, and ASMC controller are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Key parameters of the EEC PEM electrolyzer, IBC, and ASMC controller for simulation testing.
The detailed calculations of the IBC are presented in the Appendix A section.
6.1. Performance Validation of Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for a Reference Step in PEM Electrolyzer Voltage
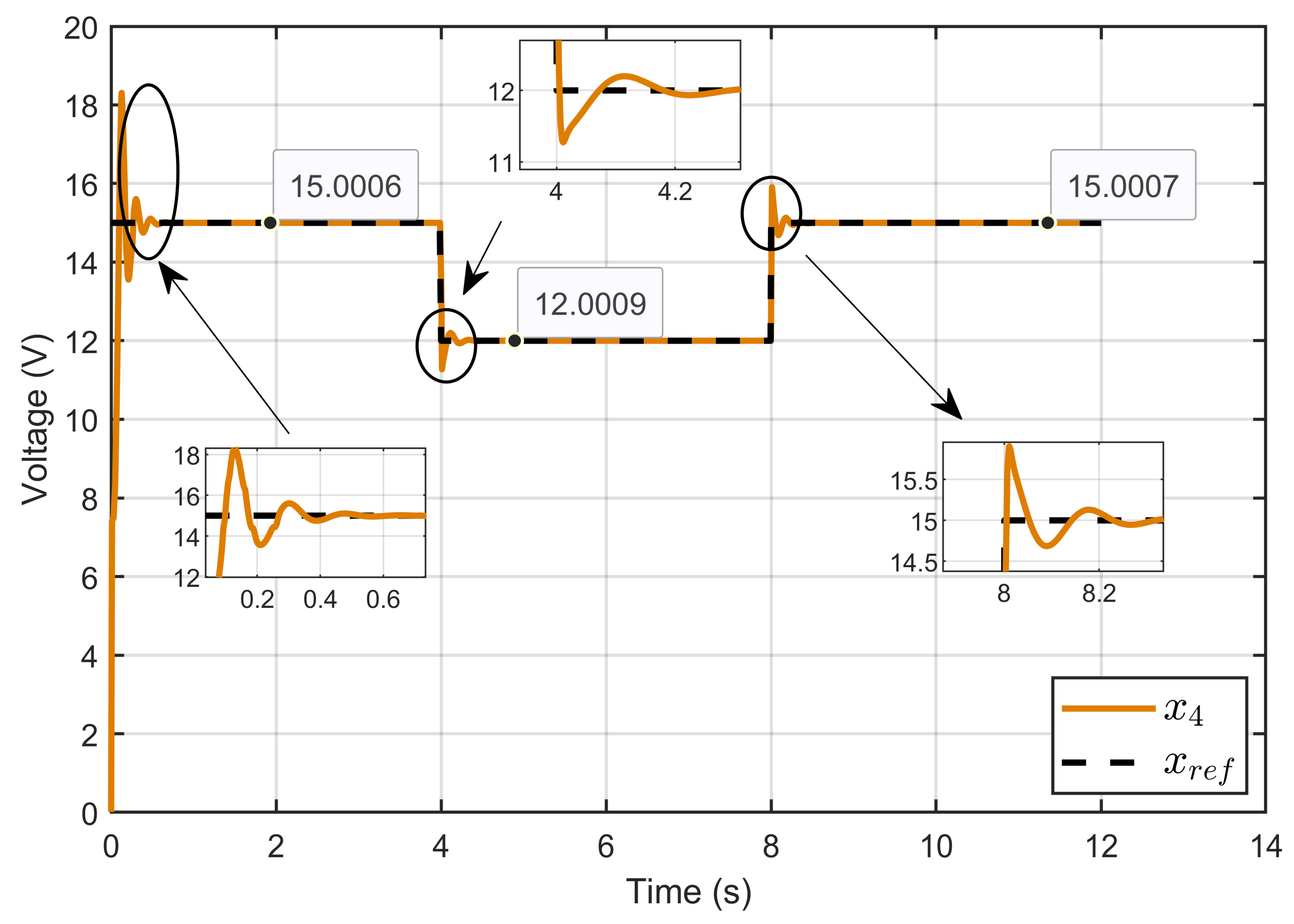
This section is dedicated to validating the performances and robustness of our designed ASMC under fixed operating conditions (Rohm = 1.5 Ω and Erev = 7.45 V) while varying the voltage of the PEM electrolyzer. Two voltage reference steps were applied: the first step occurred at 4 s, where the voltage decreased from 15 V to 12 V, and the second step occurred at 8 s, where the voltage increased from 12 V to 15 V.
Figure 4 shows the performance of the developed ASMC in controlling the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), demonstrating its ability to closely follow the reference voltage (xref) over various step changes. Initially, the voltage rose quickly to match the reference with a small overshoot, and then stabilized rapidly. The controller responded well to step changes at 2 and 8 s, adjusting the voltage with minimal overshoot and rapid settling times. During steady-state operation, the voltage consistently aligned with the reference value, showing values of 15.0006 V, 12.0009 V, and 15.0007 V, demonstrating the high accuracy of the developed controller.
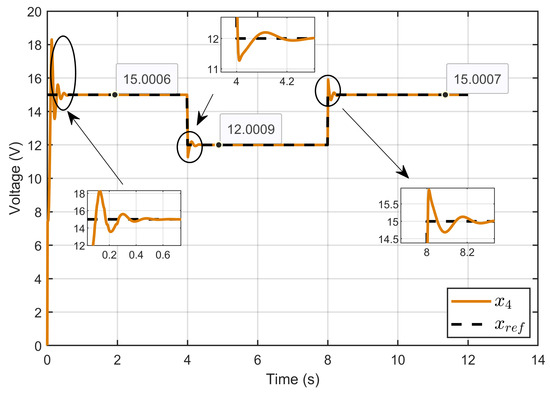
Figure 4.
Dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its reference under step reference voltage (simulation results).
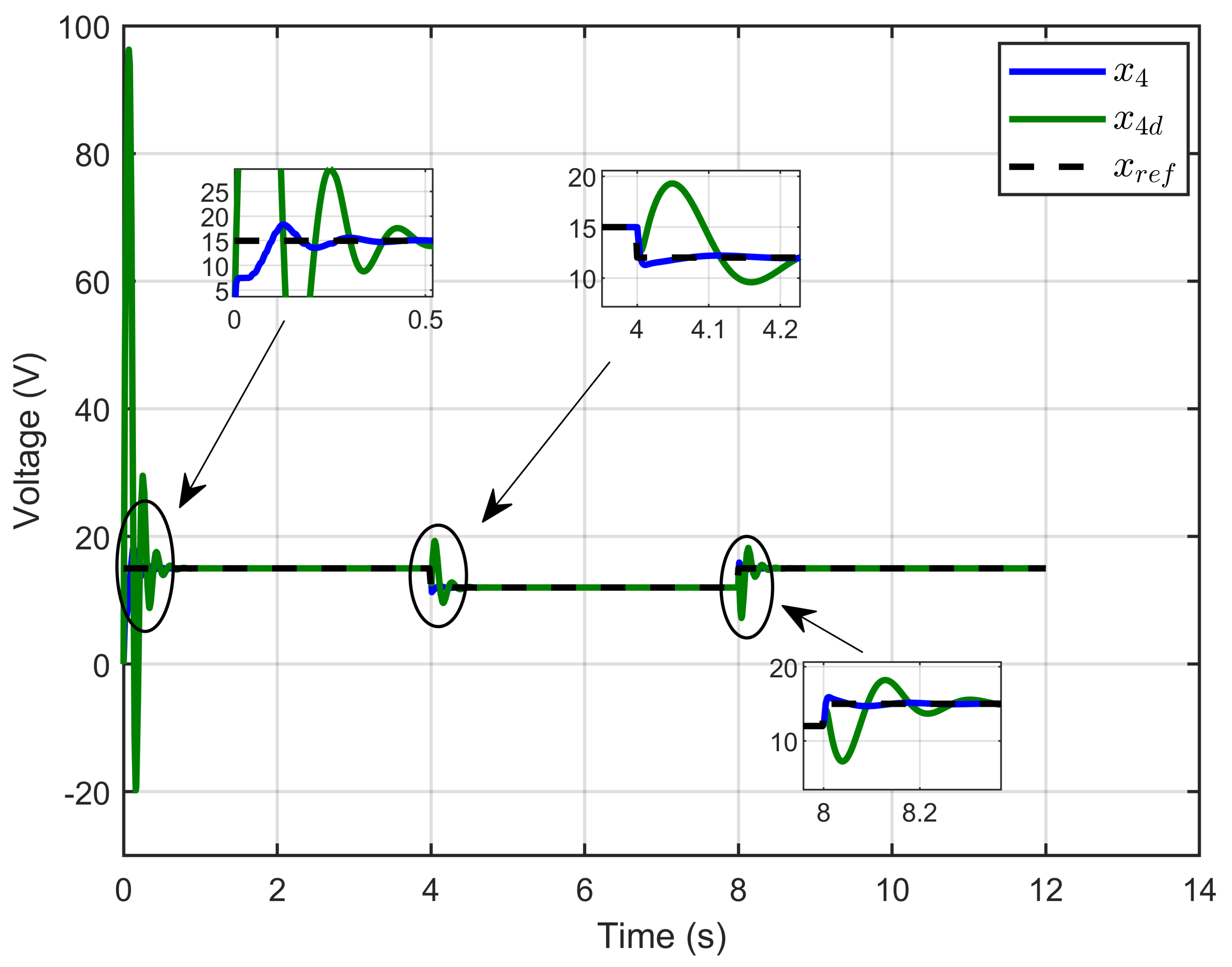
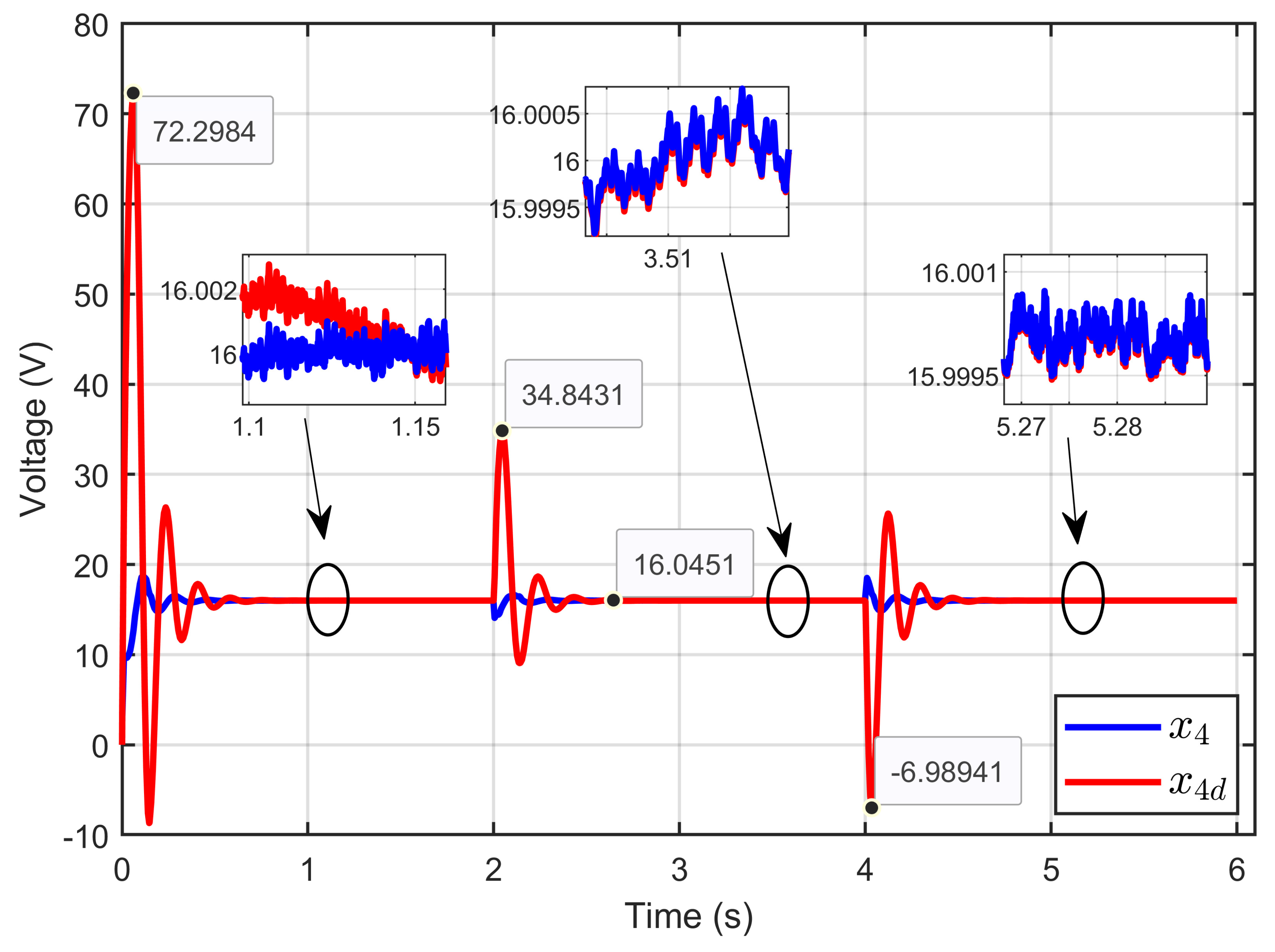
Figure 5 illustrates the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its desired dynamic response, which demonstrated that the PEM electrolyzer (x4) precisely tracked the desired dynamic voltage (x4d), defined by Equation (29), despite the large abrupt steps in the PEM electrolyzer voltage reference.
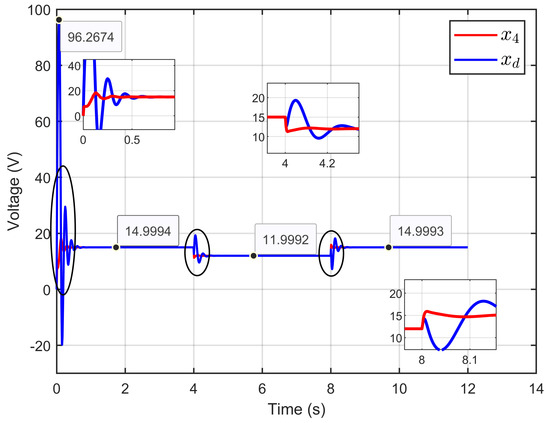
Figure 5.
PEM electrolyzer voltage and its desired dynamic response under step reference voltage (simulation results).
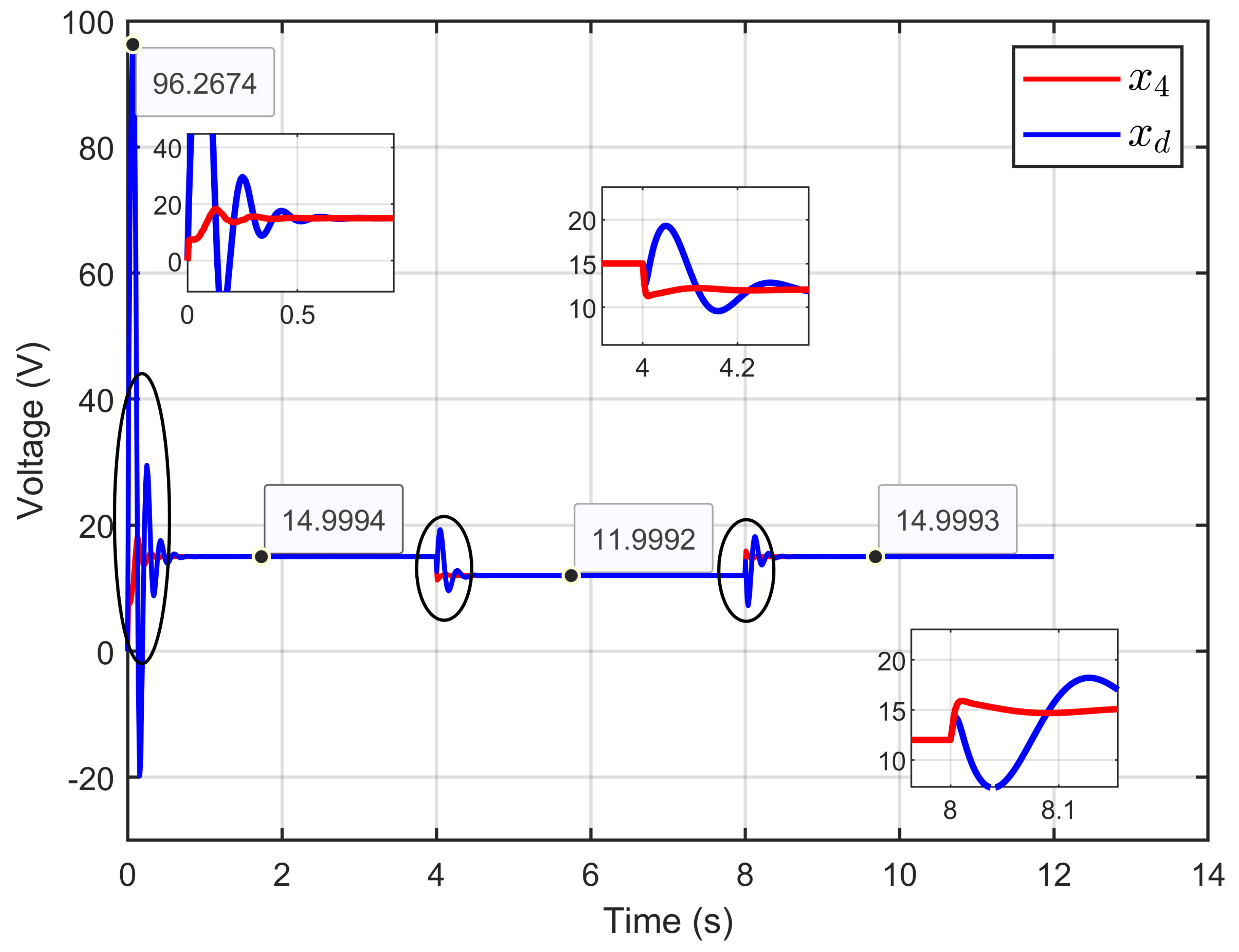
Figure 6 illustrates the PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired dynamic response, showing the alignment between the three voltages: the PEM electrolyzer voltage, the reference voltage, and the desired dynamic voltage. This demonstrates satisfactory agreement with the developed theoretical analysis.
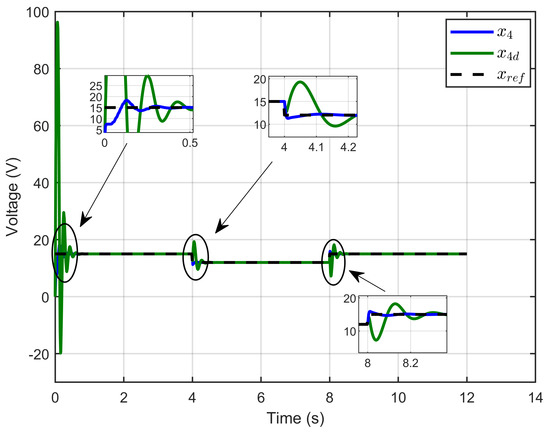
Figure 6.
PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired dynamic response under step reference voltage (simulation results).
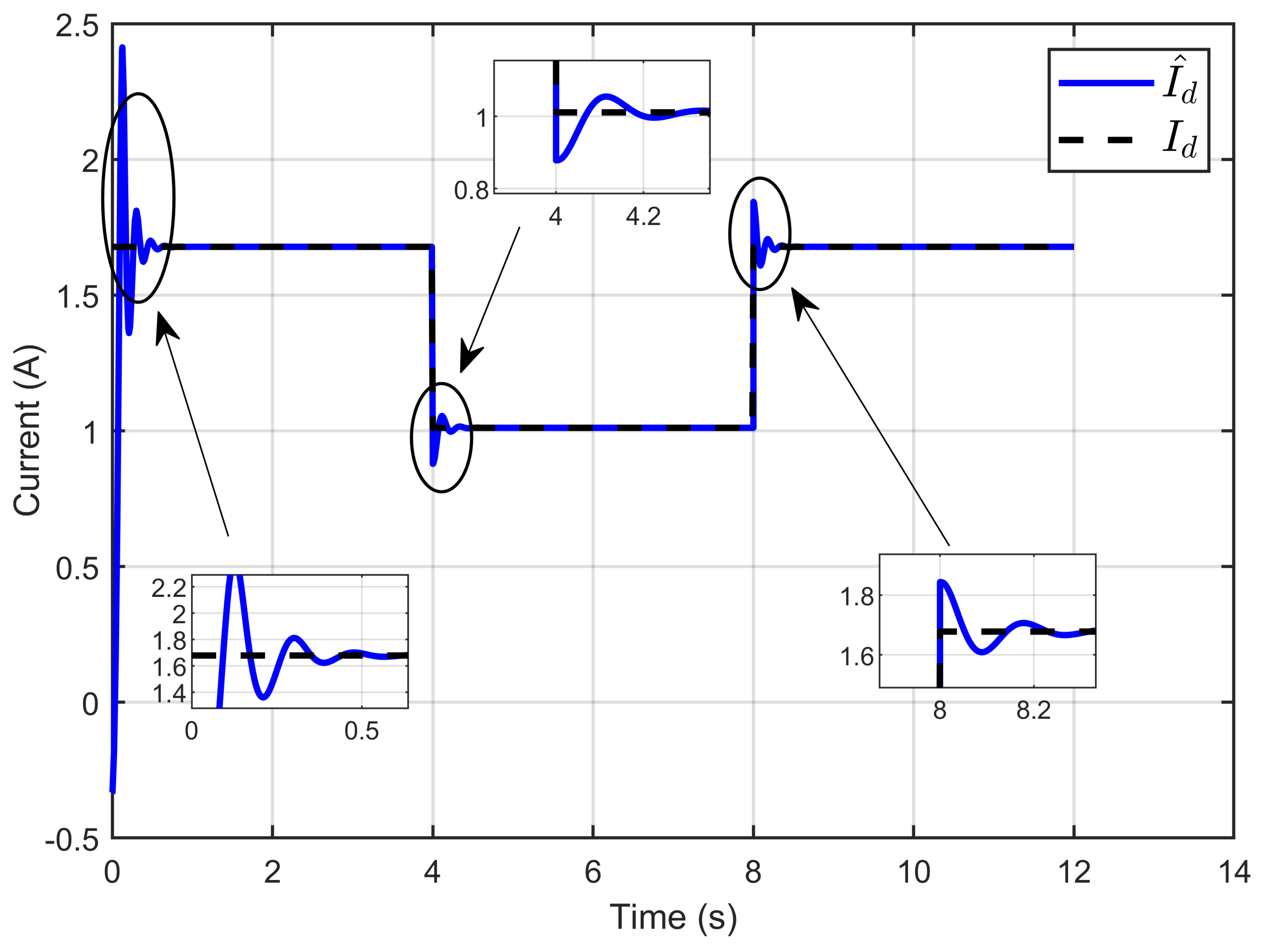
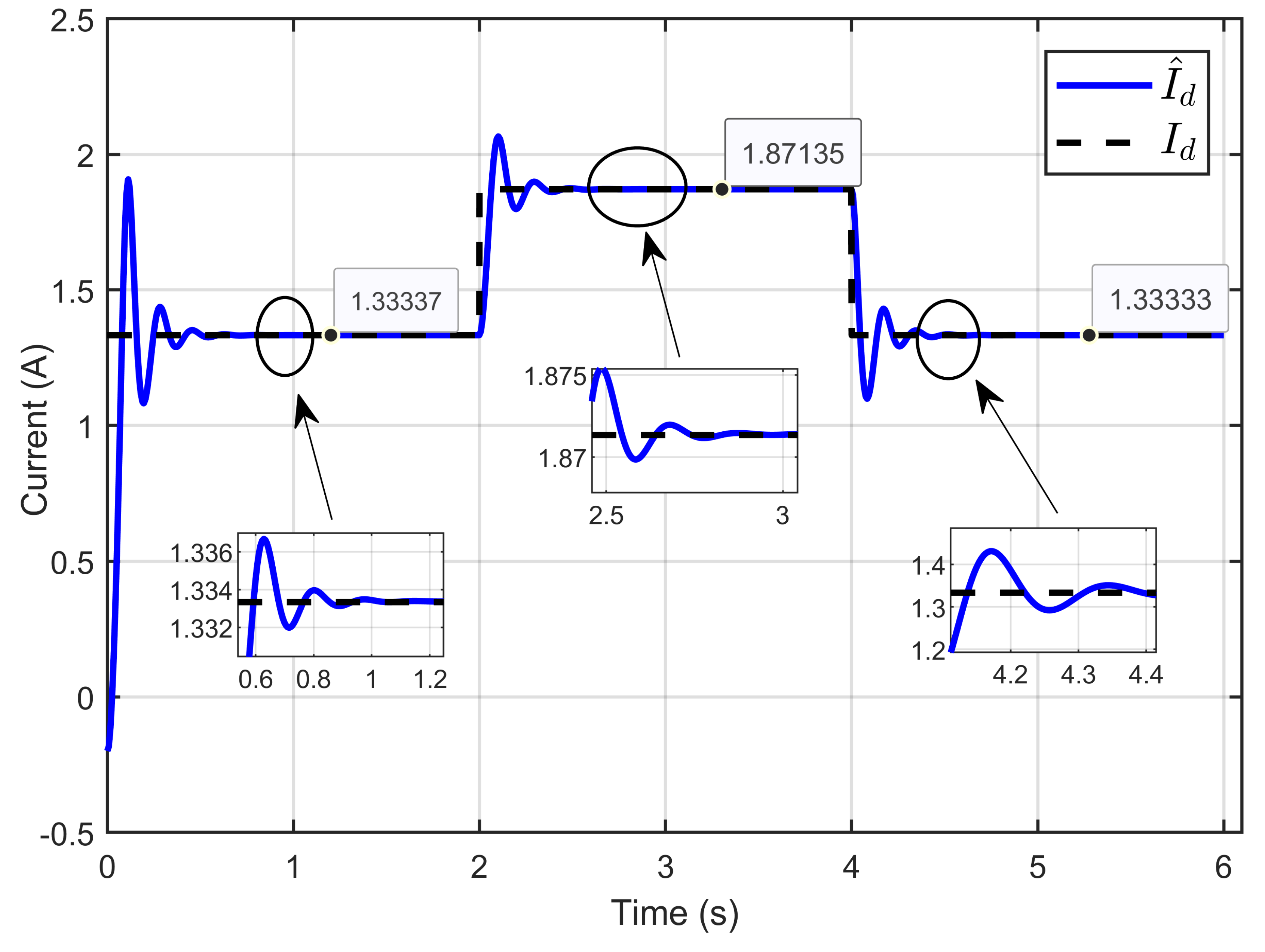
Figure 7 illustrates the dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current and its actual value, effectively demonstrating the close correlation between the estimated and actual inductor reference current. This highlights the accurate estimation of the unknown parameter vector.
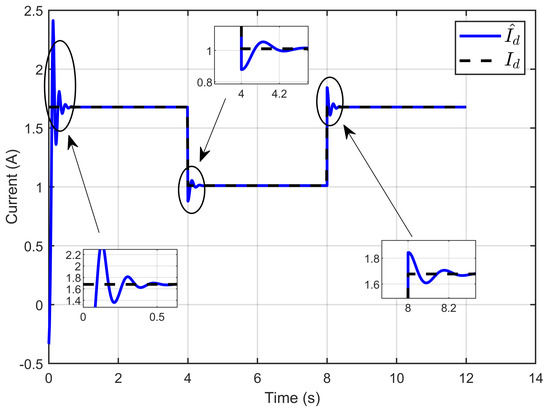
Figure 7.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current and its actual value under step reference voltage (simulation results).
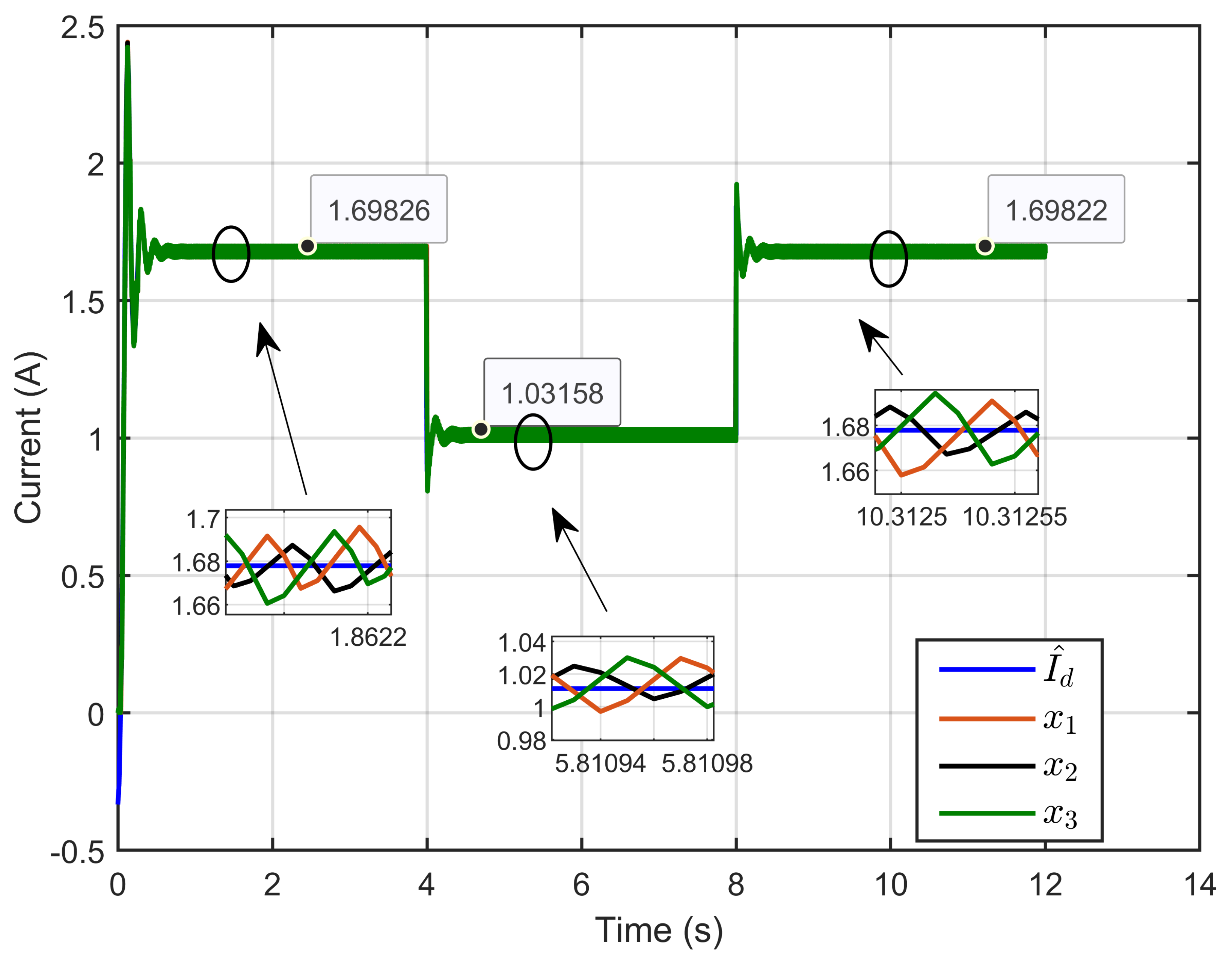
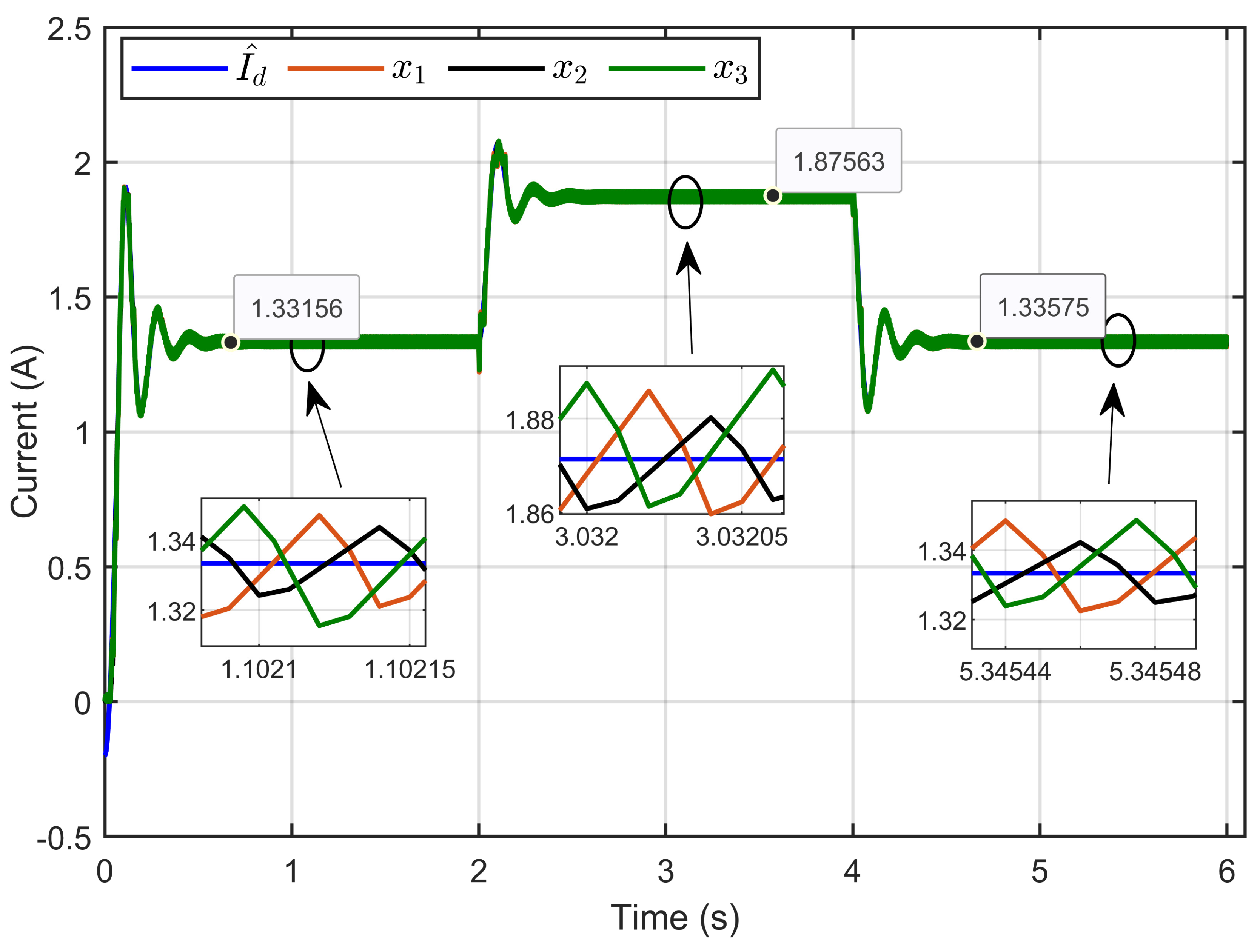
Figure 8 illustrates the dynamic response of the three inductor currents and their estimated references, showing the rapid convergence of the inductor currents (x1, x2, and x3) toward the desired estimated current during transient periods. This convergence indicates a balanced current distribution across the three parallel legs. The zoomed-in plot further highlights the minimal current ripple and the high accuracy achieved during steady-state operation.
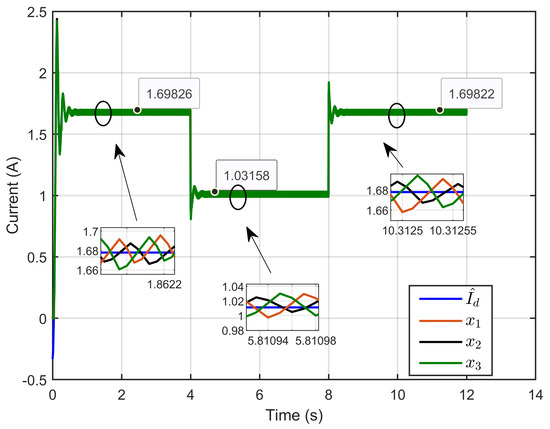
Figure 8.
The dynamic response of three inductor currents and their estimated reference under step reference voltage (simulation results).
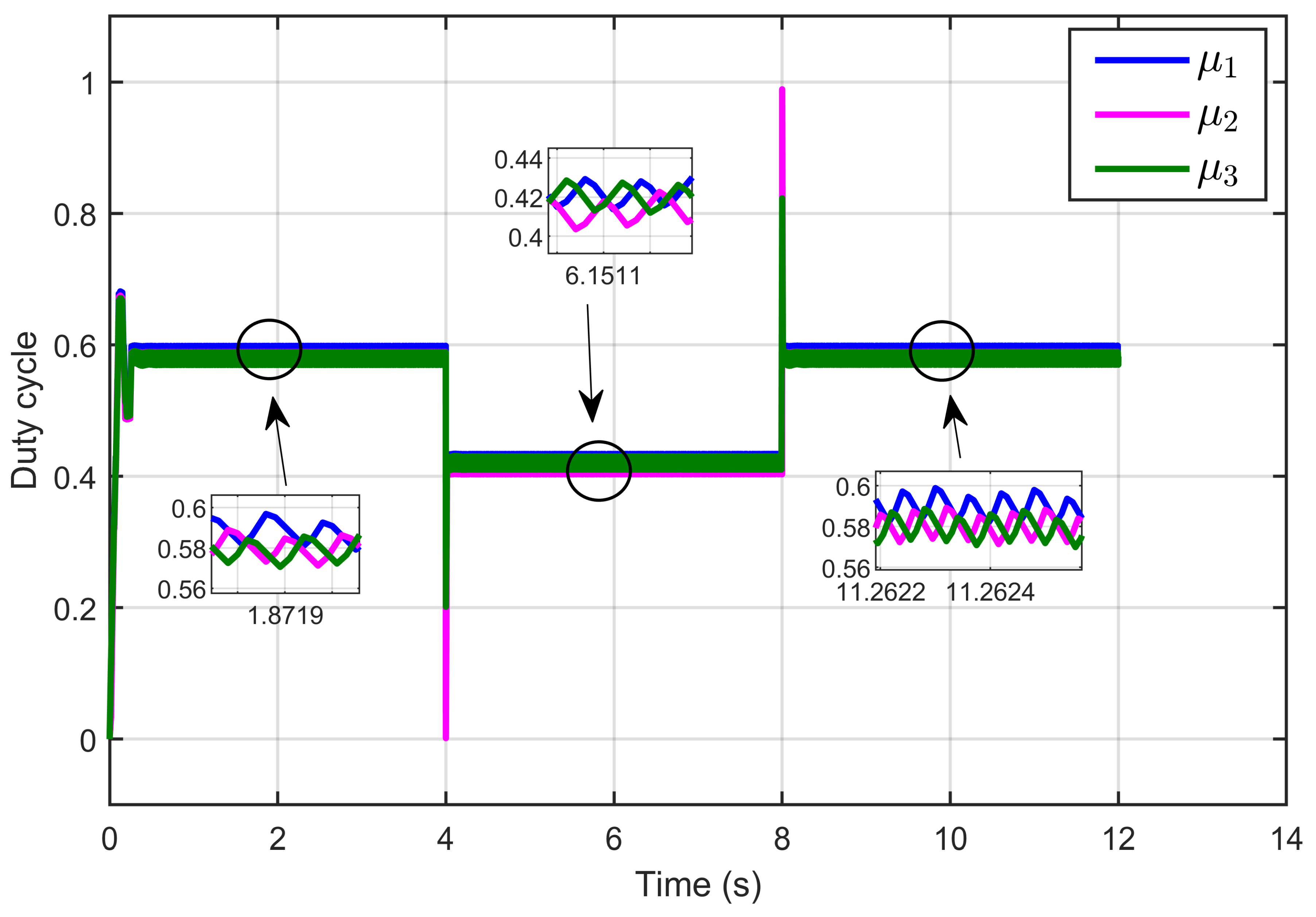
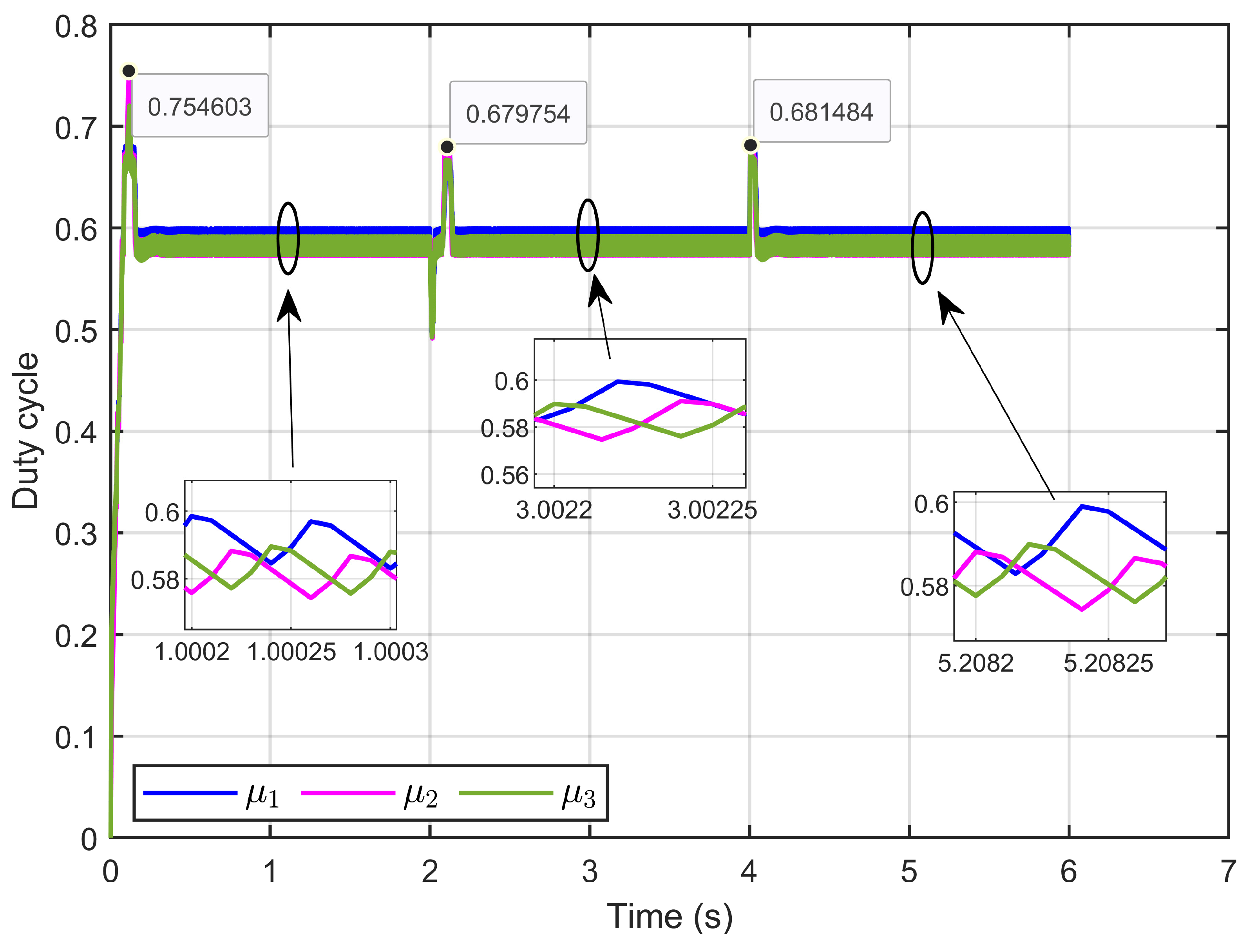
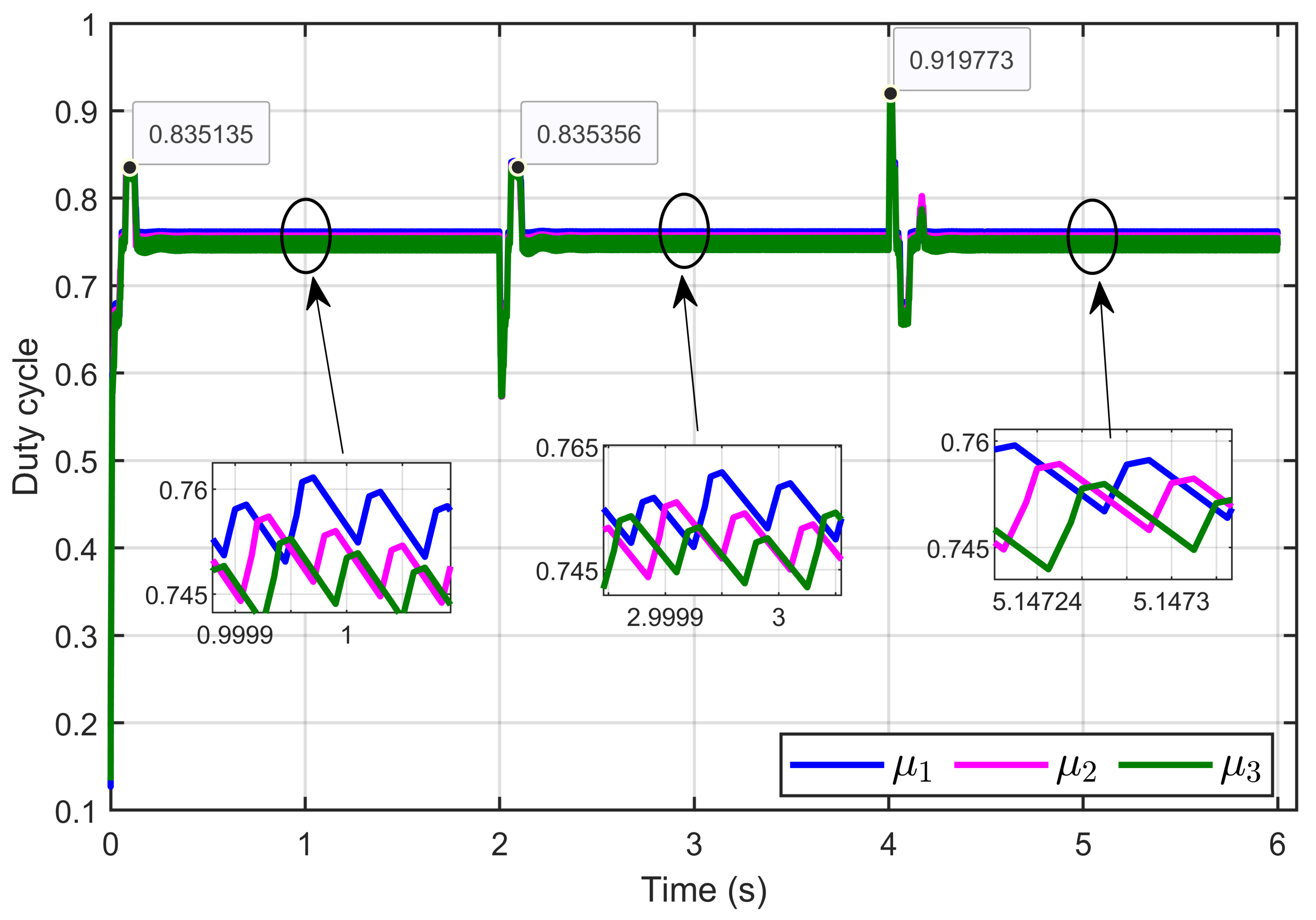
Figure 9 depicts the control inputs (duty cycle) of the designed ASMC, showing that these signals remained within a bounded range of 0 to 1, which aligns with the duty cycle. Furthermore, the signals exhibited minimal ripples.
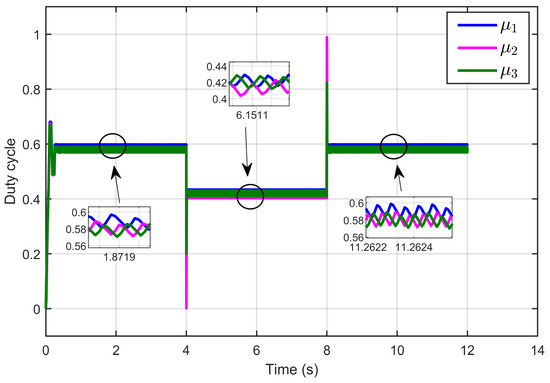
Figure 9.
Control inputs signal (duty cycle) under step reference voltage (simulation results).
The simulation results obtained when applying an abrupt and significant change in the reference voltage demonstrated that the developed ASMC successfully achieved its objectives (PEM electrolyzer voltage regulation and current equal sharing) under unknown PEM electrolyzer parameters. The performance metrics for each step are summarized in Table 2 below:

Table 2.
Performance Metrics of the ASMC for a reference step in PEM electrolyzer voltage (simulation).
These simulations performance metrics demonstrated that the ASMC can effectively maintain voltage regulation and current sharing with minimal errors, even under significant changes in the reference voltage. The small errors observed in voltage regulation, tracking, current estimation, and current sharing highlight the controller’s precision, robustness, and accuracy in achieving the desired objectives.
6.2. Performance Validation of the Controller Sensitivity to Perturbations Caused by Sudden Variations in PEM Electrolyzer Operation Conditions
Next, the performance and robustness of the developed ASMC were evaluated against perturbations caused by sudden variations in the operating conditions of the PEM electrolyzer. The evaluation was conducted in three scenarios, detailed below.
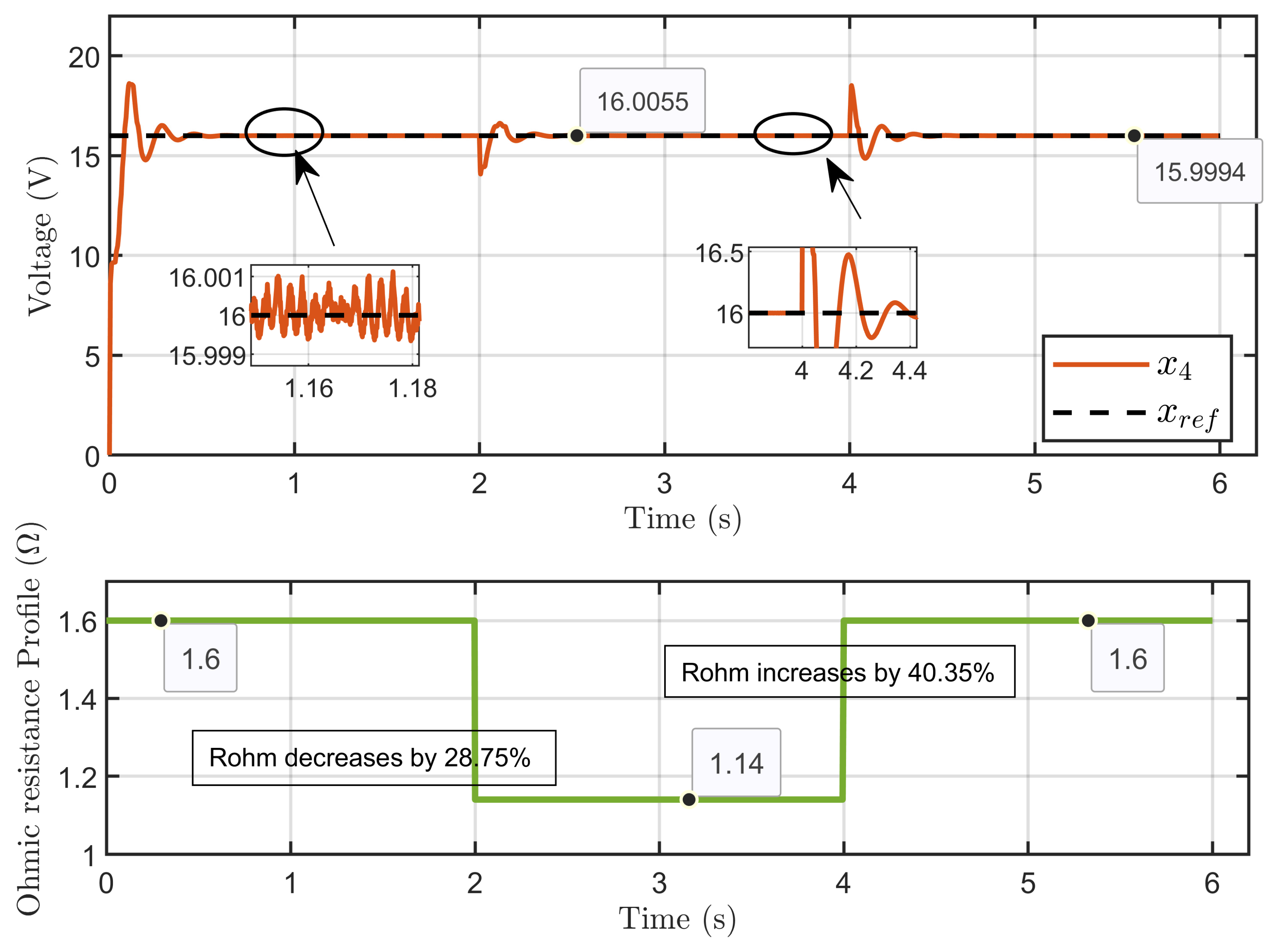
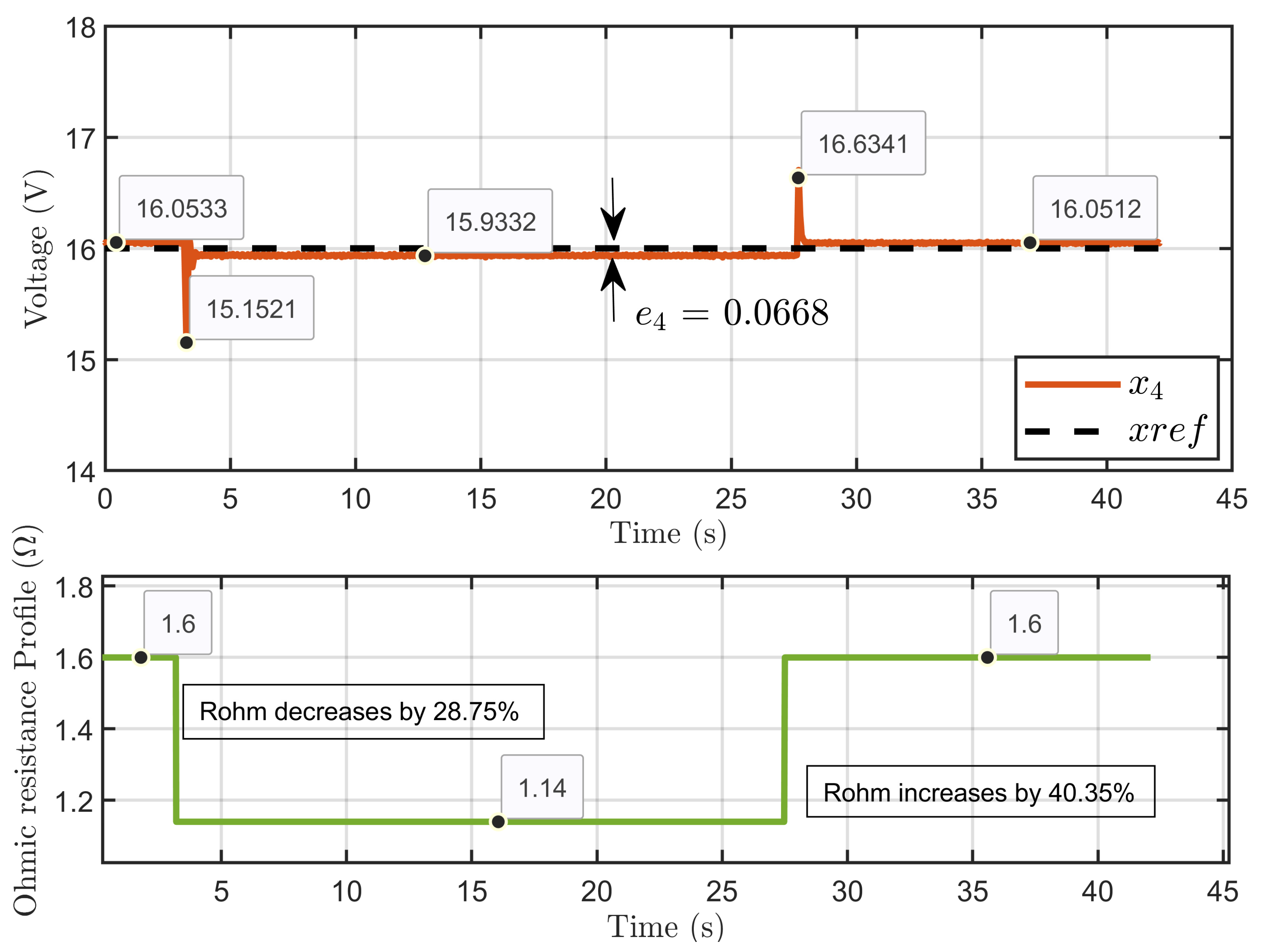
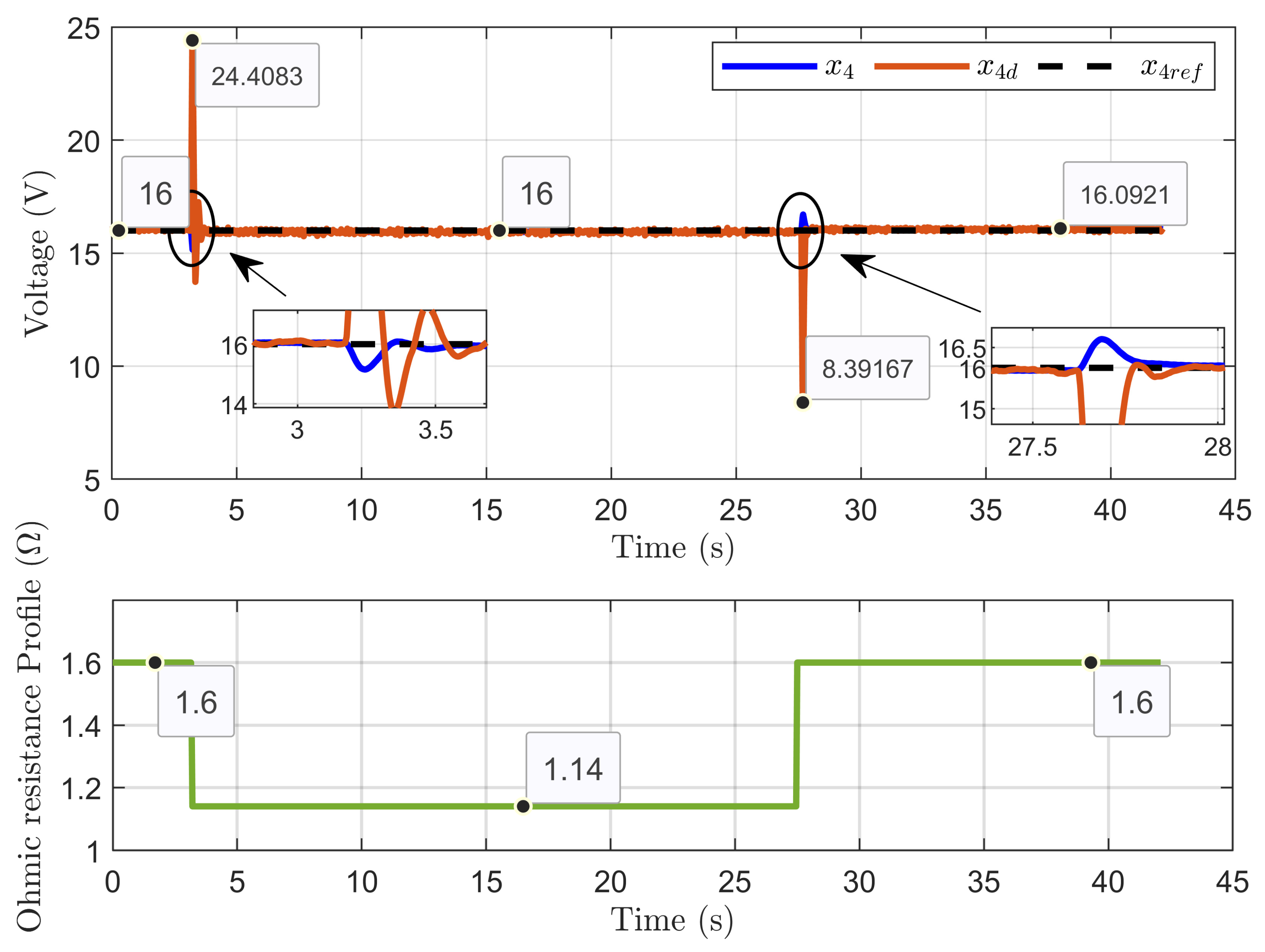
Scenario 1: In this scenario, the reference voltage of the PEM electrolyzer was set to xref = 16 V and the reversible voltage to Erev = 9.6 V while introducing a perturbation to its ohmic resistance. The resistance started at 1.6 Ω, decreased by 28.75% to 1.14 Ω over 2 s, and then increased by 40.35% to return to 1.6 Ω at the 4 s mark.
Figure 10 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) under a large perturbation to the ohmic resistance. It shows the effective regulation of the PEM electrolyzer voltage despite the sudden variations in the ohmic resistance. The voltage exhibited a small overshoot during the transition of the ohmic resistance variation, which then stabilized in the steady state, reaching its reference value.
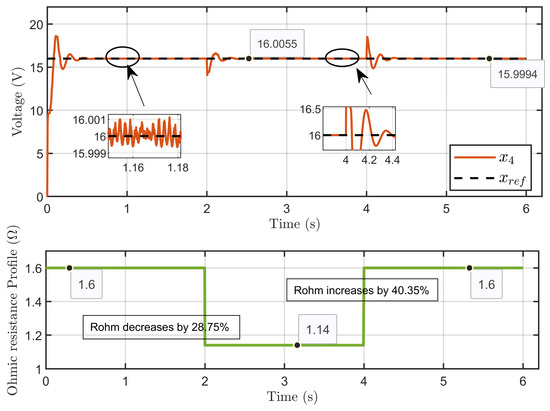
Figure 10.
Dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its reference under ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
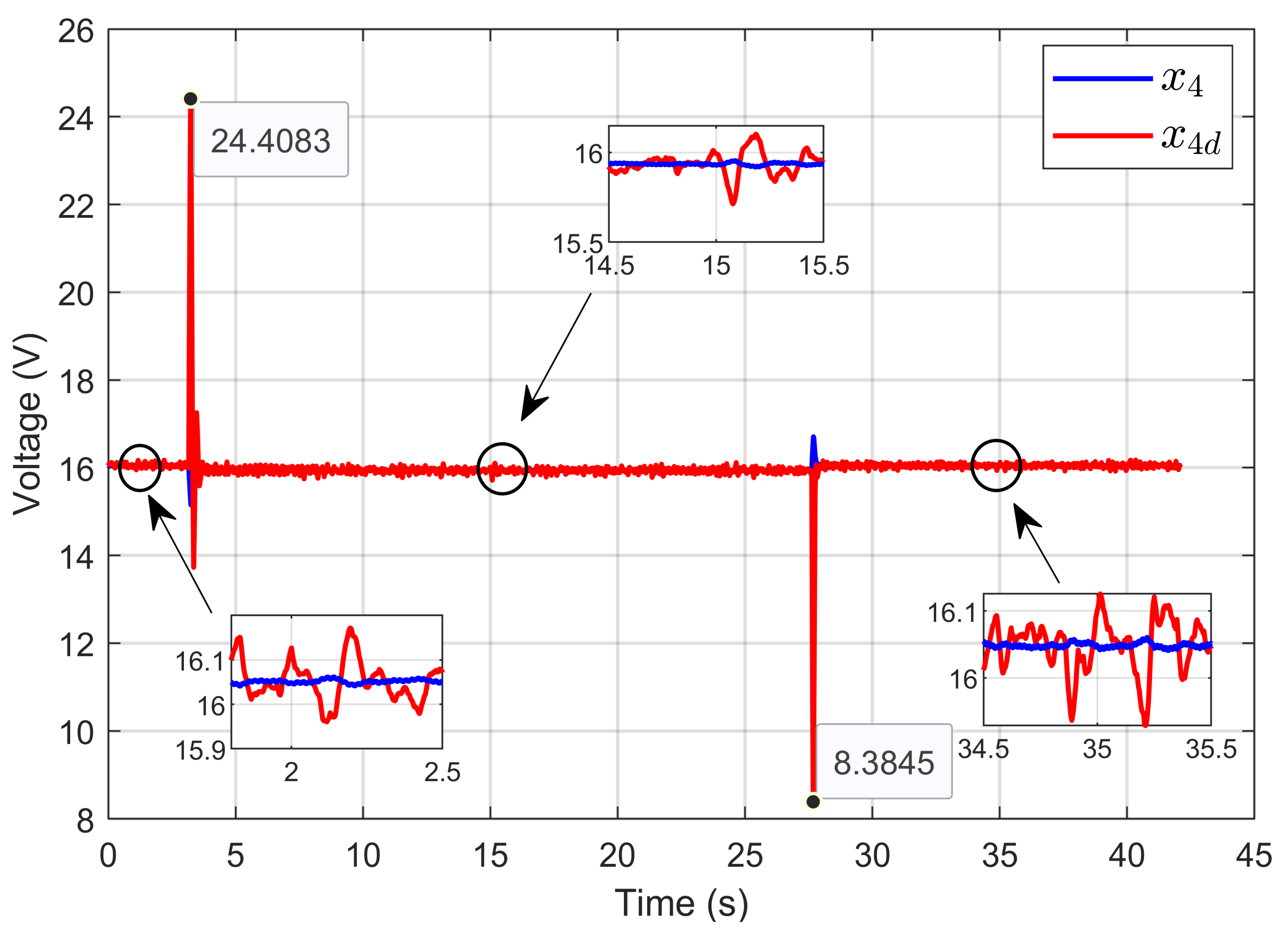
Figure 11 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) and its desired dynamic trajectory (x4d). It shows that the PEM electrolyzer voltage tracked its desired trajectory perfectly and quickly, even during sudden variations in the ohmic resistance.
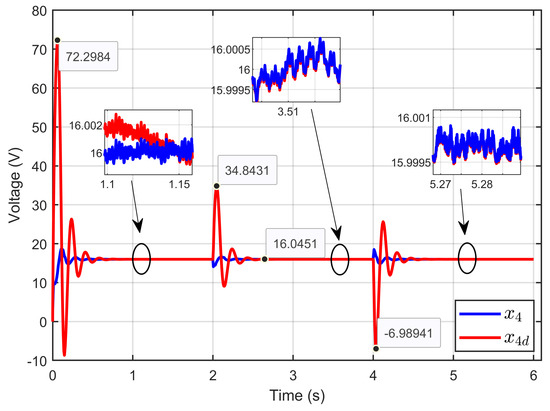
Figure 11.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage and its desired trajectory under ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
Figure 12 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), its reference value (xref), and the desired dynamic trajectory (x4d). It shows that the voltages aligned with high accuracy during steady-state operation.
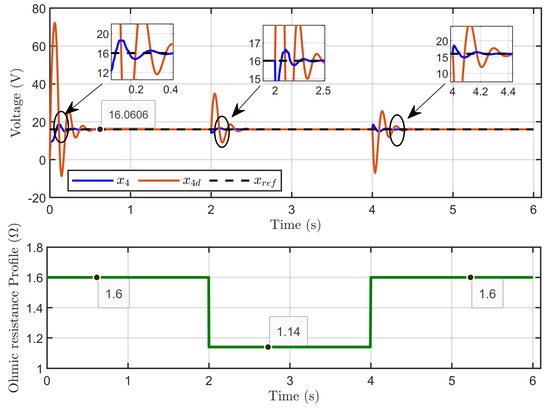
Figure 12.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired trajectory under ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
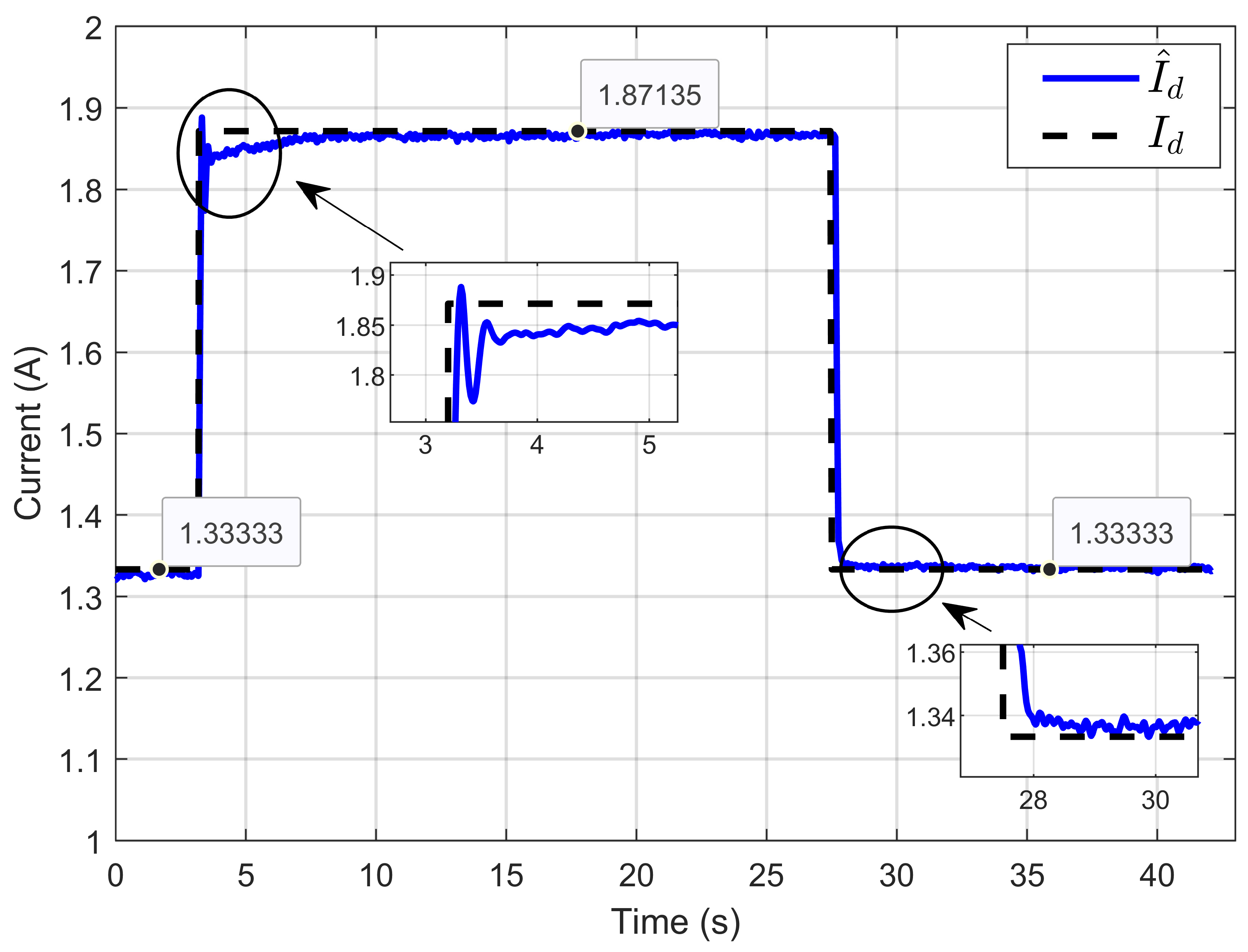
Figure 13 illustrates that the reference-estimated inductor current consistently tracked its true value Id across all operating conditions due to the effectiveness of the designed ASMC. This control method adapted to the variations in system parameters, such as changes in ohmic resistance, by dynamically adjusting the estimated current to align with the actual inductor current.
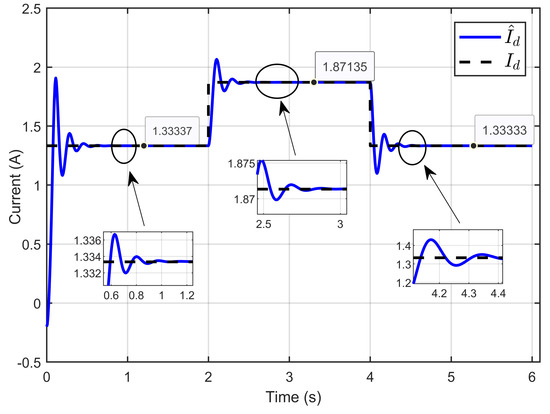
Figure 13.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current and its actual value under ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
Figure 14 presents the dynamic response of the three inductor currents (x1, x2, and x3) and their estimated reference inductor current () under ohmic resistance perturbation. It clearly demonstrates that the three parallel legs of the IBC shared equal currents. The insets show a more detailed picture and show that even though the ohmic resistance changed, the currents in each leg stayed close to their reference value.
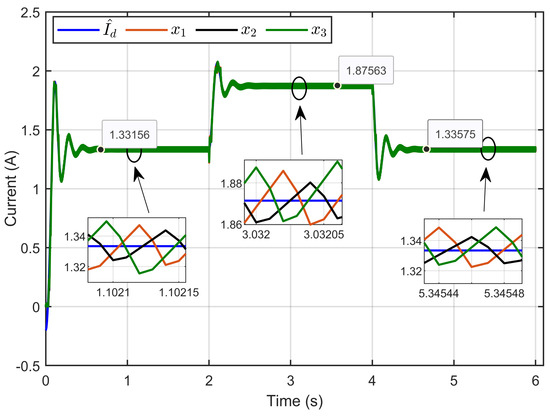
Figure 14.
The dynamic response of three inductor currents and their estimated reference under ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
This ensures that the inductors work together properly and that the load is evenly distributed.
Figure 15 depicts the control inputs (duty cycle) under ohmic resistance perturbation, showing that these signals remained within a bounded range of 0 to 1, which aligned with the duty cycle. Furthermore, the signals exhibited minimal ripples.
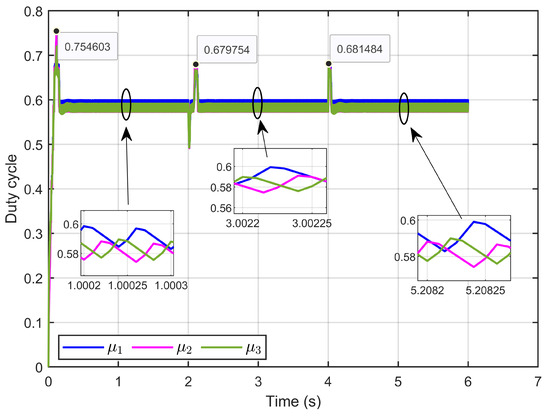
Figure 15.
The control inputs signals (duty cycle) under ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
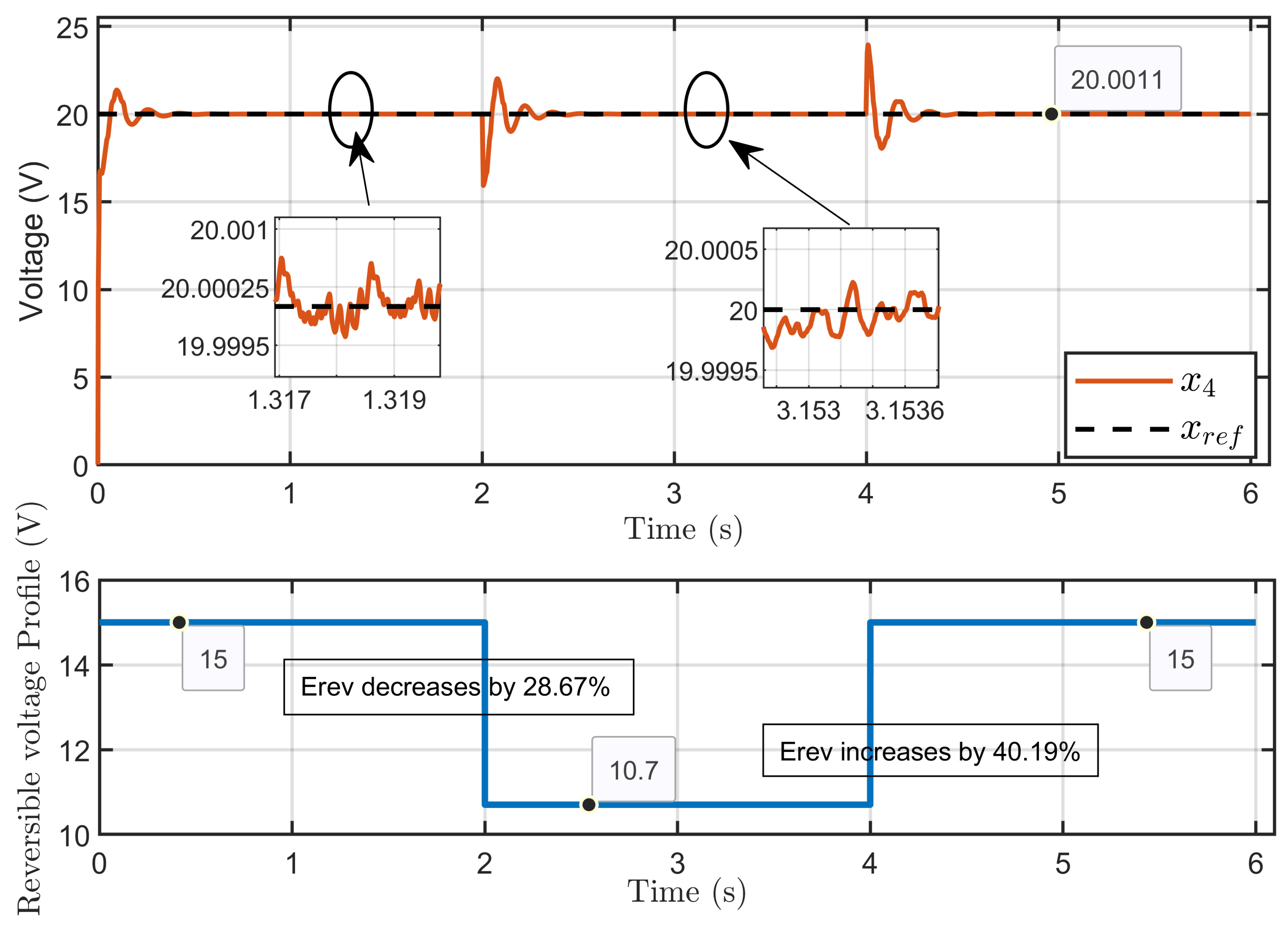
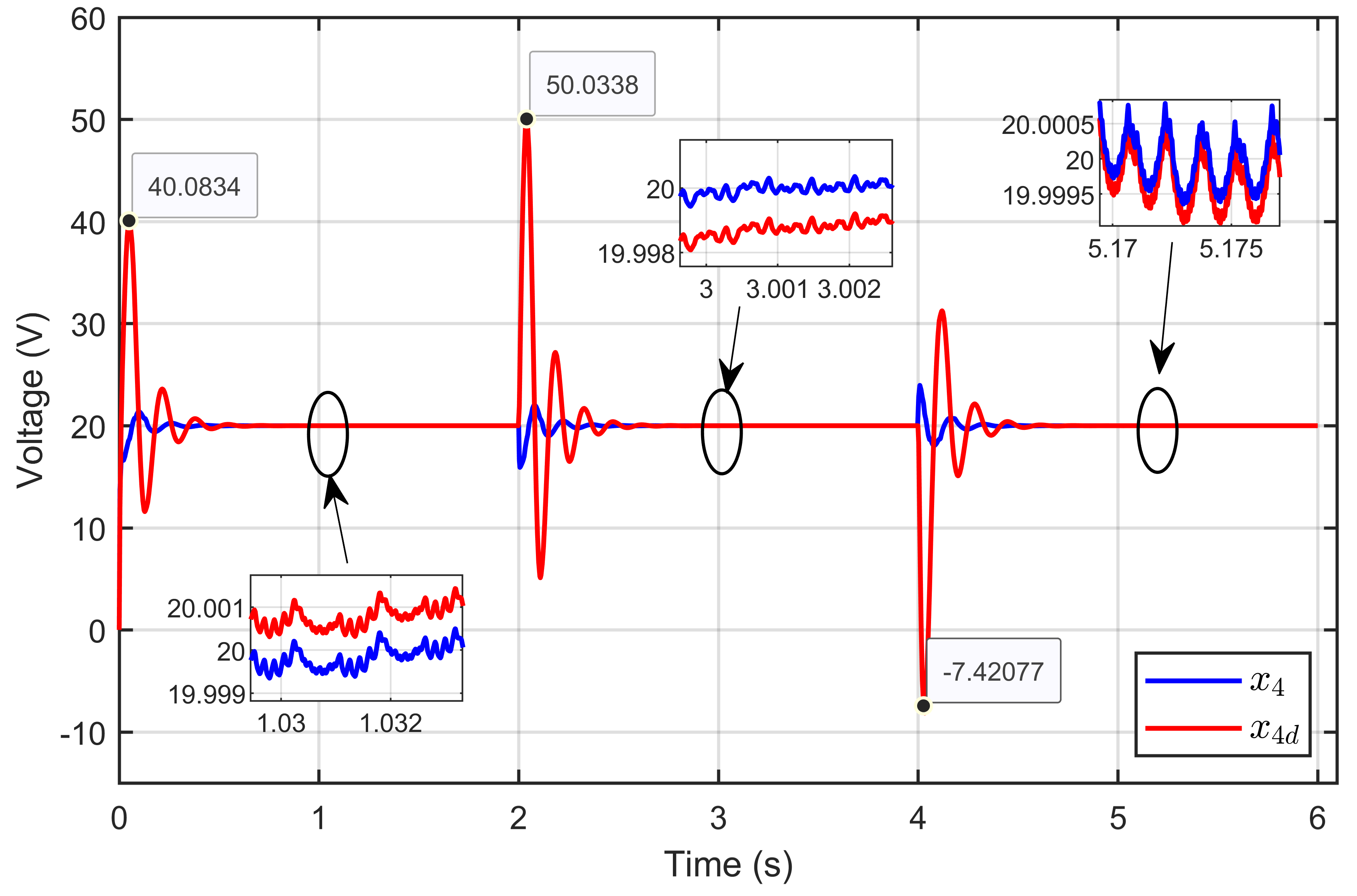
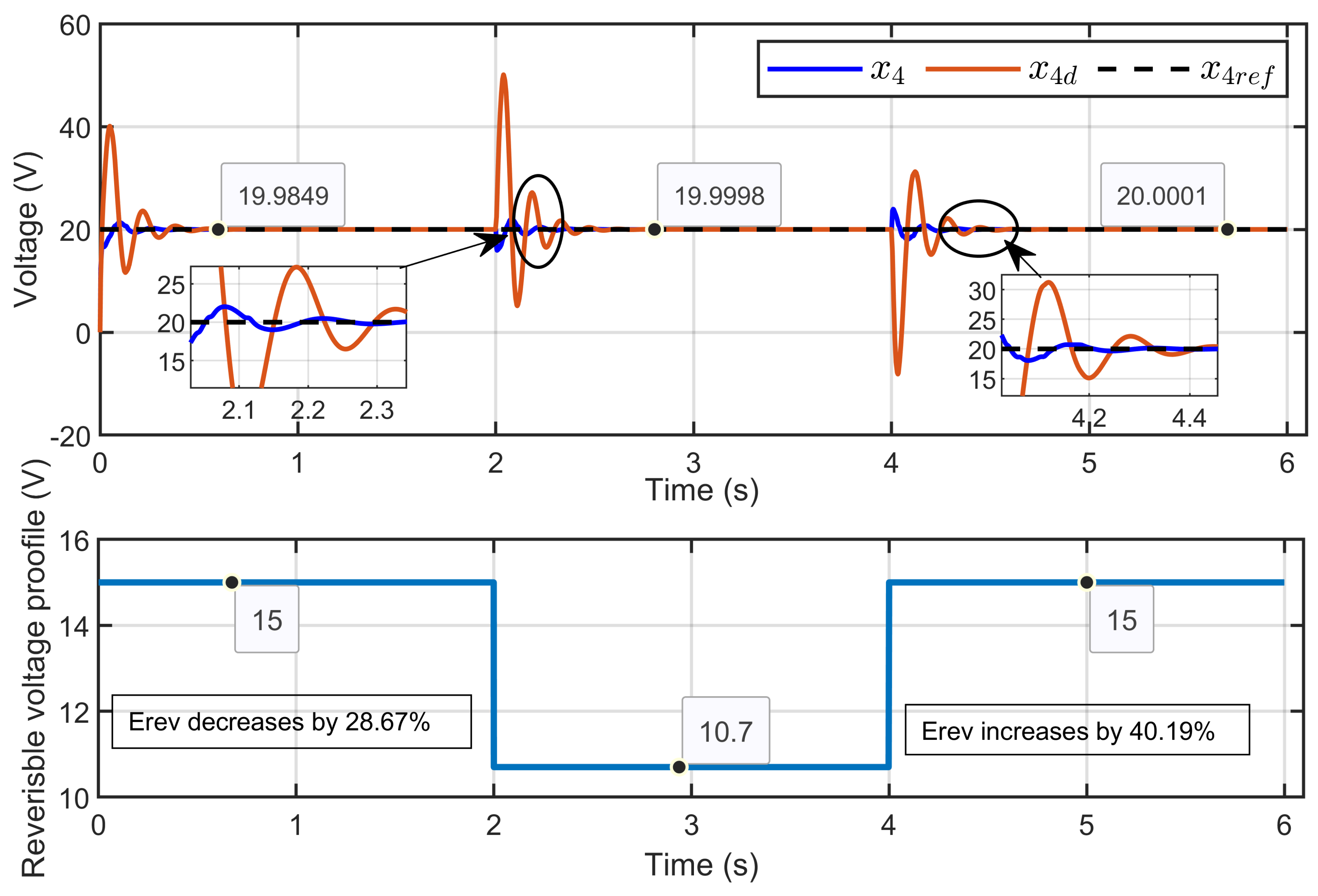
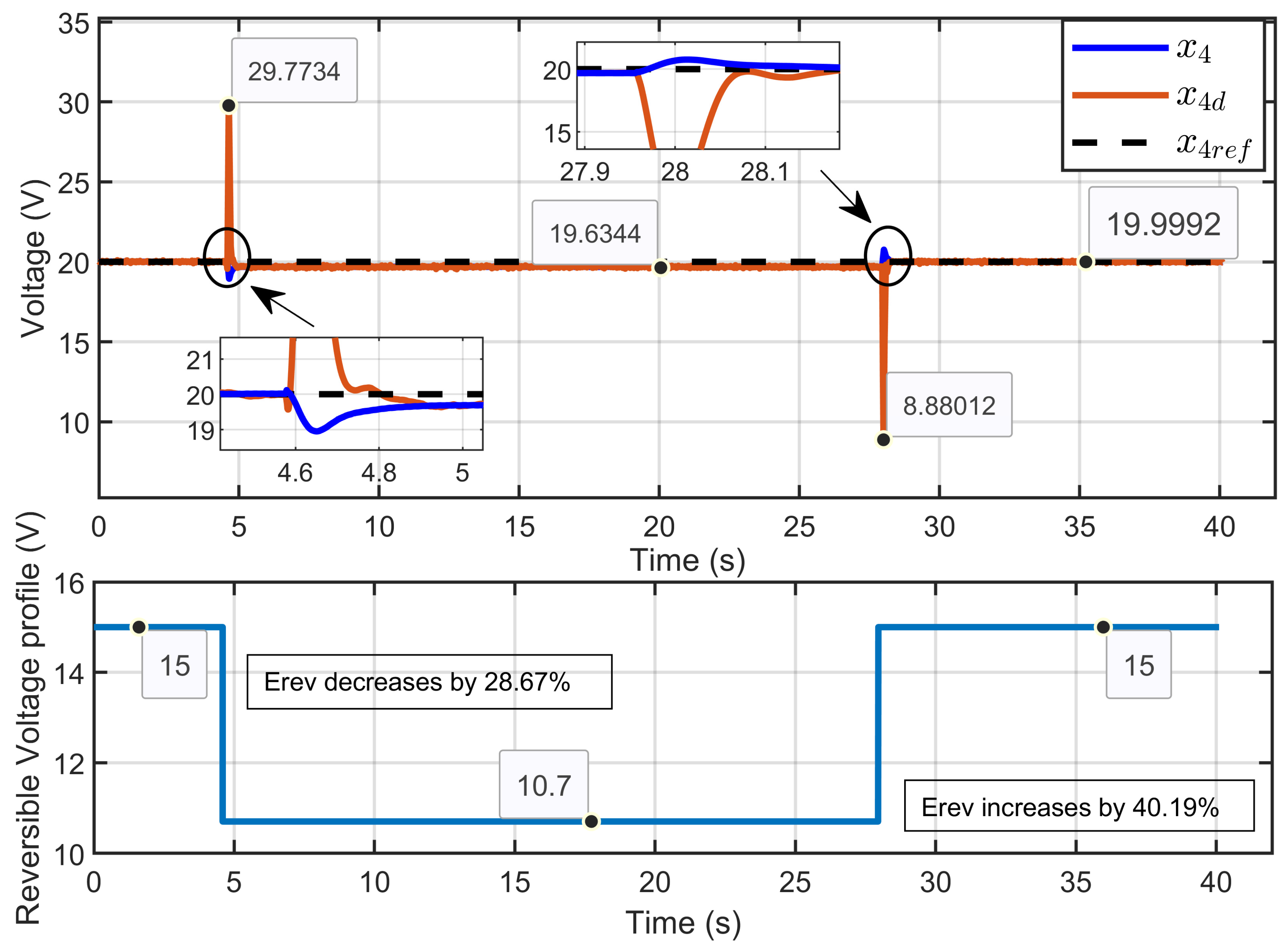
Scenario 2: In this scenario, the reference voltage of the PEM electrolyzer was set to xref = 20 V and the ohmic resistance to Rohm = 1.5 Ω while a perturbation was introduced in its reversible voltage. The reversible voltage started at 15 V, decreased by 28.67% to 10.7 V over 2 s, and then increased by 40.19% to return to 15 V at the 4 s mark.
Figure 16 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its reference, which shows the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) when subjected to significant perturbations to the reversible voltage. The figure highlights the system’s ability to effectively regulate the electrolyzer voltage despite abrupt changes in the reversible voltage. Although a slight overshoot was observed during the transitions, the voltage quickly stabilized and returned to its reference value, maintaining steady-state performance.
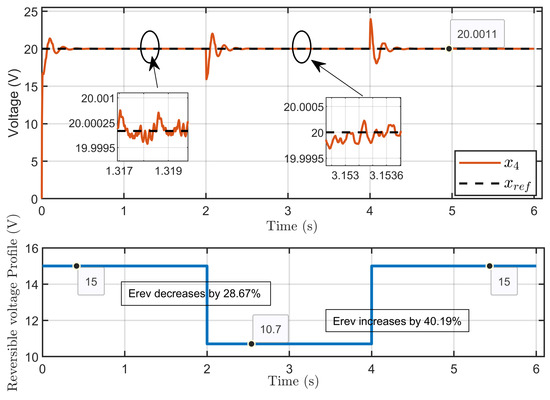
Figure 16.
Dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its reference under reversible voltage perturbation (simulation results).
Figure 17 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) and its desired dynamic trajectory (x4d). The results demonstrated that the PEM electrolyzer voltage accurately and rapidly tracked the desired trajectory, even during abrupt changes in the reversible voltage. The figure also highlights critical points where the system responded to sudden disturbances, maintaining stability and minimizing deviations from the desired trajectory voltage.
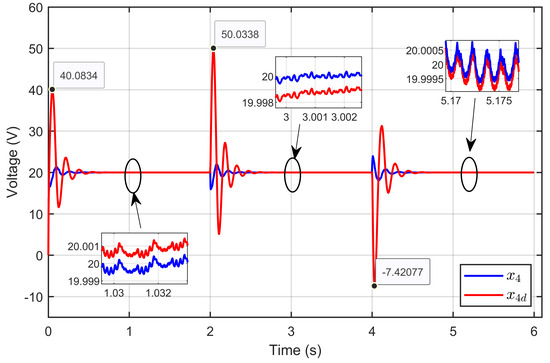
Figure 17.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage and its desired trajectory under reversible voltage perturbation (simulation results).
Figure 18 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), its reference voltage (xref), and the desired dynamic trajectory (x4d). The results showed that the PEM electrolyzer voltage closely aligned with both the reference and the desired trajectory with high accuracy during steady-state operation.
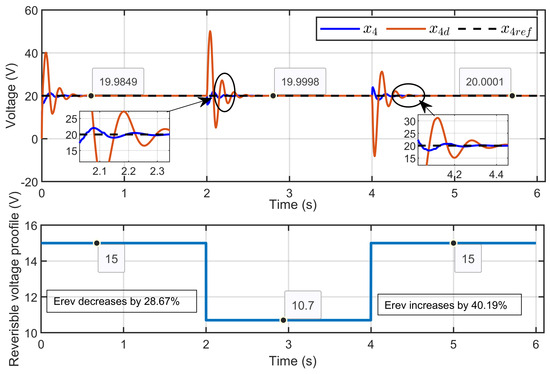
Figure 18.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired trajectory under reversible voltage perturbation (simulation results).
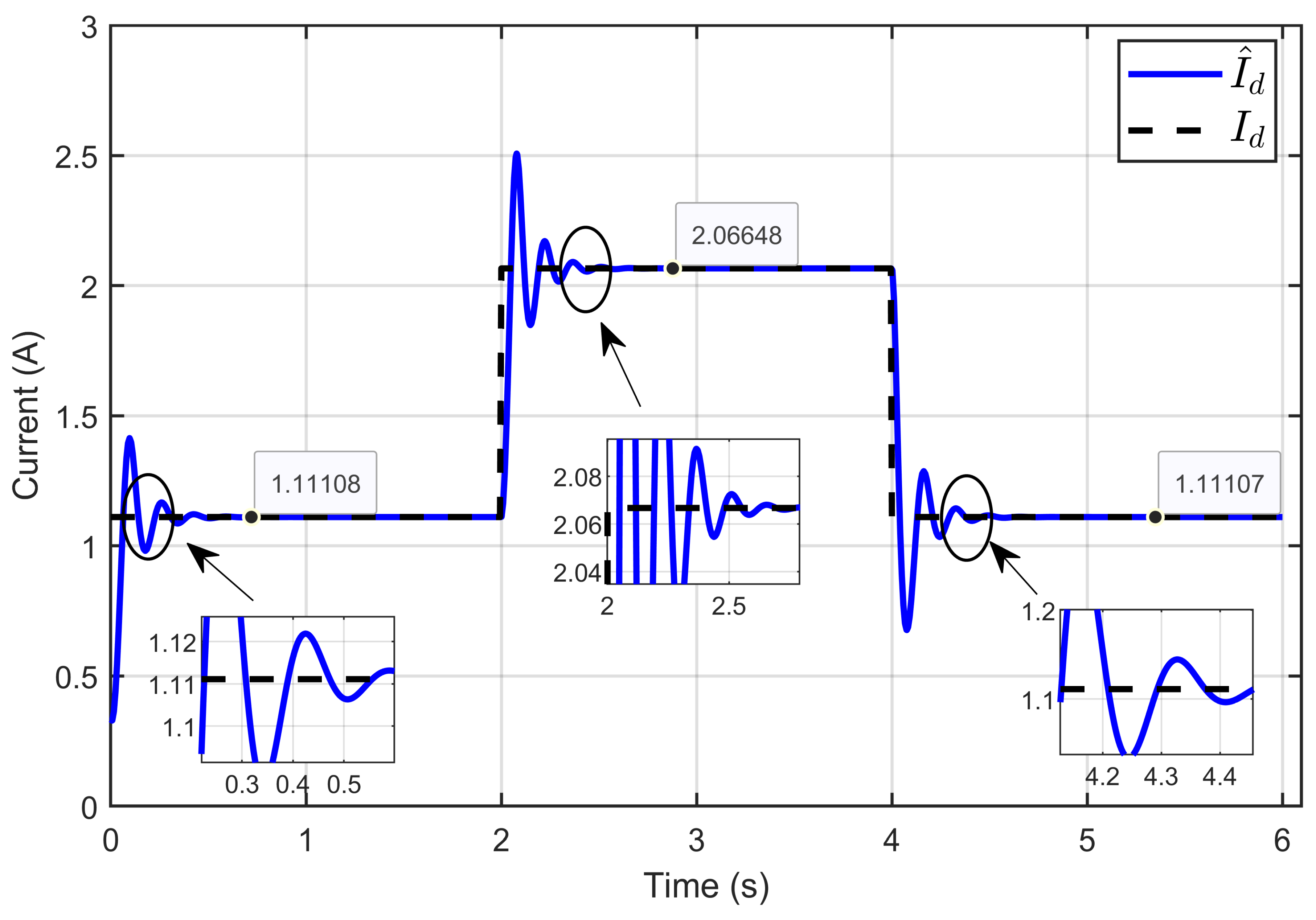
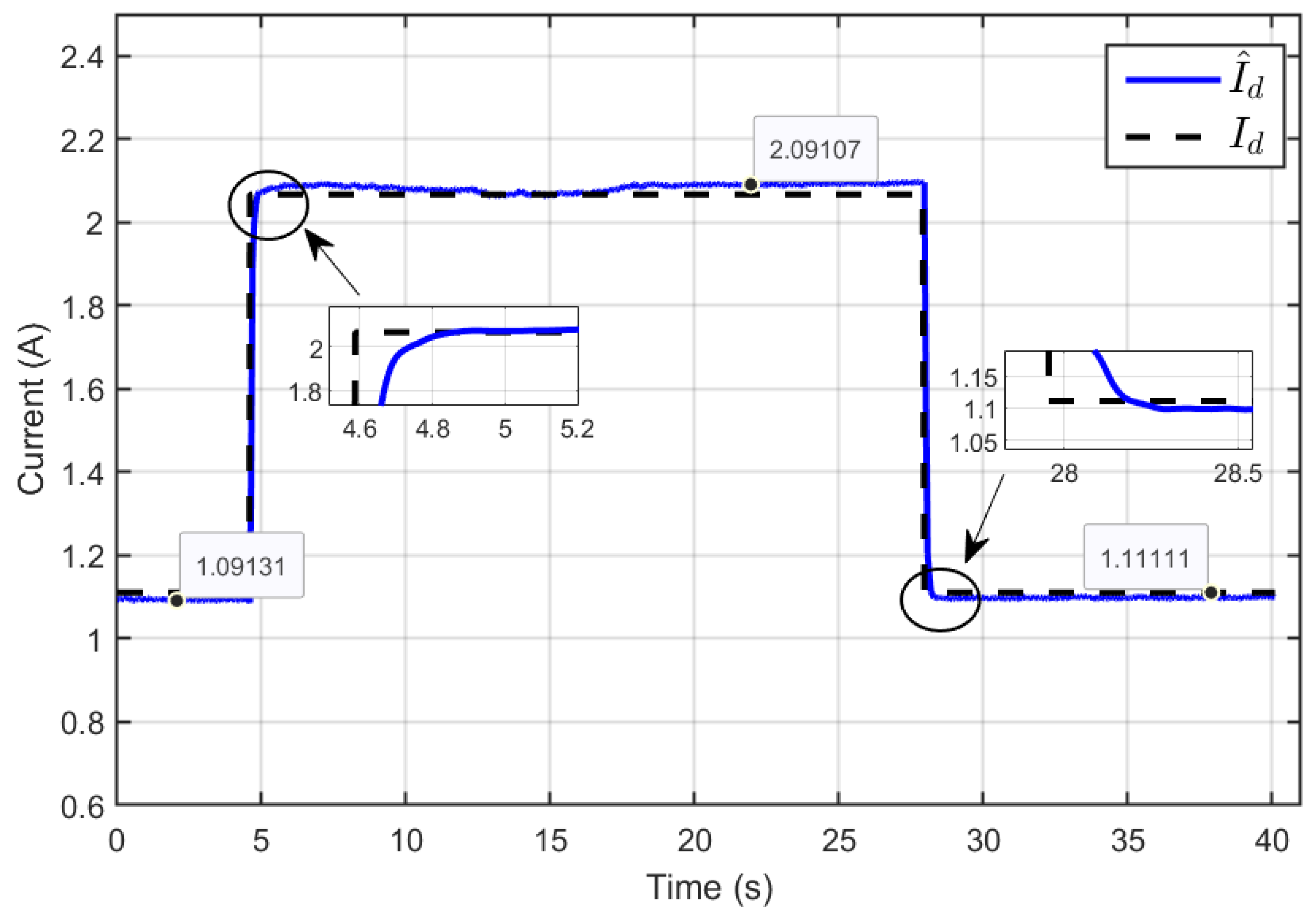
Figure 19 illustrates the dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current () and its actual value (Id) showed that the estimated inductor current reliably tracked the actual inductor current under all operating conditions. This highlights the accurate estimation of the vector parameters and demonstrates the robustness of the developed ASMC in response to reversible voltage changes.
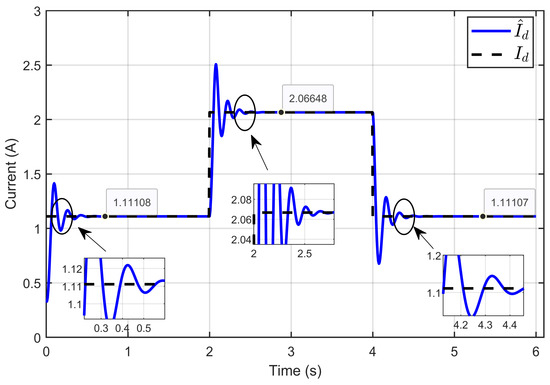
Figure 19.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current and its actual value under reversible voltage perturbation (simulation results).
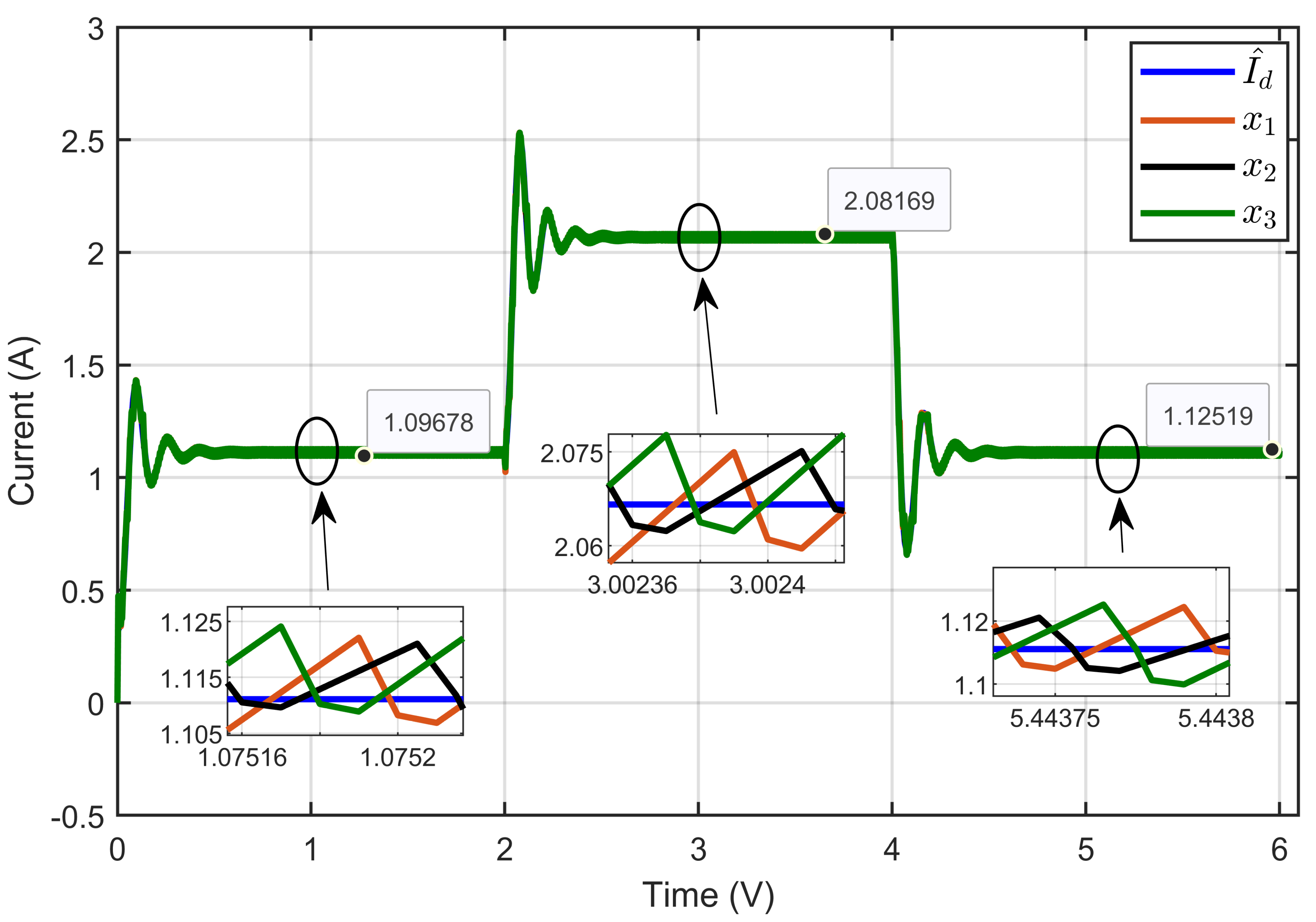
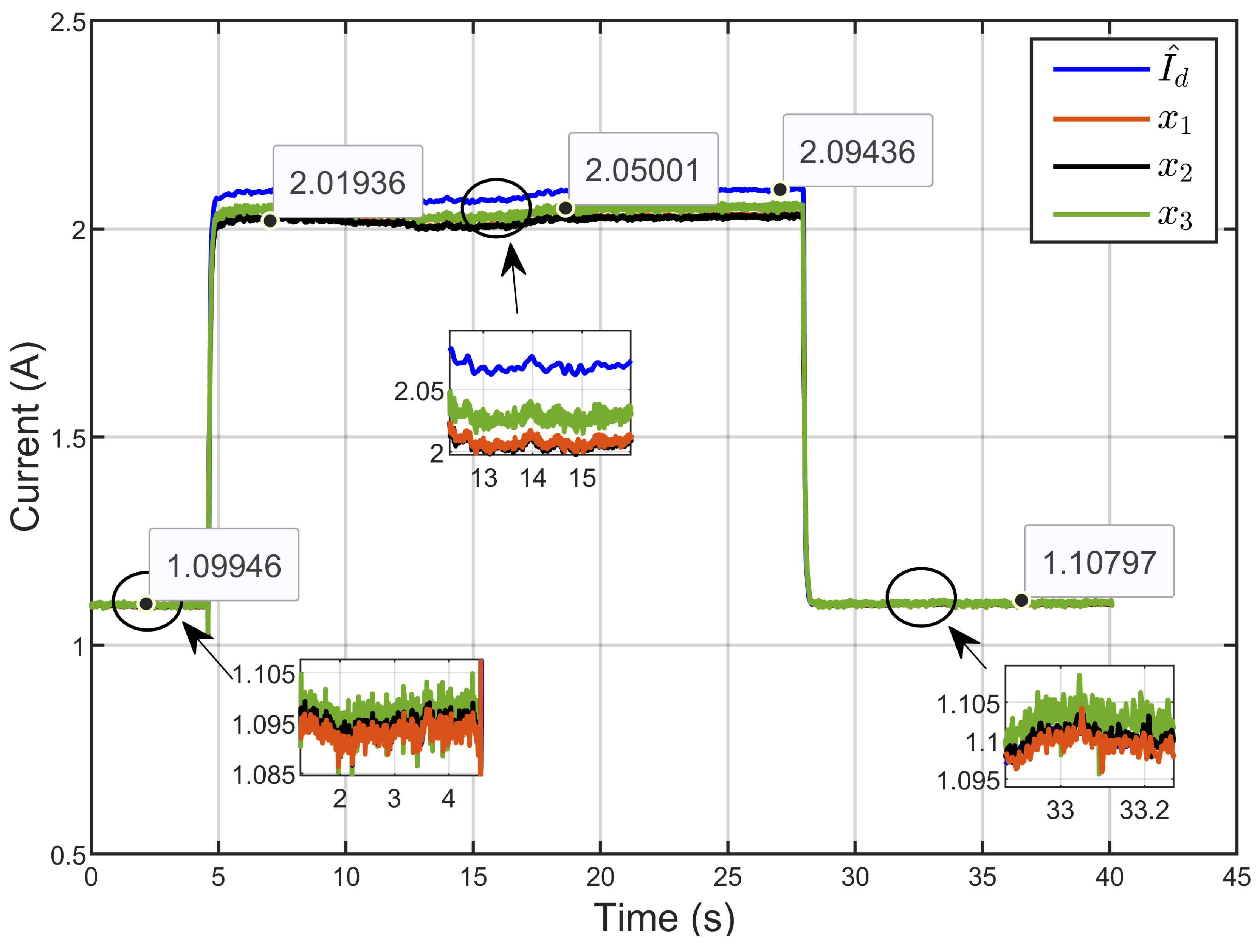
Figure 20 illustrates the dynamic response of three inductor currents (x1, x2, and x3), and their estimated reference () shows the currents of the three inductors alongside their estimated reference current under reversible voltage perturbation. The figure clearly demonstrates equal current sharing between the three parallel legs of the IBC. The insets provide detailed views, highlighting that even with reversible voltage perturbations, the currents in each leg closely followed the reference value, ensuring balanced operation and effective load sharing among the inductors.
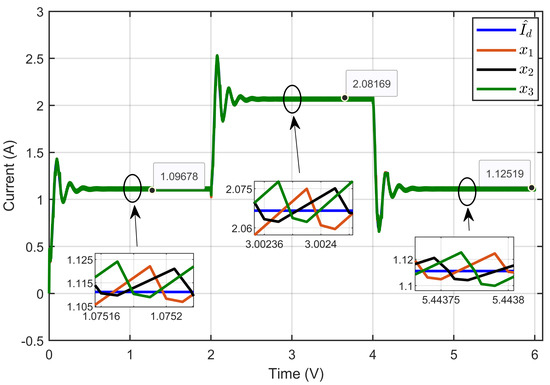
Figure 20.
The dynamic response of three inductor currents and their estimated reference under reversible voltage perturbation (simulation results).
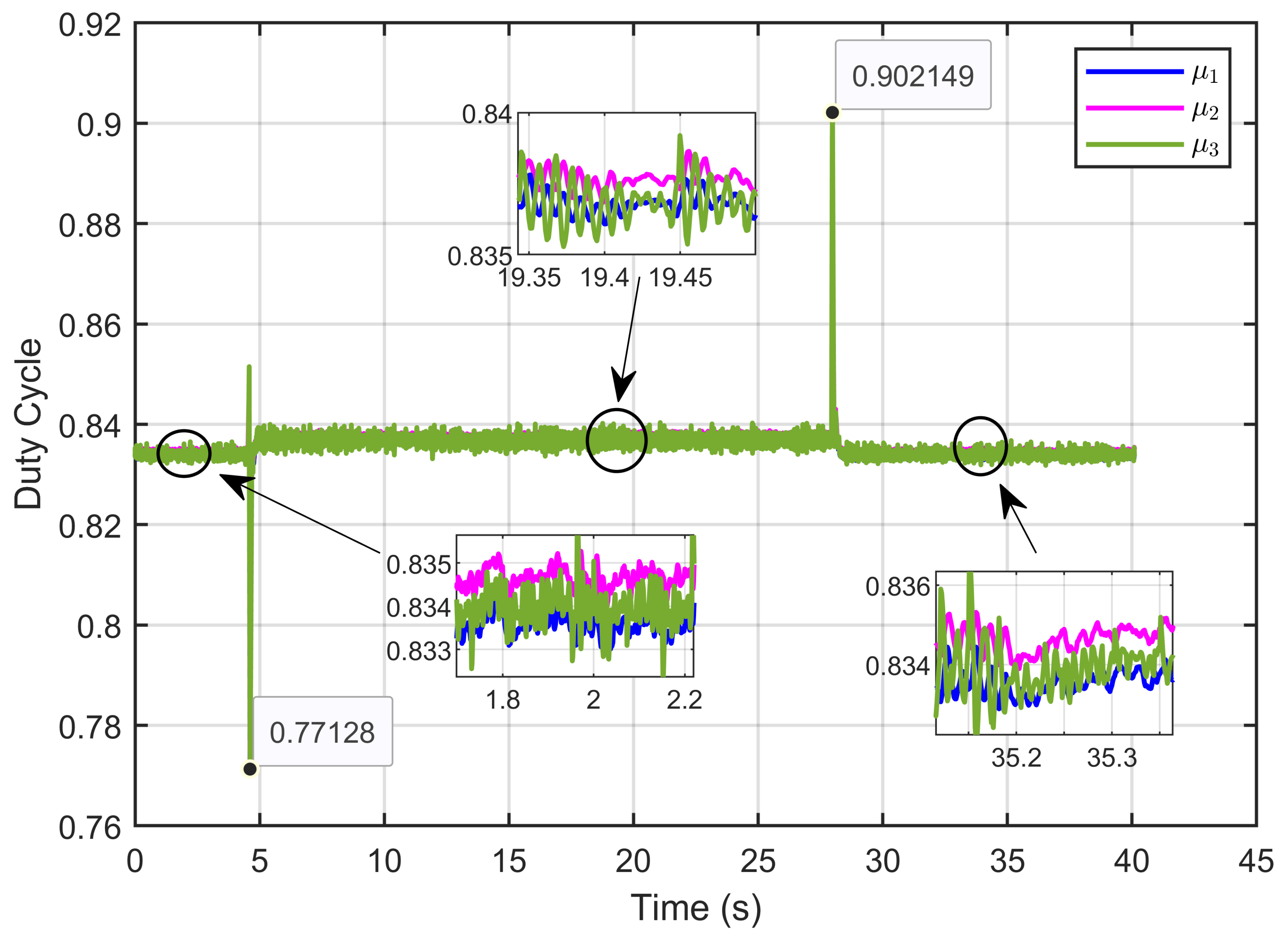
Figure 21 presents the control inputs (duty cycles) under reversible perturbation, demonstrating that these signals remained within the expected range of 0 to 1, consistent with the duty cycle limits.
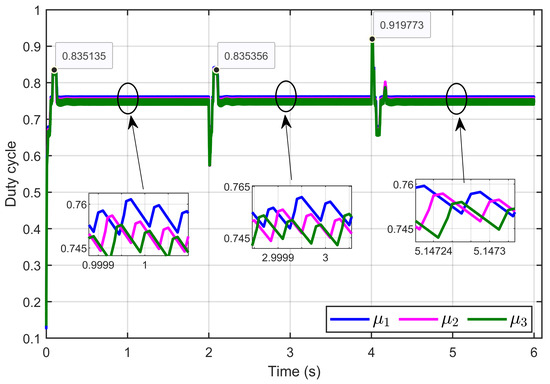
Figure 21.
The control inputs signals (duty cycle) under reversible voltage perturbation (simulation results).
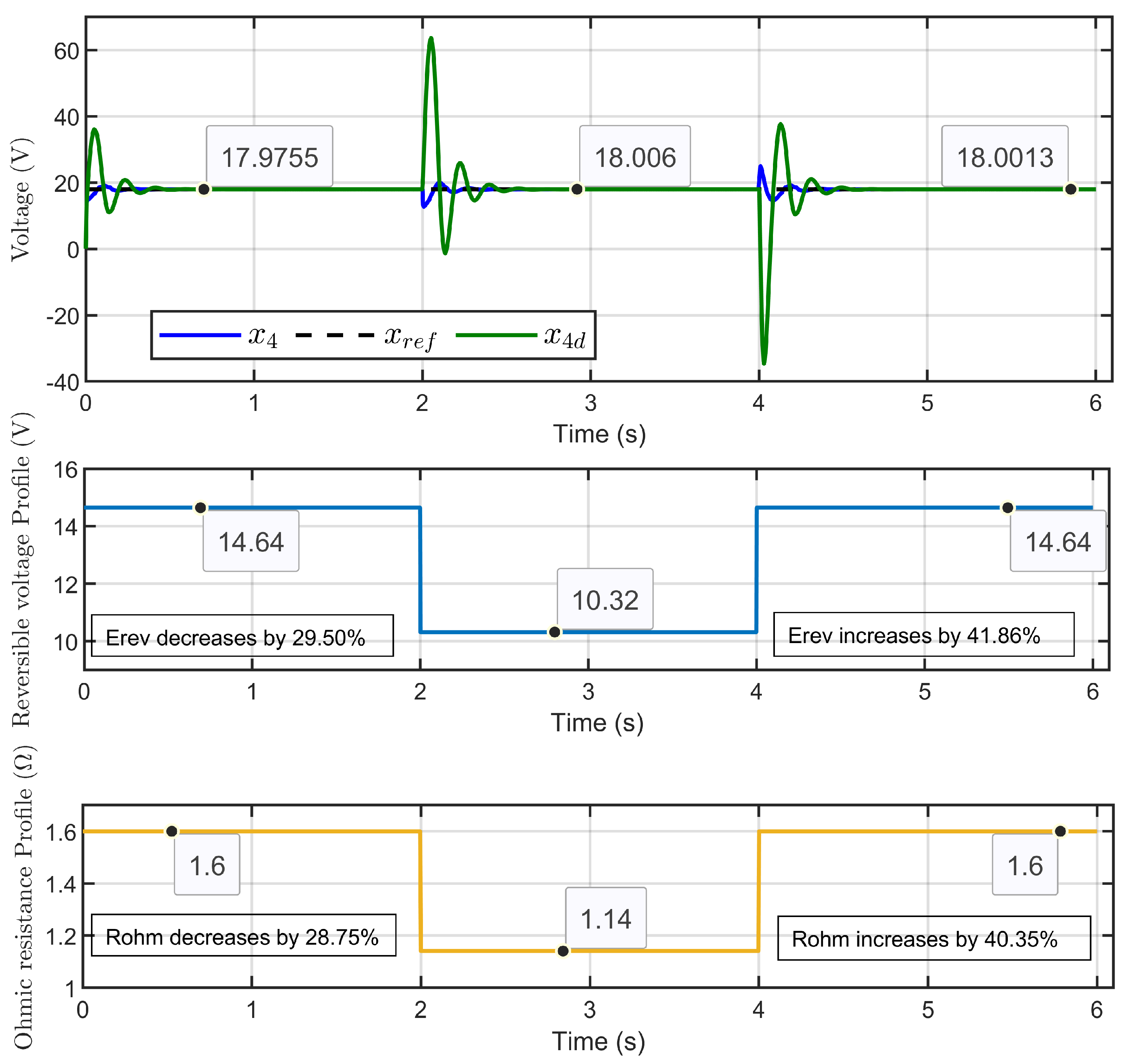
Scenario 3: In this scenario, the reversible voltage Erev and the ohmic resistance Rohm were simultaneously perturbed. The reversible voltage started at 14.64 V, decreased by 29.50% to 10.32 V in 2 s, and then increased by 41.86% to return to its initial value at the 4 s mark. Similarly, the ohmic resistance started at 1.6 Ω, decreased by 28.75% to 1.14 Ω, and then increased by 40.35% to return to its initial value at the same time. The reference voltage for the PEM electrolyzer was set to 18 V.
Figure 22 illustrates the dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), its reference (xref), and its desired (x4d). The results clearly showed that the PEM electrolyzer voltage closely followed its reference value and was perfectly aligned with the desired dynamic trajectory. Notably, the desired dynamic trajectory showed an overshoot during the disturbances, but the error decreased rapidly, reflecting the robustness and precision of the control strategy even during disturbances.
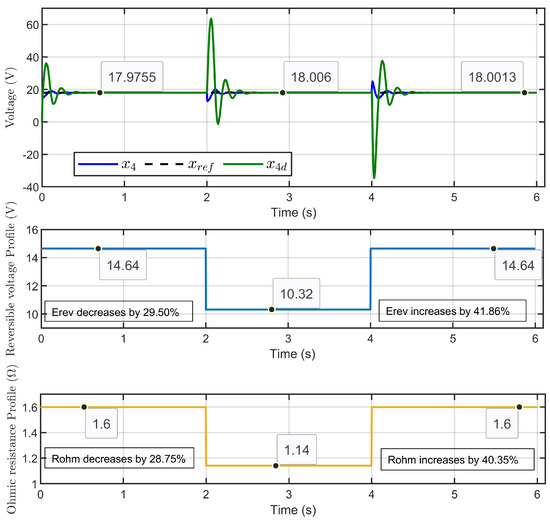
Figure 22.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired trajectory under reversible voltage and ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
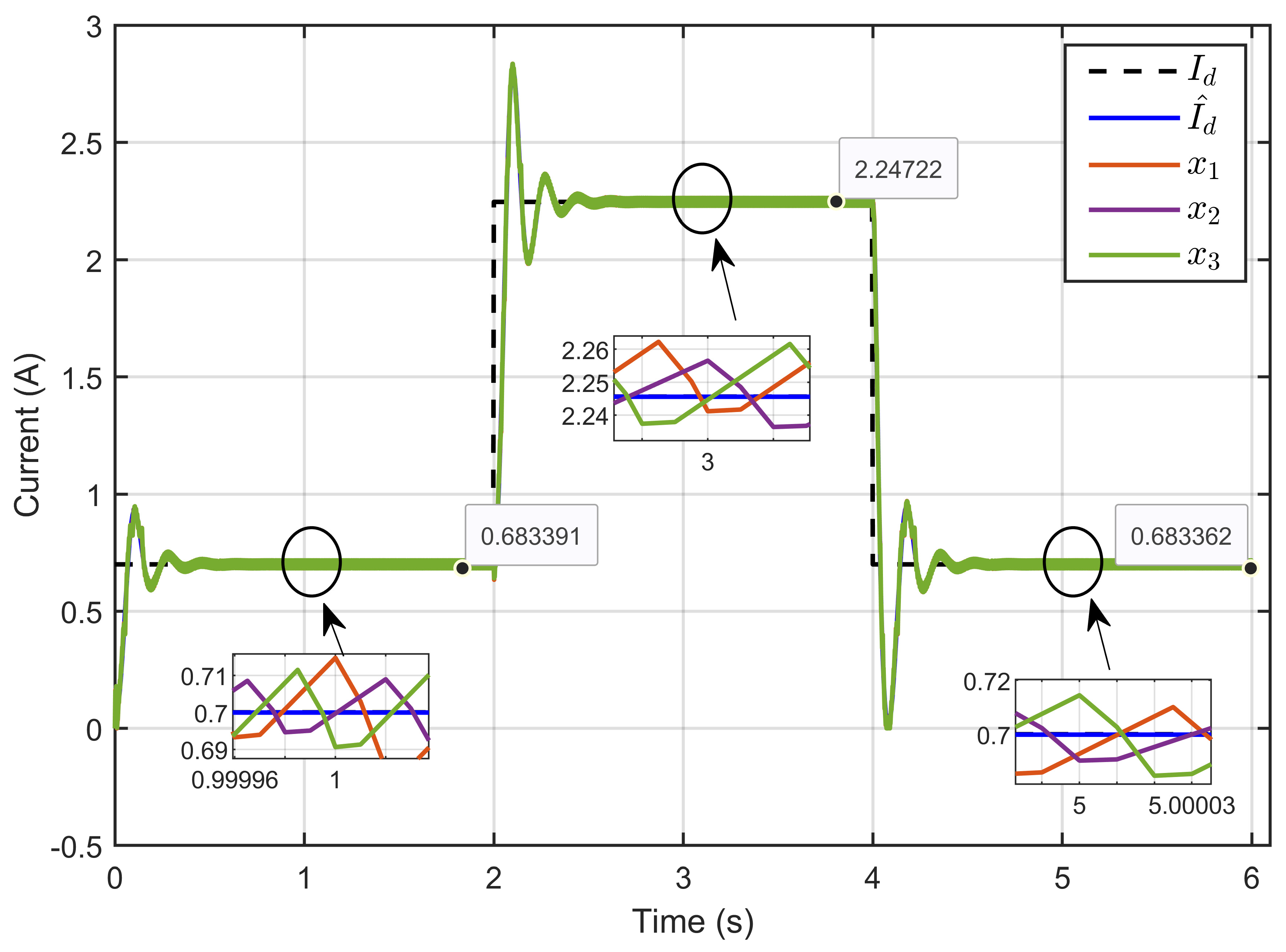
Figure 23 illustrates the dynamic responses of the estimated current , its true value Id, and the inductor currents (x1, x2, and x3). The results demonstrated that the estimated desired current perfectly tracked its true value. Additionally, the inductor currents closely followed their reference values, confirming the equal sharing of current among the three parallel legs, even under significant parameter perturbations.
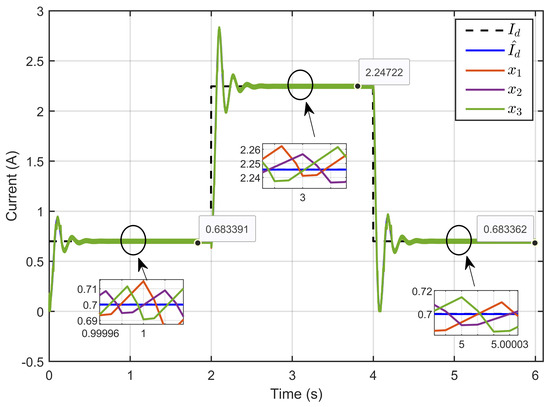
Figure 23.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current, its actual value, and the three inductor currents under reversible voltage and ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
Figure 24 presents the control inputs, specifically the duty cycle, demonstrating that the control signals remained bounded between 0 and 1, as expected for duty cycle operation. The figure also shows that the control signals exhibited small ripples, indicating stable and efficient performance.
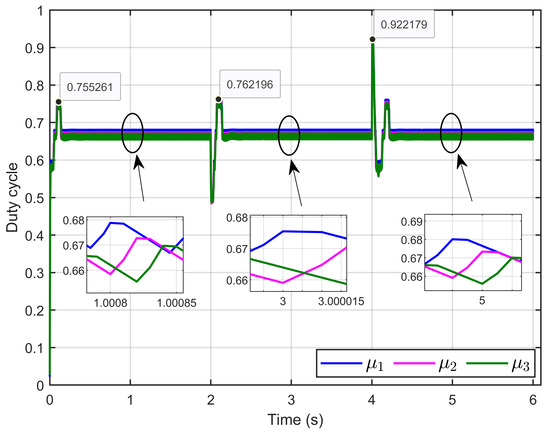
Figure 24.
The control inputs signals (duty cycle) under reversible voltage and ohmic resistance perturbation (simulation results).
The key performance metrics obtained during the validation of the controller’s sensitivity to perturbations caused by sudden variations in PEM electrolyzer operation conditions are presented in Table 3. These metrics highlight the ASMC’s ability to maintain stability and performance under significant perturbations to the PEM electrolyzer model parameters.

Table 3.
Performance metrics of the ASMC under PEM electrolyzer parameter perturbations (simulations).
7. Experimental Results
A hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) implementation was utilized to evaluate the performance, robustness, and effectiveness of our designed ASMC. Figure 25 presents the experimental test bench. For experimental validation, the same parameters specified in Table 4 were used, with the exception of the controller design parameters. These parameters were adjusted to account for unmolded components, parameter variations, sensor noise, and computational limitations encountered during real-time implementation.
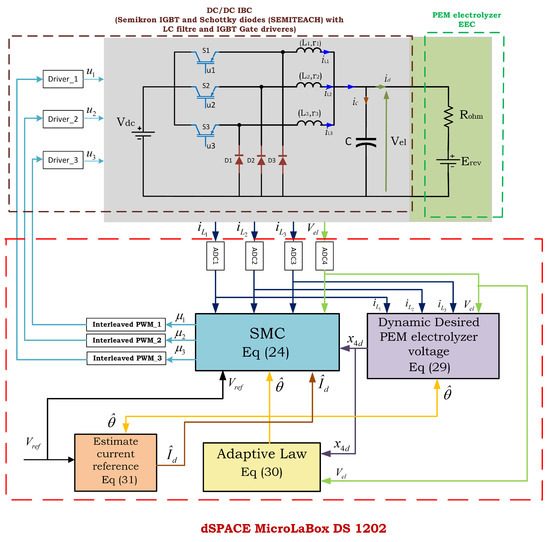
Figure 25.
Experimental test bench for ASMC.

Table 4.
Adjustment of key parameters for ASMC in experimental implementation.
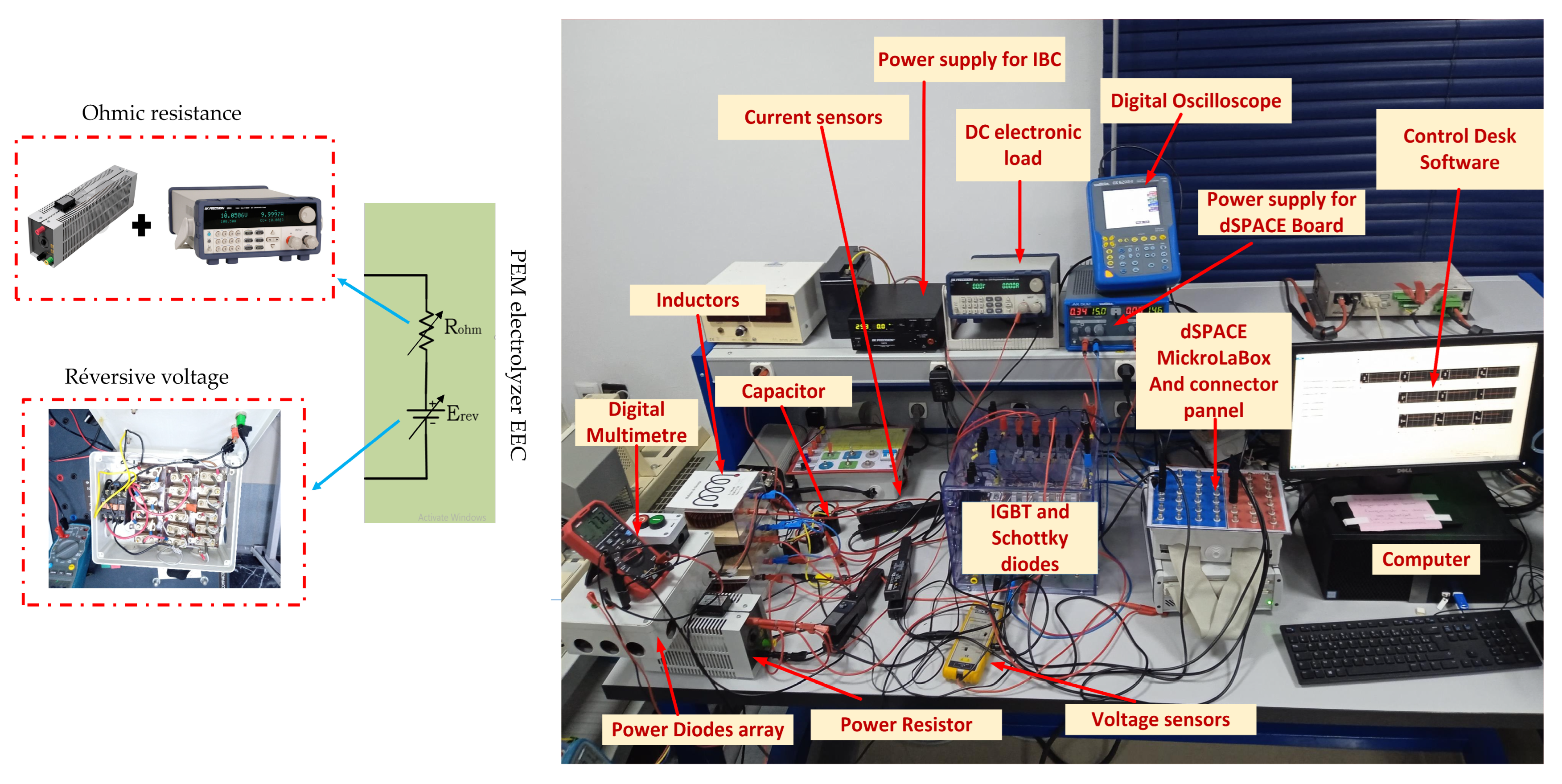
As illustrated in Figure 26, the HIL used to validate the performance, robustness, and effectiveness of the designed ASMC encompassed a diverse array of components. This included a computer running MATLAB®/Simulink® and ControlDesk software and a dSPACE 1202 MicroLabBox for real-time control support provided by a Semikron IGBT and Schottky diode (SEMITEACH) designed for the IBC. Inductors with ferrite cores were used to filter the current, and a capacitor (C) was employed to filter the output voltage. The EEC of the PEM electrolyzer was represented by a power resistor connected in parallel with a DC electronic load to emulate the ohmic resistance (Rohm) of the PEM electrolyzer and an adjustable series of power diodes, which can vary the number of diodes connected in series to emulate the reversible voltage (Erev) of the PEM electrolyzer. The system also featured two adjustable DC power sources for powering the IBC and the dSPACE board, a voltage sensor for monitoring the output voltages across the PEM electrolyzer’s EEC, and current sensors for measuring the inductor currents. A digital multimeter was used to monitor the output voltage, and a digital oscilloscope was used to monitor the generated PWM signal.
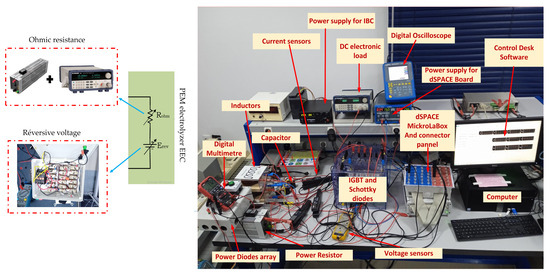
Figure 26.
Laboratory prototype used for experimental validation of the designed ASMC.
For experimental validation, the same setup and test conditions as those used in the simulation were applied, facilitating a direct comparison of the results.
7.1. Performance Validation of Adaptive Sliding Mode Control for a Reference Step in PEM Electrolyzer Voltage
In this section, the operating conditions were fixed (Rohm = 1.5 Ω and Erev = 7.45 V), and the performance of the designed ASMC was tested in response to reference steps while varying the voltage of the PEM electrolyzer. Two voltage reference steps were applied: the first step involved decreasing the voltage from 15 V to 12 V and the second step involved increasing the voltage from 12 V to 15 V
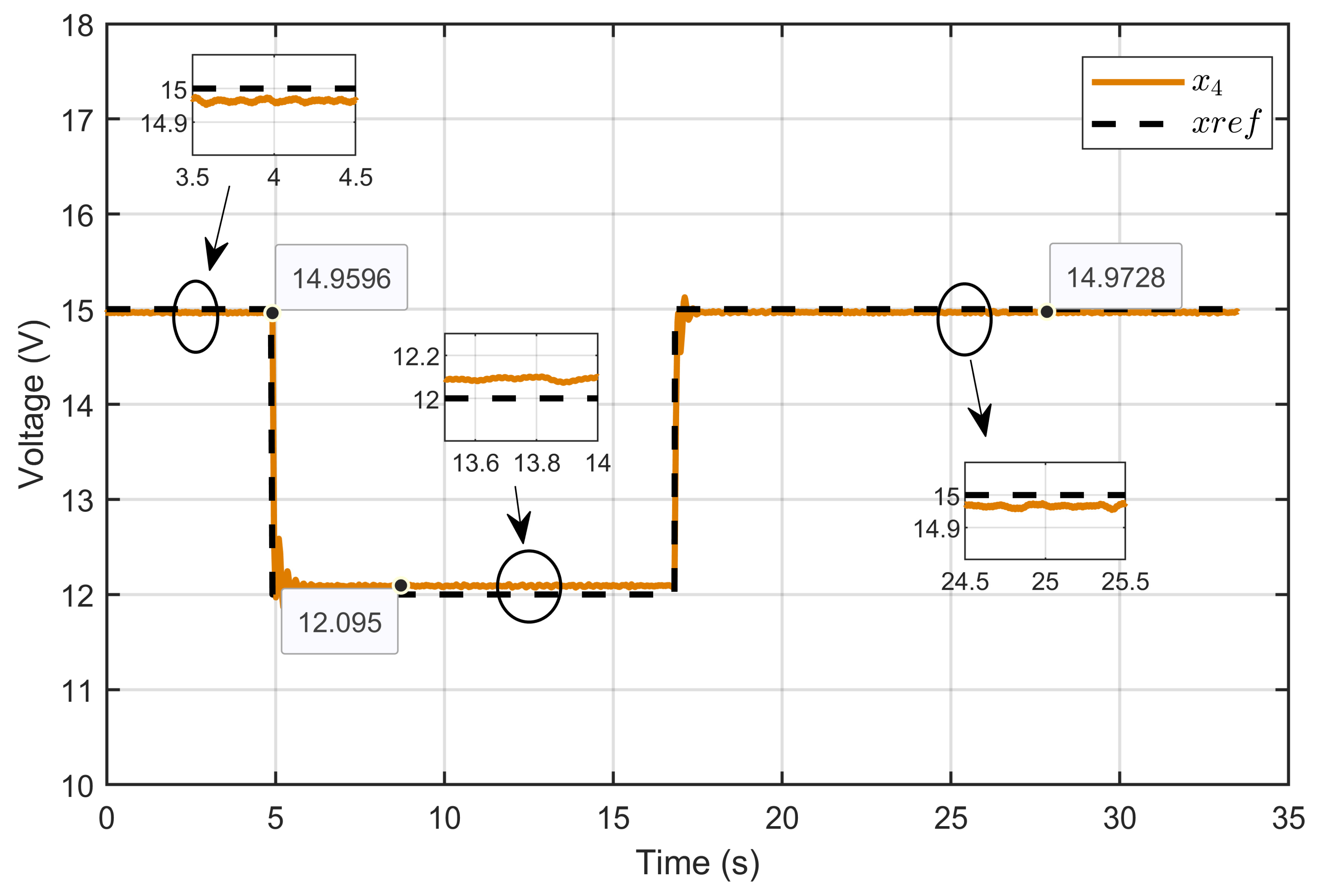
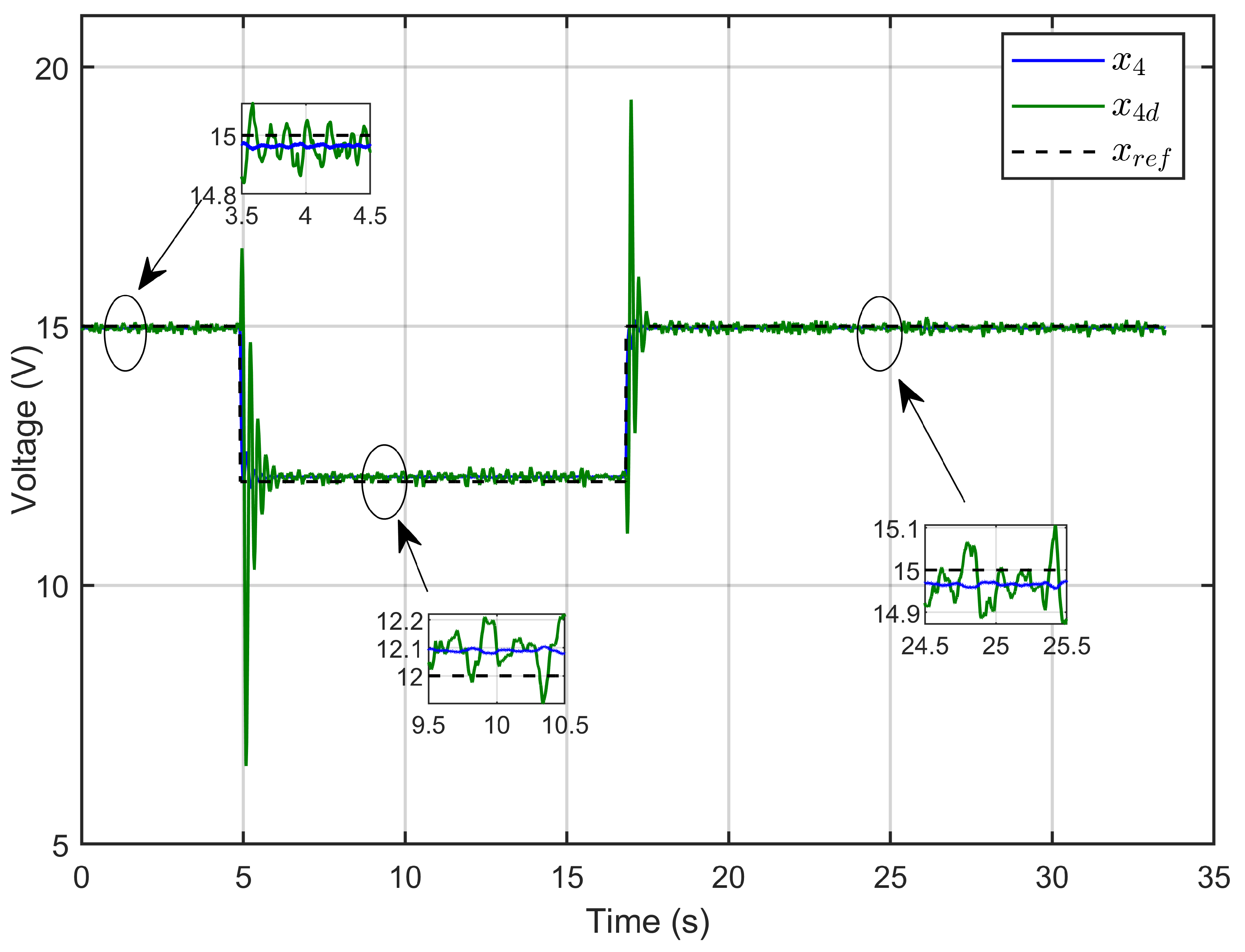
Figure 27 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) and its reference (xref). The figure highlights the PEM electrolyzer voltage’s ability to closely track the reference voltage over various step changes. Initially, the voltage rose rapidly to match the reference with minimal overshoot and then stabilized rapidly. The controller responded promptly to step changes, adjusting the voltage with negligible overshoots and rapid settling times. During steady-state operation, the voltage consistently matched the reference with values of 14.9596 V, 12.095 V, and 14.9728 V, demonstrating the high accuracy of the designed ASMC.
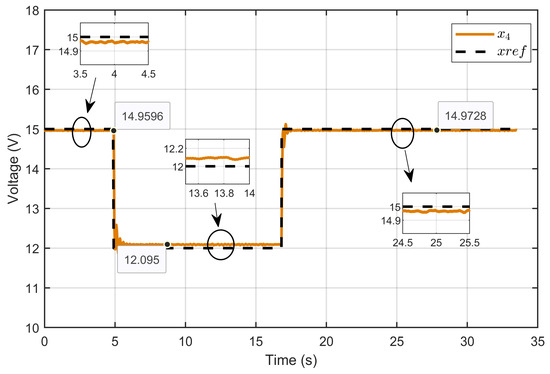
Figure 27.
Dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its reference under step reference voltage (experimental results).
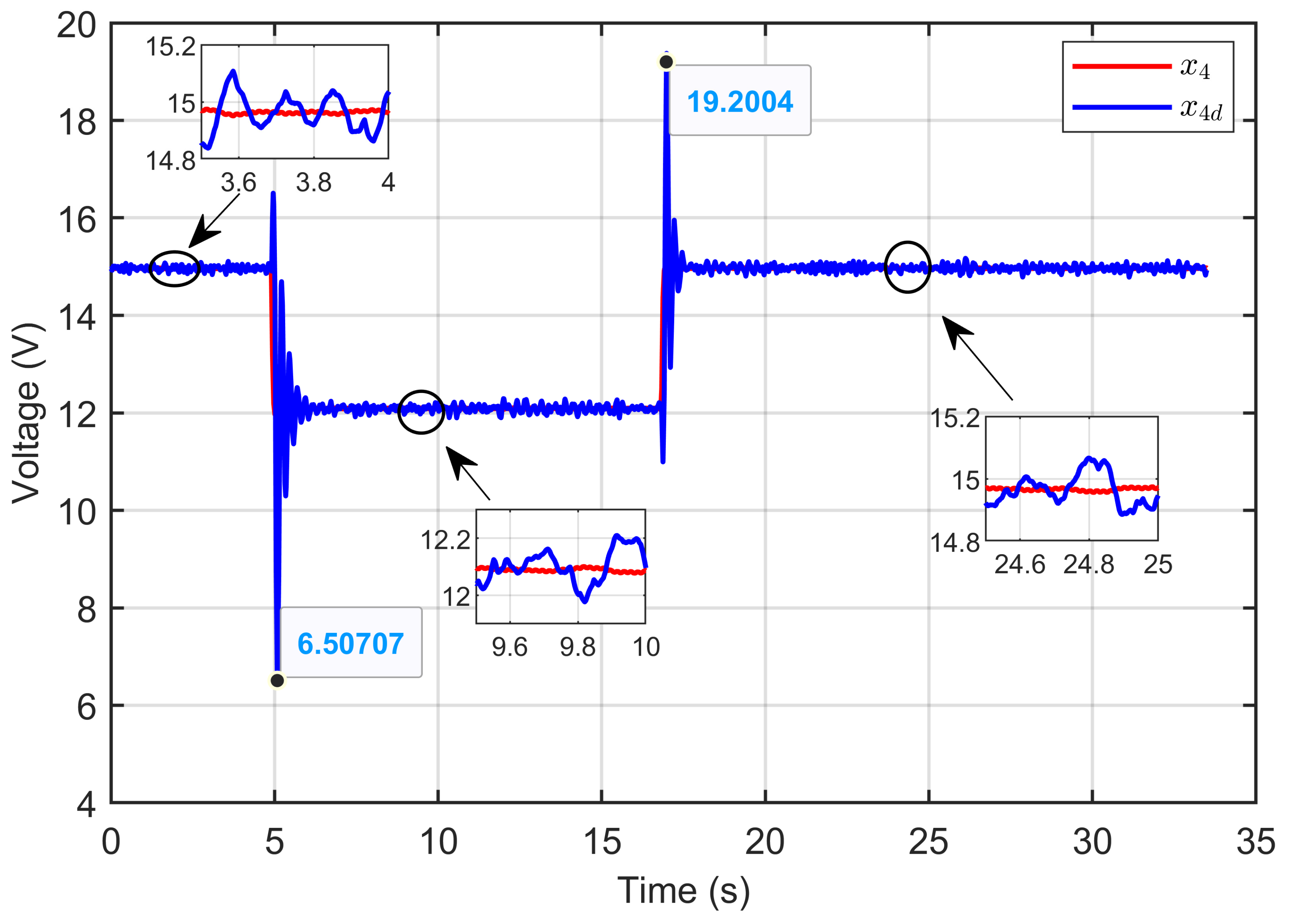
Figure 28 demonstrates the ASMC’s ability to effectively control the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) by precisely tracking the desired dynamic voltage (x4d), as defined in Equation (24). The dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), its reference (xref), and its desired dynamic response (x4d) confirmed that the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) perfectly tracked its reference value (xref) under reference voltage steps and also followed the desired dynamic trajectory (x4d).
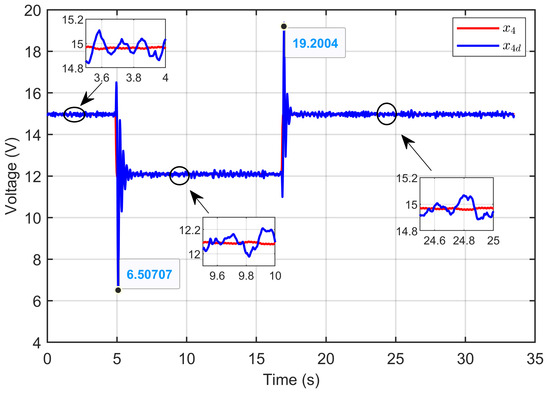
Figure 28.
PEM electrolyzer voltage and its desired dynamic response under step reference voltage (experimental results).
Figure 29 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x₄), its reference (xref), and its desired dynamic response (x4d). The results confirmed that the PEM electrolyzer voltage accurately tracked its reference value under reference voltage steps and closely followed the desired dynamic trajectory.
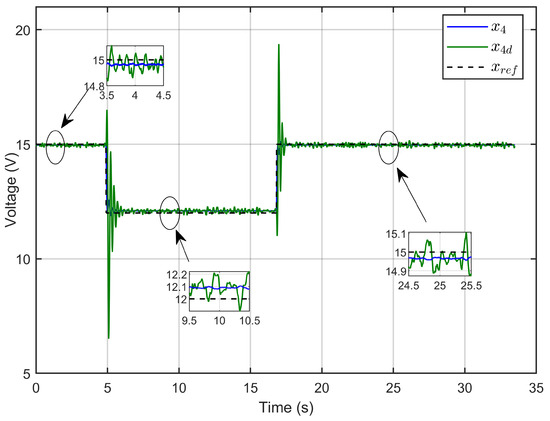
Figure 29.
PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired dynamic response under step reference voltage (experimental results).
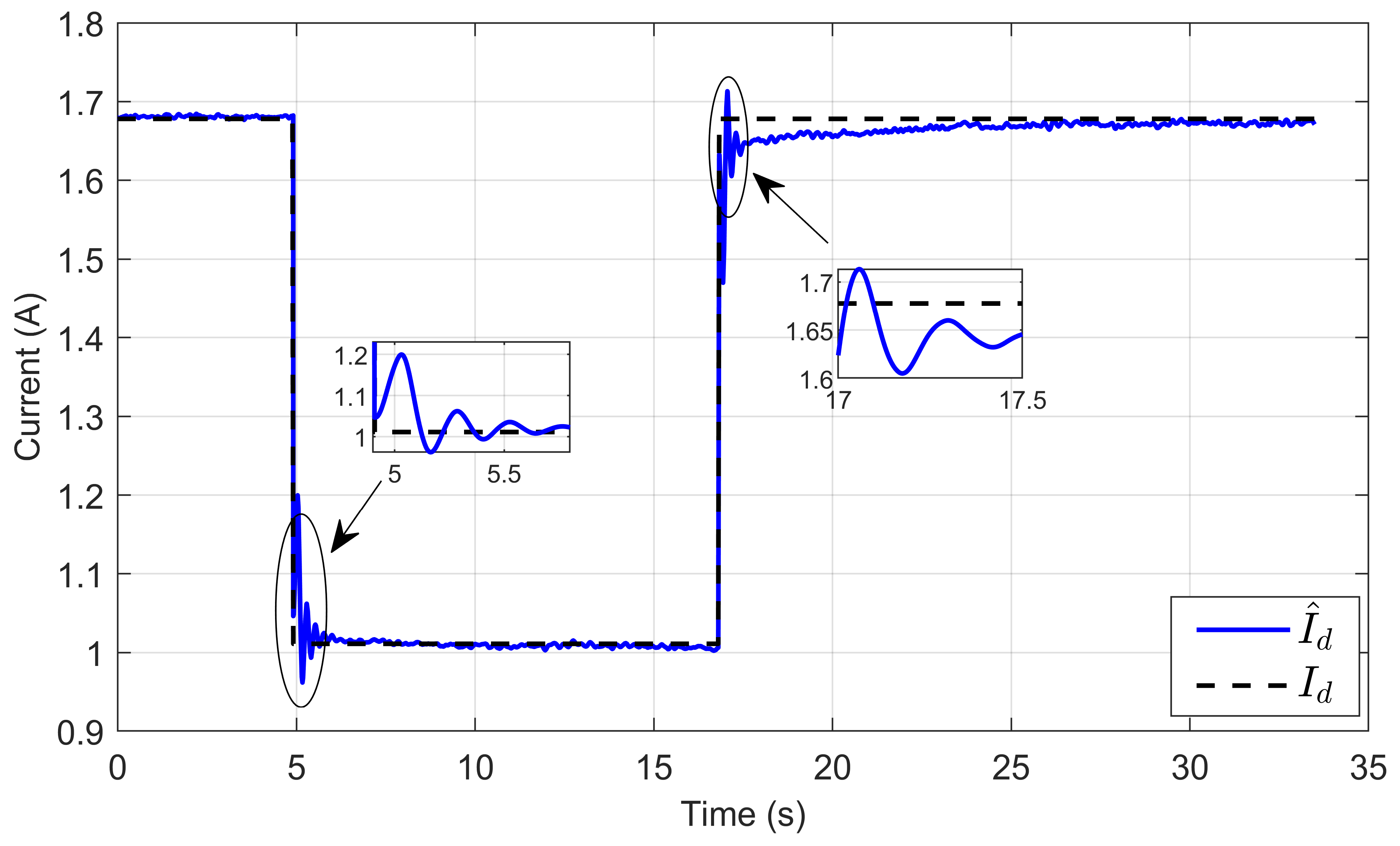
Figure 30 illustrates the dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current () and its actual current (Id). It shows that the estimated reference current tracked its true value with high accuracy under voltage reference steps. This demonstrates the performance and robustness of the developed ASMC to accurately estimate the reference inductor current.
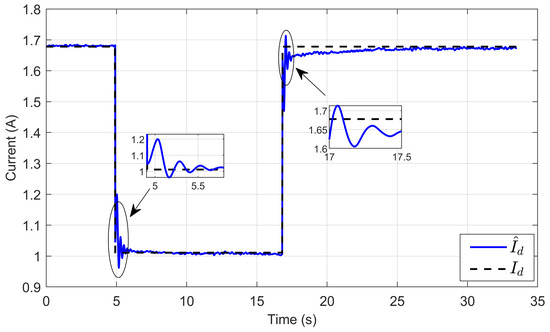
Figure 30.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current and its actual value under step reference voltage (experimental results).
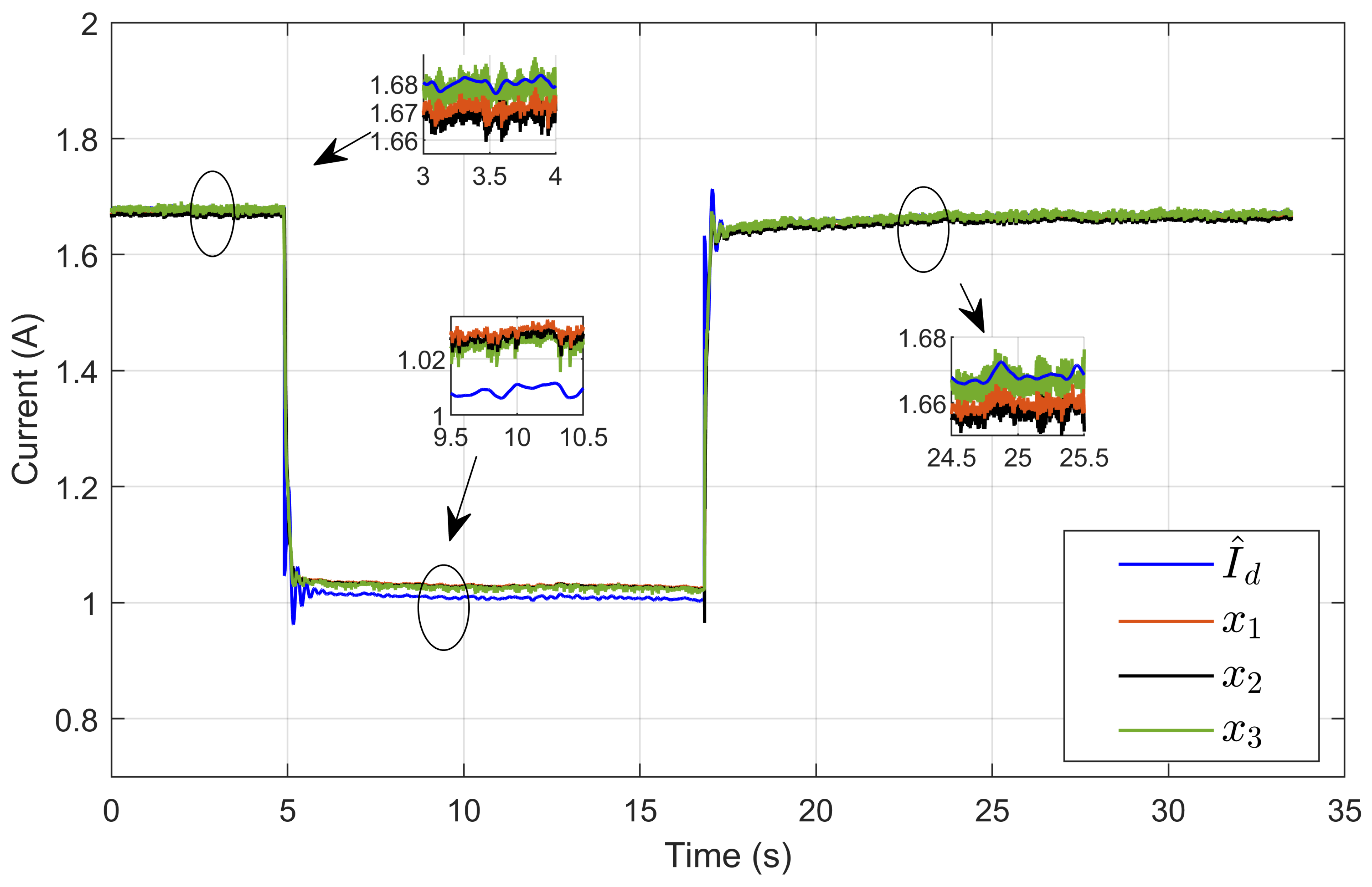
Figure 31 illustrates the dynamic response of three inductor currents (x1, x2, and x3), and their estimated reference () showed the rapid convergence of the inductor currents to the desired estimated current during transient periods. This convergence indicates a well-balanced current distribution among the three parallel legs. The zoomed-in plot highlights the minimal current ripple and the high accuracy achieved during steady-state operation.
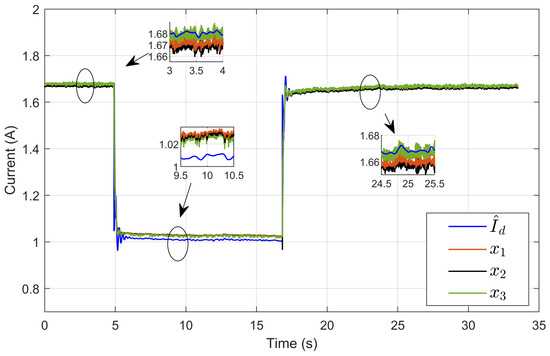
Figure 31.
The dynamic response of three inductor currents and their estimated reference under step reference voltage (experimental results).
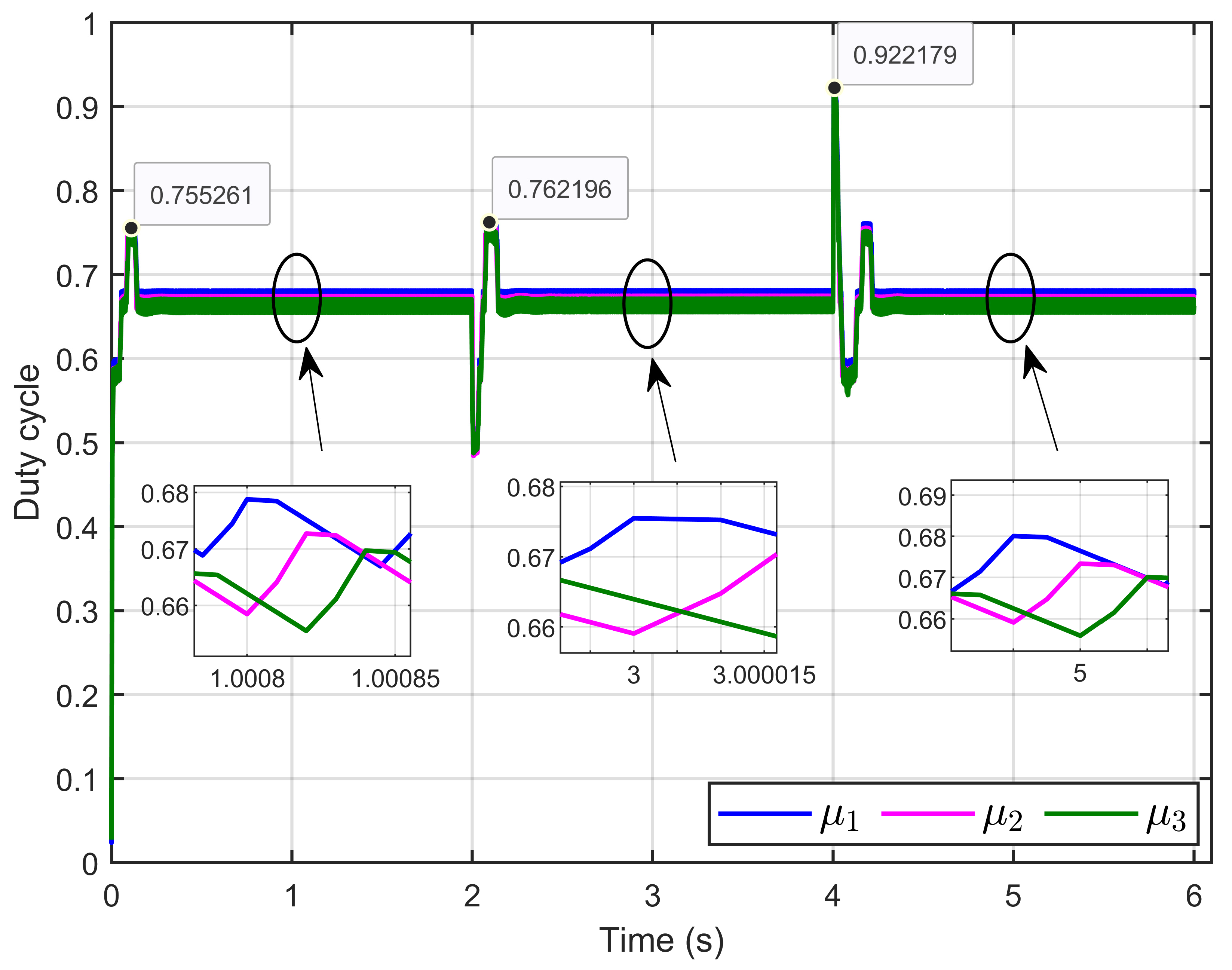
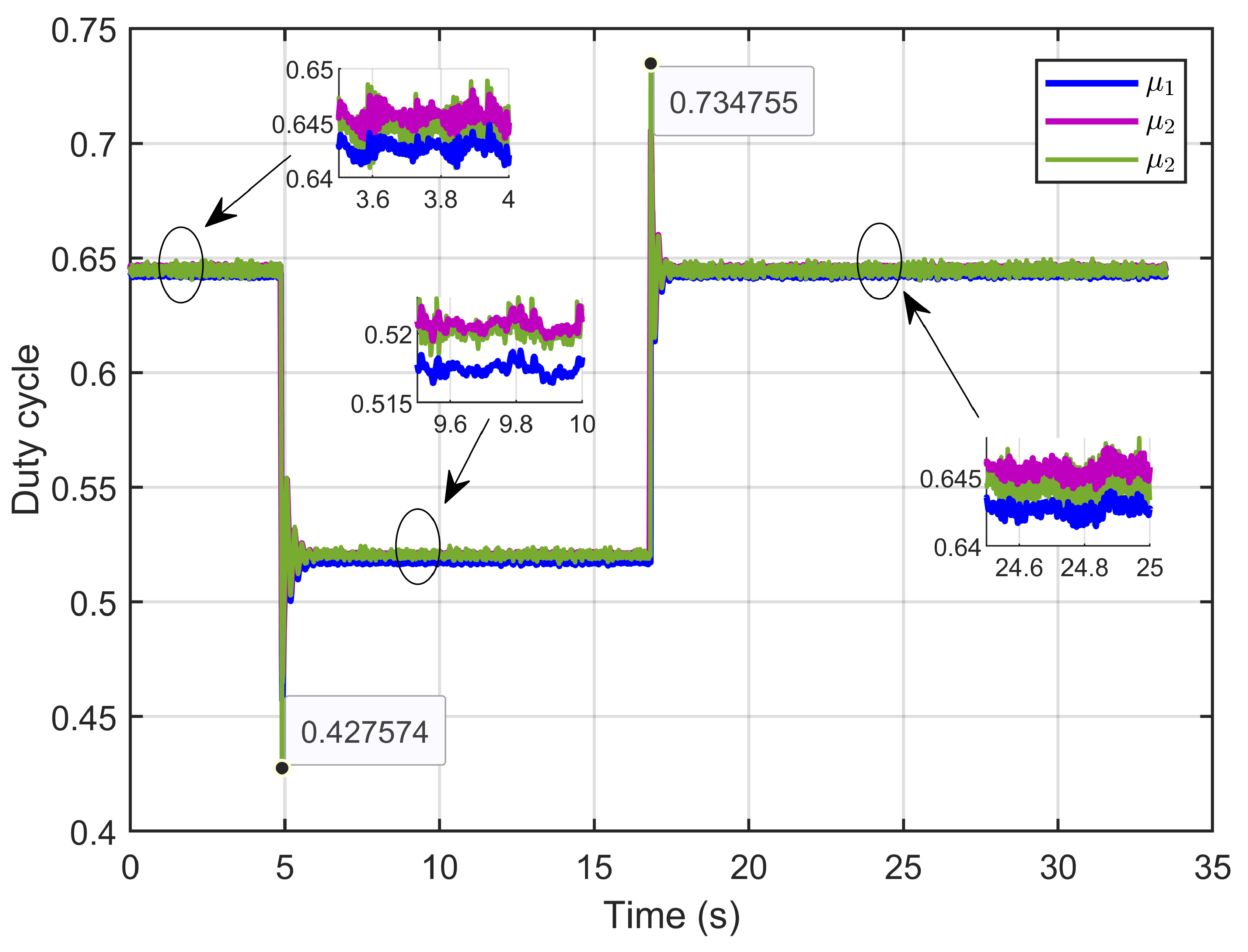
Figure 32 depicts the control inputs (duty cycle), showing that these signals remained within a bounded range of 0 to 1, which aligned with the duty cycle. Furthermore, the signals exhibited minimal ripples.
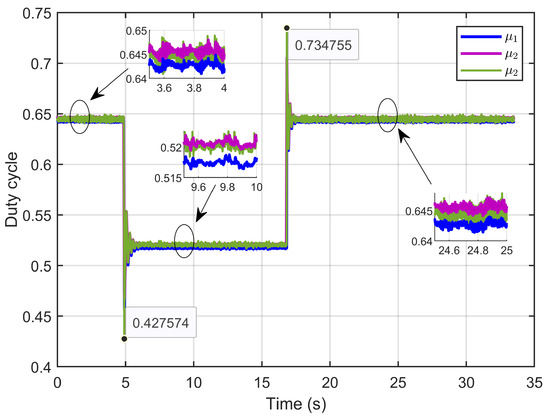
Figure 32.
The control inputs signals (duty cycle) under step reference voltage (experimental results).
The experimental performance metrics presented in Table 5 confirmed that the developed Adaptive Sliding Mode Controller (ASMC) successfully achieved PEM electrolyzer voltage regulation and current sharing under significant perturbations to the reference voltage and unknown system parameters. The ASMC maintained precise control with minimal errors in voltage regulation, tracking, current estimation, and current sharing, demonstrating its robustness, accuracy, and adaptability. These experimental results aligned with and confirmed the simulation findings, highlighting the controller’s effectiveness in achieving stable and reliable performance under dynamic and uncertain conditions.

Table 5.
Performance metrics of the ASMC in for a reference step in PEM electrolyzer voltage (experimentation).
7.2. Experimental Validation of Performance and Sensitivity to Perturbations Caused by Sudden Variations in PEM Electrolyzer Operation Conditions
Next, we performed experimental validation to evaluate the performance and reliability of the innovative developed ASMC. Our focus was on the PEM electrolyzer’s response to rapid changes in its operating conditions. The evaluation was performed using three different scenarios.
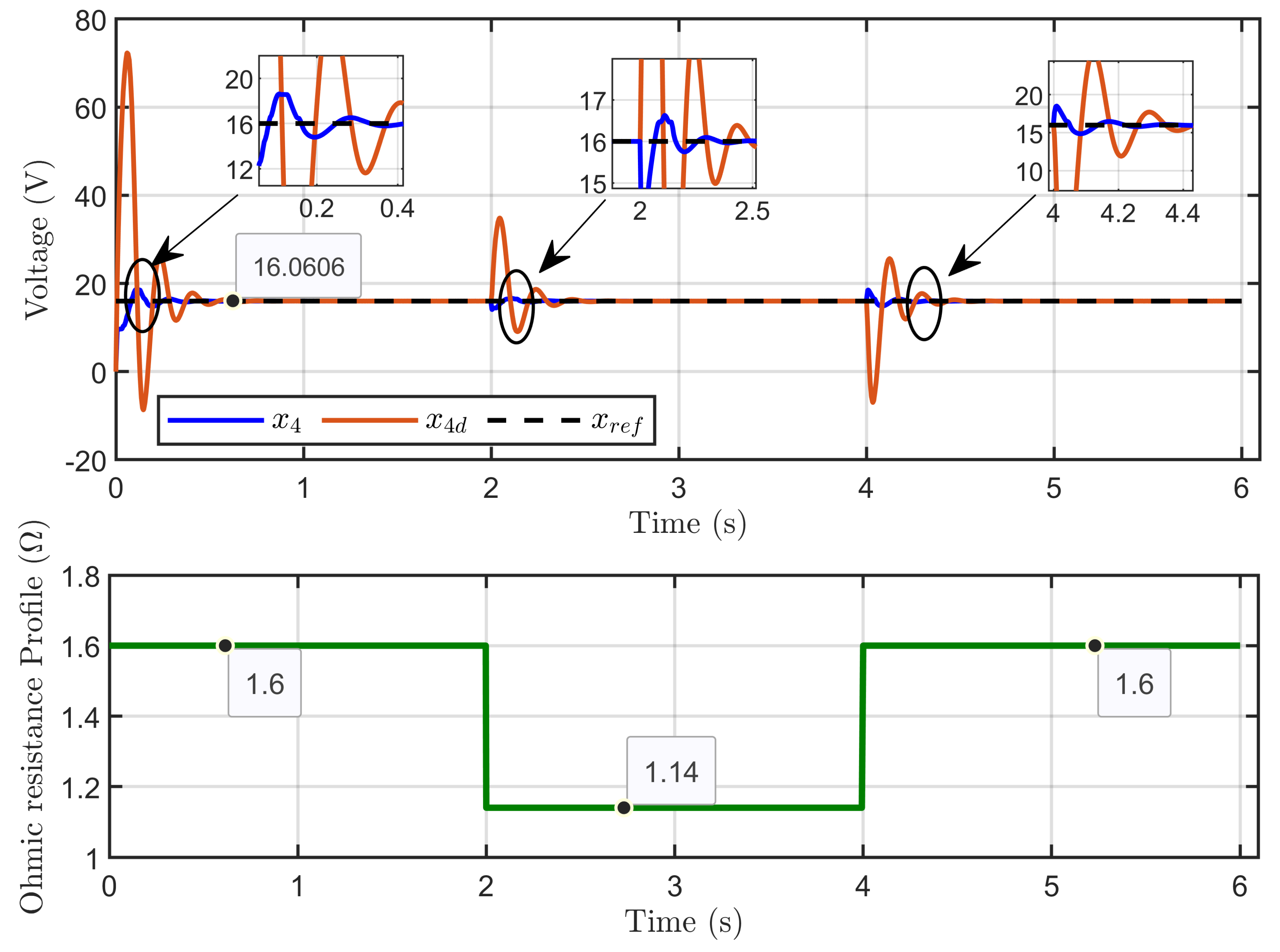
Scenario 1: In this scenario, the reference voltage of the PEM electrolyzer was set to xref =16 V and the reversible voltage was set to Erev = 9.6 V while a perturbation to its ohmic resistance was introduced. The resistance started at 1.6 Ω, decreased by 28.75% to 1.14 Ω, and then increased by 40.35% to return to 1.6 Ω.
Figure 33 presents the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage x4 in the presence of significant perturbations to the ohmic resistance. Despite these abrupt changes, the PEM electrolyzer voltage was effectively regulated. The voltage x4 experienced minor overshoots during the transitions in ohmic resistance but quickly stabilized and closely followed the reference value xref. In the steady state, the system maintained a small error of e4 = 0.0668 V, demonstrating the control system’s robust performance.
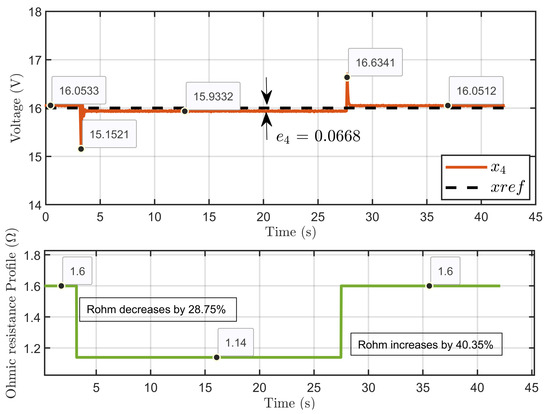
Figure 33.
Dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its reference under ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
Figure 34 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage x4 as it tracked its desired dynamic trajectory x4d. The PEM electrolyzer voltage closely and rapidly followed the desired trajectory, even in the face of sudden variations in ohmic resistance.
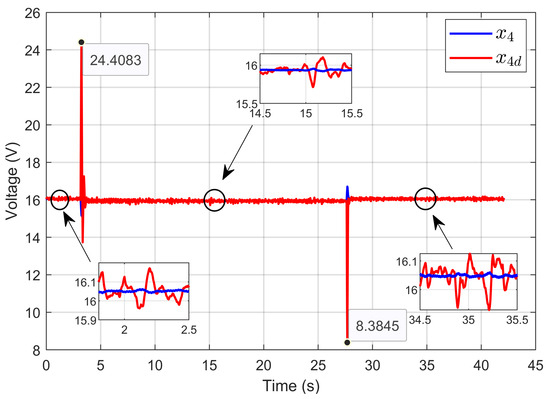
Figure 34.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage and its desired trajectory under ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
Figure 35 illustrates the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), its reference value (xref), and the desired dynamic trajectory (x4d). The figure shows that the voltages aligned with high accuracy during steady-state operation.
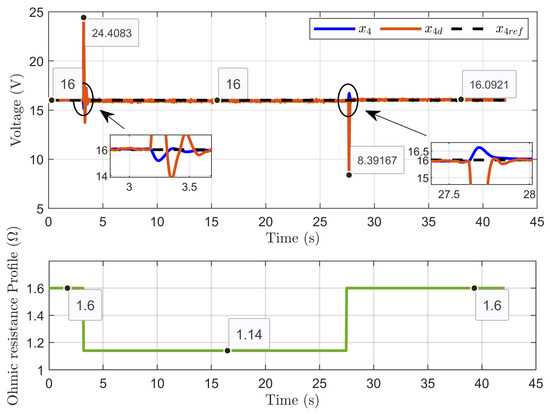
Figure 35.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired trajectory under ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
Figure 36 shows that the estimated inductor current () was consistently close to its true value (Id) in all operating conditions, even in the presence of ohmic resistance perturbations. This performance underscores the robustness of the ASMC to estimate the unknown vector parameters.
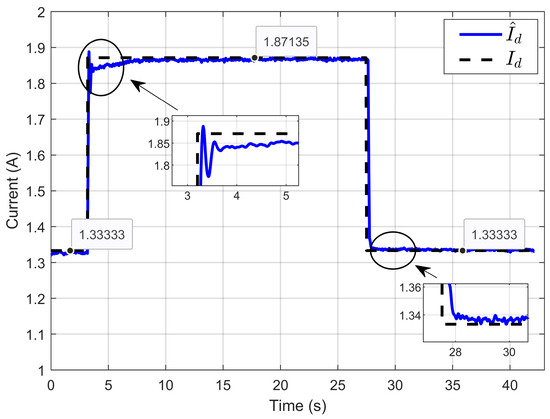
Figure 36.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current and its actual value under ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
Figure 37 illustrates the currents of the three inductors (x1, x2, and x3) and their estimated reference () under perturbations caused by ohmic resistance. The currents were evenly distributed across the three legs of the IBC and closely followed their respective reference values, even under the perturbations. The zoomed-in sections of the figure further emphasize the minimal current ripples, demonstrating the control strategy’s effectiveness in maintaining current balance, minimizing ripples, and ensuring high precision.
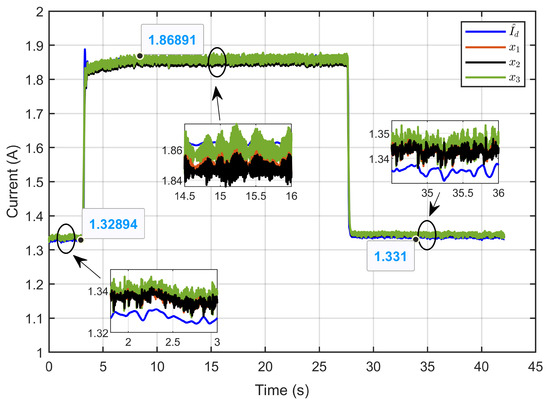
Figure 37.
The dynamic response of three inductor currents and their estimated reference under ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
Figure 38 presents the control inputs (duty cycles) in response to ohmic resistance perturbations. The figure shows that the duty cycles remained within the expected range of 0 to 1, adhering to the imposed duty cycle limits.
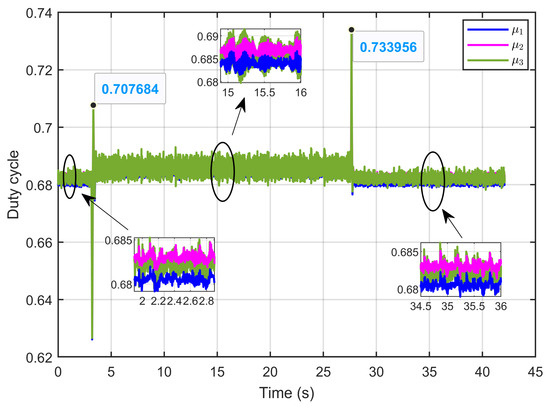
Figure 38.
The control inputs signals (duty cycle) under ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
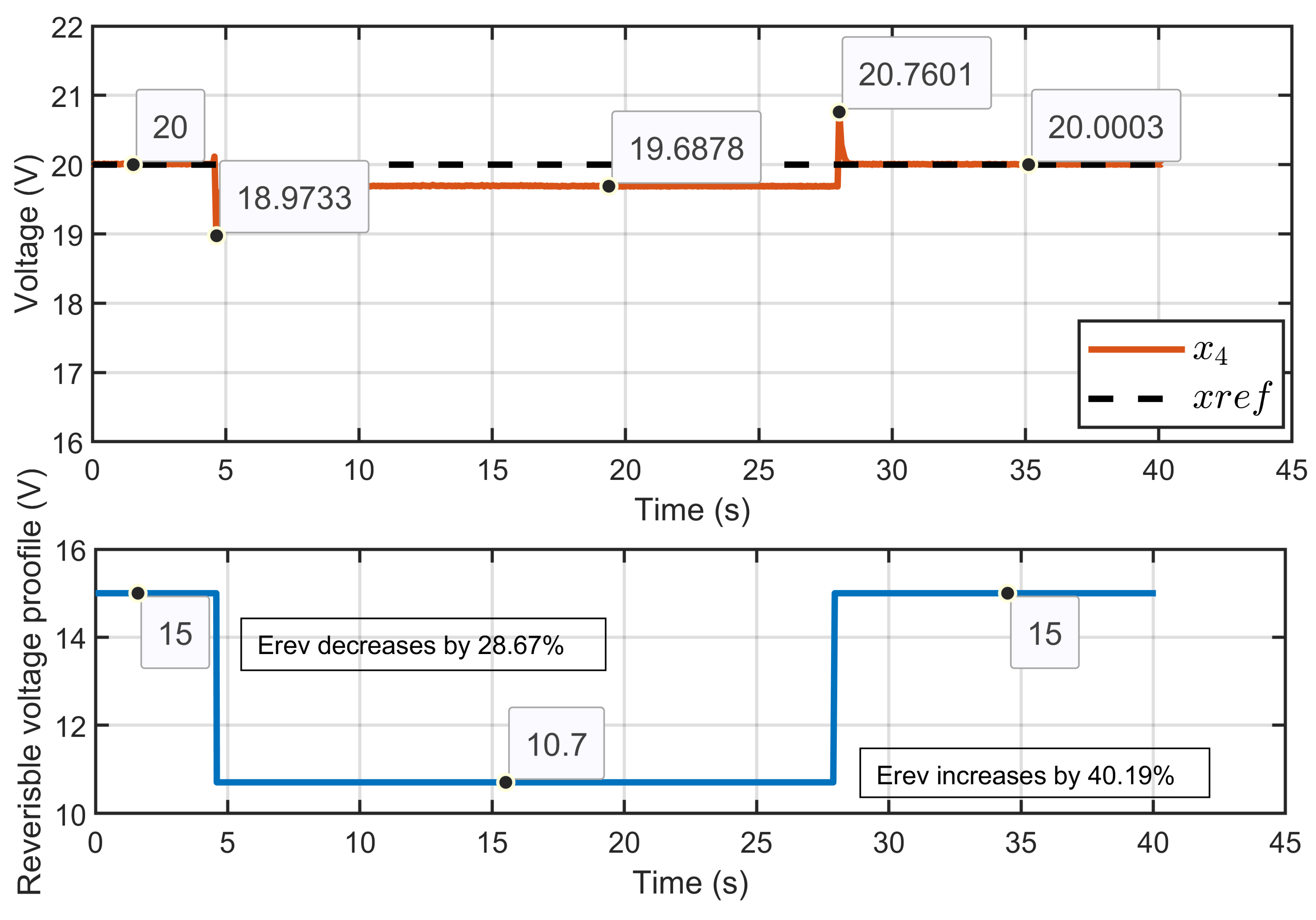
Scenario 2: In this scenario, the reference voltage of the PEM electrolyzer was set to xref = 20 V and the ohmic resistance to Rohm = 1.5 Ω while a perturbation to its reversible voltage was introduced. The reversible voltage started at 15 V, decreased by 28.67% to 10.7 V, and then increased by 40.19% to return to 15 V.
Figure 39 shows that the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4) remained well regulated and rapidly stabilized to its reference value (x4ref), even during significant changes in the reversible voltage. The developed controller quickly corrected small overshoots, showcasing its robustness and performance.
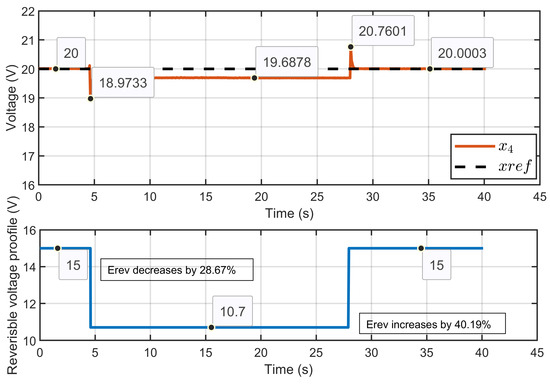
Figure 39.
Dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage and its reference under reversible volta perturbation (experimental results).
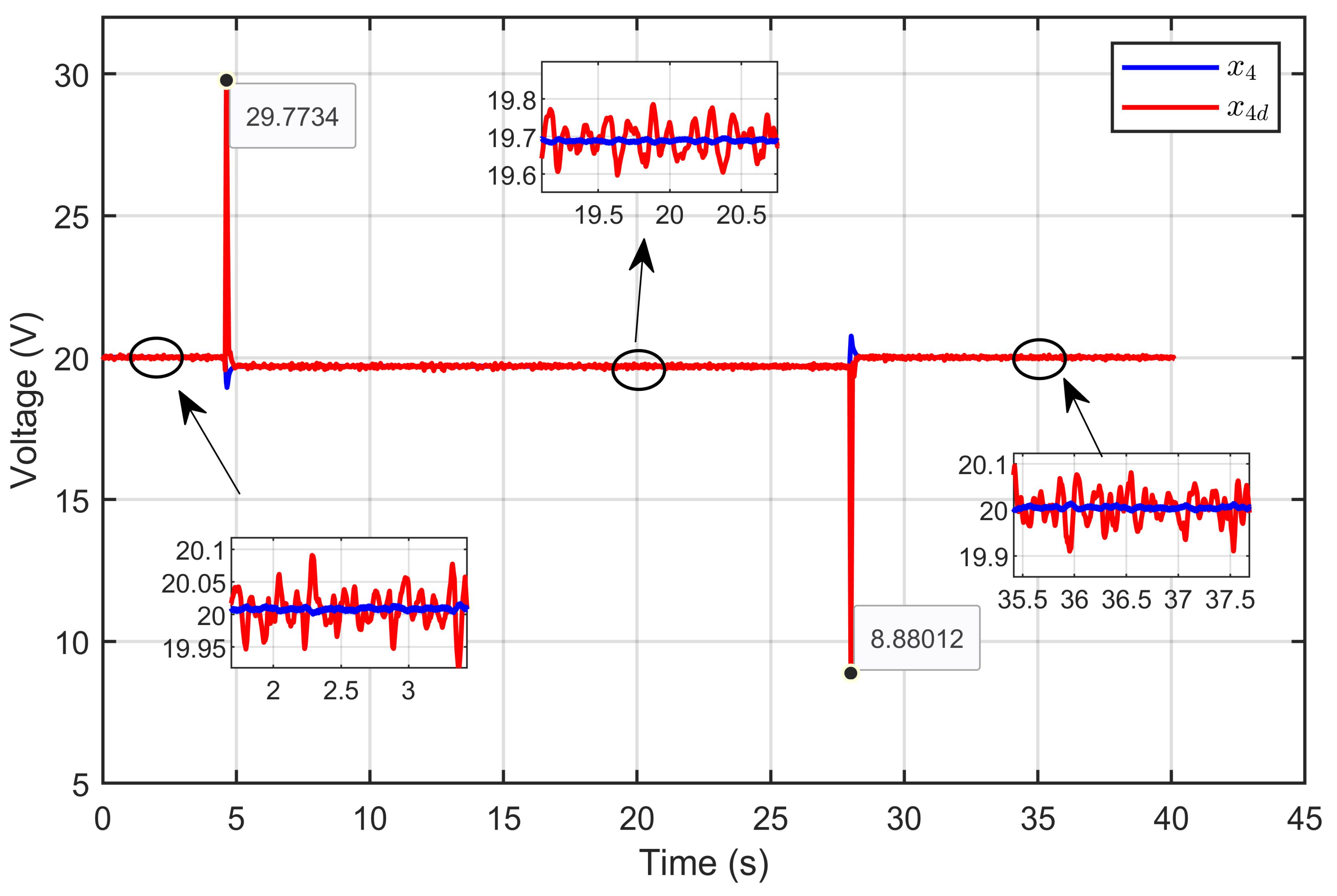
Figure 40 illustrates the dynamic response (x4) of the PEM electrolyzer voltage compared to its desired trajectory (x4d). The results showed that the PEM electrolyzer voltage closely and quickly followed the desired trajectory, even during sudden changes in the reversible voltage. The figure also highlights key moments where the system effectively handled abrupt perturbations, maintaining stability and minimizing deviations from the desired voltage trajectory.
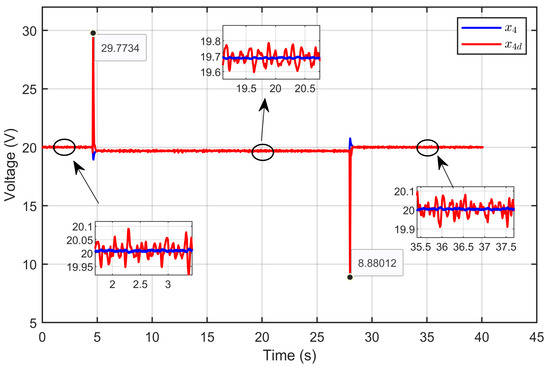
Figure 40.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage and its desired trajectory under reversible voltage perturbation (experimental results).
Figure 41 presents the dynamic response of the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), its reference (xref), and its desired trajectory (x4d). The results demonstrated that the PEM electrolyzer voltage consistently tracked both the reference and the desired trajectory with high accuracy, particularly during steady-state conditions.
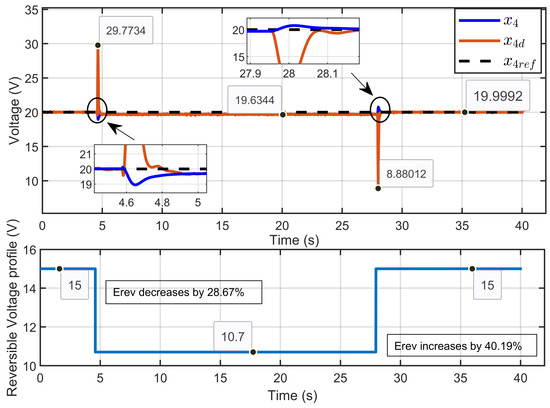
Figure 41.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired trajectory under reversible voltage perturbation (experimental results).
Figure 42 illustrates the dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current () and its actual value (Id), demonstrating that the estimated inductor current consistently and accurately tracked the actual inductor current across various operating conditions. This highlights the robustness and precision of the designed ASMC. The control strategy effectively responded to changes in system parameters, such as reversible voltage variations, by dynamically adjusting the estimated current to maintain close alignment with the actual inductor current.
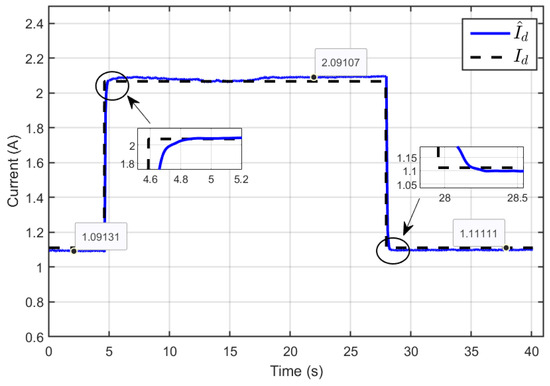
Figure 42.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current Id and its actual value under reversible voltage perturbation (experimental results).
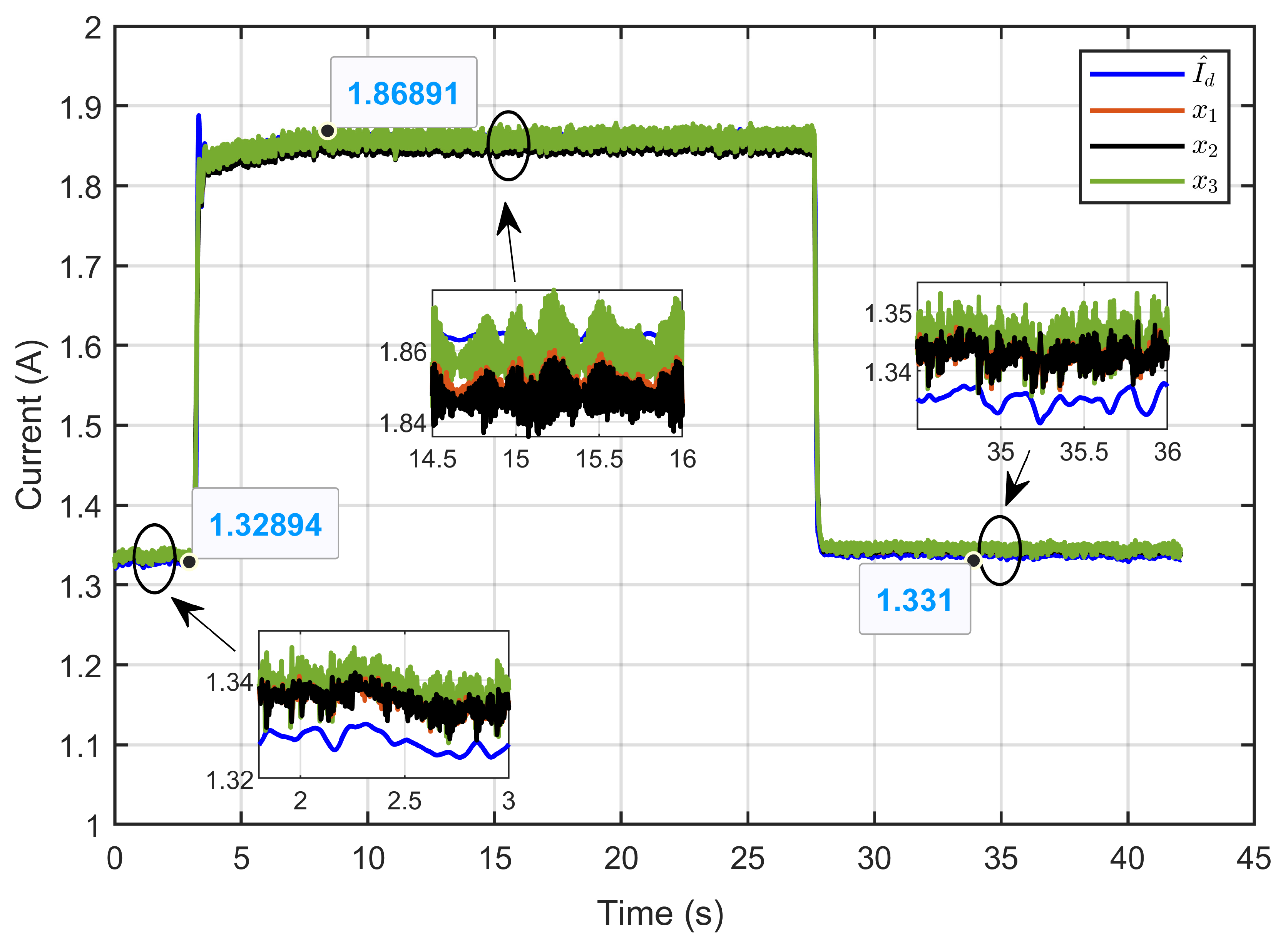
Figure 43 illustrates the currents of the three inductors (x1, x2 and x3) along with their estimated reference current () under the conditions of reversible voltage disturbance. The figure clearly shows the equal current distribution among the three parallel legs of the IBC. The insets show in more detail how, even when there are reversible voltage changes, the currents in each leg stayed close to the reference value.
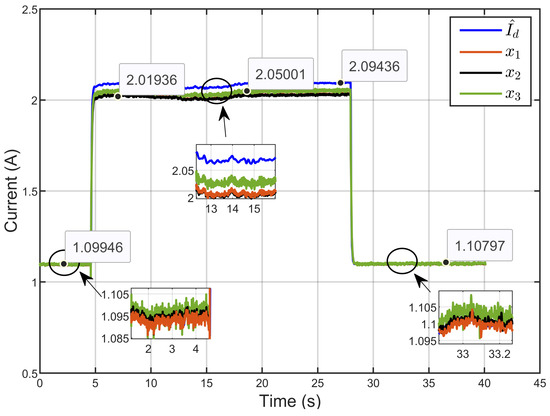
Figure 43.
Dynamic response of three inductor currents and their estimated reference under reversible voltage perturbation (experimental results).
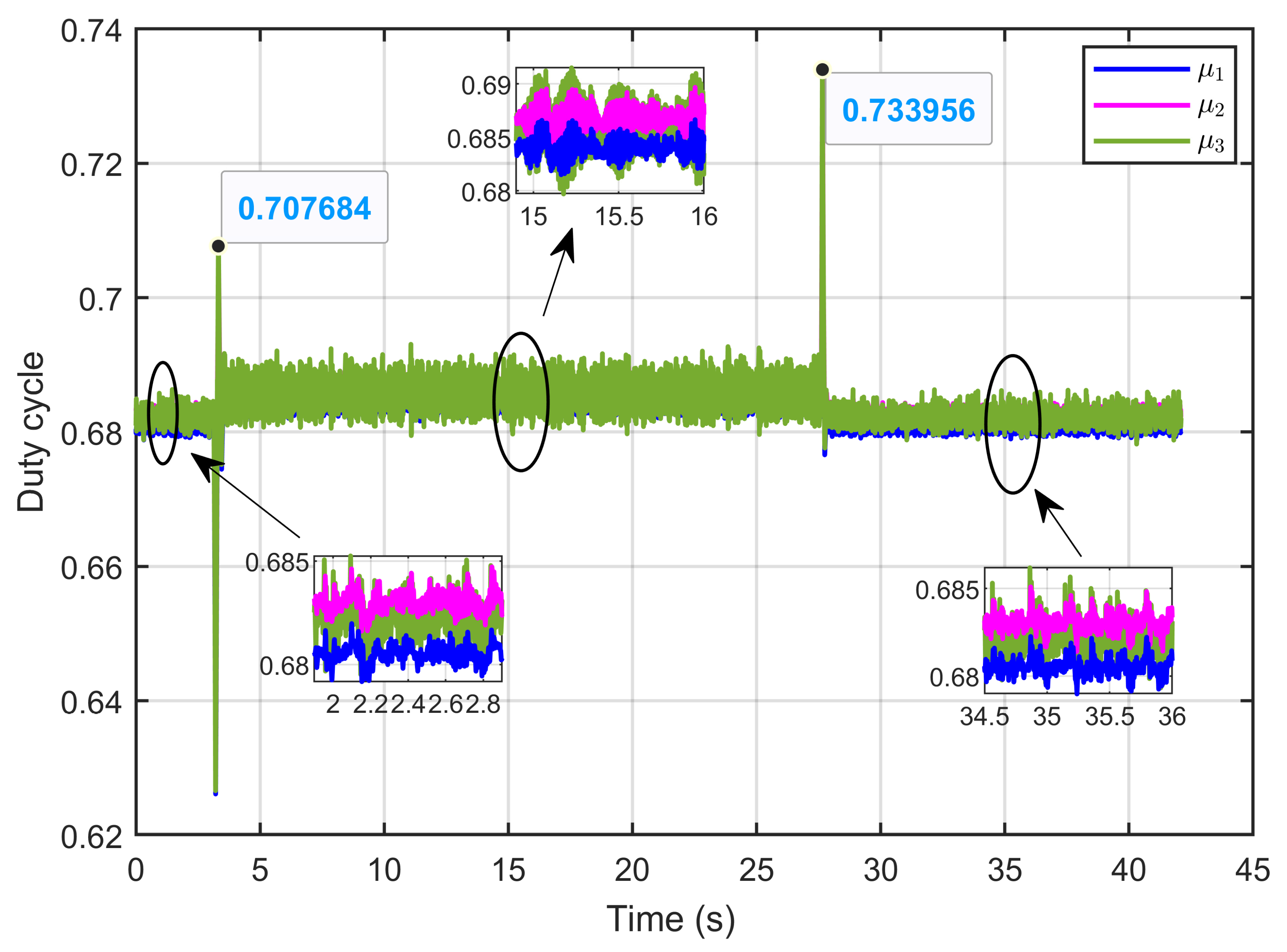
Figure 44 illustrates the control inputs (duty cycles) under reversible perturbations, demonstrating that these signals consistently remained within the expected range of 0 to 1, in alignment with the specified duty cycle limits.
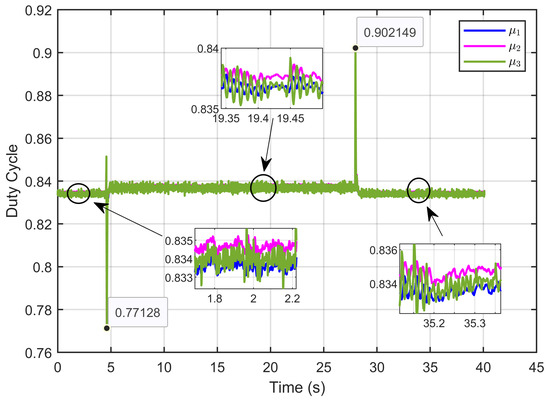
Figure 44.
The control inputs signals (duty cycle) under reversible voltage perturbation (experimental results).
Scenario 3: In this scenario, the reversible voltage Erev and the ohmic resistance Rohm were simultaneously perturbed. The reversible voltage started at 14.64 V, decreased by 29.50% to 10.32 V, and then increased by 41.86% to return to its initial value. Similarly, the ohmic resistance started at 1.6 Ω, decreased by 28.75% to 1.14 Ω, and then increased by 40.35% to return to its initial value. The reference voltage for the PEM electrolyzer was set to 18 V.
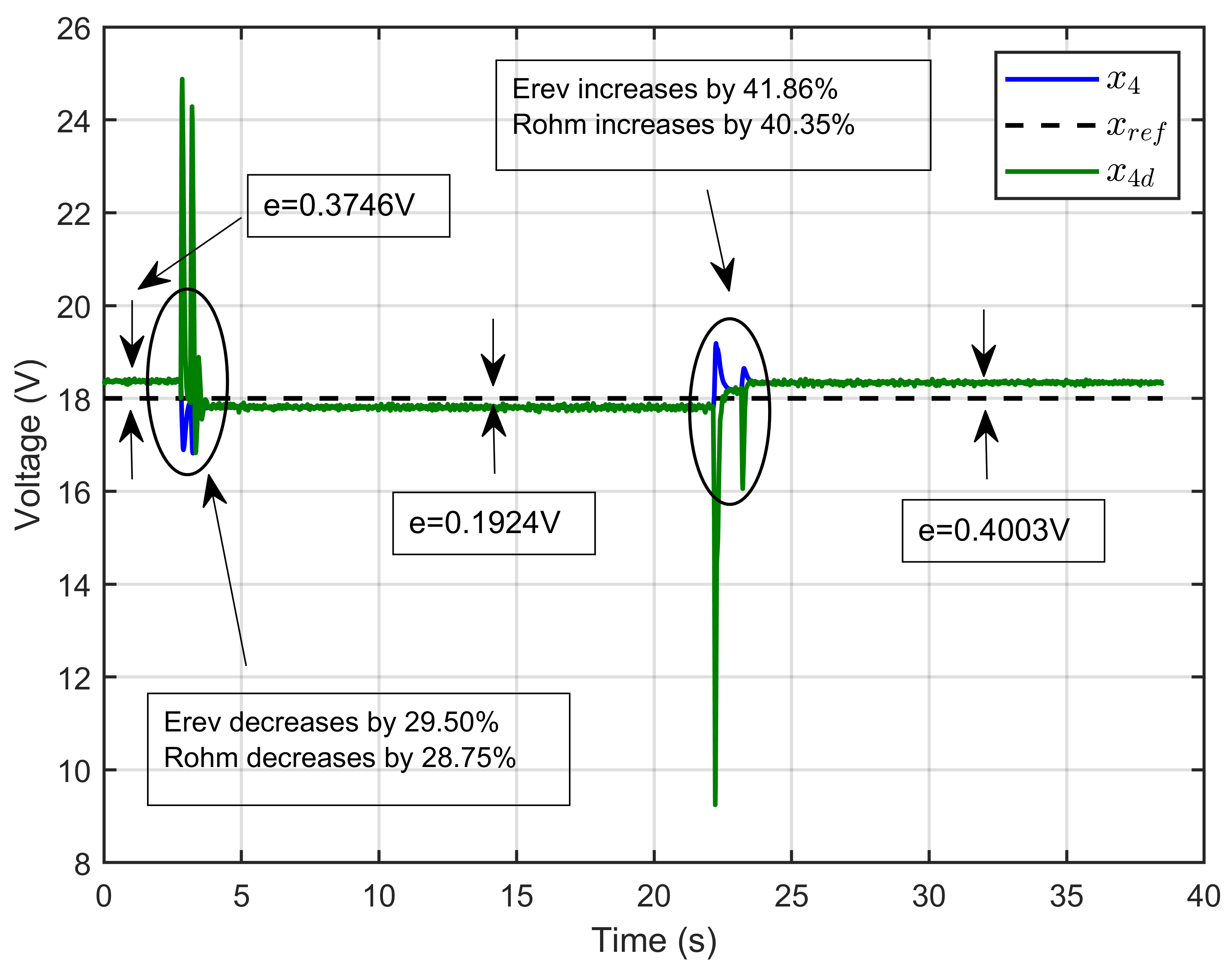
Figure 45 illustrates the PEM electrolyzer voltage (x4), its reference value (xref), and the desired dynamic trajectory (x4d). The results demonstrated that the PEM electrolyzer voltage closely followed its reference value and aligned well with the desired dynamic trajectory, even in the presence of significant disturbances. The figure highlights periods where the system experienced overshoots and perturbations, with detailed annotations indicating specific voltage errors and changes in parameters such as Erev and Rohm. Notably, the figure shows two steady-state errors: e = 0.1924 V after the initial disturbance around 15 s, and e = 0.4003 V after the second disturbance around 30 s. Despite these disturbances, the ASMC strategy effectively minimized the errors, showcasing its robustness and precision in maintaining the desired performance.
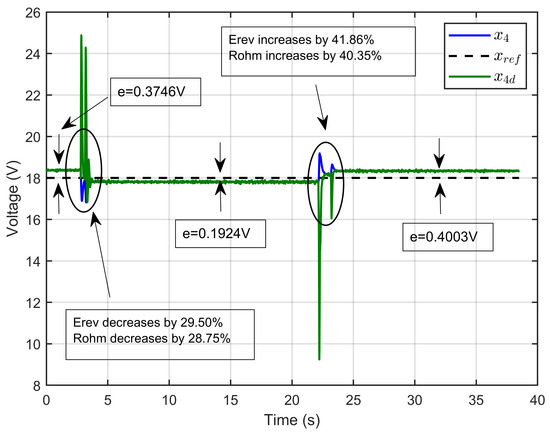
Figure 45.
Dynamic response of PEM electrolyzer voltage, its reference, and its desired trajectory under reversible voltage and ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
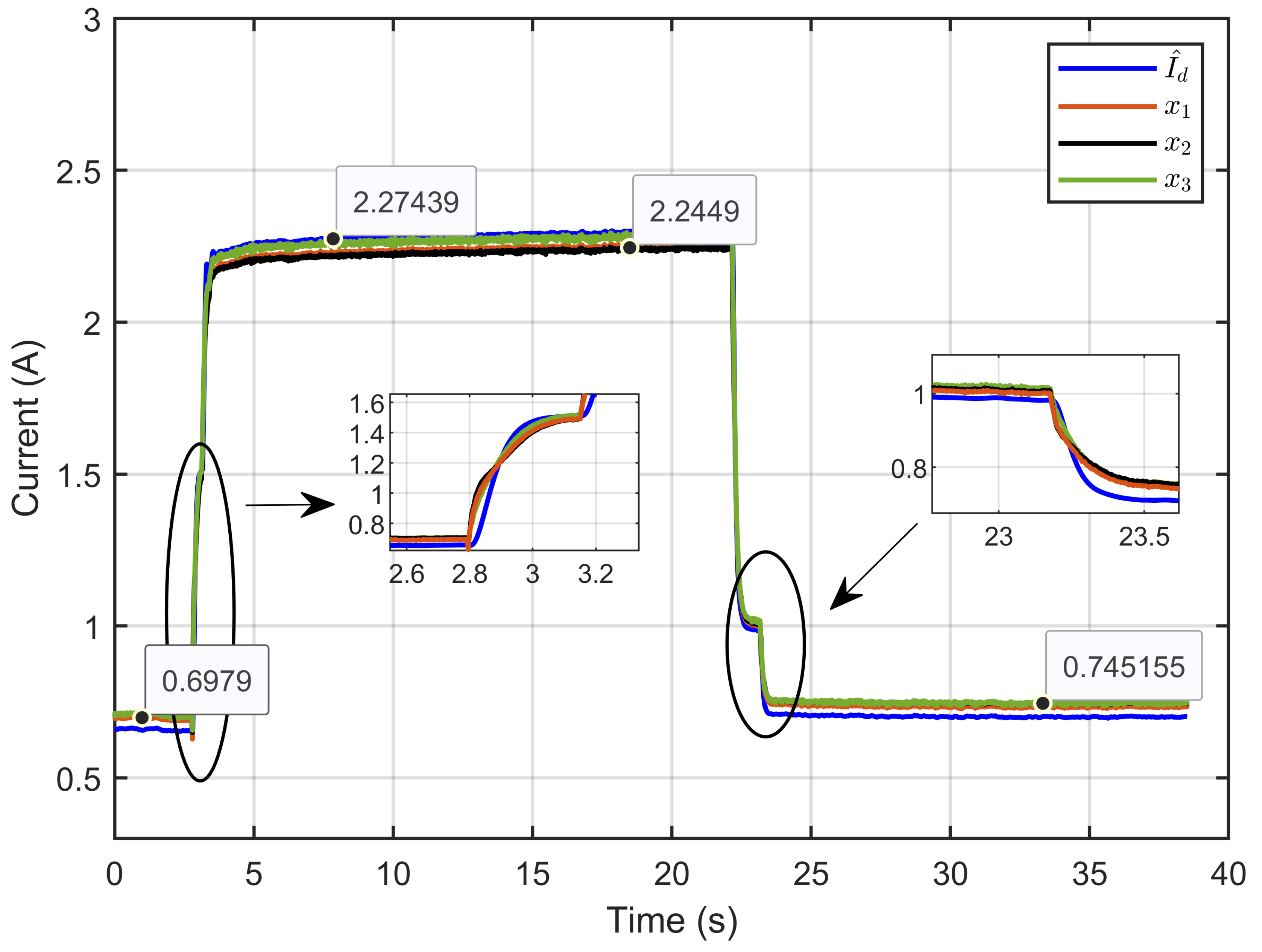
Figure 46 illustrates the dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current (), its actual value (Id), and the three inductor currents (x1, x2 and x3). The results demonstrated that the inductor currents effectively tracked the estimated reference current over time. The close alignment between these currents highlights the system’s ability to distribute current evenly across the three parallel legs, ensuring that each inductor follows the reference current accurately. The insets provide a detailed view of the system’s response to operational changes, showing that the ASMC strategy maintained precise and stable current tracking even under dynamic conditions.
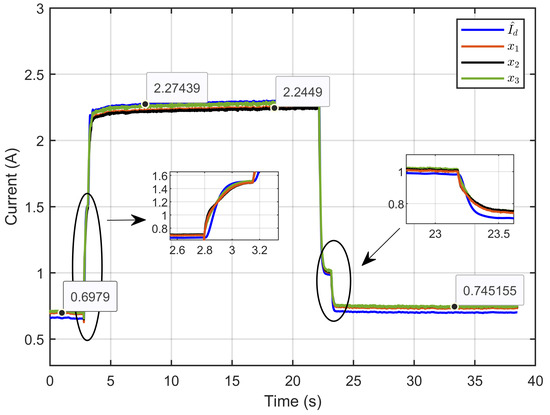
Figure 46.
Dynamic response of the estimated reference inductor current, its actual value, and the three inductor currents under reversible voltage and ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
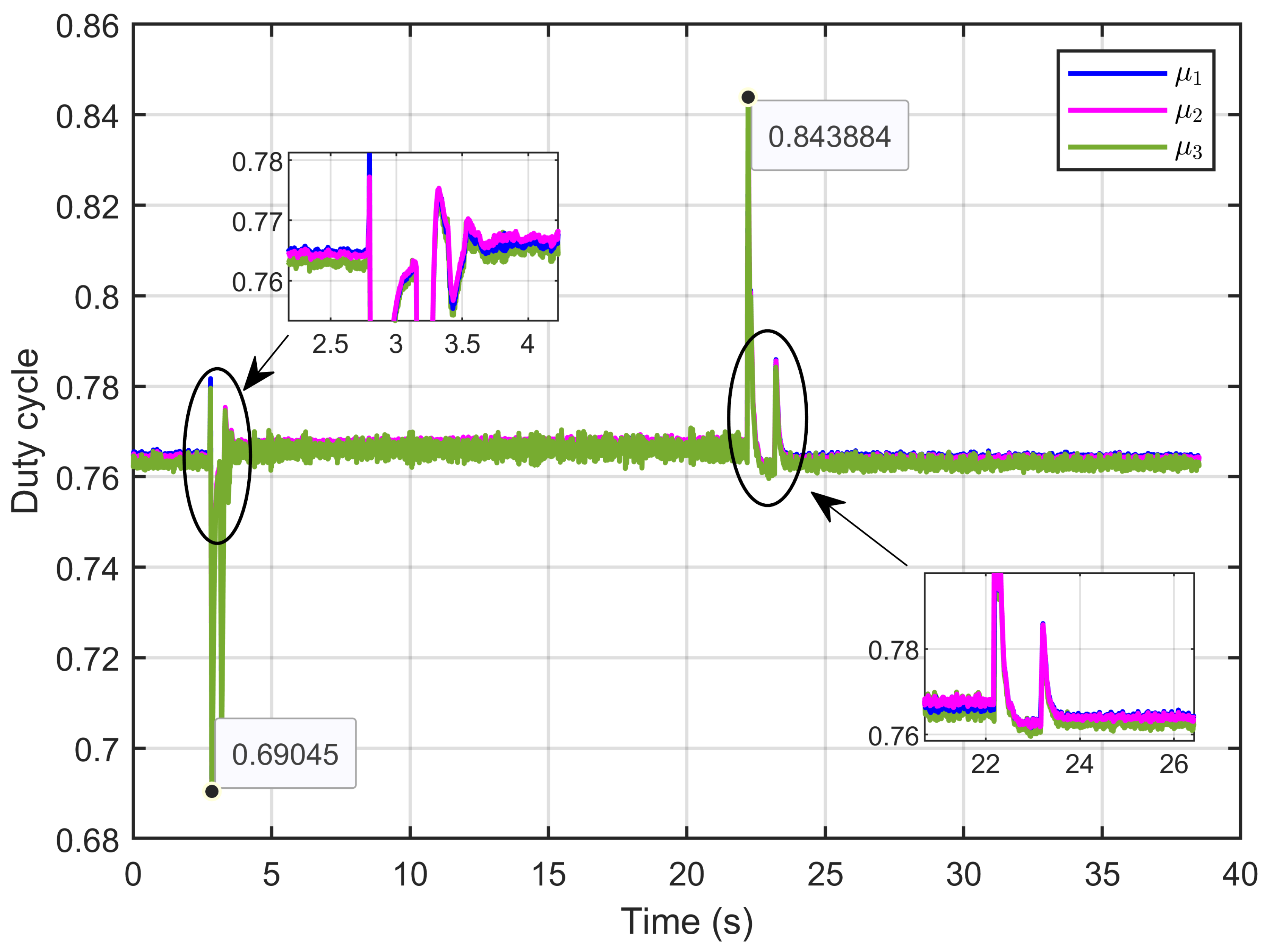
Figure 47 illustrates the control inputs, specifically the duty cycle. The data revealed that the control signals were consistently constrained within the expected bounds of 0 to 1, which is typical for duty cycle operations. Additionally, the figure shows that there were minimal ripples in the control signals, indicative of stable and efficient performance.
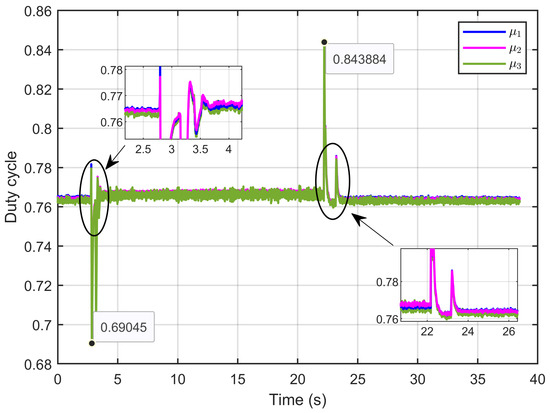
Figure 47.
The control inputs signals (duty cycle) under reversible voltage and ohmic resistance perturbation (experimental results).
The key experimental performance metrics obtained during the validation of the controller’s sensitivity to perturbations caused by sudden variations in PEM electrolyzer operating conditions are presented in Table 6. These metrics highlight the ASMC’s ability to maintain stability and performance under significant perturbations to the PEM electrolyzer model parameters, demonstrating its robustness and precision in real-world experimental scenarios. Importantly, these experimental results confirmed the simulation findings.

Table 6.
Performance metrics of the ASMC under PEM electrolyzer parameter perturbations (experimentation).
8. Discussion
The findings of this study highlight the effectiveness of the ASMC strategy in addressing the challenges of voltage regulation for the PEM electrolyzer and ensuring balanced current sharing among the three parallel legs of the IBC in a hydrogen production system based on an IBC-PEM electrolyzer configuration. The proposed approach demonstrated exceptional robustness and precision under various operating conditions, including significant variations in intrinsic PEM electrolyzer parameters, such as ohmic resistance and reversible voltage.
The proposed ASMC framework effectively compensates the uncertainties of the PEM electrolyzer’s model, which are known to vary with temperature and pressure.
Unlike traditional PID and PI controllers presented in the literature [7,8,14], which perform well for linear models and under fixed operating conditions, the proposed ASMC dynamically adapts to changes and effectively handles non-modeled nonlinear behavior as a nonlinear control strategy. This ensures precise voltage tracking and current balancing, even in the presence of significant fluctuations in operating conditions. Such adaptability is particularly crucial for hydrogen production systems, where operating conditions can vary considerably, as illustrated in Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14, Figure 15, Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18, Figure 19, Figure 20, Figure 21, Figure 22, Figure 23, Figure 24, Figure 25, Figure 26, Figure 27, Figure 28, Figure 29, Figure 30, Figure 31, Figure 32, Figure 33, Figure 34, Figure 35, Figure 36, Figure 37, Figure 38, Figure 39, Figure 40, Figure 41, Figure 42, Figure 43, Figure 44, Figure 45, Figure 46 and Figure 47. By maintaining robust performance under these challenging conditions, the ASMC framework could significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of the hydrogen production process.
The simulation results underscored the robustness of the ASMC under various scenarios, including step changes in the reference voltage and perturbations to the PEM electrolyzer’s parameters. The controller consistently maintained the PEM electrolyzer voltage close to its reference value, with minimal overshoots and rapid settling times. Furthermore, the ASMC achieved equal current distribution among the three branches of the IBC, effectively mitigating the impact of inductance mismatches. This ensures balanced operation and enhances the overall efficiency of the power conversion process.
The experimental validation using a hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) setup corroborated the simulation findings, demonstrating the practical feasibility of the ASMC. The controller exhibited high accuracy in tracking the desired voltage and current trajectories, even under challenging operating conditions. Additionally, the duty cycle signals generated by the controller remained within the expected range.
The broader implications of this work lie in its potential to advance green hydrogen production technologies. By addressing the key limitations of conventional control strategies, the proposed ASMC contributes to enhancing the reliability and efficiency of renewable energy-driven hydrogen systems.
Despite its promising results, this study has some limitations. The linear approximation of the PEM electrolyzer’s V-I characteristics, while effective for the ohmic region, may not fully capture the system’s behavior under extreme conditions or in the presence of significant nonlinearity. Future research could focus on integrating more comprehensive models that account for such complexities. Additionally, while the HIL experiments provide valuable insights, field-level validation in real-world operating conditions would be necessary to assess the controller’s performance under practical constraints.
In conclusion, the developed ASMC strategy proved to be a robust and efficient solution for controlling IBC-PEM electrolyzer systems, addressing critical challenges in hydrogen production. Its ability to handle uncertainties, maintain precise voltage regulation, and ensure equal current distribution makes it highly suitable for real-world applications. The findings pave the way for future advancements in control strategies for renewable energy-based hydrogen production, ensuring scalability and adaptability in diverse operating environments.
9. Conclusions
In conclusion, the developed ASMC strategy for the IBC in a hydrogen production system based on a PEM electrolyzer showed excellent performance. The PEM electrolyzer model, which included an ohmic resistor to account for the ionic membrane and electronic resistance, as well as a voltage source to represent the reversible voltage, supported the assumption that the electrolyzer operates primarily in the ohmic region.
The ASMC was specifically designed to achieve three main objectives:
- ▪
- Accurate regulation of the PEM electrolyzer voltage under varying operating conditions.
- ▪
- Equal current sharing between the parallel legs of the IBC despite different inductance values.
- ▪
- Ensure overall stability system.
Extensive testing, including both simulation and experimental validation, confirmed the effectiveness and robustness of the developed ASMC. The system was evaluated under various scenarios, such as voltage steps, variations in ohmic resistance and reversible voltage, and combined disturbances. The results not only showed that the ASMC met its design objectives but also agreed with the theoretical analysis presented in Theorem 1, proving its ability to maintain optimal control of the PEM electrolyzer in a hydrogen production system.
The ASMC strategy not only overcomes the technical challenges associated with controlling IBC-PEM electrolyzers, but also offers an economically viable route to industrial-scale green hydrogen production. Its advantages such as adaptability to varying operating conditions, reduced sensitivity to perturbations, and scalability make it a compelling alternative to conventional methods. Future work should focus on field trials to validate cost projections and refine the controller for heterogeneous industrial environments. By bridging the gap between theoretical robustness and practical deployment, the ASMC framework lays the foundation for large-scale, sustainable hydrogen ecosystems aligned with global decarbonization goals.
Author Contributions
Methodology, M.K. and H.E.F.; Software, A.L.; Validation, M.K., A.L. and Y.E.A.; Formal analysis, M.K.; Resources, Y.E.A.; Writing—original draft, M.K. and H.E.F.; Writing—review & editing, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
In this appendix, a detailed analysis and calculations are provided for the selection of key components in the interleaved DC/DC buck converter and boost converter employed in the project. The focus is on the criteria for choosing the IGBT transistor and Schottky diode, as well as determining the optimal values for filtering capacitance and inductance. Proper selection of these components is essential for achieving high performance, reducing the voltage and current ripple, and ensuring reliable operation.
Appendix A.1. Selection of Filtering Capacitance
Appendix A.1.1. Capacitance Value
The filtering capacitance was chosen to minimize the voltage ripple at the output of the buck converter. The key factors influencing the choice of capacitance include the output voltage, output current, switching frequency, and allowable voltage ripple.
To achieve a desired voltage ripple ΔVout, the output capacitance Cout was selected as follows:
where ΔVout, Iout, D, fs, and Cout are the peak-to-peak output voltage ripple, the output current, the duty cycle of the converter, the switching frequency, and the output capacitance, respectively.
Appendix A.1.2. Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of the capacitor should be higher than the output voltage, with a margin for safety.
Recommendation: Choose a capacitor with a voltage rating at least 20–30% higher than the maximum output voltage.
Appendix A.2. Selection of Filtering Inductance
The filtering inductance is crucial for controlling the current ripple in the inductor, which directly affects the performance and efficiency of the converter.
Appendix A.2.1. Inductance Value
The inductance L was selected to limit the inductor current ripple ΔIL to an acceptable level:
Appendix A.2.2. Current Rating (IL)
The inductor must be designed to handle the peak current without entering saturation. The peak current was calculated as the sum of the output current and half of the current ripple.
The formula for calculating the peak current is
Appendix A.2.3. Core Material
The choice of core material affects the inductor’s performance at high frequencies. Ferrite cores are commonly used in boost converters due to their low core losses at high switching frequencies.
Appendix A.3. Selection of the Schottky Diode
Schottky diodes are used for their low forward voltage drop (0.2–0.4 V) and fast switching speed, which enhance efficiency and reduce power losses in high-frequency and high-speed applications. Their minimal reverse recovery time also improves performance in switching power supplies.
Appendix A.3.1. Reverse Voltage Rating (VRRM)
The reverse voltage rating of the diode must be higher than the maximum input voltage of the converter. A common practice is to select a diode with a reverse voltage rating at least 20–30% higher than the maximum input voltage:
Appendix A.3.2. Forward Current Rating (IF)
The diode must handle the maximum current flowing through it during operation. The average forward current rating should be higher than the maximum output current of the converter:
Appendix A.4. Selection of the IGBT Transistor
The IGBT in a buck and boost converter acts as the main switch, and its characteristics greatly impact the efficiency and performance of the converter.
Appendix A.4.1. Collector-Emitter Voltage Rating (VCE)
The IGBT’s voltage rating should be higher than the maximum input voltage to the buck converter or the maximum output voltage to the boost converter. Typically, a safety margin of 20–30% above the maximum input voltage is used.
Appendix A.4.2. Current Rating (IC)
The IGBT must handle the maximum current flowing through it during operation. The continuous collector current rating should exceed the maximum output current of the buck converter or the maximum input current of the boost converter.
Appendix A.4.3. Switching Frequency and Switching Losses
IGBTs are generally used in applications with moderate switching frequencies (up to a few tens of kHz). An IGBT with low switching losses was chosen to improve efficiency. Both the turn-on and turn-off switching energies (Eon and Eoff) were considered.
We ensured that the IGBT could handle the intended switching frequency without excessive losses.
Appendix A.4.4. Gate Drive Requirements
IGBTs require a specific gate voltage to turn on fully. We ensured that the gate driver circuit could provide the necessary gate voltage and current to switch the IGBT effectively.
Appendix A.5. Thermal Considerations
Both the Schottky diode and IGBT will generate heat during operation. We ensured that the chosen components could dissipate heat effectively through proper heatsinking or other cooling methods. The junction temperature was maintained within the specified limits for reliable operation.
Thermal Resistance: The junction-to-case and junction-to-ambient thermal resistance was checked to ensure that the cooling system could maintain a safe operating temperature.
References
- Yodwong, B.; Guilbert, D.; Phattanasak, M.; Kaewmanee, W.; Hinaje, M.; Vitale, G. Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer Modeling for Power Electronics Control: A Short Review. C—J. Carbon Res. 2020, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodwong, B.; Guilbert, D.; Phattanasak, M.; Kaewmanee, W.; Hinaje, M.; Vitale, G. AC-DC converters for electrolyzer applications: State of the art and future challenges. Electronics 2020, 9, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundi, M.; El Fadil, H.; EL Idrissi, Z.; Lassioui, A.; Intidam, A.; Bouanou, T.; Nady, S.; Rachid, A. Investigation of hydrogen production system-based PEM EL: PEM EL modeling, DC/DC power converter, and controller design approaches. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 531–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshan, I.S.; Manikandan, V.V.S.; Ram Sundhar, V.; Sajiv, R.; Shanthi, C.; Kottayil, S.K.; Ramachandran, T. Regulated hydrogen production using solar powered electrolyser. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 10322–10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingole, D.; Drgoňa, J.; Kalúz, M.; Klaučo, M.; Bakošová, M.; Kvasnica, M. Model predictive control of a combined electrolyzer-fuel cell educational pilot plant. In Proceedings of the 2017 21st International Conference on Process Control (PC), Strbske Pleso, Slovakia, 6–9 June 2017; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Koundi, M.; El Fadil, H.; Rachid, A.; El Idrissi, Z.; Giri, F.; Guerrero, J. Output Feedback Sliding Mode Control of PEM EL-IBC System for Hydrogen Production. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.E.; Okumuş, H.İ.; Aydemir, M.T. Implementation of an electrolysis system with DC/DC synchronous buck converter. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 6802–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodwong, B.; Guilbert, D.; Kaewmanee, W.; Phattanasak, M. Energy Efficiency Based Control Strategy of a Three-Level Interleaved DC-DC Buck Converter Supplying a Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer. Electronics 2019, 8, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbert, D.; Sorbera, D.; Vitale, G. A stacked interleaved DC-DC buck converter for proton exchange membrane electrolyzer applications: Design and experimental validation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarghot, M.; Rolland, L. MATLAB/Simulink modelling and experimental results of a PEM electrolyzer powered by a solar panel. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference (EPEC), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 12–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nafeh, A.E.-S.A. Hydrogen production from a PV/PEM electrolyzer system using a neural-network-based MPPT algorithm. Int. J. Numer. Model. Electron. Netw. Devices Fields 2011, 24, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundi, M.; El Idrissi, Z.; El Fadil, H.; Belhaj, F.Z.; Lassioui, A.; Gaouzi, K.; Rachid, A.; Giri, F. State-Feedback Control of Interleaved Buck–Boost DC–DC Power Converter with Continuous Input Current for Fuel Cell Energy Sources: Theoretical Design and Experimental Validation. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Gómez, Á.; Ramirez, V.; Guilbert, D. Investigation of PEM electrolyzer modeling: Electrical domain, efficiency, and specific energy consumption. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 14625–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamouri, R.; Guilbert, D.; Zasadzinski, M.; Rafaralahy, H. Proton exchange membrane water electrolysis: Modeling for hydrogen flow rate control. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 7676–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makineni, R.R.; Agalgaonkar, A.P.; Muttaqi, K.M.; Islam, M.R.; Sutanto, D. Integral sliding mode control of a stacked interleaved buck converter for electrolyzers supplied with renewable energy sources. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 61, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbert, D.; Yodwong, B.; Kaewmanee, W.; Phattanasak, M.; Hinaje, M. Hydrogen Flow Rate Control of a Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer. In Proceedings of the 2019 Research, Invention, and Innovation Congress (RI2C), Bangkok, Thailand, 11–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Torok, L.; Mathe, L.; Nielsen, C.K.; Munk-Nielsen, S. Modeling and Control of Three-Phase Grid-Connected Power Supply With a Small DC-Link Capacitor for Electrolyzers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 4634–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, L.; Nielsen, C.K.; Munk-Nielsen, S.; Rømer, C.; Flindt, P. High efficiency electrolyser power supply for household hydrogen production and storage systems. In Proceedings of the 2015 17th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’15 ECCE-Europe), Geneva, Switzerland, 8–10 September 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Collura, S.M.; Guilbert, D.; Vitale, G.; Luna, M.; Alonge, F.; D’Ippolito, F.; Scipioni, A. Design and experimental validation of a high voltage ratio DC/DC converter for proton exchange membrane electrolyzer applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7059–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azer, P.; Emadi, A. Generalized state space average model for multi-phase interleaved buck, boost and buck-boost DC-DC converters: Transient, steady-state and switching dynamics. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 77735–77745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotine, J.J.E. Sliding Controller Design for Nonlinear Systems. Int. J. Control 1984, 40, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).