Abstract
The pressing need to enhance the efficiency of wastewater treatment is underscored by the significant threat that water pollution poses to human health and environmental stability. Among current remediation techniques, photocatalysis has emerged as a promising approach due to its reliance on advanced material properties. Cerium oxide’s tunable bandgap and defect engineering, combined with graphene’s high surface area, conductivity, and functionalization, synergistically enhance photocatalytic performance. This makes CeO2-graphene composites highly promising for environmental remediation applications. This review paper systematically examines water pollution challenges and evaluates existing treatment methodologies, with a particular emphasis on CeO2-based photocatalysts modified with graphene and its derivatives, such as graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO). These composites demonstrate potential for superior photocatalytic performance and reactor design. Key issues, including environmental impact, stability, reusability, and compatibility of these materials with evolving technologies, are thoroughly discussed. Additionally, considerations for scaling production and commercializing these composites are addressed, suggesting avenues for future research and industrial applications. This review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the synergistic effects of CeO2 and graphene-based materials, opening new possibilities for advanced clean water treatment technologies.
1. Introduction
Industrialization has led to growth in technology and an increase in economic status, but this has come with negative impacts such as release of untreated waste like dyes into the environment. As the industries grow rapidly in many sectors including textile, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing, the dumping of raw wastewater with numerous pollutants is a normal occurrence [1]. Contamination of water by dyes represents a significant environmental challenge that needs immediate remediation and collective efforts for effective and efficient solution [2]. The increasing release of organic waste to water bodies leads to tremendous impacts on biological diversity and has indirect consequences on human health [3]. Figure 1 shows various sources of water contamination, indicating that industrial organic wastes are the main contributors.
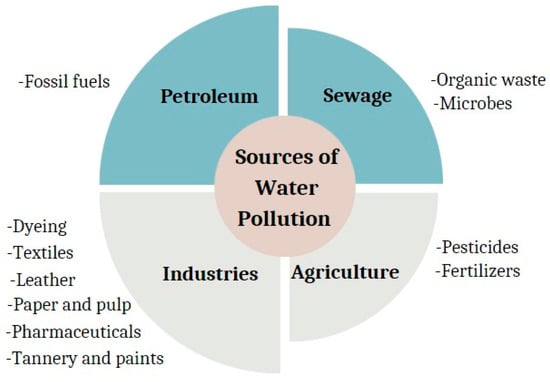
Figure 1.
Various sources of water contamination.
1.1. Methods of Wastewater Treatment
Wastewater treatment can be done using the following methods as indicated in Figure 2 below. Due to this environmental problem, advanced oxidation technologies (AOTs) have become the central solution for the removal of dyes from wastewater [4]. Of these technologies, photocatalysis is considered one of the most suitable technologies that has the potential for highly effective and efficient degradation of organic dyes [5]. In 1972, Fujishima and Honda first introduced photocatalysis as an outcome of their research on the electrochemical photocatalysis of water [6]. The critical drawbacks of the conventional techniques are discussed; these include high costs, partial mineralization, and the need for high concentration of hydroxyl radicals [7].
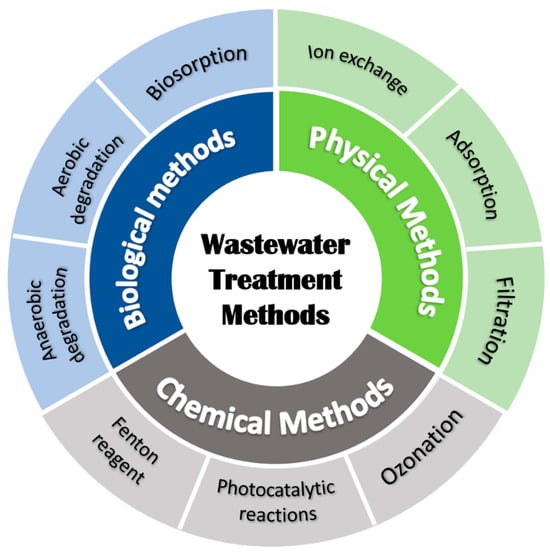
Figure 2.
Various methods of wastewater treatment methods.
This process involves the use of light energy to trigger photocatalysts to allow reactions to take place in a controlled manner. This is a built-in characteristic of photocatalysis, in that it uses light or photon sources to regulate reactions, and this shows the applicability of photocatalysis for the controlled breakdown of pollutants. The benefits of photocatalysis over the traditional methods are numerous. As compared to adsorption and chemical coagulation methods where further treatment is required, photocatalysis can degrade most of the pollutants to a very low level without secondary pollution [8].
1.2. Cerium Oxide for Photocatalysis
The part played by different oxides in photocatalysis for wastewater treatment is central. Other semiconductor oxides which have been reported to have the ability to degrade pollutants include TiO2 [9,10,11], V2O5 [12,13,14], Y2O3 [15,16], and CeO2 [17,18,19]. Although TiO2 is well researched for its stability and cost, the efficiency of V2O5 and Y2O3 varies in the degradation of pollutants. In particular, CeO2 NPs have attracted considerable interest because of the specific characteristics of their surface and high catalytic activity, which can have a great effect on the effectiveness and efficiency of the processes of pollutant degradation [20,21,22,23,24]. At the nanoscale, the ability of Ce3+ to switch to Ce4+ in CeO2 NPs helps in the redox reactions. When a foreign element, either divalent or trivalent, substitutes Ce⁴⁺ ions in CeO2, the number of positive ions decreases, creating a charge imbalance within the lattice. To ensure the material remains electrically neutral for stability, oxygen ions vacate their lattice positions and migrate to the surface. This reduces their contribution within the lattice and results in the formation of oxygen vacancies (VO) that support the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Substantial studies have shown that CeO2 NPs are non-toxic, which has supported their use in other fields apart from photocatalysis [25]. Chahal et al. synthesized La-doped CeO2 NPs and the degrading efficiency was identified to have risen to 76.7 to 86.7% with La content (8%). This improvement was attributed to a smaller band gap that enabled faster electron transportation. VO and the changes in morphology also contributed to tuning the photocatalytic activity of the La-doped system [26]. In another study, authors synthesized spindle-shaped Mg-doped CeO2 NPs to degrade p-Nitrophenol dye and observed that the photocatalytic efficiency enhanced with the Mg content up to 6% in the CeO2 lattice with the degradation efficiency of 90.2%, before falling to 8%. This enhancement was attributed to the decrease in band gap because of Mg doping, which is dependent on the VO defects in the lattice [27]. La-doped CeO2 nanostructures with different doping concentrations of 2, 4, 6, and 8 mol% were prepared using the solvothermal method. The 4% La-doped sample showed enhanced photocatalytic activity than the other samples, as it degraded about 95% of RhB in 130 min under solar light due to the high concentration of VO and surface area [28]. A study explored the degradation of RB dye on UV irradiation using oxygen-deficient Gd doped CeO2 doped. They observed a rise in degradation with Gd3+ ion concentration, from 72.03% (CeGd0) to 92.32% (CeGd8), suggesting their potential significance in environmental applications [29]. Moreover, the environmentally friendly synthesis methods of CeO2 NPs have resulted in NPs with enhanced surface properties and superior catalytic performance [30,31].
1.3. Graphene and Its Derivatives for Photocatalysis
Graphene, a 2D lattice of carbon atoms organized in a honeycomb network, has drawn considerable interest since its discovery in 2004, owing to its remarkable properties [32]. It exhibit superior charge carrier mobility and exceptional electronic quality, outstanding mechanical strength, electrical conductivity (200,000 cm2V−1s−1), and thermal conductivity (~5000 Wm−1K−1) [33,34]. The theoretical specific surface area of a single graphene sheet is impressive (~2600 m2g−1), making it well-suited for a wide range of applications, including nanoelectronics, hydrogen storage, supercapacitors, and sensors [35,36,37,38]. Graphene oxide (GO), with its lattice defects, facilitates the nucleation and trapping of semiconductors. Its functional groups serve as nucleation sites, enabling control over various properties of semiconductor materials. When graphene is mixed with semiconductors, it improves the transport and acceptance of electrons. This helps in the formation of photogenerated electrons and slows down the e−-h+ pairs recombination in semiconductor materials [39]. Various techniques, such as chemical, electrochemical, thermal, and photochemical reduction pathways, can reduce GO to eliminate oxygen functional groups from its surfaces [40]. Reducing GO decreases its water dispersibility, stabilizing it in the body and reducing cytotoxicity [41]. rGO is biodegraded enzymatically, demonstrating enhanced biosafety and stability compared to GO in vivo [42].
However, graphene is prone to agglomeration because of Van der Waals interactions, hindering its widespread application. To address this limitation, graphene can be hybridized with NPs. While graphene offers immense potential, its susceptibility to oxidative environments remains a challenge when used alone as a catalyst as a result of its zero band gap nature [43]. Further, an efficient strategy to enhance the performance of semiconductor photocatalysts entails incorporating carbon-based materials into the composite, facilitating efficient electron transfer. To this end, 2D graphene, GO, and rGO have been utilized as superior support carriers for semiconductor materials [44,45]. In recent years, graphene-based nanocomposite photocatalysts have shown significant potential, as in composites with wide band gap semiconductors, graphene reduces the effective band gap of semiconductors, broadening their spectral absorption range [46]. In the case of Ag0.04ZrO2/rGO heterojunction, the band gap of Ag0.04ZrO2 was reduced from 3.11 eV to 2.99 eV [47]. Additionally, the inclusion of graphene efficiently increases the surface area, thereby improving semiconductor adsorption capacity. Additionally, the catalyst’s absorptivity increases due to the π−π interactions between the organic pollutant and the aromatic regions of graphene [48,49]. This increased adsorption capacity fosters more interfacial interaction between the photocatalyst and pollutant molecules [50]. Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that graphene and semiconductors act as stabilizers, preventing mutual aggregation and significantly enhancing semiconductor photocatalysts’ degradation performance [51].
Recently, significant attention has been directed toward the use of CeO2 and graphene-based materials in diverse fields especially in photocatalytic environmental remediation, as shown in Figure 3. The paradigm shifts towards CeO2/graphene-based photocatalyst composites underscores their potential to revolutionize photocatalytic applications, promising improved efficiency and efficacy in environmental remediation and other pertinent fields. This article attempts to review the recent advancements in CeO2/graphene-based photocatalysts and how they work better when exposed to UV or visible light. In CeO2/graphene-based systems, CeO2 act as a source of e−-h+ pairs on light irradiation while graphene has been selected for high pollutant adsorption and charge transportation that helps to improve the charge recombination. This review also provides an updated summary of the current state of these photocatalysts in different environmental cleanup processes, such as the nonselective breakdown of pollutants through photocatalytic water splitting for organic compounds from wastewater. Recent advancements in photocatalytic strategies involving CeO2 and graphene-based photocatalysts are also briefly reviewed. Additionally, this review summarizes the existing challenges and future directions for optimizing these photocatalysts such as the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) and the commercialization of photocatalysts.
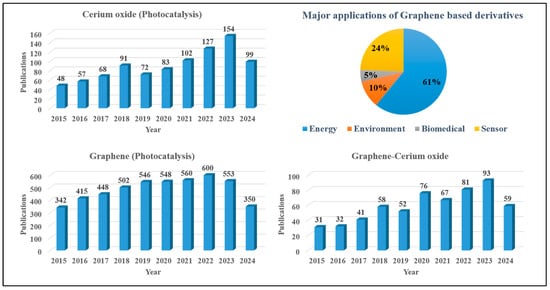
Figure 3.
Publications on CeO2 and graphene-based composites (as per Scopus data, keywords: cerium oxide and photocatalysis; graphene and photocatalysis; graphene and cerium oxide with various applications such as energy, environment, biomedical, and sensor).
2. Photocatalytic Wastewater Treatment Using CeO2-Graphene Oxide Based Composites
Graphene oxide is instrumental in enhancing the photocatalytic performance of CeO2 in wastewater treatment applications. CeO2, known for its economic viability and high efficiency compared to other semiconductor materials, benefits from its high surface area and variable morphology, which create favorable conditions for pollutant degradation. However, CeO2 faces limitations, such as a wide-band gap that restricts its absorption to ultraviolet light, and susceptibility to photocorrosion leading to cerium pollution over prolonged exposure [52]. Graphene, however, has a nearly zero bandgap, with the VB and CB being almost touching each other. Because of numerous functional groups and O-atoms on the graphene surface, semiconductor NPs can be well anchored on it [53]. CeO2/GO composites are prepared by incorporating the features of GO into the CeO2 structure. Lattice defects in GO help in nucleation and anchoring of semiconductors. This integration improves the electron transport and thus the generation of excited electrons and decreases the recombination of excitons [40].
Besides, attempts are made to narrow the CeO2 bandgap and enhance the charge transfer in visible light by creating heterojunctions with GO [54]. The change of Ce3+ to Ce4+ in CeO2 generates VO which facilitates the electron transfer process and enhances its photocatalytic activity. Thus, the synergistic effects of the CeO2/GO composites can be used to achieve effective and stable photocatalytic treatment of wastewater. The following are some of the recent research done on CeO2/GO for improved photocatalytic activity. GO/Fe3O4/CeO2 heterojunction photocatalyst facilitated the photodegradation of diazinon under visible light stimulation. The absorbance analysis disclosed bandgap values of 3.19, 3.08, and 2.98 eV, correspondingly, for GO, GO@Fe3O4, and GO@Fe3O4@CeO2. Investigation into crucial parameters such as pH (2 to 9), photocatalyst dosage (10 to 40 mg), and contact duration (0 to 180 min) was carried out. The highest observed diazinon degradation rate reached 97.9% within 60 min. These findings underscore the potential of the GO@Fe3O4@CeO2 nanocomposite as an effective photocatalyst for eliminating organic pollutants from water mediums [55]. In Figure 4A–F, the TEM images represent the nano-sized spherical morphology of CeO2 and their decoration on 2D GO in GO@CeO2 nanocomposite. The impact of light on GO nanocomposites incorporating biosynthesized CeO2 NPs on the adsorption and photodegradation of AO, CV, and MB from aqueous solutions were studied using a GO@CeO2 nanocomposite, as presented in Figure 4G. When exposed to visible light as opposed to complete darkness, it was found that both the adsorption and photodegradation processes proceeded noticeably more quickly and effectively. In just 90 min, the GO@CeO2 composite demonstrated the capacity to eliminate 87% of AO, 91.81% of MB, and 85% of CV. While photodegradation under visible light showed higher efficiency, adsorption alone proved ineffective against AO, CV, and MB [56]. The enhanced photocatalytic efficiency of the GO@CeO2 composite for CV, MB, and AO degradation is attributed to the synergistic effects of electrostatic interactions, reactant entrapment, and photogenerated electron-hole pairs. Factors such as graphene’s high surface area, excellent structure, and superior charge carrier dynamics further contribute to its remarkable performance.
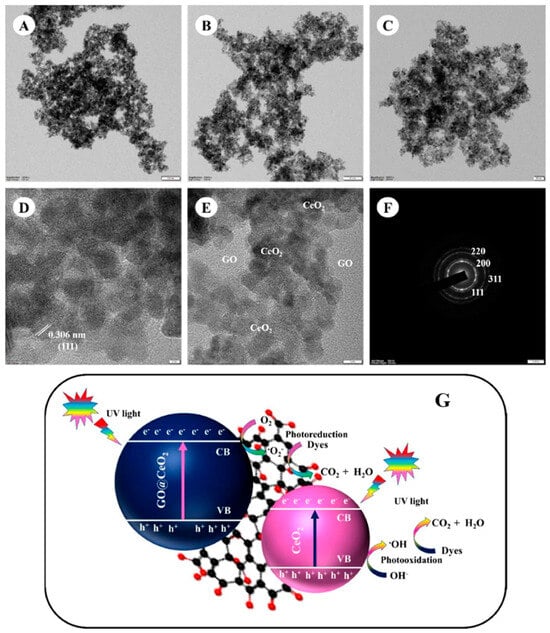
Figure 4.
(A–F) HRTEM images of CeO2 decorated GO (representing morphology and crystallinity of CeO2 and GO), and (G) photocatalytic mechanism of GO@CeO2 nanocomposites [56]. Reprinted with permission ©Elsevier (License Number: 5958020518301).
Figure 5 represents the CeO2 nanoparticles, structures of N-GO sheets, composites of CeO2/g-C3N4 and crystalline planes in HRTEM images of composites. Optimized composite sample displayed outstanding degradation performance, achieving a close to 100% degradation of MBT with remarkable stability and recyclability. The catalyst outperformed g-C3N4 by approximately eight times and CeO2 by two times. Strong interfacial electric fields (IEF) and the S-scheme heterostructure of the photocatalyst enhance its performance by improving the redox capabilities of the photogenerated e−-h+. Moreover, the catalyst’s ability to convert Ce4+ to Ce3+ ensures effective use of these charge carriers. Further, inclusion of N-GO aids in electron transfer across the interfaces between CeO2 and g-C3N4, thus boosting e−-h+ separation efficiency. Figure 5j illustrates the schematic for the breakdown of the pollutant by two possible pathways along with various intermediates. This study presented deep insights into the transportation of charges across multiple interfaces during photocatalysis, as illustrated in Figure 5g–m, and elucidates the mechanisms of degradation and charge transfer [57].
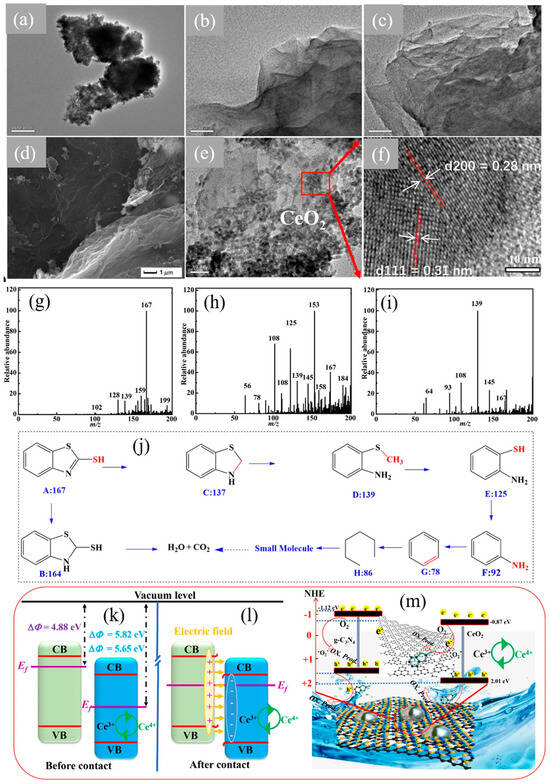
Figure 5.
TEM images of (a) CeO2 nanoparticles, (b) layered N-GO, and (c) g-C3N4. The (d) SEM, (e) TEM, and (f) HR-TEM images of CeO2@N-GO/g-C3N4; m/z of MBT (g) initial solution, (h) after 60 min, (i) after 120 min, (j) various intermediates during MBT removal; charge transfer mechanism in CeO2 and g-C3N4 (k) before and (l) after contact, and (m) schematic for proposed degradation mechanism [57]. Reprinted with permission ©2023 Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences (License Number: 5958120074450).
The CeO2 NPs synthesized via facile sol-gel method, subsequently decorating them onto MWCNTs and GO to form binary and ternary composites using ultrasonication, termed as 2GO-5CNT exhibited exceptional photocatalytic efficiency, achieving up to 96.9% degradation of RB dye within 50 min. They emphasized the role of GO in delocalizing photogenerated e− through its π-network enhanced recombination time, while CNTs increased spacing between GO nanosheets, inhibiting their aggregation and enhancing the number of active sites for photocatalysis. By leveraging these mechanisms, CeO2 NPs were effectively decorated on CNTs and GO to form semiconductor heterojunctions. This configuration potentially increases the recombination time of excitons, thereby enhancing photodegradation performance [58].
Researchers conducted a study wherein they utilized hydrothermal techniques to fabricate a crystalline GO-supported In2O3/CeO2 ternary nanocomposite (CIG), confirmed by the SEM images, HR-TEM images, and SAED pattern depicted in Figure 6a–e. In and Ce are well dispersed over the GO nanosheets as confirmed by the EDS spectra in Figure 6f. This composite was evaluated for its photocatalytic efficacy in degrading two textile dyes, CR and MB under visible light exposure. It demonstrated an enhancement in photocatalytic performance of both CR and MB dye upon decorating the conjugated network of GO with the redox-active binary nanocomposite (Figure 6g–j). Notably, MB reached 95% degradation within 91 min, while CR exhibited a peak degradation of 94% within 130 min. Enhanced degradation was due to reduced charge recombination, increased band gap, and enhanced absorption of light due to GO coupling. Mechanistically, high ROS, particularly hydroxide radicals, mineralized the pollutants (Figure 6k). The photocatalyst’s stability was confirmed by cycling experiments across multiple cycles [59].
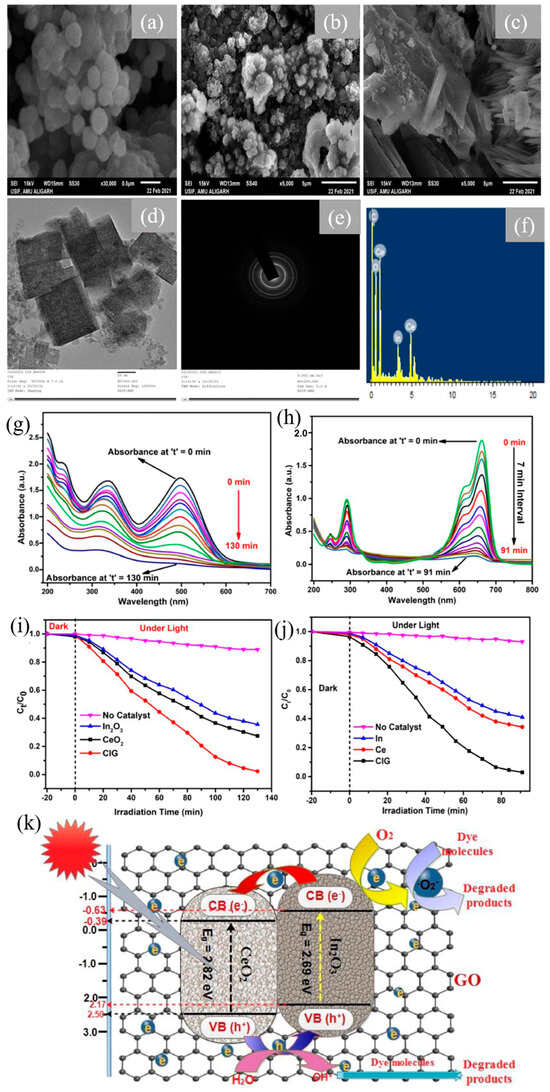
Figure 6.
SEM micrographs of (a) CeO2, (b) In2O3, (c) CIG, and (d) TEM image of CIG; (e) SAED pattern and (f) EDS spectra of CIG nanocomposites; absorbance spectra of (g) CR and (h) MB using CIG nanocomposite; decomposition of (i) CR dye and (j) MB dye using synthesized catalysts; and (k) proposed mechanism of dye photodegradation [59]. Reprinted with permission ©Elsevier (License Number: 5958111413790).
GO@Fe3O4 combined with CeO2 NPs with a charge separation of 3.17 eV were studied for the photocatalytic degradation of DOX and TMX in visible light. The photocatalytic study also investigated the effects of pH (3 to 10) and photocatalyst dosage. The results depict that TMX and DOX showed 97% and 98% degradation in 60 and 90 min, respectively, using the ternary photocatalyst [60]. Nanocomposites of GO/CeO2 with varying GO content were synthesized using a biogenic approach. Degradation efficiency of GO/CeO2 for MO dye (100 ppm), in visible light, indicated that the optimal nanocomposite was GO(30%)-CeO2, achieving a photocatalytic degradation efficiency of 93% [61]. Free-radical polymerization of acrylamide using CeO2 NPs and GO in an aqueous system created the synthesized ternary composite, which consists of CeO2 NPs, GO, and PAM. The photocatalytic process was pH-dependent, with an optimum pH value of 12 showed 90% MB degradation in 90 min. The equilibrium data showed an excellent rate constant (0.0259 min⁻1). Additionally, it was observed that photocatalytic activity decreased to only 75% after nine uses, indicating promising reusability potential [8]. A study demonstrated the effective degradation of the dye DOX through a synergistic combination of adsorption and photocatalysis using GO–CeO2 nanocomposites. Figure 7a–c represents the morphology of the synthesized CeO2 and the histogram shows the average particle size of 7–11 nm in Figure 7d. Figure 7e,g showed the SEM images for GO–CeO2 nanocomposites and CeO2 particles with their corresponding EDS spectra confirming elemental composition in Figure 7f,h, respectively. The synthesized nanocomposites exhibited high crystallinity and superior photocatalytic activity. The effect of different pH conditions on the adsorption of dye and photocatalytic degradation efficiency over the photocatalysts is shown in Figure 7i–l. Under neutral and alkaline conditions, a remarkable 97% removal of DOX was achieved within 360 min. Importantly, the nanocomposites showed excellent stability and recyclability, maintaining a high removal efficiency even after multiple cycles. The synergic effect of adsorption and photocatalysis results in higher removal of DOX over the composite, which is illustrated in Figure 7m via schematic diagram. High-performance liquid chromatography analysis confirmed a 99.8% removal efficiency, indicating complete eradication of DOX (Figure 7n). This eco-friendly approach presents a promising method for dye degradation in wastewater treatment, offering potential applications in environmental remediation [62].
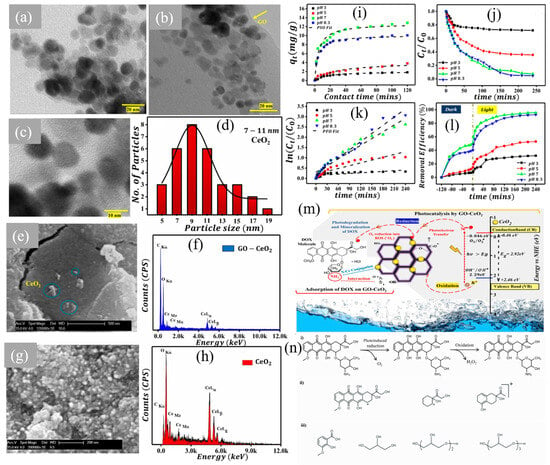
Figure 7.
HR-TEM of (a) CeO2 NPs, (b,c) GO-CeO2 nanocomposites, (d) distribution of CeO2 particle size, (e) SEM image, and (f) EDS of GO−CeO2, (g) SEM micrograph, and (h) EDS of CeO2, (i) adsorption kinetic, (j) relative degradation, (k) linear fitting of ln(Ct/C0), (l) % degradation of DOX using GO-CeO2 at various pH, and (m) schematic presentation of DOX degradation. The DOX adsorption on GO-CeO2 surface is depicted on the left side ascribed to the conjugation between the N and Ce atoms of DOX and GO-CeO2, respectively, or to the electrostatic interaction between (−NH3+) and the functional groups of DOX and GO, respectively. (n) The pathway of DOX photodegradation following adsorption and exposure to light is depicted on the right side. The e−-h+ pair significantly degrades the DOX via redox reaction supported by the interfacial charge transfer. Additionally, the DOX photocatalytic reaction in aqueous conditions produces H2O2 (i), photodegraded products (ii), and mineralized products [62]. Reprinted with permission ©2021 Elsevier (License Number: 5958120574597).
GO-ZnO@CeO2 nanohybrids synthesized via the hydrothermal method demonstrated promising results in the photocatalytic removal of organic dyes [63]. HR-TEM images (Figure 8a–c) exhibit a ultrathin 2D layered structure with well-dispersed ZnO and CeO2 nanoparticles over GO nanosheets. The SAED pattern (Figure 8d) confirms high crystallinity of the nanohybrids with corresponding crystallographic planes from ZnO and CeO2 nanoparticles. The unique nanohybrids facilitated enhanced interfacial contact and efficient utilization of semiconducting materials. This resulted in a remarkable 96.66% degradation efficiency of MB dye, surpassing the performance of individual GO-ZnO nanostructures and CeO2 NPs (Figure 8e,f). This enhancement was attributed to the thin layers of ternary nanohybrids, which promote interfacial transport and a high surface area, all of which are favorable for improving photocatalytic performance, as illustrated by Figure 8g [63].
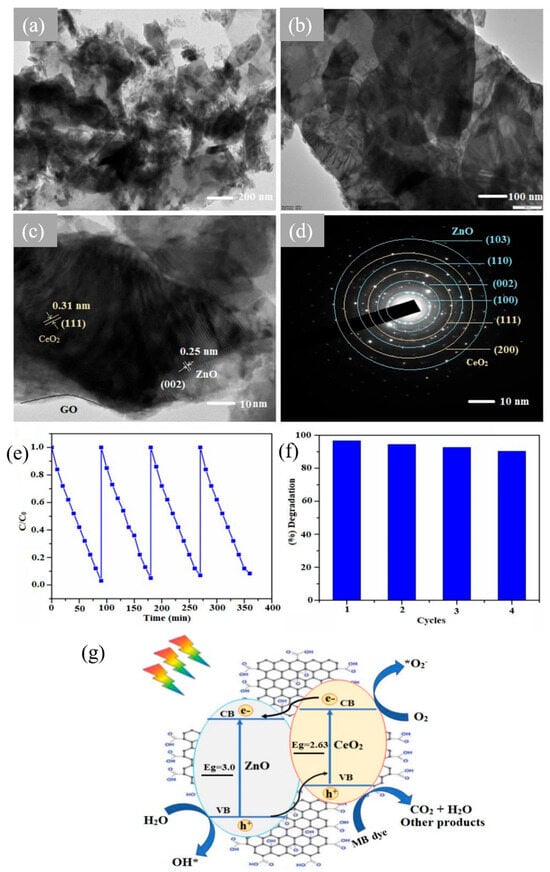
Figure 8.
(a–c) HR-TEM images of GO-ZnO@CeO2 composites and (d) SAED pattern; (e) stability, (f) recyclability, and (g) schematic mechanism using GO-ZnO@CeO2 [63]. Reprinted with CC BY 4.0.
A range of CeO2-GO composites was evaluated for their efficacy towards the photocatalytic removal of MB under visible light and showed that the composite with a weight ratio of 5 wt% had much better photocatalytic activity than pure CeO2. The optimal weight ratio of GO to CeO2 reduced the CeO2 NPs’ size and expanded the surface area, facilitating efficient separation of excitons and thereby improving photocatalytic performance. Importantly, a direct relationship was observed between the electrocatalytic and photocatalytic efficiency of CeO2-GO for MB degradation [64]. Kashinath et al. described the formation of CeO2-GO hybrid nanocomposites via a chemical method, followed by treatment with microwave irradiation while omitting surfactants or organic solvents. The investigation focused on in situ hexagonal CeO2 on the layered GO sheets for their efficacy in BY dye and removing chromium ions. It was revealed that hybrid nanocomposites exhibited a five-fold enhancement in photocatalytic activity under UV illumination and demonstrated superior efficacy in chromium ion elimination compared to pure GO and CeO2 counterparts. This improvement was attributed to proficient photosensitive electron inoculation and control over e−-h+ recombination processes [65]. In another experimental study, GO/CeO2 were investigated and elucidated the photocatalytic mechanism associated with this composite. A notable enhancement was observed in the efficiency of GO/CeO2 in degrading MO, with the degradation rate improving from 50% to 87% within 120 min under visible light, as compared to bare CeO2 [66].
Channei et al. conducted a study wherein they synthesized GO and CeO2/GO composites and the investigation revealed that under visible light, the degradation efficiency of CeO2/GO nanocomposites was twice that of pure CeO2 in photocatalytic degradation of MB. The increment in photocatalytic performance was ascribed to excellent charge transportation, as well as enhanced absorptivity [67]. Later, a nanocomposite photocatalyst composed of NaLuF4:Gd,Yb,Tm@SiO2@CeO2 graphene, leveraged a synergistic effect to enhance the photocatalytic performance of CeO2. The RhB degradation on sunlight irradiation revealed the markedly improved photocatalytic performance of the synthesized nanocomposite than pristine CeO2. Several factors contribute to this enhancement, including the expansion of the light-responsive range, the red-shifted absorption edge, improved e−-h+ pair separation in CeO2, and increased dye adsorption due to upconversion nanocrystals, graphene, and Tm-doping [68]. Huang and his team synthesized CuO-CeO2/GO nanocomposite photocatalyst possessing a notable photocatalytic activity. The photodegradation efficiencies of CuO, CuO/GO, and CuO-CeO2/GO were determined to be 65.7%, 79.8%, and 97.8%, respectively, after 150 min of irradiation. This enhancement in CuO-CeO2/GO composite is attributed to its improved capacity for visible light absorption, higher surface area, and efficient separation of photoexcited e−-h+ pairs [69]. In summary, the photocatalytic enhancement for the treatment of wastewater is attained with the help of the incorporation of GO with CeO2 nanoparticles. This combination addresses challenges of CeO2, such as a large band gap and photocorrosion. Thus, CeO2/GO composites enhance the electron transport and decrease the rate of recombination and charge transfer thus increasing degradation efficiencies under visible light. These composites have improved structural strength, reusability, and active surface area, which improves their performance in the degradation of the various pollutants.
3. Photocatalytic Wastewater Treatment Using CeO2-rGO Based Composites
The incorporation of rGO along with CeO2 is an excellent addition for photocatalytic application in wastewater treatment. CeO2, which is distinguished by its chemical inactivity and the capacity to control the oxidation state to produce VO, is the key component in this composite system. These VO, importantly, control the proportion of Ce4+ and Ce3+ ions in CeO2. The change of these ions leads to the decrease of CeO2 bandgap, which enhances its photocatalytic activity in the visible light range [70]. Furthermore, VO in CeO2 are reactive and help in the interaction with graphene [71]. This synergistic coupling improves the composite’s catalytic performance. The rGO with its structural and chemical properties enhances the photocatalytic efficiency of the composite additionally. This makes it have a large surface area to support the catalytic reactions while at the same time being chemically stable to support the required functionality for a long time. Additionally, rGO has a high electron mobility, which enhances charge transfer in photocatalysis processes. For instance, rGO also plays the role of a good electron acceptor that helps in separating and utilizing photogenerated charge carriers [72,73]. Thus, the synergistic effects of rGO and CeO2 lead to enhanced degradation using composites as compared to the bare materials. This improved performance has enormous potential for efficient wastewater treatment [74]. The latest research on the CeO2/rGO composites showed higher efficiency in photocatalysis. The morphology of the synthesized samples and elemental confirmation have been shown in Figure 9a–e. The HRTEM image (Figure 9d) of CeO2 represents the highly crystalline behavior and dominating crystal planes. Subsequent section will delve into research endeavors discussing these developments. N-doped rGO-CeO2 photocatalysts were synthesized which displayed remarkable efficiency in degrading various organic dyes. It exhibited the highest photocatalytic degradation of 77.43% for TC. They claimed that incorporating rGO and N doping facilitated effective photoexcited e− and h+ separation, and improved charge transfer rates. The composites are endowed with anti-H+ capability in TC degradation, promoting increased generation of ·O2− under light exposure. In addition, N doping added a level of 2p impurity to CeO2, which made the rGO surface have more reactive sites (Figure 9f–j). They concluded that the N-doped rGO-CeO2 photocatalyst holds significant potential for wastewater treatment [75].
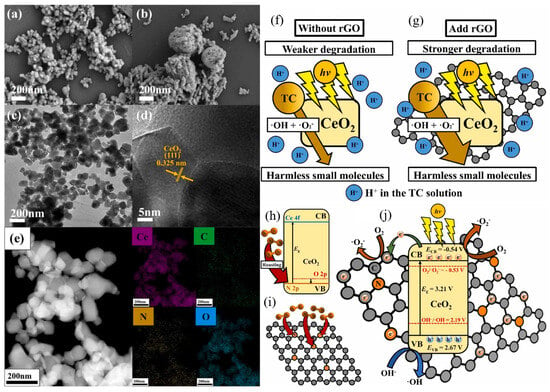
Figure 9.
SEM images of (a) rGO-CeO2-900N2 and (b) CeO2-900N2; (c) TEM, (d) HRTEM image, and (e) EDX mapping of rGO-CeO2-900N2; schematic photocatalytic mechanism: (f) CeO2-900N2; (g) rGO-CeO2-900N2, (h) N doped CeO2, (i) N doped rGO, and (j) rGO in the N doped rGO-CeO2 samples [75]. Reprinted with permission ©2024 Elsevier (License Number: 5958120829233).
A photocatalytic system combining CeO2-V2O5 with rGO demonstrated the degradation of CTX under visible light. Optimal conditions were determined to be a catalyst dosage of 1 g/L and pH 6, resulting in an approximate 99% CTX decomposition in 150 min under visible light. Under sunlight, the catalyst exhibited a CTX removal rate of 88.1% after 250 min. When exposed to real sunlight conditions, the photocatalytic efficiency was influenced by sunlight intensity, yet maintained high CTX photodegradation yields, though slightly lower COD removal efficiency compared to color measurement, possibly due to the formation of intermediates. Furthermore, the CeO2-V2O5/rGO system exhibited excellent reusability for CTX degradation under visible light [76]. The synthesized Ag@CeO2/rGO catalyst showed enhanced photocatalytic activity over bare CeO2 towards MB dye and achieved 100% degradation in 60 min. The degradation process obeyed first-order kinetics and a reaction rate constant of 0.0198 min⁻1 [77]. Khan et al. prepared CeO2 and rGO/CeO2 nanocomposites using the hydrothermal method in one step. The nanocomposites showed enhancement in the degradation of RhB under 100 min of sunlight. This enhancement was due to a strong reduction in the recombination of excitons, electron transport through the rGO sheets and a decrease in the bandgap of nanocomposite. Due to the beneficial characteristics mentioned for the rGO/CeO2 nanocomposite, it has potential application in contaminant removal from the environment [78]. Sun et al. fabricated CeO2@rGO nanocomposites by controlling the functional groups’ density on rGO using surface hydrothermal method and calcination. In situ TEM analysis was employed to study the growth process of CeO2 NPs on rGO. They claimed that this new strategy provided better control over the size, dispersion, and VO of CeO2 NPs on rGO sheets compared to the one-step hydrothermal method. The prepared composites displayed excellent adsorption and photocatalytic efficiency of RhB and MO dyes, ascribed to abundant active sites and electron-donating capabilities of CeO2 and rGO [79].
The magnetic heterostructured composite of g-C3N4/CeO2/M-rGO revealed that the multi-interface contacts were formed which enhanced the electron photogeneration and transport in the composite. In addition, the Ce4+ → Ce3+ redox transformation made it easy to separate the photogenerated excitons, thus increasing the photodegradation efficiency of Estrone and CR. Therefore, the degradation of Estrone and CR were determined to be 74% and 91%, respectively. Notably, the synthesized g-C3N4/CeO2/M-rGO composite demonstrated remarkable photocatalytic performance and excellent reusability over four consecutive cycles [80]. In a study, hydrothermal technique was employed to produce ternary ZnIn2S4–rGO–CeO2 composites. When exposed to solar irradiation, the composite photocatalyst demonstrated superior performance in removing tetracycline compared to both bare and binary photocatalysts. The ternary composites achieved the highest degradation rate of TC under solar irradiation, reaching 94.5%, surpassing that of the bare catalysts. This enhancement in photocatalytic degradation is attributed to the substantial reduction in photon-induced charge recombination [81]. Gomathi et al. introduced a ternary CeO2/Fe2O3/r-GO composite for the decomposition of MB and MO dyes. Remarkably, the hybrid catalysts achieved 90% and 86% degradation of MO and MB dyes, respectively, under UV illumination, and the mechanism has been presented in Figure 10. The mechanism represents the charge transfer mechanism between CeO2 and Fe2O3, and the electrons adsorbed on the surface of rGO nanosheets, which ultimately enhanced the recombination time of excitons. Furthermore, the composite was successfully recycled for five cycles. The enhancement in photocatalytic results was because of the synergistic effects of the heterojunctions at the interface [82].
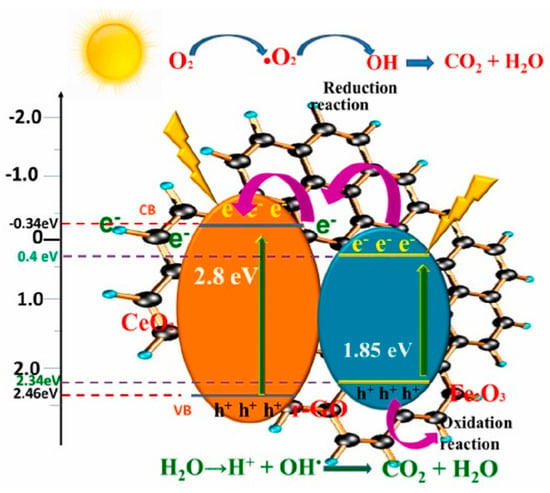
Figure 10.
Proposed photocatalytic mechanism for degradation of dyes using CeO2/Fe2O3/r-GO composites [82]. Reprinted with permission ©2023 Elsevier (License Number: 5958121017798).
The Fe3+/Gd3+-CeO2@rGO nano-hybrid named FGC@rGO was synthesized for the degradation of CV dye in visible light. These catalysts showed superior photocatalytic performance compared to Fe3+/Gd3+-CeO2 (FGC) NPs. Specifically, FGC@rGO achieved nearly 94% degradation of CV within 40 min, whereas FGC accomplished only 77% degradation. This enhancement in FGC@rGO was attributed to the presence of Fe and Gd dopants, along with rGO, which prolonged the lifetime of photo-induced e−-h+ pairs and facilitated rapid charge transfer across the interface [83].
The research highlighted the sonochemical method to fabricate rGO/Ag3PO4/CeO2 nanocomposites and exhibited excellent photocatalytic decomposition of MB dye in sunlight. The improved degradation rate was due to fast electron transfer to rGO nanosheets which reduced e−-h+ recombination. The presence of Ag3PO4 and CeO2 improved the efficiency and stability of the photocatalyst even more. The MB dye degradation rate was enhanced with optimized photocatalyst concentration, pH, and temperature. In particular, at 400 mg/L dosage, rGO/Ag3PO4/CeO2 nanocomposite prepared by ultrasonication, MB dye was almost completely degraded under certain circumstances. Furthermore, 99.2% of MB dye decolorizations was noted after 20 min of exposure at a reaction temperature of 55 °C. Additionally, an ANN model was used to predict MB dye degradation under different conditions with high accuracy [74]. CeO2/CdS/rGO photocatalysts with multifunctional properties were evaluated for the photodegradation and photoreduction processes. It showed high activity for CIP with degradation efficiency of 90.04% obtained in sunlight for 120 min. However, CeO2/CdS/rGO8 showed excellent photocatalytic activity in the photoreduction of Cr(VI) to Cr(III) within 60 min of simulated sunlight exposure. In addition, the photocatalyst possessed high efficiency in degrading different pollutants: RhB-89.24%, NFX-89.18%, MV-100%, MB-92.36%, TC-87.05%, MO-75.02%, and RB-72.31%. This was due to the effective reduction of the composite’s bandgap through the CeO2-CdS heterostructure, which minimizes the recombination of excitons. Additionally, Figure 11 showcased that the loading of CeO2/CdS onto rGO facilitated better dispersion of active components and provided an alternative pathway for electron transmission, enhancing pollutant adsorption capability and extending the lifetime of photogenerated charges. Moreover, cyclic experiments and structural characterization confirmed the good reusability and structural stability of CeO2/CdS/rGO [84].
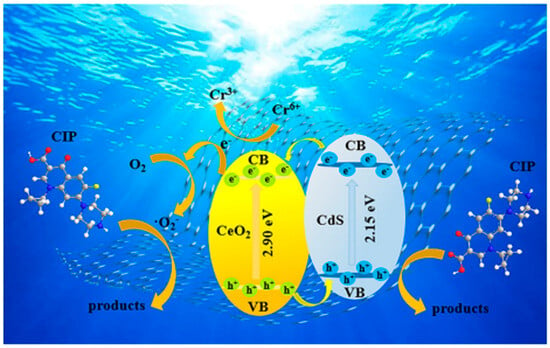
Figure 11.
The mechanism for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using CeO2/CdS/RGO composites [84]. Reprinted with permission ©2021 Elsevier (License Number: 5960611094544).
The ternary ZnO/CeO2/rGO nanocomposites were fabricated with different ZnO/CeO2 weight proportions. Among these composite materials, ZCG3 (ZnO/CeO2 = (85:15) effectively suppressed the recombination rate of charge carriers and facilitated electron transfer from the CB of CeO2 and ZnO to rGO. This resulted in enhanced MB degradation with a rate constant of 0.0201 min−1. Surface defects, such as VO and Ce3+ ions, reduce recombination sites, thereby extending the lifetime of excitons. The combined influence of Ce3+ ions and surface VO, along with the function of rGO as an electron acceptor, enhanced charge carrier, and transportation. This also promoted the formation of Schottky-type junctions and an electric field (internal) [85]. Garg et al. utilized CeO2 anchored onto rGO surfaces for the efficient degradation of pollutants under sunlight. In another report, CeO2@rGO broke down MB (about 92%) and CR (about 83%) better than pure CeO2 at the same concentration (2 mg). Further, the CeO2@rGO was incorporated into polymer hydrogel derived from tragacanth. The resulting hydrogel composite (CeO2@rGO-TG) demonstrated degradation of MB approximately 91%, utilizing only half of CeO2@rGO amount. Crucially, the dye solution could easily separate CeO2@rGO-TG, allowing for multiple degradation cycles [86]. Another study evaluated the photocatalytic efficiency of CeO2/rGO nanocomposite by reducing 4-nitroaniline to p-phenylenediamine under visible light exposure. The CeO2 photocatalyst, containing 5 wt% rGO, demonstrated the best efficiency among the prepared photocatalysts [87]. The ternary PS/rGO@CeO2 nanocomposites exhibited high efficiency in degrading MB dye. Various factors contributed to the improved performance, including the elevated surface area, increased MB adsorption facilitated by the electron interaction among the aromatic regions of rGO and MB, which resulted in higher local MB concentration around the photocatalyst, and the transfer of charges between CeO2 NPs and rGO, which suppressed the recombination of excitons. Additionally, these nanocomposite particles were highly stable and recyclable [88].
In a previous report, Seeharaj et al. (2019) successfully prepared photocatalysts by combining surface modified TiO2 NPs with rGO and CeO2. The TiO2/rGO/CeO2 photocatalysts demonstrated improved performance, generating methanol at 641 μmol/gcath and ethanol at 271 μmol/gcath. This significant increase in CO2 photoconversion efficiency is primarily ascribed to the increased interfacial contact area and robust connection between the reactively delaminated TiO2 nanosheets, rGO, and CeO2. These things made it easier for a lot of photogenerated charge carriers to move through and react with absorbed species. The heterojunction effect also helped with multiple steps of charge transportation, which stopped the recombination of e− and h+ [89]. Hybrid hierarchical flower-like nanostructure (HFNs) and rGO–CeO2 NPs were prepared via solvothermal and hydrothermal techniques, respectively. The rGO–CeO2-HFNs were characterized by the twining of CeO2-HFNs with rGO, while CeO2-NPs were dispersed uniformly on rGO in the case of rGO–CeO2-NPs. The observed reduction in band gaps was because of the synergistic effects of CeO2 and rGO. When compared to CeO2 HFNs (73%) and CeO2 NPs (67%), the photodegradation rate of MB was notably enhanced with rGO–CeO2-HFNs (96%) compared to rGO–CeO2-NPs (88%). This enhancement was primarily ascribed to efficient separation of excitons and large surface area exhibited by rGO–CeO2-HFNs [90].
A systematic investigation was conducted to thoroughly examine the structural, morphological, and optical properties of the prepared nanocomposites. This analysis established a correlation that confirms the superior photocatalytic efficiency of hydrothermally developed rGO-CeO2 composites. It is worth mentioning that the synthesized nanocomposites showed an excellent degradation rate (72% vs. 35%) when the MB dye was broken down in direct sunlight. The presence of rGO aided the enhanced separation of e−-h+ pairs and superior adsorption, leading to this notable improvement [54]. Priyadharsan et al. synthesized the ternary photocatalyst, CeO2/SnO2/rGO (CSG), through a hydrothermal process, with smaller particle size and uniform distribution as depicted in Figure 12a–c. The corresponding HR-TEM images and SAED pattern of composites depict high crystallinity for CeO2, SnO2, and their coordination with rGO (Figure 12d–f). The resulting CSG nanocomposites were employed for degrading MB under solar irradiation. The CSG catalyst achieved a remarkable 95% removal of MB within 90 min, showcasing the synergistic effect between the CeO2/rGO and SnO2/rGO binary composites (Figure 12g,h). The shape and size of the photocatalysts were depicted using TEM images. The particle size distribution of composites is displayed in Figure 12d and the crystalline properties in Figure 12e,f. The electrons transfer from CB of CeO2 to rGO and CB of SnO2, thus enhancing the recombination time of excitons. This enhancement in photocatalytic performance was attributed to increased light absorption intensity, reduction in bandgap facilitating electron transfer, scavenging of reactive species, and extended lifespan of photogenerated charge carriers, as presented in Figure 12i,j [91].
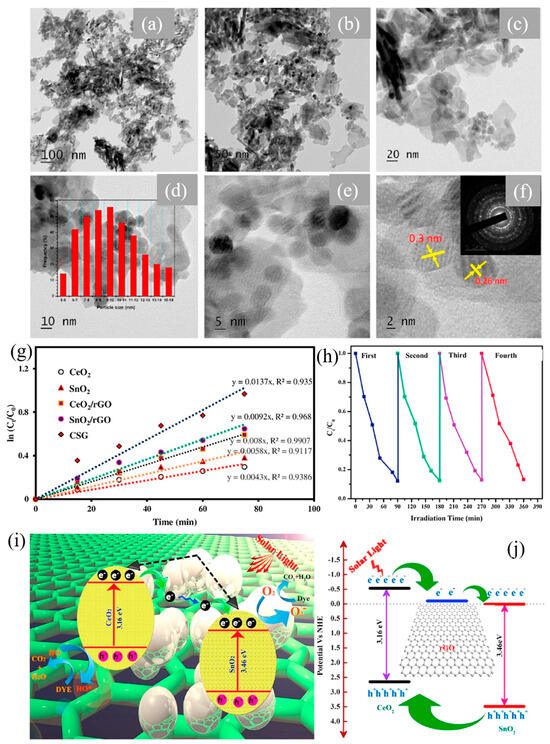
Figure 12.
(a–f) HR-TEM images, (d) particle size distribution (middle), and (f) SAED patterns (right corner) of CSG composites, (g) kinetic MB removal by synthesized catalysts, (h) stability of CSG, (i,j) charge transfer in CSG composites in the presence of light [91]. Reprinted with permission © 2017 Elsevier (License Number: 5958121291661).
A range of La2CuO4/CeO2/rGO hybrid nanocomposites (Figure 13a–f) demonstrated excellent photocatalytic efficacy against the organic dye RB160. Consequently, the ternary photocatalyst attained degradation of over 95.7% of the organic dye within 150 min. The decomposition of RB160 dye within the La2CuO4/CeO2/rGO system followed pseudo-first-order kinetics, and a significant increase in rate constant as compared to binary and pure samples. The photodegradation using the ternary composites was greatly improved when La-based perovskite-type material was added. This is because it absorbs visible light better [92]. In another study, the photocatalytic performance of CeO2 NPs and the rGO-CeO2 composite was evaluated by MB dye degradation under sunlight. Figure 13a–c represents the TEM micrograph (with the SAED pattern inset), their HRTEM image showing the crystalline behavior, and a histogram for the particle size distribution of CeO2 NPs, respectively. The average particle size was determined to be 9.6 ± 1.4 nm. Figure 13d–h showed the HRTEM image of rGO, TEM image of rGO-CeO2 composite, HRTEM image of the rGO-CeO2 nanocomposite (with the SAED pattern displayed inset), and a zoom HRTEM image of the CeO2 nanoparticle formed on rGO (and the original HR-TEM picture of the CeO2 nanoparticle formed on rGO are shown in the inset) and the particle size distribution of rGO-CeO2 nanocomposite, respectively. The findings showed that the rGO-CeO2 composite had better photocatalytic activity than CeO2 NPs and broke down 90% of the MB dye in 10 min of being exposed to sunlight (Figure 13i–l). The e−-h+ pairs are produced by CeO2 and e− transport on the GO surface due to their high electrical conductivity, rather than recombining with h+ in the VB. The star (in Figure 13m) indicates the defect energy states that are responsible for reducing the effective band gap of the material. Thus, the enhanced activity was attributed to a substantial reduction in e−-h+ pairs recombination, facilitated by charge transportation between rGO and CeO2, as well as the reduced band gap observed in rGO-CeO2, as shown in Figure 13m [93].
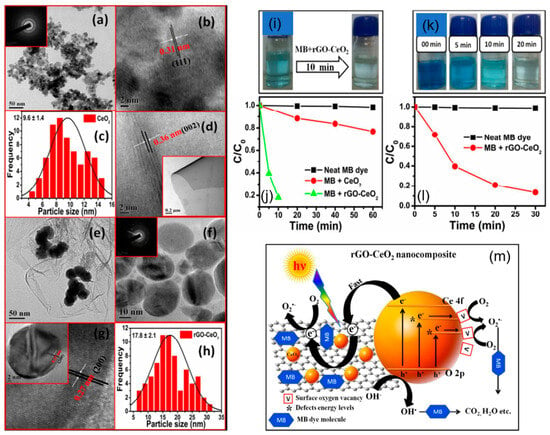
Figure 13.
The following images depict CeO2 NPs: (a) TEM micrograph (with the SAED pattern inset), (b) HRTEM picture, and (c) particle size distribution of CeO2 NPs. (d) HR-TEM images of rGO, (e) TEM image of the rGO-CeO2 composite, (f) a high-resolution TEM image of the rGO-CeO2 nanocomposite (with the SAED pattern displayed inset), and (g) a zoom HR-TEM image of the CeO2 nanoparticle formed on rGO (and the original HR-TEM picture of the CeO2 nanoparticle formed on rGO are shown in the inset). (h) The particle size distribution of rGO-CeO2 nanocomposite. (i) The rGO-CeO2 catalyst for the degradation of MB dye at low concentration (1 mg/L). (j) Photodegradation of a solution containing only MB dye, MB dye with CeO2 NPs, and MB dye with rGO-CeO2 composite, for 1 mg/L dye concentration with time; (k) MB dye decomposition at a higher concentration (5 mg/L) using rGO-CeO2 catalyst; (l) photodegradation of MB dye using rGO-CeO2 composite for 5 mg/L dye concentration with time; and (m) a schematic illustration of a potential mechanism leading to the photodegradation of MB dye in the presence of rGO-CeO2 composite under solar irradiation [93]. Reprinted with permission © RSC (License ID: 1573508-1).
A green synthetic method to self-assemble CeO2-rGO aerogels was analyzed for their photocatalytic degradation performance in the presence of simulated solar light, employing RhB. The degradation rate of RhB notably increased with CeO2/rGO aerogels; after 120 min of light exposure, 85% of the RhB dye had degraded, a significant improvement compared to pure CeO2 nanostructures attributed to better charge transfer from CeO2 to rGO sheets [94]. A study presented the in situ CeO2-grafted graphene where the concentration of CeO2 was manipulated instead of graphene. The improvement in photocatalytic activity is due to the enhanced dye adsorption capacity, longer photosorption time, and better charge transportation. From the investigation, it was noted that the photoactivity of the composite depended on the CeO2/rGO ratio and the 2:1 composite had a better performance compared to pure CeO2. These findings provide quantitative validation of the previously proposed idea about the importance of the graphene–CeO2 interface for charge separation, and the importance of CeO2 content in the material [95]. Wang and his group synthesized a ternary composite of CeO2 nanorods, g-C3N4, and N-rGO using the ultrasonic heat treatment method and the photocatalytic activity of the synthesized composite was higher than other composites. Among the mixtures that were tested, CeO2 nanorods/(g-C3N4/0.25% N-rGO) at the concentration of 2% was the most efficient in the degradation of RhB. These are: improved charge separation of photogenerated excitons due to enhanced electrical conductivity of N-rGO, increased visible light absorption and surface area. Moreover, the N-rGO enhanced the active adsorption sites and allowed dissolved oxygen to be activated during the degradation process. In addition, the ternary composite showed high stability and reusability even after five cycles [35]. Moreover, highly uniform CeO2 hollow nanospheres (CeO2HS) were also prepared and then anchored on rGO. The CeO2HS/rGO hybrid thus displayed enhanced photocatalytic activity over MO. After 50 min of UV irradiation, the decomposition of MO was 97% for CeO2HS/rGO, which indicates that CeO2HS/rGO has the possibility of being used as a highly efficient and stable photocatalyst in the process of photocatalytic dye degradation [96]. Therefore, it can be summarized that the inclusion of rGO with CeO2 improves photocatalytic activity. The combined effect of CeO2 and rGO enhances the charge trapping, slows down the recombination processes, and enhances the electron transfer process thereby enhancing the degradation of various pollutants. The results for the degradation of different pollutants using GO based photocatalysts is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Photocatalytic degradation of various dyes using CeO2-graphene derivatives based catalysts.
The novel composites of rGO–CeO2 nanocubes (NCs) are prepared by hydrothermal method; the CeO2 NCs are well dispersed on the rGO sheets. Further, CeO2 nanowires (NWs) and rGO–CeO2 NWs were synthesized and used as reference photocatalysts. Photocatalytic tests showed that CeO2 NCs were better photocatalysts than CeO2 NWs due to the reduced band gap. In addition, the rGO–CeO2 NCs composites show higher activity than both pure CeO2 NCs and rGO–CeO2 NWs for the degradation of MB dye. This enhancement in photocatalytic activity was attributed to the strong ability to reduce the photogenerated e−-h+ pair recombination due to the incorporation of rGO [97]. CeO2 NPs supported on rGO through two distinct methods: The formation of the nanostructures is carried out through in situ growth and a self-assembly method. The findings indicated that the self-assembly method enables one to synthesize CeO2 NPs of the desired size and uniform dispersion on rGO sheets, which enables the density to be adjusted. The photocatalytic activity of the synthesized rGO/CeO2 nanocomposites was higher than that of CeO2 NPs for the degradation of MB under simulated sunlight. This enhancement can be attributed to the fact that the e−-h+ pairs are well separated and the adsorption capacity is also increased because of the presence of rGO. It was revealed that the optimum concentration of CeO2 and rGO is critical for the enhancement of the photocatalytic performance of these composites [98].
4. Reactor Design
The design of photocatalytic reactor plays a vital role in achieving maximum efficiency during environmental applications of photocatalysis. Selection of an appropriate reactor depends on the evaluation of performance indicators which include throughput, energy efficiency, mass transfer efficiency, and cost-effectiveness [99]. The design process requires attention to specific factors that determine reactor performance effectiveness [100].
4.1. Reactor Type and Configuration
The main categories of photocatalytic reactors include batch, continuous, and semi-batch systems which further split into hydrodynamic behavior groups like plug flow reactors (PFR) and continuously stirred tank reactors (CSTR). Plug flow reactors demonstrate superior space-time yield (STY) because they maintain optimal residence time while enhancing mass transfer performance which leads to more efficient pollutant treatment. The high STY values of micro-reactors (MRs) and packed bed reactors (PBRs) result from their increased surface-to-volume ratio that boosts reaction kinetics and overall process efficiency.
4.2. Catalyst Immobilization vs. Suspension
The contact efficiency between catalysts and pollutants increases in suspended catalyst reactors which results in enhanced degradation performance. These systems achieve high effectiveness but create complex difficulties in recovering catalysts after the process which complicates their large-scale implementation. The use of catalysts immobilized within micro-structured reactors and packed bed reactors provides enhanced stability and simplified separation processes which leads to decreased operational complexities. These systems encounter mass transfer restrictions that negatively affect their total operational efficiency. Researchers have explored magnetic nanoparticles combined with fluidized bed reactors (FBRs) as an effective method to recover catalysts and sustain high reactivity levels in sustainable operations.
4.3. Energy Efficiency and Light Utilization
The use of traditional UV lamps in photocatalytic reactors leads to inefficient performance because they consume high amounts of energy while generating excessive heat. Light-emitting diode (LED)-based reactors represent a superior technology that boosts energy efficiency through precise wavelength illumination and reduces unabsorbed photon flux. The packed bed reactors together with LED-based systems achieve the best photocatalytic space-time yield (PSTY) because they optimize illumination effectiveness. The design of the reactor needs to achieve deep light penetration while reducing scattering effects to maximize photonic efficiency and quantum yield, which results in an improved sustainable and economically viable photocatalytic process [101].
4.4. Hydrodynamics and Mass Transfer
The efficiency of photocatalytic reactions depends directly on effective mixing and turbulence because these factors help overcome mass transfer limitations [102]. The advanced reactor designs incorporating spinning disk reactors (SDRs) with fluidized bed reactors (FBRs) use dynamic fluid flow systems to enhance degradation rates through better reactant-catalyst interactions. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modelling stands as a crucial optimization tool for reactors because it helps researchers evaluate fluid behavior and light intensity distribution and optimize reaction kinetics. The combination of these advanced techniques allows reactor engineers to optimize design features, which results in higher performance levels for efficient pollutant breakdown and improved photocatalytic activity.
4.5. Economic and Scalability Considerations
The design of cost-effective photocatalytic reactors needs to find an equilibrium between initial capital outlays, operational costs, and total process efficiency for widespread practical use. The industrial process benefits from continuous flow reactors with packed bed reactors because they demonstrate long-term stability and reduced operational costs through immobilized catalysts. The reactor system operates efficiently as an alternative to suspended catalyst systems because it reduces catalyst loss while improving recovery processes. The integration of photocatalysis with membrane filtration or electrochemical processes through hybrid systems will improve performance while expanding the environmental remediation scope of photocatalysis at an affordable cost scale.
Photocatalytic reactor development should focus on optimizing three key factors: complete light absorption, improved mass transfer capabilities, and effective catalyst retrieval systems for peak operational performance. The combination of LED-based photocatalytic reactors with packed bed designs represents an optimal solution for large-scale applications since it delivers both high energy efficiency and effective performance. The current performance of micro-reactors in small-scale operations requires additional modifications to achieve industrial readiness. Future research needs to concentrate on building energy-efficient scalable designs that unite several treatment processes, such as photocatalysis with membrane filtration or electrochemical methods, to improve pollutant degradation while expanding photocatalytic system use in environmental remediation.
5. Challenges and Future Scope
5.1. Environmental Challenges
CeO2 NPs and graphene derivatives (GO, rGO) used in the composites can be considered as potential contaminants of aquatic environment. The emission of these NPs during the wastewater treatment processes is worrisome due to their stability in the environment and accumulation in the tissues of aquatic organisms. Research must be conducted to evaluate the long-term effects of these nanomaterials on the natural environment and their toxicity. The CeO2 and graphene NPs in the treated wastewater effluents can be toxic to aquatic life such as fish, invertebrates, and algae. The knowledge of the processes of NPs’ interaction with aquatic organisms and the consequences of these interactions is crucial for assessing and managing the risks of negative effects on aquatic environments. NPs can transform in the environment and change their properties, mobility, and final destination. The environmental fate of CeO2-graphene composites including sedimentation, bioaccumulation, and leaching potential into the groundwater need to be investigated systematically. Evaluation of the bioavailability and biodegradation of CeO2 and graphene NPs is important to determine their behavior in the environment and possible hazards. Research should be directed toward understanding the behavior of these materials with microbial populations in natural water systems and the consequences on microbial populations.
The photocatalytic degradation of pollutants using CeO2-graphene composites may result in the formation of transformation products that are even more toxic and/or persistent than the parent pollutants. There is a need to carry out research in order to identify and describe these transformation products and their effects on the environment. Solving these environmental issues calls for multi-disciplinary research that combines environment science, nanotechnology, ecotoxicology, and environmental engineering. Possible measures may include improving the design of the composite to reduce the emission of NPs, finding green synthesis methods, and monitoring and controlling the use of CeO2-graphene composites in wastewater treatment.
5.2. Integration with Emerging Technologies
AI and ML approaches can be used in the synthesis and enhancement of CeO2-graphene composites. Using big data on the properties of the materials, the conditions of their synthesis, and the performance characteristics of the composites, AI can recommend new compositions of the composites and estimate their photocatalytic activity. This enhances the rate at which new materials are developed that are more efficient and have a longer life span. The use of AI in predictive modelling allows for the representation of CeO2-graphene composites’ behavior under various environmental conditions and operational parameters. This capability enables the researchers to predict the composite performance, and degradation and predict the reusability strategies without conducting many experiments. AI tools are particularly useful in handling and analyzing the big data that is produced from experiments, modelling, and review of literature. They can recognize trends, relationships, and other peculiarities that may be unnoticed by human researchers, which can help to make correct decisions concerning the further development and improvement of composites.
AI can be used in the synthesis of CeO2-graphene composites to control the synthesis procedures to produce materials of the same quality and in large quantities. There are some examples of materials such as perovskite solar cells, high-entropy alloys, metal-organic frameworks, graphene-based composites, etc. that have been recently developed using AI and ML algorithms. Thus, by incorporating real-time monitoring and control systems, AI can improve process productivity, minimize losses, and achieve similar levels of composite performance regardless of the scale of production [103]. AI can play a role in environmental impact assessment by estimating the behavior and the destiny of NPs that are emitted during the use and recycling of composites. This encompasses evaluating the risks that may be posed to the ecology and evaluating measures of mitigation and compliance with the set regulations. Robotic and automation in the field of AI can help reduce the time taken in experiments related to the synthesis and characterization of materials and their performance. This cuts down on time-consuming work, eliminates errors that may be made by human beings, and speeds up the process of innovation. In general, the application of AI tools in the study of CeO2-graphene nanocomposites increases effectiveness, speeds up the creation of new knowledge, and optimizes decision making. Thus, with the help of AI, researchers can solve multifaceted problems and move towards more efficient photocatalytic wastewater treatment.
5.3. Potential for Scaling up and Commercialization
The potential for scaling up and commercializing CeO2-graphene nanocomposites in photocatalytic wastewater treatment holds promise but necessitates addressing several key considerations: The synthesis methods employed for CeO2-graphene nanocomposites must be scalable from the laboratory scale to the industrial scale to meet the increasing demand for the nanocomposites. The ability to achieve reproducibility and retain the composite performance is essential to meet the markets’ needs while creating efficient processes. The quality and performance of CeO2-graphene nanocomposites should be uniform across the batches of large-scale production. Ensuring the quality of the materials and the photocatalytic activity of the coatings will be important for commercial application and compliance with the existing legislation. One of the major issues in the commercialization of nanocomposite technologies is to offer the products at competitive prices and at the same time meet the performance benchmarks. Minimizing raw material costs, improving the synthesis process, and increasing yields are some of the ways through which cost and market can be improved.
Therefore, the CeO2-graphene nanocomposites need to be optimized to fit the application needs and environmental conditions for the product to be accepted in the market. Adjusting the composite formulations, surface treatments, and compatibility with the current wastewater treatment systems can improve the versatility and efficiency in various environments. It is important to meet regulatory requirements and to consider environmental issues related to nanomaterials in order to achieve market acceptance and sustainability. The regulatory pathways require that proper environmental impact assessments are conducted, proper handling of the products is observed, and that the public is well informed. The involvement of industry partners, stakeholders, and potential end-users during the CeO2-graphene nanocomposites development phase can help fast-track the market acceptance of the nanocomposites. Strategic partnerships for technology transfer, pilot scale-up, and commercialization can help to enter and expand the market. In summary, for the practical application of CeO2-graphene nanocomposites in the photocatalytic treatment of wastewater, future research and developments should focus on the following aspects: scalability, quality control, cost, legal issues, and marketing. Tackling these aspects will create a foundation for the successful deployment of enhanced nanotechnologies to solve the global water pollution problems.
6. Conclusions
This review has provided a detailed analysis of the use of CeO2 and graphene-based composites in photocatalytic wastewater treatment. The incorporation of CeO2 with graphene derivatives like GO and rGO has been found to improve the photocatalytic activity for the degradation of pollutants. Thus, the properties of CeO2, such as high OSC and redox activity, are in harmony with the outstanding electronic, thermal, and mechanical characteristics of graphene materials, enhancing photocatalytic activity. Nevertheless, several issues should be resolved to further develop these materials for practical use. The effects of the environment, especially the possible discharge of nanomaterials into ecosystems, must be studied. The problems associated with stability and reusability of the composites are still pertinent, and hence, there is a need to design more stable and durable photocatalysts. Moreover, the use of these materials in combination with modern technologies like nanotechnology and renewable energy sources may be more effective.
The opportunities for scaling up and commercialization are quite high; however, it requires a lot of research and development to make the processes efficient and cost effective. Therefore, future research should be directed towards the elimination of these challenges through the invention of new composite structures, synthesis techniques, and field trials. In conclusion, CeO2-graphene composites are one of the most promising classes of photocatalysts for effective and environmentally friendly wastewater treatment. Further studies and cooperation between different disciplines, as well as between universities, industries, and other authorities, will be necessary to apply these findings and developments, made at the laboratory level, to solve environmental problems.
Author Contributions
L.P.: Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing—original draft. R.K.: Writing—original draft. V.K.: Supervision, Writing—review and editing. S.V.M.: Writing—review and editing. A.S. (Amanvir Singh): Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing. M.S.: Writing—review and editing. A.S. (Amanpreet Singh): Investigation, Writing—original draft. J.M.: Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. S.C.: Conceptualization, Validation, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| GO | graphene oxide |
| rGO | reduced graphene oxide |
| CV | crystal violet |
| MB | methylene blue |
| AO | acid orange |
| MBT | 2-mereaptobenzothiazole |
| MWCNT | multi-walled carbon nanotube |
| RB | rose Bengal |
| CR | Congo red |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TMX | tamoxifen |
| DOX | doxorubicin |
| PAM | polyacrylamide |
| BY | brilliant yellow |
| MO | methyl orange |
| RhB | rhodamine B |
| NIR | near infra-red |
| TC | tetracycline |
| CTX | cefotaxime |
| NPs | nanoparticles |
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| PS | polystyrene |
| FESEM | field emission scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | high resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| HRTEM | high resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| reactive blue | 160 RR160 |
| VO | oxygen vacancy |
| e− | electrons |
| h+ | holes |
| CIP | ciprofloxacin |
| k | rate constant |
References
- Bhatia, S.C. Pollution Control in Textile Industry, 1st ed.; WPI Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Pollution and Treatment of Dye Waste-Water. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 514, 052001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.C.; Shirini, F.; Pendashteh, A.R. Advanced Oxidation Process as a Green Technology for Dyes Removal from Wastewater: A Review. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2021, 40, 1467–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashuri, S.I.S.; Ibrahim, M.L.; Kasim, M.F.; Mastuli, M.S.; Rashid, U.; Abdullah, A.H.; Islam, A.; Mijan, N.A.; Tan, Y.H.; Mansir, N.; et al. Photocatalysis for Organic Wastewater Treatment: From the Basis to Current Challenges for Society. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaycıoğlu, Z.; Uysal, B.Ö.; Pekcan, Ö.; Erim, F.B. Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solution with Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Graphene Oxide-Doped Polyacrylamide. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13004–13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANajafidoust, A.; Allahyari, S.; Rahemi, N.; Tasbihi, M. Uniform coating of TiO2 nanoparticles using biotemplates for photocatalytic wastewater treatment. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 4707–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutam, S.P.; Saxena, G.; Singh, V.; Yadav, A.K.; Bharagava, R.N.; Thapa, K.B. Green synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles using leaf extract of Jatropha curcas L. for photocatalytic degradation of tannery wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAl-Mamun, M.; Kader, S.; Islam, M.; Khan, M. Photocatalytic activity improvement and application of UV-TiO2 photocatalysis in textile wastewater treatment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenifer, A.; Sastri, M.S.; Sriram, S. Photocatalytic dye degradation of V2O5 Nanoparticles—An experimental and DFT analysis. Optik 2021, 243, 167148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashery, M.H.; Elnouby, M.; El-Maghraby, E.M.; Elsehly, E.M. Structural control of V2O5 nanoparticles via a thermal decomposition method for prospective photocatalytic applications. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.; Nikolova, M.P.; Phuruangrat, A.; Pushpa, S.; Revathi, V.; Subbulakshmi, M. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of V2O5 nanoparticles for photocatalytic and antibacterial studies. Mater. Res. Innov. 2020, 24, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.P.; Ramgopal, G.; Vidya, Y.; Anantharaju, K.; Prasad, B.D.; Sharma, S.; Prashantha, S.; Premkumar, H.; Nagabhushana, H. Bio-inspired synthesis of Y2O3: Eu3+ red nanophosphor for eco-friendly photocatalysis. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 141, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalane, C.M.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Vijaya, J.J.; Siddhardha, B.; Jeyaraj, B.; Kennedy, J.; Maaza, M. Evaluation on the heterostructured CeO2/Y2O3 binary metal oxide nanocomposites for UV/Vis light induced photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine—B dye for textile engineering application. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 727, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atran, A.A.; Ibrahim, F.A.; Awwad, N.S.; Abd-Rabboh, H.S.M.; Hamdy, M.S. Remarkable enhancement in the photocatalytic activity of porous CeO2 nanoparticles through nickel doping for wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Sharma, P.; Singh, D.; Umar, A.; Kumar, R. Chemical and Pathogenic Cleanup of Wastewater Using Surface-Functionalized CeO2 Nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6803–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusmierek, E. A CeO2 Semiconductor as a Photocatalytic and Photoelectrocatalytic Material for the Remediation of Pollutants in Industrial Wastewater: A Review. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phor, L.; Trabelsi, Y.; Anurag; Malik, J.; Kumari, H.; Kumar, A.; Chahal, S. CeO2 microspheres/Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4/MWCNT ternary hybrid composites for ultrasonic-enhanced photocatalytic wastewater treatment. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 35600–35608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankita, A.; Chahal, S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P. Europium-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles: Investigating oxygen vacancies and their role in enhanced photocatalytic and magnetic properties. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 31, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phor, L.; Ankush; Suman; Malik, J.; Sharma, S.; Sonia; Chaudhary, V.; Rani, G.M.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; et al. Magnetically separable NiZn-ferrite/CeO2 nanorods/CNT ternary composites for photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 123064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. Erbium-doped oxygen deficient cerium oxide: Bi-functional material in the field of spintronics and photocatalysis. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 1721–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Rani, N.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. UV-irradiated photocatalytic performance of yttrium doped ceria for hazardous Rose Bengal dye. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahive, E.; Jurkschat, K.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Svendsen, C. Toxicity of cerium oxide nanoparticles to the earthworm Eisenia fetida: Subtle effects. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, P. Oxygen-deficient lanthanum doped cerium oxide nanoparticles for potential applications in spintronics and photocatalysis. Vacuum 2020, 177, 109395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Phor, L.; Singh, S.; Singh, A.; Malik, J.; Goel, P.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Ankita; Kumar, P. An efficient and unique method for the growth of spindle shaped Mg-doped cerium oxide nanorods for photodegradation of p-Nitrophenol. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 28961–28968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Mondal, M.; Sukul, T.; Mal, S.; Ghosh, K.; Das, S.; Pradhan, S.K. Superior photocatalytic performance and photo disinfection of bacteria of solvothermally synthesized mesoporous La-doped CeO2 under simulated visible light irradiation for wastewater treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 942, 169135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaan, V.; Kumar, K. Remediation of industrial pollutants in wastewater by photocatalytic treatment with Gadolinium doped CeO2 with composition GdxCe1-xO2 (0 < x < 0.1). J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2023, 178, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaycıoğlu, Z.; Geçim, B.; Erim, F.B. Green synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles from turmeric and kinds of honey: Characterisations, antioxidant and photocatalytic dye degradation activities. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaygusuz, H.; Erim, F.B. Biopolymer-assisted green synthesis of functional cerium oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 2357–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geim, A.K. Graphene: Status and Prospects. Science 2009, 324, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ding, J.; Chai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ren, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, W.-L. CeO2 nanorod/g-C3N4 /N-rGO composite: Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance and the role of N-rGO as electronic transfer media. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 11223–11234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, C.V.; Krueger, M.; Eck, M.; Weber, S.; Erdem, E. Comparative electron paramagnetic resonance investigation of reduced graphene oxide and carbon nanotubes with different chemical functionalities for quantum dot attachment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 132102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wu, S.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, H. Graphene-based electronic sensors. Chem. Sci. 2012, 3, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, Z.; Neff, D.; Zhamu, A.; Jang, B.Z. Graphene-Based Supercapacitor with an Ultrahigh Energy Density. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4863–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Assal, M.E.; Tahir, M.N.; Khan, M.; Ashraf, M.; Hatshan, M.R.; Khan, M.; Varala, R.; Badawi, N.M.; Adil, S.F. Graphene/inorganic nanocomposites: Evolving photocatalysts for solar energy conversion for environmental remediation. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2022, 26, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Tahir, M.N.; Adil, S.F.; Khan, H.U.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Al-Warthan, A.A.; Tremel, W. Graphene based metal and metal oxide nanocomposites: Synthesis, properties and their applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18753–18808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Rentería, J.; Cházaro-Ruiz, L.; Rangel-Mendez, J. Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) films onto carbon steel by cathodic electrophoretic deposition: Anticorrosive coating. Carbon 2017, 122, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Yu, P.; Shi, X.; Ling, T.; Zeng, W.; Chen, A.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Z. Hierarchically Porous Hydroxyapatite Hybrid Scaffold Incorporated with Reduced Graphene Oxide for Rapid Bone Ingrowth and Repair. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9595–9606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, A.; Scheer, E.; Polarz, S. Synthesis of graphene–transition metal oxide hybrid nanoparticles and their application in various fields. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 688–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavel, S.; Thangavel, S.; Raghavan, N.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Venugopal, G. Visible-light driven photocatalytic degradation of methylene-violet by rGO/Fe3O4/ZnO ternary nanohybrid structures. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 665, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.; O’rourke, C.; Moore, K. Powder semiconductor photocatalysis in aqueous solution: An overview of kinetics-based reaction mechanisms. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2015, 310, 66–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q. Cobalt Doped TiO2/rGO Nanocomposites as Highly Efficient Photocatalyst for Water Purification. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2021, 37, 29249–29257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.M.A.; Akhtar, T.; Sitara, E.; Nasir, H.; Fazal, A.; Rafique, U.; Ullah, S.; Mehmood, A. Development of Ag0.04ZrO2/rGO heterojunction, as an efficient visible light photocatalyst for degradation of methyl orange. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doluel, E.C.; Kartal, U.; Dikici, T.; Yurddaskal, M. Effect of Ag Content on Photocatalytic Activity of Ag@TiO2/rGO Hybrid Photocatalysts. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 3849–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, N.; Ihsanullah; Sajid, M.; Saleh, T.A. Graphene-based adsorbents for the removal of toxic organic pollutants: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Gupta, K.; Joshi, P.; Khatri, O.P. Adsorptive removal and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using metal oxides and their composites: A comprehensive review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 272, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-Q.; Li, Y.-H.; Tang, Z.-R.; Xu, Y.-J. Roles of Graphene Oxide in Heterogeneous Photocatalysis. ACS Mater. Au 2021, 1, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Weng, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Lu, K.; Han, B. Recent Advances of CeO2-Based Composite Materials for Photocatalytic Applications. ChemSusChem 2024, 17, e202301778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.N.; Li, J. Cerium modified rod-like ZnO graphene complex and its photocatalytic properties under visible-light irradiation. Opt. Mater. 2020, 108, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, A. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of rGO-CeO2 nanocomposites driven by sunlight. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2017, 223, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naynava, S.K.; Lorestani, B.; Cheraghi, M.; Sobhanardakani, S.; Shahmoradi, B. Efficient Degradation of Diazinon Pesticide under Visible Light Irradiation Using CeO2 Functionalized Magnetite Graphene Oxide Heterojunction-Based Photocatalyst. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siranjeevi, R.; Vasumathi, V.; Suganya, S.; Saravanan, A.; Usha, R.; Azhagurajan, M.; Jeyalakshmi, R. Evaluation of biosynthesized GO@CeO2 nanocomposites as a catalyst for UV-assisted degradation of organic dyes and phytotoxicity studies. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 44, 103748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xing, X.; Qi, Q.; Shen, W.; Wu, H.; Li, D.; Li, B.; Liang, J.; Tang, X.; Zhao, J.; et al. Fabrication of graphene modified CeO2/g-C3N4 heterostructures for photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2023, 42, 100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, S.; Phor, L.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, P. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic dye by CeO2/CNT/GO hybrid nanocomposites under UV light for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 124964–124975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganie, A.S.; Bashar, N.; Bano, S.; Hijazi, S.; Sultana, S.; Sabir, S.; Khan, M.Z. Development and application of redox active GO supported CeO2/In2O3 nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of toxic dyes and electrochemical detection of sulfamaxole. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 38, 102774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashtchi, N.; Sobhanardakani, S.; Cheraghi, M.; Goodarzi, A.; Lorestani, B. High-efficient photocatalytic degradation of tamoxifen and doxorubicin by novel ternary heterogeneous GO@Fe3O4@CeO2 photocatalyst. Toxin Rev. 2023, 42, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Ahamad, T.; Qais, F.A.; Ahmad, N.; Shafi, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Srivastava, S. Proficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic and anti-biofilm activity of biosynthesized CeO2-graphene oxide nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 298, 127397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Amin, K.M.; Ali, M.; Ali, Z.; Atif, M.; Ensinger, W.; Khalid, W. Synergetic effect of adsorption-photocatalysis by GO-CeO2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpuraranjith, M.; Chen, Y.; Manigandan, R.; Srinivas, K.; Rajaboopathi, S. Hierarchical Ultrathin Layered GO-ZnO@CeO2 Nanohybrids for Highly Efficient Methylene Blue Dye Degradation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Lei, X.; Gu, G.; Zou, R.; Wu, Q. Facile synthesis of CeO2-graphene oxide composites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 244, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashinath, L.; Namratha, K.; Byrappa, K. Microwave mediated synthesis and characterization of CeO2-GO hybrid composite for removal of chromium ions and its antibacterial efficiency. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 76, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, L. Graphene oxide (GO) doped CeO2 as potential enhancer of methyl orange degradation. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2019, 27, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channei, D.; Nakaruk, A.; Phanichphant, S. Influence of graphene oxide on photocatalytic enhancement of cerium dioxide. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, C.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z. Greatly enhanced photocatalytic activity of semiconductor CeO2 by integrating with upconversion nanocrystals and graphene. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 103795–103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, T.; Zhang, J.; Xu, A.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhou, R.; et al. Synthesis and photocatalytic performance of CuO-CeO2/Graphene Oxide. Mater. Lett. 2016, 185, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yao, M.; Liu, B.; Li, Q.; Liu, R.; Lv, H.; Lu, S.; Gong, C.; Zou, B.; Cui, T.; et al. Controlled Synthesis of CeO2 /Graphene Nanocomposites with Highly Enhanced Optical and Catalytic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11741–11745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, A.S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Faridbod, F. Facile sonochemical synthesis and electrochemical investigation of ceria/graphene nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2362–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ojha, A.K. In-situ synthesis of reduced graphene oxide decorated with highly dispersed ferromagnetic CdS nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic activity under UV irradiation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 171, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Soin, N.; Roy, S.S. Role of graphene/metal oxide composites as photocatalysts, adsorbents and disinfectants in water treatment: A review. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3823–3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulzele, N.N.; Bhanvase, B.A.; Pandharipande, S.L. Sonochemically prepared rGO/Ag3PO4/CeO2 nanocomposite photocatalyst for effective visible light photocatalytic degradation of methylene dye and its prediction with ANN modelling. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 292, 126809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Zhang, J.; Murali, A.; Lan, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Advancements in organic pollutant remediation: The role of nitrogen-doped rGO-CeO2 in photocatalytic efficiency enhancement, Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 685, 133282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.-T.; Ha, T.-H.; Vu, T.-P.; Nguyen, V.-N.; Pham, T.-D. Novel CeO2-V2O5/rGO tertiary photocatalyst for improved cefotaxime degradation using visible-light. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanasundari, K.; Ponnarasi, P.; Mahalakshmi, G. A green approach to synthesis of Ag-doped CeO2 nanorods embedded reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for excellent photocatalytic and antimicrobial activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 165, 112523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.M.; Rani, S.; Ansari, A.A.; Ahamed, M.; Ahmed, J.; Kumar, S.; Rana, A.U.H.S. Anchoring Ceria Nanoparticles on Reduced Graphene Oxide and Their Enhanced Photocatalytic and Electrochemical Activity for Environmental Remediation. J. Electron. Mater. 2024, 53, 930–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Chen, W.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.X.; Elmarakbi, A.; Fu, Y. In-situ controlled growth of ultrafine CeO2 nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxides for efficient photocatalytic degradation. J. Catal. 2023, 424, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, H. Photocatalytic degradation of Estrone and Congo red by the magnetic antibacterial photocatalyst g-C3N4/CeO2/M-rGO under visible light and optimization by Box-Behnken statistical design (BBD). J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1272, 134205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.; Son, N.; Kang, M. Direct Z-scheme ZnIn2S4 spheres and CeO2 nanorods decorated on reduced-graphene-oxide heterojunction photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution and photocatalytic degradation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 607, 155087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomathi, A.; Prabhuraj, T.; Gokilapriya, S.; Vasanthi, G.; Maadeswaran, P.; Kumar, K.R. Design of ternary CeO2/Fe2O3/reduced graphene oxide-based hybrid nanocomposite for superior photocatalytic degradation material for organic dyes. Dye. Pigment. 2023, 218, 111473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburaih, H.; Aadil, M.; Hassan, W.; Amaral, L.S.; Ejaz, S.R.; Aman, S.; Alsafari, I.A. Multifunctional Fe and Gd co-doped CeO2-RGO nanohybrid with excellent solar light mediated crystal violet degradation and bactericidal activity. Synth. Met. 2022, 287, 117093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Gao, Z.; Meng, Q.; He, G.; Chen, H. One-step synthesis of reduced graphene oxide based ceric dioxide modified with cadmium sulfide (CeO2/CdS/RGO) heterojunction with enhanced sunlight-driven photocatalytic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murali, A.; Sarswat, P.K.; Free, M.L. Minimizing electron-hole pair recombination through band-gap engineering in novel ZnO-CeO2-rGO ternary nanocomposite for photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25042–25056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Matai, I.; Garg, A.; Sachdev, A. Tragacanth Hydrogel Integrated CeO2 @rGO Nanocomposite as Reusable Photocatalysts for Organic Dye Degradation. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 10663–10672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.H.; Bakiro, M.; Aljasmi, F.I.A.; Albreiki, A.M.O.; Bayane, S.; Alzamly, A. Investigation of the band gap and photocatalytic properties of CeO2/rGO composites. Mol. Catal. 2020, 486, 110874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Zhang, J.; Hong, L.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Reduced graphene oxide@ceria nanocomposite-coated polymer microspheres as a highly active photocatalyst. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 567, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeharaj, P.; Kongmun, P.; Paiplod, P.; Prakobmit, S.; Sriwong, C.; Kim-Lohsoontorn, P.; Vittayakorn, N. Ultrasonically-assisted surface modified TiO2/rGO/CeO2 heterojunction photocatalysts for conversion of CO2 to methanol and ethanol. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 58, 104657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, H.; Yan, H. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of hybrid reduced graphene oxide–CeO2 hierarchical flower-like nanostructures. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 2729–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharsan, A.; Vasanthakumar, V.; Karthikeyan, S.; Raj, V.; Shanavas, S.; Anbarasan, P. Multi-functional properties of ternary CeO2 /SnO2 /rGO nanocomposites: Visible light driven photocatalyst and heavy metal removal. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 346, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanavas, S.; Priyadharsan, A.; Vasanthakumar, V.; Arunkumar, A.; Anbarasan, P.; Bharathkumar, S. Mechanistic investigation of visible light driven novel La2CuO4/CeO2/rGO ternary hybrid nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic performance and antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 340, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Ojha, A.K.; Patrice, D.; Yadav, B.S.; Materny, A. One-step in situ synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles grown on reduced graphene oxide as an excellent fluorescent and photocatalyst material under sunlight irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 11157–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Reddy, D.A.; Islam, M.J.; Ma, R.; Kim, T.K. Self-assembly of CeO2 nanostructures/reduced graphene oxide composite aerogels for efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Samdarshi, S.K. In Situ Decorated Optimized CeO2 on Reduced Graphene Oxide with Enhanced Adsorptivity and Visible Light Photocatalytic Stability and Reusability. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 22281–22290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Ma, W.; Tong, Z.; Chen, J. CeO2 hollow nanospheres decorated reduced graphene oxide composite for efficient photocatalytic dye-degradation. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, Y.; Lin, S.; Liang, C.; Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, D.; Yang, H.; Lang, P.; Zhang, R.; et al. One-step synthesis of reduced graphene oxide–CeO2 nanocubes composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater. Lett. 2014, 124, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Shen, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, G.; Chen, K. Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/CeO2 nanocomposites and their photocatalytic properties. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblebici, M.E.; Stefanidis, G.D.; Van Gerven, T. Comparison of photocatalytic space-time yields of 12 reactor designs for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2015, 97, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, K.P.; Kanmani, S. Progression of Photocatalytic reactors and it’s comparison: A Review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 154, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, A.; van Ommen, J.R.; Kreutzer, M.T.; Lammertink, R.G.H. Photocatalytic Reactor Design: Guidelines for Kinetic Investigation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 5349–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Fung, C.S.; Kumar, A.; Lo, I.M. Magnetically separable BiOBr/Fe3O4@SiO2 for visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen: Mechanistic investigation and prototype development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badini, S.; Regondi, S.; Pugliese, R. Unleashing the Power of Artificial Intelligence in Materials Design. Materials 2023, 16, 5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).