Chitosan Nanoparticulate System Loaded with Cannabidiol: A Topical Formulation for Potential Alopecia Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
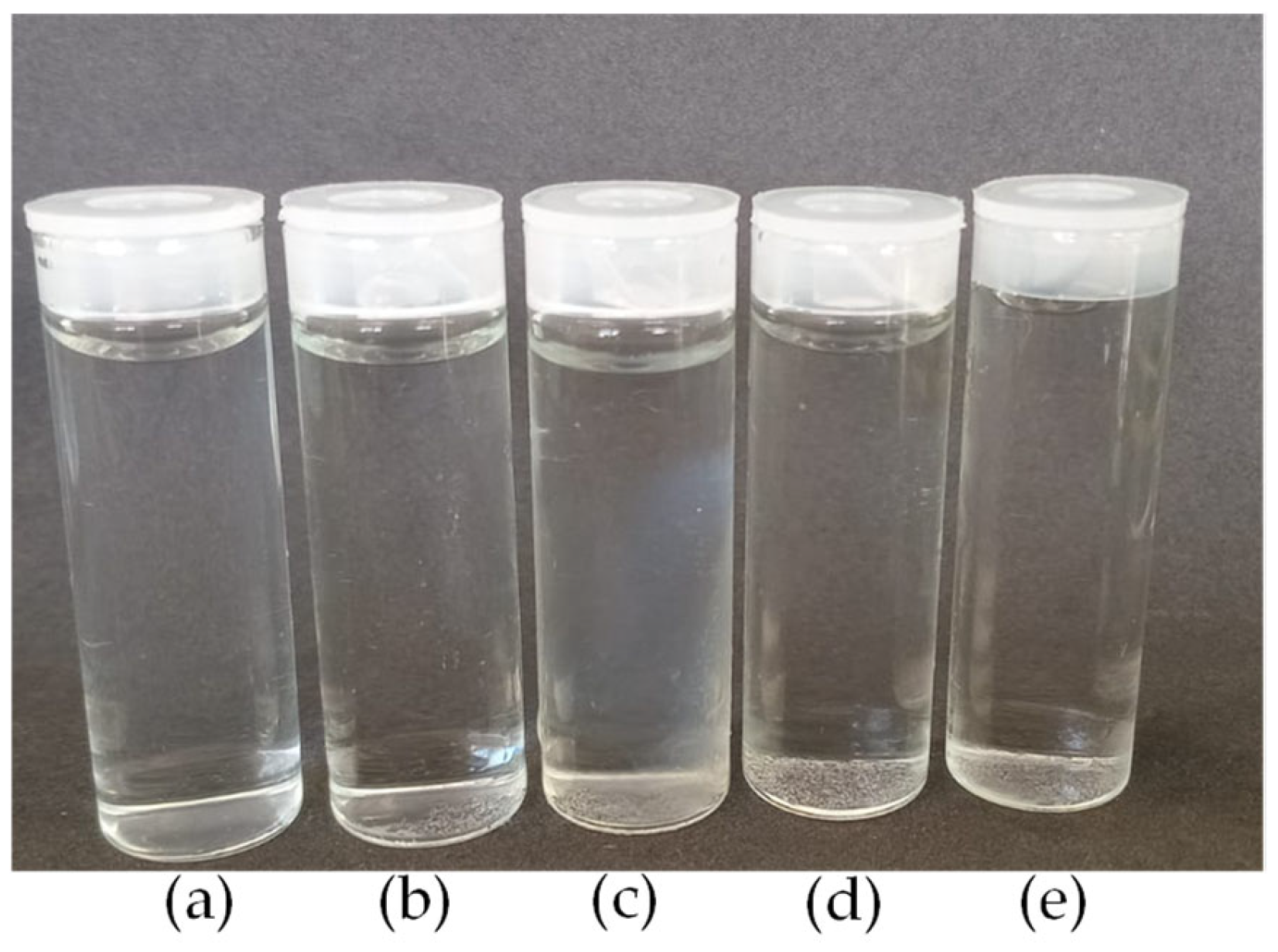
2.2.1. Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles
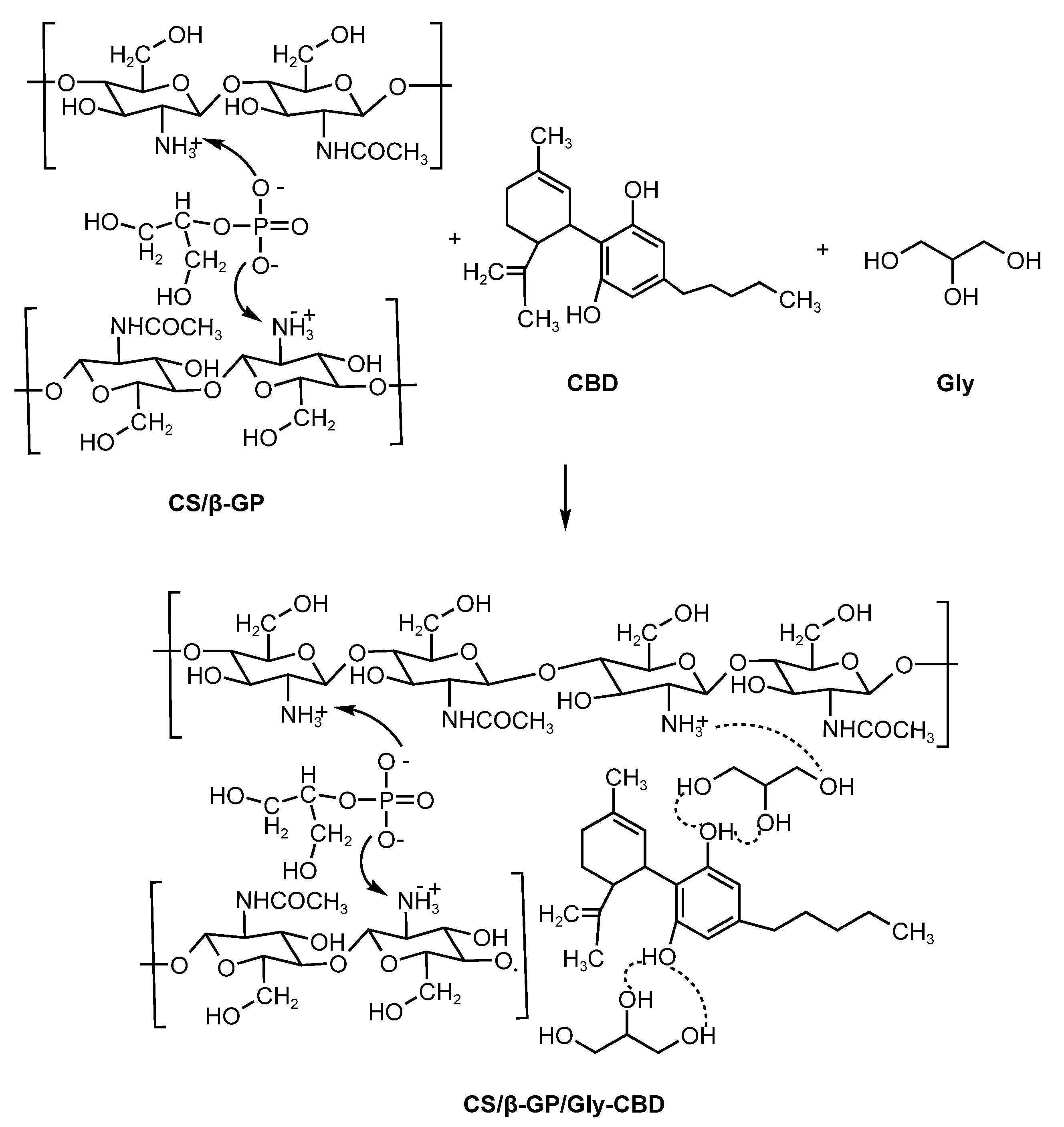
2.2.2. Preparation of Chitosan/CBD Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.2. Zeta Potential (ζ)
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3. Results and Discussion
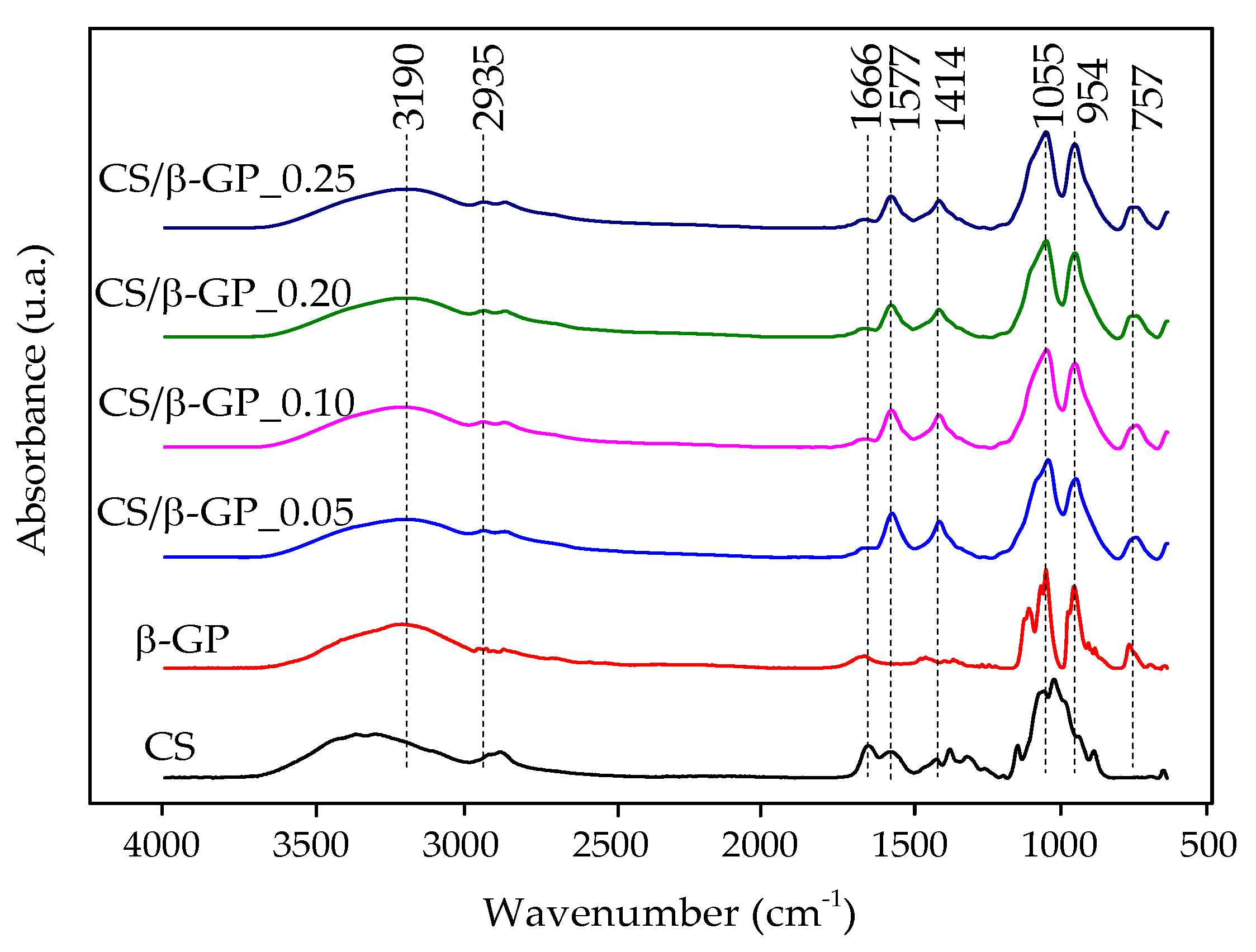
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.1.1. Characterization of CS/β-GP Nanoparticles
3.1.2. Integration of CBD and Glycerol in CS/β-GP Nanoparticles
3.1.3. FTIR Analysis of CS/β-GP/Gly-CBD Nanoparticles
3.2. Zeta Potential (ζ)
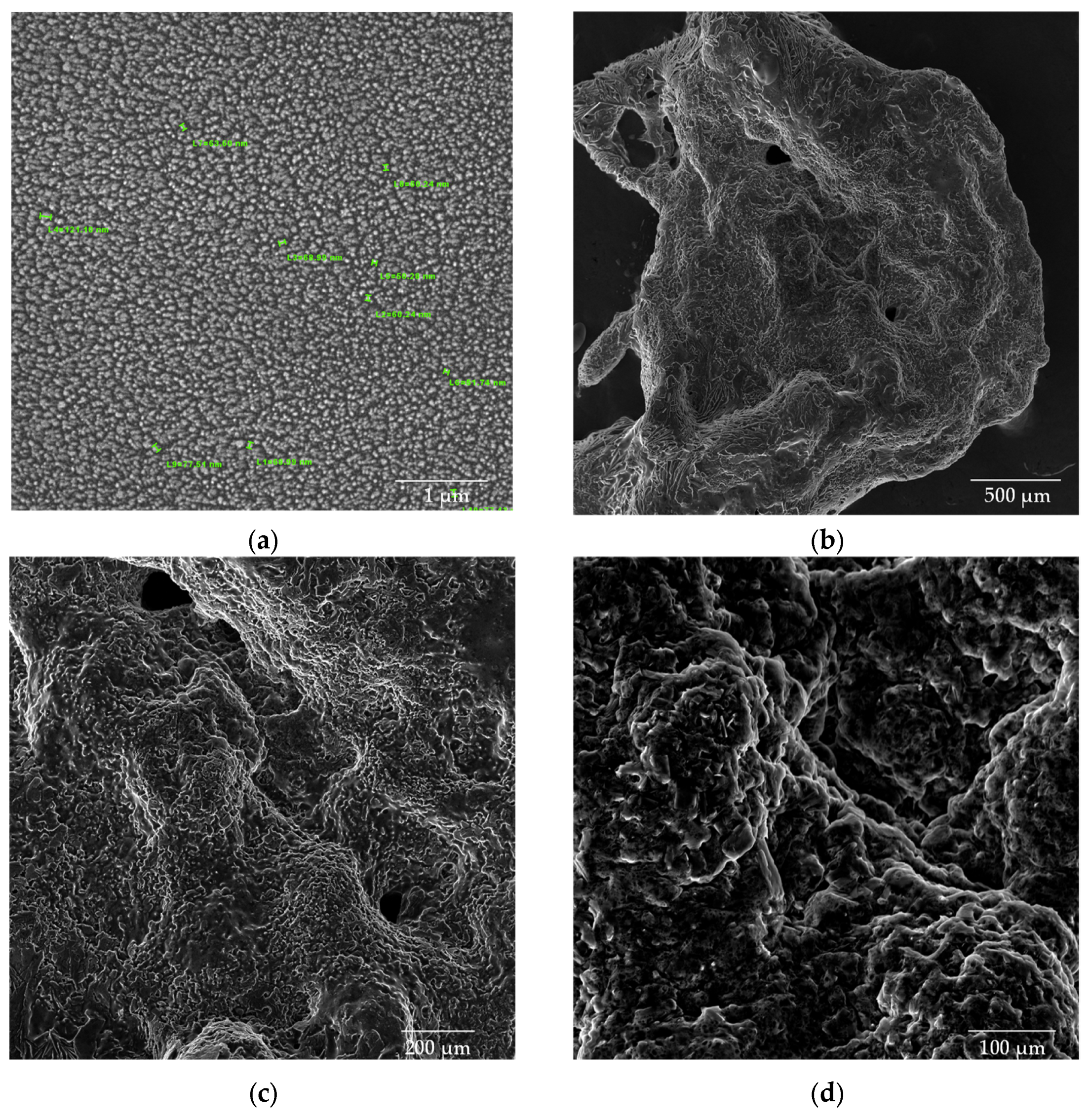
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ntshingila, S.; Oputu, O.; Arowolo, A.T.; Khumalo, N.P. Androgenetic alopecia: An update. JAAD Int. 2023, 13, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, M.S.; Ablon, G.; Gade, A.; Han, H.; Fischer, D.L. Treatment options for androgenetic alopecia: Efficacy, side effects, compliance, financial considerations, and ethics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3759–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S.; Kamalasanan, K. Controlled drug delivery for alopecia: A review. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, F.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, C. An androgenetic alopecia remedy based on marine collagen peptide-incorporated dissolving microneedles. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 650, 123629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Handa, M.; Ujjwal, R.R.; Singh, V.; Kesharwani, P.; Shukla, R. Potential of nanoparticulate based delivery systems for effective management of alopecia. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, E.; Boschetto, F.; Pezzotti, G. Biomaterials and biocompatibility: An historical overview. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 1617–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Bhuiyan, M.A.R.; Islam, M.N. Chitin and Chitosan: Structure, Properties and Applications in Biomedical Engineering. J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 25, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, S.; Sun, B.; Gao, S.; Guo, S.; Zhao, K. Biomedical Applications of Chitosan and Its Derivative Nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, and Biomedical Application of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels. Polymers 2023, 15, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, G.M.; Smart, J.D.; Ingram, M.J.; Barnes, L.-M.; Burnett, G.R.; Rees, G.D. Chitosan microparticles for the controlled delivery of fluoride. J. Dent. 2012, 40, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipoli, C.C.; Santana, N.; Shimojo, A.A.M.; Azzoni, A.R.; Torre, L.G.d.l. Scalable production of highly concentrated chitosan/TPP nanoparticles in different pHs and evaluation of the in vitro transfection efficiency. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 94, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Zou, X. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, J.; Liu, F.; Majeed, H.; Qi, J.; Yokoyama, W.; Zhong, F. Physicochemical and morphological properties of size-controlled chitosan–tripolyphosphate nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 465, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algharib, S.A.; Dawood, A.; Zhou, K.; Chen, D.; Li, C.; Meng, K.; Zhang, A.; Luo, W.; Ahmed, S.; Huang, L.; et al. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles by ionotropic gelation technique: Effects of formulation parameters and in vitro characterization. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1252, 132129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, P.; Pedroso-Santana, S.; Kumar, Y.; Joly, N.; Martin, P.; Bocchetta, P. Ionotropic Gelation of Chitosan Flat Structures and Potential Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymaǹska, E.; Sosnowska, K.; Miltyk, W.; Rusak, M.; Basa, A.; Winnicka, K. The Effect of β-Glycerophosphate Crosslinking on Chitosan Cytotoxicity and Properties of Hydrogels for Vaginal Application. Polymers 2015, 7, 2223–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiz-Fernández, S.; Guaresti, O.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Ruiz-Rubio, L.; Gabilondo, N.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. β-Glycerol phosphate/genipin chitosan hydrogels: A comparative study of their properties and diclofenac delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.J.; Faneca, H.; Lima, M.P.; Gil, M.H.; Figueiredo, M.M. In situ forming chitosan hydrogels prepared via ionic/covalent co-cross-linking. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salustiano, R.L.C.; Bortoli, S. Canabidiol: Aspectos gerais e aplicações farmacológicas. Conjecturas 2022, 22, 1157–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, S.A.; Stone, N.L.; Yates, A.S.; O’Sullivan, S.E. A Systematic Review on the Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol in Humans. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadpour, E.; Rezaei, A.; Das, S.S.; Krishna Rao, B.V.; Singh, S.K.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; Prieto, M.A.; Jafari, S.M. Cannabidiol-Loaded Nanocarriers and Their Therapeutic Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirda, E.; Idroes, R.; Khairan, K.; Tallei, T.E.; Ramli, M.; Earlia, N.; Maulana, A.; Idroes, G.M.; Muslem, M.; Jalil, Z. Synthesis of Chitosan-Silver Nanoparticle Composite Spheres and Their Antimicrobial Activities. Polymers 2021, 13, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawtarie, N.; Cai, Y.; Lapitsky, Y. Preparation of chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles with highly tunable size and low polydispersity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 157, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamer, W.; Cellesi, F.; Tirelli, N. Chitosan/β-glycerophosphate-based microparticles manufactured by laminar jet break-up technology. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloti, M.; Bohidar, H.B. Kinetics of coacervation transition versus nanoparticle formation in chitosan-sodium tripolyphosphate solutions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.L.; Satino, J. Hair Regrowth with Cannabidiol (CBD)-rich Hemp Extract—A Case Series. Cannabis 2021, 4, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanti, G.; Grifoni, L.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Antiga, E.; Montefusco, F.; Caproni, M.; Bilia, A.R. Development and optimisation of biopharmaceutical properties of a new microemulgel of cannabidiol for locally-acting dermatological delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 121036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.P.; Costa, G.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F.; Pires, P.C.; Heidarizadeh, F.; Giram, P.S.; Mazzola, P.G.; Cabral, C.; Veiga, F.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Skin applications of cannabidiol: Sources, effects, delivery systems, marketed formulations and safety. Phytochem. Rev. 2023, 22, 781–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, Q.; Ting, J.; Harwood, S.; Browning, N.; Simm, A.; Ross, K.; Olier, I.; Al-Kassas, R. Chitosan nanoparticles for enhancing drugs and cosmetic components penetration through the skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 160, 105765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Bégin, A.; Carreau, P.J. Physical Gelation of Chitosan in the Presence of β-Glycerophosphate: The Effect of Temperature. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3267–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montembault, A.; Viton, C.; Domard, A. Rheometric study of the gelation of chitosan in a hydroalcoholic medium. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeini, A.H.; Mahdavipour, K.; Rastegari, A.; Aghsami, M.; Montazeri, H.; Faghihi, H.; Mohammadi, Z. Chitosan and its amphiphilic derivative nanoparticles loaded with Minoxidil for induction of hair growth: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, T.; Wan, Z.; Wang, T. Dispersing insoluble yolk low-density lipoprotein (LDL) recovered by complexing with carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) for the nanoencapsulation of hemp cannabidiol (CBD) through emulsification at neutral pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demisli, S.; Galani, E.; Goulielmaki, M.; Kyrilis, F.L.; Ilić, T.; Hamdi, F.; Crevar, M.; Kastritis, P.L.; Pletsa, V.; Nallet, F.; et al. Encapsulation of cannabidiol in oil-in-water nanoemulsions and nanoemulsion-filled hydrogels: A structure and biological assessment study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 634, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi, A.H.; Fang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Effect of glycerol on formation, stability, and properties of vitamin-E enriched nanoemulsions produced using spontaneous emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 411, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchette, C.; Mercuri, A.; Arcangeli, L.; Kriechbaum, M.; Laggner, P. Self-emulsification of Lipidic Drug Delivery System in Pure Water and in Concentrated Glycerol Solution. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 3053–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampucci, S.; Paganini, V.; Burgalassi, S.; Chetoni, P.; Monti, D. Nanostructured Drug Delivery Systems for Targeting 5-α-Reductase Inhibitors to the Hair Follicle. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohaeti, E.; Laksono, E.W.; Rakhmawati, A.J.A.J.P.K. Bacterial cellulose from rice waste water and its composite which are deposited nanoparticle as an antimicrobial material. ALCHEMY J. Penelit. Kim. 2016, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelminiak-Dudkiewicz, D.; Smolarkiewicz-Wyczachowski, A.; Mylkie, K.; Wujak, M.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Nowak, P.; Bocian, S.; Goslinski, T.; Ziegler-Borowska, M. Chitosan-based films with cannabis oil as a base material for wound dressing application. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Mumtaz, M.W.; Fakhar, M.; Rashid, U. Response Surface Methodology Based Optimized Purification of the Residual Glycerol from Biodiesel Production Process. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2017, 44, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Li, L.J.; Sun, D.; Wang, M.; Shi, J.R.; Yang, D.; Wang, L.H.; Zou, S.C. Preparation and properties of chitosan-based microspheres by spray drying. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattu, C.; Li, R.; Ciardelli, G. Chitosan nanoparticles as therapeutic protein nanocarriers: The effect of ph on particle formation and encapsulation efficiency. Polym. Compos. 2013, 34, 1538–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lapitsky, Y. Monovalent Salt Enhances Colloidal Stability during the Formation of Chitosan/Tripolyphosphate Microgels. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2011, 27, 10392–10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shagholani, H.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Sharifi, S.H. Conversion of amine groups on chitosan-coated SPIONs into carbocyclic acid and investigation of its interaction with BSA in drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 45, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancan, F.; Papakostas, D.; Hadam, S.; Hackbarth, S.; Delair, T.; Primard, C.; Verrier, B.; Sterry, W.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Vogt, A. Investigation of polylactic acid (PLA) nanoparticles as drug delivery systems for local dermatotherapy. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, T.; El-Sayed, N.; Jurisic, M.; Koenneke, A.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Cunha-Filho, M.; Taveira, S.F.; Lemor, R.; Schneider, M.; Gratieri, T. Effect of physical stimuli on hair follicle deposition of clobetasol-loaded Lipid Nanocarriers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.S.; Ng, W.M.; Lim, J.; Yeap, S.P. Dynamic Light Scattering: Effective Sizing Technique for Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Sharma, S.K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 77–111. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.K.; Boateng, J.S. Enhancing Stability and Mucoadhesive Properties of Chitosan Nanoparticles by Surface Modification with Sodium Alginate and Polyethylene Glycol for Potential Oral Mucosa Vaccine Delivery. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarudin, M.J.; Cutts, S.M.; Evison, B.J.; Phillips, D.R.; Pigram, P.J. Factors determining the stability, size distribution, and cellular accumulation of small, monodisperse chitosan nanoparticles as candidate vectors for anticancer drug delivery: Application to the passive encapsulation of [(14)C]-doxorubicin. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2015, 8, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Qian, J.; Zhao, C.; Yang, H.; Zhao, X.; Guo, H. Study on the relationship between crosslinking degree and properties of TPP crosslinked chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Purkait, M.K. Impact of synthesized amino alcohol plasticizer on the morphology and hydrophilicity of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corveleyn, S.; Remon, J.P. Formulation of a lyophilized dry emulsion tablet for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 166, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootz, A.; Vogel, V.; Schubert, D.; Kreuter, J. Comparison of scanning electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering and analytical ultracentrifugation for the sizing of poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. Off. J. Arbeitsgemeinschaft Fur Pharm. Verfahrenstechnik eV 2004, 57, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, S.K.; Khusnutdinov, R.; Murmiliuk, A.; Inam, W.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Zhang, H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy in drug delivery: A roadmap for correct characterization of nanoparticles and interpretation of results. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 5354–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branda, F.; Silvestri, B.; Costantini, A.; Luciani, G. Effect of exposure to growth media on size and surface charge of silica based Stöber nanoparticles: A DLS and ζ-potential study. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciro, Y.; Rojas, J.; Alhajj, M.J.; Carabali, G.A.; Salamanca, C.H. Production and Characterization of Chitosan-Polyanion Nanoparticles by Polyelectrolyte Complexation Assisted by High-Intensity Sonication for the Modified Release of Methotrexate. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Samples | CS (mg/L) | Acetic Acid (v/v) | β-GP (mol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 2.5 | 1% | 0 |
| CS/β-GP_0.05 | 2.5 | 1% | 0.05 |
| CS/β-GP_0.10 | 2.5 | 1% | 0.10 |
| CS/β-GP_0.20 | 2.5 | 1% | 0.20 |
| CS/β-GP_0.25 | 2.5 | 1% | 0.25 |
| Samples | Mean Diameter (nm) | Mean PDI | Mean (ζ) (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 4383.5 ± 930.1 | 13.62 ± 6.18 | 40.9 ± 0.6 |
| CS/β-GP_0.05 | 727.5 ± 55.2 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 12.5 ± 1.5 |
| CS/β-GP_0.10 | 480.1 ± 13.9 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 9.8 ± 1.3 |
| CS/β-GP_0.20 | 389.8 ± 24.7 | 0.48 ± 0.02 | 5.2 ± 0.9 |
| CS/β-GP_0.25 | 582.7 ± 6.5 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 4.9 ± 0.4 |
| CS/β-GP/Gly-CBD | 259.0 ± 30.2 | 0.18 ± 0.08 | −11.2 ± 1.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, J.R.; Lopes, D.S.; Barbosa, M.C.S.; Silva, H.N.; Fook, M.V.L.; Silva, S.M.L.; Delgado, J.M.P.Q.; Lima, A.G.B. Chitosan Nanoparticulate System Loaded with Cannabidiol: A Topical Formulation for Potential Alopecia Management. Processes 2025, 13, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030617
Oliveira JR, Lopes DS, Barbosa MCS, Silva HN, Fook MVL, Silva SML, Delgado JMPQ, Lima AGB. Chitosan Nanoparticulate System Loaded with Cannabidiol: A Topical Formulation for Potential Alopecia Management. Processes. 2025; 13(3):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030617
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, Josenildo R., Débora S. Lopes, Milena C. S. Barbosa, Henrique N. Silva, Marcus V. L. Fook, Suédina M. L. Silva, João M. P. Q. Delgado, and Antonio G. B. Lima. 2025. "Chitosan Nanoparticulate System Loaded with Cannabidiol: A Topical Formulation for Potential Alopecia Management" Processes 13, no. 3: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030617
APA StyleOliveira, J. R., Lopes, D. S., Barbosa, M. C. S., Silva, H. N., Fook, M. V. L., Silva, S. M. L., Delgado, J. M. P. Q., & Lima, A. G. B. (2025). Chitosan Nanoparticulate System Loaded with Cannabidiol: A Topical Formulation for Potential Alopecia Management. Processes, 13(3), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13030617











