Microplastic Pollution in Soil and Water and the Potential Effects on Human Health: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
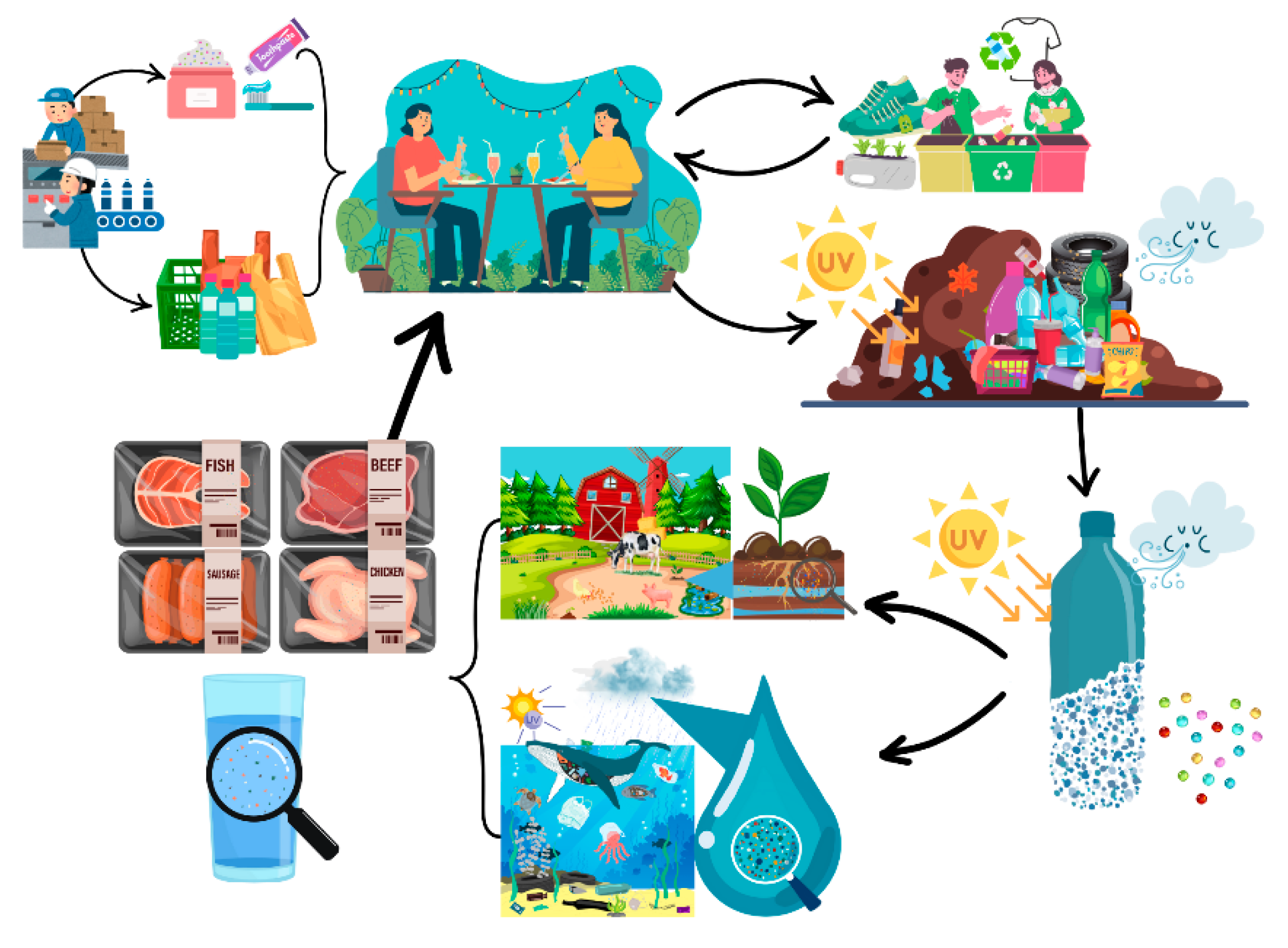
2. Microplastic Production
3. Microplastic Accumulation in Soil and Water
4. Effects of Microplastic on Health
5. Bioremediation for Microplastic Exposure
6. Policies for Avoiding Microplastic Accumulation
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rellán, A.; Ares, D.; Brea, C.; López, A.F.; Bugallo, P. Sources, sinks and transformations of plastics in our oceans: Review, management strategies and modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London Protocol 1996–2016. Global Treaty at the Forefront of Protecting Our Oceans for Present and Future Generations; OMI: London, UK, 2016.
- Nielsen, T.D.; Hasselbalch, J.; Holmberg, K.; Stripple, J. Politics and the plastic crisis: A review throughout the plastic life cycle. Wiley Interdisc. Rev. Energ. Environ. 2020, 9, e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Sherly, M.A.; Ranjan, P.; Tinoco, R.O.; Boldrin, A.; Damgaard, A.; Laurent, A. Framework for quantifying environmental losses of plastics from landfills. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debrah, J.K.; Vidal, D.G.; Dinis, M.A. Innovative use of plastic for a clean and sustainable environmental management: Learning cases from Ghana, Africa. Urban. Sci. 2021, 5, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, K.V.; Ramya, C.; Viswanathan, M.R.; Varjani, S. Plastic pollutants: Effective waste management for pollution control and abatement. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 12, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, R.W.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H.; Jang, J. Microplastic pollution in soil and groundwater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4211–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Du, M.; Jin, A.; Chen, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Ta, K.; Peng, X. Forty-year pollution history of microplastics in the largest marginal sea of the western Pacific. Geochem. Perspect. Lett. 2020, 13, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, O.A.; Ologbonjaye, K.I.; Awosolu, O.; Alalade, O.E. Public and environmental health effects of plastic wastes disposal: A review. J. Toxicol. Risk Assess. 2019, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, S.C. From Parkesine to Celluloid: The birth of organic plastics. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 8090–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, R. The plastics sunset and the bio-plastics sunrise. Coatings 2019, 9, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, R. Production, use, and fate of synthetic polymers. In Plastic Waste and Recycling; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Song, Y.K.; Hong, S.H.; Jang, Y.C.; Jang, M.; Heo, N.W.; Han, G.M.; Lee, M.J.; Kang, D.; et al. Relationships among the abundances of plastic debris in different size classes on beaches in South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetti, E.; Sureda, A.; Tejada, S.; Faggio, C. Microplastic in marine organism: Environmental and toxicological effects. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 64, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Cho, J.; Sohn, J.; Kim, C. Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea. Yansei Med. J. 2023, 64, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwmeester, H.; Hollman, P.C.; Peters, R.J. Potential Health Impact of Environmentally Released Micro- and Nanoplastics in the Human Food Production Chain: Experiences from Nanotoxicology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8932–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, N.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.K.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are we speaking the same language? Recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedgruber, M.; Hufenus, R.; Mitrano, D.M. Mechanistic understanding of microplastic fiber fate and sampling strategies: Synthesis and utility of metal doped polyester fibers. Water Res. 2019, 155, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qiao, F.; Lei, K.; Li, H.; Kang, Y.; Cui, S.; An, L. Microfiber release from different fabrics during washing. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, Z.; Xiang, S.; Yan, H.; Tian, H. Degradation of Polymer Materials in the Environment and Its Impact on the Health of Experimental Animals: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Ruz, V.; Gutow, L.; Thompson, R.C.; Thiel, M. Microplastics in the Marine Environment: A Review of the Methods used for Identification and Quantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3060–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Guan, Z.; Jiang, L.; Tanjg, K. The impact of microplastic pollution in ecological environment: A review. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auta, H.S.; Emenike, C.U.; Fauziah, S.H. Distribution and importance of microplastics in the marine environment: A review of the sources, fate, effects, and potential solutions. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhbarizadeh, R.; Moore, F.; Keshavarzi, B. Investigating microplastics bioaccumulation and biomagnification in seafood from the Persian Gulf: A threat to human health? Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2019, 36, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelms, S.E.; Galloway, T.S.; Godley, B.J.; Jarvis, D.S.; Lindeque, P.K. Investigating microplastic trophic transfer in marine top predators. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, N.; Body-Malapel, M. Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano- and microplastics: A review of the literature. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vattanasit, U.; Kongpran, J.; Ikeda, A. Airborne microplastics: A narrative review of potential effects on the human respiratory system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Vimalkumar, K. A Review of Human Exposure to Microplastics and Insights Into Microplastics as Obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 724989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balali, H.; Morabbi, A.; Karimian, M. Concerning influences of micro/nano plastics on female reproductive health: Focusing on cellular and molecular pathways from animal models to human studies. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2024, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, C.Q.Y.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Tang, B.L. Toxicity of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Mammalian Systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Tian, W.; Yang, Y.; Nie, G.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, S. Microplastics remediation in aqueous systems: Strategies and technologies. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, M.A.M.; Yousaf, B.; Ali, M.B.; Dan, C.; Abbas, Q.; Arif, M.; Yang, X. In situ synthesis of micro-plastics embedded sewage-sludge co-pyrolyzed biochar: Implications for the remediation of Cr and Pb availability and enzymatic activities from the contaminated soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 127005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Eggers, S.L.; Allhusen, E.; Katlein, C.; Peeken, I. Interactions between the ice algae Fragillariopsis cylindrus and microplastics in sea ice. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.S.; Zhang, Q.K.; Zhang, L.S.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.Y.; Hou, X.Y. Impact of a Sewage Treatment Plant on the Accumulation of Microplastics in Freshwater Organisms in the Lijiang River of the Guilin Urban Section. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 4999–5007. [Google Scholar]
- Kuklinski, P.; Wicikowski, L.; Koper, M.; Grala, T.; Leniec-Koper, H.; Barasiński, M.; Talar, M.; Kamiński, I.; Kibart, R.; Małecki, W. Offshore surface waters of Antarctica are free of microplastics, as revealed by a circum-Antarctic study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, N.; Ruberto, L.A.M.; Oberhaensli, F.; Vodopidez, C.; Metian, M.; Alonso-Hernández, C.A. Antartic wastewater: A local source of microplastic pollution. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desforges, J.W.; Galbraith, M.; Dangerfield, N.; Ross, P.S. Widespread distribution of microplastics in subsurface seawater in the NE Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, W.; Meng, Q.; Yang, J. Microplastic contamination in freshwater: First observation in Lake Ulansuhai, Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.R.; Kim, Y.N.; Yoon, J.H.; Dickinson, N.; Kim, K.H. Plastic contamination of forest, urban, and agricultural soils: A case study of Yeoju City in the Republic of Korea. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1962–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, P. Plastic in agricultural soils–A global risk for groundwater systems and drinking water supplies?—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Qi, Y.; Guo, X. The occurrence and distribution characteristics of microplastics in the agricultural soils of Shaanxi Province, in northwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Nadeem, M.A.; Aziz, A.; Safdar, M.E.; Adnan, M.; Ali, A.; Ullah, N.; Akhtar, N.; Abbas, B. Mulching improves weeds management, soil carbon and productivity of spring planted maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Botany Stud. 2020, 5, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Yan, C.; Liu, Q.; Ding, W.; Chen, B.; Li, Z. Effects of plastic mulching and plastic residue on agricultural production: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thinh, T.Q.; Sang, T.T.; Viet, T.Q.; Dan, N.P.; Strady, E.; Chung, K.L. Preliminary assessment on the microplastic contamination in the atmospheric fallout in the Phuoc Hiep landfill, Cu Chi, Ho Chi Minh city. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 62, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Ulke, J.; Font, A.; Chan, K.L.; Kelly, F.J. Atmospheric microplastic deposition in an urban environment and an evaluation of transport. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.T.; Cai, Y.F.; Chen, Y.X.; Yang, Y.W.; Xing, S.C.; Liao, X.D. Occurrence of microplastic in livestock and poultry manure in South China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellas, B.; Binda, G.; Pozzi, A.; Galafassi, S.; Volta, P.; Bettinetti, R. Microplastic contamination in freshwater environments: A review, focusing on interactions with sediments and benthic organisms. Environments 2020, 7, 30–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, D.; Mossotti, R.; Montarsolo, A. Influence of sewing on microplastic release from textiles during washing. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zuo, R.; Wu, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z. Global distribution, drivers, and potential hazards of microplastics in groundwater: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.Q.; McDonough, L.K.; Zainab, S.M.; Guo, Z.F.; Chen, C.; Xu, Y.Y. Microplastic accumulation in groundwater: Data-scaled insights and future research. Water Res. 2024, 258, 121808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, O.M.; Bisset, J.M.; Gilligan, P.J.; Hannan, M.M.; Murray, J.G. Respirators and surgical facemasks for COVID-19: Implications for MRI. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Hu, T.; Huang, W.; Song, B.; Qin, M.; Yi, H. Can incineration completely eliminate plastic wastes? An investigation of microplastics and heavy metals in the bottom ash and fly ash from an incineration plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.C.; Lam, T.H.; Cheng, K.K. Mass masking in the COVID-19 epidemic: People need guidance. Lancet 2020, 395, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y. The occurrence of microplastics in farmland and grassland soils in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Different land use and mulching time in facility agriculture. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, T.A. Surgical face masks as a potential source for microplastic pollution in the COVID-19 scenario. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, M.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y. (Micro)plastic crisis: Un-ignorable contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretti, E.; Pallottini, M.; Rossi, R.; La Porta, G.; Gardi, T.; Cenci Goga, B.T.; Elia, A.C.; Galletti, M.; Moroni, B.; Petroselli, C.; et al. Heavy metal bioaccumulation in honeybee matrix, an indicator to assess the contamination level in terrestrial environments. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, H.; Yang, S.; Gao, J.; Wu, Y.; Diao, Q.; Hou, C. Microplastic Polystyrene Ingestion Promotes the Susceptibility of Honeybee to Viral Infection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11680–11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Basantes, M.F.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Microplastics in Honey, Beer, Milk and Refreshments in Ecuador as Emerging Contaminants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, C.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Vejsnæs, F.; van der Steen, J.J.M.; Fernández-Piñas, F.; Rosal, R. Honeybees as active samplers for microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X. The impact of microplastic-microbe interactions on animal health and biogeochemical cycles: A mini-review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana-Ulloa, V.P.; Arévalo-Moscoso, P.W. Relación Entre la Distancia de Centros Urbanos y la Cantidad de Micro Plásticos Provenientes de los Cuerpos de Abejas (Apis Mellifera) de las Colmenas de Apicultores de la Zona Periurbana del Cantón Gualaceo. 2023. Available online: http://dspace.ups.edu.ec/handle/123456789/25225 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Volovych, O.; Yijia, X.; Shuguo, L.; Xiaoping, D.; Yingai, Z.; Qian, H.; Zhou, H. The potential effects of microplastic pollution on human digestive tract cells. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Trojan horse in the intestine: A review on the biotoxicity of microplastics combined environmental contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, L.; Kelly, F.J. Plastic and Human Health: A Micro Issue? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 12, 6634–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Digiacomo, L.; Xiao, S.; Wang, J.; Amici, A.; Pozzi, D.; Caracciolo, G.; Marchini, C. Insights into the effect of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) microplastics on HER2 signaling pathways. Toxicol. Vitro 2023, 93, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, P.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Lu, G.; He, C. Polystyrene microplastics alter the trophic transfer and biotoxicity of fluoxetine in an aquatic food chain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, B.; Albentosa, M. Insights into the uptake, elimination and accumulation of microplastics in mussel. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Z.; Lu, J.; Fu, G.; Yu, W. The bio-accumulation and -magnification of microplastics under predator-prey isotopic relationships. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 5, 135896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Lu, L.; Ren, H.Y.; Hua, W.; Zheng, N.; Huang, F.Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, M.; Huang, Q. The size-dependence and reversibility of polystyrene nanoplastics-induced lipid accumulation in mice: Possible roles of lysosomes. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covernton, G.A.; Cox, K.D.; Fleming, W.L.; Buirs, B.M.; Davies, H.L.; Juanes, F.; Dudas, S.E.; Dower, J.F. Large size (>100-μm) microplastics are not biomagnifying in coastal marine food webs of British Columbia, Canada. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, e2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierzynski, E.; Gawlik, P.J.; Púzniak, D.; Flieger, W.; Józwik, K.; Teresinski, G.; Forma, A.; Wdowiak, P.; Baj, J.; Flieger, J. Microplastics in the Human Body: Exposure, Detection, and Risk of Carcinogenesis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontes, B.L.M.; de Souza e Souza, L.C.; da Silva de Oliveira, A.P.S.; da Fonseca, R.N.; Neto, M.P.C.; Pinheiro, C.R. The possible impacts of nano and microplastics on human health: Lessons from experimental models across multiple organs. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2024, 27, 153–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facciolá, A.; Visalli, G.; Ciarello, M.P.; Di Pietro, A. Newly Emerging Airborne Pollutants: Current Knowledge of Health Impact of Micro and Nanoplastics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarska, E.; Jutel, M.; Zemelka-Wiacek, M. The potential impact of nano- and microplastics on human health: Understanding human health risks. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brynzak-Schreiber, E.; Schögl, E.; Bapp, C.; Cseh, K.; Kopatz, V.; Jakupec, M.A.; Weber, A.; Lange, T.; Toca-Herrera, J.L.; del Favero, G.; et al. Microplastics role in cell migration and distribution during cancer cell division. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Avignon, G.; Hsu, S.S.H.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Ricciardi, A. Feeding behavior and species interactions increase the bioavailability of microplastics to benthic food webs. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 20, 165261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, I.; Brenna, C.; Passaro, A.; Neri, L.M. Bioaccumulation Rate of Non-Biodegradable Polystyrene Microplastics in Human Epithelial Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 16, 11101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basini, G.; Bussolati, S.; Andriani, L.; Grolli, S.; Bertini, S.; Iemmi, T.; Menozzi, A.; Quintavalla, F.; Ramoni, R.; Serventi, P.; et al. The effects of nanoplastics on adipose stromal cells from swine tissues. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2022, 81, 106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.R.; Baqee, A.; Alam, M.; Khan, M.W.; Muhib, M.I.; Kabir, A. Organ-specific bioaccumulation of microplastics in market fish of Dhaka and size-dependent impacts of PVC microplastics on growth of Anabus testudineus. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Qiang, L.; Shi, H.; Cheng, J. Bioaccumulation of microplastics and its in vivo interactions with trace metals in edible oysters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shao, Z. Biodegradation of Typical Plastics: From Microbial Diversity to Metabolic Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Wu, D.; Yu, Y.; Han, S.; Sun, L.; Li, M. Impact of microplastics on bioaccumulation of heavy metals in rape (Brassica napus L.). Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Huo, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Shao, B.; Li, Y.; Song, M. The toxic effects and mechanisms of maternal exposure to Bisphenol F during gestation and lactation on lungs in female offspring mice. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Du, D.; Yu, W.; Wu, C.; Ruan, H.; Zhou, P.; Ding, Z.; et al. Bisphenol M inhibits mouse oocyte maturation in vitro by disrupting cytoskeleton architecture and cell cycle processes. Reprod. Toxicol. 2024, 124, 108667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, B.; Fytianos, G. Towards Microplastic Reduction Within Institutions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protyusha, G.B.; Robin, B.K.; Ineyathendral, T.R.; Shivani, S.S.; Sivasamy, I.A.; Samuel, S. Microplastics in oral healthcare products (OHPs) and their environmental health risks and mitigation measures. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 15, 123118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Kumar, M.; Sarsaiya, S.; Sirohi, R.; Awasthi, S.K.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A.; Bolan, N.S.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Challenges and opportunities in bioremediation of micro-nano plastics: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 1, 149823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malankowska, M.; Echaide-Gorriz, C.; Coronas, J. Microplastics in marine environment: A review on sources, classification, and potential remediation by membrane technology. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wen, X.; Chen, M.; Yi, H. Removal of microplastics via drinking water treatment: Current knowledge and future directions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, A.H.; Yesilay, G.; Hazeem, L.; Rashdan, S.; AlMealla, R.; Kilinic, Z.; Ali, F.; Abdulrasool, F.; Kamel, A.H. Micro- and Nano-Plastics Contaminants in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Toxicity, Detection, Remediation, and Sustainable Perspectives. Water 2023, 15, 3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohi Bano, K.; Kuddus, M.; Zaheer, M.R.; Zia, Q.; Khan, M.F.; Ashraf, G.M.; Gupta, A.; Aliev, G. Microbial Enzymatic Degradation of Biodegradable Plastics. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 429–440. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Biswas, K. Reports of Actinomycetes to Degrade Microplastic. In Microplastic Pollution; Shahnawaz, M., Adetunji, C.O., Dar, M.A., Zhu, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2024; pp. 473–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayaka, A.H.; Tibpromma, S.; Dai, D.; Xu, R.; Suwannarach, N.; Stephenson, S.L.; Dao, C.; Karunarathna, S.C. A Review of the Fungi That Degrade Plastic. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, J.; Khatri, M.; Arya, S.K. Recent insight into enzymatic degradation of plastics prevalent in the environment: A mini-review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 2, 100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; Luan, Y. Enzymatic degradation of synthetic plastics by hydrolases/oxidoreductases. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 189, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, J.; Martínez-Gallardo, M.R.; Jurado, M.M.; Suárez-Estrella, F.; López-González, J.A.; Estrella-González, M.J.; Toribio, A.J.; Carpena-Istán, V.; Barbani, N.; Cappello, M.; et al. Microbial consortia for multi-plastic waste biodegradation: Selection and validation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Sharma, B.; Shukla, P. Integrated approaches in microbial degradation of plastics. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skariyachan, S.; Taskeen, N.; Kishore, A.P.; Krishna, B.V. Recent advances in plastic degradation–From microbial consortia-based methods to data sciences and computational biology driven approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Resources Institute. Legal Limits on Single-Use Plastics and Microplastics: A Global Review of National Laws and Regulations. Available online: https://es.wri.org/proyectos/limites-legales-para-plasticos-y-microplasticos-de-un-solo-uso (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Congreso de la Ciudad de México. Available online: https://www.congresocdmx.gob.mx/comsoc-diputados-prohiben-venta-productosplasticos-solo-uso-cdmx-las-empresas-tendran-que-fabricar-articulos-biodegradables14661.html#:~:text=El%20Poder%20Legislativo%20de%20la,consumidor%2C%20salvo%2que%20sean%20compostables (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Microbeads in Toiletries Regulations, 2017. SOR/2017-111. Available online: https://laws-lois.justice.gc.ca/eng/regulations/SOR-2017-111/page-1.html (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- H.R.1321-114th Congress (2015–2016): Microbead-Free Waters Act of 2015. (2015, Diciembre 28). Available online: https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/house-bill/1321 (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- The Environmental Protection (Microbeads) (Wales) Regulations 2018, SI 2018/1095. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/wsi/2018/1095/article/3/made (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA). Resolution 1/6 on Marine Plastic Litter and Microplastics; UNEP/EA.1/6; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenya, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carratta, G.; Jaeckel, L. Global plastics governance: Opportunities and challenges for its improvement from a life cycle perspective. Eur. J. Legal Stud. 2023, 15, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S. International Law and Regulation of Marine Microplastics: Current Situation, Problems, and Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
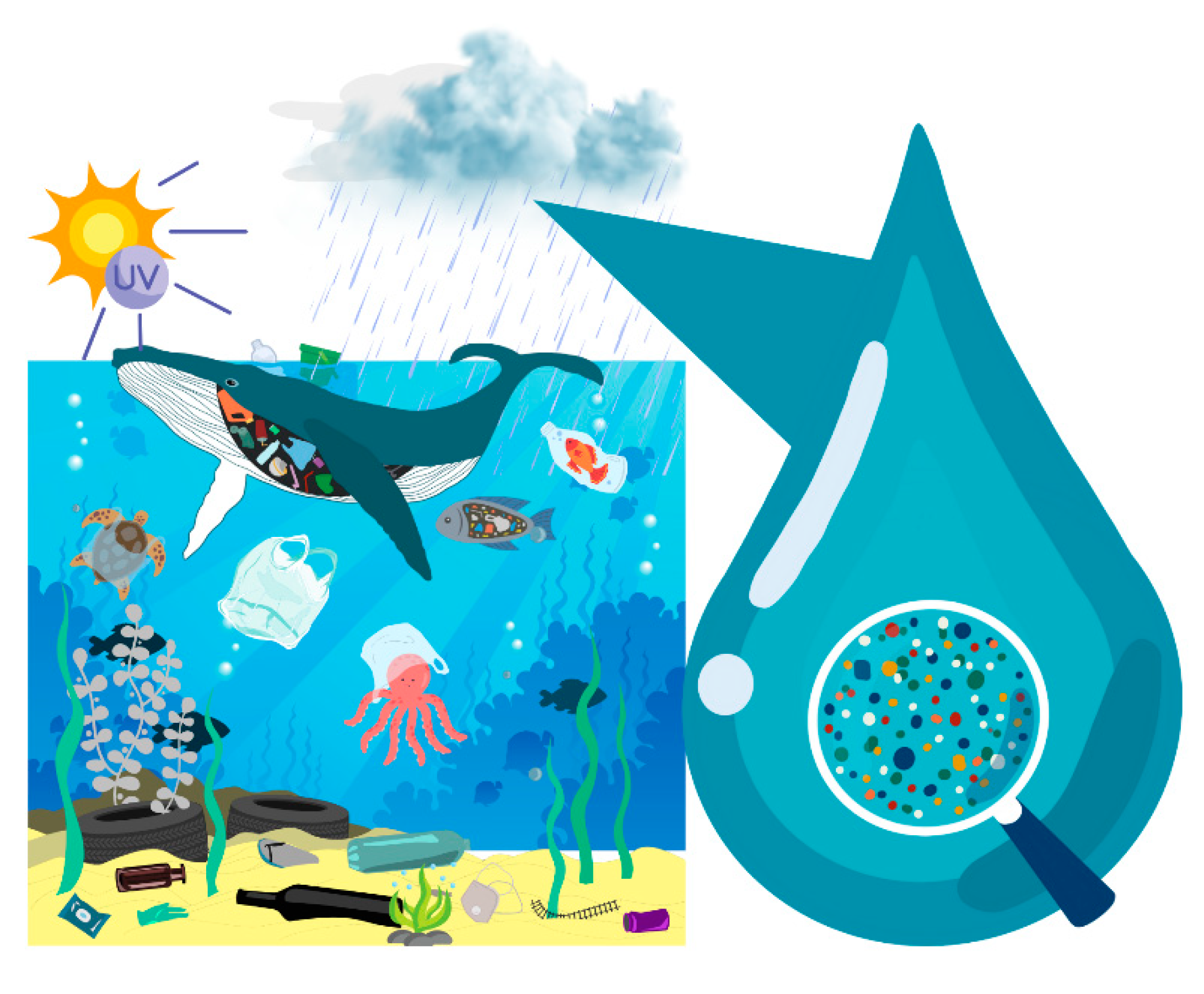


| Year | Plastic Discovered | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 1839 | Polystyrene and vulcanized rubber | [9] |
| 1860 | Parkesine | [10] |
| 1870 | Celluloid | [10] |
| 1907 | Bakelite | [11] |
| 1920 | Polyvinyl chloride | [12] |
| 1940 | Advanced durable plastics | [7] |
| Microplastic Type | Size Range (mm) | Common Polymers | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fragments | 0.02–0.2 | Polypropylene, polyethylene | [50,51] |
| Fibers | 0.02–0.05 | Polypropylene, polyamide | |
| Fibers | 0.0–0.5 | Polyethylene, polypropylene, high-density polyethylene | |
| Fibers (Groundwater) | Variable | Polyethylene | |
| Pellets (Groundwater) | Variable | Polypropylene, polystyrene |
| Findings Reported by Researchers | Reference |
|---|---|
| Polystyrene micro- and nanospheres of different sizes can enter small intestine and colon epithelial cells, with nanospheres showing greater uptake. High concentrations of 5 μm PS-MPs significantly affected mitochondrial membrane potential. | [64] |
| Microplastic pollution is a global issue, with exposure pathways through diet, inhalation, and absorption. MPs <2.5 μm pose lung risks, while larger MPs impact the gastrointestinal tract. | [66] |
| Polystyrene MPs increase fluoxetine accumulation in Artemia but reduce it in zebrafish. MPs mitigate fluoxetine’s biotoxic effects on fish neurotransmission but exacerbate oxidative damage, apoptosis, and immune responses. | [68] |
| High-density polyethylene MPs (≤22 μm) were ingested by mussels, with smaller MPs (<6 μm) persisting in the digestive gland after depuration. | [69] |
| MPs in commercially important fish species (Larimichthys polyactis and Collichthys lucidus) were mainly fibers, blue in color, and PET-based. C. lucidus had a higher tendency for MP accumulation. | [70] |
| Micro- and nanoplastics translocate through the food chain, detected in key mammalian organs after ingestion by Tenebrio molitor larvae and subsequent consumption by mice. | [83] |
| Smaller fish species ingest more MPs relative to body weight, with rapid excretion in rockfish. Trophic transfer occurs between prey and predators. | [72] |
| MP bioaccumulation in humans is linked to respiratory disorders, neurological symptoms, inflammatory bowel disease, and gut microbiota alterations. | [73,74,75,76] |
| Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics enhance cell migration in colorectal cancer cell lines, suggesting a pro-metastatic effect. | [77] |
| MPs bioaccumulate within food chains, with mussels transferring MPs to amphipods, which are then ingested by round goby fish. | [78] |
| MPs of different sizes (1 and 2 µm) showed varying bioaccumulation tendencies in human liver, lung, and intestinal epithelial cells, with the highest absorption in liver cells. | [79] |
| PET MPs can cross the gastrointestinal epithelium and interfere with HER2-driven signaling pathways, impacting cell survival. | [67] |
| MP exposure in HEK-293 and HaCaT cells alters oxidative mechanisms and inflammatory markers. | [80] |
| Market fish kidneys accumulated the highest MP concentrations, mainly fibers. Larger PVC MPs caused more growth defects in fish. | [81] |
| MPs were detected in oyster tissues, mainly in gills and mantles. Trace metals adsorbed onto MPs, increasing contamination risks. | [82] |
| Polystyrene nanoplastics exposure increased hepatic lipid accumulation in mice via autophagy and lysosomal pathways. | [71] |
| MPs facilitate heavy metal entry into rapeseed plants, affecting antioxidant enzymes and degrading plant quality. | [84] |
| Prenatal exposure to bisphenol F (BPF) led to lung inflammation and altered gene expression in offspring. | [85] |
| Bisphenol M (BPM) disrupted microtubule stability in mouse oocytes, causing meiotic arrest. | [86] |
| Thickness Category (Microns) | Countries with Regulations |
|---|---|
| 15 microns | Uzbekistan, Republic of Moldova |
| 20–25 microns | Bangladesh, Botswana, China, Mongolia, South Africa |
| 30 microns | Albania, Cambodia, Ethiopia, Mozambique, Nepal, Senegal, Uganda, etc. |
| 35–40 microns | Tunisia, Vanuatu |
| 50 microns | France, India, Italy, Madagascar, Pakistan, Romania, Monaco, Poland, UK, Andorra, Portugal, Cyprus |
| 60 microns | Cameroon, Yemen, Malawi |
| 100 microns and above | Eritrea, Jordan, Saudi Arabia |
| Region | Country | Regulation Summary |
|---|---|---|
| Africa | Burkina Faso | Prohibition of production, import, marketing, and distribution of non-biodegradable plastic packaging and bags. |
| Niger | Ban on plastic bags, except for those certified as biodegradable per standards. | |
| Asia-Pacific | India | Thickness requirement (50 microns) does not apply to compostable plastic bags meeting prescribed standards. |
| Republic of Korea | Biodegradable plastic bags may be distributed for free. | |
| Europe | Austria | Plastic bags must include a minimum percentage of recyclable materials. |
| France | Ban on single-use non-compostable plastic bags under 50 microns; bio-sourced content requirement to increase from 30% (2017) to 60% (2025). | |
| Latin America | Colombia | Plastic bags must contain at least 40% post-consumer or post-industrial recycled material, following technical standards. |
| Paraguay | Gradual transition from polyethylene bags to biodegradable alternatives. | |
| West Asia | Saudi Arabia | Disposable plastic products (polypropylene and polyethylene) must be oxo-degradable and biodegradable per regulations. |
| United Arab Emirates | Manufacturers and suppliers must comply with oxo-degradable bag standards before distribution. |
| Country | Law or Regulation Name |
|---|---|
| Canada | Microbeads in Toiletries Regulations (SOR/2017-111), 2 June 2017. |
| France | Reclaiming Biodiversity, Nature and Landscapes Act No 2016-1087 of 8, Article 124, August 2016. |
| Italy | General Budget Law 2018: Law no. 205 of 27, Art.1, Sections 543 to 548, December 2017. |
| Republic of Korea | Regulations on safety standards for cosmetics [Annex 1] {No. 2017-114, Notice, Article 3, 29 December 2017. |
| New Zealand | Waste Minimisation (Microbeads) Regulations 2017, under section 23(1)(b) of the Waste Minimisation Act 2008. |
| Sweden | Regulation amending Regulation (1998: 944) prohibiting etc. in certain cases in connection with handling, import and export of chemical products. |
| UK | The Environmental Protection (Microbeads) (England) Regulations 2017. The Environmental Protection (Microbeads) (Scotland) Regulations 2018. The Environmental Protection (Microbeads) (Wales) Regulations 2018. The Environmental Protection (Microbeads) (Northern Ireland) Regulations 2018. |
| US | Microbead-Free Waters Act of 2015. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Méndez, M.A.; Fraga-Cruz, G.S.; Domínguez-García, S.; Pérez-Méndez, M.L.; Bocanegra-Díaz, C.I.; Nápoles-Rivera, F. Microplastic Pollution in Soil and Water and the Potential Effects on Human Health: A Review. Processes 2025, 13, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020502
Pérez-Méndez MA, Fraga-Cruz GS, Domínguez-García S, Pérez-Méndez ML, Bocanegra-Díaz CI, Nápoles-Rivera F. Microplastic Pollution in Soil and Water and the Potential Effects on Human Health: A Review. Processes. 2025; 13(2):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020502
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Méndez, Mario Alberto, Guadalupe Selene Fraga-Cruz, Saúl Domínguez-García, Martha Lizeth Pérez-Méndez, Christian Israel Bocanegra-Díaz, and Fabricio Nápoles-Rivera. 2025. "Microplastic Pollution in Soil and Water and the Potential Effects on Human Health: A Review" Processes 13, no. 2: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020502
APA StylePérez-Méndez, M. A., Fraga-Cruz, G. S., Domínguez-García, S., Pérez-Méndez, M. L., Bocanegra-Díaz, C. I., & Nápoles-Rivera, F. (2025). Microplastic Pollution in Soil and Water and the Potential Effects on Human Health: A Review. Processes, 13(2), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020502







