Curved-Layer Slicing and Continuous Path Planning for Multi-Axis Printing of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Multi-Axis Printing Process Planning for FRC Structures
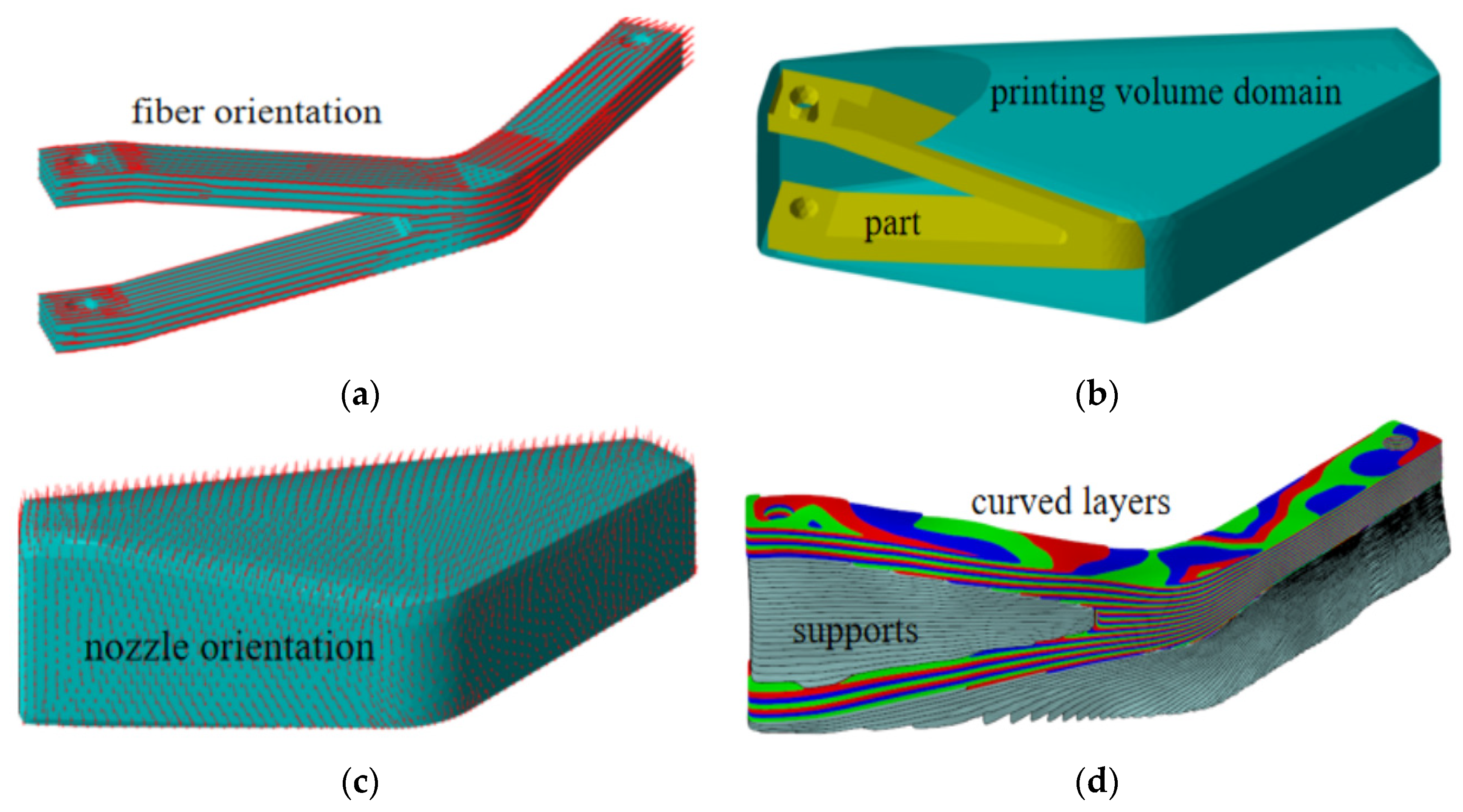
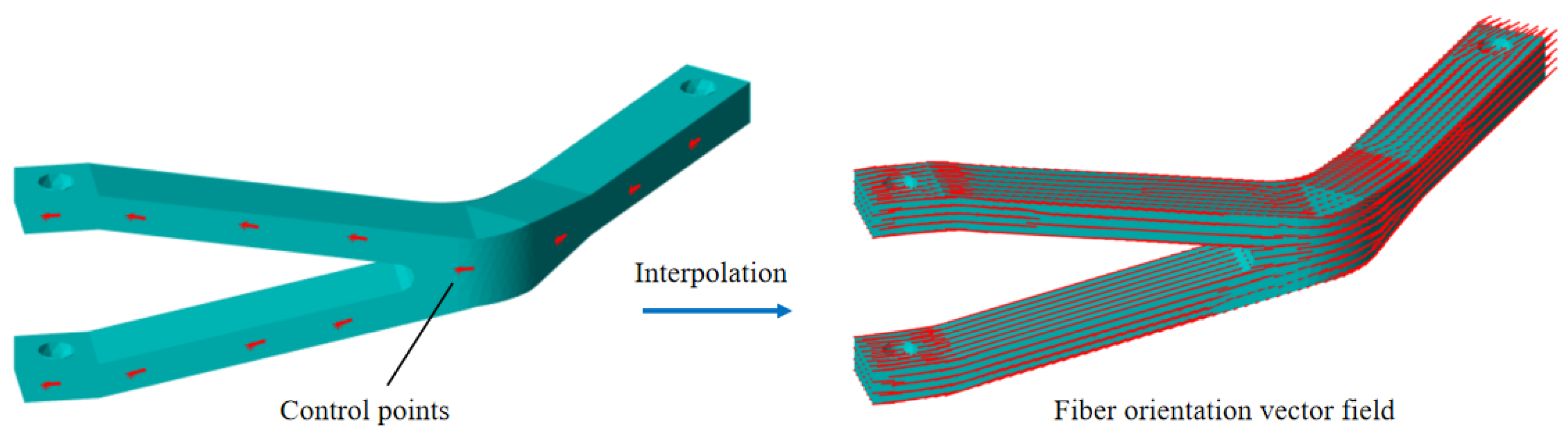
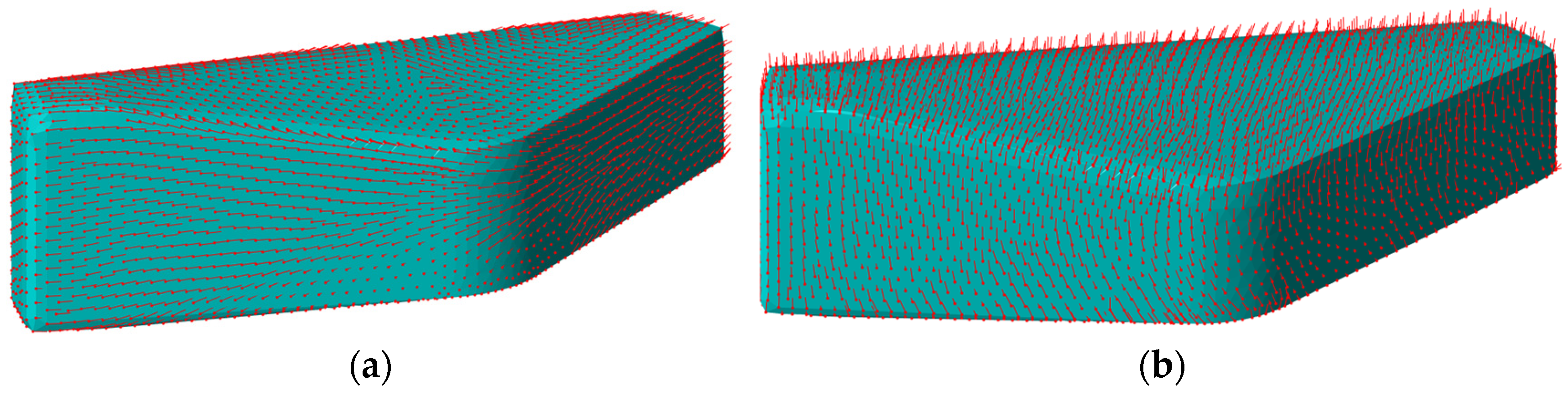
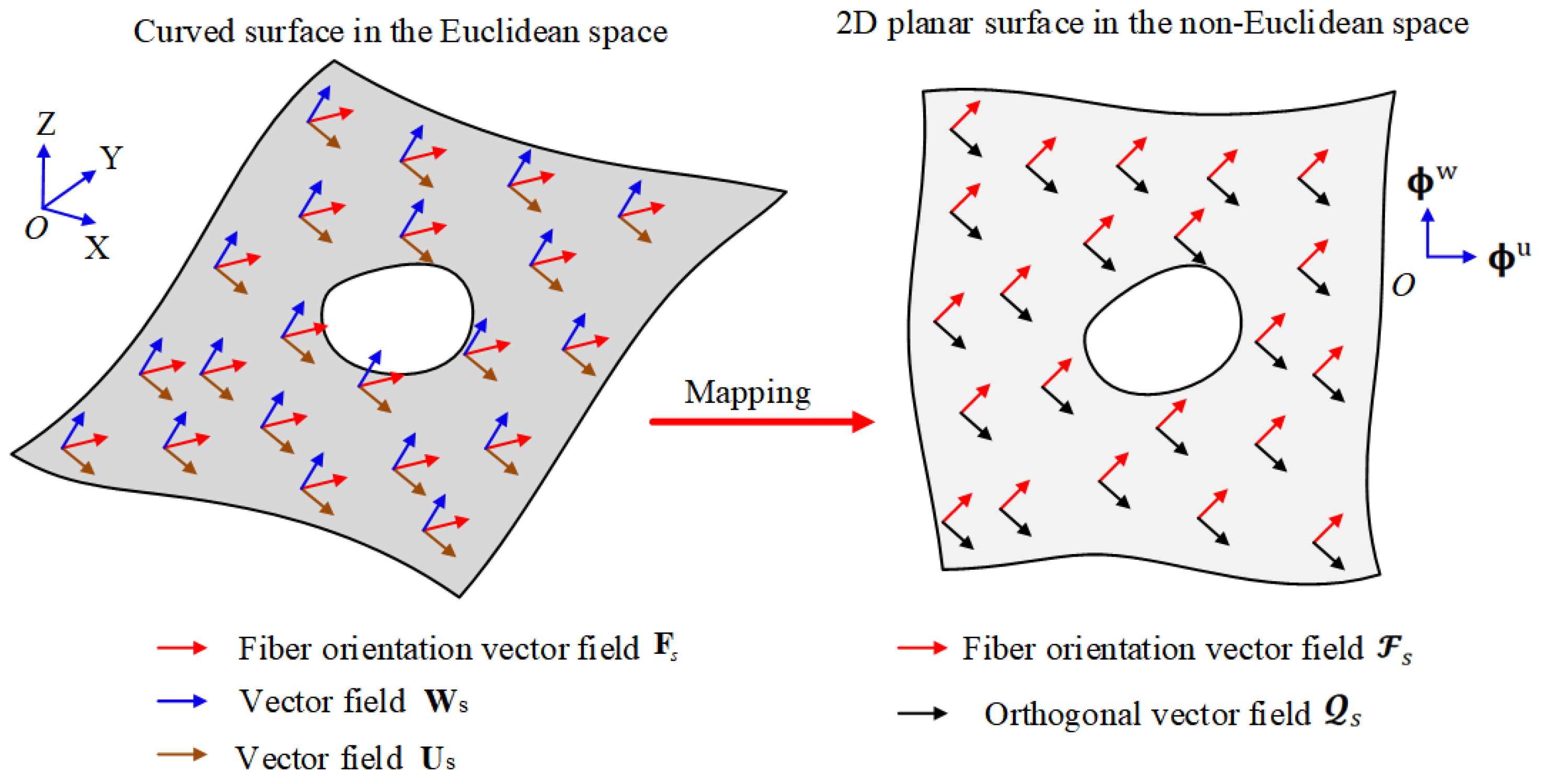
2.1. Generation of the Fiber Orientation Vector Field
2.2. Generation of the Nozzle Orientation Vector Field
2.3. Adaptive Curved-Layer Slicing Method
| Algorithm 1. Calculation of the scalar field of P. |
| Input: the orientation vector field P embedded on the tetrahedral mesh 1 2 Solve the Poisson equation and obtain the scalar field 3 Calculate the gradient vector field of 4 Let . Calculate , and let 5 Calculate the angle error between and , and let 6 if is no longer decreasing then 7 8 else 9 go to line 2 10 end |
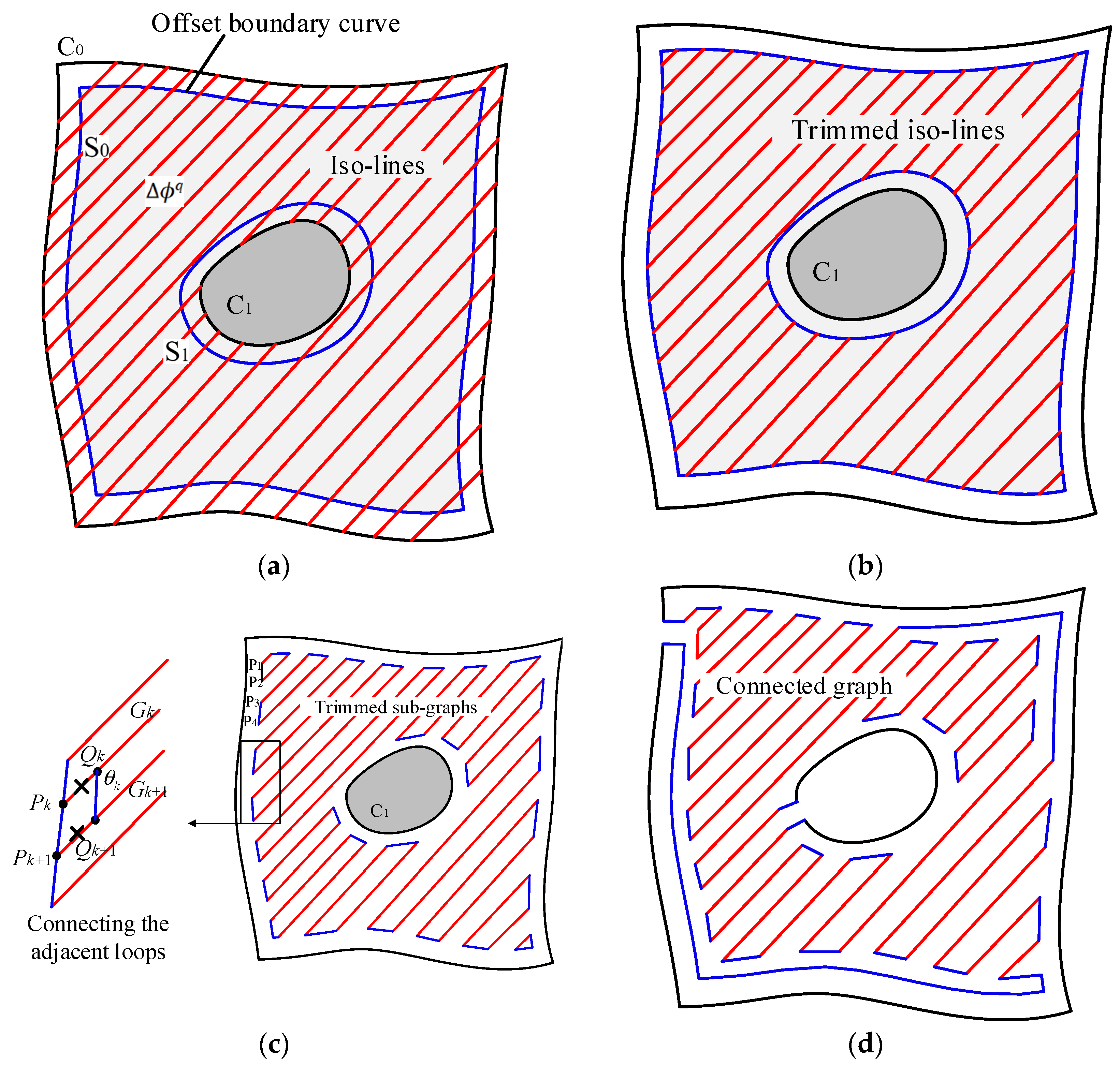
2.4. Vector Field-Driven Path Planning Method
2.5. Vector Field-Driven Path Planning Method
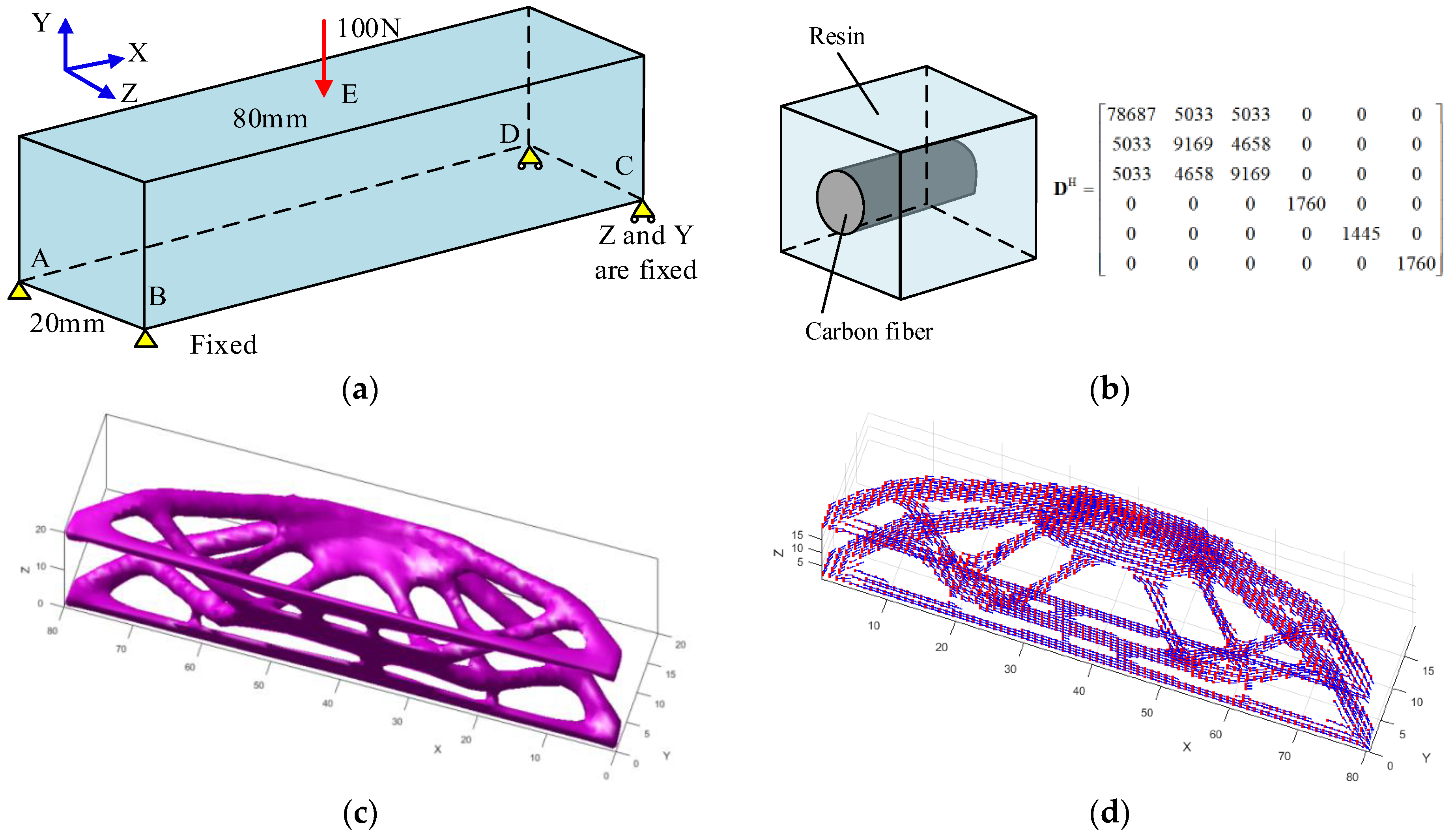
3. Experiment and Discussion
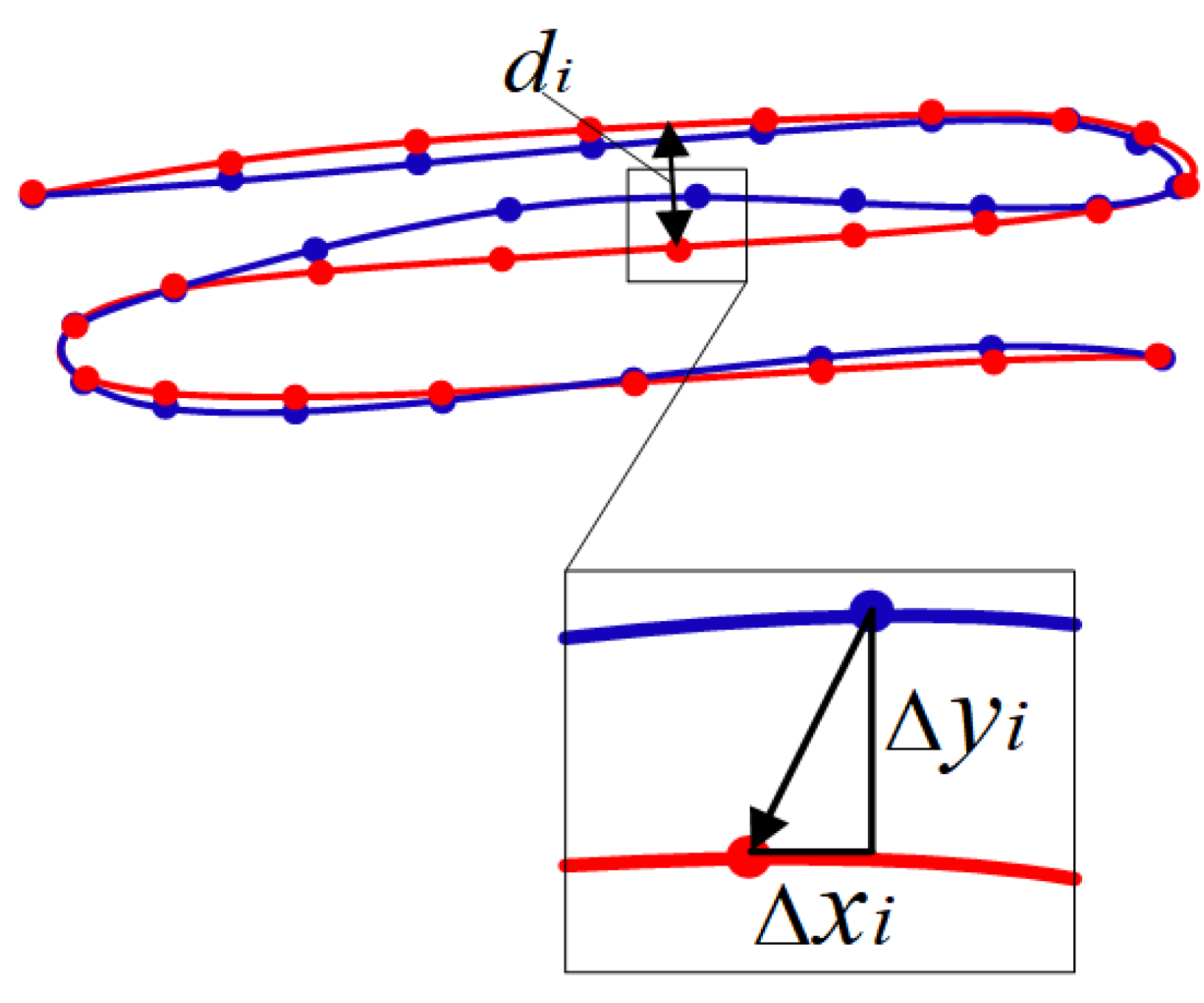
3.1. Vector Field-Driven Continuous Path Planning
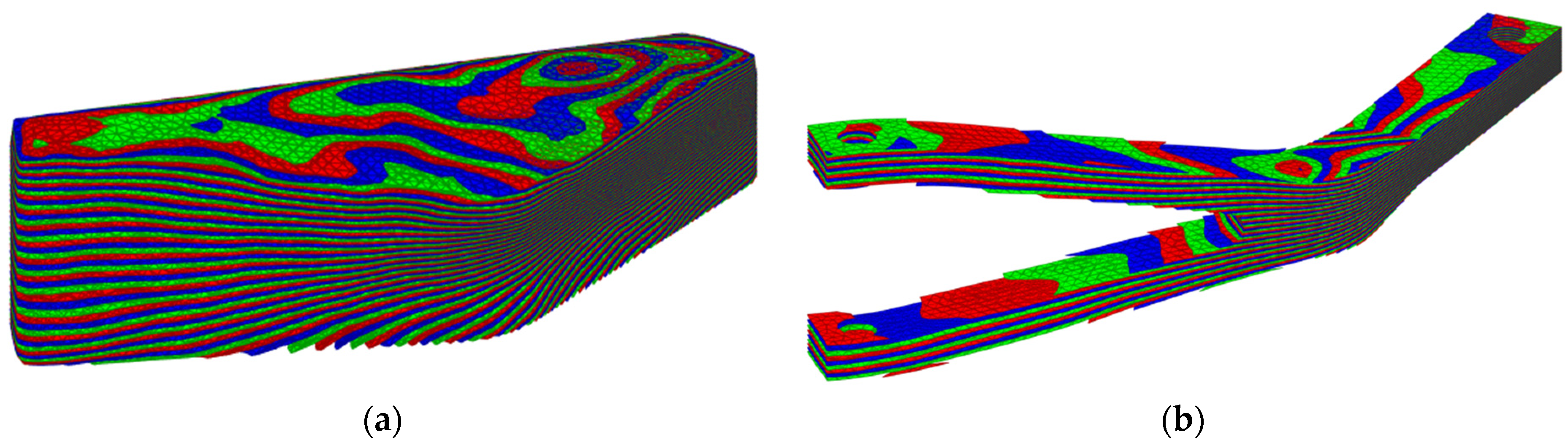
3.2. Multi-Axis Printing of 3D FRC Structures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FRC | Fiber-reinforced composite |
| AM | Additive manufacturing |
| FDM | Fused deposition modeling |
References
- Wong, J.; Altassan, A.; Rosen, D.W. Additive manufacturing of fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A technical review and status of design methodologies. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 255, 110603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, K.; He, D.; Wang, X. Multi-Axis Support-Free Printing of Freeform Parts with Lattice Infill Structures. Comput.-Aided Des. 2021, 133, 102986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, Y.D.; Joshi, S.C.; Bhudolia, S.K.; Gohel, G. Recent Advances on the Design Automation for Performance-Optimized Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite Components. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonov, A.A. 3D topology optimization of continuous fiber-reinforced structures via natural evolution method. Compos. Struct. 2019, 215, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoglund, R.; Smith, D.E. Continuous fiber angle topology optimization for polymer fused filament fabrication. In Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium; University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2016; pp. 1078–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Hoglund, R.; Smith, D.E. Continuous Fiber Angle Topology Optimization for Poly-mer Composite Deposition Additive Manufacturing Applications. Fibers 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, L.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Tong, H. Full-scale topology optimization for fiber-reinforced structures with continuous fiber paths. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 377, 113668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.H.S., Jr.; Christoff, B.G.; Tita, V.; St-Pierre, L. A concurrent fibre orientation and topology optimisation framework for 3D-printed fibre-reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 232, 109872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Lee, J.; Nomura, T.; Dede, E.M. Inverse design of three-dimensional fiber reinforced composites with spatially-varying fiber size and orientation using multiscale topology optimization. Compos. Struct. 2022, 279, 114768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Kawamoto, A.; Kondoh, T.; Dede, E.M.; Lee, J.; Song, Y.; Kikuchi, N. Inverse design of structure and fiber orientation by means of topology optimization with tensor field variables. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Mogra, M.; Sridhara, S.; Kumar, K.; Sesha, G.; Ananthasuresh, G.K. Topological-derivative-based design of stiff fiber-reinforced structures with optimally oriented continuous fibers. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 63, 703–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tian, X.; Wu, L.; Zia, A.A.; Liu, T.; Li, D. Progressive concurrent topological optimization with variable fiber orientation and content for 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 255, 110602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapetrou, V.S.; Patel, C.; Tamijani, A.Y. Stiffness-based optimization framework for the topology and fiber paths of continuous fiber composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, F.; Compel, W.S.; Lewicki, J.P.; Tortorelli, D.A. Optimal design of fiber reinforced composite structures and their direct ink write fabrication. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2019, 353, 277–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.-P.; Couret, L.; Gout, C.; Pedersen, C.B.W. Structural topology optimization with smoothly varying fiber orientations. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2020, 62, 3105–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, N.; Link, G.; Jelonnek, J.; Fleischer, J.; Dittus, J.; Kupzik, D. Load-dependent path planning method for 3D printing of continuous fiber reinforced plastics. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Link, G.; Wang, T.; Ramopoulos, V.; Neumaier, D.; Hofele, J.; Walter, M.; Jelonnek, J. Path-designed 3D printing for topological optimized continuous carbon fibre reinforced composite structures. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 182, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fang, G.; Liao, W.-H.; Wang, C.C.L. Field-Based Toolpath Generation for 3D Printing Continuous Fibre Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 49, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breseghello, L.; Naboni, R. Toolpath-based design for 3D concrete printing of carbon-efficient architectural structures. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 56, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, S.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, C.C.L. Reinforced FDM: Multi-axis filament alignment with controlled anisotropic strength. ACM Trans. Graph. 2020, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lin, S.; Ma, G. Stress-based tool-path planning methodology for fused filament fabrication. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, N.; Ueda, M. 3D-printed high-toughness composite structures by anisotropic topology optimization. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 253, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Li, Q.; Luo, Y.; Liu, S. Concurrent topology and fiber orientation optimization method for fiber-reinforced composites based on composite additive manufacturing. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 395, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Masania, K.; Wang, C.C. Exceptional mechanical performance by spatial printing with continuous fiber: Curved slicing, toolpath generation and physical verification. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 82, 104048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Fang, G.; Huang, Y.; Dutta, N.; Lefebvre, S.; Kilic, Z.M.; Wang, C.C.L. S3-Slicer: A General Slicing Framework for Multi-Axis 3D Printing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2022, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, C.C.L. Neural Slicer for Multi-Axis 3D Printing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2024, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M.; Xia, L.; Tran, P.; Li, Z.; Wan, Q.; Wang, L.; Shen, W.; Ma, G.; Xie, Y.M. Continuous contour-zigzag hybrid toolpath for large format additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 55, 102822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Gu, F.; Huang, Q.-X.; Garcia, J.; Chen, Y.; Tu, C.; Benes, B.; Zhang, H.; Cohen-Or, D.; Chen, B. Connected fermat spirals for layered fabrication. ACM Trans. Graph. 2016, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Chen, F. Path Planning of a Type of Porous Structures for Additive Manufacturing. Comput.-Aided Des. 2019, 115, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, J. A new continuous printing path planning method for gradient honeycomb infill structures. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, G.; Cortés, C.; Creus, C.; Amilibia, M.Z.; Moreno, A. Generation of continuous hybrid zig-zag and contour paths for 3D printing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 7025–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tian, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, D.; Malakhov, A.V.; Polilov, A.N. Multiscale concurrent design and 3D printing of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites with optimized fiber trajectory and topological structure. Compos. Struct. 2022, 285, 115241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, D.; Yuan, S.; Tang, K.; Zhu, J. Vector field-based curved layer slicing and path planning for multi-axis printing. Robot. Comput. -Integr. Manuf. 2022, 77, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelsbrunner, H.; Mücke, E.P. Three-dimensional alpha shapes. ACM Trans. Graph. 1994, 13, 43–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yan, H. Alpha shape and Delaunay triangulation in studies of protein-related interactions. Brief. Bioinform. 2014, 15, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
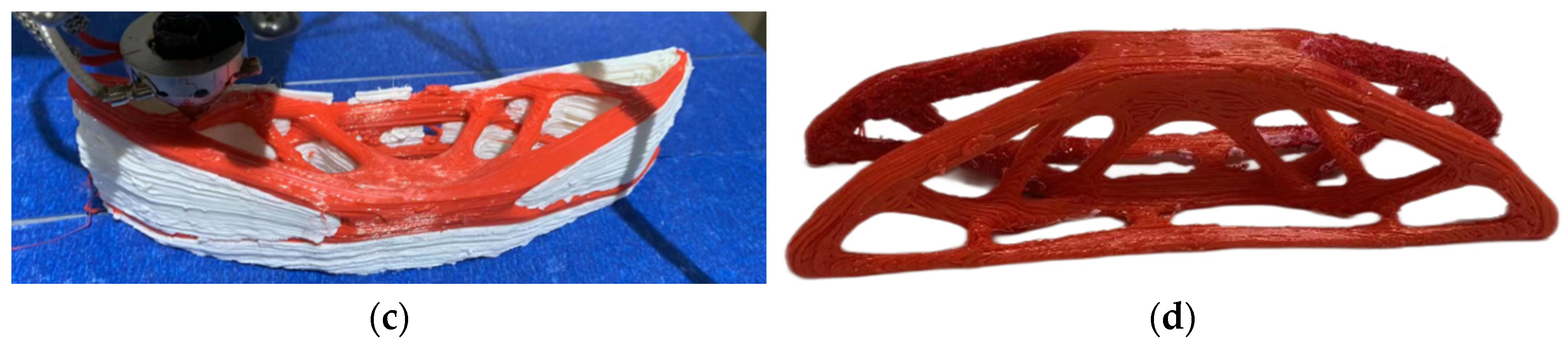
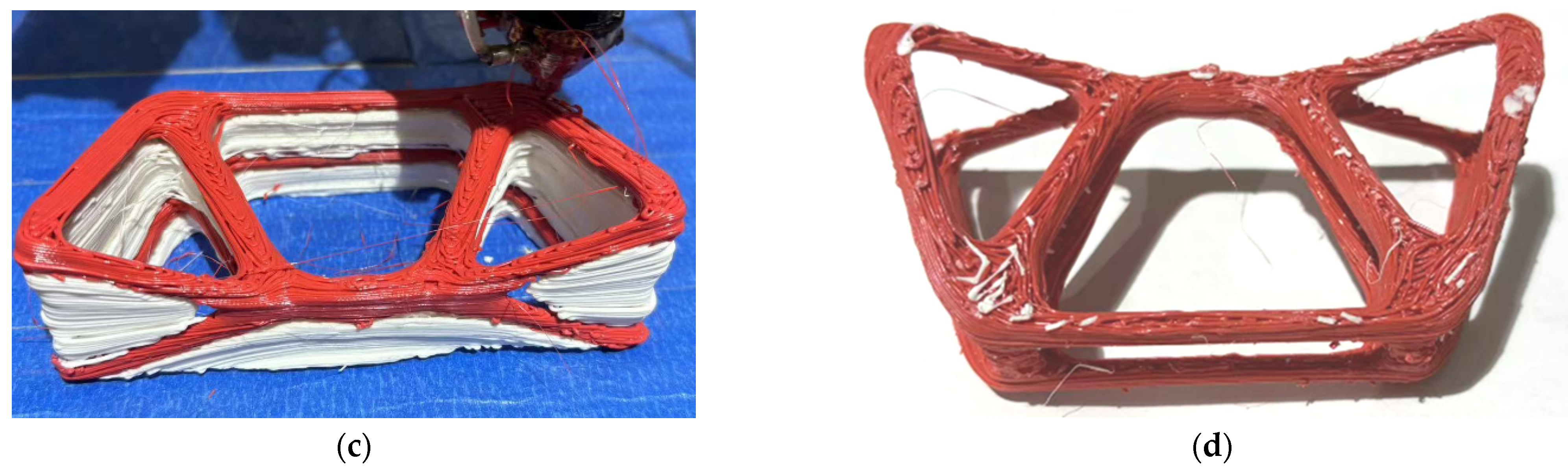




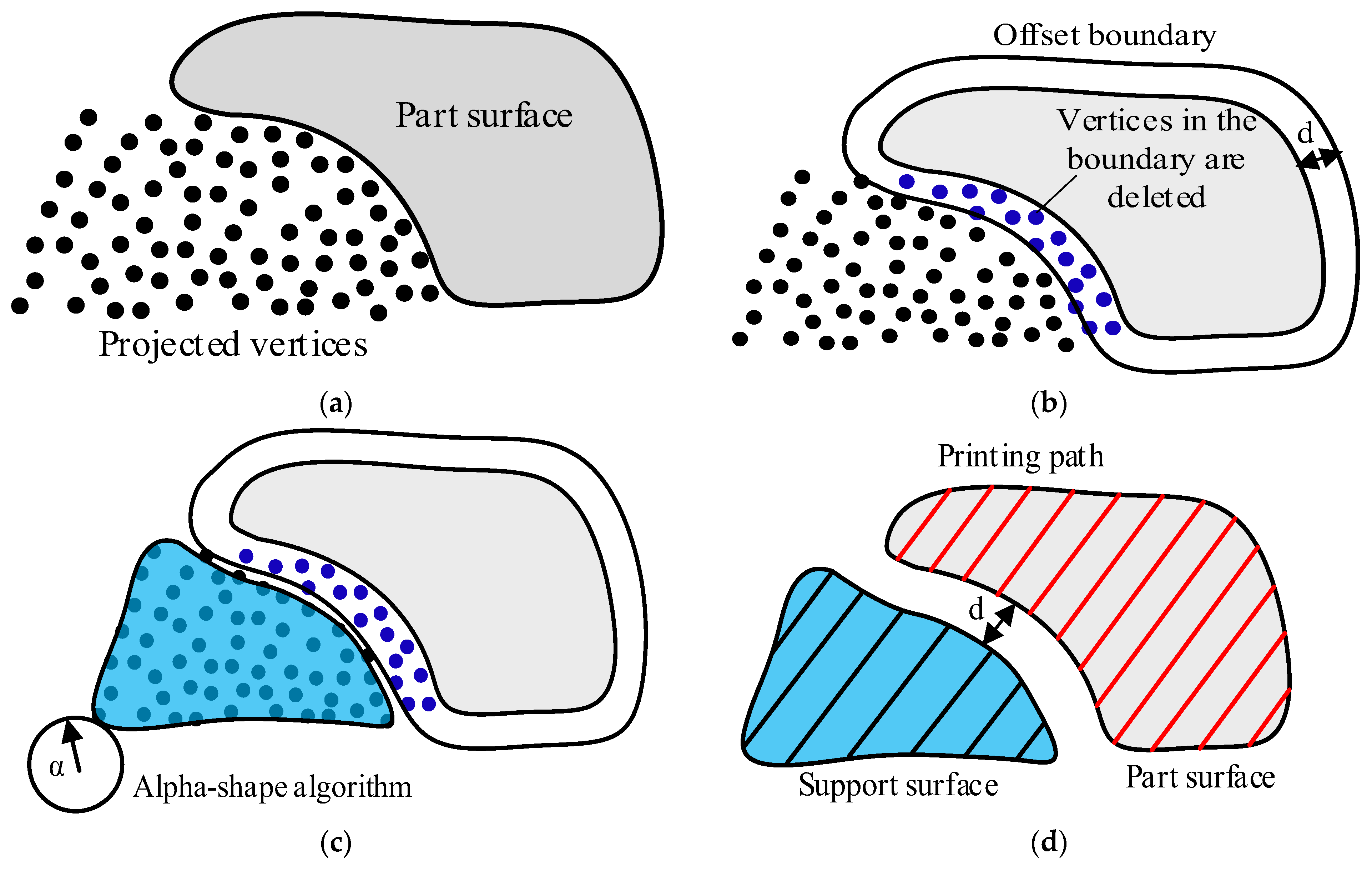
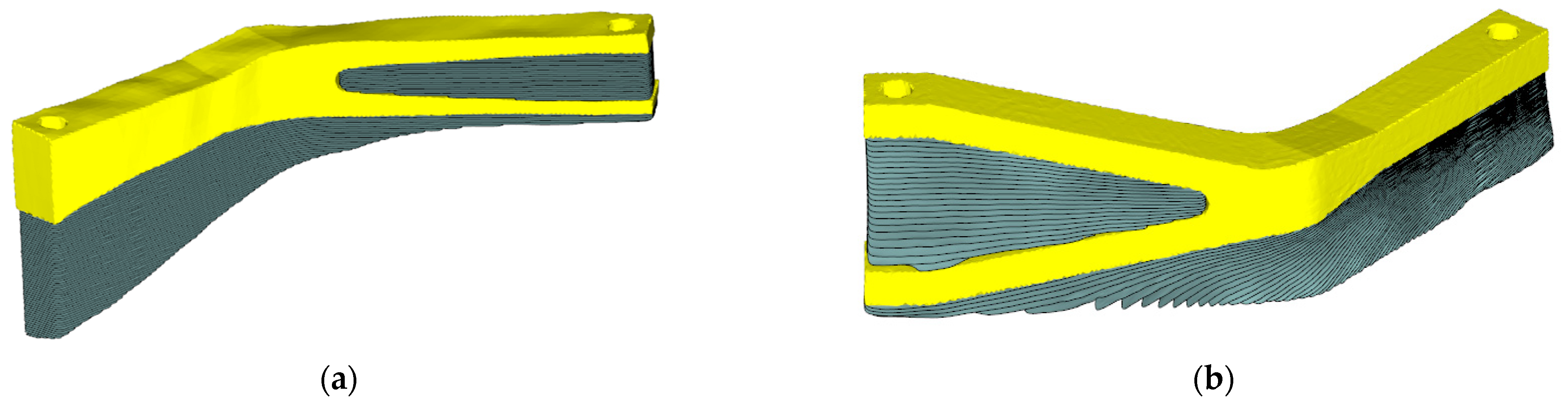

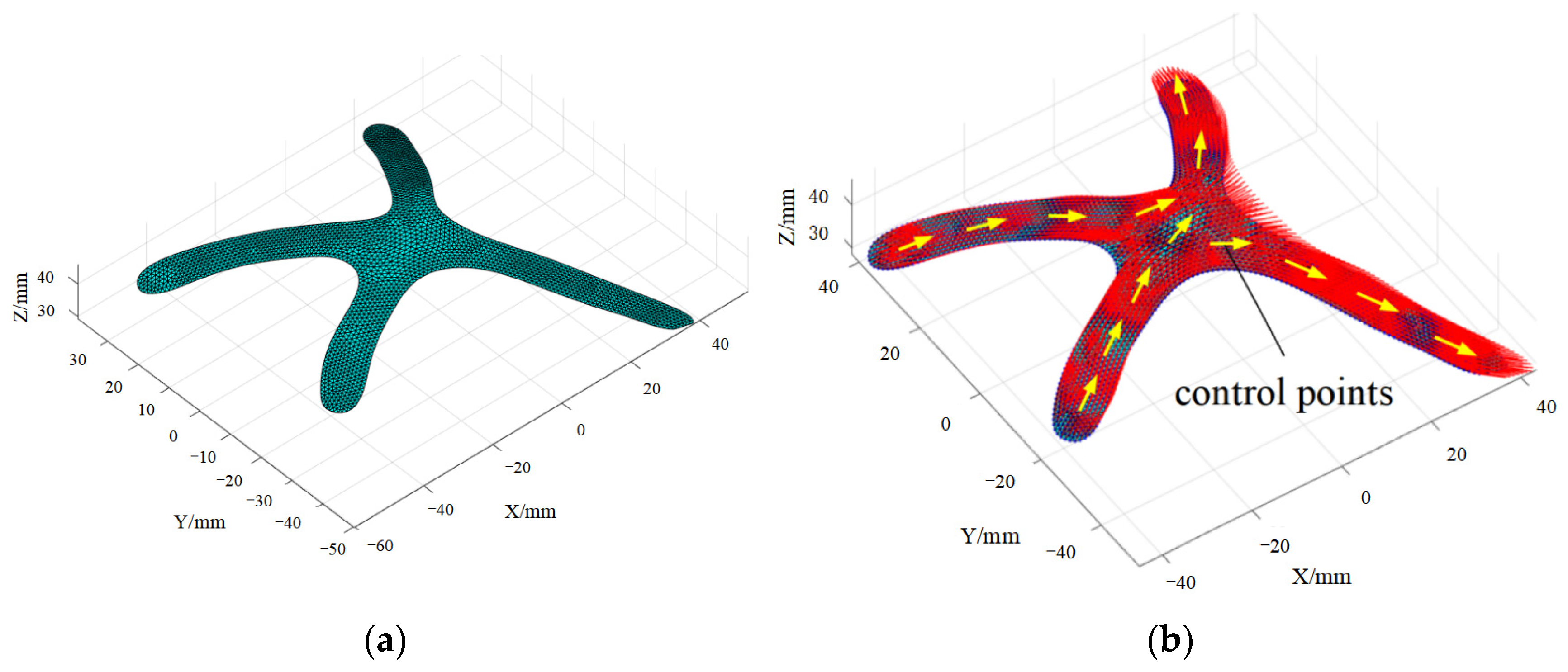


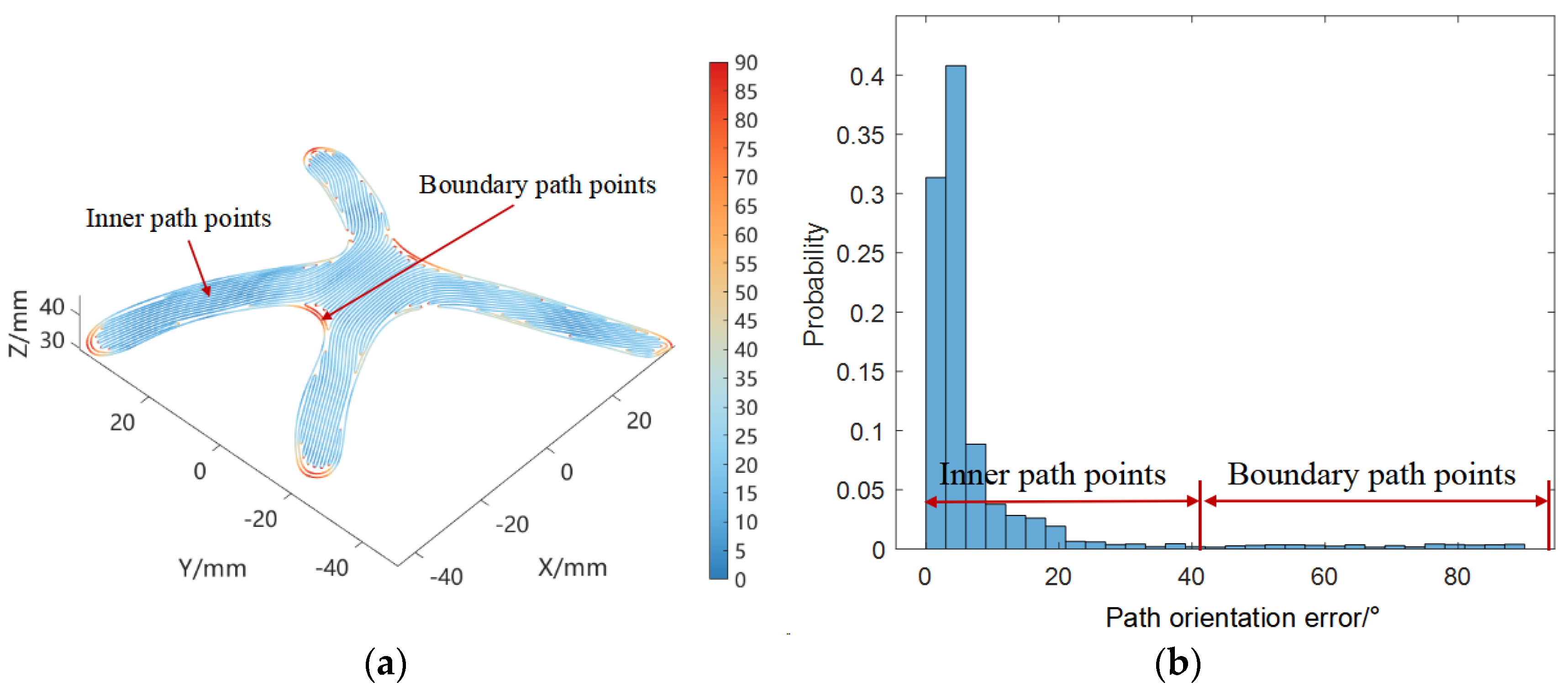


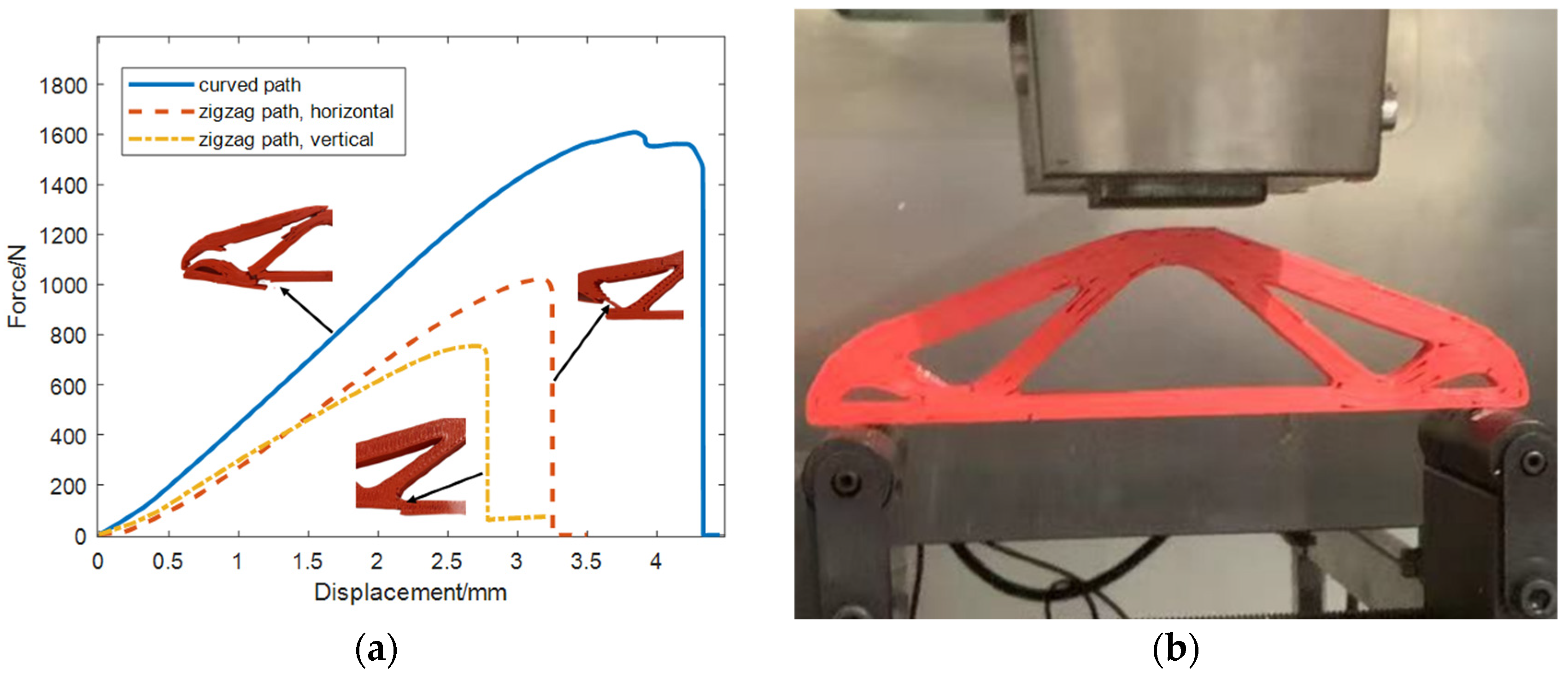



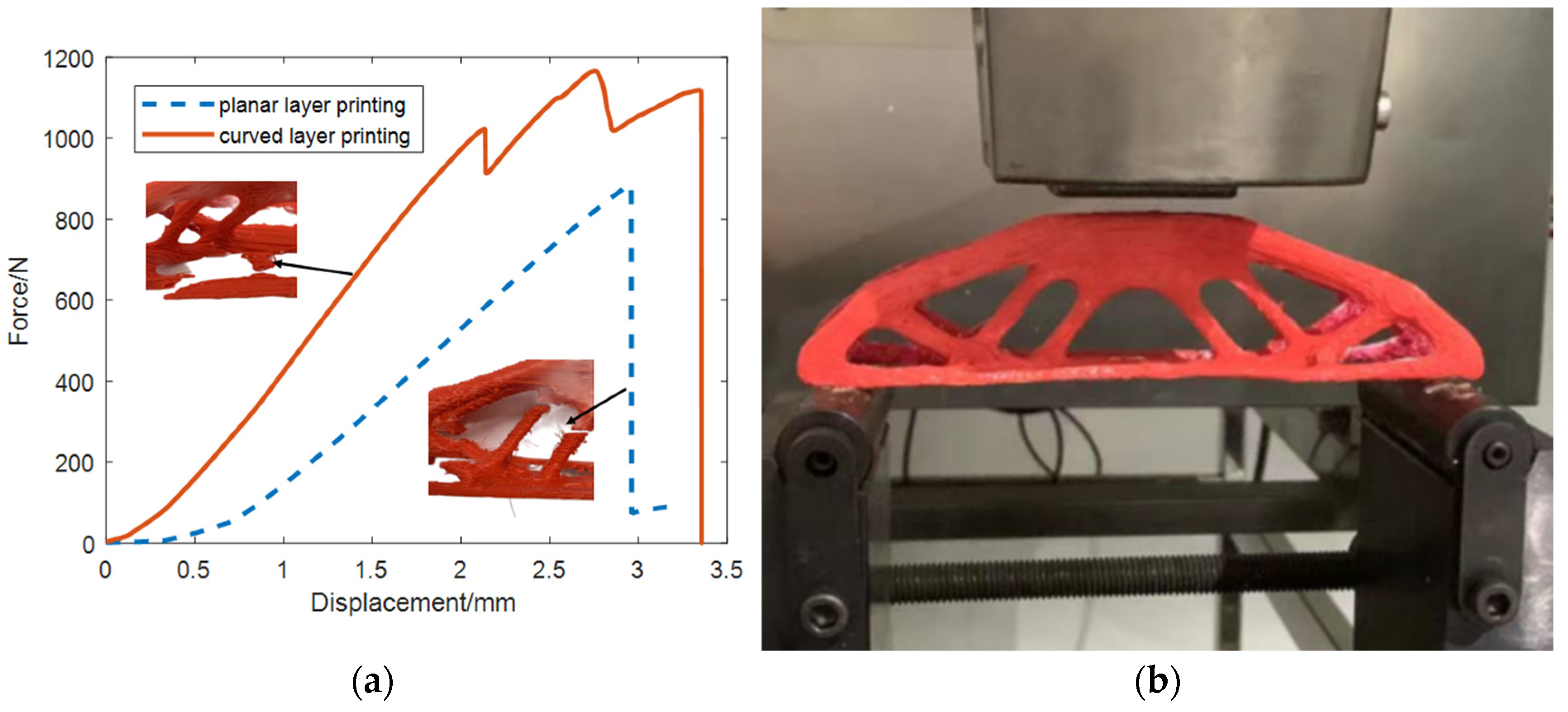


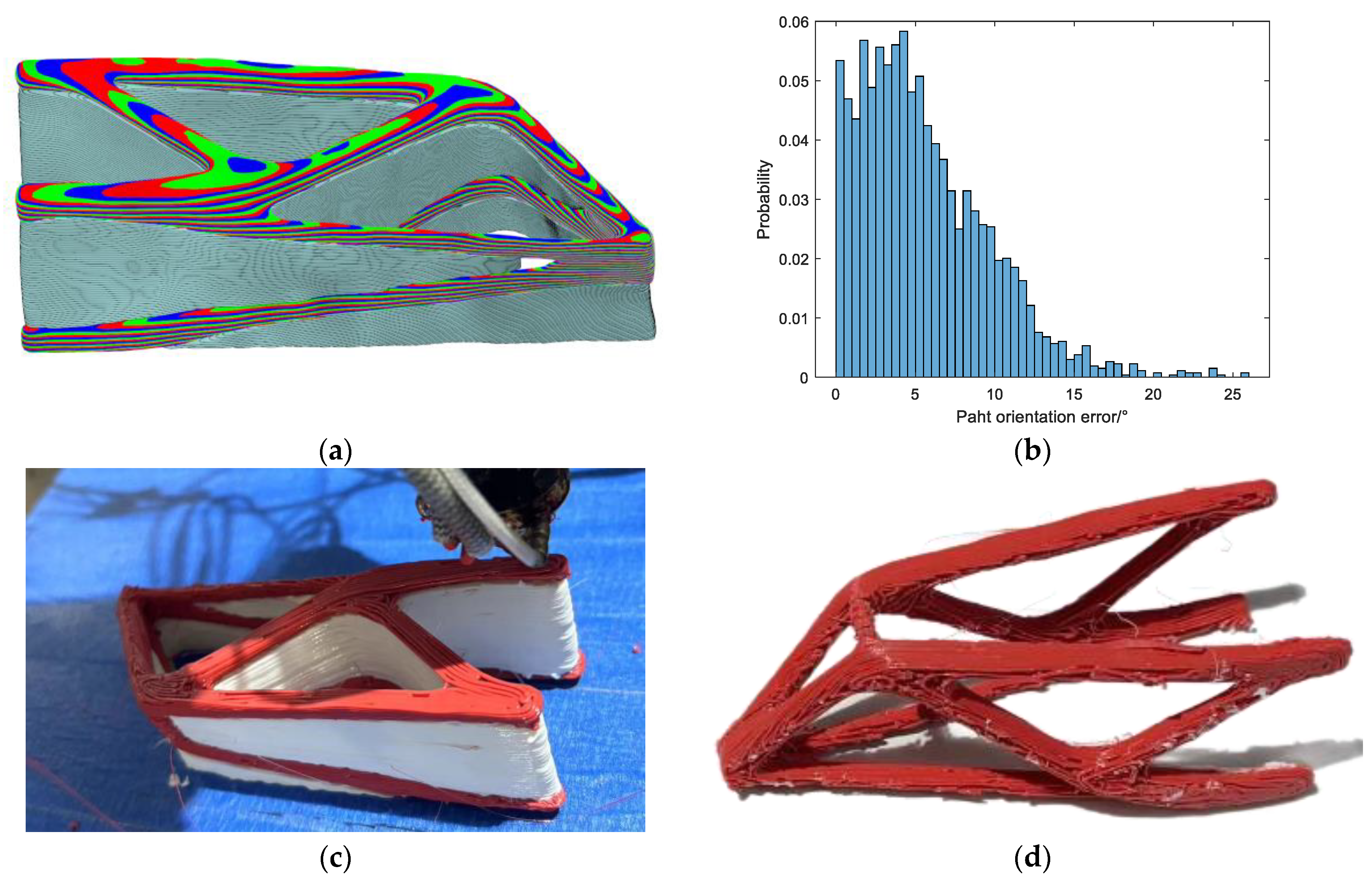


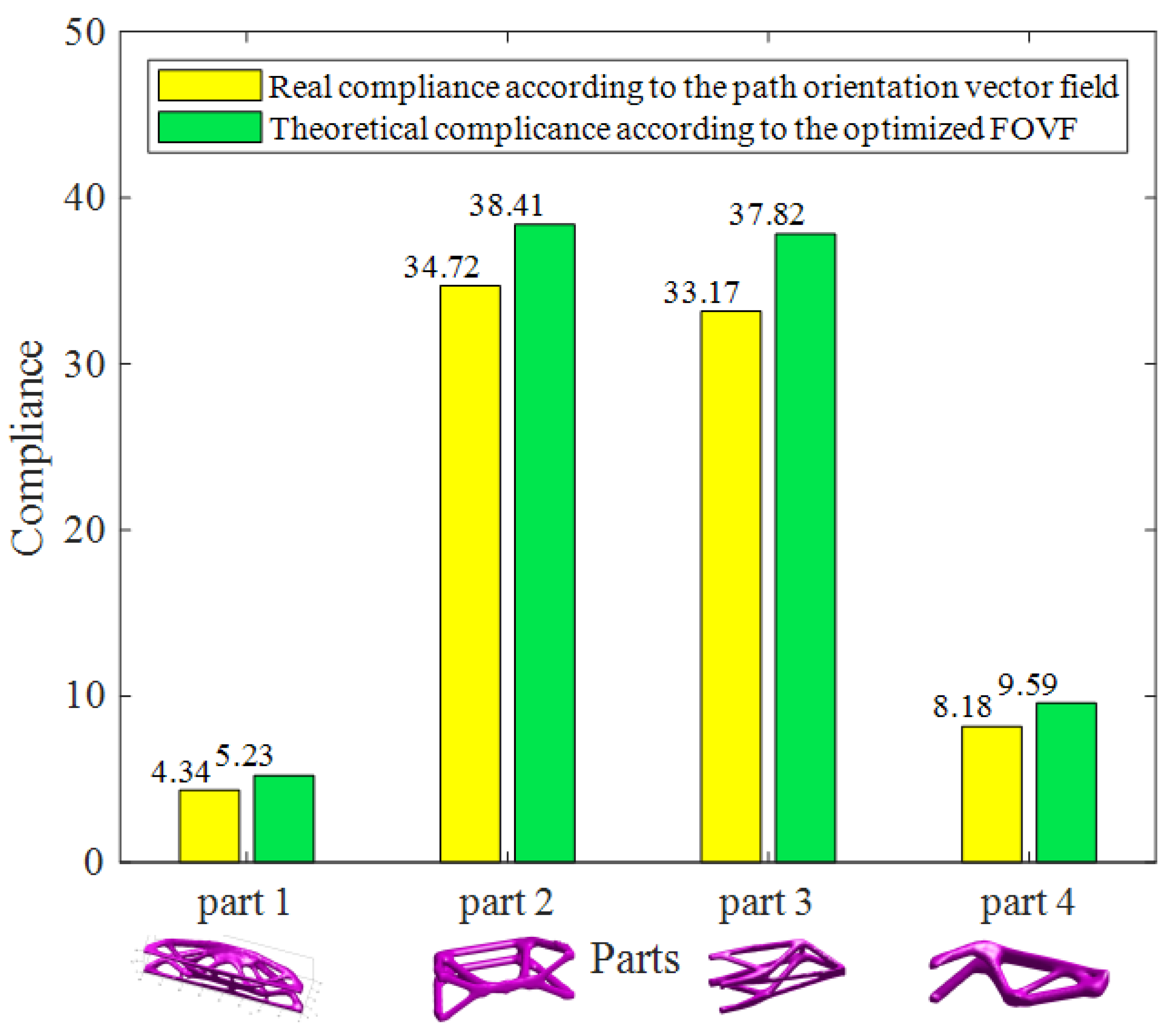
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Material | PLA |
| Layer thickness | 0.6 mm |
| Path width | 0.8 mm |
| Printing temperature | 180 °C |
| Boundary Condition | Topology Shape | Fiber Orientation Vector Field |
|---|---|---|
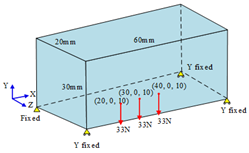 |  | 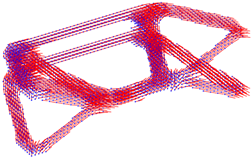 |
 | 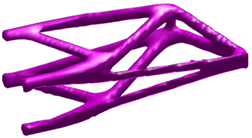 | 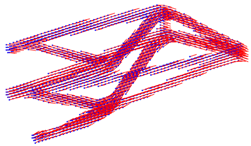 |
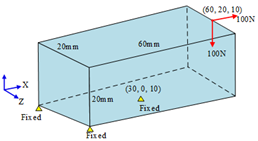 |  | 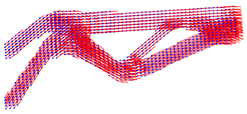 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Yan, X. Curved-Layer Slicing and Continuous Path Planning for Multi-Axis Printing of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Structures. Processes 2025, 13, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020473
Li Y, Shi C, Yan X. Curved-Layer Slicing and Continuous Path Planning for Multi-Axis Printing of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Structures. Processes. 2025; 13(2):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020473
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yamin, Chenyang Shi, and Xin Yan. 2025. "Curved-Layer Slicing and Continuous Path Planning for Multi-Axis Printing of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Structures" Processes 13, no. 2: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020473
APA StyleLi, Y., Shi, C., & Yan, X. (2025). Curved-Layer Slicing and Continuous Path Planning for Multi-Axis Printing of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Structures. Processes, 13(2), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13020473






