Abstract
The enzymatic esterification of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) with glycerophosphocholine (GPC) was investigated to produce bioactive structured DHA phospholipids with DHA esterified at the sn-2 position, which may contribute to the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s. This reaction is complex due to the low solubility of GPC in anhydrous organic media and the limited stability of enzymes under such conditions. The immobilized phospholipase Quara® LowP (QlowP-C18) proved to be the most effective catalyst, achieving a 58% yield of di-substituted DHA phospholipids (Di-DHA-PC) in just 48 h under optimal conditions (solvent-free media at 60 °C) with 95% purity. Advanced immobilization and post-immobilization techniques significantly improved the stability of QlowP-C18, increasing its longevity threefold and enabling reuse for up to five reaction cycles at 40 °C. The total production reached 120.4 mg of highly pure DHA-di-substituted phospholipid. These findings highlight the effectiveness of stable immobilized enzymes in solvent-free systems and underscore their potential for the efficient and sustainable production of highly pure Di-DHA-PC, which could be used as a functional or nutraceutical ingredient for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
1. Introduction
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an essential omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, plays a crucial role in brain development and function. Incorporating DHA into the diet has been demonstrated to have neuroprotective and neuromodulatory effects, which are particularly relevant in the context of aging [1]. However, the blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective, semi-permeable membrane that restricts the passage of most molecules, including many therapeutic compounds, to protect the central nervous system from toxins and pathogens. For these benefits to be realized, it is essential to develop DHA formulations that can effectively cross the BBB and be incorporated into neuronal cell membranes [2].
Lysophospholipids, especially those with DHA esterified at the sn-2 position of glycerol, are of significant interest due to their potential to enhance the bioavailability of DHA [3,4]. This formulation allows DHA to pass unaltered through the gastrointestinal tract, enter the bloodstream as an sn-2 lysophospholipid, and cross the BBB to integrate into neuronal membranes [5]. The mechanism by which PUFAs (such as DHA) are transported across the BBB has been the subject of much investigation, with both passive diffusion and carrier-mediated transport being implicated [6,7]. Among these, lysophosphatidylcholine is considered a particularly effective carrier for DHA, facilitating targeted delivery to the brain [8,9,10]. Such formulations have the potential to prevent or mitigate neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s [11,12].
However, commercially valuable lipids enriched in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are often found in low concentrations and mixed with less desirable lipids [13]. The challenge of producing high-purity structured lipids has led to increased interest in using lipases and phospholipases as biocatalysts in the food industry [14,15]. These enzymes can selectively modify lipid fatty acid compositions by incorporating different fatty acids, restructuring their positions, or generating new derivatives such as phospholipids (PLs) and monoglycerides (MAGs), including 2-MAGs of omega-3 PUFAs [16]. Lipases/phospholipases facilitate various synthesis reactions, including acidolysis, alcoholysis, esterification, and transesterification. Additionally, the hydrolysis and ethanolysis of natural oils provide alternative methods for obtaining omega-3 derivatives both as free fatty acids (FFAs) and as ethyl esters (EEs) [17]. These products can be used to incorporate omega-3 into bioactive lipids of interest [18].
Despite their potential, phospholipid synthesis using lipases and phospholipases is inherently complex due to factors such as high temperatures, viscous and anhydrous media, and other challenging conditions that significantly restrict enzyme activity. The current methods, such as the synthesis of lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) from glycerophosphatidylcholine (GPC) via direct esterification with free fatty acids [19,20] or transesterification with fatty acid vinyl esters [21,22,23], have demonstrated notable success. For example, the transesterification of soybean lecithin with ethyl esters of EPA and DHA using Rhizomucor miehei lipase has achieved incorporation levels of EPA and DHA as high as 45.7% into phospholipids within 24 h [24]. However, these methods are constrained by the limitations of existing enzymes under extreme conditions. We propose the development of highly active and stable enzymatic derivatives that can function under these rigorous conditions, with the goal of achieving high yields of completely pure DHA phospholipids.
Solvent-free biocatalytic processes are increasingly favored for their sustainability benefits [25]. In the case of phospholipid esterification, various factors affecting the esterification of GPC in solvent-free systems have been investigated [19]. One of the main challenges in the modification of GPC is its low solubility in these media, as it is a highly polar molecule soluble in water and polar solvents, but poorly soluble in completely anhydrous organic media. Additionally, the lack of stability of immobilized enzymes in hydrophobic, anhydrous media (e.g., oils) can be a significant drawback for the esterification of GPC in solvent-free systems. Given these complications, it is necessary to develop stabilization strategies for lipases through immobilization and post-immobilization techniques. The solution to these problems lies in enzyme engineering. The development of these strategies has enabled the conversion of soluble and unstable biocatalysts into highly stable heterogeneous enzymatic derivatives in a single process [26]. It is crucial for scaling up the process, as the use of immobilized enzymes allows for the reuse of the catalyst.
The adsorption of lipases on hydrophobic supports is a very simple immobilization protocol that produces very interesting immobilized lipase derivatives, as the open and active form of the lipase molecules is stabilized by strong adsorption on the surface of the support. This results in lipase derivatives that are much more active (hyperactivation) and stable than other immobilized derivatives [27]. For this type of immobilization, the use of commercial polyacrylic resins as immobilization supports for use in anhydrous reaction media has garnered considerable interest. In this publication, we will use the commercial resin Immobeads-C18 IB-ADS-3 (ChiralVision) with a particle size of 150–300 µm. These highly porous resins with octadecyl groups are ideal for the immobilization of lipases through interfacial adsorption, allowing for a high enzyme load due to their small pore size (58% pore volume), resulting in catalysts up to 10 times more active than those previously used [28].
On the other hand, several post-immobilization techniques can complement enzymatic immobilization to achieve better biocatalysts in terms of stability. These techniques include coating enzymatic surfaces with polymers through covalent bonding, such as dextran aldehyde (DexCHO), or through anion exchange, for example, with polyethyleneimine (PEI) [29]. For lipases, it is highly advantageous to perform physicochemical modifications of immobilized derivatives by interfacial adsorption, because in this type of immobilization, the open and active center is protected by the support from any surface modification of the immobilized lipase. This provides additional protection by creating a physical barrier between the enzyme and its environment, thereby insulating the active center without compromising it [30]. In this work, dextran sulfate biopolymer will be used, known for its strongly anionic nature and its tendency to interact with cations in the environment, making it suitable for cationic exchange [31].
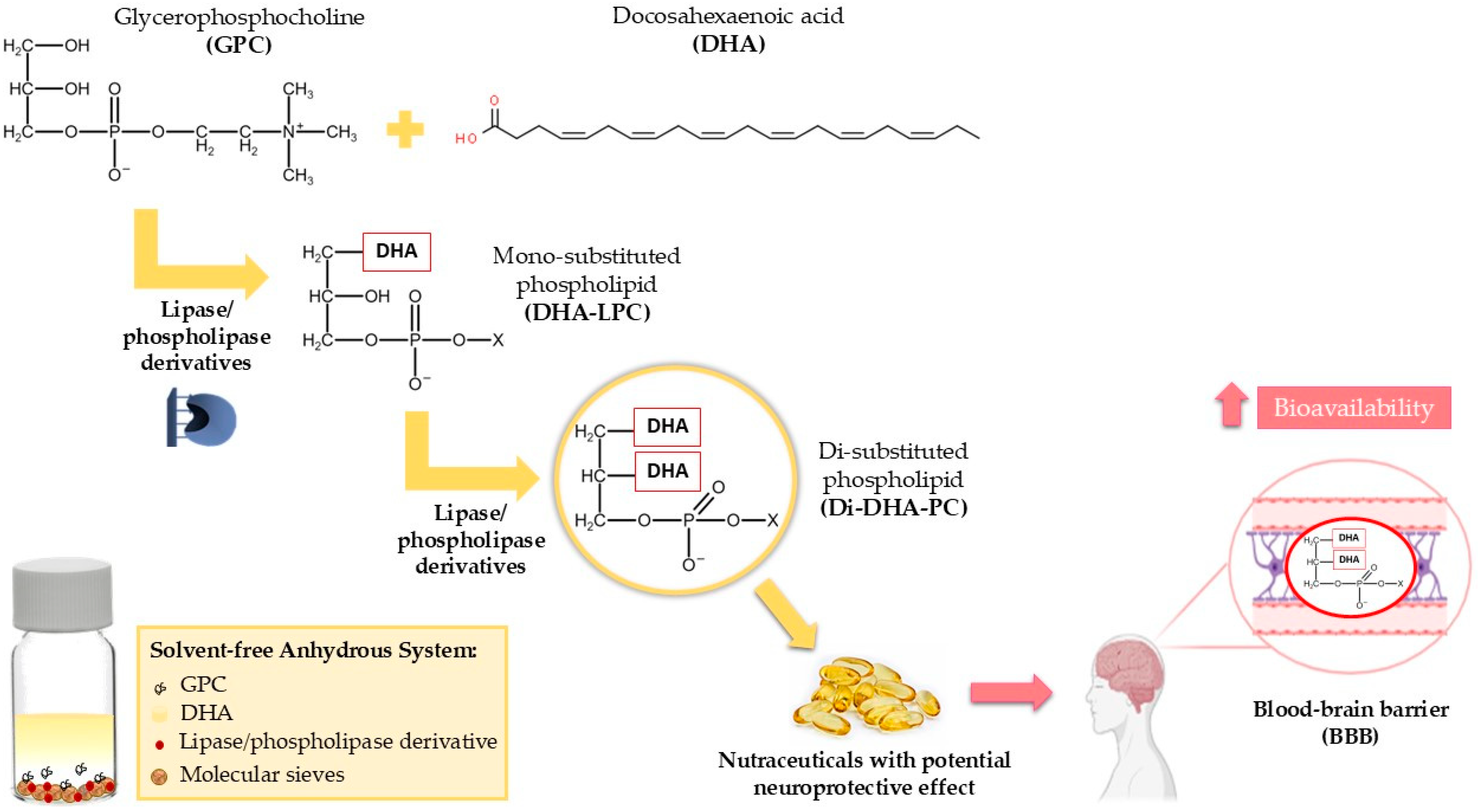
Therefore, to meet the growing interest in DHA-phospholipids with enhanced bioavailability, the use of immobilized lipases and phospholipases is proposed for the synthesis of highly pure 1,2-di-DHA-phosphatidylcholine (Di-DHA-PC) through the direct esterification of GPC with DHA in anhydrous solvent-free media. Specifically, the synthesis of Di-DHA-PC is targeted, as mentioned earlier, as the most effective form to deliver DHA to the brain [32,33]. As illustrated in Figure 1, the study focuses on optimizing the synthesis process to address these challenges and ensure high yield and biocatalyst stability.
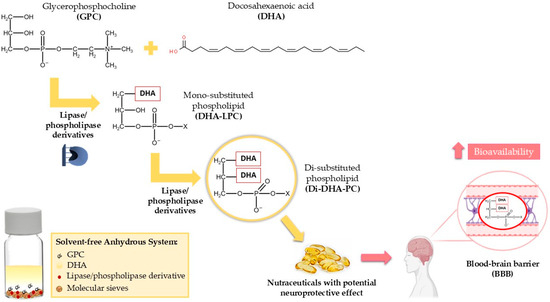
Figure 1.
Enzymatic synthesis of Di-DHA-PC using immobilized lipases/phospholipases via the direct esterification of GPC with DHA in solvent-free media. Bioactive Di-DHA-PC may serve as a functional or nutraceutical ingredient for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) was obtained from the enzymatic hydrolysis of Anchovy oil, which was purchased in capsules from NuaBiological at a Pharmacy (Madrid, Spain) and glycerophosphocholine (GPC) was purchased from Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor, MI, USA). Soluble lipases such as Lipozyme® TL from Thermomyces lanuginosa (TLL), Candida antarctica B (CALB), Palatasa® 20,000 L (PALA), Eversa® Transform 2.0 (NS40), and phospholipases Lecitase® Ultra (LECI) and Quara® LowP (QlowP) were kindly donated by Novozymes (Bagsvaerd, Denmark). Immobeads-C18 IB-ADS-3 (C18) immobilization support was provided by ChiralVision (Leiden, The Netherlands) and DEAE-Sepharose purification support from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Triton X-100, hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), sodium chloride, p-nitrophenyl butyrate (pNPB), and 3Å pore size molecular sieve (2–3 mm bead) were provided by Sigma-Aldrich. Methanol, chloroform, ammonium hydroxid, and acetonitrile were purchased from VWR Chemicals (Matsonford Road Radnor, PA, USA) and Sigma-Aldrich. 1,2-Didocosahexaenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (Di-DHA-PC) standard was purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Birmingham, AL, USA). All the other reagents and solvents used were of analytical grade.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Determination of the Activity of Different Soluble and Immobilized Lipases
The activity assay was carried out using a spectrophotometer with a thermostatted cell and continuous magnetic stirring (500 rpm) for 2 min. The increase in absorbance at 348 nm (ε = 5150 M−1cm−1) produced by p-nitrophenol (pNP) released after the hydrolysis of the 0.4 mM p-nitrophenyl butyrate (pNPB) substrate in 25 mM sodium bicarbonate at pH 8.5 was measured at 25 °C. In the case of phospholipase QlowP, this increase was measured in 10 mM sodium phosphate buffer at pH 7. To initiate the reaction, 0.1 mL of soluble lipases/phospholipases (blank or supernatant) and their immobilized preparations (suspension) were added to 2.5 mL of the substrate solution. Enzyme activity was calculated as µmol of pNPB hydrolyzed per minute per mg of enzyme (IU) under the conditions described above [34].
2.2.2. Immobilization of Lipases/Phospholipases on the Hydrophobic Support Immobeads-C18
Four different lipases (TLL, NS40, PALA, and CALB) and two phospholipases (LECI and QlowP) were immobilized on the hydrophobic support Immobeads-C18 by interfacial adsorption. These enzymes are adsorbed onto this type of support in their open and hyperactive form [34]. Using the Immobeads-C18 support, enzymatic preparations with maximum loading were achieved. The protocol established in a previous study [35] was followed to achieve this maximum loading. However, the QlowP-C18 derivative was not optimized previously and has been optimized in this study.
Firstly, the purification of QlowP-C18 was carried out using DEAE-Sepharose support through ion exchange. For this, 20 g of DEAE support was added to a buffered solution containing 1000 mg of enzyme in a 10 mM sodium phosphate buffer at pH 7 (determined to be 6 mg/mL according to the Bradford assay results). Purification proceeded for 24 h at 25 °C with continuous agitation.
To monitor the progress, the activity of both the suspension and supernatant was periodically measured using the p-NPB assay. Once all the enzyme was adsorbed onto the DEAE support, desorption was initiated. A 0.1 M NaCl solution in 158 mL of phosphate buffer was prepared, and the DEAE support containing the purified enzyme was introduced. The solution was stirred for 2.5 h, resulting in the complete desorption of the enzyme.
Following desorption, the supernatant containing the purified enzyme was collected to continue with the immobilization process. To the purified enzyme volume, 0.02% CTAB was added. Subsequently, 5 g of Immobeads-C18 immobilization support, pre-moistened, was introduced. The mixture was maintained at 25 °C with continuous agitation for 96 h. Throughout the immobilization process, the p-NPB assay was performed to monitor the enzyme’s activity.
2.2.3. Physicochemical Modifications of Immobilized Enzymes
Amination
The chemical amination of the derivatives was carried out according to the literature described in the bibliography [36]. One gram of enzyme immobilized on Immobeads-C18 was added to 10 mL of 1 M ethylenediamine (EDA) with a pH of 4.75 and continuous agitation. Then, solid 1-ethyl-3-(dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) was added to the suspension until reaching a final concentration of 10 mM. After 90 min of incubation at 25 °C with gentle agitation, the immobilized preparations were filtered and vacuum-washed using a porous filter plate.
Adsorption of Anionic Polymer
The immobilized and aminated derivatives were coated with a layer of the anionic polymer sodium dextran sulfate of different sizes (8000 and 100,000 Da) by adding 100 mg of dextran sulfate per gram of derivative. To do this, the solid polymer was dissolved in 10 mL of 10 mM sodium acetate buffer at pH 5, a gram of aminated enzymatic derivative was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h [37]. Additionally, derivatives modified with two layers of dextran were prepared (DEX 100,000 + 8000), first by coating the aminated derivative with the larger polymer (DEX 100,000) and then repeating the procedure to coat this same already modified derivative with the smaller polymer (DEX 8000) from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). All the obtained derivatives were filtered and stored in the refrigerator for future use.
2.2.4. Drying of Lipases and Phospholipases Derivatives
The enzymatic derivatives were washed and dried before use, as they were employed in reactions in anhydrous media. Consequently, the derivatives were washed with increasing volumes of water and acetone using a sintered glass funnel until completely dry. For each gram of derivative, 50 mL of each of the following solutions were used: 100% water; different water solutions (70:30, 50:50, and 30:70, v/v); and 100% acetone.
2.2.5. Enzymatic Synthesis of Structured Phospholipids from Docosahexaenoic Acid
The esterification reaction with DHA was carried out in an anhydrous solvent-free medium. The reaction mixture consisted of 250 mg of dry lipase or phospholipase derivative, 30 mg of GPC, 0.25 g of the molecular sieve with a pore size of 3 Å, and 2.5 mL of free DHA. The free DHA was previously obtained through the enzymatic hydrolysis of anchovy oil. García-Quinto et al. demonstrated that the immobilized derivatives NS40-C18 and PALA-C18 achieve 100% DHA release within just 24 h due to their high enzyme loading [38].
Additionally, the effect of adding 30% butanone relative to the final volume was studied. The reactions were conducted in glass vials (final volume of 2.5 mL) at 60 °C with constant stirring in an incubator at 150 rpm. Prior to adding the derivative, the vials were incubated and stirred for 15 min to increase the solubility of GPC in the reaction medium. For each experiment, a negative control without the lipase or phospholipase derivative was performed under the same conditions. The synthesis of DHA phospholipids was monitored by TLC and then quantified by HPLC by taking samples from the supernatant. The TLC mobile phase consisted of methanol/chloroform/ammonium hydroxide (65:25:4 v/v). For the TLC analysis, 60 μL of the reaction mixture was taken and diluted with 900 μL of chloroform. For HPLC, 100 μL of this solution was further diluted with 900 μL of methanol/acetonitrile (80:20 v/v), which was used as the mobile phase for the HPLC analysis. The experiments were performed in triplicate, and the standard deviation was always less than 5%.
2.2.6. Stability of Physicochemically Modified Derivatives for the Synthesis of DHA Phospholipids
The stability of the derivatives modified with the post-immobilization strategy using dextran sulfate was evaluated in the esterification reaction of GPC with DHA following the methodology outlined below [36,37]. Both the modified derivatives and the unmodified derivative were incubated for up to two days under specific reaction conditions: anhydrous solvent-free medium (DHA) and 40 °C. To initiate each pre-incubated reaction, the GPC substrate was first mixed with 1 mL of reaction medium (DHA) and stirred for 15 min. Subsequently, this mixture was added to the incubated reaction solution, which already contained an additional 1.5 mL of DHA. The activity of the derivatives was compared to that of a non-incubated reaction (considered as 100% activity). The stability of each derivative was determined by quantifying the Di-DHA-PC product in aliquots taken at 24 h. The analysis of the products was carried out using HPLC.
2.2.7. Reuse of Phospholipase Derivatives in the Esterification Reaction
For catalyst reuse studies, the enzymatic esterification reaction was also carried out in glass vials (final volume of 2.5 mL) at 40 °C in an anhydrous solvent-free medium. The process involved reusing the derivative for the maximum number of possible cycles under optimized reaction conditions [28]. After the optimal reaction time, the reaction volume was carefully filtered to recover the catalyst for reuse in the new reaction mixture. To effectively separate the derivative from the reaction medium, it had to be washed and dried several times with hexane and acetone to remove any remaining substrates or products. Subsequently, new substrates (DHA and GPC) were added along with the reused catalyst, ensuring that the weight of the derivative was controlled to avoid loss in successive cycles. This process was repeated as many times as possible until the enzyme completely lost its activity. The residual activity of the catalyst in each cycle was calculated based on the 100% activity of cycle 0, determined from the percentage of Di-DHA-PC formed in 24 h. The analysis of the product peaks was performed using HPLC.
2.3. Product Analysis
Quantitative Analysis by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High-performance liquid chromatography analyses were conducted using the HPLC system (Spectra Physic SP 100 pump coupled with a Spectra Physic SP 8450 UV detector) from Thermo Scientific (Rockford, IL, USA),employing a normal phase column (LiquidPurple Sil, 250 × 4.6 mm internal diameter, 5 µm particle size) with a pre-filter column (0.5 μm disk and seal). Additionally, aliquots were pre-filtered using a 4 mm/0.45 μm polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) syringe filter. Elution of the products occurred at a flow rate of 1 mL/min utilizing a methanol/acetonitrile (80:20 v/v) mobile phase. UV detection was set at 205 nm due to the molecules’ double bond content, which promotes significant absorbance at that wavelength [39]. Synthesis yields were calculated based on the areas corresponding to different concentrations of DHA phosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine, with retention times of 4.4 min (Di-DHA-PC) and 5.1 min (DHA-LPC), respectively. A calibration curve was performed using standard concentrations ranging from 0.05 mg/mL to 1 mg/mL. HPLC analyses were conducted in triplicate, and the standard deviation consistently remained below 5%.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Immobilization of Lipases/Phospholipases with Maximum Enzyme Loading
The four lipases and two phospholipases were immobilized through hydrophobic interfacial adsorption on Immobeads-C18 support with the maximum allowable enzyme loading. The enzyme loading per gram of support varied depending on the enzyme and the achieved immobilization yield. TLL, PALA, and NS40 exhibited an enzyme loading of 180 mg of protein per gram of support, achieving a 90% immobilization yield after 72 h. CALB and LECI reached a final enzyme loading of 170 mg of lipase/phospholipase per gram of support after 48 h of continuous agitation. Phospholipase QlowP achieved a loading of 160 mg per gram of support after 72 h.
3.2. Enzymatic Synthesis of Di-DHA-PC by Direct Condensation of DHA and GPC in Solvent-Free System
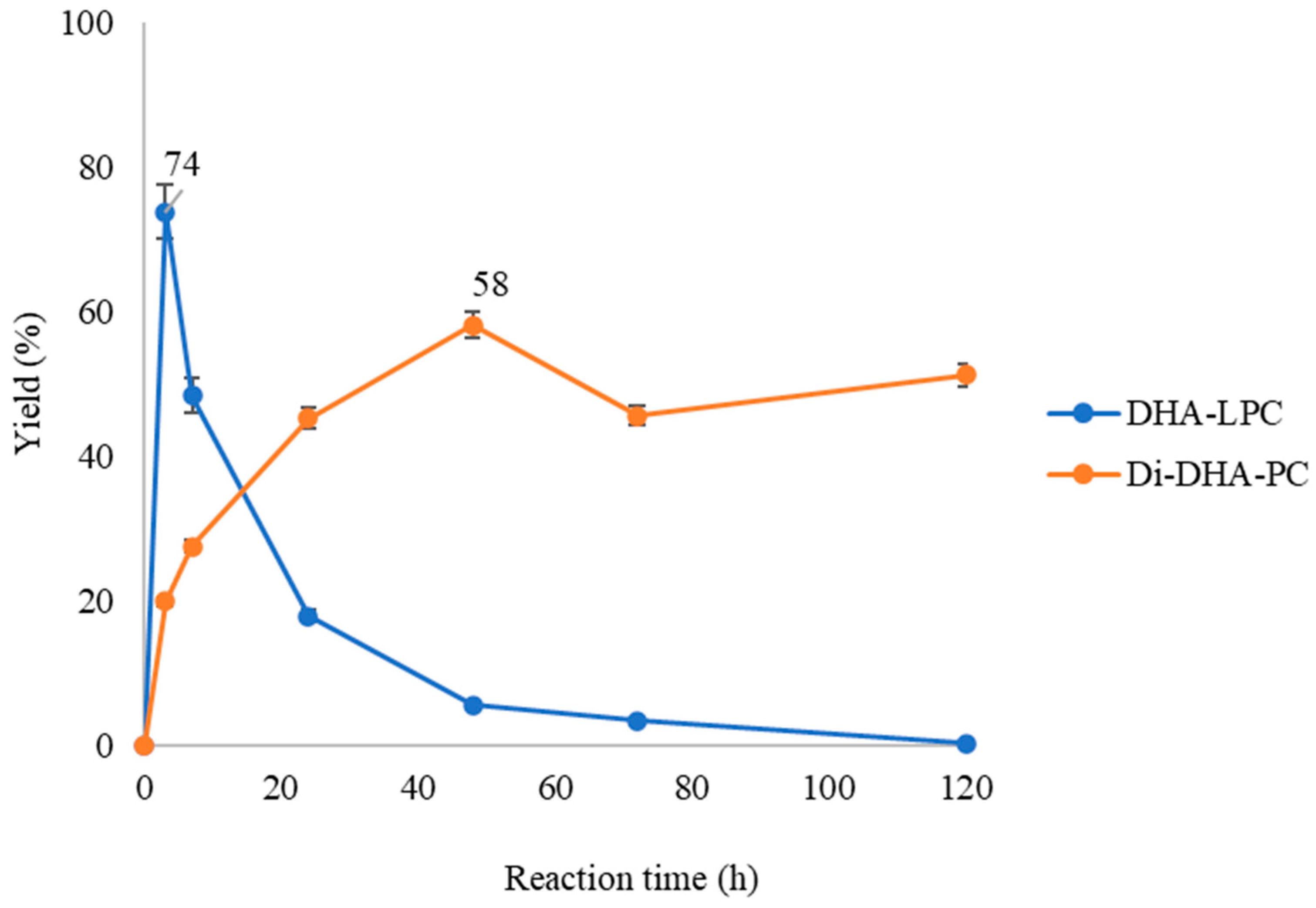
The course of the esterification of GPC with DHA in a solvent-free system catalyzed by immobilized QlowP phospholipase with maximum enzymatic load via hydrophobic adsorption onto Immobeads-C18 support was studied. As seen in Figure 2, the reaction begins with the formation of a first product or intermediate product known as DHA lysophospholipid (DHA-LPC), which reaches maximum yield at 3 h with 74%. Over time, this intermediate product gradually disappears, transforming into the final reaction product, which is the Di-DHA-phosphatidylcholine (Di-DHA-PC), reaching maximum yield at 48 h with 58%. It was observed that the progression of the reaction closely resembled that described in the esterification of oleic acid and GPC in the study by Garcia-Quinto et al., 2023 [35].
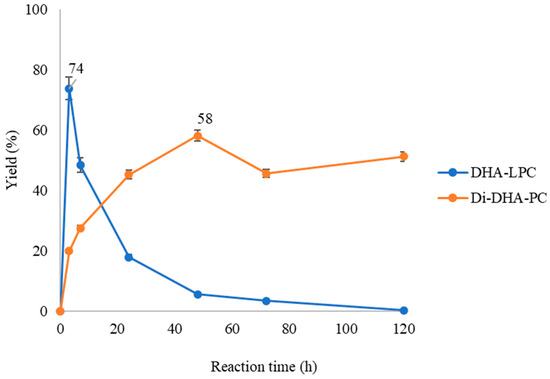
Figure 2.
Time-course esterification of GPC with DHA by QlowP-C18 derivative in solvent-free media at 60 °C and 150 rpm. Formation of DHA-LPC (blue) and Di-DHA-PC (orange) phospholipids. Note: Reaction conditions: 10% w/w phospholipase derivative and ratio GPC/DHA 1/62.
In this research, the reaction was carried out in a solvent-free system with a substrate molar ratio of 1/62 (GPC/DHA) and a temperature of 60 °C. Under these conditions, it was possible to incorporate DHA at both the sn-1 and sn-2 positions of GPC, resulting in the formation of Di-DHA-PC as the sole product of the reaction. This suggests that the reaction conditions, particularly the high molar ratio and solvent-free system, favor the selective formation of Di-DHA-PC. Next, we will study whether the reaction products can vary depending on the catalyst and reaction conditions used.
3.3. Profile of DHA Phospholipid Synthesis Catalyzed by Different Lipases and Phospholipases Immobilized on C18 in Solvent-Free Media
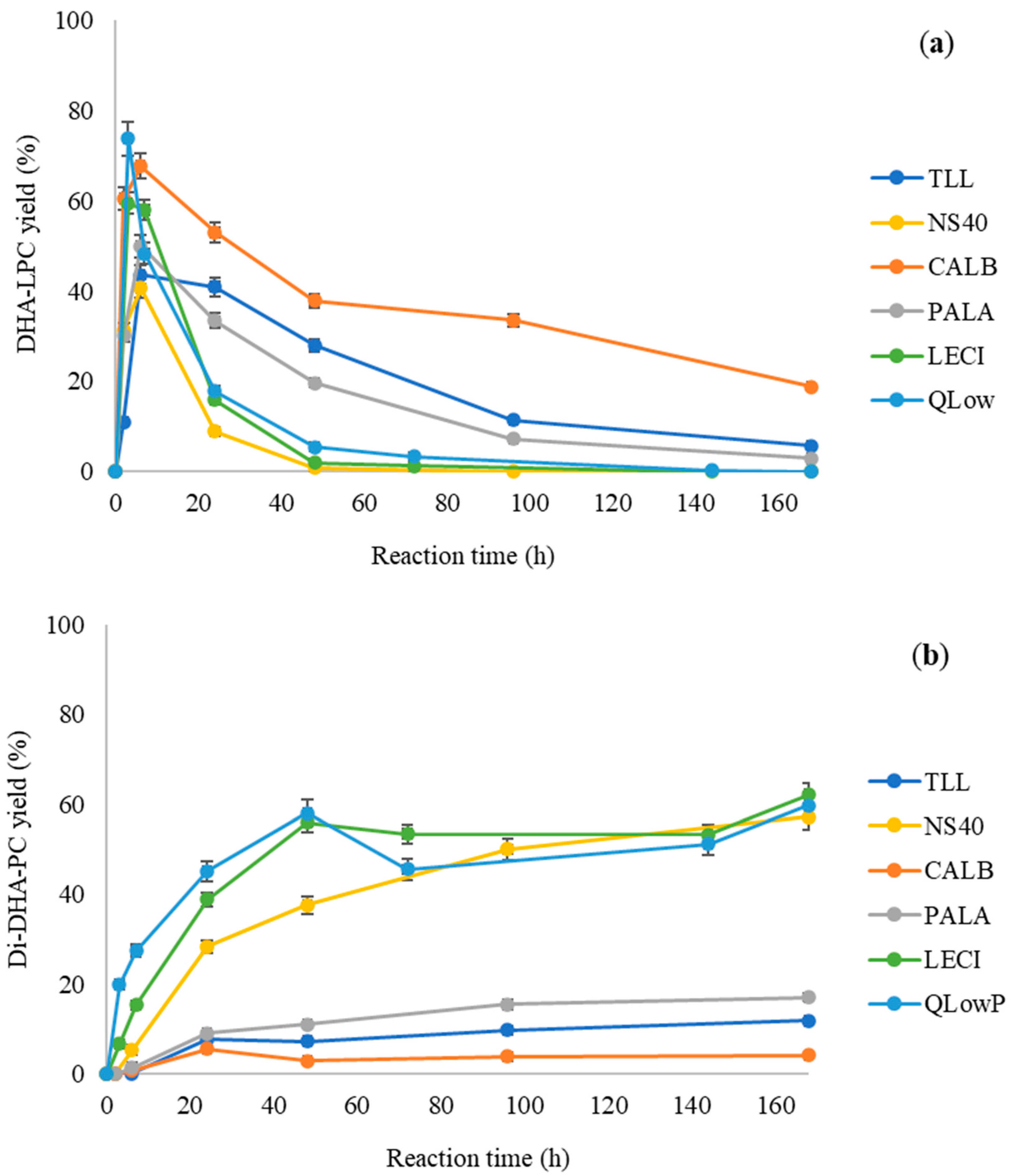
Next, the esterification reaction of GPC with DHA catalyzed by the different immobilized lipases and phospholipases was studied. The kinetics of the formation of mono- and di-substituted DHA phospholipids were investigated independently. Figure 3a shows the formation of DHA-LPC for all the immobilized biocatalysts, while Figure 3b shows the formation of Di-DHA-PC.
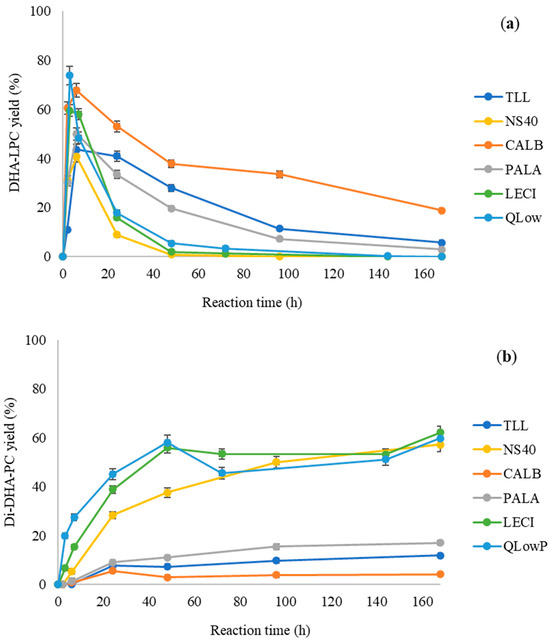
Figure 3.
Profile of synthesis products formed in the esterification of DHA with GPC catalyzed by different immobilized lipases on Immobeads-C18 in a solvent-free medium at 60 °C: TLL (dark blue), NS40 (yellow), CALB (orange), PALA (gray), LECI (green), and QlowP (light blue). (a) Synthesis yields for DHA-LPC. (b) Synthesis yields for Di-DHA-PC.
For the formation of DHA-LPC (Figure 3a), all the enzymes exhibit similar behavior, mainly differing in the rate of formation of this product. However, for the formation of Di-DHA-PC (Figure 3b), there are clear differences in behavior depending on the catalyst used. As observed, only three enzymes are capable of synthesizing the final reaction product, with LECI and QlowP, two phospholipases, and NS40, a lipase, achieving yields around 60% at 168 h. However, reaction yields for lipases PALA, TLL, and CALB are considerably low for the formation of Di-DHA-PC. It is noteworthy that when the reaction was performed with oleic acid, only CALB was unable to achieve good yields for Di-oleoyl-PC [35]. These differences could be attributed to greater difficulty in esterifying DHA at the sn-2 position of the lysophospholipid, given that the nature and structure of DHA differ significantly from oleic acid. Additionally, several factors could hinder the process, such as substrate solubility, high temperatures, or the use of highly hydrophobic and viscous anhydrous reaction media.
Due to the sn-1,3 selectivity described for lipases by other authors in this type of reaction, it would be logical for the esterification of GPC to only produce sn-1 DHA-LPC as the sole reaction product [40]. However, thanks to the immobilization strategy used, the natural sn-1,3 regioselectivity would have been altered for NS40, LECI, and QlowP after their immobilization on Immobeads-C18. These enzymes would now exhibit additional selectivity for the sn-2 position, with LECI and QlowP possessing characteristics of phospholipases and a natural substrate being a phospholipid, showing greater affinity to esterify this position. This latter aspect is related to the sn-2 selectivity previously described in the literature for phospholipases [41]. For the rest of the lipases, this effect was not observed as Di-DHA-PC is barely formed, indicating that the selectivity of each lipase is a key factor in the formation of the final product. From here, we chose QlowP as the optimal biocatalyst for the synthesis of highly pure di-substituted DHA phospholipids with 95% purity. This is because QlowP exhibits a significantly higher initial velocity compared to LECI: 10.89 versus 3.65 (mg/mL·h)·g, indicating greater activity for the reaction.
3.4. Effect of the Solvent on the Esterification of GPC with DHA Catalyzed by Immobilized Phospholipase QlowP
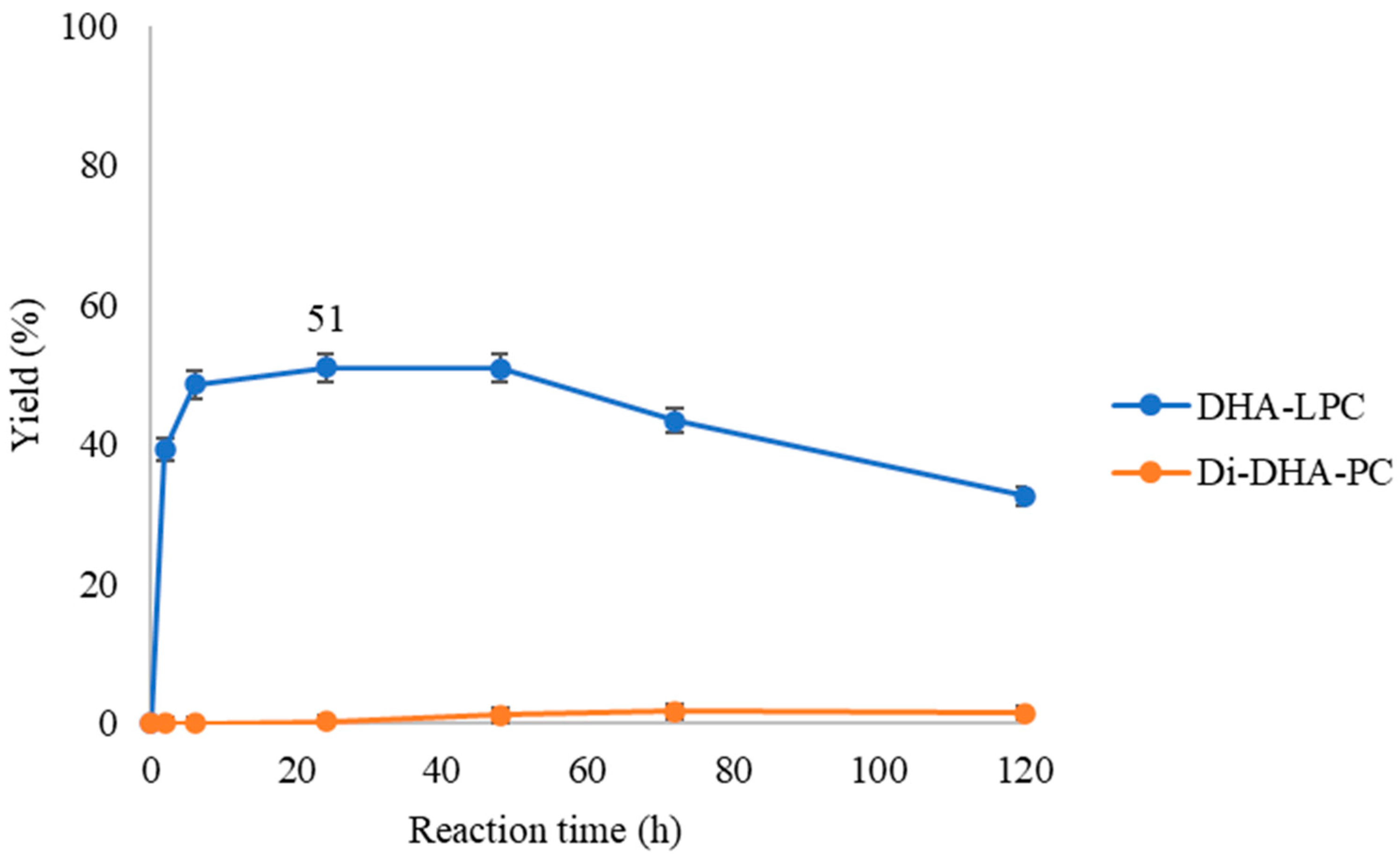
In the previous study [35], it was observed that one of the issues in the reaction was the poor solubility of the substrates used in the esterification. Therefore, the effect of solvent on their solubility was investigated. It was found that the presence of butanone in the medium favored the solubility of GPC in oleic acid. Now, with DHA, it will be checked if this also affects the reaction kinetics. Specifically, we will study how the addition of 30% of butanone influences the formation of the di-substituted DHA phospholipid. To achieve this, the reaction catalyzed by QlowP-C18 will be compared under two conditions: a solvent-free medium (Figure 2) and a medium with 30% butanone (Figure 4).
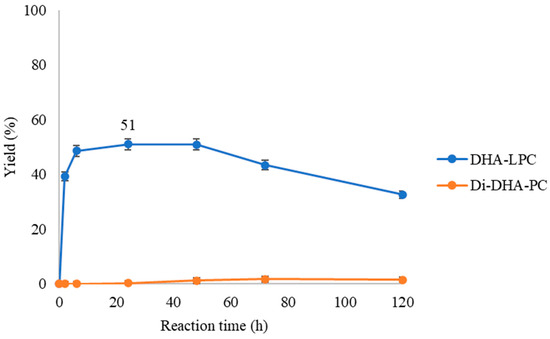
Figure 4.
Time-course esterification of GPC with DHA by QlowP-C18 derivative in a medium with 30% butanone at 60 °C and 150 rpm. Formation of DHA-LPC (blue) and Di-DHA-PC (orange) phospholipids. Reaction conditions: 10% w/w phospholipase derivative and ratio GPC/DHA 1/43.
As seen in Figure 4, the presence of butanone alters the enzyme’s behavior, as no production of di-DHA-phospholipid is observed. Furthermore, while in the solvent-free reaction, a maximum yield of 74% DHA-LPC was achieved at 3 h (Figure 2), in the presence of butanone, the formation of DHA-LPC is slower and with a lower yield (51% DHA-LPC at 24 h). Additionally, this intermediate reaction product exhibits low stability under these conditions, disappearing over time.
In view of the results, it can be inferred that the presence of butanone is likely causing a decrease in enzymatic activity. This could be due to conformational changes in the enzyme, which may hinder the entry of the substrate into the active site [26]. Previous studies have shown that organic solvents can destabilize enzymes and alter their structure, negatively affecting their catalytic efficiency. In this case, butanone appears to have a detrimental effect on the enzyme’s function, leading to a reduced reaction yield. Therefore, based on these findings, the use of butanone for the synthesis of di-substituted DHA phospholipids is not recommended due to its negative impact on the reaction outcome.
3.5. Stabilization Strategies for QlowP-C18 Using Post-Immobilization Techniques
After confirming that the QlowP-C18 derivative was the best for the formation of Di-DHA-PC in a solvent-free medium, the next objective was to stabilize the catalyst to enable its reuse over multiple cycles. Given that the reaction conditions are very harsh for enzymes, such as the use of anhydrous, highly hydrophobic, and viscous media, and high temperatures, it was proposed to design stabilization strategies using post-immobilization techniques. To this end, a post-immobilization strategy was carried out, which consisted of coating the surface of the catalyst with the polymer dextran sulfate and analyzing how the polymer size affects the enzyme activity in the esterification of GPC with DHA.
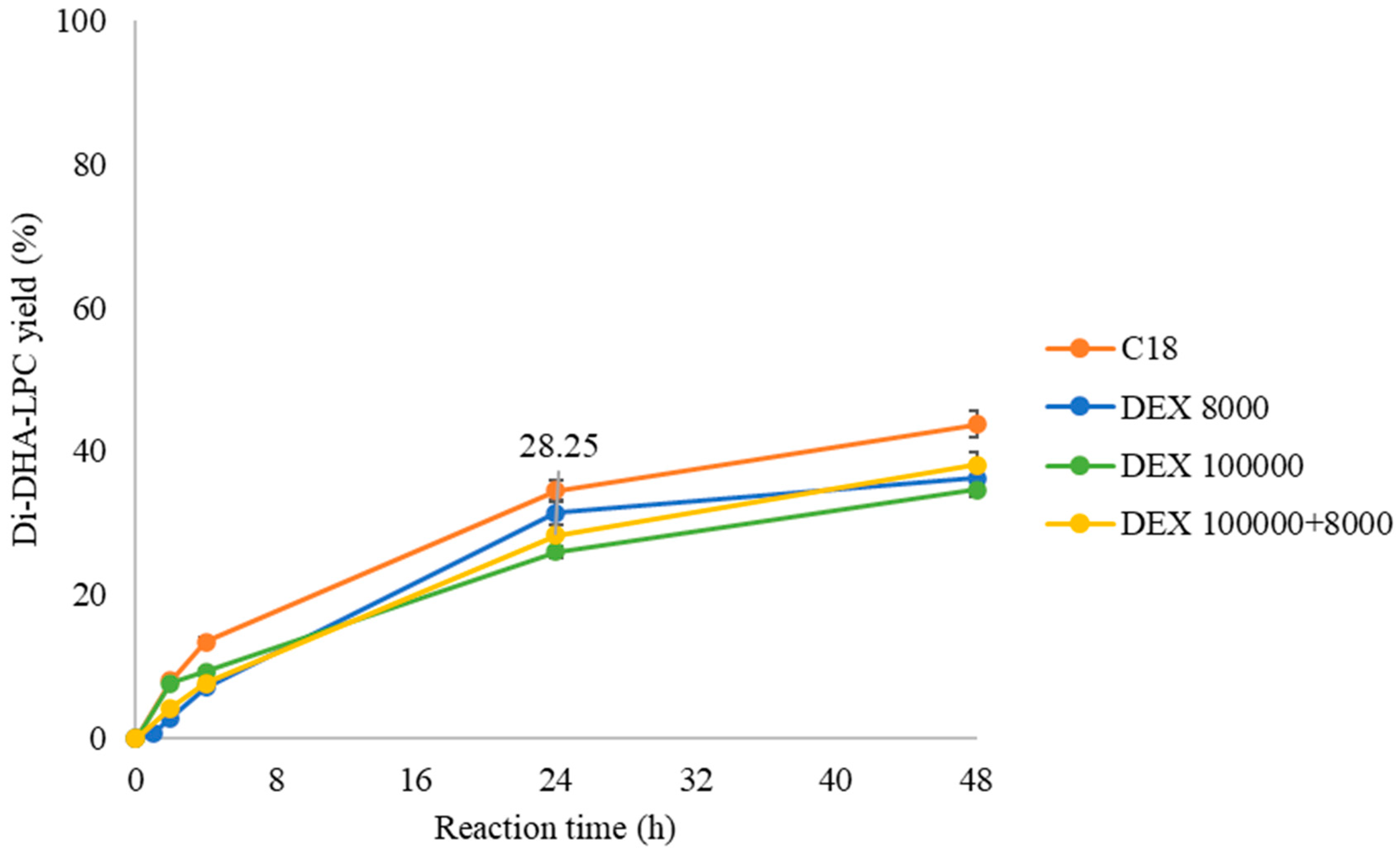
For this purpose, the esterification of GPC with DHA in a solvent-free medium at 40 °C was studied using both the unmodified QlowP-C18 derivative (C18) and three derivatives modified with dextran sulfate: one with a small polymer (DEX 8000 Da), another with a large polymer (DEX 100,000 Da), and a third with a double layer of polymers (DEX 100,000 + 8000 Da). Figure 5 shows the percentages of synthesis of the final product, Di-DHA-PC, as the reaction progresses.
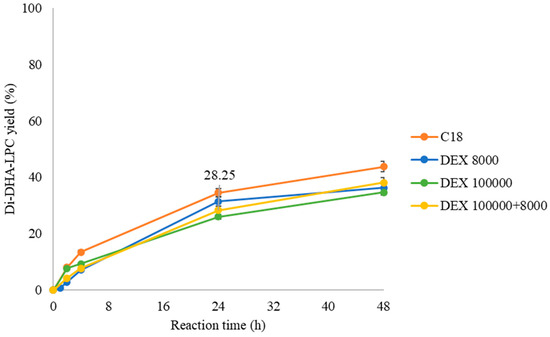
Figure 5.
Influence of the post-immobilization strategy on the synthesis yield of Di-DHA-PC catalyzed by different QlowP-C18 derivatives in a solvent-free medium at 40 °C: C18 (orange), DEX 8000 (blue), DEX 100,000 (green), and DEX 100,000 + 8000 (yellow).
The results indicate that the modification of the catalyst has little influence on enzymatic activity, as the yields are very similar in all the cases. The fact that the activity is not affected suggests that the polymer coating does not hinder the substrate from reaching the enzyme’s active site. On the other hand, although a higher reaction temperature can decrease the viscosity of the fatty acid [42], we ultimately decided to conduct the reaction at 40 °C. This temperature is less harsh on the biocatalyst compared to 60 °C and is more sustainable at an industrial level. Additionally, maintaining the reaction at 40 °C helps preserve the stability of DHA, as this compound is highly susceptible to lipid peroxidation due to the high degree of unsaturation in its long carbon chain [43].
3.6. Stability of the Different QlowP-C18 Derivatives Under the Reaction Conditions
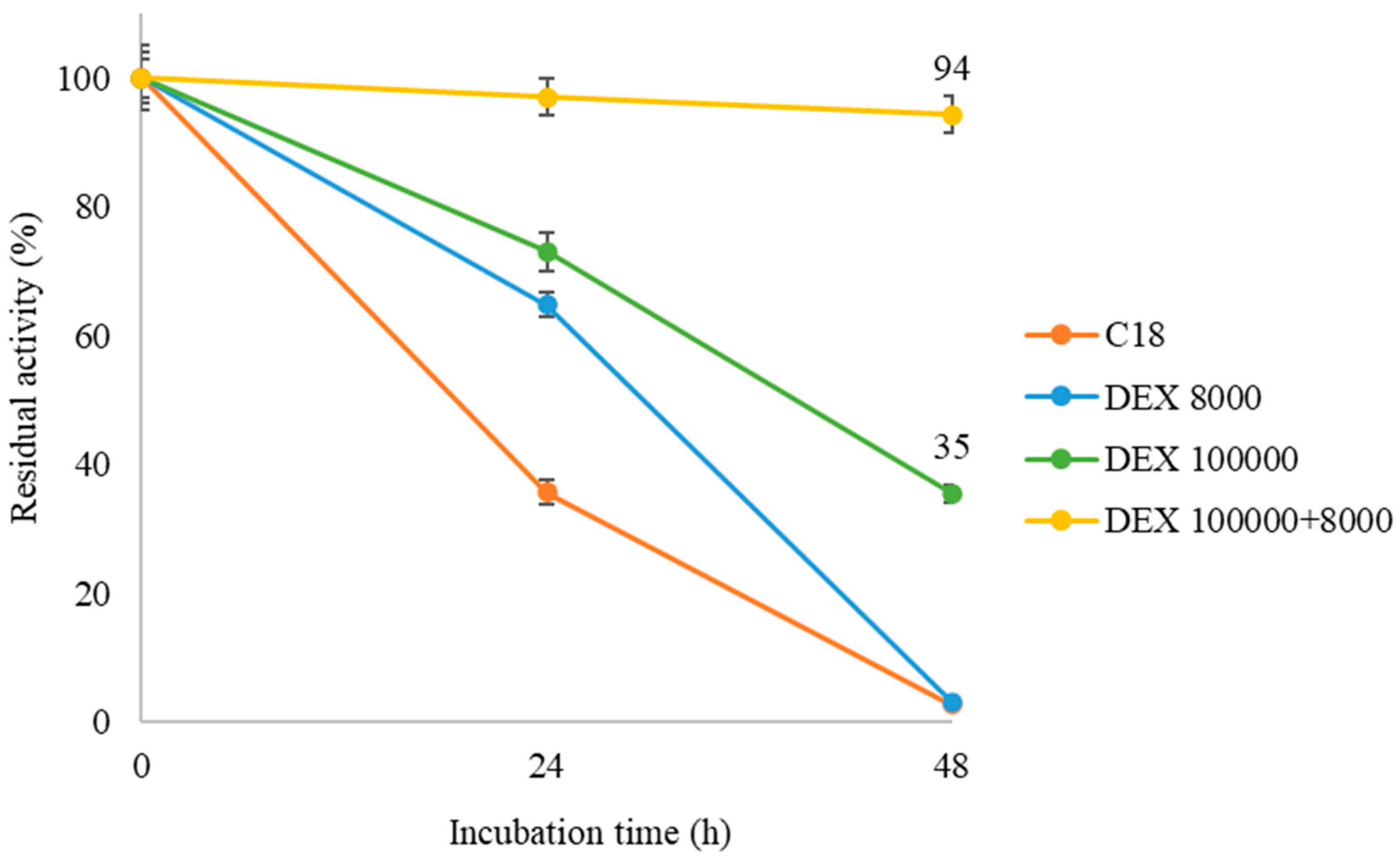
After confirming the activity of the dextran sulfate-modified derivatives, it was investigated whether the different polymer sizes used in post-immobilization offer greater stability to the unmodified QlowP-C18 derivative. The four derivatives were incubated for up to two days at 40 °C in a solvent-free medium, following the protocol described in Materials and Methods.
Figure 6 shows that in all the cases, the polymer coating improves the stability of the QlowP-C18 catalyst to varying degrees. The unmodified derivative (C18) loses 65% of its activity at 24 h and completely loses it at 48 h. In contrast, the double-layer derivative (DEX 100,000 + 8000) maintains 94% of its activity until the end of the incubation period, while the DEX 100,000-modified derivative retains only 35% of its activity at 48 h. Finally, although the derivative with DEX 8000 shows greater stability at 24 h compared to C18, it also loses all its activity by the end of the incubation period.
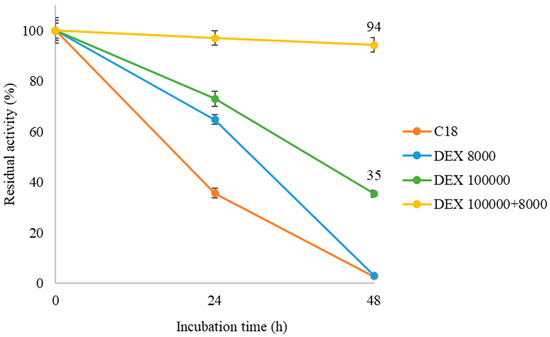
Figure 6.
Residual activity of the unmodified QlowP-C18 derivative and the modified derivatives after being incubated for 48 h in a solvent-free medium at 40 °C: C18 (orange), DEX 8000 (blue), DEX 100,000 (green), and DEX 100,000 + 8000 (yellow).
These results indicate that DEX 8000 does not provide an effective protective layer due to its insufficient size. In contrast, the double layer with dextran sulfates of different sizes significantly enhances the enzyme stability under severe reaction conditions (anhydrous hydrophobic media, highly viscous, and at 40 °C). It seems that the combination of highly hydrophilic and viscous polymers prevents the exposure of internal hydrophobic pockets of the enzyme and reduces conformational changes on its surface [37]. Therefore, the use of DEX 100,000 + 8000 is very useful to prevent the direct interaction of the immobilized enzyme with the reaction medium. This demonstrates that post-immobilization physicochemical modification improves the stability of QlowP-C18, which is a crucial property for its future industrial applications.
3.7. Operational Stability of the QlowP-C18 Catalyst
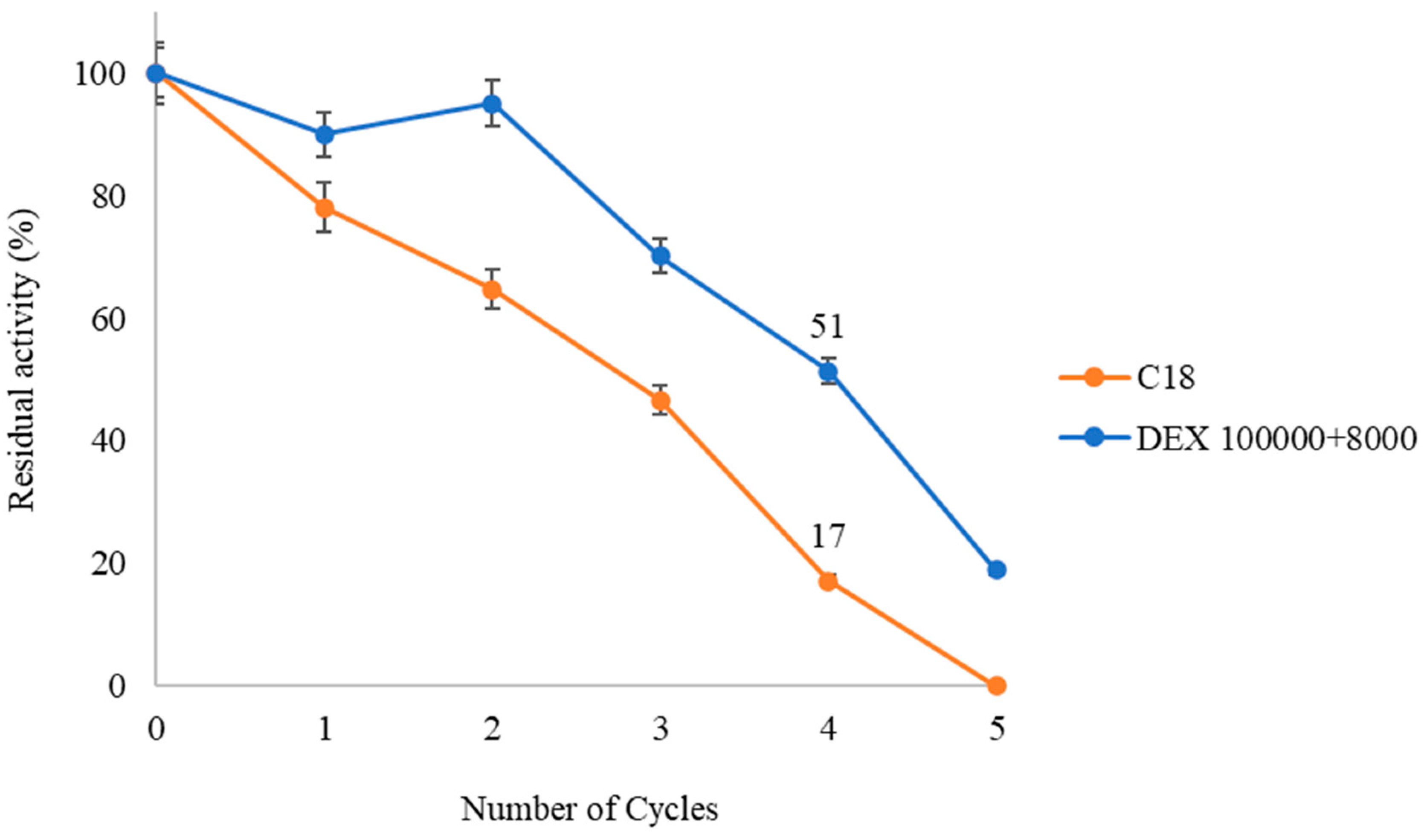
Finally, the reusability capacity of the double-layer dextran sulfate derivative (DEX 100,000 + 8000) is studied over several consecutive cycles of 24 h at 40 °C in a solvent-free medium and compared with the unmodified derivative (C18). Cycle 0 is considered as 100% catalytic activity, corresponding to 28.25% production of Di-DHA-PC for the modified derivative and 28% for the unmodified derivative (Figure 5).
Figure 7 shows that the modified derivative exhibits greater operational capacity compared to the unmodified one. QlowP-C18 coated with DEX 100,000 + 8000 is reused for up to five cycles, maintaining 51% activity in the fourth cycle, while the unmodified derivative shows only 17% in the same cycle. By the end of the cycles, the modified derivative produces 120.4 mg of Di-DHA-PC compared to 85.45 mg from the unmodified derivative. This indicates that the immobilization and post-immobilization strategy increases the lifetime of the QlowP biocatalyst, making it more effective for the synthesis of di-substituted DHA phospholipids.
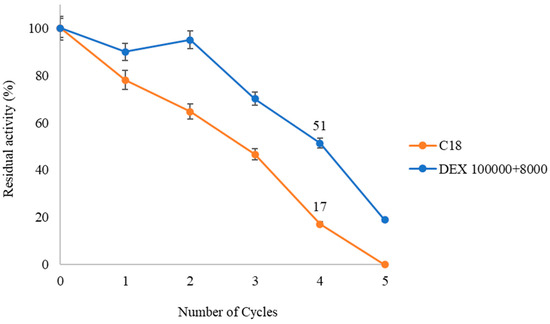
Figure 7.
Recovered Activity (%) of QlowP-C18 (orange) and QlowP-C18 + DEX 100,000 + 8000 (blue) after multiple cycles of reuse for the esterification reaction of GPC and DHA. Reaction conditions: 40 °C, 10% phospholipase derivative (w/w), substrate ratio 1/62 (GPC/DHA), agitation 150 rpm, and solvent-free medium. Reuse was evaluated in 24 h reaction cycles.
The reuse of the derivative has been made possible by our hydrophobic adsorption immobilization strategy, which has imparted greater stability to the QlowP enzyme compared to its soluble form. It is noteworthy that the esterification reaction of DHA with GPC was impossible under the same conditions using the soluble enzyme, failing to synthesize the desired product, highly pure Di-DHA-PC. Furthermore, our post-immobilization strategy with double-layer dextran sulfate has provided the enzyme with greater stability compared to the uncoated derivative. In the future, further post-immobilization strategies using polymers with different chemical structures will be explored to further enhance the catalytic properties of the derivative and increase the production of the desired phospholipid.
4. Conclusions
The course of the DHA and GPC esterification reaction depends greatly on the lipase or phospholipase used, the immobilization strategy, and the experimental conditions, as all of these factors modulate the activity and selectivity of the synthesis reaction. Thanks to the immobilization strategy using hydrophobic adsorption on Immobeads-C18 support, derivatives with maximum enzymatic load are obtained, highly active and enabling the synthesis of structured DHA phospholipids in a solvent-free medium at 60 °C. The QlowP-C18 phospholipase derivative stands out as the most promising candidate, achieving a maximum synthesis yield of Di-DHA-PC of 58% in just 48 h. The results obtained demonstrate that di-substituted DHA phospholipids have been synthesized with 95% purity. This high purity allows these phospholipids to be used as functional ingredients in foods, requiring lower concentrations compared to phospholipids obtained by concentrating oils or extracts. Additionally, they offer a significant advantage in nutraceutical applications by enabling formulations with high DHA concentrations.
The post-immobilization technique with a double layer of dextran sulfate has tripled the stability of QlowP-C18. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that this derivative can be reused for up to five reaction cycles at 40 °C, achieving a total production of 120.4 mg of highly pure DHA-disubstituted phospholipid. Therefore, the immobilization and post-immobilization strategies are used to ensure proper enzyme orientation on the support, providing high stability and enabling operation under adverse reaction conditions such as solvent-free anhydrous media, highly hydrophobic and viscous environments with low substrate solubility, and high temperatures. This is the key to making this bioprocess of high interest in the food industry economically viable on an industrial scale in the future.
Despite its promise, this approach is still in the early stages. Future research should focus on optimizing reaction conditions, enhancing enzyme stability over time, and scaling up for industrial applications. Additionally, evaluating the economic viability of this bioprocess and its integration with existing food production systems will be essential. Another key step will be conducting clinical trials to assess the efficacy of these Di-DHA phospholipids in preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases, as DHA deficiency in the brain is a growing concern in aging populations [44].
Author Contributions
E.G.-Q.: methodology, investigation, writing—original draft, and review and editing. J.M.G.: conceptualization, supervision, writing—original draft, and review and editing. G.F.-L.: conceptualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, writing—original draft, and review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Open Access funding was provided thanks to the CRUE-CSIC agreement with Springer Nature. This research was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, Spain (Number project No. RTI2018-093583-B-I00).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Novozymes for generously donating the commercial enzymes. Ernestina Garcia gratefully acknowledges the Spanish National Research Council for his predoctoral contract.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Gloria Fernandez-Lorente reports financial support was provided by Spanish Scientific Research Council. Gloria Fernandez-Lorente reports a relationship with the Spanish Scientific Research Council that includes: employment.
References
- Dangour, A.D.; Uauy, R. N-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids for Optimal Function during Brain Development and Ageing. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S1), 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Huang, Q. Common Delivery Systems for Enhancing in Vivo Bioavailability and Biological Efficacy of Nutraceuticals. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 7, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, M.; Al Sayed Mahmoud, C.; Linder, M.; Fanni, J. Polar Lipids: N-3 PUFA Carriers for Membranes and Brain: Nutritional Interest and Emerging Processes. Oléagineux Corps Gras Lipides 2007, 14, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burri, L.; Hoem, N.; Banni, S.; Berge, K. Marine Omega-3 Phospholipids: Metabolism and Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15401–15419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachem, M.; Nacir, H. Emerging Role of Phospholipids and Lysophospholipids for Improving Brain Docosahexaenoic Acid as Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Strategies for Neurological Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Scanlon, M.J.; Owada, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Porter, C.J.H.; Nicolazzo, J.A. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 5 Facilitates the Blood–Brain Barrier Transport of Docosahexaenoic Acid. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4375–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellet, M.; Emond, V.; Chen, C.T.; Julien, C.; Bourasset, F.; Oddo, S.; LaFerla, F.; Bazinet, R.P.; Calon, F. Diffusion of Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids through the Blood–Brain Barrier: An in Situ Cerebral Perfusion Study. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 55, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard-Watkins, R.; Lacombe, R.J.S.; Metherel, A.H.; Masoodi, M.; Bazinet, R.P. DHA Esterified to Phosphatidylserine or Phosphatidylcholine Is More Efficient at Targeting the Brain than DHA Esterified to Triacylglycerol. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1801224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugasini, D.; Yalagala, P.C.R.; Goggin, A.; Tai, L.M.; Subbaiah, P.V. Enrichment of Brain Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Is Highly Dependent upon the Molecular Carrier of Dietary DHA: Lysophosphatidylcholine Is More Efficient than Either Phosphatidylcholine or Triacylglycerol. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 74, 108231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semba, R.D. Perspective: The Potential Role of Circulating Lysophosphatidylcholine in Neuroprotection against Alzheimer Disease. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencreac’h, G.; Ergan, F.; Poisson, L. Production of Lysophospholipids Rich in DHA. Lipid Technol. 2011, 23, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pencreac’h, G.; Ergan, F.; Poisson, L. DHA-Lysophospholipid Production. Curr. Org. Chem. 2013, 17, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, B.K.; Morrison, E.N.; Emery, R.J.N.; Farrow, S.C. Customizing Lipids from Oleaginous Microbes: Leveraging Exogenous and Endogenous Approaches. Trends Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 482–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castejón, N.; Señoráns, F.J. Enzymatic Modification to Produce Health-Promoting Lipids from Fish Oil, Algae and Other New Omega-3 Sources: A Review. New Biotechnol. 2020, 57, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Tang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Mao, X.; Li, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Biotechnology in Future Food Lipids: Opportunities and Challenges. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 14, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, D.; Zou, S.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X. Synthesis and Concentration of 2-Monoacylglycerols Rich in Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Pérez, S.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Selective Ethanolysis of Fish Oil Catalyzed by Immobilized Lipases. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, P.A.; Alfaia, C.M.; Pestana, J.M.; Prates, J.A.M. Structured Lipids Engineering for Health: Novel Formulations Enriched in n-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids with Potential Nutritional Benefits. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, B.-G. Lipase-Catalyzed Synthesis of Lysophosphatidylcholine Using Organic Cosolvent for in Situ Water Activity Control. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.I.; Kim, Y.; Kim, C.T.; Kim, I.H. Enzymatic Synthesis of Lysophosphatidylcholine Containing CLA from Sn-Glycero-3-Phosphatidylcholine (GPC) under Vacuum. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virto, C.; Svensson, I.; Adlercreutz, P. Enzymatic Synthesis of Lysophosphatidic Acid and Phosphatidic Acid. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1999, 24, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virto, C.; Adlercreutz, P. Lysophosphatidylcholine Synthesis with Candida Antarctica Lipase B (Novozym 435). Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnasri, T.; Hérault, J.; Gauvry, L.; Loiseau, C.; Poisson, L.; Ergan, F.; Pencréac’h, G. Lipase-Catalyzed Production of Lysophospholipids. OCL 2017, 24, D405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marsaoui, N.; Naghmouchi, K.; Baah, J.; Raies, A.; Laplante, S. Incorportation of Ethyl Esters of EPA and DHA in Soybean Lecithin Using Rhizomucor Miehei Lipase: Effect of Additives and Solvent-Free Conditions. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malipeddi, H.; Das, P.; Karigar, A. Green Technique-Solvent Free Synthesis and Its Advantages. IJRAP 2011, 2, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Guisan, J.M. Immobilization of Enzymes as the 21st Century Begins. In Immobilization of Enzymes and Cells; Guisan, J.M., Ed.; Methods in BiotechnologyTM; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–13. ISBN 978-1-59745-053-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Cabrera, Z.; Godoy, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Palomo, J.M.; Guisan, J.M. Interfacially Activated Lipases against Hydrophobic Supports: Effect of the Support Nature on the Biocatalytic Properties. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facin, B.R.; Quinto, E.G.; Valerio, A.; Oliveira, D.D.; Oliveira, J.V.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Strategies for the Immobilization of Eversa® Transform 2.0 Lipase and Application for Phospholipid Synthesis. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar, J.M.; Rocha-Martín, J.; Mateo, C.; Guisan, J.M. Stabilization of a Highly Active but Unstable Alcohol Dehydrogenase from Yeast Using Immobilization and Post-Immobilization Techniques. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.A.; Trobo-Maseda, L.; Lima, F.A.; de Morais Júnior, W.G.; De Marco, J.L.; Salum, T.F.C.; Guisán, J.M. Omega-3 Production by Fish Oil Hydrolysis Using a Lipase from Burkholderia Gladioli BRM58833 Immobilized and Stabilized by Post-Immobilization Techniques. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 29, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.-C.; Yu, D.-G.; Yang, M.-C. Blood Compatibility of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Membrane Immobilized with Water-Soluble Chitosan/Dextran Sulfate. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2005, 44, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thies, F.; Pillon, C.; Moliere, P.; Lagarde, M.; Lecerf, J. Preferential Incorporation of M-2 1ysoPC DHA over Unesterified DHA in the Young Rat Brain. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1994, 267, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thies, F.; Delachambre, M.C.; Bentejac, M.; Lagarde, M.; Lecerf, J. Unsaturated Fatty Acids Esterified in 2-Acyl- 1-Lysophosphatidylcholine Bound to Albumin Are More Efficiently Taken up by the Young Rat Brain than the Unesterified Form. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastida, A.; Sabuquillo, P.; Armisen, P.; Ferná Ndez-Lafuente, R.; Huguet, J.; Guisá, J.M. A Single Step Purification, Immobilization, and Hyperactivation of Lipases via Interfacial Adsorption on Strongly Hydrophobic Supports. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1998, 58, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Quinto, E.; Garcia-Garcia, P.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Enzymatic Synthesis of Mono- and Disubstituted Phospholipids by Direct Condensation of Oleic Acid and Glycerophosphocholine with Immobilized Lipases and Phospholipase. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Godoy, C.A.; Volpato, G.; Ayub, M.A.Z.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Guisan, J.M. Immobilization-Stabilization of the Lipase from Thermomyces Lanuginosus: Critical Role of Chemical Amination. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abian, O.; Wilson, L.; Mateo, C.; Fernández-Lorente, G.; Palomo, J.M.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Guisán, J.M.; Re, D.; Tam, A.; Daminatti, M. Preparation of Artificial Hyper-Hydrophilic Micro-Environments (Polymeric Salts) Surrounding Enzyme Molecules: New Enzyme Derivatives to Be Used in Any Reaction Medium. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2002, 19–20, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Quinto, E.; Aranda-Cañada, R.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G. Production of Docosahexaenoic Acid through Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Omega-3 Rich Oil. J. Catal. 2024, 440, 115797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotapati, H.K.; Bates, P.D. Normal Phase HPLC Method for Combined Separation of Both Polar and Neutral Lipid Classes with Application to Lipid Metabolic Flux. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1145, 122099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Enzymatic Synthesis of Lysophosphatidylcholine with N−3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid from Sn-Glycero-3-Phosphatidylcholine in a Solvent-Free System. Food Chem. 2017, 226, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, D.M.; Madoery, R.; Diehl, B.W.K.; Tomás, M.C. Emulsifying Properties of Different Modified Sunflower Lecithins. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeduba, E.A.; Akoh, C.C. Modification of Stearidonic Acid Soybean Oil by Immobilized Rhizomucor Miehei Lipase to Incorporate Caprylic Acid. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montine, T.J.; Morrow, J.D. Fatty Acid Oxidation in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaki, T.; Haniu, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Tsukahara, T. Lysophospholipids: A Potential Drug Candidates for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).